KLASIFIKASI TANAH DESA SIHIONG, SINAR SABUNGAN, DAN LUMBAN LOBU KECAMATAN BONATUA LUNASI
KABUPATEN TOBA SAMOSIR BERDASARKAN TAKSONOMI TANAH 2010
S K R I P S I
OLEH:
INGRID OVIE YOSEPHINE 070303014
ILMU TANAH
DEPARTEMEN ILMU TANAH FAKULTAS PERTANIAN UNIVERSITAS SUMATERA UTARA
KLASIFIKASI TANAH DESA SIHIONG, SINAR SABUNGAN, DAN LUMBAN LOBU KECAMATAN BONATUA LUNASI
KABUPATEN TOBA SAMOSIR BERDASARKAN TAKSONOMI TANAH 2010
S K R I P S I
OLEH:
INGRID OVIE YOSEPHINE 070303014
ILMU TANAH
Skripsi Sebagai Salah Satu Syarat Untuk Memperoleh Gelar Sarjana Di Departemen Ilmu Tanah Fakultas Pertanian
Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan
DEPARTEMEN ILMU TANAH FAKULTAS PERTANIAN UNIVERSITAS SUMATERA UTARA
Judul Skripsi : Klasifikasi Tanah Desa Sihiong, Sinar Sabungan, dan Lumban Lobu Kecamatan Bonatua Lunasi Kabupaten Toba Samosir Berdasarkan Taksonomi Tanah 2010
Nama : Ingrid Ovie Yosephine
NIM : 070303014
Departemen : Ilmu Tanah
Minat Studi : Klasifikasi Tanah dan Evaluasi Lahan
Disetujui Oleh : Komisi Pembimbing
Ketua Anggota
(Ir. Purba Marpaung, SU) (Ir. Fauzi, MP
NIP. 19540205198003 1 003 NIP. 19571110198601 1 003
)
Mengetahui,
Ketua Departemen Agroekoteknologi (Ir. T. Sabrina, M.Agr.Sc, Ph.D
ABSTRAK
Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk mengklasifikasikan tanah mulai dari tingkat
ordo sampai sub group. Penelitian ini dilakukan di Desa Sihiong, Sinar Sabungan, dan Lumban Lobu, Kecamatan Bonatua Lunasi, Kabupaten
Toba Samosir. Analisis laboratorium dilakukan di Laboratorium Kimia-Kesuburan Tanah, Riset dan Teknologi, Fakultas Pertanian, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan.
Dilakukan pengamatan profil di lapangan pada tiga lokasi. Profil I di Desa Sihiong berada pada kemiringan lereng 21% (bergelombang) dengan ketinggian tempat 1024 m dpl. Profil II di Desa Sinar Sabungan berada pada kemiringan lereng 15% (bergelombang) dengan ketinggian tempat 991 m dpl. Profil III di Desa Lumban Lobu berada pada kemiringan lereng 15% (bergelombang) dengan kemiringan tempat 1071 m dpl. Pada masing-masing profil diamati sifat-sifat fisik tanah, seperti warna, struktur, tekstur, konsistensi, perakaran serta kedalaman efektif, dan diambil sampel masing-masing profil dari setiap horizon untuk dianalisis di laboratorium. Analisis di laboratorium meliputi tekstur tanah, bulk
density, C-organik, basa-basa dapat tukar (Ca2+, Mg2+, K+, dan Na+), pH H2O,
pH KCl serta kapasitas tukar kation (KTK).
Dari hasil penelitian memperlihatkan bahwa klasifikasi tanah berdasarkan Taksonomi Tanah 2010 di Desa Sihiong adalah : Ordo Inceptisol, Sub Ordo Udept, Great Group Humudept, dan Sub Group Fluventic Humudept. Desa Sinar Sabungan adalah Ordo Inceptisol, Sub Ordo Udept, Great Group Humudept, dan Sub Group Pachic Humudept. Desa Lumban Lobu adalah Ordo Entisol, Sub Ordo Orthent, Great Group Udorthent, dan Sub Group Typic Udorthent.
ABSTRACT
This research aims to clasify the soil starting from the level of orders to sub group. This research is being held in Desa Sihiong, Sinar Sabungan and Lumban Lobu, Kecamatan Toba Lunasi, Kabupaten Toba Samosir. Laboratory analysis is being held in Laboratory Chemistry-Soil Fertility, Research and Technology, Faculty of Agriculture, University of North Sumatra, Medan.
Observations made in the feld profile at three locations. Profile I in Desa Sihiong was at 21% slope (wavy) with altitude 1024 m dpl. Profile II in
Desa Sinar Sabungan was at 15 slope (wavy) with altitude 991 m dpl. Profile III in Desa Lumban Lobu was at 15 slope (wavy) with 1071 altitude m dpl. In each of the observed profile of physical properties such as color, structure, texture, consistency, roots and depth of effective and taken samples of each profile of each horizon to be analyzed in the laboratory. Analysis in the laboratory include soil
texture, bulk density,C-organic, base exchange (Ca2+, Mg2+, K+, dan Na+), pH H2O, pHKCl, and cation change capacity (CEC).
From the research result show that the classification of soil based on Soil
Taxonomy 2010 in Desa Sihiong is Ordo Inceptisols, Sub Ordo Udepts, Great Group Humudepts, dan Sub Group Fluventic Humudepts. Desa Sinar Sabungan is Ordo Inceptisols, Sub Ordo Udepts, Great Group Humudepts,
dan Sub Group Pachic Humudepts. Desa Lumban Lobu is Ordo Entisol, Sub Ordo Orthent, Great Group Udorthent, dan Sub Group Typic Udorthent.
RIWAYAT HIDUP
Ingrid Ovie Yosephine dilahirkan di Medan pada tanggal 02 September 1989. Anak pertama dari empat bersaudara. Putra dari Ayahanda Ir.
E. Sitompul dan Ibunda D.br. Marpaung. Riwayat Pendidikan
- SD Swasta Budi Utomo, lulus pada tahun 2001. - SLTP Negeri 29 Medan, lulus pada tahun 2004. - SMA Negeri 11 Medan, lulus pada tahun 2007.
- Tahun 2007 lulus seleksi masuk Universitas Sumatera Utara melalui jalur
SPMB di Program Studi Ilmu Tanah, Departemen Ilmu Tanah, Fakultas Pertanian.
Aktivitas Selama Pendidikan
- Anggota Ikatan Mahasiswa Ilmu Tanah (IMILTA) Fakultas Pertanian Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan.
- Asisten Laboratorium mata kuliah Praktikum Genesis dan Morfologi tahun 2011.
- Asisten Laboratorium mata kuliah Praktikum Agrogeologi tahun 2011. - Asisten Laboratorium mata kuliah Praktikum Pengelolaan Tanah dan Air
tahun 2011.
- Peserta Seminar Nasional “Tindak Lanjut Pembangunan Pertanian Pasca Swasembada Beras 2008” pada 8 Agustus 2009 di FP USU Medan.
Berbasis Pembangunan Berkelanjutan (Sustainable Development)” pada 12 Februari 2010 di FP USU Medan.
- Peserta Seminar Pertanian 2011 “Meningkatkan Ketahanan Pangan Nasional” pada 29 Mei 2011 di FP USU Medan.
- Panitia Pengkaderan Nasional II Forum Komunikasi Himpunan Mahasiswa Ilmu Tanah Indonesia (FOKUSHIMITI) “Mengoptimalkan Kader yang Mampu Menjadi Barometer Dunia Pertanian di Indonesia” pada 22 – 26 Januari 2011 di FP USU Medan.
KATA PENGANTAR
Puji dan syukur penulis panjatkan kehadirat Tuhan Yang Maha Esa, karena atas berkat dan rahmatNya penulis dapat menyelesaikan skripsi ini.
Adapun judul skripsi adalah “Klasifikasi Tanah Desa Sihiong, Sinar Sabungan dan Lumban Lobu Kecamatan Bonatua Lunasi, Kabupaten Toba Samosir Berdasarkan Taksonomi Tanah 2010”, yang
merupakan salah satu syarat untuk memperoleh gelar sarjana pada Fakultas Pertanian, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan.
Pada kesempatan ini penulis mengucapkan terima kasih kepada Ir.Purba Marpaung, SU selaku Ketua Komisi Pembimbing dan Ir.Fauzi, MP
selaku Anggota Komisi Pembimbing.
Penulis menyadari bahwa skripsi ini belum sempurna. Oleh karena itu, penulis mengharapkan saran dan kritik untuk kesempurnaan skripsi ini.
Akhir kata penulis mengucapkan terima kasih. Semoga skripsi ini bermanfaat bagi kita semua.
Medan, February 2012
DAFTAR TABEL
1. Hasil Analisis Sifat Fisik Tanah pada Profil I, II, III...73 No Tabel Hal
DAFTAR GAMBAR
DAFTAR LAMPIRAN
No Lampiran Hal 1. Data Iklim Hujan selama 5 tahun terakhir Kabupaten Toba Samosir (2007-2011)
2. Penampang Profil Tanah di Desa Sihiong
3. Penampang Profil Tanah di Desa Sinar Sabungan 4. Penampang Profil Tanah di Desa Lumban Lobu
DAFTAR ISI
Kegunaan Penelitian ... 3
ABSTRAK
Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk mengklasifikasikan tanah mulai dari tingkat
ordo sampai sub group. Penelitian ini dilakukan di Desa Sihiong, Sinar Sabungan, dan Lumban Lobu, Kecamatan Bonatua Lunasi, Kabupaten
Toba Samosir. Analisis laboratorium dilakukan di Laboratorium Kimia-Kesuburan Tanah, Riset dan Teknologi, Fakultas Pertanian, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan.
Dilakukan pengamatan profil di lapangan pada tiga lokasi. Profil I di Desa Sihiong berada pada kemiringan lereng 21% (bergelombang) dengan ketinggian tempat 1024 m dpl. Profil II di Desa Sinar Sabungan berada pada kemiringan lereng 15% (bergelombang) dengan ketinggian tempat 991 m dpl. Profil III di Desa Lumban Lobu berada pada kemiringan lereng 15% (bergelombang) dengan kemiringan tempat 1071 m dpl. Pada masing-masing profil diamati sifat-sifat fisik tanah, seperti warna, struktur, tekstur, konsistensi, perakaran serta kedalaman efektif, dan diambil sampel masing-masing profil dari setiap horizon untuk dianalisis di laboratorium. Analisis di laboratorium meliputi tekstur tanah, bulk
density, C-organik, basa-basa dapat tukar (Ca2+, Mg2+, K+, dan Na+), pH H2O,
pH KCl serta kapasitas tukar kation (KTK).
Dari hasil penelitian memperlihatkan bahwa klasifikasi tanah berdasarkan Taksonomi Tanah 2010 di Desa Sihiong adalah : Ordo Inceptisol, Sub Ordo Udept, Great Group Humudept, dan Sub Group Fluventic Humudept. Desa Sinar Sabungan adalah Ordo Inceptisol, Sub Ordo Udept, Great Group Humudept, dan Sub Group Pachic Humudept. Desa Lumban Lobu adalah Ordo Entisol, Sub Ordo Orthent, Great Group Udorthent, dan Sub Group Typic Udorthent.
ABSTRACT
This research aims to clasify the soil starting from the level of orders to sub group. This research is being held in Desa Sihiong, Sinar Sabungan and Lumban Lobu, Kecamatan Toba Lunasi, Kabupaten Toba Samosir. Laboratory analysis is being held in Laboratory Chemistry-Soil Fertility, Research and Technology, Faculty of Agriculture, University of North Sumatra, Medan.
Observations made in the feld profile at three locations. Profile I in Desa Sihiong was at 21% slope (wavy) with altitude 1024 m dpl. Profile II in
Desa Sinar Sabungan was at 15 slope (wavy) with altitude 991 m dpl. Profile III in Desa Lumban Lobu was at 15 slope (wavy) with 1071 altitude m dpl. In each of the observed profile of physical properties such as color, structure, texture, consistency, roots and depth of effective and taken samples of each profile of each horizon to be analyzed in the laboratory. Analysis in the laboratory include soil
texture, bulk density,C-organic, base exchange (Ca2+, Mg2+, K+, dan Na+), pH H2O, pHKCl, and cation change capacity (CEC).
From the research result show that the classification of soil based on Soil
Taxonomy 2010 in Desa Sihiong is Ordo Inceptisols, Sub Ordo Udepts, Great Group Humudepts, dan Sub Group Fluventic Humudepts. Desa Sinar Sabungan is Ordo Inceptisols, Sub Ordo Udepts, Great Group Humudepts,
dan Sub Group Pachic Humudepts. Desa Lumban Lobu is Ordo Entisol, Sub Ordo Orthent, Great Group Udorthent, dan Sub Group Typic Udorthent.
PENDAHULUAN
Latar Belakang
Tanah merupakan medium alam untuk pertumbuhan tanaman. Tanah menyediakan unsur-unsur hara sebagai makanan tanaman untuk pertumbuhannya. Tanah yang terbentuk dari bahan-bahan berupa bahan mineral dan organik, air serta udara tersusun didalam ruangan yang membentuk tubuh tanah. Akibat berlangsungnya proses pembentukan tanah, maka terbentuklah perbedaan sifat
kimia, fisis, biologi dan morfologi dari tanah yang berbeda-beda pula (Hakim, dkk, 1986).
Tanah tidak terbentuk secara sendiri tanpa ada faktor-faktor pembentuknya. Ada 5 faktor pembentuk tanah yaitu iklim (climate), bahan induk
(parent material), organisme (organism), topografi (relief), dan waktu (time). Faktor-faktor tersebut tidak berjalan atau bekerja sendiri-sendiri tetapi bekerja
secara simultan atau saling bekerja sama. Pembentukan dan perkembangan tanah membutuhkan waktu sehingga menghasilkan jenis-jenis tanah tertentu yang berbeda sesuai dengan kondisi faktor-faktor pembentuknya (Hasibuan, 2006).
Di Indonesia, sejak tahun 1975 dikenal dengan tiga sistem klasifikasi tanah yang banyak digunakan oleh Lembaga Penelitian, Perguruan Tinggi, Dinas Teknis dan Teknisi di lapangan, yaitu :
(1) Sistem Klasifikasi Tanah Nasional (Dudal & Soepraptohardjo, 1957; Soepraptohardjo, 1961),
(2) Sistem Klasifikasi Tanah Internasional, dikenal sebagai Taksonomi Tanah (Soil Taxonomy, USDA, 1975; 2003), dan
(3) Sistem FAO/UNESCO (1974).
Sistem klasifikasi tanah yang sekarang dikenal dengan nama Taksonomi Tanah atau Soil Taxonomy (USDA, 1975) merupakan penyempurnaan dari The
Comprehensive System of Soil Classification 7th Aprroximation (USDA, 1960). Sistem tersebut disebut Comprehensive System karena dapat
digunakan untuk seluruh tanah di dunia. Disebut 7th Aprroximation karena sistem tersebut dibuat dengan beberapa kali pendekatan dan perbaikan, hingga pendekatan yang ke-7.
Daerah penelitian belum pernah diklasifikasikan, berdasarkan hal tersebut penulis tertarik melakukan penelitian di Desa Sihiong, Sinar Sabungan, dan Lumban Lobu di dalam mengklasifikasikan tanah berdasarkan Taksonomi Tanah 2010.
Tujuan Penelitian
Adapun tujuan dari penelitian ini adalah untuk mengklasifikasikan tanah mulaidari tingkat ordo sampai sub group di Desa Sihiong, Sinar Sabungan, dan Lumban Lobu, Kecamatan Bonatua Lunasi, Kabupaten Toba Samosir berdasarkan Taksonomi Tanah 2010.
Kegunaan Penelitian
- Bahan informasi klasifikasi tanah ini dapat dipergunakan untuk pengelolaan tanah pertanian yang lebih tepat.
TINJAUAN PUSTAKA
Klasifikasi Tanah
Klasifikasi tanah ditemukan sekitar tahun 1880 oleh ilmuwan Rusia yang bernama Dokuchaev. Kemudian dikembangkan oleh peneliti-peneliti Eropa dan Amerika. Sistem ini didasarkan teori bahwa setiap tanah mempunyai morfologi yang pasti (bentuk dan struktur) dan berkaitan dengan kombinasi faktor pembentuk tanah tertentu. Sistem ini mencapai perkembangan pesat pada tahun 1949 dan dalam penggunaan utama (terutama di Amerika Serikat) sampai tahun 1960. Pada tahun 1960, Departemen Pertanian Amerika Serikat menerbitkan Soil Classification, a Comprehensive System. Sistem klasifikasi ini lebih menekankan pada morfologi tanah dan memberi sedikit tekanan pada genesis atau faktor-faktor pembentuk tanah dibandingkan dengan sistem sebelumnya (Foth, 1994).
Klasifikasi tanah adalah pemilahan tanah yang didasarkan pada sifat-sifat tanah yang dimilikinya tanpa menghubungkannya dengan tujuan penggunaan tanah tersebut. Klasifikasi ini memberikan gambaran dasar terhadap sifat-sifat fisik, kimia, mineral tanah yang dimiliki masing-masing kelas yang selanjutnya dapat digunakan sebagai dasar untuk pengelolaan bagi penggunaan tanah (Hardjowigeno, 1986).
dan minerologi tanah yang dimiliki masing-masing kelas yang selanjutnya dapat digunakan sebagai dasar untuk pengelolaan bagi berbagai penggunaan tanah.
Sedangkan klasifikasi teknis adalah klasifikasi tanah yang didasarkan atas sifat-sifat yang mempengaruhi kemampuan tanah untuk penggunaan-penggunaan
tertentu
Ilmu klasifikasi tanah berkembang cukup pesat mulai dari klasifikasi
sederhana hingga klasifikasi yang menggunakan kaidah ilmu pengetahuan. Di Indonesia telah digunakan beberapa sistem klasifikasi, misalnya Sistem
Klasifikasi Dudal dan Soepraptohardjo. Pada Kongres ke-5 Himpunan Ilmu Tanah Indonesia (HITI) tahun 1989 di Medan disepakati untuk menggunakan Sistem
Klasifikasi Soil Taxonomy secara nasional. Pada sistem klasifikasi Soil Taxonomy, tanah diklasifikasikan menurut hirarki ordo, sub ordo, great
group, sub group, family dan seri. Ada 12 ordo tanah di dunia, yaitu (1) Alfisol, (2) Andisol, (3) Aridisol, (4) Entisol, (5) Gellisol, (6) Histosol, (7) Inceptisol, (8) Mollisol, (9) Oksisol, (10) Spodosol, (11) Ultisol, (12) Vertisol (Musa, dkk, 2006).
Sistem klasifikasi berdasarkan taksonomi tanah dimulai pada tahun 1951 dan dikembangkan berdasarkan nomor approximation yaitu pendekatan dan perbaikan, Approximation ke-7 dipublikasikan pada tahun 1960. Disebut 7th Aprroximation karena sistem tersebut dibuat dengan beberapa kali pendekatan dan perbaikan, hingga perbaikan yang ke-7. Ada 6 tingkatan kategori yaitu : (1) Ordo,
Tujuan klasifikasi tanah adalah :
- Mengorganisasi (menata) pengetahuan kita tentang tanah.
- Untuk mengetahui hubungan masing-masing individu tanah satu sama lain.
- Memudahkan mengingat sifat-sifat tanah.
- Mengelompokkan tanah untuk tujuan-tujuan yang lebih yang lebih praktis dalam hal : menaksir sifat-sifatnya, menentukan lahan-lahan terbaik, menaksir produktivitasnya, dan menentukan areal-areal untuk penelitian. - Mempelajari hubungan-hubungan dan sifat-sifat tanah yang baru.
(Buol, dkk, 1980).
Di negara-negara yang telah maju pertaniannya, klasifikasi tanah merupakan bahan penting dalam mempersiapkan rencana pengembangan pertanian sebagai pedoman penggunaan lahan. Tujuan umum klasifikasi tanah adalah menyediakan suatu susunan yang teratur (sistematik) bagi pengetahuan mengenai tanah dan hubungannya dengan tanaman, baik mengenai produksi maupun perlindungan kesuburan tanah. Tujuan ini meliputi berbagai segi, antara lain peramalan pertanian di masa yang akan datang. Pada lahan yang telah rusak akibat proses erosi atau longsor, klasifikasi tanah disertai dengan petanya
digunakan sebagai langkah pertama dalam usaha perbaikan kesuburan tanah (Darmawijaya, 1997).
Suatu sistem klasifikasi tanah harus memiliki dasar pemikiran sebagai berikut :
- Pembagian akan menjadi lengkap pada setiap tingkat. Misalnya, semua klas terbagi lagi menjadi subklas-subklas.
- Suatu klas akan selalu dibagi menjadi subklas-subklas yang non- overlapping.
(Abdulah, 1991)
Klasifikasi tanah memiliki berbagai versi. Terdapat kesulitan teknis dalam melakukan klasifikasi untuk tanah karena banyak hal yang memengaruhi pembentukan tanah. Dalam melakukan klasifikasi tanah para ahli pertama kali
melakukannya berdasarkan ciri
lapisan-lapisan yang membent berkembang para ahli juga melihat aspe serta prose pada tanah yang terbentu
Sistem klasifikasi tanah yang dikembangkan oleh Amerika Serikat dengan nama Soil Taxonomy (USDA, 1975) berbeda dengan sistem yang sudah ada sebelumnya. Sistem klasifikasi Soil Taxonomy (USDA, 1975) ini memiliki keistimewaan terutama dalam hal:
1. Penamaan atau tata nama atau cara penamaan. 2. Definisi horison penciri.
3. Beberapa sifat penciri lainnya.
Taksonomi Tanah
Taksonomi tanah adalah bagian dari klasifikasi tanah baru yang dikembangkan oleh Amerika Serikat dengan nama Soil Taxonomy (USDA, 1975) menggunakan 6 kategori yaitu ordo, sub ordo, great group, sub group, family dan seri. Sistem ini merupakan sistem yang benar-benar baru baik mengenai cara-cara penamaan (tata nama) maupun definisi mengenai horizon penciri ataupun sifat penciri lain yang dugunakan untuk menentukan jenis tanah. Dari kategori tertinggi (ordo) ke kategori terendah (seri) uraian mengenai sifat-sifat tanah semakin detail (Rayes, 2007).
dan sifat tanah lainnya terukur secara kuantitatif
Sifat umum dari taksonomi tanah adalah : 1. Taksonomi tanah merupakan sistem multikategori.
2. Taksonomi tanah harus memungkinkan modifikasi karena adanya penemuan-penemuan baru dengan tidak merusak sistemnya sendiri.
3. Taksonomi tanah harus mampu mengklasifikasikan semua tanah dalam suatu landscape dimanapun ditemukan.
4. Taksonomi tanah harus dapat digunakan untuk berbagai jenis survai tanah. Kemampuan penggunaan Taksonomi Tanah untuk survai tanah harus dibuktikan dari kemampuannya untuk interpretasi berbagai penggunaan tanah. (Hardjowigeno, 1993).
Dalam caba sejumlah peubah yang mencirikan keadaan suatu jenis
awal tidak sistematis, pada tahun 1975 tim dari Soil Survey Staff Departemen Pertanian Amerika Serikat
dalam taksonomi tanah. Sejak saat itu, setiap jenis tanah paling sedikit memiliki dua nama seperti : Ultisol-Podsolik Merah Kuning. Meskipun nama baru sudah diberikan, nama lama seringkali masih dipakai karena aturan dari Soil Survey Staff dianggap terlalu rinci
1. Ordo
Terdiri dari 12 taksa. Faktor pembeda adalah ada tidaknya horison penciri serta jenis (sifat) dari horison penciri tersebut.
2. Sub Ordo
Terdiri dari 64 taksa. Faktor pembeda adalah keseragaman genetik, misalnya ada tidaknya sifat-sifat tanah yang berhubungan dengan pengaruh air, regim kelembaban, bahan induk utama, pengaruh vegetasi yang ditunjukkan oleh adanya sifat-sifat tanah tertentu, tingkat pelapukan bahan organik (untuk tanah-tanah organik).
3. Great Group
Terdiri dari 317 taksa. Faktor pembeda adalah kesamaan jenis, tingkat perkembangan dan susunan horison, kejenuhan basa, regim suhu dan kelembaban, ada tidaknya lapisan-lapisan penciri lain seperti plinthite, fragipan dan duripan.
4. Sub Group
Jumlah taksa masih terus bertambah yaitu > 1400 taksa. Faktor pembeda terdiri dari sifat-sifat inti dari great group (subgroup Typic), sifat-sifat tanah peralihan ke great group peralihan ke great group lain, sub ordo atau ordo, sifat-sifat tanah peralihan ke bukan tanah).
5. Family
untuk family antara lain adalah : sebaran besar butir, susunan mineral (liat), regim temperatur pada kedalaman 50 cm.
6. Seri
Jumlah seri tanah di Amerika saja lebih besar 19.000. Faktor pembedanya adalah : jenis dan susunan horison, warna, tekstur, struktur, konsistensi, reaksi tanah dari masing-masing horison, sifat-sifat kimia dan mineral masing-masing horison.
Kategori ordo tanah sampai great group disebut kategori tinggi sedangkan kategori sub group sampai seri disebut kategori rendah. Jenis dan jumlah faktor pembeda meningkat dari kategori rendah ke kategori tinggi (Hardjowigeno, 1993).
Taksonomi Tanah 2010
Taksonomi tanah adalah cabang dari klasifikasi tanah. Dalam taksonomi tanah 2010 disajikan secara lengkap tentang prosedur pengelompokan tanah mulai dari kategori tinggi sampai kategori rendah. Prosedur taksonomi tanah adalah mengikuti :
1. Deskripsi profil tanah.
2. Penentuan horison penciri (epipedon dan horizon bawah penciri). 3. Penentuan sifat-sifat lain.
4. Pemakaian kunci taksonomi dengan urutan : ordo (ada 12 ordo), sub ordo, kelompok besar (great group), anak kelompok (sub group), keluarga (family) dan seri.
Horison penciri digunakan untuk mengklasifikasikan ke dalam ordo. Horison penciri yang terbentuk di permukaan dinamakan dengan epipedon. Horison penciri yang langsung di bawahnya dan dapat diamati dinamakan dengan horison bawah penciri (Darmawijaya, 1990).
Menurut Taksonomi Tanah 2010 terdapat 8 epipedon penciri yaitu : Mollik, Antropik, Umbrik, Folistik, Histik, Melanik, Okrik dan Plagen.
A. Epipedon Mollik
Epipedon mollik mempunyai sifat perkembangan struktur tanah cukup kuat, terletak di atas permukaan, mempunyai value warna ≤ 3.5 (lembab) dan kroma warna ≤ 3.5 (lembab), kejenuhan basa > 50%, kandungan C-organik > 0.6%, P2O5 < 250 ppm, dan n-value < 0.7.
B. Epipedon Antropik
Epipedon antropik menunjukkan beberapa tanda-tanda adanya gangguan manusia, dan memenuhi persyaratan mollik kecuali P2O5 < 250 ppm.
C. Epipedon Umbrik
Epipedon mollik mempunyai sifat perkembangan struktur tanah cukup kuat, terletak di atas permukaan, mempunyai value warna ≤ 3.5 (lembab)
dan kroma warna ≤ 3.5 (lembab), kejenuhan basa < 50%, kandungan C-organik > 0.6%, P2O5 < 250 ppm, dan n-value < 0.7.
D. Epipedon Folistik
E. Epipedon Histik
Epipedon Histik merupakam suatu lapisan yang dicirikan oleh adanya saturasi (selama 30 hari atau lebih, secara kumulatif) dan reduksi selama
sebagian waktu dalam sebagian waktu dalam tahun-tahun normal (dan telah drainase). Sebagian besar epipedon histik tersusun dari bahan
tanah organik. F. Epipedon Okrik
Epipedon Okrik mempunyai tebal permukaan yang sangat tipis dan kering,
value dan kroma (lembab) ≥ 4. Epipedon okrik juga mencakup horison-horison bahan organik yang terlampau tipis untuk memenuhi
persyaratan epipedon histik atau folistik. G. Epipedon Plagen
Epipedon Plagen adalah suatu lapisan permukaan buatan manusia setebal 50 cm atau lebih, yang telah terbentuk oleh pemupukan (pupuk kandang) secara terus menerus dalam jangka waktu yang lama. Biasanya epipedon plagen mengandung artifak seperti pecahan-pecahan bata dan keramik pada seluruh kedalamannya.
A. Horison Agrik
Horison Agrik adalah suatu horison iluvial yang telah terbentuk akibat pengolahan tanah dan mengandung sejumlah debu, liat, dan humus yang telah tereluviasi nyata.
B. Horison Albik
Pada umumnya Horison Albik terdapat di bawah horison A, tetapi mungkin juga berada pada permukaan tanah mineral. Horison ini merupakan horison eluvial dengan tebal 1.0 cm dan mempunyai 85% atau lebih bahan-bahan andik.
C. Horison Argilik
Horison Argilik secara normal merupakan suatu horison bawah permukaan dengan kandungan liat phylosilikat secara jelas lebih tinggi. Horison
tersebut mempunyai sifat adanya gejala eluviasi liat, KTK tinggi (> 6 cmo/kg).
D. Horison Duripan
Horison Duripan merupakan horison yang memadas paling sedikit setengahnya dengan perekat SiO2, dan tidak mudah hancur dengan air atau
HCl.
E. Horison Fragipan
Horison Fragipan mempunyai ketebalan 15 cm atau lebih adanya tanda-tanda pedogenesis didalam horison serta perkembangan struktur
F. Horison Glosik
Horison Glosik terbentuk sebagai hasil degradasi suatu horison argilik, kandik atau natrik dimana liat dan senyawa oksida besi bebasnya telah dipindahkan.
G. Horison Gipsik
Horison Gipsik adalah suatu horison iluvial yang senyawa gypsum sekundernya telah terakumulasi dalam jumlah yang nyata, dimana tebalnya lebih dari 15 cm.
H. Horison Kalsik
Horison Kalsik merupakan horison iluvial mempunyai akumulasi kalsium karbonat sekunder atau karbonat yang lain dalam jumlah yang cukup nyata.
I. Horison Kandik
Horison Kandik memiliki sifat adanya gejala iluviasi liat, kandungan liat tinggi dan KTK rendah (<6 cmol/kg).
J. Horison Kambik
Horison kambik adalah horison yang terbentuk sebagai hasil alterasi secara fisik, transformasi secara kimia, atau pemindahan bahan, atau merupakan hasil kombinasi dari dua atau lebih proses-proses tersebut.
K. Horison Natrik
L. Horison Orstein
Horison Orstein tersusun dari bahan spodik, berada didalam suatu lapisan yang 50% atau lebih (volumenya) tersementasi dan memiliki ketebalan 25 cm atau lebih
M. Horison Oksik
Horison Oksik merupakan horison bawah permukaan yang tidak memiliki sifat-sifat tanah andik dan KTK rendah (< 6 cmol/kg)
N. Horison Petrokalsik
Horison Petrokalsik merupakan suatu horison iluvial dimana kalsium karbonat sekunder atau senyawa karbonat lainnya telah terakumulasi mencapai tingkat, seluruh horison tersebut, tersementasi atau mengeras. O. Horison Petrogipsik
Horison Petrogipsik merupakan suatu horison iluvial dengan ketebalan 10 cm atau lebih dimana gypsum sekundernya telah terakumulasi mencapai tingkat, seluruh horison tersebut, tersementasi atau mengeras.
P. Horison Placik
Horison Placik adalah suatu padas tipis yang berwarna hitam sampai merah gelap, yang tersementasi oleh senyawa besi serta bahan organik. Q. Horison Salik
R. Horison Sombrik
Horison Sombrik berwarna gelap, mempunyai sifat-sifat seperti epipedon
umbrik dengan mengandung iluviasi humus yang berasosiasi dengan Al atau yang terdispersi dengan natrium.
S. Horison Spodik
Horison Spodik adalah suatu lapisan iluvial yang tersusun 85% atau lebih dari bahan spodik.
Berdasarkan Keys to Soil Taxonomy 2010, ordo tanah terdiri atas 12 ordo. Yaitu :
A. Gelisol
Tanah yang mempunyai permafrost (lapisan tanah beku) dan bahan-bahan gelik yang berada didalam 100 cm dari permukaan tanah.
B. Histosol
Tanah yang tidak mempunyai sifat-sifat tanah andik pada 60% atau lebih ketebalan diantara permukaan tanah dan kedalaman 60 cm.
C. Spodosol
Tanah lain yang memiliki horison spodik, albik pada 50% atau lebih dari setiap pedon, dan regim suhu cryik.
D. Andisol
E. Oksisol
Tanah lain yang memiliki horison oksik (tanpa horison kandik) yang mempunyai batas atas didalam 150 cm dari permukaan tanah mineral dan kandungan liat sebesar 40% atau lebih dalam fraksi tanah.
F. Vertisol
Tanah yang memiliki satu lapisan setebal 35 cm atau lebih, dengan batas atas didalam 100 cm dari permukaan tanah mineral, yang memiliki bidang kilir atau ped berbentuk baji dan rata-rata kandungan liat dalam fraksi tanah halus sebesar 30% atau lebih.
G. Aridisol
Tanah yang mempunyai regim kelembaban tanah aridik dan epipedon okrik dan antropik atau horison salik dan jenuh air pada satu lapisan atau lebih di dalam 100 cm dari permukaan tanah selama satu bulan atau lebih. H. Ultisol
Tanah lain yang memiliki horison argilik atau kandik, tetapi tanpa fragipan dan kejenuhan basa sebesar kurang dari 35% pada kedalaman 180 cm. I. Mollisol
Tanah lain yang memiliki epipedon mollik dan kejenuhan basa sebesar 50% atau lebih pada keseluruhan horison.
J. Alfisol
K. Inceptisol
Tanah yang mempunyai sifat penciri horison kambik, epipedon plagen, umbrik, mollik serta regim suhu cryik atau gelic dan tidak terdapat bahan sulfidik didalam 50 cm dari permukaan tanah mineral.
L. Entisol
Tanah yang memiliki epipedon okrik, histik atau albik tetapi tidak ada horison penciri lain.
(Soil Survey Staff, 2010).
Berdasarkan Taksonomi Tanah 2010, sub ordo dan great group dibagi berdasarkan setiap jenis tanah, sebagai berikut :
• Alfisol Sub Ordo : - Aqualfs
Key to Great Groups : Cryaqualfs, Plinthaqualfs, Duraqualfs, Natraqualfs, Fragiaqualfs, Kandiaqualfs, Vermaqualfs, Albaqualfs, Glossaqualfs, Epiaqualfs, Endoaqualfs.
Albaqualfs, Udollic Albaqualfs, Aeric Albaqualfs, Aquandic Albaqualfs, Mollic Albaqualfs, Umbric Albaqualfs, Typic Albaqualfs, Histic Glossaqualfs, Arenic Glossaqualfs, Aeric Fragic Glossaqualfs, Fragic Glossaqualfs, Aeric Glossaqualfs, Mollic Glossaqualfs, Typic Glossaqualfs, Aeric Chromic Vertic Epiaqualfs, Aeric Vertic Epiaqualfs, Chromic Vertic Epiaqualfs, Vertic Epiaqualfs, Aquandic Epiaqualfs, Aeric Fragic Epiaqualfs, Fragic Epiaqualfs, Arenic Epiaqualfs, Grossarenic Epiaqualfs, Aeric Umbric Epiaqualfs, Udollic Epiaqualfs, Aeric Epiaqualfs, Mollic Epiaqualfs, Umbric Epiaqualfs, Typic Epiaqualfs, Aquandic Endoaqualfs, Chromic Vertic Endoaqualfs, Vertic Endoaqualfs, Aeric Fragic Endoaqualfs, Fragic Endoaqualfs, Arenic Endoaqualfs, Grossarenic Endoaqualfs, Udollic Endoaqualfs, Aeric Umbric Endoaqualfs, Aeric Endoaqualfs, Mollic Endoaqualfs, Umbric Endoaqualfs, Typic Endoaqualfs.
- Cryalfs
Key to Great Groups : Palecryalfs, Glossocryalfs, Haplocryalfs.
Haplocryalfs, Umbric Xeric Haplocryalfs, Ustollic Haplocryalfs, Xeric Haplocryalfs, Ustic Haplocryalfs, Mollic Haplocryalfs, Umbric Haplocryalfs, Eutric Haplocryalfs, Typic Haplocryalfs.
- Ustalfs
Key to Great Groups : Durustalfs, Plinthustalfs, Natrustalfs, Kandiustalfs, Kanhaplustalfs, Paleustalfs, Rhodustalfs, Haplustalfs.
Haplustalfs, Vertic Haplustalfs, Aquic Arenic Haplustalfs, Aquultic Haplustalfs, Aquic Haplustalfs, Oxyaquic Haplustalfs, Vitrandic Haplustalfs, Lamellic Haplustalfs, Psammentic Haplustalfs, Arenic Aridic Haplustalfs, Calcidic Haplustalfs, Aridic Haplustalfs, Kanhaplic Haplustalfs, Inceptic Haplustalfs, Calcic Udic Haplustalfs, Ultic Haplustalfs, Calcic Haplustalfs, Udic Haplustalfs, Typic Haplustalfs.
- Xeralfs
Key to Great Groups : Durixeralfs, Natrixeralfs, Fragixeralfs, Plinthoxeralfs, Rhodoxeralfs, Palexeralfs, Haploxeralfs.
Fragic Haploxeralfs, Lamellic Haploxeralfs, Psammnetic Haploxeralfs, Plinthic Haploxeralfs, Calcic Haploxeralfs, Inceptic Haploxeralfs, Ultic Haploxeralfs, Mollic Haploxeralfs, Typic Haploxeralfs.
- Udalfs
Glossudalfs, Aquic Glossudalfs, Arenic Oxyaquic Glossudalfs, Oxyaquic Glossudalfs, Fragic Glossudalfs, Arenic Glossudalfs, Haplic Glossudalfs, Typic Glossudalfs, Lithic Hapludalfs, Aquertic Chromic Hapludalfs, Aquertic Hapludalfs, Oxyaquic Vertic Hapludalfs, Chromic Vertic Hapludalfs, Vertic Hapludalfs, Andic Hapludalfs, Vitrandic Hapludalfs, Fragiaquic Hapludalfs, Fragic Oxyaquic Hapludalfs, Aquic Arenic Hapludalfs, Arenic Oxyaquic Hapludalfs, Anthraquic Hapludalfs, Albaquultic Hapludalfs, Albaquic Hapludalfs, Glossaquic Hapludalfs, Aquultic Hapludalfs, Aquollic Hapludalfs, Aquic Hapludalfs, Mollic Oxyaquic Hapludalfs, Oxyaquic Hapludalfs, Fragic Hapludalfs, Lamellic Hapludalfs, Psammentic Hapludalfs, Arenic Hapludalfs, Glossic Hapludalfs, Inceptic Hapludalfs, Ultic Hapludalfs, Mollic Hapludalfs, Typic Hapludalfs.
• Andisol Sub Ordo : - Aquands
Key to Great Groups : Gelaquands, Cryaquands, Placaquands, Duraquands, Vitraquands, Melanaquands, Epiaquands, Endoaquands.
Pachic Melanaquands, Hydric Melanaquands, Pachic Melanaquands, Thaptic Melanaquands, Typic Melanaquands, Duric Epiaquands, Histic Epiaquands, Alic Epiaquands, Hydric Epiaquands, Thaptic Epiaquands, Typic Epiaquands, Lithic Endoaquands, Duric Endoaquands, Histic Endoaquands, Alic Endoaquands, Hydric Endoaquands, Thaptic Endoaquands, Typic Endoaquands.
- Gelands
Key to Great Groups : Vitrigelands.
Key to Subgroups : Humic Vitrigelands, Turbic Vitrigelands, Typic Vitrigelands. - Cryands
Key to Great Groups : Duricryands, Hydrocryands, Melanocryands, Fulvicryands, Vitricryands, Haplocryands.
Haplocryands, Acrudoxic Haplocryands, Vitric Haplocryands, Thaptic Haplocryands, Xeric Haplocryands, Typic Haplocryands.
- Torrands
Key to Great Groups : Duritorrands, Vitritorrands, Haplotorrands.
Key to Subgroups : Petrocalcic Duritorrands, Vitric Duritorrands, Typic Duritorrands, Lithic Vitritorrands, Duric Vitritorrands, Aquic Vitritorrands, Calcic Vitritorrands, Typic Vitritorrands, Lithic Haplotorrands, Duric Haplotorrands, Calcic Haplotorrands, Typic Haplotorrands.
- Xerands
Key to Great Groups : Vitrixerands, Melanoxerands, Haploxerands.
Key to Subgroups : Lithic Vitrixerands, Aquic Vitrixerands, Thaptic Vitrixerands, Alfic Humic Vitrixerands, Ultic Vitrixerands, Alfic Vitrixerands, Humic Vitrixerands, Typic Vitrixerands, Pachic Melanoxerands, Typic Melanoxerands, Lithic Haploxerands, Aquic Haploxerands, Thaptic Haploxerands, Calcic Haploxerands, Ultic Haploxerands, Alfic Humic Haploxerands, Alfic Haploxerands, Humic Haploxerands, Typic Haploxerands.
- Vitrands
Key to Great Groups : Ustivitrands, Udivitrands.
- Ustands
Key to Great Groups : Durustands, Haplustands.
Key to Subgroups : Aquic Durustands, Thaptic Durustands, Humic Durustands, Typic Durustands, Lithic Haplustands, Aquic Haplustands, Dystric Vitric Haplustands, Vitric Haplustands, Pachic Haplustands, Thaptic Haplustands, Calcic Haplustands, Dystric Haplustands, Oxic Haplustands, Ultic Haplustands, Alfic Haplustands, Humic Haplustands, Typic Haplustands.
- Udands
Key to Great Groups : Placudands, Durudands, Melanudands, Hydrudands, Fulvudands, Hapludands.
Hapludands, Duric Hapludands, Aquic Hapludands, Oxyaquic Hapludands, Alic Hapludands, Acrudoxic Hydric Hapludands, Acrudoxic Thaptic Hapludands, Acrudoxic Ultic Hapludands, Acrudoxic Hapludands, Vitric Hapludands, Hydric Thaptic Hapludands, Hydric Hapludands, Eutric Thaptic Hapludands, Thaptic Hapludands, Eutric Hapludands, Oxic Hapludands, Ultic Hapludands, Alfic Hapludands, Typic Hapludands.
• Aridisol Sub Ordo : - Cryids
Key to Great Groups : Salicryids, Petrocryids, Gypsicryids, Argicryids, Calcicryids, Haplocryids.
Key to Subgroups : Aquic Salicryids, Typic Salicryids, Xereptic Petrocryids, Duric Xeric Petrocryids, Duric Petrocryids, Petrogypsic Petrocryids, Xeric Petrocryids, Ustic Petrocryids, Typic Petrocryids, Calcic Gypsicryids, Vitrixerandic Gypsicryids, Vitrandic Gypsicryids, Typic Gypsicryids, Lithic Argicryids, Vertic Argicryids, Natric Argicryids, Vitrixerandic Argicryids, Vitrandic Argicryids, Xeric Argicryids, Ustic Argicryids, Typic Argicryids, Lithic Calcicryids, Vitrixerandic Calcicryids, Vitrandic Calcicryids, Xeric Calcicryids, Ustic Calcicryids, Typic Calcicryids, Lithic Haplocryids, Vertic Haplocryids Vitrixerandic Haplocryids, Vitrandic Haplocryids, Xeric Haplocryids Ustic Haplocryids, Typic Haplocryids,
Key to Subgroups : Gypsic Aquisalids, Calcic Aquisalids, Typic Aquisalids, Duric Haplosalids, Petrogypsic Haplosalids, Gypsic Haplosalids, Calcic Haplosalids, Typic Haplosalids.
- Durids
Key to Great Groups : Natridurids, Argidurids, Haplodurids.
Key to Subgroups : Vertic Natridurids, Aquic Natrargidic Natridurids, Aquic Natridurids, Natrixeralfic Natridurids, Natrargidic Natridurids, Vitrixerandic Natridurids, Vitrandic Natridurids, Xeric Natridurids, Typic Natridurids, Vertic Argidurids, Aquic Argidurids, Abruptic Xeric Argidurids, Abruptic Argidurids, Haploxeralfic Argidurids, Argidic Argidurids, Vitrixerandic Argidurids, Vitrandic Argidurids, Xeric Argidurids, Ustic Argidurids, Typic Argidurids, Aquicambidic Haplodurids, Aquic Haplodurids, Xereptic Haplodurids, Cambidic Haplodurids, Vitrixerandic Haplodurids, Vitrandic Haplodurids, Xeric Haplodurids, Ustic Haplodurids, Typic Haplodurids.
- Gypsids
Key to Great Groups : Petrogypsids, Natrigypsids, Argigypsids, Calcigypsids, Haplogypsids.
Argigypsids, Vitrandic Argigypsids, Xeric Argigypsids, Ustic Argigypsids, Typic Argigypsids, Lithic Calcigypsids, Petronodic Calcigypsids, Vitrixerandic Calcigypsids, Vitrandic Calcigypsids, Xeric Calcigypsids, Ustic Calcigypsids, Typic Calcigypsids, Lithic Haplogypsids, Leptic Haplogypsids, Sodic Haplogypsids, Petronodic Haplogypsids, Vitrixerandic Haplogypsids, Vitrandic Haplogypsids, Xeric Haplogypsids, Ustic Haplogypsids, Typic Haplogypsids. - Argids
Key to Great Groups : Petroargids, Natrargids, Paleargids, Gypsiargids, Calciargids, Haplargids.
Ustic Calciargids, Arenic Calciargids, Durinodic Xeric Calciargids, Durinodic Calciargids, Petronodic Xeric Calciargids, Petronodic Ustic Calciargids, Petronodic Calciargids, Vitrixerandic Calciargids, Vitrandic Calciargids, Xeric Calciargids, Ustic Calciargids, Typic Calciargids, Lithic Ruptic-Entic Haplargids, Lithic Xeric Haplargids, Lithic Ustic Haplargids, Lithic Haplargids, Xerertic Haplargids, Ustertic Haplargids, Vertic Haplargids, Aquic Haplargids, Arenic Ustic Haplargids, Arenic Haplargids, Durinodic Xeric Haplargids, Durinodic Haplargids, Petronodic Ustic Haplargids, Petronodic Haplargids, Vitrixerandic Haplargids, Vitrandic Haplargids, Xeric Haplargids, Ustic Haplargids, Typic Haplargids.
- Calcids
Key to Great Groups : Petrocalcids, Haplocalcids.
- Cambids
Key to Great Groups : Aquicambids, Petrocambids, Anthracambids, Haplocambids.
Key to Subgroups : Sodic Aquicambids, Durinodic Xeric Aquicambids, Durinodic Aquicambids, Petronodic Aquicambids, Vitrixerandic Aquicambids, Vitrandic Aquicambids, Fluventic Aquicambids, Xeric Aquicambids, Ustic Aquicambids, Typic Aquicambids, Sodic Petrocambids, Vitrixerandic Petrocambids, Vitrandic Petrocambids, Xeric Petrocambids, Ustic Petrocambids, Typic Petrocambids, Typic Anthracambids, Lithic Xeric Haplocambids, Lithic Ustic Haplocambids, Lithic Haplocambids, Xerertic Haplocambids, Ustertic Haplocambids, Ustertic Haplocambids, Vertic Haplocambids, Durinodic Xeric Haplocambids, Durinodic Haplocambids, Petronodic Xeric Haplocambids, Petronodic Ustic Haplocambids, Petronodic Haplocambids, Sodic Xeric Haplocambids, Sodic Ustic Haplocambids, Sodic Haplocambids, Vitrixerandic Haplocambids, Vitrandic Haplocambids, Xerofluventic Haplocambids, Ustifluventic Haplocambids, Fluventic Haplocambids, Xeric Haplocambids, Ustic Haplocambids, Typic Haplocambids.
• Entisol Sub Ordo : - Wassents
Key to Great Groups : Frasiwassents, Psammowassents, Sulfiwassents, Hydrowassents, Fluviwassents, Haplowassents.
Psammowassents, Fluventic Psammowassents, Aeric Psammowassents, Typic Psammowassents, Lithic Sulfiwassents, Haplic Sulfiwassents, Thapto-Histic Sulfiwassents, Fluventic Sulfiwassents, Aeric Sulfiwassents, Typic Sulfiwassents,
Sulfic Hydrowassents, Grossic Hydrowassents, Lithic Hydrowassents, Thapto-Histic Hydrowassents, Typic Hydrowassents, Sulfic Fluviwassents, Lithic
Fluviwassents, Thapto-Histic Fluviwassents, Aeric Fluviwassents, Typic Fluviwassents, Sulfic Haplowassents, Lithic Haplowassents, Aeric Haplowassents, Typic Haplowassents.
- Aquents
Key to Great Groups : Sulfaquents, Hydraquents, Gelaquents, Cryaquents, Psammaquents, Fluvaquents, Epiaquents, Endoaquents.
Key to Subgroups : Haplic Sulfaquents, Histic Sulfaquents, Thapto-Histic Sulfaquents, Typic Sulfaquents, Sulfic Hydraquents, Sodic Hydraquents, Thapto-Histic Hydraquents, Typic Hydraquents, Typic Gelaquents, Aquandic Cryaquents, Typic Cryaquents, Lithic Psammaquents, Sodic Psammaquents, Spodic Psammaquents, Humaqueptic Psammaquents, Mollic Psammaquents, Typic Psammaquents, Sulfic Fluvaquents, Vertic Fluvaquents, Thapto-Histic Fluvaquents, Aquandic Fluvaquents, Aeric Fluvaquents, Humaqueptic Fluvaquents, Mollic Fluvaquents, Typic Fluvaquents, Aeric Epiaquents, Humaqueptic Epiaquents, Mollic Epiaquents, Typic Epiaquents, Sulfic Endoaquents, Lithic Endoaquents, Sodic Endoaquents, Aeric Endoaquents, Humaqueptic Endoaquents, Mollic Endoaquents, Typic Endoaquents.
Key to Subgroups : Haplic Ustarents, Sodic Xerarents, Duric Xerarents, Alfic Xerarents, Haplic Xerarents, Sodic Torriarents, Duric Torriarents, Haplic Torriarents, Alfic Udarents, Ultic Udarents, Mollic Udarents, Haplic Udarents. - Psamments
Key to Great Groups : Cryopsamments, Torripsamments, Quartzipsamments, Ustipsamments, Xeropsamments, Udipsamments.
- Fluvents
Key to Great Groups : Gelifluvents, Cryofluvents, Xerofluvents, Ustifluvents, Torrifluvents, Udifluvents.
Key to Subgroups : Aquic Gelifluvents, Typic Gelifluvents, Andic Cryofluvents, Vitrandic Cryofluvents, Aquic Cryofluvents, Oxyaquic Cryofluvents, Mollic Cryofluvents, Typic Cryofluvents, Vertic Xerofluvents, Aquandic Xerofluvents, Andic Xerofluvents, Vitrandic Xerofluvents, Aquic Xerofluvents, Oxyaquic Xerofluvents, Durinodic Xerofluvents, Mollic Xerofluvents, Typic Xerofluvents, Aquertic Ustifluvents, Torrertic Ustifluvents, Vertic Ustifluvents, Anthraquic Ustifluvents, Aquic Ustifluvents, Oxyaquic Ustifluvents, Aridic Ustifluvents, Udic Ustifluvents, Mollic Ustifluvents, Typic Ustifluvents, Ustertic Torrifluvents, Vertic Torrifluvents, Vitrixerandic Torrifluvents, Vitrandic Torrifluvents, Aquic Torrifluvents, Oxyaquic Torrifluvents, Duric Xeric Torrifluvents, Duric Torrifluvents, Ustic Torrifluvents, Xeric Torrifluvents, Anthropic Torrifluvents, Typic Torrifluvents, Aquertic Udifluvents, Vertic Udifluvents, Andic Udifluvents, Vitrandic Udifluvents, Aquic Udifluvents, Oxyaquic Udifluvents, Mollic Udifluvents, Typic Udifluvents.
- Orthents
Key to Great Groups : Gelorthents, Cryorthents, Torriorthents, Xerorthents, Ustorthents, Udorthents.
Torriorthents, Vertic Torriorthents, Vitrandic Torriorthents, Aquic Torriorthents, Oxyaquic Torriorthents, Duric Torriorthents, Ustic Torriorthents, Xeric Torriorthents, Typic Torriorthents, Lithic Xerorthents, Vitrandic Xerorthents, Aquic Xerorthents, Oxyaquic Xerorthents, Durinodic Xerorthents, Dystric Xerorthents, Typic Xerorthents, Aridic Lithic Ustorthents, Lithic Ustorthents, Torrertic Ustorthents, Vertic Ustorthents, Anthraquic Ustorthents, Aquic Ustorthents, Oxyaquic Ustorthents, Durinodic Ustorthents, Vitritorrandic Ustorthents, Vitrandic Ustorthents, Aridic Ustorthents, Udic Ustorthents, Vermic Ustorthents, Typic Ustorthents, Lithic Udorthents, Vitrandic Udorthents, Aquic Udorthents, Oxyaquic Udorthents, Vermic Udorthents, Typic Udorthents.
• Gellisol Sub Ordo : - Histels
Key to Great Groups : Folistels, Glacistels, Fibristels, Hemistels, Sapristels. Key to Subgroups : Lithic Folistels, Glacic Folistels, Typic Folistels, Hemic Glacistels, Sapric Glacistels, Typic Glacistels, Lithic Fibristels, Terric Fibristels, Fluvaquentic Fibristels, Sphagnic Fibristels, Typic Fibristels, Lithic Hemistels, Terric Hemistels, Fluvaquentic Hemistels, Typic Hemistels, Lithic Sapristels, Terric Sapristels, Fluvaquentic Sapristels, Typic Sapristels.
- Turbels
Key to Subgroups : Lithic Histoturbels, Glacic Histoturbels, Ruptic Histoturbels, Typic Histoturbels, Lithic Aquiturbels, Glacic Aquiturbels, Sulfuric Aquiturbels, Ruptic-Histic Aquiturbels, Psammentic Aquiturbels, Typic Aquiturbels, Lithic Anhyturbels, Glacic Anhyturbels, Petrogypsic Anhyturbels, Gypsic Anhyturbels, Nitric Anhyturbels, Salic Anhyturbels, Calcic Anhyturbels, Typic Anhyturbels, Lithic Molliturbels, Glacic Molliturbels, Vertic Molliturbels, Andic Molliturbels, Vitrandic Molliturbels, Folistic Molliturbels, Cumulic Molliturbels, Aquic Molliturbels, Typic Molliturbels, Lithic Umbriturbels, Glacic Umbriturbels, Vertic Umbriturbels, Andic Umbriturbels, Vitrandic Umbriturbels, Folistic Umbriturbels, Cumulic Umbriturbels, Aquic Umbriturbels, Typic Umbriturbels, Lithic Psammoturbels, Glacic Psammoturbels, Spodic Psammoturbels, Typic Psammoturbels, Lithic Haploturbels, Glacic Haploturbels, Folistic Haploturbels, Aquic Haploturbels, Typic Haploturbels.
- Orthels
Key to Great Groups : Historthels, Aquorthels, Anhyorthels, Mollorthels, Umbrorthels, Argiorthels, Psammorthels, Haplorthels.
Mollorthels, Folistic Mollorthels, Cumulic Mollorthels, Aquic Mollorthels, Typic Mollorthels, Lithic Umbrorthels, Glacic Umbrorthels, Vertic Umbrorthels, Andic Umbrorthels, Vitrandic Umbrorthels, Folistic Umbrorthels, Cumulic Umbrorthels, Aquic Umbrorthels, Typic Umbrorthels, Lithic Argiorthels, Glacic Argiorthels, Natric Argiorthels, Typic Argiorthels, Lithic Psammorthels, Glacic Psammorthels, Spodic Psammorthels, Typic Psammorthels, Lithic Haplorthels, Glacic Haplorthels, Fluvaquentic Haplorthels, Folistic Haplorthels, Aquic Haplorthels, Fluventic Haplorthels, Typic Haplorthels.
• Histosol Sub Ordo : - Folists
Key to Great Groups : Cryofolists, Torrifolists, Ustifolists, Udifolists.
Key to Subgroups : Lithic Cryofolists, Typic Cryofolists, Lithic Torrifolists, Typic Torrifolists, Lithic Ustifolists, Typic Ustifolists, Lithic Udifolists, Typic Udifolists.
- Wassists
Key to Great Groups : Frasiwassists, Sulfiwassists, Haplowassists.
Key to Subgroups : Fibric Frasiwassists, Sapric Frasiwassists, Typic Frasiwassists, Sulfic Haplowassists, Fibric Haplowassists, Sapric Haplowassists, Typic Haplowassists.
- Fibrists
Key to Subgroups : Hydric Cryofibrists, Lithic Cryofibrists, Terric Cryofibrists, Fluvaquentic Cryofibrists, Sphagnic Cryofibrists, Typic Cryofibrists, Hydric Sphagnofibrists, Lithic Sphagnofibrists, Limnic Sphagnofibrists, Terric Sphagnofibrists, Fluvaquentic Sphagnofibrists, Hemic Sphagnofibrists, Typic Sphagnofibrists, Hydric Haplofibrists, Lithic Haplofibrists, Limnic Haplofibrists, Terric Haplofibrists, Fluvaquentic Haplofibrists, Hemic Haplofibrists, Typic Haplofibrists.
- Saprists
Key to Great Groups : Sulfosaprists, Sulfisaprists, Cryosaprists, Haplosaprists. Key to Subgroups : Typic Sulfosaprists, Terric Sulfisaprists, Typic Sulfisaprists, Lithic Cryosaprists, Limnic Cryosaprists, Terric Cryosaprists, Fluvaquentic Cryosaprists, Typic Cryosaprists, Liptic Haplosaprists, Limnic Haplosaprists, Halic Terric Haplosaprists, Halic Haplosaprists, Terric Haplosaprists, Fluvaquentic Haplosaprists, Hemic Haplosaprists, Typic Haplosaprists.
- Hemists
Key to Great Groups : Sulfohemists, Sulfihemists, Luvihemists, Cryohemists, Haplohemists.
• Inceptisol Sub Ordo : - Aquepts
- Anthrepts
Key to Great Groups : Plagganthrepts, Haplanthrepts.
Key to Subgroups : Typic Plagganthrepts, Typic Haplanthrepts. - Gelepts
Key to Great Groups : Humigelepts, Dystrogelepts, Haplogelepts.
Key to Subgroups : Lithic Humigelepts, Andic Humigelepts, Aquic Humigelepts, Oxyaquic Humigelepts, Fluventic Humigelepts, Turbic Humigelepts, Eutric Humigelepts, Typic Humigelepts, Lithic Dystrogelepts, Andic Dystrogelepts, Aquic Dystrogelepts, Fluventic Dystrogelepts, Turbic Dystrogelepts, Typic Dystrogelepts, Lithic Haplogelepts, Andic Haplogelepts, Aquic Haplogelepts, Fluventic Haplogelepts, Turbic Haplogelepts, Typic Haplogelepts.
- Cryepts
Dystrocryepts, Spodic Dystrocryepts, Xeric Dystrocryepts, Ustic Dystrocryepts, Eutric Dystrocryepts, Typic Dystrocryepts, Lithic Haplocryepts, Aquandic Haplocryepts, Haploxerandic Haplocryepts, Vitrixerandic Haplocryepts, Haplustandic Haplocryepts, Ustivitrandic Haplocryepts, Andic Haplocryepts, Vitrandic Haplocryepts, Fluvaquentic Haplocryepts, Aquic Haplocryepts, Oxyaquic Haplocryepts, Lamellic Haplocryepts, Fluventic Haplocryepts, Calcic Haplocryepts, Xeric Haplocryepts, Ustic Haplocryepts, Typic Haplocryepts. - Ustepts
Key to Great Groups : Durustepts, Calciustepts, Humustepts, Dystrustepts, Haplustepts.
Haplustepts, Calcic Udic Haplustepts, Calcic Haplustepts, Aridic Haplustepts, Dystric Haplustepts, Udic Haplustepts, Typic Haplustepts.
- Xerepts
Key to Great Groups : Durixerepts, Fragixerepts, Humixerepts, Calcixerepts, Dystroxerepts, Haploxerepts.
- Udepts
Key to Great Groups : Sulfudepts, Durudepts, Fragiudepts, Humudepts, Eutrudepts, Dystrudepts.
Ruptic-Alfic Dystrudepts, Ruptic-Ultic Dystrudepts, Humic Dystrudepts, Typic Dystrudepts.
• Mollisol Sub Ordo : - Albolls
Key to Great Groups : Natralbolls, Argialbolls.
Key to Subgroups : Leptic Natralbolls, Typic Natralbolls, Xerertic Argialbolls, Vertic Argialbolls, Argiaquic Xeric Argialbolls, Argiaquic Argialbolls, Xeric Argialbolls, Aquandic Argialbolls, Typic Argialbolls.
- Aquolls
Key to Great Groups : Cryaquolls, Duraquolls, Natraquolls, Calciaquolls, Argiaquolls, Epiaquolls, Endoaquolls.
Thapto-Histic Endoaquolls, Aquandic Endoaquolls, Duric Endoaquolls, Cumulic Endoaquolls, Fluvaquentic Endoaquolls, Typic Endoaquolls.
- Rendolls
Key to Great Groups : Cryrendolls, Haprendolls.
Key to Subgroups : Lithic Cryrendolls, Typic Cryrendolls, Lithic Haprendolls, Vertic Haprendolls, Inceptic Haprendolls, Entic Haprendolls, Typic Haprendolls. - Gelolls
Key to Great Groups : Haplogellols.
Key to Subgroups : Lithic Haplogellols, Andic Haplogellols, Aquic Haplogellols, Oxyaquic Haplogellols, Turbic Haplogellols, Cumulic Haplogellols, Typic Haplogellols.
- Cryolls
Key to Great Groups : Duricryolls, Natricryolls, Palecryolls, Argicryolls, Calcicryolls, Haplocryolls.
Vertic Haplocryolls, Andic Haplocryolls, Vitrandic Haplocryolls, Aquic Cumulic Haplocryolls, Cumulic Haplocryolls, Fluvaquentic Haplocryolls, Aquic Haplocryolls, Oxyaquic Haplocryolls, Calcic Pachic Haplocryolls, Pachic Haplocryolls, Fluventic Haplocryolls, Calcic Haplocryolls, Ustic Haplocryolls, Xeric Haplocryolls, Typic Haplocryolls.
- Xerolls
Key to Great Groups : Durixerolls, Natrixerolls, Pallexerolls, Calcixerolls, Argixerolls, Haploxerolls.
Argixerolls, Calcic Pachic Argixerolls, Pachic Ultic Argixerolls, Pachic Argixerolls, Argiduridic Argixerolls, Duric Argixerolls, Calciargidic Argixerolls, Aridic Argixerolls, Calcic Argixerolls, Ultic Argixerolls, Typic Argixerolls, Aridic Lithic Haploxerolls, Lithic Ultic Haploxerolls, Lithic Haploxerolls, Torrertic Haploxerolls, Vertic Haploxerolls, Andic Haploxerolls, Vitritorrandic Haploxerolls, Vitrandic Haploxerolls, Aquic Cumulic Haploxerolls, Cumulic Ultic Haploxerolls, Cumulic Haploxerolls, Fluvaquentic Haploxerolls, Aquic Duric Haploxerolls, Aquultic Haploxerolls, Aquic Haploxerolls, Oxyaquic Haploxerolls, Calcic Pachic Haploxerolls, Pachic Ultic Haploxerolls, Pachic Haploxerolls, Torrifluventic Haploxerolls, Duridic Haploxerolls, Calcidic Haploxerolls, Torripsammentic Haploxerolls, Torriorthentic Haploxerolls, Aridic Haploxerolls, Duric Haploxerolls, Psammentic Haploxerolls, Fluventic Haploxerolls, Vermic Haploxerolls, Calcic Haploxerolls, Entic Ultic Haploxerolls, Ultic Haploxerolls, Entic Haploxerolls, Typic Haploxerolls.
- Ustolls
Key to Great Groups : Durustolls, Natrustolls, Calciustolls, Paleustolls, Argiustolls, Vermustolls, Haplustolls.
- Udolls
Key to Great Groups : Natrudolls, Calciudolls, Paleudolls, Argiudolls, Vermudolls, Hapludolls.
Key to Subgroups : Petrocalcic Natrudolls, Leptic Vertic Natrudolls, Vertic Natrudolls, Leptic Natrudolls, Glossic Natrudolls, Calcic Natrudolls, Typic Natrudolls, Lithic Calciudolls, Vertic Calciudolls, Aquic Calciudolls, Fluventic Calciudolls, Typic Calciudolls, Vertic Paleudolls, Petrocalcic Paleudolls, Aquic Pachic Paleudolls, Pachic Paleudolls, Aquic Paleudolls, Oxyaquic Paleudolls, Calcic Paleudolls, Typic Paleudolls, Lithic Argiudolls, Aquertic Argiudolls, Oxyaquic Vertic Argiudolls, Alfic Vertic Argiudolls, Vertic Argiudolls, Andic Argiudolls, Vitrandic Argiudolls, Aquic Pachic Argiudolls, Pachic Argiudolls, Aquic Argiudolls, Oxyaquic Argiudolls, Lamellic Argiudolls, Psammentic Argiudolls, Arenic Argiudolls, Abruptic Argiudolls, Alfic Argiudolls, Oxic Argiudolls, Calcic Argiudolls, Typic Argiudolls, Lithic Vermudolls, Haplic Vermudolls, Typic Vermudolls, Lithic Hapludolls, Aquertic Hapludolls, Pachic Vertic Hapludolls, Vertic Hapludolls, Andic Hapludolls, Vitrandic Hapludolls, Aquic Cumulic Hapludolls, Cumulic Hapludolls, Fluvaquentic Hapludolls, Fluventic Hapludolls, Aquic Pachic Hapludolls, Pachic Hapludolls, Aquic Hapludolls, Oxyaquic Hapludolls, Vermic Hapludolls, Calcic Hapludolls, Entic Hapludolls, Typic Hapludolls.
Key to Subgroups : Plinthic Acraquox, Aeric Acraquox, Typic Acraquox, Aeric Plinthaquox, Typic Plinthaquox, Histic Eutraquox, Plinthic Eutraquox, Aeric Eutraquox, Humic Eutraquox, Typic Eutraquox, Histic Haplaquox, Plinthic Haplaquox, Aeric Haplaquox, Humic Haplaquox, Typic Haplaquox.
- Torrox
Key to Great Groups : Acrotorrox, Eutrotorrox, Haplotorrox.
Key to Subgroups : Petroferric Acrotorrox, Lithic Acrotorrox, Typic Acrotorrox, Petroferric Eutrotorrox, Lithic Eutrotorrox, Typic Eutrotorrox, Petroferric Haplotorrox, Lithic Haplotorrox, Typic Haplotorrox.
- Ustox
Aquic Kandiustox, Humic Rhodic Kandiustox, Humic Xanthic Kandiustox, Humic Kandiustox, Rhodic Kandiustox, Xanthic Kandiustox, Typic Kandiustox. - Perox
Key to Great Groups : Sombriperox, Acroperox, Eutroperox, Kandiperox, Haploperox.
- Udox
Key to Great Groups : Sombriudox, Acrudox, Eutrudox, Kandiudox, Hapludox. Key to Subgroups : Petroferric Sombriudox, Lithic Sombriudox, Humic Sombriudox, Typic Sombriudox, Aquic Petroferric Acrudox, Petroferric Acrudox, Aquic Lithic Acrudox, Lithic Acrudox, Anionic Aquic Acrudox, Anionic Acrudox, Plinthic Acrudox, Aquic Acrudox, Eutric Acrudox, Humic Rhodic Acrudox, Humic Xanthic Acrudox, Humic Acrudox, Rhodic Acrudox, Xanthic Acrudox, Typic Acrudox, Aquic Petroferric Eutrudox, Petroferric Eutrudox, Aquic Lithic Eutrudox, Lithic Eutrudox, Plinthaquic Eutrudox, Plinthic Eutrudox, Aquic Eutrudox, Kandiudalfic Eutrudox, Humic Inceptic Eutrudox, Inceptic Eutrudox, Humic Rhodic Eutrudox, Humic Xanthic Eutrudox, Humic Eutrudox, Rhodic Eutrudox, Xanthic Eutrudox, Typic Eutrudox, Aquic Petroferric Kandiudox, Petroferric Kandiudox, Aquic Lithic Kandiudox, Lithic Kandiudox, Plinthic Kandiudox, Aquic Kandiudox, Andic Kandiudox, Humic Rhodic Kandiudox, Humic Xanthic Kandiudox, Humic Kandiudox, Rhodic Kandiudox, Xanthic Kandiudox, Typic Kandiudox, Aquic Petroferric Hapludox, Petroferric Hapludox, Aquic Lithic Hapludox, Lithic Hapludox, Plinthaquic Hapludox, Plinthic Hapludox, Aquic Hapludox, Inceptic Hapludox, Andic Hapludox, Humic Rhodic Hapludox, Humic Xanthic Hapludox, Humic Hapludox, Rhodic Hapludox, Xanthic Hapludox, Typic Hapludox.
Key to Great Groups : Cryaquods, Alaquods, Fragiaquods, Placaquods, Duraquods, Epiaquods, Endoaquods.
Key to Subgroups : Lithic Cryaquods, Placic Cryaquods, Duric Cryaquods, Andic Cryaquods, Entic Cryaquods, Typic Cryaquods, Lithic Alaquods, Duric Alaquods, Histic Alaquods, Alfic Arenic Alaquods, Arenic Ultic Alaquods, Arenic Umbric Alaquods, Arenic Alaquods, Grossarenic Alaquods, Alfic Alaquods, Ultic Alaquods, Aeric Alaquods, Typic Alaquods, Histic, Plagganthreptic Fragiaquods, Argic Fragiaquods, Typic Fragiaquods, Andic Placaquods, Typic Placaquods, Histic Duraquods, Andic Duraquods, Typic Duraquods, Lithic Epiaquods, Histic Epiaquods, Andic Epiaquods, Alfic Epiaquods, Ultic Epiaquods, Umbric Epiaquods, Typic Epiaquods, Lithic Endoaquods, Histic Endoaquods, Andic Endoaquods, Argic Endoaquods, Umbric Endoaquods, Typic Endoaquods.
- Gelods
Key to Great Groups : Humigelods, Haplogelods.
Key to Subgroups : Lithic Humigelods, Andic Humigelods, Aquic Humigelods, Turbic Humigelods, Typic Humigelods, Lithic Haplogelods, Andic Haplogelods, Aquic Haplogelods, Turbic Haplogelods, Typic Haplogelods.
- Cryods
Key to Great Groups : Placocryods, Duricryods, Humicryods, Haplocryods.
Oxyaquic Humicryods, Typic Humicryods, Lithic Haplocryods, Aquandic Haplocryods, Andic Haplocryods, Folistic Haplocryods, Aquic Haplocryods, Oxyaquic Haplocryods, Typic Haplocryods.
- Humods
Key to Great Groups : Placohumods, Durihumods, Fragihumods, Haplohumods. Key to Subgroups : Andic Placohumods, Typic Placohumods, Andic Durihumods, Typic Durihumods, Typic Fragihumods, Lithic Haplohumods, Andic Haplohumods, Plagganthreptic Haplohumods, Typic Haplohumods.
- Orthods
Key to Great Groups : Placorthods, Durorthods, Fragiorthods, Alorthods, Haporthods.
Key to Subgroups : Typic Placorthods, Andic Durorthods, Typic Durorthods, Aquic Fragiorthods, Alfic Oxyaquic Fragiorthods, Oxyaquic Fragiorthods, Plagganthreptic Fragiorthods, Alfic Fragiorthods, Ultic Fragiorthods, Entic Fragiorthods, Typic Fragiorthods, Oxyaquic Alorthods, Arenic Ultic Alorthods, Arenic Alorthods, Entic Grossarenic Alorthods, Entic Alorthods, Grossarenic Alorthods, Plagganthreptic Alorthods, Alfic Alorthods, Ultic Alorthods, Typic Alorthods
• Ultisol Sub Ordo : - Aquults
Key to Subgroups : Kandic Plinthaquults, Typic Plinthaquults, Aeric Plinthaquults, Plinthic Plinthaquults, Umbric Plinthaquults, Typic Plinthaquults, Vertic Albaquults, Kandic Albaquults, Aeric Albaquults, Typic Albaquults, Acraquoxic Kandiaquults, Arenic Plinthic Kandiaquults, Arenic Umbric Kandiaquults, Arenic Kandiaquults, Grossarenic Kandiaquults, Plinthic Kandiaquults, Aeric Kandiaquults, Umbric Kandiaquults, Typic Kandiaquults, Aquandic Kanhaplaquults, Plinthic Kanhaplaquults, Aeric Umbric Kanhaplaquults, Aeric Kanhaplaquults, Umbric Kanhaplaquults, Typic Kanhaplaquults, Vertic Paleaquults, Arenic Plinthic Paleaquults, Arenic Umbric Paleaquults, Arenic Paleaquults, Grossarenic Paleaquults, Plinthic Paleaquults, Aeric Paleaquults, Umbric Paleaquults, Typic Paleaquults, Plinthic Umbraquults, Typic Umbraquults, Vertic Epiaquults, Aeric Fragic Epiaquults, Arenic Epiaquults, Grossarenic Epiaquults, Fragic Epiaquults, Aeric Epiaquults, Typic Epiaquults, Arenic Endoaquults, Grossarenic Endoaquults, Aeric Endoaquults, Typic Endoaquults.
- Humults
Key to Great Groups : Sombrihumults, Plinthohumults, Kandihumults, Kanhaplohumults, Palehumults, Haplohumults.
Kanhaplohumults, Xeric Kanhaplohumults, Anthropic Kanhaplohumults, Typic Kanhaplohumults, Aquandic Palehumults, Andic Palehumults, Aquic Palehumults, Plinthic Palehumults, Oxyaquic Palehumults, Ustic Palehumults, Xeric Palehumults, Typic Palehumults, Lithic Haplohumults, Aquandic Haplohumults, Aquic Haplohumults, Andic Haplohumults, Plinthic Haplohumults, Oxyaquic Haplohumults, Ustic Haplohumults, Xeric Haplohumults, Typic Haplohumults.
- Udults
Key to Great Groups : Plinthudults, Fragiudults, Kandiudults, Kanhapludults, Paleudults, Rhodudults, Hapludults.
Arenic Plinthaquic Paleudults, Aquic Arenic Paleudults, Anthraquic Paleudults, Plinthaquic Paleudults, Fragiaquic Paleudults, Aquic Paleudults, Oxyaquic Paleudults, Lamellic Paleudults, Arenic Plinthic Paleudults, Psammentic Paleudults, Grossarenic Plinthic Paleudults, Plinthic Paleudults, Arenic Rhodic Paleudults, Arenic Paleudults, Grossarenic Paleudults, Fragic Paleudults, Rhodic Paleudults, Typic Paleudults, Lithic Rhodudults, Psammentic Rhodudults, Typic Rhodudults, Lithic-Ruptic-Entic Hapludults, Lithic Hapludults, Vertic Hapludults, Fragiaquic Hapludults, Aquic Arenic Hapludults, Aquic Hapludults, Fragic Hapludults, Oxyaquic Hapludults, Lamellic Hapludults, Psammentic Hapludults, Arenic Hapludults, Grossarenic Hapludults, Inceptic Hapludults, Humic Hapludults, Typic Hapludults.
- Ustults
Key to Great Groups : Plinthustults, Kandiustults, Kanhaplustults, Paleustults, Rhodustults, Haplustults.
Arenic Haplustults, Ombroaquic Haplustults, Plinthic Haplustults, Kanhaplic Haplustults, Typic Haplustults.
- Xerults
Key to Great Groups : Palexerults, Haploxerults.
Key to Subgroups : Aquandic Palexerults, Aquic Palexerults, Andic Palexerults, Typic Palexerults, Lithic Ruptic-Inceptic Haploxerults, Lithic Haploxerults, Aquic Haploxerults, Andic Haploxerults, Lamellic Haploxerults, Psammentic Haploxerults, Arenic Haploxerults, Grossarenic Haploxerults, Typic Haploxerults.
• Vertisol Sub Ordo : - Aquerts
Key to Great Groups : Sulfaquerts, Salaquerts, Duraquerts, Natraquerts, Calciaquerts, Dystraquerts, Epiaquerts, Endoaquerts.
Endoaquerts, Ustic Endoaquerts, Aeric Endoaquerts, Leptic Endoaquerts, Entic Endoaquerts, Chromic Endoaquerts, Typic Endoaquerts.
- Cryerts
Key to Great Groups : Humicryerts, Haplocryerts.
Key to Subgroups : Sodic Humicryerts, Typic Humicryerts, Sodic Haplocryerts, Chromic Haplocryerts, Typic Haplocryerts.
- Xererts
Key to Great Groups : Durixererts, Calcixererts, Haploxererts.
Key to Subgroups : Hallic Durixererts, Sodic Durixererts, Aquic Durixererts, Aridic Durixererts, Udic Durixererts, Haplic Durixererts, Chromic Durixererts, Typic Durixererts, Lithic Calcixererts, Petrocalcic Calcixererts, Aridic Calcixererts, Leptic Calcixererts, Entic Calcixererts, Chromic Calcixererts, Typic Calcixererts, Lithic Haploxererts, Halic Haploxererts, Sodic Haploxererts, Aridic Haploxererts, Aquic Haploxererts, Udic Haploxererts, Leptic Haploxererts, Entic Haploxererts, Chromic Haploxererts, Typic Haploxererts.
- Torrerts
- Usterts
Key to Great Groups : Dystrusterts, Salusterts, Gypsiusterts, Calciusterts, Haplusterts.
Key to Subgroups : Lithic Dystrusterts, Aquic Dystrusterts, Aridic Dystrusterts, Udic Dystrusterts, Leptic Dystrusterts, Entic Dystrusterts, Chromic Dystrusterts, Typic Dystrusterts, Lithic Salusterts, Sodic Salusterts, Aquic Salusterts, Aridic Salusterts, Leptic Salusterts, Entic Salusterts, Chromic Salusterts, Typic Salusterts, Lithic Gypsiusterts, Halic Gypsiusterts, Sodic Gypsiusterts, Aridic Gypsiusterts, Udic Gypsiusterts, Leptic Gypsiusterts, Entic Gypsiusterts, Chromic Gypsiusterts, Typic Gypsiusterts, Lithic Calciusterts, Halic Calciusterts, Sodic Calciusterts, Petrocalcic Calciusterts, Aridic Calciusterts, Udic Calciusterts, Leptic Calciusterts, Entic Calciusterts, Chromic Calciusterts, Typic Calciusterts, Lithic Haplusterts, Halic Haplusterts, Sodic Haplusterts, Petrocalcic Haplusterts, Gypsic Haplusterts, Calcic Haplusterts, Aridic Leptic Haplusterts, Aridic Haplusterts, Leptic Haplusterts, Udic Haplusterts, Entic Udic Haplusterts, Chromic Udic Haplusterts, Udic Haplusterts, Leptic Haplusterts, Entic Haplusterts, Chromic Haplusterts, Typic Haplusterts.
- Uderts
Key to Great Groups : Dystruderts, Hapluderts.
BAHAN DAN METODE
Tempat dan Waktu Penelitian
Penelitian ini dilakukan di Desa Sihiong, Sinar Sabungan, dan Lumban Lobu, Kecamatan Bonatua Lunasi, Kabupaten Toba Samosir. Analisis
laboratorium dilakukan di Laboratorium Riset dan Teknologi, Kimia-Kesuburan Tanah Fakultas Pertanian, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan,
pada bulan April 2011 sampai dengan selesai.
Bahan dan Alat
Adapun bahan yang digunakan adalah sampel tanah dari setiap lapisan profil, bahan-bahan kimia yang digunakan untuk menganalisa tanah di laboratorium, formulir isian deskripsi profil tanah, dan bahan lain untuk analisis tanah di lapangan dan di laboratorium.
profil tanah serta keadaan daerah penelitian, kantong plastik untuk tempat sampel tanah, pisau pandu untuk menentukan horison dan batas horison, cangkul untuk menggali profil tanah, label nama sebagai penanda sampel tanah, alat tulis dan alat pendukung lainnya seperti spidol permanen.
Metode Penelitian
Metode yang dilakukan pada penelitian ini adalah metode survai dengan melakukan pengamatan di lapangan untuk membandingkan jenis tanah berdasarkan peta jenis tanah yang ada. Dan setelah dilakukan pengamatan, ditentukan profil pewakil tanah untuk membandingkan jenis tanah dengan menggunakan Taksonomi Tanah 2010.
Pelaksanaan Penelitian
Persiapan
Sebelum dilakukan penelitian, terlebih dahulu dilakukan konsultasi dengan dosen pembimbing, telaah pustaka, penyusunan usulan penelitian, pengadaan peta-peta yang diperlukan, mengadakan pra survey ke lapangan dan penyediaan bahan serta peralatan yang digunakan di lapangan.
Kegiatan di Lapangan
a) Pemilihan daerah penelitian
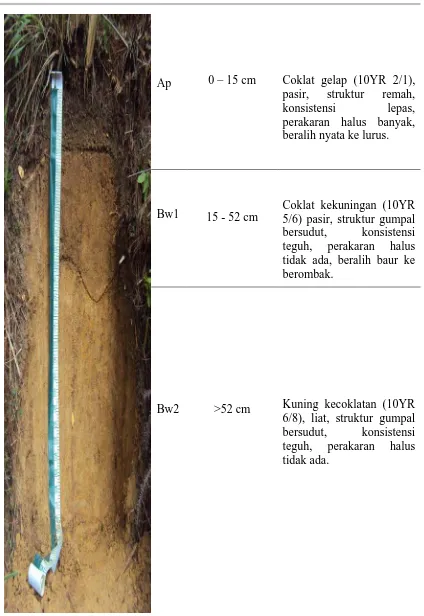
- Profil I di Desa Sihiong terletak dengan ketinggian tempat 1024 m dpl dan koordinat 2031'12.38" LU– 9907'14.81" BT.
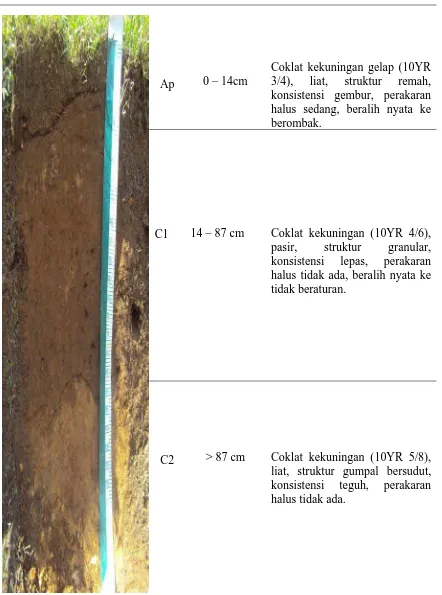
-Profil II di Desa Sinar Sabungan terletak dengan ketinggian tempat 991 m dpl dan koordinat 2031'56.64" LU– 9907'54.51" BT.
- Profil III di Desa Lumban Lobu terletak dengan kemiringan tempat 1071 m dpl dan koordinat 2030'26.96" LU- 9909'41.37" BT.
b) Pembuatan profil tanah
Profil tanah dibuat dengan menggali sampai kedalaman maksimal (solum tanah) dengan ukuran 1 m x 1 m x 1,5 m dan digambarkan menurut
lapisan atau horizon tanahnya. Pada tiap daerah penelitian dilakukan penggalian profil yang mewakili tiap daerah penelitian untuk karakterisasi tanah yang menunjukkan sifat dan ciri morfologi tanah yang akan diamati. c) Pengamatan sifat-sifat tanah pada profil tanah
Pengamatan sifat-sifat tanah ini meliputi batas horison atau lapisan, warna tanah, tekstur tanah, struktur tanah, konsistensi tanah dan kedalaman efektif.
d) Pengambilan contoh tanah