i
AN ANALYSIS ON FORM, FUNCTION, AND REASON
OF CODE-SWITCHING AND CODE-MIXING USED
IN VLOG OF SHIRIN AL ATHRUS
A GRADUATING PAPER
Submitted to the Board Examiners as a Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements for the Degree of Sarjana Pendidikan (S.Pd)
By:
Lailatul Maghfiroh 113-14-200
ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
TEACHER TRAINING AND EDUCATION FACULTY
STATE INSTITUTE FOR ISLAMIC STUDIES (IAIN)
ii
DECLARATION
In the name of Allah, The most gracious and merciful
Hereby, the researcher declares that this graduating paper is written by the writer herself. This paper doesn’t contain any materials which have been published by other people and it doesn’t cite any other people’s ideas except the information from the references.
In addition, this declaration is written by the writer to be understood.
iii
agree if the library of IAIN Salatiga publish this graduating paper.
Salatiga, 13
September 2018
The writer
Lailatul Maghfiroh
Salatiga, September 13th, 2018
Sari Famularsih, S.Pd.I., M.A
The Lecturer of English Education Department State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga
ATTENTIVE COUNSELOR’S NOTE
Case: Lailatul Maghfiroh’s Graduating Paper
Dear,
Dean of Teacher Training and Education Faculty
Assalamualaikum Wr.Wb
iv
accepted by the Teacher Training and Education Faculty I hope this paper will be examined as soon as possible.
Wassalamualaikum Wr.Wb
Counselor,
Sari Famularsih, S.Pd.I., M.A.
v
MOTTO
“NEVER STOP DOING NEW THINGS BEFORE YOU GET WHAT YOU WANT”
(WRITER)
vi
DEDICATION
1. My God Allah SWT who always beside me, blessing me, listen all my prays, take care me, and give me all the best thing in this whole world.
2. My parents, especially for my beloved mother (Sri Rahayu) and my beloved father (Muhammad Ghozali) thanks for your pray, your supports, your love and anything. Without you, my live faded.
3. My beloved brother (Irfan Ghozali) and my beloved sister (Tasniatul Mughibah) who always give me support and anything about my study.
4. Almarhum K.H Zoemri RWS and Nyai Latifah Zoemri as the founder of Islamic Boarding School Al Falah Salatiga, who always gives me advise and motivation to be a good person.
5. My counselor, Mrs. Sari Famularsih, S.Pd.I.,M.A. who always gives me guidance, suggestion and motivation to finish my graduating paper.
6. My Big Familiy Bani Ghozali who become my best motivator. 7. Someone who always give lot of spirit and support.
8. My best friends all member of PPTI Al Falah 14, especially Erika, Ummah, Malikah, Ulfah, and Hanifah who always support me and always inside me. 9. All of My TBI F class IAIN Salatiga, whom I can’t mention one by one.
Thank for become my friend in IAIN Salatiga .
10. My best friend ever “Waduk Sempor” ( Agus, Awalia, Iis, Arif, Nidya) who always beside me whenever I need, always giving me a lot of supports, smile, laugh, and anything which can make my study more colorful.
vii
12. My Friends of TOEFL CLUB who always help me to finish this graduating paper.
13. PPL Grissa Squad who give me motivation and knowledge,
viii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Bismillahirrahmanirrahim,
All praise due to Allah, the Most Gracious and the Most Merciful because of His wonderful blessing and His mercy, the writer can finish this graduating paper successfully. The incredible blessings make realize that nothing is impossible in the eyes. Thanks for Your will and endless blessing in my life. Peace and salutation always be given to our beloved prophet Muhammad SAW that we hope his blessing in the Judgment day. However, this success would not be achieved without the support, guidance, advice, help and encouragement from individuals and institutions. Therefore, the writer would like to express the deepest gratitude to:
1. Dr. Rahmat Hariyadi, M. Pd., Rector of State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga.
2. Suwardi, M. Pd., Dean of Teacher Training and Education Faculty of State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga
3. Noor Malihah, Ph. D., as the Head of English Education Department.
4. Sari Famularsih, S.Pd.I., M.A , as the consultant of this research thanks for suggestion and recommendation for this research from beginning until the end. 5. All lecturers of English Education Department of IAIN Salatiga, thank for your
advice, knowledge, and kindness.
ix
7. My beloved family who always support and advise me.
8. All of my friends in IAIN Salatiga, especially for English Education Department’14, from A class until F class whose names cannot be mentioned one by one, thank for being my friends.
Finally, this graduating paper is expected to be able to provide useful knowledge and information to the readers.
Salatiga, 13 September 2018
The writer
Lailatul Maghfiroh
x
ABSTRACT
Maghfiroh, Lailatul. 2018. An Analysis on Form, Function and Reason of Code-Switching and Code-Mixing Used in Vlog of Shirin Al Athrus. A Graduating Paper . English Education Department of State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga.
Consultant: Sari Famularsih, S.Pd.I., M.A
This research focuses on form, function and reason of Switching and Code-Mixing used in Vlog of Shirin Al Athrus. This research is aimed to answer the following problem: 1.What are the forms of Code-Switching and Code-Mixing used in Vlog of Shirin Al Atrus. 2.What are the functions of Code-Switching and Mixing used in Vlog of Shirin Al Atrus. 3.What are the reasons of Code-Switching and Code-Mixing used in Vlog of Shirin Al Atrus. To answer the problem, the researcher used descriptive qualitative research and validated through theoretical triangulation. The total data 133 unit of analysis of Code-Switching found that 26 data used tag switching, 24 data used inter-sentential switching and 73 datas used intra-sentential switching. Furthermore, the total data of Code-Mixing was 138 unit analysis which found 73 insertion of words, 38 insertion of phrases, 23 insertin of hybrid, and 4 insertion of reduplications. The result of the functions performed Code-Switching were 28 addressee specifications, 7 repetitions, 8 interjections, 14 message qualifications, 38 personalizations and objectivizations, and 38 facility of expressions. Moreover, the result of the functions performed through Code-Mixing were 4 addressee specifications, 3 repetitions, 10 interjections, 4 message qualifications, 0 personalizations and objectivization, and 117 facility of expressions. This research also found that there are 4 reasons of using Code-Switching. Those are 7 data talking about particular topics, 8 data interjections (Inserting sentence fillers or sentence connectors), 7 data repetition used for clarifications, and 111 data intention of clarifying the speech content for interlocutors.While the researcher found that there are 5 reasons of using Code-Mixing. Those are 2 data talking about particular topics, 10 data interjections (Inserting sentence fillers or sentence connectors), 3 data repetition used for clarifications, 29 data intention of clarifying the speech content for interlocutors, and 94 data because of real lexical needs.
xi
E. Significance of the study ... 6
1. Theoretical Benefit ... 6
G. Graduating paper Outline ... 9
CHAPTER II: THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK A. Previous Study ... 11
B. Review of related Theory... 14
xii
2. Code-Switching ... 15
3. Code-Mixing ... 16
4. Form of Code-Switching ... 19
a. Form of Code-Mixing ... 19
4) Insertion of Reduplication ... 28
5) Insertion of Idiom ... 29
6) Insertion of Caluse ... 29
5. Function of Code-Switching and Code-Mixing ... 30
a. Quotation ... 30
b. Addressee Specification ... 31
c. Repetition ... 32
d. Interjection ... 32
e. Message Qualification ... 33
f. Personalization and Objectivization ... 34
g. Facility of Expression ... 35
6. Reason of Code-Switching and Code-Mixing ... 35
a. Talking about a particular topic ... 35
b. Quotation somebody else ... 36
c. Being emphatic about something (Express Solidarity) ... 36
d. Interjection (Inserting sentence fillers or sentence connectors). 37 e. Repetition used for clarification ... 37
f. Intention of clarifying the speech content for the interlocutor .. 38
g. Expressing group identity ... 38
xiii
i. Because of real lexical need ... 39
j. To exclude other people when a comment is intended for only a limited audience ... 39
7. Video-Blogging (Vlog) ... 40
CHAPTER III: RESEARCH METHODOLOGY A. Type of the Study ... 42
B. Object of the Study ... 43
C. Source of the Data ... 43
D. Technique of Data Collections... 43
E. Technique of Data Analysis ... 44
1. Identification ... 44
2. Coding ... 44
3. Categorizing ... 48
4. Classifying ... 48
5. Producing an Account ... 49
F. Validity of Dhe Data ... 49
CHAPTER IV: RESEARCH FINDING AND DATA ANALYSIS A. Research Finding ... 51
B. Data Analysis ... 55
1. Code-Switching ... 54
a. Tag Switching ... 55
b. Inter-sentential Switching ... 56
c. Intra-sentential Switching ... 58
2. Code-Mixing ... 59
a. Insertion of Word ... 59
b. Insertion of Phrase ... 61
c. Insertion of Hybrid ... 62
d. Insertion of Reduplication ... 64
xiv
a. Addressee Secification ... 65
b. Repetition ... 66
c. Interjection ... 67
d. Message Qualification ... 68
e. Personalization and Objectivization ... 68
f. Facility of Expression ... 69
4. Reason of Code-Switching and Code-Mixing ... 70
a. Talking about particular topic ... 71
b. Interjection ... 72
c. Repetition used for clarification ... 72
d. Intention of clarifying the speech content for interlocutor ... 74
e. Because of real lexical need ... 74
CHAPTER V: CLOSURE A. Conclusion ... 76
B. Suggestion ... 79
1. For the researcher ... 78
2. For the readers ... 78 REFFERENCES
APPENDICES
xv
LIST OF THE TABLES
Table 2.1 Table Differences between Code-Switching and Code-Mixing 18
Table 2.2 Table Part of Speech ... 23
Table 2.2 Table Phrase ... 24
Table 2.3 Table Hybrid ... 28
Table 3.1 Table Coding of Videos... 45
Table 3.2 Table Coding of Form Code-Switching ... 45
Table 3.3 Table Coding of Form Code-Mixing ... 46
Table 3.4 Table Coding of Function of Swtching and Code-Mixing... ... 46
Table 3.5 Table Coding of Reason of Switching and Code-Mixing ... 47
Table 4.1 Table The Frequencies Form of Switching and Code-Mixing ... 52
Table 4.2 Table The Frequencies Function of Code-Switching and Code-Mixing ... 53
1 CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
The researcher tries to present the introduction related to the study. It consist of background of the study, problem of the study, object of the study, limitation of the study, benefits of the study, definition of key term and graduating paper outline.
A. Background of the Study
In daily interaction, people use a language or more either written or spoken to do their communication. Brown (2000, p.17) explained “Language is a system of arbitrary conventionalized vocal, written and gesture symbols that enables members of a given community to communicate intelligibly with one another”. Human as social creature, they live in their community within language, culture and also tradition. Therefore, it is impossible to communicate with others without language. People use language to gain understanding their willingness, needs or intention. In the way to communicate, there are many languages are use in the world. One of them is English.
2
to be mastered to know the information in the different countries in the world. In Indonesia, English is considered at the first foreign language and become compulsory subject learned by all students from the elementary school to university level.
In our daily life, we will be faced with different society who has the different language. Language and societies are two things that cannot be separated. Both of them have a close relation. It refers to human role as a social creature in the world which needs to keep in touch with another human being. In linguistic, it is known as sociolinguistics. According to Holmes (1992, p.1) “Sociolinguistic studies the relationship between language and society, speak different social context, concerned with identifying the social function of language and the way it is used to convey social meaning, examining the way people use language in different social contexts provides a wealth of information about the way language works, as well as about the social relationship in a community”. While according to Wardhaugh (2006, p.1), “sociolinguistic is the study of language use in society that did not focus on the composition of sentence structure but focuses on differences in language use and language development in society”. Thus, sociolinguistics provides the insight about the language change during the communication in a society.
3
bilingual languages. It is to establish a good communication based on the social factors in communication, such as the participant, the setting or social context of the interaction, the topic, the function and the reason of the communication. According to Lado (1964, p.214) argues that bilingualism is the ability to use 2 languages by someone with as good or almost as good, which is related to the knowledge of two languages regardless of level. It can be concluded that bilingualism is the use of two languages by speaker in the interaction with other speakers in different language. Bilingualism is related to Code-Switching and Code Mixing since all of them get in touch with two different languages. Many Code-switching and Code-Mixing’s events occur both in Indonesian people conversation to make the interlocutor understand, sometimes they do it with the same language background and it may do so many times.
Hymes (1974, p.103) defines “Code switching is common term for alternative use of two languages, varieties of a language or even speech styles”. While Bokamba (1989) explains “Code Switching is mixing word,
4
and Code-Mixing are usually used by Indonesian to attain a good communication in a society. Code-Switching and Code-Mixing not only used in direct interaction but also in a social media.
In globalization era, internet develops many aspect of life. Most of people in the world alike are seeing new ways to express their art though technological means. YouTube has become the fourth most visited website in the world (Lewis, 2018)- behind emails sent, messages and text messages. Since its creation on February 2005, YouTube saw repid growth, sixteen months after its creation, 100 million clips were being view per day (comScore, 2006). Many famous sites are on YouTube, one of them is Vlog. Vlog or Video-Blogging is a form of blogging activity by using video medium and text or audio as a media source device. Vlog can be refereed as another form of internet television. In Indonesia, Vlog began to be realized in 2009 when appeared a private recording video of famous actress and singer. Nowadays, not only private video but also Vlog is used to market a product or brand. Many Indonesian actress use Vlog, because they realize that Indonesian people begun to leave television and it more interesting to find more fans.
It was discovered when the researcher watched actress’s Vlog in YouTube. The researcher found the phenomena about Code-Switching and Code-Mixing usage in the Vlog of Shirin Al Athrus. For Example:
5
bahasanya because I much more comfortable speaking at that way. Dimulai dari 2007 aku umur 6 tahun, aku inget banget ke rumah om aku, dia sok iseng2 bikinin aku Facebook account, dia asal bikinin aja padahal aku belum pernah mainin sampe 1 tahun 2 tahun kedepanya dimana facebook itu lagi booming banget di Indonesia.
In that utterance, Shirin was speaking using both bahasa Indonesian as her mother tongue and English as the second language. That utterance is contained Code-Switching and Code-Mixing phenomenon. It is because there are some switches within sentence boundary and some insertion of English words within bahasa Indonesia sentences.
This research focuses in analyzing Switching and Code-Mixing phenomena in Shirin’s Vlog an entitled How I Start My Career, First Magazine Cover, Dubai Cloting haul, and My Lombok Trip which are uploaded on Shirin’s YouTube account. They are chosen for this research, because these videos are contained Indonesian-English language. This research selects Shirin Al Athrus because she is one of Indonesian public figure and models who is fluent in speaking both bahasa Indonesia and English, even though she is not a native speaker.
6
Shirin Al Athrus. Therefore, the researcher formulates a research study entitled “AN ANALYSIS ON FORM, FUNCTION AND REASON OF CODE-SWITCHING AND CODE-MIXING USED IN VLOG OF SHIRIN AL ATHRUS”.
B. Problem of the Study
Based on the background of study, the researcher formulates some statements of the problems as follows:
1. What are the forms of Code-Switching and Code-Mixing used in Vlog of Shirin Al Athrus?
2. What are the functions of Code-Switching and Code-Mixing used in Vlog of Shirin Al Athrus?
3. What are the reasons of Code-Switching and Code-Mixing used in Vlog of Shirin Al Athrus?
C. Object of the Study
Dealing with the statement of the problems above, the researcher intends to achieve some objectives through the study as follows:
1. To identify form of Code-Switching and Code-Mixing used in Vlog of Shirin Al Athrus.
2. To examine the function of Code-Switching and Code-Mixing used in Vlog of Shirin Al Athrus
7 D. Limitation of the Study
This research focuses on form, function, and reason of Code-Switching and Code-Mixing used by Shirin Al Athrus in her Vlog. The researcher only analyzes the Indonesian-English Switching and Code-Mixing.
E. Significant of the Study 1. Theoretical Benefits
This study is expected to enrich theoretical prespective on code-Switching and Code-Mixing used by Shirin Al Athrus, especially, how to analyze the utterance of language research in switching and Code-Mixing theory as that shown by Shirin’s Vlog.
2. Practical Benefits a. For lecturers
This study not only contains the theory about Code-Switching and Code-Mixing, but also the usage in the interaction based on form, function and reason. Therefore, the English lectures are able to use the data to provide the real usage of switching and mixing codes in the interaction for teaching and learning activity, especially in speaking skill.
b. For teachers
8
mixing codes. Moreover, the teachers can practice to switch and mix the codes to interact with the students who are not fluent yet in speaking English.
c. For students
This research aims as the one of the references for the students while studying about Code-Switching and Code-Mixing. In addition, this study is made as the bridge to fill the gap between the previous study to the further study about Code-Mixing and Code-Switching in the development of the future communication technology.
F. Definition of Key Terms
The researcher defines some of key terms used in the study, in order to avoid miss understanding about those terms, here is the list of definition which has been conducted by the researcher.
1. Code-Switching
Code-9
Switching used between bilingual or multilingual communities who are fluent in each used language. The reasons people code switch are complex, but it is often the case that people use a particular language or dialect to announce their identity (Brown & Attaardo, 2000, p.91). Indeed, switching codes used on its reason to inform their identity.
2. Code-Mixing
Code-Mixing is ability to use or mixing two or more languages in a conversation. Sridhar as Quoted by Risdianto (2013: 43-44) explained “Code mixing as the transition from using linguistic units (word, phrase, clause, etc) of one language to using those of another within a single sentence”. Differs from Code-Switching which emphasizes a bilingual or multilingual movements from one grammatical system to another, Code-Switching is formed by grammatical distiction and emphasizes the formal aspects of language structures or linguistic competence. In another hand, Hoffman (1991: 104) said that “Code-Mixing refers to switch occurring at the lexical level.”
3. Vlog
10
YouTube is one of social media based on video. Many contends of various video can be accessed in YouTube, as like music, film, news an information, sport, style, game and Vlog. Vlog is video that contain an opinion, story or daily activity that usually written on a blog.
G. Graduating Paper Outline
The researcher wants to arrange the graduating paper in order to be understood by the reader easily. It is devising into five chapters.
Chapter I presents the background of the study, problem of the study, objective of the study, limitation of the study, significant of the study, definition of the key terms and graduating paper outline.
Chapter II is the theoretical framework. It consists of the previous studies and review of related theory in order to strengthen the theory of the research.
Chapter III is research Methodology. It consists of type of the research, object of the research, data sources, technique of data collection, data analysis, and procedure of the research.
Chapter IV is research findings. It is consist of finding about the form used in Code Switching and Code Mixing. Furthermore, the finding talk about the function and the reason of using Code-Switching and Code-Mixing.
11 CHAPTER II
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
In this chapter the researcher intends to present the theoretical farmwork of the study, it consists of previous studies and literature review which related to the study.
A. Previous study
The researcher has found some of the previous studies about improving students’ proficiency in English as follows:
Indonesian-12
English is likely to be the most frequent language combinations used in the tweets (73.33%). Moreover, in relation to the reason, real lexical need may be considered as the main reason to switch the language in Twitter (60%).
The second study is graduating paper which proposed by Rosyida (2017). In this descriptive qualitative study, the research mainly focuses on grammatical items usage and the function of Switching and Code-Mixing performed in the written form of Celebgram interaction. The data are collected from status updates during January 1st until March 31st 2017. The research used theory of Moleong (2009) for analyzing the data and validated through theoretical triangulation. The result showed there are some functions on using Code-Switching and Code-Mixing, they are quotation, specifications, repetitions, interjections, qualifications, personalizations and objecivizations. Based on the data that found by researcher, the common function to be used is interjection.
The third is a graduating paper which written by Yolla Shinta Noer Aini (2017). This research focuses in analyzing Maudy Ayunda’s
13
that there are six reasons of using Code-Switching and Code-Mixing, three types of interference as the impact of Code-Switching and Code-Mixing usage.
14 B. Review of Related Theory
1. Sociolinguistics
Noam Chomsky in Romaine (2000, p.1) stated that sociolinguistics focus on differences in the use of language in society so that an object can be the object language learning another language. Then Chomsky said that the question of language is the fundamental question of power. From the statement, it is clear that sociolinguistic is the study of language use in a society that does not focus on the composition of sentence structure but focuses on differences in language use and language development.
Holmes (1992, p.2) defines sociolinguistic study the relationship between language and society. They are interested in explaining why we speak differently in different social contexts, and they are concerned with identifying the social functions of language and the ways it is used to convey social meaning. The statement implies that sociolinguistic focuses on speaking in different social context, and it is concerned with identifying the social function and the social meaning when it is used.
15
function in communication”. It deals with the aim of the language
function in a social context and the development of language in society. Sociolinguistic studies about social and language. It goals to do research about social function based on what kind of thing language that used.
2. Code Switching
People use language as a code to communicate with others. Usually, the code is useful for speakers to get better understanding with others. Wardhaugh (2006, p.101), " people then, are usually required to select particular code whenever they choose to speak, and they may also decide to switch from one code to another or to mix even within sometimes very short utterances and create a new code in a process known as code-switching". Code-Switching is possibly common by bilingual or multilingual users from one language to another language.
16
their right and obligation. It can be concluded that code-switching is a strategy that is used in bilingual or multilingual communities by using more one language.
Code-Switching is the use of multiple languages in the words, phrases, and sentences even in a paragraph. According to Offiong and Okon (2013) state that code-switching is a practice of parties in discourse to signal changes in context by using alternative grammatical system or subsystem or codes. While according to Bokamba (1989) defies that code-switching is the mixing of words phrases and sentence from two distinct grammatical (sub) system across sentence boundaries within the same speech event. Based on these statements, code-switching occurs when there is a combination of two or more languages and it combines word, phrases, and sentences. The switches are often very short and they are made primarily for the social reasons-to signal the speaker's ethnic identity and solidarity with the address (Holmes, 1992, p.41). Furthermore, some switching is used as a conversational strategy to express solidarity with an addressee.
3. Code Mixing
17
referred to all cases where lexical items and grammatical features from two languages appear in one sentence". Kachru in Nusjam (2004) as quoted by Ansar (2017) defines code mixing as the term refers to the use of one more languages for consistent transfer of linguistic units from one language into other, and by such a language mixture developing a new restricted or not so restricted code of linguistic interaction.
From the definition above, it can be concluded that code-mixing refers to code-mixing some parts of another language such as word or phrases in a certain topic without breaking grammatical rules and it can involve the various level of language. In some situation, the speakers mix the language because they cannot find the exact term or idiom from the other language. Therefore, it is possible to mix another term or idiom from the other language.
For example:
Sekarang aku pengen ganti baju, tadi sudah lihat kan? snick pic nya warnanya tuh kaya earthy terus ada yang rose gold juga dan menurutku si warnanya aku banget.
18
Code-Switching and Code-Mixing have strong similarities. It is necessary to understand the difference between Code-Switching and Code-Mixing. The table below shows the summarized differences between code switching and code mixing according to Jendra (2010, p.80):
Table 2.1
Differences between Code-Switching and Code-Mixing
Points of View Code-Switching Code-Mixing Grammatical
items involved
Sentence and clause Phrase, word, morpheme, phonemes
Base language Clear Sometimes unclear Topics May change Maintained
Situations Formal and informal More likely informal Bilingual
fluencies
Partial Total
19
“kalau seseorang menggunakan satu kata atau frase
dari satu bahasa, dia telah menggunakan campur kode. Tetapi apabila satu kalausa jelas-jelas memiliki struktur gramatika suatu bahasa , dan klausa berikutnya di susun menurut struktur gramtika bahasa lain, maka peristiwa yang terjadi
adalah alih kode”.
(“if someone uses a word or phrase from a language, she/he has been using code-mixing. But if the clause clearly has a grammatical structure of a language, and the clause drawn up with the grammatical structure in another language, then it is called code-switching”)
On the other hand, the base of the language of code-switching and code-mixing is different. The base language of code-switching is clear while the base language of code-mixing is unclear because the listener may not expect which of language is the base language. Moreover, the code called switch when there is changing the topic or situation that causes the speaker needs switch the code to another language while mix appears because there is no changing topic or situation in one sentence. In another difference can be seen in the situation take place. Switch commonly occurs in a formal and informal situation whereas mix more likely takes place in the informal situation.
4. Form of Code Switching and Code Mixing
a. Form of Code-Switching
inter-20
sentential switching and the third is intra-sentential switching.
1) Tag Switching
Emblematic switching or tag switching is the switch in simply an interjection, a tag, or a sentence filter in the other language which serves as an ethnic identity marker (Holmes, 1992, p.42). Tag switching occurs when bilingual puts short expression (tag) at the end of utterance in a different language. Alcnauerova (2013) as quoted by Sihite (2016, p.22) states "tag as isolated words or phrases which are not related syntactically to the rest of utterance".
Example:
(a) Tamati: Engari (SO) now we turn to more important matters. (Switch between Maori and English)
(b) Ming :Confiscated by Customs, da gai (PROBABLY). (switch between English and Chainese)
(c) A : Well I’m glad I met you. Ok?
B : adale pues (OK SWELL), and do come again. Mm? (switch between Spanish and English)
Holmes (1992, p.41-42)
21 2) Inter-sentential Switching
According to Tatsioka (2010, p.130) “Inter-sentential switching is described as the switch between sentence boundaries, where the sentence is in one language and other in another. In same what Tatsioka said, inter-sentential switching occurs at sentence level, where each clause or sentence is in one language or the other. This also may include a switch from a whole sentence or more than one sentence produced completely in one language.
Example:
“ini lagu lama, tahun 60an. It’s oldiest but goodies,
they said. Tapi, masih enak kok didengerin”
In addition, Hoffman (1991, p.112) argues “inter -sentential switching is the switch from one language into another which occurs between sentence of speech”.
3) Intra-sentential Switching
22
another language. Here the example Intra-sentential Switching:
Open your books and kerjakan page 23!
Can you give me the example of kalimat passive?
Jika kalian bisa menjawab pertanyaan dengan benar, I will give you a special score.
b. Form of Code-Mixing
Suwito (1985) as cited by Siskawati (2012, p.13) defines that there are six forms of code-mixing according to the linguistic elements. They are an insertion of word, insertion of phrase, insertion of hybrid, insertion of word reduplication, insertion of idiom and insertion of clause.
1) The Insertion of Word
McCharthy (2002, p.13) states “Word as fundamental unit out of which phrases and sentences are composed”. One of
23
Table 2.2 Part of Speech
Part of Speech Basic Function Example
Noun Names a person, Preposition Shows a relationship
between a noun (or pronoun) and other words in a sentence.
Up, over, into, for, from, apart, by, etc.
Conjunction Joins words, phrases, and clauses.
And, but, or, yet, etc
Interjection Expresses emotion and can usually stand alone.
24 2) The Insertion of Phrase
According to Bull (2008, p.329) in Oxford Learner Pocket Dictionary defines as "group of words without a finite verb, especially one that forms an art of sentence". There are many kinds of phrases as a noun phrase, verb phrase, adjective phrase, adverbial phrase, prepositional phrase, infinitive phrases, principle phrases, gerund phrases, and absolute phrase.
Table 2.3 Phrase
Type of Phrase
Explanation and Example
Noun phrase Noun phrase is a phrase which consist of a noun and modifier. the modifier started with determiner (the, an, this, that, etc) followed by adjective, or adverb, and ends with noun. The examples of noun phrase:
I went t an amazing beach yesterday.
She drinks the delicious chocolate milk.
We go to the next page
Verb phrase Verb phrase is a phrase which consist of the main verb and any auxiliaries.
The example of verb phrase:
25
She has graduated.
Jane will start to speak English.
Adjective Phrase
Adjective phrase is a phrase which is formed by an adjective and modifier or intensifier. I
Jane plays the piano very well.
He wakes up early morning.
Prepositional Phrase
Prepositional phrase is a phrase which is the combination of preposition and object. It has a function as an adjective or adverb.
The examples of prepositional phrase:
We meet new friends at school.
The girl with the blue shirt is my twin.
26 and/or modifies to complete the thought. The examples of infinitive phrase:
I go home to take a rest.
She goes to market to buy oranges.
Ron studies to get good mark.
Participle Phrase
Participle phrase started with present or past participle. The present participle always ends by-ing, whereas the regular past participle ends with –ed and the irreguler past participle can be seen in the form of irregular verb II. The examples of participle phrase:
Gerund Phrase Gerund phrase looks similar with participle phrase. The difference of both is the function. Gerund phrase has a function as nouns; it will be a subject, subject complements, or object; in the sentence.
The example of gerund phrase:
27
pollution.
My father is washing his motorcycle
She likes cooking cake.
Absolute Phrase
An absolute phrase combines a noun and a participle with any accompanying modifies or objects.
The examples of absolute phrase:
His brow knitted in frustasion, Thomas tried again to iron a perfect crease in his dress pants.
Fracine played the difficult concerto, her fingers flying over the piano keys.
3) The Insertion of Hybrid
Hornby (2000) states that hybrid is the composed part of words. Hybrid happens when there are combining of two elements from different language and it will create meaning. Example:
Kalo denger lagunya Siti Badriah jadi pengen
nge-dance.
Jadi orang itu jangan suka nge-judge orang lain. Tadi uangnya sudah di-transfer sama ayah.
Wihh Aldi keren banget bisa meng-handle acara ini dengan sukses
28
Table 2.4 Hybrid
Prefix Word Hybrid
Nge- Dance Ngedance
Nge- Judge Ngejudge
Di- Transfer Ditransfer
Meng- Handle Menghandle
Men- Gosip Mengosip
According to example above, they construct from two different languages. Dance, judge, transfer, handle and gosip are English word meanwhile nge-, di-, meng- and men- are suffix in Indonesian language. So, ngedance, ngejudge, ditransfer, menghandle and mengosip belong to hybrid because they come from the combination between English and Indonesian language.
4) The Insertion of Reduplication
Word reduplication is the repetition of one word becomes two words in one sentence or utterance (Sihite, 2016). it means that the speaker makes repetition in the same word in a sentence.
Example:
29
(word smie-smile belongs to word reduplication because it is written or soken twice).
Bagaimana kabar kamu, fine-fine aja kan? (word fine-fine belongs to word reduplication because it is written or spoken twice).
5) The Insertion of Idiom
McCarthy (2002, p.143) defines that an idiom as an expression whose meaning is not predictable on the basis of the meanings of its component. An idiom can be definite a series of words to assume a specific meaning. It means that Idiom has the different meaning from real meaning if the words are translated word by word.
Example:
Good luck buat ujian munaqosahnya, semoga berhasil
dan lancar. (good luck belongs to idiom because the meaning is not predictable from each words meaning) Cowok ganteng itu easy going sama orang disekitarnya. (easy going has a different meaning if we translate word by word.
6) The Insertion of Clause
30 Example:
Ani, What are doing? di panggil dari tadi kok gak
nyambung.
I just want to tell you something. Karena ini penting
banget.
As stated the types of code-mixing above, the researcher has different opinion with Suwito. The researcher says that the insertion of clause belongs to code-switching. As Jandra's theory that had written in previous page. So, the insertion of clause here is not a kind of Mixing, it is considered as Code-Switching.
5. Functions of Code Switching and Code Mixing
Code-Switching and Code-Mixing have each function in communication. There are several functions according to Marasigan (1983). The first is the quotation, address specification, repetition, interjection, message qualification, personalization and objectivization, and facility expression.
a. Quotation
31 Example: (Gumperz, 1982, p.76)
(20) Spanish-english. from the conversation among two chicano professionals. The speaker talking about her baby-sister.
She doesn’t speak English, so, dice que la reganan:”si se les va olvidar el idioma a las criaturas” (she says that they would scold her: “the children are surely going to forget their language”.)
A quotation can be seen from example above by switching the language from English to Spanish in order to retain the message.
b. Addressee Specification
Marasigan (1983, p.73) stated in this type of switch, it recognizes not only interacting members of the speech events but also recognizes that either language behaviors may be more than merely a matter of individual preference or facility, but also role relation. Furthermore, addressee specification immediately happens in order to convey the message to the listener even though the message is posted. Halim & Maros (2013) gave an example (cited in Rosyida, 2017, p.36) as follows:
has headache preparing timetable for the 1st time ~ ~ tima kaseyy la kpd (thanks to) Ophelyatie Zin atas tunjuk ajar yg diberikan (for your assistance)
32 c. Repetition
A message is repeated in the other code aimed to clarify what the speaker said, strengthen or emphasize the message, or mark the joke (Marasign, 1983, p.79). Moreover, repetition proposed to make the message is more clear and understandable to the listeners.
Example:
OK I may sound like a noob/jakun/sakai, but I just found out that my Maybankard Visa Debit works like a credit too. WOW. So I don’t need to applay for a credit card now right? Or what do you guys think? Is the debit card as handy as a proper credit card? *The hubster and I kind of have this ‘thing’ against credit cards. (Halim & Maros, 2013, p.130)
In example above, the term ‘noob’ repeat in other language ‘jakun’ and ‘sakai’ in order to prevent confusion from the listener
or writer. It made to establish the understandable message.
d. Interjection
Based on Marasign (1983, p.81), interjection used to change the interaction from the "we" to "they" code or from the "they" to the "we" code. It means that the speaker used interjection to switch and mix the code. Interjection expresses strong feeling and emotions. Therefore, interjection is clearest than other language base on language expression. Here the example of interjection based on Marasign (1983):
33
eat her banana (A’s banana) for dessert. A: Very bad! akinyan (that’s mine) B: Hep, hepsaamingdalawa (that’s ours)
A: Ay, nag-bell (Hey, the bell is ringing for our next class)! The conversation indicated that the English interjection ‘very bad’ was influenced by setting. It is common learned by student in school since they are used by teachers to assess their performance or behavior. The using interjection ‘very bad’ is to
express her disapproval C’s behavior.
e. Message Qualification
As Marasigan (1983, p.84) states, "Message qualification is to express the time of concept". She (1983) also explained that another large group of switches consist of qualifying constructions such as clauses, sentences, and phrases (verb and noun complements).
Example:
Two teachers were supposted to meet one day in school. Both of them claimed that they came, but for some reason they did not meet each other.
A: Nanditoako (I was here)
C: Walaka ditto (you weee not here)
A: Nanditoako (I was here). Friday? Nanditoako (I was here)
C: Not this Friday. Before All Saints’ Day. Yun angusapan (that’s the appointment day).
34
specific or exact. Heiser in Marasigan (1983) remarked, “Filipinos to comprehend the important to time as viewed by westerners”.
f. Personalization and Objectivization
The function of personalization and objectivization based on Marasigan (1983, p.85), "The code contrast here seems to relate to such thing as the degree of speaker involvement in, or distance form, a message or an address; whether a statement reflects personal opinion, feeling, or knowledge; whether it refers to specific instance, or whether it has the status of generally known fact". In addition, Marasigan (1983) divided the function of personalization and objectivization into: "objective marks that the speaker gives about the fact" and "subjective argument from the speaker as personalize marks". Personalization and objectivization can be seen in the example from Marasign (1983) below:
It’s a Crispa-Toyota deal. I’m one of the Crispa die-hard fans. Sana manalo sila (I hope they win).
In the example above, the speaker switches to philipino to express his personal wish. Here the speaker is not only explaining the message but also express his personal involvement in it.
g. Facility of Expression
35
difficulty in finding the right word at the time of speaking or writing or merely as a sign of the subject's lack of familiarity with the style he is using". Meanwhile, Marasigan (1983) provided the composition written by a grade six girl as the example of switching for facility of expression:
My barkada’s are Andrea, Maricis and Lora (My friends are ...). They are minsan pikon and minsan good (They are sometimes good). We always together, sometimes
nagkakroon kami ng misunderstandng at madalas kaming magaway (we sometimes misunderstand each other and we quarrel often).
The writter switches to Philipino in order to facility in expressing the term that the writer does not know the exact word in English. Therefore the writer changes the language to Philiphino.
6. Reason of Code Switching and Code Mixing
Hoffman (1991, p.116) classifies the function of code-switching and code-mixing in seven points, which are:
a. Taking a particular topic
36
about the particular topic also used by the speaker when there is another topic discussed.
b. Quoting somebody else
Hoffman (1991, p.116) suggests that "people sometimes like to quote a famous expression or saying of some well-known figures". In Indonesia, those well-known figures are mostly from some English-speaking countries. The switch like a set of quotation marks. Here the example of quotation (Holmes, p.45)
Li: People here get divorce too easily. Like exchanging faulty goods. In China it’s not the same. Jia gou sui gou, jia ji sui ji. (IF YOU HAVE MARRIED A DOG, YOU FOLLOW A DOG, IF YOU MARRIED A CHICKEN, YOU FOLLOW A CHICKEN).
c. Being emphatic about something (express solidarity)
Hoffman (1991) stated, "he/she, either intentionally or unintentionally, will switch from his or her second language to his or her first language". Usually, the speaker switches from the second language to the first language because the speaker feels more convenient to be emphatic in the second language rather that first language.
Example:
37
d. Interjection (Inserting sentence fillers or sentence connectors) Hoffman (1991) suggests that "language switching and language mixing among bilingual or multilingual people can sometimes mark an interjection or sentence connector. It may happen unintentionally or intentionally". The interjection includes in part of speech that commonly used in informal language than formal writing or speech ad it doesn't have grammatical value. Basically, interjection has a function to express emotions such as excitement, joy, surprise, or disgust.
The interjection that usually used are: Look!, Well!, Hey!, Shit!, Argh! and etc.
e. Repetition used for clarification
When a bilingual wants to clarify his/her speech so that it will be understood more by the listener, he/she can sometimes use both of languages that he masters saying the same utterance (the utterance is said repeatedly) (Hoffman, 1991). Sometimes, someone speaks in a bilingual or multilingual language, the listener doesn't understand well so that the speakers need to clarify their speech. A repetition is not only served to clarify what is said but also to amplify or emphasize a message. For example:
38
Keep spirit, tetap semangat! kamu pasti mendapatkannya.
f. Intention of clarifying the speech content for interlocutor
When bilingual/ multilingual talks to another bilingual/ multilingual, there will be lots of code switching and code mixing occurs (Hoffman, 1991). It means to make the content of his speech runs smoothly and can be understood by the listener. A message is one code is repeated in the other code in the somewhat modified form.
g. Expressing group identity
Code-switching and Code-Mixing can also be used to express group identity. The way of communication between academic people in their disciplinary groupings are obviously different from another group (Hoffman, 1991). In addition, the way to communicate in a community is different from the people who are out of the community.
Savile-Troike (as cited in Sihite, 2016, p.27) also gives some additional reasons for bilingual and multilingual person to switch or mix their languages, these are:
h. To soften or strengthen sequest or command
39
native language. Besides that, Code-Switching and Code-Mixing can also be used to strengthen a command since the speaker can feel more powerful than the listener because she/he can use a language that everybody cannot.
i. Because of real lexical need
The most common reason for the bilingual/multilingual person to switch or mix their languages is due to the lack of equivalent lexicon in the languages. When an English-Indonesian bilingual has a word that is lacking in English, the speaker will find it easier to say it in Indonesian, the speaker will use the English term. If it put into Indonesian, the meaning will be hazy/vague, and sometime it would not be used. For example, in Indonesia, the technical topics are firmly associated with English and the topic itself can trigger a switch or mix to/with English.
j. To exclude other people when a comment is intended for only a limited audience
40 7. Video-Blogging (Vlog)
The word vlog derived from the word ‘video' and ‘blogging'.
Vlog entries often combine embedded video (or video link) with supporting text, images, and other media data. Vlog maker is commonly known as a vlogger. As reported in Wikipedia, on January 2000 Adam Kontras uploading a video along with a post in the blog and it becomes the first vlog uploading The tools used for video blogging are different from those used for text blogs. Whereas text blogging requires only text editing tools but video blogging requires video recording and uploading tools.
Video blogging is different from video posting. A video post may refer to any video randomly posted on the web (e.g. commercial, film preview or any news article). Video blogs are videos recorded by an individual on his own and content of the video is usually related to the person's life or his opinion on some issue. According to Dean (2005) as cited by Mogallapu (2011, p.5), a popular technology news website, most video blogs have a home-grown, experimental feel, often including clips of the author's daily activities.
41
LoriLewis on her twitter (@LoriLewis), in 2018 Youtube has increased significantly user (4,3 million viewed) after sent emails (187 million), the message (38 million) and text message (18 million). There are three types of Vlogs: personal vlogs, news shows, and entertainment orientated Vlogs (Luers, 2007).
Vlog is very famous website nowadays. People used it to share their personal life, entertain reason or some people used for business. Not only used by ordinary people, Vlog is also used by celebrities around the world. It used to facilitate their fans. In this research, the researcher chose account Vlog of Shirin Al Athrus.
42 CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
Research method is very important in conducting a research, it is necessary for researcher to apply an appropriate method. In this chapter, the researcher would like to explain the methodology of this research. It consist of type of the study, object of the study, source of the data, technique of collecting data, technique of data analysis and validity of the data.
A. Type of the Study
43 B. Object of the Study
The researcher used the utterance and sentences that were used by Shirin Al Athrus which contain Indonesian-English Code-Switching and Code-Mixing.
C. Source of the Data
This research only used primary data. Primary data are data which are taken from the first source using some procedures (Azwar, 2005. P.36). this research uses primary data which are taken directly from the data sources which are Shirin’s Vlog (random videos). The data in this research are all of Shirin’s utterances which are contained Indonesian-English Code-Switching and Code-Mixing in Shirin’s Vlog.
D. Technique of Data Collections
The researcher collected the data by doing some steps
1. Observing the Vlog that made by Shirin Al Athrus to be selected. 2. Watching and listening more the videos which are chosen.
3. Making transcription from the videos. 4. Encoding the collecting data.
44
6. Analyzing the form, function and reason of Code Switching and Code Mixing.
7. Concluding the data.
E. Technique of Data Analysis
The researcher used the theory from Moleong (2009) to analyze the data bellow:
1. Identification
According to Bull as cited in Oxford (2008, p.218), “Identification is the action or process of identifying someone or something or the fact of being identified”. At the first step, the researcher chooses the Vlog account
to be identified. Furthermore, the researcher identifies of the utterance which consist of Indonesian-English Code-Switching and Code-Mixing. It used to find out the data which related to the focus and formulated problems.
2. Coding
The second step in this analyzing data is coding. To facilitated the study, the researcher encodes the collected data after identifying. Craswell (2012, p.266) explains “Coding is the process of something and labeling
45
order to facilitate the researcher in investigating the data and knowing the source of the data”. Coding could be found in a form of numbering,
lattering, symboling or others. In this study, the researcher used letters and numbers. Here is the coding of the gained data.
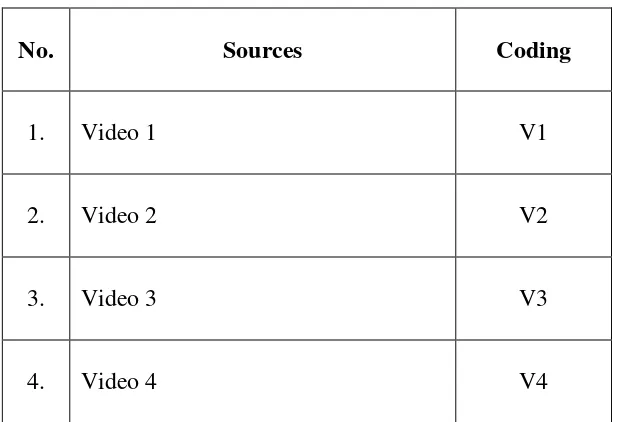
Table 3.1 Coding of Videos
No. Sources Coding
1. Video 1 V1
2. Video 2 V2
3. Video 3 V3
4. Video 4 V4
Table 3.2
Coding of Form Code-Switching
No. Form of Code-Switching Coding
1. Tag-Switching F1
46
3. Intra-Sentential Switching F3
Table 3.3
Coding of Form of Code-Mixing
No. Form of Code-Mixing Coding
1. Insertion of Word G1
2. Insertion of Phrase G2
3. Insertion of Hybrid G3
4. Insertion of Word Reduplication G4
5. Insertion of Idiom G5
6. Insertion of Clause G6
Table 3.4
Coding of Function of Code-Switching and Code-Mixing
No. Function of Code-switching and Code-Mixing
Coding
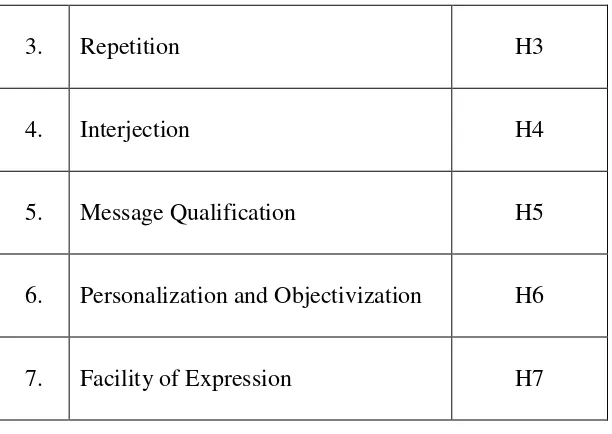
1. Quotation H1
47
3. Repetition H3
4. Interjection H4
5. Message Qualification H5
6. Personalization and Objectivization H6
7. Facility of Expression H7
Table 3.5 Coding of Reason
No. Reason of Code-Switching and Code-Mixing
Coding
1. Talking about a particular topic I1
2. Quotation somebody else I2
3. Being emphatic about something I3
4. Interjection I4
5. Repetition used for clarification I5
6. Intention of clarifying the speech content for the interlocutor
I6
48
8 To soften or strengthen request or command
I8
9 Because of real lexical need I9
10 To exclude other people when a comment is intended for only a limited audience
I10
3. Categorizing
Categorizing is sorting the collected data into smaller unit based on the similarity (Moleong, 2009, p.288). In other hand, Craswell (2012, p.268) defines “Them (also called categorizes) are similar codes aggregated together to form a major idea in the database”. In this step, the researcher categorizes the data into two categorizes: Code-switching utterance and Code-Mixing utterance based on the form, function and reason.
4. Classifying
According to Bull explain in Oxford (2008, p.75) as quoted by Rosyida (2017, p.54) “Classifying is arranging something into groups according to the features that they have in common”. After categorizing,
49 5. Producing an account
The last step in this analyzing data is producing an account. According to Moelong (2009, p.295), “Producing an account is done by
making diagram, tabulation and texting”. After making classification, the
researcher describes and analyzes the data classification to examine the form, function and reason of code-switching and code-mixing used by Shiri Al Atrus in her Vlog. Furthermore, the researcher can provide the necessary insight about code-switching and code-mixing especially in form, function and reason based on detailed description of the study.
F. Validity of the Data
In this study, the researcher tried to obtain the validity of the data. The researcher chose triangulation in order to check the validity of the data. Triangulation refers to the use of two or more data sources, methods, investigators and approach to analyzing the data. Moleong (2009, p.330) defines “Triangulation is technique of checking the validity of the data by
employing the other data”. It is function for comparing the data. According to Denzin (1978) as quoted by Moleong, triangulation is a technique to check the validity of the data through source, methodological, investigator and theoretical triangulation.
50
51
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DATA ANALYSIS
This chapter consists of the result of the research and the explanation to answer the statements of the problem. The researcher analyzes form, function and reason of Code-Switching and Code-Mixing used in Vlog of Shirin Al Athrus.
A.Research Findings
As what has been mentioned in previous chapter, the form of Code-Switching basically divided into three types according to Romine: tag switching (F1), inter-sentential switching (F2) and intra-sentential switching (F3), while types of Code-Mixing are divided into six types. They are insertion of word (G1), insertion of phrase (G2), insertion of hybrid (G3), insertion of reduplication (G4), insertion of idiom (G5) and insertion of clause (G6).
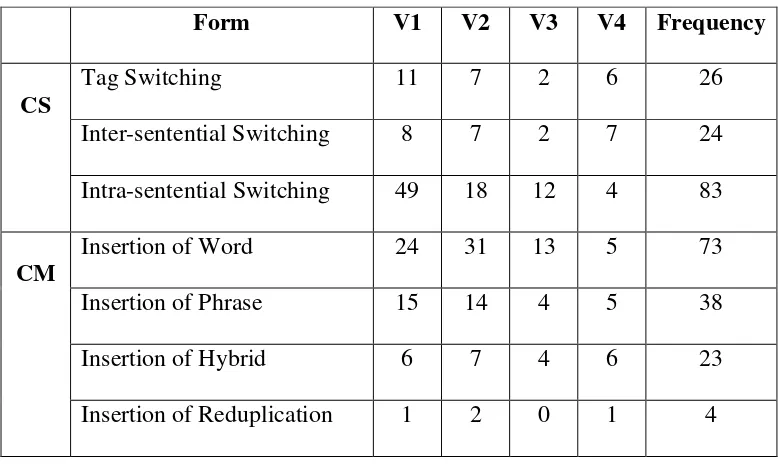
52 Table 4.1
The Frequencies Form of Code-Switching and Code-Mixing
Form V1 V2 V3 V4 Frequency
CS
Tag Switching 11 7 2 6 26
Inter-sentential Switching 8 7 2 7 24
Intra-sentential Switching 49 18 12 4 83
CM
Insertion of Word 24 31 13 5 73
Insertion of Phrase 15 14 4 5 38
Insertion of Hybrid 6 7 4 6 23
Insertion of Reduplication 1 2 0 1 4
53 Table 4.2
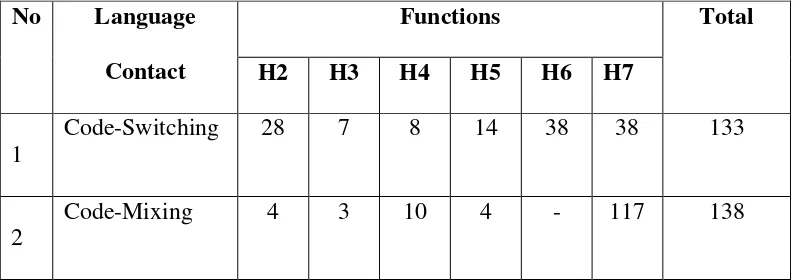
The Frequencies Functions of Code-Switching and Code-Mixing
No Language Contact
Functions Total
H2 H3 H4 H5 H6 H7
1
Code-Switching 28 7 8 14 38 38 133
2
Code-Mixing 4 3 10 4 - 117 138
Based on the data above, the researcher found only six functions that used by Shirin in order to perform both Code-Switching and Code-Mixing. From the 4 videos of Shirin's Vlog, the researcher was able to split the Code-Switching data into 133 unit data and the Code-Mixing data into 138 data to be analyzed on the form, function, and reason.
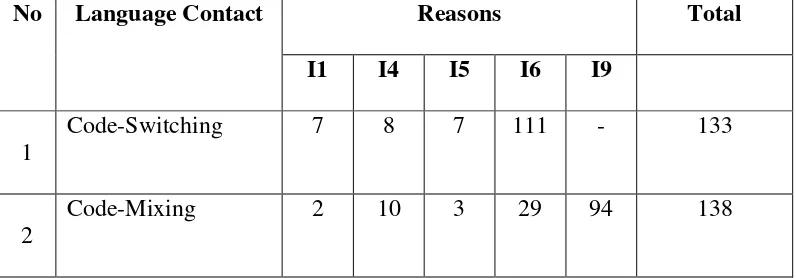
54 Table 4.3
The Frequencies Reasons of Code-Switching and Code-Mixing
No Language Contact Reasons Total
I1 I4 I5 I6 I9
1
Code-Switching 7 8 7 111 - 133
2
Code-Mixing 2 10 3 29 94 138
Based on the data that had been found by the researcher, there are 5 reasons of using Code-Switching and Code-Mixing. From the 133 unit data of Code-Switching, the reason which showed are 7 talking about a particular topics, 8 interjections, 7 repetition used for clarifications, 111 intention of clarifying the speech content for the interlocutors, and 0 because of lexical need. Furthermore, Code-Mixing data showed the reason 2 talking about a particular topics, 10 interjections, 3 repetition used for clarifications, 29 intention of clarifying the speech content for the interlocutors, and 94 because of lexical needs.
B.Data Analysis 1. Code Switching
55
all types of Code-Switching in Shirin’s utterances. They are tag switching, inter-sentential switching and intra-sentential switching.
a. Tag Switching (F1)
Tag switching is simply the insertion of a tag in one language in an utterance which is entirely in the other language. The researcher just found some tag switching which used by Shirin in her Vlog. In this data, the researcher provides some examples of tag switchings.
Extract 1.
“Jadi ceritanya tu ada 1 keluarga,aku gak tau orang mana, kayanya orang Australi or kaya bule gitu deh, trus mereka tuh mau buat villa cuman si orang ini kecelakaan dan tiba-tiba pas dia udah kecelakaan itu dia gak punya ahli waris atau keturunan gitu, akhirnya villanya baru segini terus didiemin gitu deh, let’s go!”
The italic word performed Code-Switching as emblematic switching or tag switching. "let's go!" is the short expression that used the speaker to switch the code in her utterance. Shirin used interjection at the end of her utterance to show up her strong intention to continue her doing. Furthermore, it can be seen that by switching, she intended to give the clear command.
Extract 2.
“Sumpah rame banget, ini semua isinya anak-anak kecil dari keluarga papah , dari keluarga mamah semuanya ngumpul jadi satu hotel, how do you like
56
"how do you like this place?" was another language switched by the speaker in her utterance. The researcher thinks that the italic sentence belongs to tag switching because the speaker made the stressed tone to clarify the statement and there is a question word.
Extract 3.
“...Gilanya aku jadi model bla bla bla I was so excited karena kaya wow! my dream become true.”
The italic words above are Code-Switching through emblematic switching or tag switching, because the tag switching often takes place in tags of sentence. In this utterance, the tag switching is in exclamatory form.
b. Inter-sentential Switching (F2)
In inter-sentential switching is the type of code-switching, where the language occurs at the clause or sentence boundary. From the data, the researcher only found 24 codes from all the data. Some examples are analyzed as follow:
Extract 4.
57
In extract above, the speaker told about accessories that had bought from London accessories store. She spoke Bahasa at that time and then switched into English when she told about the accessories price. It can be seen that switch occurred between sentence boundaries. So, this extract belongs to inter-sentential switching.
Extract 5.
“Oh ya, sebelum aku upload d youtube, aku juga upload di fb jadi aku sama sahabat aku Nadia sepupu aku juga si. we upload make up tutorial and
everything in youtube and it’s so funny.”
From data above, it is categorized as inter-sentential switching because this data shows a switch between two languages, from Indonesian to English between sentences. Shirin said “Oh ya, sebelum
aku upload d youtube, aku juga upload di fb jadi aku sama sahabat aku
Nadia sepupu aku juga si”. This is Indonesian language, which followed by English sentence “we upload make up tutorial and everything in
YouTube and it’s so funny.”