Reza Purbaya, 2015
THE EFFECTIVENESS OF CHAIN OF SHORT MESSAGE SERVICE OF VOCABULARY IN ENHANCING
HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
THE EFFECTIVENESS OF CHAIN OF SHORT MESSAGE
SERVICE OF VOCABULARY IN ENHANCING HIGH
SCHOOL STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY
(A research to examine the improvement of high school students’ vocabulary through chain of short message service of vocabulary)
A Research Paper
Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the
Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
Reza Purbaya
(0902394)
ENGLISH EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM
FACULTY OF LANGUAGE AND LITERATURE EDUCATION
INDONESIA UNIVERSITY OF EDUCATION
Reza Purbaya, 2015
THE EFFECTIVENESS OF CHAIN OF SHORT MESSAGE SERVICE OF VOCABULARY IN ENHANCING
HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY
Reza Purbaya, 2015
THE EFFECTIVENESS OF CHAIN OF SHORT MESSAGE SERVICE OF VOCABULARY IN ENHANCING
HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
THE EFFECTIVENESS OF CHAIN OF SHORT MESSAGE
SERVICE OF VOCABULARY IN ENHANCING HIGH
SCHOOL STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY
(A research to examine the improvement of high school students’ vocabulary through chain of short message service of vocabulary)
Oleh Reza Purbaya
Sebuah skripsi yang diajukan untuk memenuhi salah satu syarat memperoleh gelar Sarjana Pendidikan (S.Pd.) pada Fakultas Pendidikan Bahasa dan Seni
© Reza Purbaya 2015 Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia
Januari 2015
Hak Cipta dilindungi undang-undang.
Reza Purbaya, 2015
THE EFFECTIVENESS OF CHAIN OF SHORT MESSAGE SERVICE OF VOCABULARY IN ENHANCING
HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY
Reza Purbaya, 2015
THE EFFECTIVENESS OF CHAIN OF SHORT MESSAGE SERVICE OF VOCABULARY IN ENHANCING
HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
THE EFFECTIVENESS OF CHAIN OF SHORT MESSAGE SERVICE OF
VOCABULARY IN ENHANCING HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS’
VOCABULARY
KERUNGKASAN DARI RANTAI PESAN PENDEK BERISI KOSAKATA
DALAM MENINGKATKAN PERBENDAHARAAN KOSAKATA BAHASA
Faculty of Language and Literature Education
Indonesia University of Education
Email: purbayareza72@gmail.com
Abstract: The research was aimed at discovering the effectiveness of chain of
short message service of vocabulary in enhancing high school students’ vocabulary and finding out the students’ responses toward the technique. This
technique was one of the intentional learning strategies applied as complementary activity included two steps: teacher sent the vocabulary and the students continued the vocabulary as a chain message in which the last student sent back to the teacher as a confirmation that all the students in the experimental group had received the message. The subjects of the research were second grade students of Senior High School in Bandung in which one class was divided into experimental group and control group. Each group consists of 15 students. In collecting the data, the quasi-experimental desaign was utilized. The mean scores of the pre-test
were the bases scores to identify the initial participants’ learning framework.
Reza Purbaya, 2015
THE EFFECTIVENESS OF CHAIN OF SHORT MESSAGE SERVICE OF VOCABULARY IN ENHANCING
HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
between pre-test and post-test from experimental group. The discussion of the questionnaire analysis discovered some findings that the Chain of Short Message Service of Vocabulary has a lot of benefits in teaching vocabulary, such as giving additional time to learn as complementary activity outside the classroom, helping student to enrich their vocabulary especially verb, and giving students chance to a joyful learning through their mobile phones instead of using them only for playing
game, texting, and browsing. Therefore, it could be said that the students’
responses toward the Chain of Short Message Service of Vocabulary technique were positive.
Keywords: Short Message Service, intentional learning, vocabulary mastery
Abstrak: Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk mengetahui kerungkasan dari rantai pesan
Reza Purbaya, 2015
THE EFFECTIVENESS OF CHAIN OF SHORT MESSAGE SERVICE OF VOCABULARY IN ENHANCING
HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
bermain game, mengirim pesan, dan browsing. Akhirnya, dapat dikatakan bahwa respon siswa terhadap teknik rantai pesan pendek berisi kosakata adalah positif.
Reza Purbaya, 2015
THE EFFECTIVENESS OF CHAIN OF SHORT MESSAGE SERVICE OF VOCABULARY IN ENHANCING
HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
TABLE OF CONTENTS
PAGE OF APPROVAL ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
STATEMENT ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
PREFACE ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
ABSTRACT ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... iii
LIST OF TABLES ... vi
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION ... Error! Bookmark not defined. 1. 1 Background ... Error! Bookmark not defined. 1. 2 Research Questions ... Error! Bookmark not defined. 1. 3 Aims of the Study ... Error! Bookmark not defined. 1. 4 Scope of the Research ... Error! Bookmark not defined. 1. 5 Significance of the Research ... Error! Bookmark not defined. 1. 6 Clarification of the Key Terms ... Error! Bookmark not defined. 1. 7 Organization of the Paper ... 4
CHAPTER II LITERATURE REVIEW ... 6
2. 1 Definition of Vocabulary ... 6
2. 2 Teaching Vocabulary ... 7
2. 2. 1 Principles in Teaching Vocabulary ... 7
2. 2. 2 Criteria of a Good Vocabulary Exercise ... 9
2. 3 Types of Vocabulary ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
2. 3. 1 Spoken and Written Vocabulary ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
2. 3. 2 Core and Non-core Vocabulary ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
2. 3. 3 Discourse Structuring Vocabulary and Procedural Vocabulary Error!
Bookmark not defined.
2. 3. 4 Technical, Semi-technical, and General Vocabulary ... Error!
Reza Purbaya, 2015
THE EFFECTIVENESS OF CHAIN OF SHORT MESSAGE SERVICE OF VOCABULARY IN ENHANCING
HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
2. 3. 5 Academic Vocabulary ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
2. 4 Incidental Vocabulary Learning and Intentional Vocabulary Learning
Error! Bookmark not defined.
2. 5 Complementary Activity ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
2. 5. 1 Definition of Complementary ActivityError! Bookmark not defined.
2. 6 Chain of Short Message Service of Vocabulary ... Error! Bookmark not
defined.
2. 6. 1 Chain of Short Message Service of VocabularyError! Bookmark not defined.
2. 6. 2 Chain of Short Message Service of Vocabulary Technique ... Error!
Bookmark not defined.
2. 6. 3 Advantages of Chain of Short Message Service of Vocabulary Technique ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
2. 6. 4 Related Studies ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHODOLOGY ... Error! Bookmark not
defined.
3. 1 Research Design ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
3. 1. 1 Hypothesis ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
3. 2 Data Collection ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
3. 2. 1 Population and Sample ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
3. 2. 2 Research Instrument ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
3. 3 Research Procedures ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
3. 4 Data Analysis ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
3. 4. 1 Scoring Technique ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
3. 4. 2 The Validity Test of the Pilot-test ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
3. 4. 3 The Reliability Test of the Pilot-test . Error! Bookmark not defined.
3. 4. 4 The Difficulty Index ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
3. 4. 5 Data Analysis on Pre-test and Post-testError! Bookmark not defined.
Reza Purbaya, 2015
THE EFFECTIVENESS OF CHAIN OF SHORT MESSAGE SERVICE OF VOCABULARY IN ENHANCING
HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
CHAPTER IV ANALYSIS AND DISCUSSIONS ... Error! Bookmark not
defined.
4. 1 Analysis ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
4. 1. 1 The Pilot Test Analysis ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
4. 1. 2 Pre-test Score Analysis ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
4. 1. 3 Post-test Score Analysis ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
4. 1. 4 The Questionnaire Analysis ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
4. 2 Discussions ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
4. 2. 1 The Effectiveness of Chain of Short Message Service of Vocabulary Technique ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
4. 2. 2 The Students’ Responses toward the Chain of Short Message Service of Vocabulary Technique ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
4. 2. 3 Summary of Discussion ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
CHAPTER V CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS . Error! Bookmark not
defined.
5. 1 Conclusions ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
5. 2 Suggestions ... 50
REFERENCES ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
APPENDICES ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
Appendix 1
Appendix 2
Appendix 3
Appendix 4
Reza Purbaya, 2015
THE EFFECTIVENESS OF CHAIN OF SHORT MESSAGE SERVICE OF VOCABULARY IN ENHANCING
HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
LIST OF TABLES
Table 3.1 The Schematic of The Quasi-experimental DesignError! Bookmark
not defined.
Table 3.2 The Schematic of Treatment Schedule ... Error! Bookmark not
defined.
Table 3.3 Category of Coefficient Correlation of Reliability.. Error! Bookmark
not defined.
Table 3.4 The Scale of Effect Size ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
Table 4.1 The Validity Result of Pilot-test 1 ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
Table 4.2 The Validity Result of Pilot-test 2 ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
Table 4.3 The Difficulty Index of Pilot-test 1 .... Error! Bookmark not defined.
Table 4.4 The Difficulty Index of Pilot-test 2 .... Error! Bookmark not defined.
Table 4.5 The Pre-test Scores ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
Table 4.6 One-Sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov Test ... Error! Bookmark not
defined.
Table 4.7 Test of Homogeneity of Variances ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
Table 4.8 Independent Samples Test ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
Table 4.9 Descriptive Statistics ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
Table 4.10 One-Sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov Test ... Error! Bookmark not
defined.
Table 4.11 Test of Homogeneity of Variances ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
Table 4.12 Independent Samples Test ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
Table 4.13 Paired Samples Correlations ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
Reza Purbaya, 2015
THE EFFECTIVENESS OF CHAIN OF SHORT MESSAGE SERVICE OF VOCABULARY IN ENHANCING
HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
This chapter describes the general thoughts of the paper. It consists of
background of the research, research questions, aims of the study, scopes of the
research, significance of the research, clarification of key terms and organization
of the research.
1.1 Background
Nowadays, the current educational system in Indonesia pushes teachers to
conduct a contextual learning. In addition, in the newest educational system, the
contextual learning is more emphasized as the centre of the learning where
grammar and vocabulary are taught implicitly. Many practices of language
teaching in Indonesia as an EFL country tend to focus on the framework of syntax
or grammar. As Maiguascha (1993), cited in Mehring (2005), believed that the
teaching of grammar generally is based on a set of rules with a coherent structure
that students can follow and remember. Furthermore this concept does not hold
true for the teaching on vocabulary.
In the other hand, in the background of standard competence and basic
competence for high school in Indonesia (Depdikbud, 2006), one of the purposes
of senior high school students is to achieve informational level that is a literacy
level in which students are expected to be able to access knowledge using
language ability because they are prepared for continuing study to higher
education. Besides epistemic level is considered as too high to achieve for high
school students in Indonesia because English is taught as foreign language.
Meanwhile, students are facing difficulties in meaning the vocabulary. Somehow,
vocabulary is very important to understand any language. Although people do not
say it grammatically, people can understand the meaning by recognizing the
Reza Purbaya, 2015
THE EFFECTIVENESS OF CHAIN OF SHORT MESSAGE SERVICE OF VOCABULARY IN ENHANCING
HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
is to master the vocabulary. As Wilkins (1972), cited in Burston & Zhang (2011),
said that “without grammar very little can be conveyed, without vocabulary
activity to help students gain vocabulary. Based on pedagogical perspective, there
is a need for research that helps teachers to find out learning tasks in providing
opportunities for L2 vocabulary learning (Derakhshan & Khodabakhshzadeh,
2011), especially on the usage of mobile media. Due to the fact that mobile media
such as mobile phones and internet are now widely used, it is appropriate to
implement them in learning activities. In addition, mobile learning would work
well since students need a flexible solution for training and learning where the
students can do their activities while learning and gaining new vocabulary
(Dudeney & Hockly, 2007).
Nowadays, children and juvenile are more familiar with the technology. It is
supported by the data from Asosiasi Telekomunikasi Selular Indonesia (ATSI) in
the late of 2011. It showed that there were about 250 millions people who used
hand phone, meanwhile the population of Indonesia was about 240 millions
people. It means 10 millions people in Indonesia were using more than one hand
phone. If the population of teenager were only 1% of the whole population in
Indonesia, so there would be about 25 millions teenager who use hand phone. As
an additional data, the data from Gramedia Majalah in Indonesian Hottest Insight
2013 showed that 40% kids have their own handphones. They can stay for so
much time to play mobile phone and computer. Therefore, instead of letting them
play their mobile phone and computer only, teacher can involve the technology in
Reza Purbaya, 2015
THE EFFECTIVENESS OF CHAIN OF SHORT MESSAGE SERVICE OF VOCABULARY IN ENHANCING
HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
and Burston (2011) that vocabulary learning with computers or technology can be
more effective than through the use of traditional learning methods. Moreover, the
vocabulary learning with mobile phones allows learners to be exposed to spaced
repetition of vocabulary items which is believed to be more effective than massed
repetition (Nation, 2001).
Furthermore, according to the researcher’s experience during teaching practicum, most of students in the senior high school face difficulty in inferring
vocabulary. They even seem lazy to open dictionary. It is proved by their laziness
to bring dictionary. Thus, the present study seeks to investigate the effectiveness
of the technique called chain of short message service of vocabulary in enhancing
students’ vocabulary since there are still limited number of publication on this
issue especially in Indonesia.
Some studies (see for example Derakhshan & Khodabakhshzadeh in 2011)
have suggested the use of technology such as hand phone in the research to help
students increase their vocabulary. Thus, the research investigates the use of chain
of short message service of vocabulary in enhancing students’ vocabulary. In
order to complete data of the implementation of the data, the research also
investigates the students’ responses toward the use of chain of short message service of vocabulary technique outside the classroom.
1.2 Research Questions
The research is aimed at discovering the use of chain of short message
service of vocabulary to develop the students’ vocabulary. In order to shape the research, the researcher tries to answer the research questions formulated as
follows:
Reza Purbaya, 2015
THE EFFECTIVENESS OF CHAIN OF SHORT MESSAGE SERVICE OF VOCABULARY IN ENHANCING
HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
2. What are the students’ responses toward the use of chain of short message service of vocabulary technique outside the classroom?
1.3 Aims of Study
Based on the description in the background, the research is aimed at:
1. Discovering whether chain of short message service of vocabulary can
enhance the students’ vocabulary or not;
2. Finding out the students’ responses toward the use of chain of short message service of vocabulary technique outside the classroom.
1.4 Scope of the Research
The research focuses on how some learners who conduct chain of short
message service of vocabulary in language learning can improve their vocabulary
in eleventh grade of Senior High School Student Level. A Senior High School in
Bandung is choosen for the research.
1.5 Significance of the Research
The research is expected to give some beneficial contributions for teachers,
students, and further researchers. For the teachers, the research hopefully can be
an additional activity to enrich their methods in teaching language beside in the
classroom. For the students, the research is expected to give them a fun activity to
enrich their vocabulary. While for the further researchers, the research is expected
to be used as an additional source or reference, especially for those who will
conduct a research on investigating the use of chain of short message service of
Reza Purbaya, 2015
THE EFFECTIVENESS OF CHAIN OF SHORT MESSAGE SERVICE OF VOCABULARY IN ENHANCING
HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
1.6 Clarification of Key Terms
Some of terms related to the topic are concisely described below in order to
avoid misinterpretation. Three terms are clarified, as follows:
1. Vocabulary is all the words known and used by a particular person which
exist in particular language or subject (Cambridge Advanced Learner’s
Dictionary, 2003)
2. Chain text message is a text message sent to a number of people asking each
recipient to send copies with the same request to a specified number of others.
The circulation of a chain text message increases in geometrical progression
as long as the instructions are followed by all recipients. (freedictionary.com)
3. Mobile phone is a cellular telephone.
1.7 Organization of Paper
The research is presented into five chapters. The first chapter is
introduction. In this chapter consists of background of the study, review of
literature, research questions, aim of the study, limitation of the study, research
methodology, clarification of terms, and organization of writing. The background
of the study is elaborated. It elaborates the problem of in meaning the words. The
second chapter is literature review. This chapter discusses some theories related to
the effectiveness of using chain of short message service of vocabulary via mobile
phone which is relevant to answer the research questions. The third chapter is
research methodology. This chapter gives clear discussion about how the study is
conducted and analyzed. The data analysis also is briefly explained. The fourth
chapter is findings and discussions. This chapter discusses the findings of the
study and analyzes those findings in discussion clearly. It also portrays how chain
of short message service of vocabulary via mobile phone can improve students’
vocabulary. In addition, the interpretation of the questionnaire is also discussed in
Reza Purbaya, 2015
THE EFFECTIVENESS OF CHAIN OF SHORT MESSAGE SERVICE OF VOCABULARY IN ENHANCING
HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
the conclusion and several suggestions of the study based on the analysis in
chapter four. The conclusion states the answer to the research questions.
Reza Purbaya, 2015
THE EFFECTIVENESS OF CHAIN OF SHORT MESSAGE SERVICE OF VOCABULARY IN ENHANCING
HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This chapter presents the methodology in conducting the research. This
chapter provides four main parts of the investigation: research design, data
collection technique, research procedures, and data analysis technique.
3. 1 Research Design
According to the aim of the research that investigates the effectiveness of
using chain of short message service of vocabulary to enhance students’
vocabulary of EFL high school students, the quantitative research method called
quasi-experimental study was conducted. Sugiyono (2009, p. 77) stated that the
quasi experimental design is a study aimed at revealing the effect of a particular
treatment. The quasi experimental is also better used than pre-experimental design
since it is not easy to obtain a control group which is used for the research
(Sugiyono, 2012, p. 77). The quasi experimental design is also an expansion of
true experimental design which is not easy to be conducted (Sugiyono, Ibid).
Schematically, the design of the quasi experimental can be drawn as follows:
Table 1
The Schematic of The Quasi-Experimental Design
Group Pre-test Treatment Post-test
Experimental O1 X O2
Control O3 - O4
Note:
X represents the exposure of a group to an experimental variable
Reza Purbaya, 2015
THE EFFECTIVENESS OF CHAIN OF SHORT MESSAGE SERVICE OF VOCABULARY IN ENHANCING
HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
Hatch and Farhaday (1982) stated that the variables are defined as an
attribute of an object which divides from one object to another. There are two
kinds of variable, that is independent and dependent variables. Independent
variable is the selected, manipulated, and measured variable, while dependent
variable is the variable which the researcher tries to determine the effect of the
independent variable. The Chain of Short Message Service of Vocabulary is the
independent variable and the scores of vocabulary test are the dependent variable.
In order to strengthen the analysis, a qualitative research method in form of
questionnaire is also conducted in the research.
3. 1. 1 Hypothesis
Hypothesis is defined as a prediction about the result of research. There are
two hypothesis namely null hypothesis and alternative hypothesis. The null
hypothesis (Ho) states that there is no difference between the result of
experimental and control group after the treatment. The alternative hypothesis
(H1) states opposite to the null hypothesis (Hatch & Farhady, 1982, pp. 3-4).
Thus, the hypotheses of the research are as follow:
Ho = The use of Chain of Short Message Service of Vocabulary technique does not increase the students’ vocabulary gains.
H1 = The use of Chain of Short Message Service of Vocabulary technique increases the students’ vocabulary gains.
The result of independent t-test and dependent test gained from the scores of
pre-test and post-test in experimental group and control group is the measurement
of the acceptance of null hypothesis. If the result from each test is similar or
higher than critical value of α=0.05, therefore the null hypothesis (Ho) is rejected
because it means that the use of Chain of Short Message Service of Vocabulary
technique increases the students’ vocabulary gains. In the other hand, if the result
Reza Purbaya, 2015
THE EFFECTIVENESS OF CHAIN OF SHORT MESSAGE SERVICE OF VOCABULARY IN ENHANCING
HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
means that use of Chain of Short Message Service of Vocabulary technique does
not improve the students’ vocabulary gains.
3. 2 Data Collection
3. 2. 1 Population and Sample
Population is a group of people having one or more characteristics that
become the researcher’s interest, while samples are selected part of population for
observation and analysis (Best & Khan,1995, p. 13). The sample of the research
was chosen in purpose since quasi-experimental design was not a random
selection of subjects. Another reason underlying the selection of participants was
that the researcher had conducted teaching practicum in the school so that it is
considered much easier to gain the data. It was based on the same number of
students and absence of significants difference of scores from two groups. The
difference was determined by independent t-test from pre-test scores.
The population involved in the research was eleventh grade students from
one of Senior High School in Bandung and the samples were two groups from one
class that was divided into two groups.
3. 2. 2 Research Instrument
There were four instruments used in the research, namely pilot-test, pre-test,
post-test, and questionairre. Based on those intruments, the collected data were
analyzed to determine whether or not Chain of Short Message Service of
intepretation and its purpose. On the other hand, reliability reveals the consistency
Reza Purbaya, 2015
THE EFFECTIVENESS OF CHAIN OF SHORT MESSAGE SERVICE OF VOCABULARY IN ENHANCING
HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
The pre-test was conducted in experimental and control group before
employing the treatment in order to measure the current state of vocabulary
knowledge of the students. On the other hand, the post-test was conducted in both
groups at the end of the treatment to find out whether or not there is an
improvement on students’ vocabulary.
The questionairre was administered in experimental group after conducting
the post-test. The questionairre was aimed at finding out students’ responses
toward Chain of Short Message Service of Vocabulary technique employed
outside the classroom. There were ten statements formed in positive and negative
sentences in the questionnaire to gain a serious and consistent response from the
respondents. The instruments were constructed in checklist type based on Likert
scale. Sugiyono (2012, pp. 96) states that the advantages of forming the checklist
type in positive and negative sentences are the simplicity in forming, paper-less,
the convenience in tabulating data, and visually interesting. The data gained are
interval data.
3. 3 Research Procedures
Basicaly, the procedures of the research are as follows:
1. Organizing the Teacher Roles
The researcher had roles as a non-participant observer for both experimental
and control group. However, the observer constructed the vocabulary
materials for the teacher. The teacher roles were to initiate the Chain of Short
Message Service of Vocabulary by sending the vocabulary materials to the
students and and making sure that every students in experimental group had
achieved the vocabulary. The vocabulary materials which were sent to
students were only verb. The teacher also had to employ further treatment by
giving students more exposure before beginning the class in term of the
vocabulary sent the day before the class. The complementary activity done
Reza Purbaya, 2015
THE EFFECTIVENESS OF CHAIN OF SHORT MESSAGE SERVICE OF VOCABULARY IN ENHANCING
HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
Service of Vocabulary and the control group was only received the exposure
in the class as well as the treatment given in the experimental group since
they were in the same class.
2. Organizing the Research Instrument
Organizing the research instruments includes creating the test item for both
pre-test and post-test, piloting the pre-test and post-test and forming
items. The participants of the pilot test were students in eleventh grader at the
same school who did not participate in experimental group and control group.
4. Administering Pre-test to Experimental and Control Group
The pre-test was conducted in experimental and control group before
employing the treatment in order to measure the current state of vocabulary
knowledge of the students.
5. Conducting the Treatment
The Chain of Short Message Service of Vocabulary and an exposure of the
vocabulary given in the message was employed in experimental group and in
the control group was the exposure of the vocabulary only which is
conducted. However, the learning materials given to them were
approximately similar since the core treatment was employed outside the
classroom, as can be seen in the following treatment schedule:
Table 3.2
The Schematic of Treatment Schedule
27th 28th
Reza Purbaya, 2015
THE EFFECTIVENESS OF CHAIN OF SHORT MESSAGE SERVICE OF VOCABULARY IN ENHANCING
HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
6th 7th 8th 9th 10th 11th 12th 13th 14th 15th
16th 17th 18th 19th 20th 21st 22nd 23rd 24th 25th
26th 27th 28th 29th 30th 1st 2nd 3rd 4th 5th
6th 7th 8th 9th 10th 11th 12th 13th 14th 15th
Blue = Pilot test on 27th August 2014
Green = Pre-test on 30th August 2014 - Post-test on 11th September 2014
Yellow = Treatment days
Red = Mid-term test
6. Administering Post-test to Experimental and control Group
After applying the treatment, post-test was given to both experimental and
control group at the end of the program to reveal the use of Chain of Short
Message Service of Vocabulary in developing students’ vocabulary.
7. Employing Questionnaire
The questionnaire was formed based on Likert scale. The questionnaire,
consisting of ten questions, was employed to see students responses toward
Chain of Short Message Service of Vocabulary. The respondents ticked one
area on the rating scale based on their opinion.
3. 4 Data Analysis
3. 4. 1 Scoring Technique
The research used the formula of processing scoring system without minus
system to avoid a negative score. Pre-test and post-test were in the form of filling
in the blank in 30 numbers. The score was determined by dividing the correct
answers by 0.3. therefore the maximum score of the students is 100.
3. 4. 2 The Validity Test of The Pilot-test
Content validity was conducted to test the validity in the research. Sugiyono
Reza Purbaya, 2015
THE EFFECTIVENESS OF CHAIN OF SHORT MESSAGE SERVICE OF VOCABULARY IN ENHANCING
HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
conducted program can be made by comparing the contents of the instrument
with the determined contents of the draft. The research employed the Pearson
product-moment correlation formula to find out the validity. The formula was
proposed as follows:
� =
∑
− ∑
∑
√[ ∑
− ∑
][ ∑
− ∑
]
X= Score item which its validity is assessed
Y= Total score gained by the sample
r= Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient
N= Number of respondent
(Kranzler & Moursund, 1999, p. 56)
Anates V4 was employed to calculate the data. The obtained value from
correlation coefficient (r) value was compared to rcritical. If robtained ≥ rcritical, it means
that the item is valid, and if the robtained ≤ rcritical, it means that the item is not valid.
3. 4. 3 The Reliability Test of the Pilot-test
Reliability was used to reveal the consistency of the result. Split-half
method was conducted in the research to test the reliability. The Spearman-Brown
formula was used that is defined as follows:
� =
�
⁄ ⁄+ �
⁄ ⁄� = Coefficient Correlation of Reliability
� ⁄ ⁄ = Correlation between X (odd items) and Y (even items)
(Arikunto, 2012, pp. 106-110)
In processing the test, the research used AnatesV4 and the obtained
Reza Purbaya, 2015
THE EFFECTIVENESS OF CHAIN OF SHORT MESSAGE SERVICE OF VOCABULARY IN ENHANCING
HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
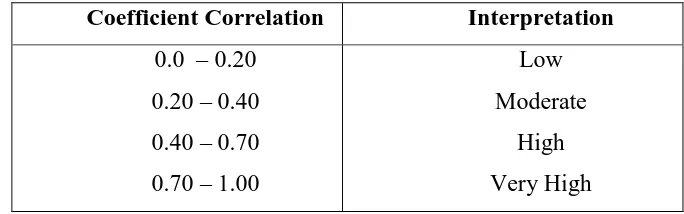
Table 3.1
Category of Coefficient Correlation of Reliability
Coefficient Correlation Interpretation
3. 4. 4 The Difficulty Index
The difficulty index is an assumption that a good item should not be too
difficult or too easy (Arikunto, 2012, pp. 222-225). The formula used to find the
difficulty index is as follows:
� =
��
�
P = difficulty index
B = number of students who answers the item correctly
JS = number of students
3. 4. 5 Data Analysis on Pre-test and Post-test
3. 4. 5. 1 The Normal Distribution Test
The data are determined as normal distribution when the students’ score are
closed to the average score, above or below one standard deviation. Field (2009,
p. 144) stated that in investigating the normal distribution, the
Kolmogorov-Smirnov test can be employed. The test compares the scores in the sample to a
normally distributed set of scores with the same mean and standard deviation. The
data was calculated through SPSS 20 for Windows.
There are steps conducted in the normal distribution test of the
Reza Purbaya, 2015
THE EFFECTIVENESS OF CHAIN OF SHORT MESSAGE SERVICE OF VOCABULARY IN ENHANCING
HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
level, analyzing the groups’ scores, and interpreting the output data. The first step is setting the alpha level at 0.05 (two-tailed test) and the hypotheses are as
significantly different from normal distribution (probably normal) and the null
hypothesis is rejected. In contrast, if the result is significant (p > 0.05) then the
distribution is approaching the normal distribution and the null hypothesis is
accepted (Field, 2009, p. 139).
3. 4. 5. 2 The Homogeneity of Variance Test
Field (2009, p. 149) stated that homogeneity of variance means when the
research goes through levels of one variable, the variance of the other variables
should not change. If the research has collected groups of data, it means the
variance of the outcome variables of the research should be the same in each of
these groups. In addition, Kranzler & Moursund (1999) stated that the more
homogeneous the group, the lower the variance.
The research used the Levene’s test to examine the homogeneity of variance
of the scores. The test was computed through SPSS 20 for Windows. There were
three steps in employing the Levene’s test. The first steps is stating hypothesis and
setting the alpha level. The alpha level set is at 0.05 (α = 0.05) and it is the
maximum error points that can be tolerated. The hypotheses are as follow:
H0 = the variances of the control and experimental group are homogenous.
Reza Purbaya, 2015
THE EFFECTIVENESS OF CHAIN OF SHORT MESSAGE SERVICE OF VOCABULARY IN ENHANCING
HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
The second was analyzing the scores using Levene’s test through SPSS 20.
The last is Intepreting the result. The result were interpreted by this way: if the
result of the test is interpreted to be significant at p ≤ 0.05 and it means that the
null hypothesis is rejected and the variances are significantly difference. In
contrast, the result is interpreted to be non-significant if p > 0.05 and it is
concluded that the null hypothesis is accepted and the variances are approximately
equal (Field, 2009, p. 150).
3. 4. 5. 3 Independent t-test
The independent t-test is used to analyze a relevant relationship between the
independent variable (treatment) and the dependent variable (vocabulary score)
that is measured on experimental and control group. Field (2009, p. 239) stated
that the test is focused on determining whether or not there is a significant
difference between the predictor (independent variable) and the model (dependent
variable).
There were three steps in employing the independent t-test. The first step
was stating the hypothesis and setting the alpha level. The alpha level was set at
0.05 (two-tailed test) and the hypotheses are as follow:
Ho = the two samples are from the same population; there is no
significant difference between the two samples.
Ho = the two samples are from the same population; there is a significant
difference between the two samples.
The second step is analyzing the groups’ scores using the independent t-test
in SPSS 20 for windows. The formula of the independent t-test is as follows:
� = −
√� + �
Reza Purbaya, 2015
THE EFFECTIVENESS OF CHAIN OF SHORT MESSAGE SERVICE OF VOCABULARY IN ENHANCING
HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu M = mean
s2 = variance
N = numbers of participants
(Kranzler & Moursund, 1999)
The last is comparing the result with the significance level. The null
hypothesis (Ho) is rejected if the result ≥ 0.05 which means there is a significant
difference of mean between experimental and control group. In contrast, if the
result < 0.05, the null hypothesis (Ho) is accepted which means that there is a no
significant difference of mean between experimental and control group.
3. 4. 5. 4 Dependent t-test
In the research, dependent t-test was aimed to find out whether or not the
experimental group have a progression after conducting the treatment. There were
three steps in employing the dependent t-test. The first was stating the hypothesis
and setting the alpha level. The alpha level was set at 0.05 (two-tailed test) and the
hypotheses are as follow:
Ho = the two samples are from the same population; there is no
significant difference between the two samples.
Ho = the two samples are from the same population; there is a significant
difference between the two samples.
The second was analyzing the groups’ scores using the dependent t-test in
SPSS 20 for windows. The results is in the value or tobt. The formula of the
dependent t-test is as follows:
� = � ∑ � − ∑ ��
� � −
t = dependent t-test
Reza Purbaya, 2015
THE EFFECTIVENESS OF CHAIN OF SHORT MESSAGE SERVICE OF VOCABULARY IN ENHANCING
HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu n = numbers of participant
D = difference between pre-test and post-test
(Kranzler & Moursund, 1999)
Lastly, the result was compared with the significance level. The null
hypothesis (Ho) is rejected if the result ≥ 0.05. It means there is a significant
difference between the pre-test and post-test scores. In contrast, if the result <
0.05, the null hypothesis (Ho) is accepted which means there is no significant
difference between the pre-test and post-test scores before and after the treatment.
3. 4. 5. 5 The Calculation of Effect Size
The effect size is used to determine the strength of relationship between
independent variables and dependent variables (Field, 2009, p. 57). To calculate
the effect size, the research used a correlation coefficient of effect size. The
formula was proposed as follows:
� = √
� + ��
�
r = effect size
t = the independent t-test value
df = degree of freedom (N1+N2-2)
After calculating the effect size, its value is compared and analyzed by using
the table’s scale. The correlation coefficient of effect size is always positive and
range from 0 to 1.00. The scale is as follows:
Table 3.4
The Scale of Effect Size
Reza Purbaya, 2015
THE EFFECTIVENESS OF CHAIN OF SHORT MESSAGE SERVICE OF VOCABULARY IN ENHANCING
HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu Small
Medium
Large
0.100
0.243
0.371
(Coolidge F. L., 2000, p. 151)
3. 4. 6 Data Analysis on Questionnaire
The questionnaire was used to find out the strengths and weaknesses of
Chain of short message service of vocabulary according to the students’ point of
view. The questionnaire was constructed using Likert scale.
The data gained were analyzed and intepreted based on the frequency of
students’ answer. Hatch and Farhady (1982, p. 46) proposed the percentile formula as follows:
� =
�
P = Percentile
F = Frequency of students’ answer
Reza Purbaya, 2015
THE EFFECTIVENESS OF CHAIN OF SHORT MESSAGE SERVICE OF VOCABULARY IN ENHANCING
HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
CHAPTER V
CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS
In this chapter, various findings of the research are explained together in
conclusions. In addition, the suggestions of the research are presented concisely
which is aimed at providing references for the teachers, further researchers and
readers.
5. 1 Conclusions
The research was focused on the implementation of the chain of short
message service of vocabulary in enhancing the students’ vocabulary. The
research was intended to find out whether or not the chain of short message
service of vocabulary had developed students’ vocabulary when compared with
classroom teaching activity. Furthermore, the research was also aimed at finding
out the students’ responses toward the chain of short message service of vocabulary technique.
The result of the research supported the effectiveness of chain of short
message service of vocabulary technique in increasing the students’ vocabulary.
The chain of short message service of vocabulary was applied in experimental
group in which the students achieved more intended vocabulary than the students
in control group in which conventional teaching activity was applied. The chain of
short message service of vocabulary technique was applied as an additional
activity outside the classroom in which the students could improve their
vocabulary. This technique had stimulated the students to use their technology as
the part of learning tools.
Most of the students agreed that employing the chain of short message
Reza Purbaya, 2015
THE EFFECTIVENESS OF CHAIN OF SHORT MESSAGE SERVICE OF VOCABULARY IN ENHANCING
HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
because they could simply open their mobile phones and they could see learning
material which could be opened wherever and whenever they wanted. In addition,
they also admitted the flexibility of mobile phones conducted in learning activity.
5. 2 Suggestions
Teachers can design their own vocabulary materials based on this technique.
They can equalize the materials to the learning goal from school. The teachers are
expected to give more exposure to vocabulary. O’Dell (1997) supported the notion of giving vocabulary a high profile in the syllabus and the classroom so
that students can see the importance of vocabulary and understand that learning a
language is not only learning about grammar. As the basic structure of a language,
vocabulary is an avoidably being the core of language. Without knowing any
single word, mastering the grammar becomes useless.
The teachers can use this technique as an additional activity to enhance
students’ vocabulary. In addition, this technique can stimulate them to use the technology, mobile phones, they have in a positive way. They can engage the
mobile phones as one of learning tools. The technique also gives students another
way to have a joyfull learning activity since its flexibility to open up and read the
vocabulary whenever and wherever they want to.
Some of the research limitations lead naturally into suggestions for further
research. The first suggestion is that the Chain of Short Message Service of
Vocabulary could be promoted not only in terms of vocabulary mastery but also
other language skills such as reading and writing since the technique gave
students more exposures to certain vocabulary so that they can recognize the
meaning and the form of the word.
The second suggestion, the further researcher can involve students more in
the activity. The researcher could have the students to find the vocabulary by
Reza Purbaya, 2015
THE EFFECTIVENESS OF CHAIN OF SHORT MESSAGE SERVICE OF VOCABULARY IN ENHANCING
HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
teacher can encourage the students to be more active in this activity. Those all can
be conducted to discover its effectiveness in enriching the students’ vocabulary.
Finally, since the research had been conducted for four meetings and got
large effect from the treatment, there is still an expectation for further researchers
to cover longer period of time with more vocabulary in order to discover more
Reza Purbaya, 2015
THE EFFECTIVENESS OF CHAIN OF SHORT MESSAGE SERVICE OF VOCABULARY IN ENHANCING
HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
REFERENCES
Arikunto, S. (2012). Dasar-dasar evaluasi pendidikan (2nd ed.). Jakarta: Bumi
Aksara.
Best, J.W., & Khan, J.V. (1995). Research in education (7th ed.). New Delhi:
Houghton Mifflin Company.
Brown, H. D. (2001). Teaching by principle: An interactive approach to language
pedagogy (2nd ed.). New York: Addison Wesley Longman, Inc.
Cavus, N & Ibrahim, D. (2009). M-learning: An experiment in using sms to
support learning new english language words. British Journal of
Educational Technology. Vol. 40, issue 1, p. 78-91, January 2009.
Coolidge, F. I. (2000). Statistics: A gentle introduction. London, Thousand Oaks,
New Delhi: SAGE Publications.
Departemen Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan. (2006). Standar Isi SD, SMP, SMA.
Jakarta: Depdikbud.
Derakhshan, A. & Khodabakhshzadeh, H. (2011). Why call why not mall: An
in-depth. Academy Publisher.
vocabulary learning via mobile phones. Turkish Online Journal Of
Educational Technology, Vol. 10, pp. 203-214, Education Research
Complete, EBSCOhost, Retrieved on March, 1st 2014 from:
http://www.tojet.net/articles/v10i3/10323.pdf
Hatch, E., & Farhady, H. (1982). Research design and statistics for applied
Reza Purbaya, 2015
THE EFFECTIVENESS OF CHAIN OF SHORT MESSAGE SERVICE OF VOCABULARY IN ENHANCING
HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
Hughes, A. (2003). Testing for Language Teachers (2nd ed.). United Kingdom:
University Press, Cambridge.
Kranzler, G., & Moursund, J. (1999). Statistics for terrified (2nd ed.). Upper
Saddle River, New Jersey: Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Kukulska-Hulme, A., Traxler, J. & Pettit, J. (2007). Designed and user-generated
activity in the mobile age‘, Journal of Learning Design, 2 (1), 52-65.
Laufer, B. (1998). The development of passive and active vocabulary in a second
language: Same or different? Applied Linguistics. 12, 255–71.
McCarten, J. (2007). Teaching vocabulary lessons from the corpus lessons for the
classroom. New York: Cambridge University Press.
Mehring, J.G. (2005). Developing vocabulary in second language acquisition
from theories to classroom. Retrieved on January, 3th 2014 from:
http://www.hpu.edu/CHSS/LangLing/TESOL/ProfessionalDevelopment/2
00680TWPfall06/03Mehring.pdf
Nation, I.S.P.. (2001). Learning vocabulary in another language. Cambridge:
Cambridge University Press.
Nation, I.S.P. (1990). Teaching and learning vocabulary. Newbury House, New
York.
Nation, P. Teaching vocabulary. University of Wellington: Asian EFL Journal,
viewed on January, 23th 2014.
Pikulski, J., & Chard, D. J. (2003). Fluency: Bridge from decoding to reading
comprehension. Boston, MA: Houghton Mifflin.
Schmitt, N. (2008). Teaching vocabulary. New York: Cambridge University.
Schmitt, N. (2000). Vocabulary in language teaching. New York: Cambridge
University Press.
Sugiyono. (2012). Metode penelitian kuantitatif, kualitatif dan R&D (17th ed.).
Bandung: CV.ALFABETA.
Sugiyono. (2009). Metode penelitian kuantitatif, kualitatif dan R&D (7th ed.).
Reza Purbaya, 2015
THE EFFECTIVENESS OF CHAIN OF SHORT MESSAGE SERVICE OF VOCABULARY IN ENHANCING
HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
Thornton, P. & Houser, C. (2005). Using mobile phones in english education in
Japan. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, Vol. 21, 217–228.
Wilkins, D. A. (1972). Linguistics in language teaching. London: Edward Arnold.
Winters, N. (2006). What is mobile learning? In: Sharples, M. (Eds.), big issues in
mobile learning. Report of a workshop by the Kaleidoscope Network of
Excellence Mobile Learning Initiative. Nottingham: University of
Nottingham.
Wu, J & Binbin, W. (2009). The role of vocabulary in esp teaching and learning.
Guangdong College of Finance. Retrieved on January, 1st 2014 from:
http://www.celea.org.cn/pastversion/lw/pdf/wujiangwen.pdf
www.chip.co.id/news/corporate-web_internet-gadget/6270/survei_35_persen_