THE IMPACT OF STRATEGY IMPLEMENTATION AS A SOLUTION
FOR DEALING WITH CORPORATE GOVERNACE ISSUES IN
ZIMBAMWE
Michael Chamunorwa Tigere and Research scholar SimbaraheMasamba
Holder of Masters in strategic and corporate governance
Email: michaeltiger25@yahoo.com
Email: masambasimplex@gmail.com
ABSTRACT
This research was done to explore the impact of strategy implementation as a solution for corporate governance issues in Zimbabwe. The research introduced the global perspective issues related to strategy implementation as a solution for corporate governance. The objectives of the study were to assess the effect of strategy implementation on fairness, to assess the effect of strategy implementation on accountability, to assess the effect of strategy implementation on transparency and to assess the effect of strategy implementation on independence assurance. Research methodology of this study used mixed approach and data collection instruments included interviews and questionnaires. Data analysis was done using Stata 11 statistical package. The findings indicated a correlation between study variables and this was shown by ‘t’-tests that were above two and ‘p’-values that were below 5%. The research was concluded with recommendations on what companies in Zimbabwe need to do to improve on performance and ensuring that good corporate governance practices are maintained and area of further research was established.
Keywords: Strategy implementation and corporate governance
1.0 Introduction
done on the impact of corporate governance issues on performance and non on strategic implementation. Therefore, this paper seeks to assess the impact of strategy implementation as a solution for dealing with corporate governance issues in Zimbabwe. The paper will be arranged in the following sections, background or conceptual and theoretical framework, objectives, hypothesis testing, significant of the study as well as need for the study, literature review, research methodology, data presentation and analysis, recommendation and the paper will be concluded by area of further research.
1.2 Conceptual and Theoretical framework
According to Hugrieves et al (2011), several firms from around the world are operating in a complexity environment that is associated by business issues that need to be addressed and are affecting operations. In support of the above Wein and Gibbs (2013), hypothesized that most of the problems that are affecting business operation are as a result of poor corporate governance practices within companies. Aaron (2012), in the same school of thought elaborated that for such firms, to deal with such issues require strategy implementation and practical implementation of different strategies in resolving corporate problems as way of enhancement of competitive advantage.
In Europe, there is a company known as Enron which was in the energy sector, the company was audited and passed and the company went on to liquidate as a result of poor corporate governance issues.Mark et al (2012), cited that most of these companies are not putting in practice co-pillar of corporate governance pillars for instance fairness, transparency, accountability and independence assurance. According to James (2013), companies in Europe that have been affected by poor corporate governance have since adopted turnaround strategies that include management turnaround, financial turnaround and operational turnaround. Such control measure has helped such companies to excel and their performance have improved drastically.
support of the above Donald (2013), elaborated that strategy implementation has helped several countries in Africa to develop control measures in dealing with corporate governance issues and in South Africa, tollgates and monitoring cameras have been put in place as a way of resolving poor corporate governance.
Strategy implementation has proven not to be effective in dealing with corporate governance issues as companies like Air Zimbabwe, ZETDC, National railways of Zimbabwe, PSMAS, Zimbabwe broadcasting corporation, ENG and many more only to mention but a few have been affected by poor corporate governance practices . According to Mlambo (2014, The Sunday mail), companies in Zimbabwe have been affected by poor corporate governance seeing many companies liquidated, placed under schemes of arrangement for instance Shabani mine in Zvishavane , some have lost subscribers for instance PSMAS has lost more than 6 000 000 health subscribers due to poor governance issues caused by Cuthbert Dube the company CEO, ZBC has been affected by these issues when Happison Muchechetere who frauded approximately $1 000 000 from a broadcasting vehicle that he claimed that it costed $200 000, Recently Prof Jonathan Moyo frauded the government $500 000 that he bought bicycles for people in Tsholotsholo and Air Zimbabwe bosses stole engines for airplanes leading to the company facing financial crisis and failed to settle its debts and retrenched more than 50 employees in 2015.
1.2 Statement of the problem
Corporate governance has become a major concern on performance of organization and it is still not clear on whether strategic implementation will be effective on sound corporate governance practices. Several studies have been done on poor corporate governance practices in Europe especially with regards to fraud and none has been done to Zimbabwe focusing on corruption and embezzlement of funds. This is the reason that motivated the researcher to carry out the impact of strategy implementation as a solution for dealing with corporate governance issues in Zimbabwe
1. To assess the effect of strategy implementation on fairness. 2. To assess the effect of strategy implementation on accountability. 3. To assess the effect of strategy implementation on transparency
4. To assess the effect of strategy implementation on Independence assurance.
1.4 Hypothesis Testing
H1 There is a relationship between strategy implementation and fairness.
H0 There is no relationship between strategy implementation and fairness.
H2 There is a relationship between strategy implementation and accountability.
H0 There is no relationship between strategy implementation and accountability.
H3There is a relationship between strategy implementation and transparency.
H0 There is no relationship between strategy implementation and transparency.
H4There is a relationship between strategy implementation and independence assurance.
Source: Raw data
1.6 Need for the study
The study will be of great importance to the researcher on expanding the body of knowledge and the nation of Zimbabwe at large in coming up with strategies that can be adopted and implemented to improve corporate governance practices in Zimbabwe
1.7 Operational Definition
Strategic implementation is the process that puts plans and strategies into action to reach goals
1.8 Review of Literature
According Smith and Harrison (2014), to Strategy implementation is the translation of chosen strategy into organizational action so as to achieve strategic goals and objectives. Strategy implementation is also defined as the manner in which an organization should develop, utilize, and amalgamate organizational structure, control systems, and culture to follow strategies that lead to competitive advantage and a better performance as also supported by (Joseph et al 2013 and Gibbs 2011:12).
1.8.1 Effect of strategy implementation on fairness.
According to Ellis et al (2013), fairness means “treating all stakeholders s including minorities, reasonably, equitably and provide effective redress for violations. Establishing effective communication mechanism is important in ensure just and timely protection of resource sand people asset as well correcting of wrongs as also supported by (James 2012 and Grace et al 2012).In the same manner Baaij et al (2012), supported that there is a positive relationship between strategy implementation and fairness as both promote a positive impact in promoting organisational performance. However regardless of the implementation of strategies as a way of assuring good corporate governance practices, Zimbabwe is facing a lot of challenges in addressing such issues as corruption and embezzlement of fund is at pick and still there is no clue on what can be done to deal with the issue as supported by Mashava 2015, (The standard).Furthermore, Fairness in Zimbabwe exists only in theory as there is inconsistence policy changing and abuse of citizens as the nation is not practicing democracy and strategies that are in place currently are in favor of those with political muscle as hypothesized by the Julious 2015, (Newsday).
1.8.2 Effect of strategy implementation on accountability.
to improve their performance. This applies from the staff all the way up to top leadership embracing Risk management within defined formal appetite for risk. According to Henry et al (2014. According to Berchicci et al (2012), this also include fostering culture of compliance to create real and perceived believe that the entity is operation within internal and external boundaries and to achieve this, organisation’s in Zimbabwe must ensure that strategies are put in place to ensure that good culture and ethics are molded in vision and mission of entities. Furthermore, Carney et al (2011), cited that strategy implementation is still lacking in Zimbabwe as many authors elaborate that it is the main key to ensure accountability of employees in promoting good corporate governance practices. However Stone and Joshua (2012), argued that in Zimbabwe accountability is maintained in most companies as corruption is at its pick.
1.8.3 Effect of strategy implementation on transparency
According to Jansen et al (2012), transparency “means having nothing to hide” that allows its processes and transactions observable to outsiders. It also makes necessary disclosures, informs everyone affected about its decisions. Transparency is a critical component of corporate governance because it ensures that all of entity’s actions can be checked at any given time by an outside observer. This makes its processes and transactions verifiable, so if a question does come up about a step, the company can provide a clear answer. Donald and Keith (2012), postulated that strategy implementation is lacking in most and if not all companies in Zimbabwe in ensuring that transparency is practiced in entities. However, Harvard institution in 2016, cited that strategy implementation in Zimbabwean companies can be achieved when companies practice rotation of employees to ensure that employees do not familiarize with the systems as well as with the people they work with as also supported by (Nadolsk et al 2014).
1.8.4 Effect of strategy implementation on independence assurance.
for QA and acceptance of the product/deliverable and/or the reliability of test results obtained from quality control and acceptance testing. This independent assurance insures that (1) the representation or acceptance test results are accurate and provide a fair and equitable basis for construction acceptance and (2) quality control testing is accurate and thus will properly indicate process quality. Furthermore, Lillian et al (2014), stated that companies in Zimbabwe should ensure that entities should have board of directors that are both from within and outside the organisation as well as external auditors that are independent. Wijen et al (2014), supported the above school of thought citing that these members are independent on judgement and in most cases do not accept bribes therefore enhancing good corporate governance practices.
1.8.5 Theoretical perspectives
The study will make use corporate governance theories for instance sabarnise Oxley and agency theory since the theories covered strategic implementation and good corporate governance practices
1.9 Methodology
The purpose of the study is to explore the impact of strategy implementation as a solution for corporate governance issues in Zimbabwe. This researched used a mixed approach that is both qualitative and quantitative techniques. According to Kumar et al (2015), states that there many philosophies namely ontology, epistemology, constructivism, naturalism, positivism and pragmatism. The researcher choose pragmatism for this study because there is possibility of a predictive or generalizable knowledge and will therefore proceed with a pragmatic position of what constitutes science and the possibility of knowing the world
1.10 Research design
comprising discrete, observable elements and events that interact in an observable, determined and regular manner” (Steve et al 2013).
1.11 The ResearchPopulation:
The population of this research study included a selected number of firms in Zimbabwe for instance Air Zimbabwe, PSMAS, ZBC and ZETDC. The population can be in two categories, the target and the study population. (Creswell 2012). The target population is the actual population to which the researcher would really like to generalize. The target population in this study is the populationconsisted the management and employees of selected firms. A total of 8 managers and 12 employees was used totaling to 20 participants
1.11.1 Selection of Sample Size:
According to Kumar (2014) sample size refers to the sampling portion that is drawn from the target population. According to Donald et al (2012), when target population is small, the whole population can be used as sample size. Therefore, the sample size for this study is 20 in line with Donald model of sample size.
.
1.11.2 Sampling procedures:
The researcher adopted stratified random sampling as it is probability sampling technique and ensures the grouping of variables in an orderly manner to assess the relationship. Trish et al (2013) conducted their research similar to the researcher’s topic and used stratified random sampling. The author argued that the advantages of this sampling technique are the capacity to catch key populace attributes, it frequently requires a smaller sample which gives a more prominent precision, consequently minimizing costs, and fundamentally it guarantees that specific groups in a research population are sufficiently represented in the sample and enhances effectiveness by increasing more control on the composition of the sample.
1.12 Research instruments:
In order to attained adequate, appropriate and reliable information, the research work uses mainly 5-minute telephone interviews and a questionnaire mainly because these two methods were the most appropriate
1.12.2 Interviews
The researcher conducted face to face interviews as part of data collecting instruments and they helped to cover the weaknesses of questionnaires. Interviews resulted by respondents resulted in obtaining accurate information. In contrast to some reports in the literature, Obilor (2013) used interviews in support of the questionnaires.
1.13 Methods of Data Collection:
Questionnaires will be designed by the aid of 5-point likert scaling and they will be in the form of closed ended questionnaire to reduce further clarification. To ensure validity, the questionnaires will be supported by planned face to face interview. A pilot test will be done to few selected captains of industries to test for reliability.
Ordinal least squares model
Where: α+β1X1+β2X2+β3X3+β4X4+ε Fairness = іα+β 1іE+ SI і + іϵ Transparency = іα+β 2іT+ SI і + іϵ
Independence assurance= іα+β 3іA+ SI і + іϵ Accountability = іα+β 1іR+ SI і + іϵ
1.13 Analysis of Data:
Analysis and presentation:
Table???: Response Rate on questionnaires and interviews
Category Administered Returned Total %
Employees 12 12 100
Management 8 8 100
Total 20 20 100
Source: Primary Data
Table 1.1 above shows the questionnaires that were distributed to both employees and manager and from the 20 that were distributed only 20 were successful giving an overall response rate of 100%.The overall response rate is deemed favorable as it will yield reliability and validity as supported by (Kumar et al 2013).
1.14 Findings and presentation
Table ;Correlation between strategy implementation and fairness
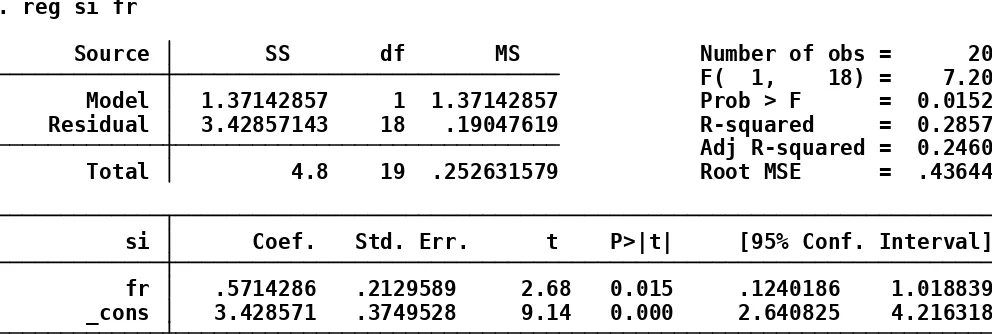
_cons 3.428571 .3749528 9.14 0.000 2.640825 4.216318 fr .5714286 .2129589 2.68 0.015 .1240186 1.018839 si Coef. Std. Err. t P>|t| [95% Conf. Interval] Total 4.8 19 .252631579 Root MSE = .43644 Adj R-squared = 0.2460 Residual 3.42857143 18 .19047619 R-squared = 0.2857 Model 1.37142857 1 1.37142857 Prob > F = 0.0152 F( 1, 18) = 7.20 Source SS df MS Number of obs = 20 . reg si fr
study variables is indicated by a ‘t’-value that is above 2 and a ‘p’-value that is below 5%.There is a positive correlation between strategy implementation and fairness as indicated by a ‘t’-value of 2,68 that is above 2 and a ‘p’-value of 0,015 that is below 0,05.Therefore an increase in strategy implementation by 1-unit will lead to an increase on the corresponding variable by 57% level of coefficient.
Correlation between strategy implementation and transparency
_cons 3.486957 .3235749 10.78 0.000 2.807151 4.166762 tr .5217391 .1767878 2.95 0.009 .1503217 .8931566 si Coef. Std. Err. t P>|t| [95% Conf. Interval] Total 4.8 19 .252631579 Root MSE = .42392 Adj R-squared = 0.2886 Residual 3.23478261 18 .179710145 R-squared = 0.3261 Model 1.56521739 1 1.56521739 Prob > F = 0.0085 F( 1, 18) = 8.71 Source SS df MS Number of obs = 20 . reg si tr
The findings above indicated that there is a positive relationship between the dependent and independent variables. According to Chen et al (2012), the relationship between study variables is indicated by a ‘t’-value that is above 2 and a ‘p’-value that is below 5%. There is a positive correlation between strategy implementation and transparency as indicated by a ‘t’-value of 2,95 that is above 2 and a ‘p’-value of 0,009 that is below 0,05.Therefore an increase in strategy implementation by 1-unit will lead to an increase on the corresponding variable by 52% level of coefficient.
The findings above indicated that there is a positive relationship between the dependent and independent variables. According to Chen et al (2012), the relationship between study variables is indicated by a ‘t’-value that is above 2 and a ‘p’-value that is below 5%.There is a positive correlation between strategy implementation and accountability as indicated by a ‘t’-value of 2,95 that is above 2 and a ‘p’-value of 0,009 that is below 0,05.Therefore, an increase in strategy implementation by 1-unit will lead to an increase on the corresponding variable by 49% level of coefficient.
1.15 Conclusions
To conclude the study has proven a positive relationship between strategic implementation and corporate governance as deduced by t-values above 2 and p-values that are significant at 5%
1.16 Implications
The main aim of this study was to address the impact of strategic implementation as a solution for corporate governance in Zimbabwe. The paper have been done so by the help of regression analysis to test correlation of study variables.
1.17 Recommendations
Companies in Zimbabwe should put in place strategic policies that are consistent and these promote organizational performance and in return this will promote investor confidence.
Companies should also put in place control measures that reduce pilferages and fraud for instance the installation of CCTV and make use of software packages that are reduces fraudulent for instance accounting packages like pastel and serge.
The parliament of Zimbabwe must put in place still laws that attach stiff penalties that restrict members of political parties from embezzlement of funds and they must raise number of years to be saved by people involved in poor corporate governance issues. Organizations in Zimbabwe must mound a culture that restrict people from corruption
and accepting bribes and organization should practice internal recruitment to maintain good culture within the organization.
“unofficial” ways. Van Rijckeghem and Weder (2001) did some empirical work showing that in a sample of less developed countries, there is an inverse relationship between the level of public sector wages and the incidence of corruption.
Creating transparency and openness in government spending, Subsidies, tax exemptions, public procurement of goods and services, soft credits, extra-budgetary funds under the control of politicians all are elements of the various ways in which governments manage public resources. Governments collect taxes, tap the capital markets to raise money, receive foreign aid and develop mechanisms to allocate these resources to satisfy a multiplicity of needs. Some countries do this in ways that are relatively transparent and make efforts to ensure that resources will be used in the public interest. The more open and transparent the process, the less opportunity it will provide for malfeasance and abuse. Collier (2007) provides persuasive evidence on the negative impact of ineffective systems of budget control. Countries where citizens are able to scrutinize government activities and debate the merits of various public policies also makes a difference. In this respect, press freedoms and levels of literacy will, likewise, shape in important ways the context for reforms. Whether the country has an active civil society, with a culture of participation could be an important ingredient supporting various strategies aimed at reducing corruption.
Cutting red tape, the high correlation between the incidence of corruption and the extent of bureaucratic red tape as captured, for instance, by the Doing Business indicators suggests the desirability of eliminating as many needless regulations while safeguarding the essential regulatory functions of the state. The sorts of regulations that are on the books of many countries—to open up a new business, to register property, to engage in international trade, and a plethora of other certifications and licenses—are sometimes not only extremely burdensome but governments have often not paused to examine whether the purpose for which they were introduced is at all relevant to the needs of the present. Rose-Ackerman (1998) suggests that “the most obvious approach is simply to eliminate laws and programs that breed corruption.”
energy products amount to some $1.9 trillion per year, equivalent to about 2.5 percent of global GDP or 8 percent of government revenues.
1.17.1 Area of further research
The next researcher should now focus on the effectiveness of strategic human resources management on enhancing financial performance on companies listed on the Zimbabwe stock exchange.
1.18 Limitations
The paper could have covered all companies in Zimbabwe but due to limited resources and the size of the country, a fewer companies were selected.
The researcher conducted the researcher will a limited number of researcher and some key aspect of this paper could have been ignored.
REFERENCE LIST
Berchicci, L., Dowell, G. and King, A.A. (2012). Environmental Capabilities and Corporate Strategy: Exploring Acquisitions Among US Manufacturing Firms. Strategic Management Journal, 33 (9), 1053-1071.
Carney, M., Gedajlovic, E.R., Heugens, P.P.M.A.R., Essen, M. van and Oosterhout, J. van (2011). Business group affiliation, performance, context, and strategy: A meta-analysis. Academy of Management Journal, 54 (3), 437-460.
Ellis, K. M., T. H. Reus, B. T. Lamont, and A. L. Ranft (2011). Transfer effects in large acquisitions: How size-specific experience matters. Academy of Management Journal, 54: 1261-1276.
Jansen, J.J.P., Simsek, Z. and Cao, Q. (2012). Ambidexterity and Performance in Multi-unit Contexts: Cross-level Moderating Effects of Structural and Resource Attributes.Strategic Management Journal, 33 (11), 1286-1303.
Nadolska, A.M. andBarkema, H.G. (2014). Good learners:how top management team affect behavior and performance of acquisitions. Strategic Management Journal, 35 (10), 1483-1507.
Volberda, H.W., Weerdt, N.P. van der, Verwaal, Ernst andStienstra, M. (2012). Contingency Fit, Institutional Fit and Firm Performance: A Meta-fit Approach to Organization Environment Relationships. Organization Science, 23 (4), 1040-1054.
Vrande, V.J.A. van de (2013). Balancing your technology-sourcing portfolio: How sourcing mode diversity enhances innovative performance. Strategic Management Journal, 34 (5), 610-621.