The Verbal Humor in
The SpongeBob Movie: Sponge Out of Water
Animated Film
THESISSubmitted as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Sarjana Degree of English Department Faculty of Arts and Humanities
State Islamic University of Sunan Ampel Surabaya
By:
RISMA NUR IZZAH
Reg. Number: A73212116
ENGLISH DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF ARTS AND HUMANITIES
STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY OF SUNAN AMPEL
SURABAYA
ABSTRACT
Izzah, Risma Nur. 2016. The Verbal Humor in The Spongebob Movie: Sponge Out of Water. Thesis. English Department. Faculty of Letters and Humanities. The State Islamic University of Sunan Ampel Surabaya.
The Advisor : M. Thoriqussu’ud, M. Pd.
Key words : verbal humor, violation maxim, The Spongebob Movie: Sponge Out of Water, animated film.
Textually, an aspect of language in which exploited is often happen in the humor conversation to achieve humorous effect. Moreover the violation maxim in humor conversation also could amuse the hearer. The aim of this research is to know how the humor conversation formed in The Spongebob Movie: Sponge Out of Water, animated film. In analyzing the humor conversation, this research focuses on the verbal humor and violation maxim.
This research employs a descriptive qualitative research. The data is collected from the script of The Spongebob Movie: Sponge Out of Water, Animated Film by downloaded form internet in which had adjusted to the movie manually. The data are categorized based on some theories. The first is the general theory of verbal humor proposed by Attardo Salvatore (1991) and the second is maxim principle proposed by Paul Grice (1875).
INTISARI
Izzah, Risma Nur. 2016. The Verbal Humor in The Spongebob Movie: Sponge Out of Water. Tesis. Sastra Inggris. Fakultas Adab dan Humaniora. Universitas Islam Negeri Sunan Ampel Surabaya.
Pembimbing : M. Thoriqussu’ud, M. Pd.
Kata Kunci : verbal humor, violation maxim, The Spongebob Movie: Sponge Out of Water, animated film.
Secara teks, sebuah aspek bahasa yang disalahgunakan sering terjadi dalam percakapan humor untuk menghasilkan efek lucu. Selain itu, pelanggaran maxim dalam percakapan humor juga bisa membuat tertawa pendengarnya. Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk mengetahui bagaimana percakapan humor itu terbentuk dalam film animasi, The Spongebob Movie: Sponge Out of Water. Dalam menganalisa percakapan humor, penelitian ini fokus pada verbal humor dan pelanggaran maxim.
Penelitian ini menggunakan metode penelitian secara qualitatif deskriptif. Data dikumpulkan dari naskah film animasi, The Spongebob Movie: Sponge Out of Water, yang diunduh dari internet dan disesuaikan dengan filmnya secara manual. Data dikategorikan berdasarkan beberapa teori. Pertama adalah teori verbal humor yang dikemukakan oleh Attardo Salvatore (1991) dan yang kedua adalah teori prinsip maksim yang dikemukakan oleh Paul Grice (1875).
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Inside Cover ... i
Inside Title ... ii
Declaration ... iii
Thesis Advisor’s Approval Sheet ... iv
Thesis Examiner’s Approval Sheet ... v
2.2.9. Malapropism ... 17
2.3. The Cooperative Principle ... 19
CHAPTER III: RESEARCH METHODOLOGY ... 24
4.1.2. Violation Maxim of Humor Conversation ... 46
4.1.2.1. Violation maxim of quality ... 47
4.1.2.2. Violation maxim of quantity ... 47
4.1.2.3. Violation maxim of relation ... 48
4.1.2.4. Violation maxim of manner ... 49
CHAPTER V: CONCLUSION ... 56
5.1. Conclusion ... 56
5.1.1. Kinds of Verbal Humor ... 56
5.1.2. Violation Maxim of Humor Conversation ... 57
5.2. Suggestion ... 57
REFERENCES ... 59
1 CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
This chapter presents background of study, research problems, objectives of the study, significance of the study, scope and limitation, and definition of key terms.
1.1Background of Study
Humor is used as device to attract attention for some purposes such as making others laugh. Humor is something related to funny. It is possible to claim that something is funny, even though no one laughed at the time. In other hand, it can often happen that people laugh but the other claim ‘that is not funny’ (Ross, 2005:1).
Rush (1998) said that “Humor replaced the comic and was treated as a neutral term; i.e. not restricted to positive meanings”. Humor can be defined in terms of its effect and response. In other words, humor can be inferred from its effect, i.e., intended (laugh) or unintended (no reaction). However, Vandaele (2002) said that "humour is whatever has a humorous effect" (Hassaine, 2014:91-92).
2
Eventhough humor differs from individual to individual, there is one distinction which seems that the humorous effect is achieved, that is Freud’s distinction between verbal humor and conceptual humor. Verbal humor is when an aspect of language is exploited in order to achieve a humorous effect, while conceptual humor is a concept or idea that is thought as humorous thing without using aspects of language (kim, 2009:2).
According to Psychology which concerned with people, humor has positive effect. Study about correlation between sense of humor and anxiety to the exam described that psychologically, students who have high sense of humor possessed low anxiety to the exam. This study similar with Yovetick, Dale & Hudak which described that a person who has high sense of humor felt less anxious than a person who has low sense of humor in anxious situation (Zulkarnain, 2009:52).
Other positive effect of humor described in study about humor in Islamic psychology. Physically, humor increased body resistance. Study Dr. Lee Berk and Dr. Stanley stated that humor benefits for health. They are increased immunity cells which work on attack virus, increased body resistance to attack infection of upper respiration and increased diafragma activity as like aerobic exercises (Istiningtyas, 2014:5). Beside Physical or psychological effect, Islam viewed that humor is benefit as worship. Humor are social charity, spiritual medicine and sign of happiness (2014:12).
3
textual linguistic. However, humor nowadays is spoken. “It is possible to approach humor in literature because it covers a wide of spectrum of genres and styles but lot of contemporary humor is spoken” (Ross, 2005:73). The researcher take an animated
film as object of research. This study is important to understand how humor conversation is formed in order to achieve humorous effect.
4
Raskin (1985): superiority, incongruity, and relief theory. Then she analysed joke techniques (such paralanguage, ridicule, satire, and so on), the figurative language (such wordplay, allusion, hyperbole, and so on) and linguistic features (such repetition, formulaicity, discourse markers, disfluencies, and intonation) used in stand-up comedy. By the transcription of their performance, she found combination of various linguistic features of joke telling such as wordplay and punning, hyperbole, repetitions, timing, and paralinguistic choices in the way both 2 American comedians organize and perform their material. She precisely indicated the length of the pauses in order to analyze the comedian's strategy of timing. Then, concerning the audience's reaction, she only indicated the most important periods of laughter, in which the audience obviously reacted with continuous laughter because of their appreciation of the joke or in which they hesitated and only reacted with weak laughter. In addition, they developed a specific stage persona and create their own style of performing.
5
analyzed these conversational utterances where humor and other phenomena appeared as communicative strategies. After analyzing of colloquial conversation utterance examples and applied the theories, he got utterances which contain non-prototypical irony and humor. Then he found the examples confirm that irony and humor are mostly utilized to show solidarity (positive effect). This is based on an idea that authors such Attardo (2001b: 174), Kotthoff (2007: 264), Holmes and Marra (2002: 1684) or Hay (2000: 716) often linked exclusively to humor. He proved it in (1), (2) and (3) that irony and humor coexist and may cause a positive effect, thus following scheme proposed theory of Alvarado (2009). In other words, their conversational strategies used to include or exclude someone from the conversational group. This means that the tradition of belief that negative irony was linked to humor is no longer valid. Finally, he sum up that humorous ironic statements with humorous effect arose in conversation from Peninsular Spanish. Irony and humor are in turn positively related to politeness. Irony and humor are mostly utilized solidarity, which is called as positive effect. Humor with a positive effect is one of the values which the ironic utterance can convey in conversation after breaking listener’s expectations.
6
qualitative research. The data were collected manually from the VCD of Rio animated film. The VCD became the data source because the subtitling in the VCD version is more complete and clear than the DVD version. The data were words, phrases or sentences which contain verbal humor and its Indonesian subtitles. Firstly, she defined and categorized the material into group depend on what kind of verbal humor that found. For example, wordplay elements, such as homophony or homonyms. Secondly, these categories analyzed further and discussed based on their subtitling strategies. Thirdly, three respondents who have certain qualifications to assess the acceptability of the translation were involved in this research. In analyzing the data, she used the table, and questionnaire that is given to three respondents. Table is used to make the analysis easier while questionnaire is used to gain information from the respondents about translation quality assessment in term of acceptability. Started from Verbal Humor Theory proposed by Spanakaki (2007) she found wordplay, allusion and verbal irony. Then, based on subtitling strategies theory proposed by Gottlieb (2001) she found eight subtitling strategies the translator applied in translating the verbal humor dialogues. They are expansion, paraphrase, transfer, imitation, transcription, condensation, and decimation.
7
stated that cartoon SpongeBob SquarePants originally created for kids ages 6-11, this cartoon became a pop culture phenomenon. According to Nickelodeon, the show has been the number one animated kid’s show on television for over 10 years, but
millions of viewers in every age category tune in to watch the cartoon every month (Source: kidstvmovies.about.com).
Meanwhile, this study is using Discourse Analysis approach. The researcher analyzes text and context of humor conversation in order to find the kinds of verbal humor within the film and its violation maxim principle in order to achieve the goal of humor conversation. This study is extremely different with the previous studies. This study describes the kinds of verbal humor in The SpongeBob Movie: Sponge Out of Water” animated film and the violation maxim principle of humor conversation.
1.2 Research Problems
Based on the background of the study presented above, the researcher formulates the research problems as follows:
1. What kinds of verbal humor are in The SpongeBob Movie: Sponge Out of Water?
2. What are the violation maxim of humor conversation in The SpongeBob Movie: Sponge Out of Water?
1.3 Research Objectives
8
1. To describe the kinds of verbal humors are in The SpongeBob Movie: Sponge Out of Water.
2. To describe violation maxim principles of humor conversation are in The SpongeBob Movie: Sponge Out of Water.
1.4 Significance of the Study
This research is expected to be useful both theoritically and practically.
1. Theoritically, this research can enrich knowledge of linguistic fields especially in discourse analysis fields. It can also become source of information and comprehensive understanding about verbal humor and violation maxim principle of humor conversation in The SpongeBob Movie: Sponge Out of Water, animated film. 2. Practically, this research can make people understand about the humor conversation in virtual world. By having practice through this study they can understand that humor conversation can be formed by the violation maxim. It might also help next researcher to understand deeper in studying verbal humor in other source of data.
1.5 Scope and Limitation
9
1.6 Definition of Key Terms
Verbal humor is an aspect of language in which exploited in order to achieve a humorous effect (Kim E. J: 2009).
Violation Maxim is the condition where the speaker does not purposefully fulfill certain maxim (Anneke and Helen : 2008).
Animated film is a film made of individual drawing, paintings, or illustrations that photograped in frame by frame (stop-frame cinematography) which often directed to children. (filmsite.org)
10 CHAPTER II THEORETICAL BASES
This chapter presents some theories related with the topic of the resesrch, which is the verbal humor. In this part, the researcher divides the discussion of theories into three sub chapters. The first is tells about Discourse Analysis since it has become the primary theory that covers all theory used in this reseach. The second is about the General Theory of Verbal Humor proposed by Attardo Salvatore (1991). The third is about theory of maxim principle proposed by Paul Grice (1985). All theories about are used to assist the researcher in answering the statement of problem in this study.
2.1 Discourse Analysis
Brown and Yule (1983) said that Discourse Analysis is a primarily linguistic approach to the analysis of discourse. The object of Discourse Analysis is a discourse. The representation of discourse is a text. Discourse Analysis is analyzing written or spoken text in writing, conversation which contains sequence of sentences, propositions, speech, or turn-taking (Brown and Yule, 1983:5). The distinction of text had been studied by some researcher but this no means that the distinction between spoken discourse and written text universally accepted distinction. German writers use ‘text’ to refer to speech as
11
and they articulate different discourses together in various ways. Discourses can be differentiated in terms of semantic relations (synonymy, hyponymy, antonymy) between words – how they classify parts of the world – as well collocations, assumptions, and various grammatical features (Fairclough, 2004:133). The analysis of discourse is the analysis of language in use. It means that any kind of language we used in this world is included as a discourse. There is no clear distinction between spoken or written text because it is linked each other. “The analysis of discourse is, necessarily, the analysis of language in use.” (Brown and Yule, 1983:1).
James Paul Gee (2011) said that “Any speech data can be transcribed in more or less detailed ways”. It means that a discourse analysis is made from the details of speech (gaze, gesture and action) or writing that are arguably deemed relevant in the context and that are relevant to the arguments the analysis is attempting to make. (Gee, 2011:117). Moreover, the dialogue and conversation that occurred in the movie can be included as a text. Then, the script is also included as discourse because it made from detail of speech but in form of writing.
Beyond the discourse itself, the discourse analysis is also study about the context within the text. Context is something ‘beyond the sentence’. Since
12
In analyzing text and context in the animated film, The researcher focuses on humor conversation. In this case, General Theory of Verbal Humor (GTVH) is used for the analyzing humor. Then the researcher also analyzing maxim violation in humor conversation using Grice’s theory of maxim.
2.2 General Theory of Verbal Humor
The General Theory of Verbal Humor (GTVH) is revised version of The Script-based Semantic Theory of Humor (SSTH) which is done by Attardo and Raskin (1991). GTVH is a linguistic theory which includes in other areas of linguistics as well, including textual linguistic, the theory of narrativity and pragmatics inside. These broadenings are achieved by the introduction of six other Knowledge Resources (KR) that have to tap into when generating a joke. There are the script opposition (SO), logical mechanism (LM), The target (T), narrative strategy (NS), the language (LA) and the situation (SI) (Attardo: 2001:22).
In the General Theory of Verbal Humor, the script opposition (now called SO) is only one of six possible dimensions of a joke. The others are the target of the joke (TA), the logical mechanism by which the SO is resolved (LM), the situation in which the joke is set (SI), the language (LA), and the narrative strategy used to tell the joke (NS) (Raskin: 2008).
13
comedian can be analyzed. For instance, a wordplay which chosen to make audiences laugh on his performance.
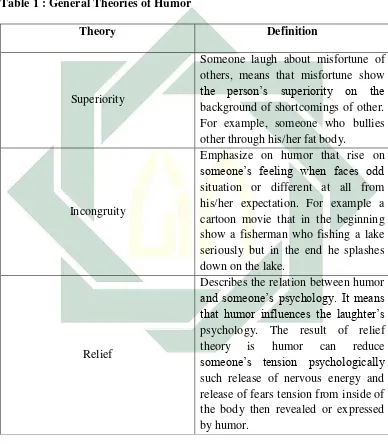
According to Salvatore Attardo (1991), there are three general theories of humor that can be found in contemporary academic literature; Superiority theory, Incongruity theory, and Relief theory. See the following table:
Table 1 : General Theories of Humor
Theory Definition that humor influences the laughter’s psychology. The result of relief theory is humor can reduce someone’s tension psychologically such release of nervous energy and release of fears tension from inside of the body then revealed or expressed by humor.
14
humor arises from perception an incongruity between a set of expectation and what is actually perceived. Linguistic field involved into this theory. The comedian selected words using in his joke telling. Attardo Salvatore (2008) stated that “The incongruity theories are essentialist (i.e., the attempt to pinpoint
what makes humor funny), linguistics has tended to side (largely unwittingly)with this kind of theory”(Raskin and Ruch, 2008:104).
Katrina E. Triezenber in Raskin’s book The Primer of Humor Research
(2008) stated that there are several literary terms that would seem to qualify a joke. Here are the following explanations of several common literary terms usually used in the discussion of humor:
2.2.1 Absurd
A side from the general meaning of illogical or impossible, absurd can specifically refer to the purposelessness of existence. This definition comes from the existentialist writings of Albert Camus (2008:531). For example, “two elephants were flying – one to the north, and the red one to the west.”
2.2.2 Ambiguity
Ambiguity is the statement of having more than one possible meaning (2008:531). For example, “a good life depends on a liver” – liver may be an organ or simply a living person. “She was on the phone” – she was talking
through the phone, or actually on top of the phone. 2 2.2.3 Antaclasis
15
repeatedly used (2008:531). For example in Shakespeare’s Literary, Othello, “put out the light, then put out the light”. The first meaning is that Othello would
extinguish the candle and in second reference its meaning is that he would end Desdemona’s life (literarydevices.net).
2.2.4 Antiphrasis
Antiphrasis is the use of a word as its own antonym. A kind of irony that is a figurative speech in which a phrase or word is employed in a way that is opposite to its literal meaning in order to create an ironic or comic effect (2008:531). For example, “yes, I killed him. I killed him for money-and a woman-and I didn’t get the money and I didn’t get the woman. Pretty, isn’t it?”(Double Indemnity by Billy Wilder and Raymond). The speaker made ironic
statement by using opposite sense of the word pretty. He has committed murder, yet he describes his act as pretty (literarydevices.net).
2.2.5 Enthymeme
16
2.2.6 Humorous triple
Humorous triple is a sequence of three statements, the last of which is in humorous opposition to the first two. Much of Woody Allen’s dialogue consists
of humorous triples (2008:532). For example, “there’s an old joke – um.. Two elderly women are at a Catskill mountain resort, and one of ’em says, “Boy, the food at this place is really terrible. ‘the one says, ‘Yeah, I know; and such small portions.’ Well, that’s essentially how I feel about life.” (Annie Hall: 1977). In
other word, the speaker means that you just cannot please some ruddy people (literarydevices.net).
2.2.7 Hyperbole
Hyperbole is common speech which used by comedians. That is a figure of speech which involves an exaggeration of ideas for the sake of emphasis. In short, hyperbole is dramatic overstatement (2008:532). For example, when you meet a friend after long time, you say, “ages have passed since I last saw you”. The word ages, exaggerates this statement to add emphasize to your wait. In real, you may not have met your friend for three or four hours a day.
2.2.8 Irony
17
Shakespeare’s Romeo and Juliet Act I Scene V, “go ask his name; if he be
married. My grave is like to be my wedding bed”. Juliet commands her nurse to find out who Romeo was. If he were married, then she is going to die on her wedding bed (literarydevices.net).
2.2.9 Malapropism
Malapropism is incorrect using of long word. It means the using of incorrect word in place of a similar sounding word that produces nonsensical and humorous expression. The word “malapropism” derived from “Mrs. Malaprop”, a character in Sheridan’s comedy “The Rivals”, who has habit of
replacing words with incorrect and absurd utterances producing a humorous effect (2008:532). For example, “his capacity for hard liquor is incredulous”. It is replacing the word incredible into incredulous.
2.2.10 Paraprosdokian
Paraprosdokian is a phrase or list with an amusingly out-of-place ending. It is type of wordplay which is final part of phrase or sentence is unexpected or surprised. (2008:533) For example, “Trin Tragula-for that was his name-was a dreamer, a thinker, a speculative philosopher or, as his wife would have it, an idiot..” (The Restaurant at the End of the Universe by Douglas Adams). The final part of phrase is a surprise to the readers and create comic effect. (literarydevices.net)
2.2.11 Pun
18
is also called as paronomasia that is intentionally or accidentally used in jokes and witty remarks (2008:533). For example, in Oscar Wilde’s Importance being Earnest Act III, “I always told you, Gwendolen, my name was Ernest, didn’t I? Well, it is Ernest after all. I mean it naturally is Ernest”. Here Jack discovers his father name which makes him truly earnest (literarydevices.net).
2.2.12 Repartee
Repartee is an expression which is rapid, witty dialogue, funny either explicitly through its content or implicitly because it contrasts so sharply with everyday speech. This implies on the power of answering quickly, pointedly, or wittily. (2008:533) For example, “if I were married to you, I’d put poison in your Coffe”. “If you were my wife, I’d drink it.”.
2.2.13 Sarcasm
Sarcasm is verbal expression of irony or satire, often with a particular vocal intonation. Sarcasm purposes to amuse and hurt someone or some section of society simultaneously. In sum, sarcasm often depends on the vocal tone (2008:533). For example, “good fences make good neighbors” (Mending walls by Robert Frost). This line point out in a sarcastic way to neighbors who have made a wall between them. However, the wall fall apart when winter, therefore the neighbors meet and mend the wall, hence they spend more time together in this way (literarydevices.net).
2.2.14 Spoonerism
19
word, spoonerism is an either intentional or unintentional transposition of the sound of two or more words (2008:534). For example, “go help me sod”. This line means to so “so help me God”.“mad bunny” means to “bad money”.
2.3 The Cooperative Principle
People have several ways in delivering their ideas when they do communication. As Garfinkle (1967) observed, “it is never possible to say what one means in ‘so many words’ ” (Coulthard, 1985:30). It means that speaker requires hearer to ‘work’ in order to derive the message from the words uttered.
Indirectly, speaker has implicated something else in doing conversation. The Speaker provided information from which hearer can deduce extra information.
Exploring the phenomenon of conversational implicature, Grice (1975) suggested that both speaker and hearer are interconnected to each other. There are turn-talking and also implied meaning of the message uttered. In this term, Grice named as co-operative principle “Conversationalists are oriented to and by an over-arching co-operative principle” (1985:31).
20
These maxims represent a descriptive statement of how conversational contribution. Conversational contributions are firstly, there will be occasions when speaker decides to violate a maxim quietly and unostentatiously, for instance, the speaker may lie, or does not give as much of the relevant information as he could, or he may offer utterances which are only later seen to be ambiguous. Secondly, and much more importantly, there will be occasions when speaker is seen to break a maxim either because he has been faced with a clash. This case spelled out by flouting maxim. For instance, the speaker deliberately fails to observe a maxim in order to create an implicature (1985:31).
Anneke and Helen (2008) in The Multiple Violations of Conversational in Lying Done by the Characters in Some Episodes of Desperate Housewives stated that violation is the condition where the speaker does not purposefully fulfill certain maxim. Usually the conversation between speaker and hearer can be unsuccessful if the speaker does violation maxim since they will misunderstand each other. Speaker who does violation maxim means does not allow the hearer to know the truth and only understand the surface meaning of speaker’s
utterances (Tupan and Natalia, 2008:63-64).
21
However, violation maxim is often occured in humor conversation. Indeed, the speakers violate maxim intentionally so that hearer laugh on their humor. Each humor conversation may contain the speaker’s purpose. Sometimes people
disobey some maxims in having conversation in order to achieve their purpose. Nanda (2014) in the Violating Maxims of Main Characters in the Hangover movie’s script stated that violation maxim of quantity is giving too much or too less information than is required. For example in The Hangover movie’s script:
PHIL : can’t you see the fun part in anything?
STU : Yeah, we’re stuck in traffic in a stolen police car…with a missing child in the back seat. Which part of this is fun?
In the example, Stu violated the maxim of quantity. He talked to Phil much than his need. Phil is only asking about did he see the fun part of their situation but Stu has answered by giving much information that is not gave exactly information of Phil’s need. It is showed that Stu added extra information in his
utterances and did not give the point. It could make Phil confused on Stu’s utterances (Nanda, 2014:162).
Violation maxim of quality is telling untrue information and hiding the truth. It happens because the speaker want to save their face embarrassed and make other people did not angry with him. An example is still taken from The Hangover movie’s script:
MELISSA : Is that a baby?
STU : Why would there be a baby? We’re at a winery. That’s a goat.
22
His utterance is proved that he is telling untrue information about the baby to Melissa (Nanda, 2014:162).
Violation maxim of relation is giving inappropriate information to the topic of conversation or change the topic because the speaker or hearer may hide and avoid talking about something. An example is still taken from The Hangover movie’s script:
STU : Oh, my God. Oh, my God. You just nailed the baby. ALAN : Are my glasses okay?
Alan has violated maxim of relation because he said irrelevant statement. He may be avoided responding Stu’s statement because he does not care of the
baby and prefer his attention of his glasses. Beside, this violation may create humor side among the conversation (Nanda, 2014:163).
Finally, violation maxim of manner is giving obscurity expression which is not easy to understand, prolixity, not in orderly or unclear information. It may happen because the speaker tried to trick the hearer(s) to keep secret or to create humor. An example is still taken from The Hangover movie’s script:
PHIL : Sir…. If I may, um… I’m assuming that squad car belongs to one of you.
POLICE OFFICER : yeah.
PHIL : Look, I’m not a cop. I’m no hero. I’m school teacher. But if one of my kids went missing on a field trip…that would look really bad on me. POLICE OFFICER : What are you getting at?
23
police officer in order to give him remission of their punishment because of stole in police car. Unfortunately the police officer did not understand and confuse on Phil’s utterance. So, he has to explain it clearly (Nanda, 2014:164). Here is the
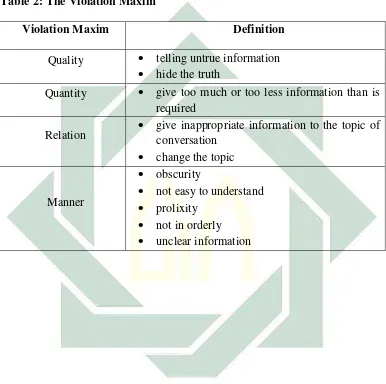
clear-cut understanding about violation maxim: Table 2: The Violation Maxim
Violation Maxim Definition
Quality telling untrue information hide the truth
Quantity give too much or too less information than is required
Relation give inappropriate information to the topic of conversation
change the topic
Manner
obscurity
not easy to understand prolixity
2
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHOD
In this chapter, the writer describes the research design, research
instrument, data and data sources, data collection and data analysis.
3.1 Research Design
This research is descriptive qualitative research. Qualitative research concerned with developing explanations of social phenomena. It helps to understand the social word in live and why things are the way they are (Hancock,
Ockleford and Windridge, 2009:7). Qualitative research aims to complete, detail description of what is observed which those purposes are contextualization, interpretation and understanding perspectives (MacDonald and Headlam, 2011:9).
Bailey (1982) stated that qualitative descriptive research discusses about general cases in social phenomena and it describes specifically why and how it is
(Mukhtar, 2013:11). The researcher agrees with Hancock, Ockleford and Windridge (2009) because this research is developing social phenomena about humor and its violation maxim. The researcher describes the kind of verbal
humors and violation maxim of humor conversation which is emerged in The SpongeBob Movie: Sponge Out of Water, animated film.
3.2 Research Instrument
The main instrument in social and cultural research is the researcher because all of researcher’s sense is used as an observation instrument (2013:109).
2
the findings. The second instrument included books, internet, data sheets, table, and laptop. Books and internet are functioned to collect some information of theories which used in this research; data sheets are employed to record the data
which will be transferred into analysis table to be analyzed further; laptop is considered as a very helpful instrument with the most of processes of this study is
finished.
3.3 Data and Data Sources
The data of research is things known or assumed (2013:99). The data of
this research are collected from the script of The SpongeBob Movie: Sponge Out of Water animated film which downloaded from internet in which had adjusted to
the movie manually. Data source are sources in which the researcher could get information or data in doing research (2013:107). The script of the animated film become the data source because it consists of humor conversation that includes
words, phrases, or sentences which contained kinds of verbal humors and violation maxim.
3.4 Data Collection
Collecting data is used to get information in order to achieve the objective of the research (Gulo, 2002:110). The researcher collects the data of the
research by following the several steps below:
1. The researcher watches and listens carefully the dialogue happen in the
2
2. The researcher reads the transcription of the animated film, The SpongeBob Movie: Sponge Out of Waterto find out humor conversation in which adjusted by action in the animated film.
3. The researcher collects humor conversation to reduce unimportant data from the script of the animated film.
3.5 Data Analysis
Miles and Huberman (1990) composed flow model analysis. There are four stages in this approach; collecting data; reduction; display data; and draw
conclusion (2013:135). W. Gulo (2002) stated that the data which has collected is raw. There are three steps in data analysis; editing, coding, and then input in
master sheet (2002:29). The researcher analyses the data by following the several steps below:
1. Collecting data
Collecting data means process in which the researcher uses instruments to get the data. The researcher collects words, phrases, or sentences of humor
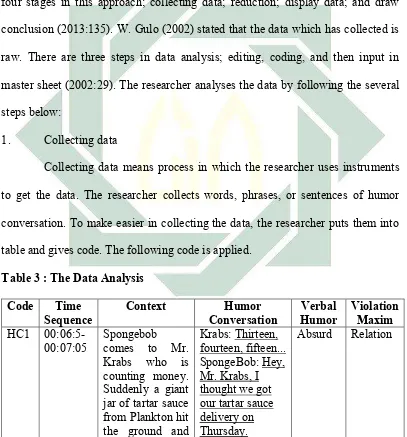
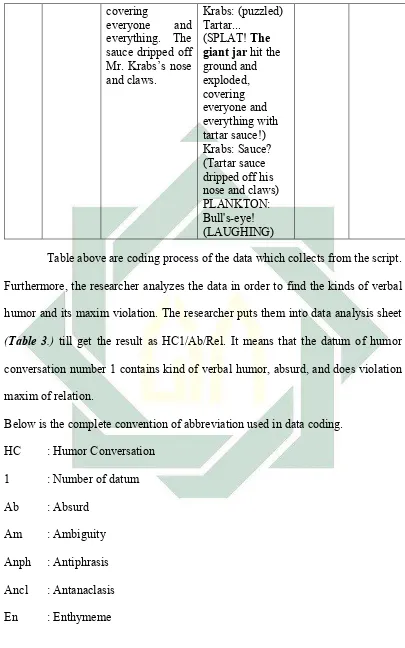
conversation. To make easier in collecting the data, the researcher puts them into table and gives code. The following code is applied.
Table 3 : The Data Analysis
Code Time
Sequence Context ConversationHumor HumorVerbal Violation Maxim
Table above are coding process of the data which collects from the script. Furthermore, the researcher analyzes the data in order to find the kinds of verbal
humor and its maxim violation. The researcher puts them into data analysis sheet (Table 3.) till get the result as HC1/Ab/Rel. It means that the datum of humor
conversation number 1 contains kind of verbal humor, absurd, and does violation maxim of relation.
Below is the complete convention of abbreviation used in data coding.
2
Htr : Humor Triple
Hyp : Hyperbole
Ir : Irony
Ma : Malapropism
Par : Paraprosdokian
Pu : Pun
Rep : Repartee
Sar : Sarcasm
Spo : Spoonerism
Qual : Maxim violation of quality
Quan : Maxim violation of quantity
Rel : Maxim violation of relation
Man : Maxim violation of Manner
2. Reduction
Reduction means selecting, focusing, and simplify the data. In this term,
the researcher collects the research finding from table 3 into table 4 and table 5 to
simplifying the display data.
3. Display data
Display data means building information systematically to drawing the
conclusion. The researcher displays data based on the research finding. Those are
kinds of verbal humor based on Attardo Salvatore (1991) and violation maxim
based on Paul Grice (1975) of humor conversation in The SpongeBob Movie:
2
on the finding so that the most kind of verbal humor and maxim violation in the
animated film is found. See the following table below:
Table 4 : The Kinds of Verbal Humor in The SpongeBob Movie: Sponge Out
of Water.
No Verbal Humor Frequency Percentage
1 2 3 ...
Total
Table 5 : The Violation Maxim in The SpongeBob Movie: Sponge Out of
Water.
No Violation Maxim Frequency Percentage
1 2 3 4
Total
4. Draw conclusion
Drawing conclusion is also analysis activity. It means the researcher
decides that the research is benefit or not. In this term, the researcher concludes
the finding based on the research problem head for answer it and giving
ϯϬ CHAPTER IV
FINDING AND DISCUSSION
In this chapter, the writer presents the analysis of the findings. By focusing on theory of verbal humor derived from Attardo Salvatore (1991), the writer able to answer the first statement of problem in this study and for answering the second problem about violation maxim, the writer focuses on the theory of Gricerian maxim (1975).
The writer divides into two parts. First, the writer presents the research finding from the analysis. In this part, the writer presented the data by serving the table of frequencies of the finding. Those are the frequencies of verbal humor and violation maxim in The SpongeBob Movie: Sponge Out of Water. Then, the writer presents the detail information or explanation of the research finding . Second, the writer provides the discussion which covers something beyond but it relates with this study.
4.1 Research Findings
The research finding here contains the result of analysis, which is in the form of numbers and percentage. There are tables and detail explanation of the findings table in this section. Besides, the deep explanation of the analysis result are provided in next part.
The tables below provide a description of the finding in percentages. It contains listing kinds of verbal humor and maxim violation that are emerged in
ϯϭ
absurd, ambiguity, irony, malapropism, paraprosdokian, hyperbole, sarcasm, repartee and pun.
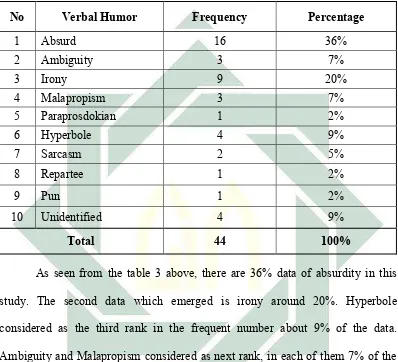
Table 4 : The frequencies of Verbal Humor in The SpongeBob Movie: Sponge Out of Water.
No Verbal Humor Frequency Percentage
1 Absurd 16 36%
2 Ambiguity 3 7%
3 Irony 9 20%
4 Malapropism 3 7%
5 Paraprosdokian 1 2%
6 Hyperbole 4 9%
7 Sarcasm 2 5%
8 Repartee 1 2%
9 Pun 1 2%
10 Unidentified 4 9%
Total 44 100%
ϯϮ
concluded that the most kind of verbal humor in this animated film is absurdity. Absurdity appears most in The SpongeBob Movie: Sponge Out of Waterto amuse the audiences.
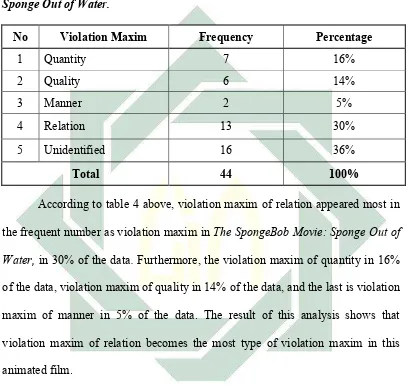
Table 5 : The frequencies of maxim violation in The SpongeBob Movie: Sponge Out of Water.
No Violation Maxim Frequency Percentage
1 Quantity 7 16%
2 Quality 6 14%
3 Manner 2 5%
4 Relation 13 30%
5 Unidentified 16 36%
Total 44 100%
According to table 4 above, violation maxim of relation appeared most in the frequent number as violation maxim in The SpongeBob Movie: Sponge Out of Water, in 30% of the data.Furthermore, the violation maxim of quantity in 16% of the data, violation maxim of quality in 14% of the data, and the last is violation maxim of manner in 5% of the data. The result of this analysis shows that violation maxim of relation becomes the most type of violation maxim in this animated film.
4.1.1. Kinds of Verbal Humor
ϯϯ
humor proposed by Attardo Salvatore (1991). These are absurd, ambiguity, irony, malapropism, paraprosdokian, hyperbole, sarcasm, repartee, and pun. Here are the deep explanations of the research finding. Detail information is presented to clarify the first objective of the research covering the kinds of verbal humor in this animated film.
4.1.1.1 Absurd
Telling or delivered something that impossible or less purpose of existence becomes one of speaker’s style to amuse hearer. This way becomes the most frequently appeared in this study. Anything illogical or has no true meaning which speaker delivered in some situations could amuse the hearer. This side is called as absurdity. The absurdity found in this animated film covered many things such absurdity of object, action, social condition, and belief. Below is the following examples of absurdity found in the verbal humor data.
HC1/Ab/Rel
Context : Spongebob came into Mr. Krabs who is counting money. Suddenly a giant jar of tartar sauce from Plankton hits the ground and covering everyone and everything. The sauce dripped off Mr. Krabs’s nose and claws.
Krabs: Thirteen, fourteen, fifteen...
SpongeBob: Hey, Mr. Krabs, I thought we got our tartar sauce delivery on Thursday.
Krabs: (puzzled) Tartar... (SPLAT! The giant jar hit the ground and exploded, covering everyone and everything with tartar sauce!)
Krabs: Sauce? (Tartar sauce dripped off his nose and claws) Plankton: Bull's-eye! (LAUGHING)
ϯϰ
big or giant size. Absurdity appeared when the giant jar of tartar sauce from
Plankton exploaded because it hits the ground and covering Mr. Krabs,
Spongebob and anything there. It is too impossible that there was a giant jar of
tartar sauce except a someone made it intentionally to break a world record.
HC3/Ab/Rel
Context : SpongeBob and Plankton shoting each other. Spongebob kept firing the
big gun. Plankton's plane shredded the potatoes into French fries, sending them
flying down toward Sandals. But just then, the potatoes knocked the wings off his
plane. Then, the plane plummeted to the ground, crash and changed into a tank.
Plankton loaded a pickle as ammunition but then the shot hit restaurant and
exploaded. The tank hit the ground.
Sandals: Hey, it's raining fries! ...
Sandals: Hey, it's raining pickles! (LAUGHS) Now it's raining... Sandals: (The tank lands on Sandals) Tanks.
Plankton: You're welcome! (The tank drives away)
Other example of absurdity appeared in datum of humor conversation
number 3, there was an absurdity of social condition. The absurdity of social
condition is describing any kinds of situation at the environment. Sandal feels
happy because of raining fries and pickles. It is too impossible there was raining
fries and pickles. Actually it was the effect of Spongebob and Plankton’s war.
ϯϱ
HC21/Ab/-Context : Sandy grabbed some papers and tore them off the curved glass dome.
Through the dome, SpongeBob and Plankton could see a big sheet of paper with
THE END on it.
Sandy: When this came down from above, I knew it could only mean one thing. (SpongeBob looked puzzled)
SpongeBob: And that would be? (Sandy whipped around and held her hands wide apart)
Sandy: It means it's the end! The sandwich gods are angry with us! (Now SpongeBob and Plankton were really confused)
BOTH: Sandwich gods?
Other example of absurdity appeared in datum of humor conversation. The
absurdity of belief appeared when Sandy told them, Spongebob and Plankton
whom would ask to join on their team, about the sender of a big sheet of paper,
that is sandwich god. This thing shows that script writer want to create the
religious character in this animated film. Although there was no mention what
belief is, but by this could be drawn a message about believe in God. It was too
impossible that there was a sandwich god in this world. As we know, god is saint
and he was taking care of his creatures in this world. So, how come there was a
god which is only take care of sandwich.
HC30/Ab/Rel
Context : Spongebob and Plankton got in the Chum Bucket restaurant. They
would like to take the key from the guard (Patrick).
SpongeBob: We're in! (Then he swung the door closed. SLAM!)
ϯϲ
Plankton: Let's take the key from around his neck. We're gonna have to be very quiet. Let's walk on the tips of our toes. (Raised himself up on the tips of his toes— which SpongeBob had never before—and skittered across the floor. There was a high, tinkling sound)
(Patrick stirred in his sleep. Plankton froze, but the high tinkling sound continued. He looked back and sawSpongeBob playing a tiny piano)
Plankton: Will you stop playing that tiny piano? (WHISPERING) You're gonna get us caught.
SpongeBob: (SpongeBob sheepishly put the tiny piano away) Sorry.
The example of absudity of action appeared in datum of humor
conversation number 30. The absurdity of action is doing something that difficult
to accept logically. The absurdity appeared when Spongebob played a tiny piano
in urgency of taking a key from the guard (Patrick). Plankton asked Spongebob to
walk on the tips of toes so that the guard does not awake. Suddenly heared
Spongebob played a tiny piano which is unknown where come from. Plankton
stop that activity and remind him that they will be caught by the guard if he does
not stop.
4.1.1.2. Ambiguity
Anything amusing or funny could put in words, or simply playful in
using language. One of them is using statement which have more than one
possible meaning. This is called as ambiguity. Below is the following examples of
ambiguity found in the verbal humor data.
HC6/Am/-Context : The robot's big mechanical hand reached toward Mr. Krabs, who
cowered and groaned, until suddenly the robot sputtered and froze. Inside the
robot's head, Plankton stared at a gauge. The needle pointed to E.
ϯϳ
Krabs: (SCREAMS) Plankton: ...to go.
Plankton: Oh, barnacles. I'm out of gas?
The example of ambiguity appeared in datum of humor conversation
number 6. Plankton is said ambiguous. His statement is ambiguous because it
carries double meaning. First that the robot is out of gas or the second is that his
body is out of gas. In this case, Plankton controled a giant robot. When the robot
suddenly stopped, Plankton saw at a gauge that the needle pointed to E.
HC32/Am/-Context : Hardly they got the key from the Guard, Patrick, then SpongeBob and
Plankton sneaked away from the Chum Bucket carrying Karen's head.
SpongeBob: I've never carried a head before. PLANKTON: You'll get used to it.
SpongeBob: It's still warm. (GASPS)
Other example of ambiguity is in datum of humor conversation number
32. The ambiguity appeared when Spongebob carried the monitor from Plankton’s
computer wife. They took the computer to build a time machine. Spongebob
called it as a head. It was ambiguity because because it carries double meaning.
First, the audiences think about Spongebob who carried a real head or not. He also
added some statement which is ringing true that the head is still warm. Whereas
he carried a monitor from Plankton’s computer wife.
4.1.1.3. Irony
Using a language that the intended meaning is different from the
ϯϴ
be defined specifically as using a word or sentence to satire someone. Below is the following examples of irony found in the verbal humor data.
HC22/Ir/-Context : Sandy was muttering. They look each other. Plankton feels bad on this situation because he thought that Sandy is appropriate person to join on his
teamwork.
PLANKTON: You got any other friends who aren't dim bulbs or nut jobs? SpongeBob: Well, I have one friend who's loyal to the very end.
The example of irony appeared in datum of humor conversation number 22. Plankton is doing irony toward Spongebob. It shown at his question about his
friend who is not ”dim bulbs or nut jobs”. This question is rerefs to Sandy Cheeks, a female squirrel whom behaved as a crazy squirrel. Actually she is really
smart but after a big sheet of paper down on his home, she is trying to solve the significance of that and also the Bikini Bottom disorder.
HC35/Ir/Rel
Context : once again, SpongeBob and Plankton hurtled through time and space. When they opened the photo booth curtain, they peeked out and saw nothing.
Everywhere they looked, they saw gray nothingness. Finally, they approached the figure.
SpongeBob: Excuse me, sir? Can you tell us when we are? Bubbles: Who dares disturb The One Who Watches?
SPONGEBOB: The One Who Watches? Your name is The One Who Watches? Bubbles: No, my true name is Bubbles.
ϯϵ
Other example of irony appeared in datum of humor conversation number 35. An irony is doing by Plankton. After hurtled through the time and space, they found a figure who watches the space. He satired that figure’s name. There is no
reason why Plankton satired the figure’s name. It could be the effect of Bubble’s welcome a while ago. Bubble feels like disturbed by those two unknown people.
He have to watch outer space so that there will be no collision. 4.1.1.4. Malapropism
Incorrect using of long word means to amuse the hearer found in this
study. The speaker used incorrect word in place of similar sounding word. This is called as malapropism. Below is the following examples of malapropism found in
the verbal humor data. HC17/Ma/Rel
Context : Plankton looked as though he had absolutely no idea what SpongeBob
was talking about.
Plankton: Well, what do we do now?
SpongeBob: Now we work together. You know, teamwork. Plankton: What's, uh, 'tee-am work"?
SpongeBob: (SpongeBob sighed) Say "team," like a sports... Plankton: Team.
SpongeBob: Team. Now say "work." Plankton: Work.
SpongeBob: Put them together. What do you got? Plankton: Time bomb work.
ϰϬ
The example of malapropism is in the example datum of humor conversation number 17. Plankton is using incorrect long word in place of a similar sounding word. He seems like difficult to pronunce teamworkand changed
into other incorrect word such Tee-am work, Tie-'em work, Tie 'em up!, but finally he can pronunced it by Time bomb work. This was humorous expression.
HC44/Ma/-Context : All is back as usual. Spongebob give the first Krabby Patty with extra mayo to Gary, his snail pet. In fact, Gary was Plankton. Plankton is detected by
Spongebob in his impersonating Gary because he really know that his snail pet does not like mayonaise.
Spongebob: Plankton! Up to your old tricks again already, eh? Plankton: Hey, I'm just putting things back back the way they were. Spongebob: What do you have to say about this, Gary? (Gary ROARS) Plankton: Oh, shrimp. (PLANKTON SCREAMING) ( Gary ROARS) Spongebob: See you later, tee-am-mate!
Other example of malapropism appeared in datum of humor conversation number 44. Spongebob shouted incorrect word in place of similar sound that
result in humorous expression toward Plankton. He shouted tee-am-mate which means teammate. This condition influenced by Plankton who used incorrect word of teamwork at first. So, this action creates humorous expression and little bit
satired Plankton because his difficulty of saying teamwork. 4.1.1.5. Paraprosdokian
ϰϭ
sentence is unexpected or surprised. Below is the example of paraprodoskian found in the verbal humor data.
HC20/Par/Rel
Context : Patrick decided to be a teamwork with Spongebob and Plankton. Suddenly he noticed his friends that he found them, Spongebob and Plankton
whom is wanted by Bikini Bottom’s people.
Patrick: I've got SpongeBob! He's over here! (started making alarm sounds) (IMITATES ALARM)
Krabs: Let's go get him!
Plankton: (Plankton started to run) Come on, SpongeBob, let's get out of here! SpongeBob: Patrick!
SpongeBob: Patrick, why are you doing this? Patrick: Because I need... Krabby... Patties! Patrick: Hurry up! I'm hungry! Over here!
Patrick: Guys, am I still on the team? Hey, what are you looking at?
In the example datum of humor conversation number 20, Patrick is doing paraprodoskian. He used wordplay which is the final part (ending) is unexpected
or surprised. It is certainly amusing the audiences. Patrick who decided to be a teamwork is betrayed them with telling his friends about Spongebob and
Plankton’s existences. In the end, he is asking innocently to his friends when the angry mob is running to catch Spongebob and Plankton.
4.1.1.6. Hyperbole
Hyperbole is using a language which involves an exaggeration of ideas for the sake of emphasis. In short, hyperbole is dramatic over statement.
ϰϮ
HC41/Ab-Hyp/-Context : Spongebob and his friends are in the food corner. They look at all of the
various snack as a giant food because they were smaller than the snack.
Patrick: SpongeBob, you will not believe the size of the ice creams here. I wonder what other giant snacks they have.(GASPS) Cotton candy?
(BOTH GASPING) (CHUCKLES) Spongebob: Wow.
Sandy: If you ate all that, you'd have enough energy to run around the whole world!
BOTH: Whoo-hoo!
Hyperbole appeared in datum of humor conversation number 41. Sandy is
over on something usual. The size of snacks were bigger than their selves. Sandy
said that Spongebob and Patrick would have good enough energy to run arround
the world after eat all the giant snack. It is too over that only eat snacks, their
energy would be boost and it could make them run around the world. In fact, they
just be happy and loud of laugh after eat it. They do not run around the world but
the background changed continuely by their friends.
HC43/Hyp/-Context : Spongebob reminds Squidward to the first plan which is done. The have
to back to the Bikini Bottom to serve the customers.
Squidward: Are you out of your patty-flipping mind? I'll never leave this place! I mean, look at me. I'm a god!
Spongebob: No, Squidward, you're a cashier.
ϰϯ
Other example of hyperbole appeared in datum of humor conversation
number 43. Squidward who does not mind to go back home is told Spongebob
hyperbolic statement. He said that he is a god, then he have not to go back home
especially as a cashier of Krusty Krab. Squidward is over on something he never
get at past. In this time, Squidward is to be a superhero who join with Spongebob
as a teamwork to win back the secret formula. That is the reason why he over on
his condition nowadays. Spongebob who is mind to bring back the Bikini Bottom
originally after win the secret formula disagree with him and write on the big
paper sheet that Squidward is a chasier of Krusty Krab.
4.1.1.7. Sarcasm
Using verbal expression of irony or satire which is often with a
particular vocal intonation is sarcasm. This way of creating humor is found in this
study. Below is the following examples of sarcasm found in the verbal humor
data.
HC38/Sar/-Context : Spongebob and Plankton has blaming each other because Spongebob
toke wrong bottle of secret formula.
Plankton: This is all your fault! (GROWLING) (ALL GASPING) Spongebob: My fault?
Plankton: You're the one who stole the wrong secret formula. Spongebob: I didn't know there were two bottles.
Plankton: Of course you didn't! Because you got cotton candy for brains! ALL: Ooh!
Plankton: No, seriously, he really does.
The example of sarcasm is in datum of humor conversation number
ϰϰ
there was cotton candy in his brain. Plankton shout it angrily because in his
opinion, Spongebob gave Mr. Krab wrong bottle of secret formula.
HC39/Sar/-Context : Plankton Blames Spongebob because of toke wrong bottle. They have
debated each other and blaming each other. Plankton insults him angrily.
Spongebob: Well, we wouldn't even be in this mess in the first place, if you weren't so selfish and evil.
Plankton: I was selfish and evil, until you ruined everything with your "teamwork"!
Spongebob: Oh! You take that back!
Plankton: You are the worst teammate ever! Spongebob: No!
Other example of sarcasm in datum of humor conversation number 39.
The sarcasm here is still done by Plankton. He is blaming Spongebob of taking
wrong bottle of secret formula. He admits that he was selfish and evil till
Spongebob asked him to be a teamwork. He insulted Spongebob angrily that
Spongebob is the worst teammate ever. It is certainly hurt Spongebob.
4.1.1.8. Repartee
An expression which is rapid, witty dialogue, funny either
explicitly through its content or implicitly because it contrasts so sharply with
everyday speech called as repartee. This way implies on the power of answering
quickly, pointedly, or wittily. Below is the example of sarcasm found in the verbal
ϰϱ
HC31/Re/-Context : The guard (Patrick) woke up and saw Plankton and Spongebob. The two
buddies struggled. Patrick kept trying to put his lips on the whistle, but
SpongeBob kept stopping him.
SpongeBob: (tackling Patrick) No!
SpongeBob: Plankton, help! (GRUNTS) I'll rock him, you tell him a bedtime story. Plankton: (STAMMERS) Once upon a time there was a big fat pink idiot who went to sleep. The end!
Patrick: Nice try, but it's gonna take more than that to... (And he fell fast asleep)
The example of repartee is in datum of humor conversation number 31.
Plankton give a rapid funny expression implicitly through its content because the
story was about Patrick, the guard. The guard does not realize it. Plankton told a
bed story to the guard so that he sleep again after awaken by Spongebob. Then, he
sleep away after Plankton told a really short bed story about him. Finally they are
save and got the key.
4.1.1.9. Pun
A wordplay in which a humorous effect is produced by using a word
of multiple meaning or word of similar sound but different meaning is pun. Pun is
also called as paronomasia that is intentionally or accidentally used in jokes and
witty remarks. Below is the example of pun found in the verbal humor data.
HC42/Pu/-Context : Plankton becomes a superhero (Plank-Ton). When the Burger Beard
insulted him, he show his self as a big green Plankton.
4
Spongebob: Plankton?
Plankton: It's Plank-Ton!
Plankton: Come on down from there, little fella.You wouldn't want to get hurt. Huh?
The example of pun is in datum of humor conversation number 42.
Plankton played on word in which a humorous effect is produced by using a word
of simmilar sound but different meaning. In this case, he played on his name
Planktonto be Plank-Ton which means a person who has super power. Plankton
have changed into a big green Plankton by the big paper sheet he seized from
Burger Beard. He turned into super hero to help his friends saving the secret
formula bottle which stolen by Burger Beard.
4.1.2 Violation Maxim of Humor Conversation
The speaker who violated maxim intentionally or not could amuse the
hearer. This is another way to create humor conversation. There are violation
maxims found in The SpongeBob Movie: Sponge Out of Water, animated film.
The data of violation maxim is divided into 4 categories. These categories are
based on theory of maxim proposed by Paul Grice (1975). These are violation
maxim of quantity, violation maxim of quality, violation maxim of relation and
violation maxim of manner. Here are the deep explanations of the research
finding. Detail information is presented to clarify the second objective of the
research covering violation maxim of humor conversation in The SpongeBob
4
4.1.2.1 Violation Maxim of Quality
The condition when the speaker is telling untrue information or hiding the
truth intentionally or not means the speaker violated maxim of quality. Below is
the example of violation maxim of quality found in the violation maxim data.
HC27/Ab/Qual
Context : Plankton popped out of SpongeBob's ear soon and landed next to their
cold campfire. His grunts and groans awakened SpongeBob.
SpongeBob: Uh, Plankton? Oh, Plankton! I just had the craziest dream! And you were in it!
Plankton: I'm sure it was nothing. Plankton: Now go back to sleep. SpongeBob: Were you in my brain? Plankton: What? No! That's crazy talk!
SpongeBob: Then why is there cotton candy on your antenna?
Plankton: Because, uh, because, uh... Okay, fine, I was in your brain.
In datum of humor conversation number 27, Plankton is doing violation
maxim of quality. He was telling untrue information. He told that he was not in
the Spongebob’s brain which is actually he was. Plankton admits that he was in
Spongebob’s brain after Spongebob asked about cotton candy on his antenna. He
was recessive, so that is why he was telling untrue information to Spongebob.
4.1.2.2. Violation Maxim of Quantity
The condition when the speaker is giving too much or too less information
than is required means that the speaker violated maxim of quantity. Below is the
4
HC11/Ab/Quan
Context : SpongeBob opens up the patty vault. He screams then Mr. Krab comes
the he looked at the freezer. The patties were out.
SpongeBob: (SCREAMS LIKE A GIRL)
Krabs: SpongeBob! What's wrong, boy?
Krabs: (SCREAMS LIKE A GIRL)
Krabs: We're out of Krabby Patties?
SpongeBob: How can we make more Krabby Patties without the secret formula? Krabs: You've got to have that formuler memorized by now!
SpongeBob: But as you are aware, sir, the employee handbook clearly states, and I quote, (reading) "No employee may, in part or in whole, commit the Krabby Patty secret formula to any recorded written or visual form, including memories, dreams, and/or needlepoint."
Krabs: (WAILING) Curse you, fine print!
The example of violation maxim of quantity is in datum of humor
conversation number 11. Spongebob gave more information than Mr. Krabs
required. Mr. Krabs just warn him to memorized how the way making a patty.
Spongebob replied of it by giving the rule of memorizing secret formula. It could
be a reminder for MR. Krabs but what Spongebob did is violation maxim of
quantity.
4.1.2.3 Violation Maxim of Relation
The condition when the speaker is giving inappropriate information or
even changed the topic of conversatiom means that the speaker violated maxim of
relation. Below is the example of violation maxim of relation found in the
violation maxim data.
HC9/-/Rel
Context : Krabs opens the door and come in the room. He sees SpongeBob and
4
tugged. They strained. They yanked with all their might. Suddenly, the bottle
vanished into thin air! SpongeBob's mouth hung open.
Krabs: Plankton!
SpongeBob: What? Where'd it go?
PLANKTON: Wait a minute. Molecular deconstruction? I proved that to be a scientific impossibility seven times!
SPONGEBOB: Wait a minute. I think I forget to empty Gary's litter box today.
The example of violation maxim of relation is in the datum of humor
conversation number 9. Spongebob did violation maxim of relation in this humor
conversation. He talked to himself with different topic of discussion. It means that
Spongebob changed the topic of conversation. Plankton was thinking about why
the formula bottle suddenly vanished. Then Spongebob was thinking different
topic about he forget to clean up the Gary’s litter box today. This situation might
amuse the audiences.
4.1.2.3. Violation Maxim of Manner
The condition when the speaker is giving unclear information or
disorderly, obscurity, not easy to understand, or prolixity, means that the speaker
violated maxim of manner. Below is the example of violation maxim of quantity
found in the violation maxim data.
HC13/-/Man
Context : Plankton was telling Karen what had happened. Karen wants to notice
him that there is an angry mob inside of Chum Bucket.
PLANKTON: I had it right in my greedy little mitts, and then... Poof! And now it's