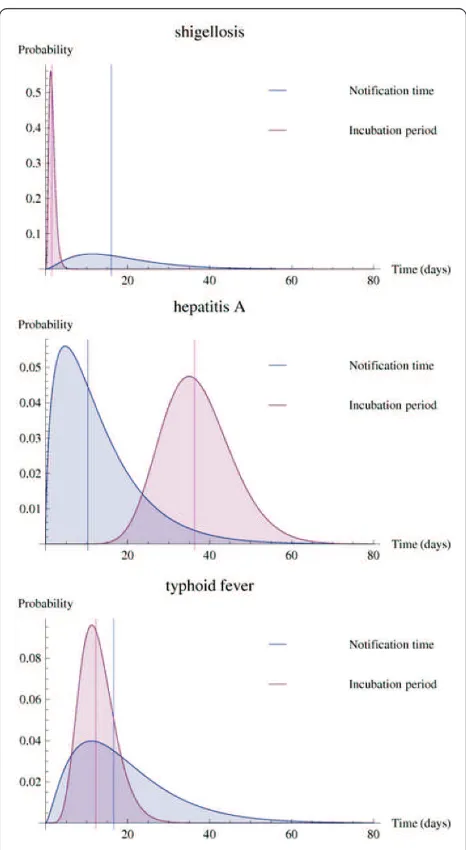
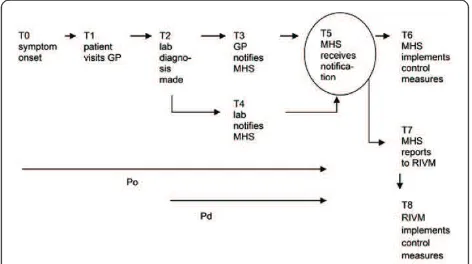
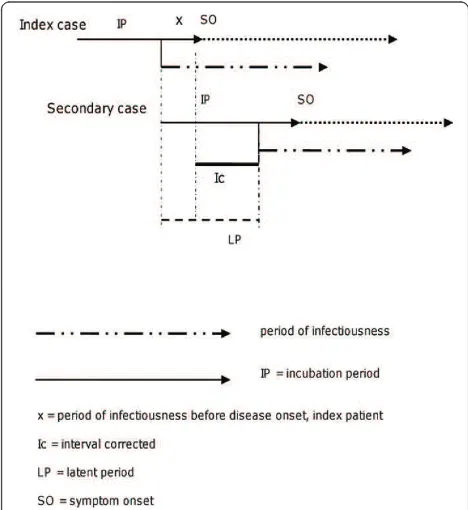
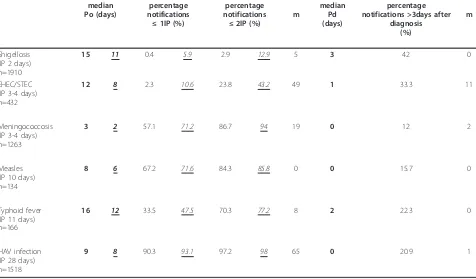
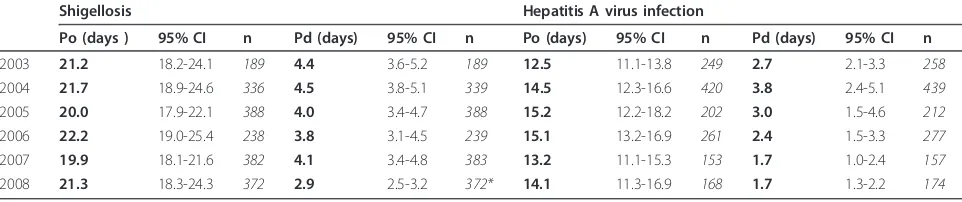
Analysis of timeliness of infectious disease reporting in the Netherlands
Teks penuh
Gambar
Dokumen terkait
ability of a cesarean section. It appears that both in Bandung and in Leiden the risk for a cesareau delivery is higher.. for women over 30 years... Crude and adjusted
By conducting character education for elementary school students and helping them to improve their morals, the moral crisis that is currently being faced can be corrected little by
A nationwide prospective multicenter Web-based surveil- lance system for nosocomial infections, the Korean Noso- comial Infections Surveillance System KONIS, was devel- oped in Korea
TABLE 5.- The effect of the route of inoculation on the multiplication of virus and the development of lesions in the CAM o/7-day embryonated eggs incubated at 35°C for 7 days
Distribution of Fallen Tree Potential Fallen Tree Potential Frequency Percentage % Low 1 3.3 Safe 29 96.7 Total 30 100 Based on Table 11, it is known that as many as 1 respondent
Travelling duration and frequency, 2014: a frequency of overseas travel all countries and Samoa: number of trips per year for adults, and number of trips over lifetime for children;
This research built a statistically realistic synthetic population with high-resolution household locations and demographic evolution over an extended period for agent-based mod- elling
Table 2: Summary of extra protection procedures in dental clinic 1 – Wash hands before and after dental treatment for both dentist and patient 2 – Cleaning and disinfection of all the