The New Zealand livestock farming system is one of the unique farming systems in the world. Some of the factors likely to be associated with pregnancy in replacement heifers are investigated in this study. The latter represented the herd's average body weight at the beginning of the grazing season.
The body weight of the heifer at the beginning of the rearing period was used to calculate the mean starting weight of the herd. Bivariate logistic regression analyzes of the relationship between pregnancy probability at herd level and the variables ADG, initial weight, length of rearing period, rearing season, breed of heifer and region of origin (n=21061). All variables, with the exception of grazing duration, were eligible for inclusion in the multivariable logistic regression model.
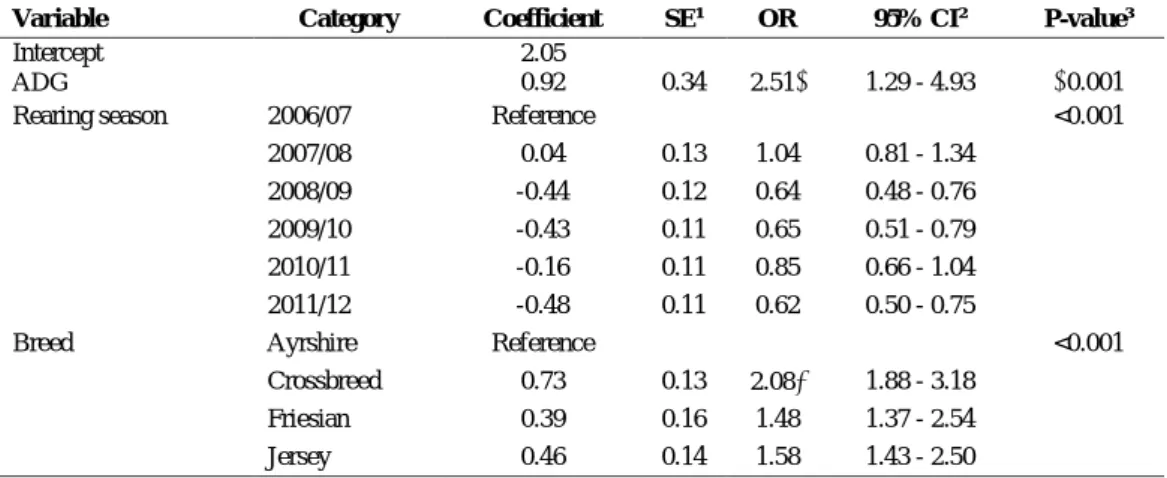
Multivariable logistic regression model of the association between the odds of pregnancy success (versus pregnancy failure) at the herd level and the explanatory variables ADG, breeding season and breed of heifers (n=21061). ⁵ The odds of pregnancy in the herd increased by a factor of 2.52 for each kilogram increase in herd ADG. In the multivariable model, the odds of pregnancy success at the herd level (versus the odds of pregnancy failure) were significantly associated with herd ADG, breed of heifer in the herd and grazing season.
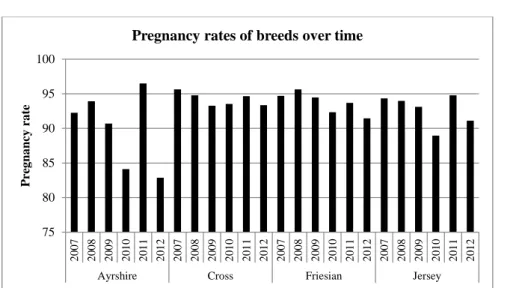
In terms of heifer breed, this study highlights the superiority of the Holstein-Jersey cross associated with the highest conception rate.
CHAPTER 3
Factors associated with growth rate in New Zealand replacement dairy heifers
In the United States, the practice of subcontracting the rearing of replacement heifers is also widespread in many parts of the country (Wolf 2003). Data included breeding period, duration of grazing, breed of heifer, average daily gain (ADG) of the heifer, entry body weight of the heifer, and region of origin of the heifers. The entry body weight represented the weight of the heifer at the beginning of the grazing season.
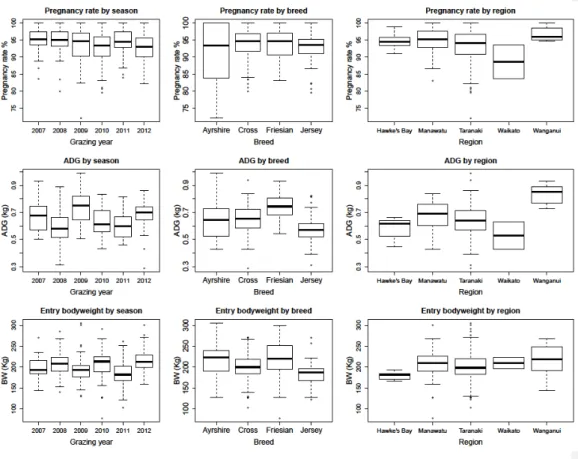
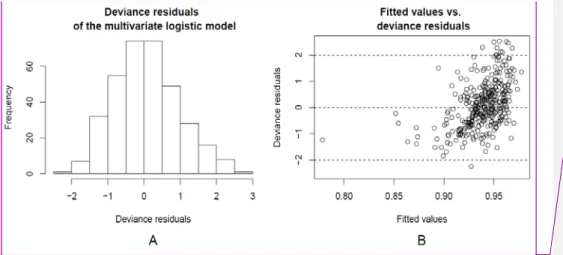
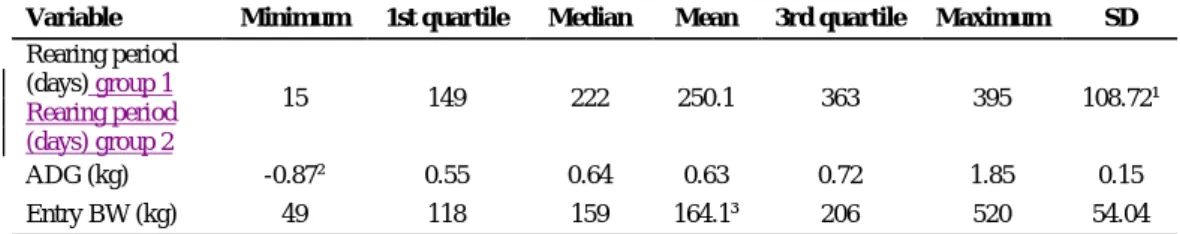
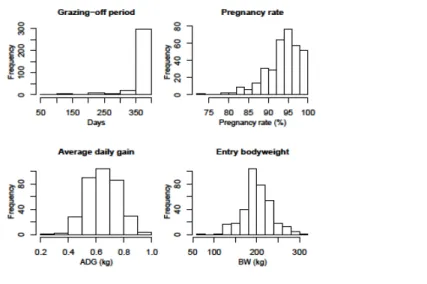
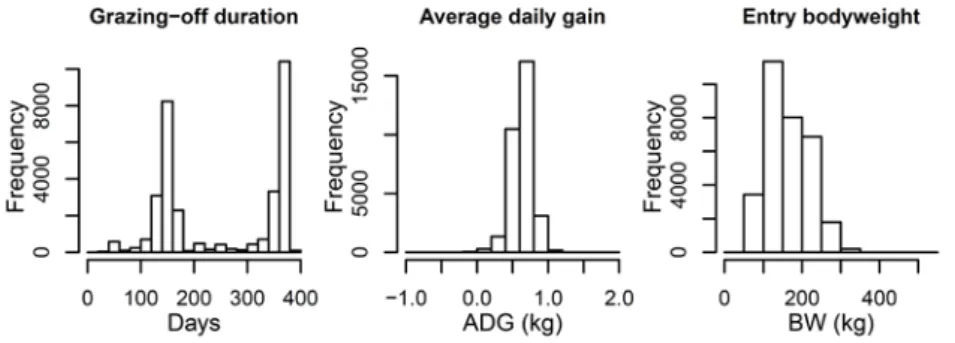
The histograms for the continuous variables of ADG, the initial body weight and the duration of the rearing period are shown in Figure 3.1. Box plots of the continuous variables of mean daily gain, entry body weight and rearing duration stratified by the categorical variables of breed, grazing season and region of origin (n=31661). Number of heifers, ADG, average entry body weight and average breeding duration stratified by the levels of the categorical variables.
⁷p-value of the anova test of the difference of the average rearing duration between the regions of origin. ⁹ Average length of the rearing period of the heifers from the Waikato region. Bivariable linear regression analyzes of the relationship between average daily gain (gram) and the variables initial weight, length of rearing period, breed of heifer, area of origin and grazing season (n=31661).
⁴ The ADG of replacement heifers bred in the 2011/12 season was approximately 264 grams higher than in the 2012/13 season, holding other variables constant. ⁵ The ADG of heifers originating from the Taranaki region was approximately 97 grams lower than that from the Wanganui region, holding other variables constant. Jersey heifers were associated with an ADG that was significantly lower than the ADG of each of the other Holstein, Holstein-Jersey cross and Ayrshire breeds (p<0.001).
The 2012/13 grazing season was associated with an ADG that was significantly less than the ADG obtained in each of the other grazing seasons (p<0.001). The Wanganui region was associated with heifers having a significantly greater ADG than the average daily gain achieved in each of the other regions (p<0.001). Average daily gain during the first two months of life of dairy heifers was positively associated with the ability of these heifers to survive into the second lactation (Bach 2011).
This was attributed to the fact that the majority of heifers originating from Wanganui Holstein were Friesian. Such information might have been useful in explaining some of the variation in growth rates of replacement heifers between rearing seasons.
General discussion
Some grazing seasons were associated with low pregnancy rates even though they were associated with high growth rates. Similarly, available records could not explain differences between regions of origin. Further investigation was recommended to provide additional information that could explain the variability between grazing seasons and regions of origin.
Other factors related to pregnancy and growth rate of replacement heifers can be determined by such an investigation.
Bibliography
Association between growth rate, age at first calving and subsequent fertility, milk production and survival in Holstein-Friesian heifers. Influence of age at calving on lactation, reproduction, health and income in first class Holsteins on commercial farms. Effects of calving age, breed fraction and calving month on calving interval and survival at parities in spring calving Irish dairy cows.
Trends in calf age and calving intervals for dairy cattle breeds in the United States. Relationships between age at first calving and first lactation milk yield, and lifetime productivity and longevity in dairy cows. Jersey x Holstein crosses compared to purebred Holsteins for body weight, body condition score, dry matter intake and feed efficiency during the first one hundred and fifty days of first lactation.
Jersey x Holstein cross compared to purebred Holstein for production, fertility and body and udder measurements during first lactation. An analysis of age and body weight at first calving for Holsteins in the United States. Effect of pre- and post-pubertal nutrition level and body weight at first calving on growth, milk production and fertility in grazing dairy cows.
Changes in conception rate, calf performance and calf health and survival using crossbred Jersey x Holstein sires as mates for Holstein dams. Effect of age at first calving on production traits and on difference between milk yield yields and rearing costs in Italian Holsteins. Comparative performance and economic assessment of Holstein-Friesian, Jersey and JerseyxHolstein-Friesian cows under seasonal pasture-based management.
Effects of winter feeding during the growing period on performance and longevity of dairy cattle. Effects of three prepubescent body growth rates on performance of Holstein heifers during first lactation. Performance comparison of Holstein-Friesian and Jersey x Holstein-Friesian crossbred dairy cows within three contrasting pasture-based dairy production systems.