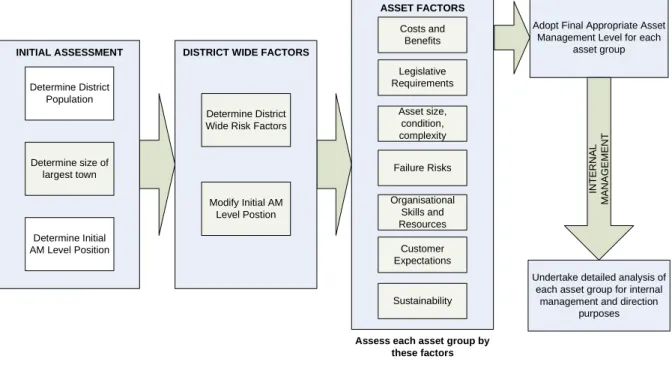
Authorities managing assets on behalf of their communities must define the appropriate level of asset management for the assets (e.g. This methodology should be logical and robust and can be used by the Council to adopt a position or policy on the appropriate level of asset management sophistication for each asset group. The asset management policy requirement is described in IIMM, Section 1.2, as shown in Figure 1.2.1 from IIMM below.
The asset management policy statement template includes the results of determining the appropriate level of AM. Authorities managing assets on behalf of their communities must define the appropriate level of asset management for the asset or activity being managed. The portion of this section dealing with the selection of an appropriate level of asset management is repeated below.
This report provides a template asset management policy statement for each asset group discussed in section 5.0.

Definition of “Core Plus” Asset Management Practice
The answer is that it could be any of these, and there may not be an appropriate individual answer due to differences in any organization. The Core Plus wealth management practice is above the core and less fully consistent with a comprehensive practice. Therefore, each asset owner must consider the appropriate level of AM based on the activity, taking into account national, regional and local factors of asset management practices for that asset.
The recommended method for assessing this is to use the detailed asset management practice assessment tables in Section 5.0 of this report to assess appropriate levels of practice for each activity or asset group. For the asset owner with the general practice set to 'Core Plus', there may still be variations in practice by asset or activity group. It is possible for some organizations that their asset management practice requires an almost all-encompassing practice for some activities (e.g. land transportation), while for other activities their practice is closer to core practice (e.g. rivers).
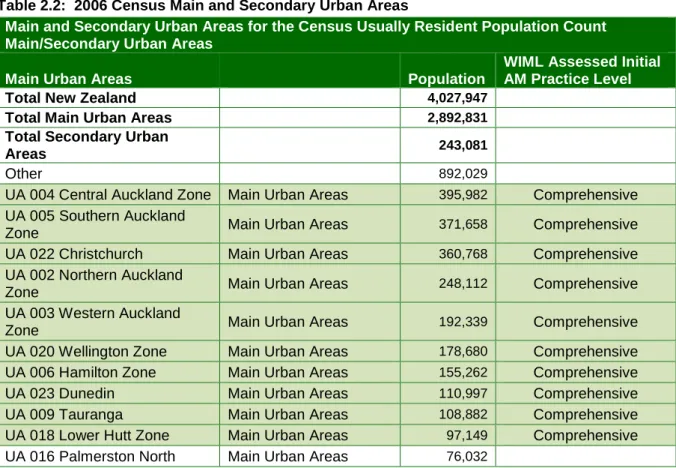
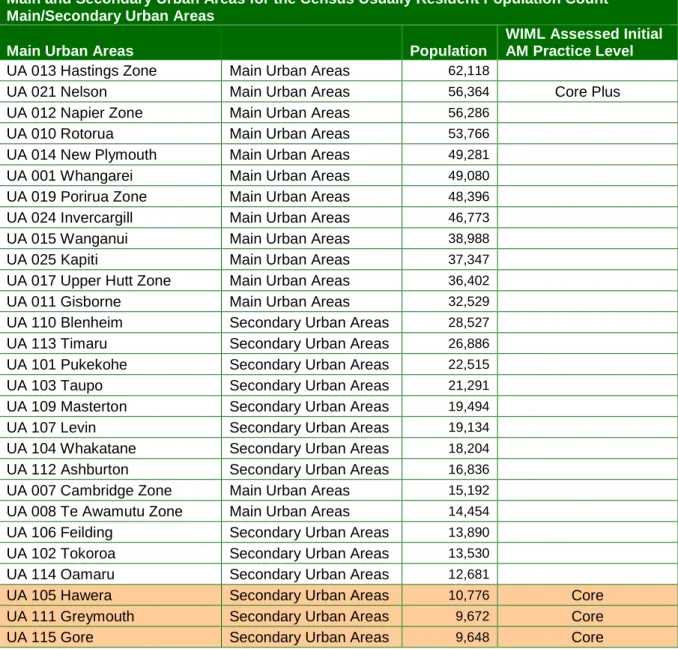
INITIAL RISK SCREEN – DISTRICT POPULATION 2.1 Overview of New Zealand City and Town Populations
Main and secondary urban areas for the census Usually residents count main/secondary urban areas. Source: http://www.stats.govt.nz/census/census-outputs/default.htm 19 August 2008 2.3 Community population analysis. The reality of the wealth management practice of local authorities in New Zealand is that it is conducted in a similar way at the municipal level.
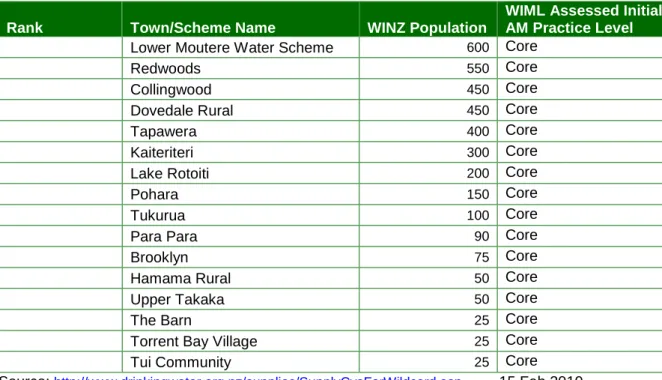
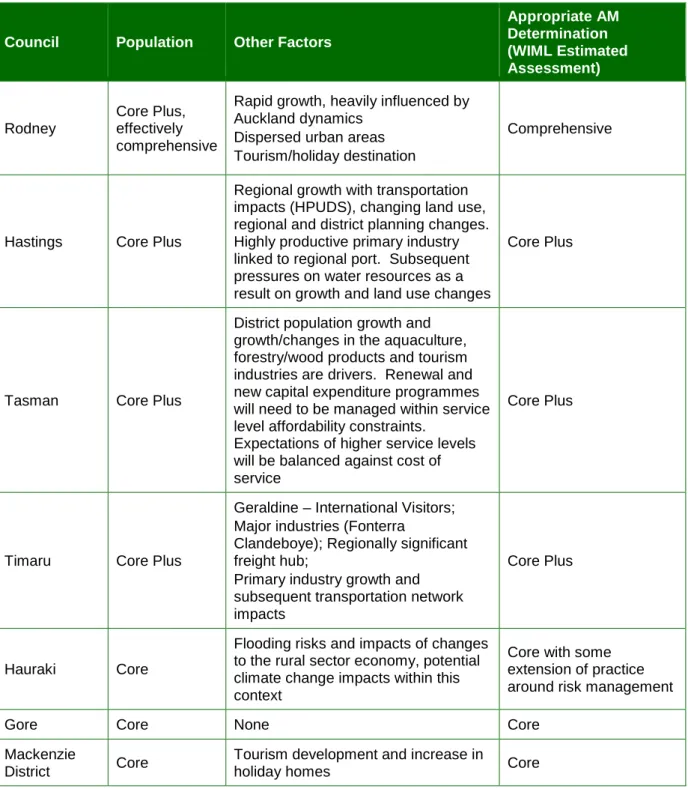
The requirements of the largest population center in the Council tend to set the appropriate level of practice. Richmond is the largest city and based on the initial provision in section 2.1 suggests a 'Core - Core Plus' asset management practice level is appropriate.
Analysis by District Total Population
Initial Risk Screen – Conclusion
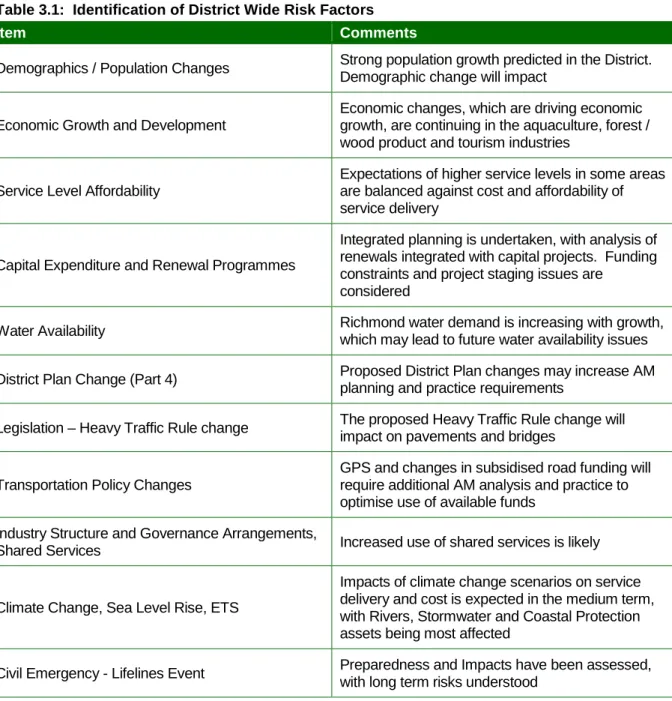
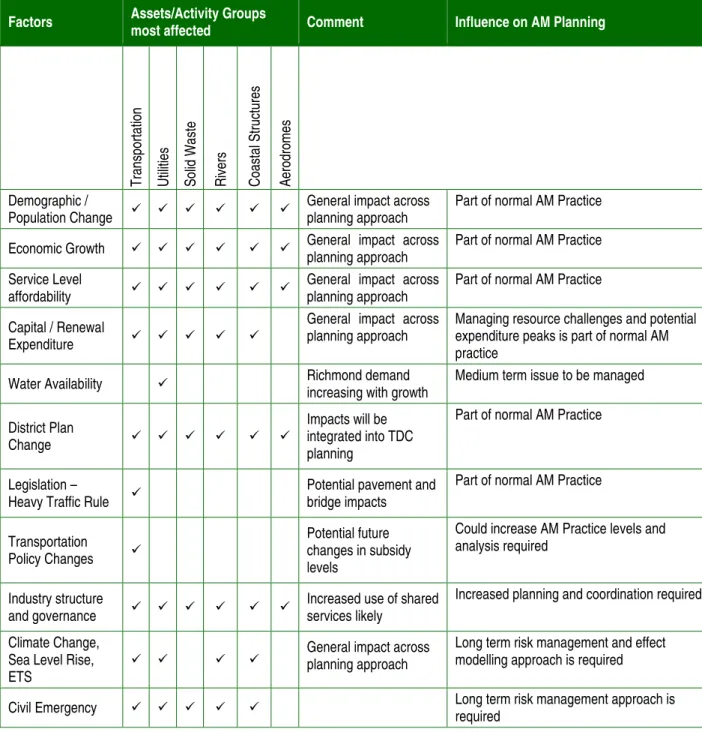
CONSIDERATION OF DISTRICT WIDE RISK FACTORS 3.1 Identification of District Wide Factors
The district's population growth and growth/changes in the aquaculture, forestry/wood products and tourism industries are drivers. Renovation and new capital expenditure programs will need to be managed within service level affordability constraints. Through the Community Council Long Term Plan 2009-2019, Tasman District Council has sought input from its community and reviewed its vision and strategic direction for the district.
Eight community outcomes were developed after extensive community involvement in 2005, for inclusion in the 2006–2016 Ten Year Plan. Protecting the productive capacity of our best soils while ensuring suitable land is available for residential, business, industrial and recreational use. The above priorities are in line with the spearheads of the Ten-Year Plan 2009-2019 and the Project Council.
These issues have been reflected in the analysis of Tasman District Council asset groups in Section 4 of this report and the policy statements in Section 5.0.
Consideration of District Wide Factors - Conclusion
IIMM SECTION 2.2.4 DETAILED FACTOR ANALYSIS
Detailed Analysis Tasman District Council Asset Groups
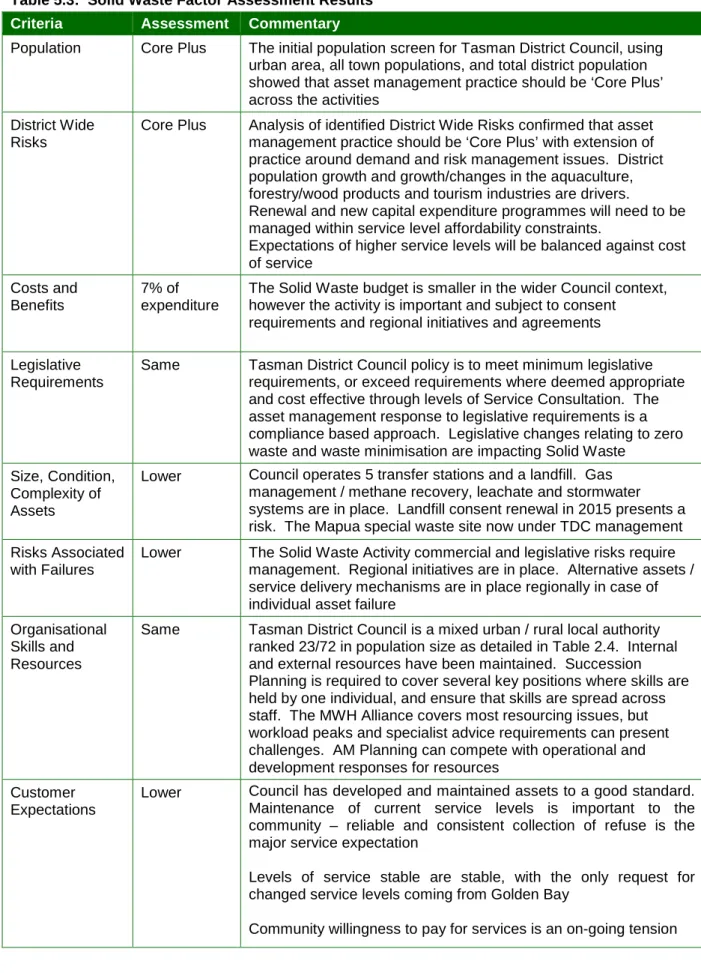
Alternative asset / service delivery mechanisms are in place in the region in case of individual asset failure. Succession planning is required to cover several key positions where skills are held by one individual and ensure that skills are distributed across staff. Stable service levels, with only request for changed service levels coming from Golden Bay.
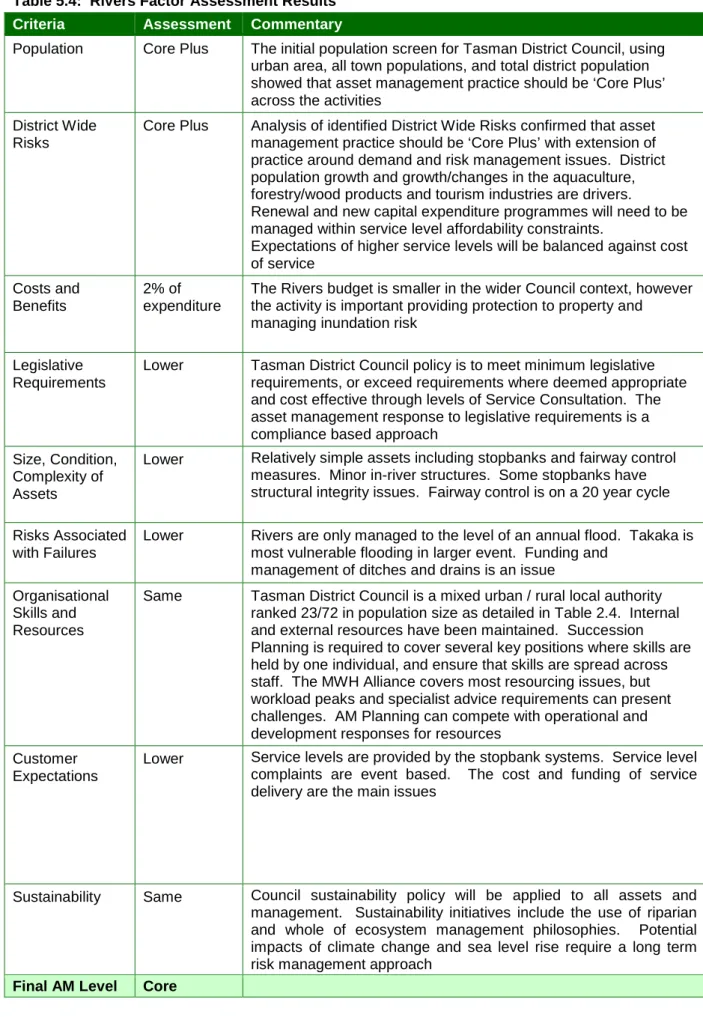
Sustainability initiatives include low impact designs, use of alternative materials, holistic management processes, education and recycling initiatives, riparian and whole ecosystem management philosophies. Potential impacts of climate change and sea level rise require a long-term risk management approach Influenced by.
Final Appropriate Asset Management Level Determination
The overall risks associated with asset failure were assessed as normal and well understood by Tasman District Council. Tasman District Council is a mixed urban/rural local authority ranked 23/72 for population size as detailed in Table 2.4. The Council is working to document knowledge, model systems and develop appropriate operational manuals and standard operating procedures.
Overall customer expectations are judged to be typical - ie stable, but with high expectations of providing services that have an economic impact on liveability, rural production and the district economy. Potential impacts of climate change and sea level rise require a long-term risk management approach. The Council also follows the sustainability regimes of the Land Transport Management Act 2003, NZTS and RLTS requirements (including subsequent amendments and revisions) for transport.
Conservation and demand management practices are applied to water and wastewater, and holistic management practices are applied to stormwater management.
ASSET MANAGEMENT POLICY STATEMENTS
Transportation
- Objective of the Land Transport Asset Management Policy
- Asset Management Policy Principles
- Policy Linkages to Other Plans
- Structured Assessment of Asset Management Practice
- Implementation and Review of Policy
- Asset Management Implementation Strategy
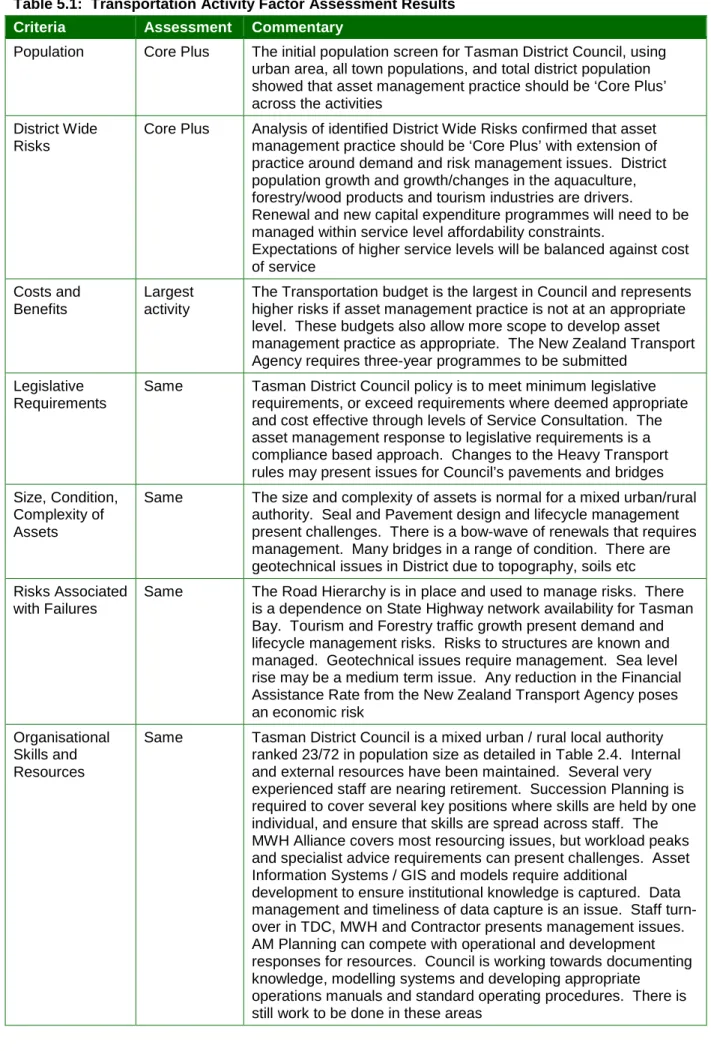
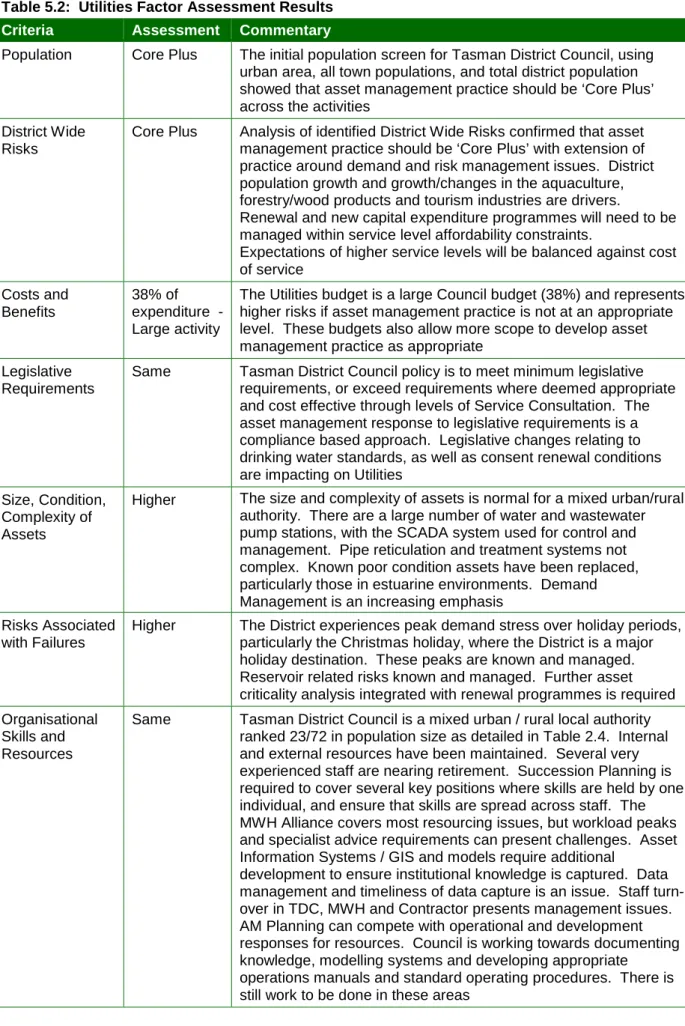
Population Core Plus The initial population survey for Tasman District Council, using urban area, all city population and total district population, showed that wealth management practice should be 'Core Plus'. Core Plus analysis of identified district-wide risks confirmed that asset management practice should be 'Core Plus' with practice expanding around demand and risk management issues. The transport budget is the largest in the Council and represents greater risks if the asset management practice is not at the right level.
Same Tasman District Council policy is to meet minimum legislative requirements or exceed requirements where deemed appropriate and cost effective through levels of service consultation. Changes to the rules for heavy transport may cause problems for the Council's pavements and bridges Size, condition,. Any reduction in the New Zealand Transport Agency financial assistance rate represents a financial risk.
The same Tasman District Council is a mixed urban/rural council ranked 23/72 by population size as shown in Table 2.4. The community's willingness to pay for services is an ongoing tension. Sustainability The same Board sustainability policy will be applied to all assets and. This Asset Management Policy will be implemented in conjunction with the 2012 Activity Management Plans and the 2012 LTCCP.
This next full review of this Asset Management Policy will be completed in June 2014 (4 years) prior to the completion of the asset plan updates to support LTCCP 2015. Council staff have completed a detailed analysis of good asset management practice within the guidance provided by this policy. This analysis examined asset description, service levels, growth management, risk management, asset life cycle decision-making, financial forecasts, planning assumptions and confidence levels, improvement programs, use of qualified personnel, and engagement of the Activity Management Planning Council.
Based on this detailed analysis, the performance level of the Board and any gaps in proper asset management practice were identified. Gaps identified in asset management practice have been forwarded to the Asset Management Improvement Program for action.
Utilities – Water Supply, Wastewater and Stormwater
- Objective of the Utilities Asset Management Policy
- Asset Management Policy Principles
- Policy Linkages to Other Plans
- Structured Assessment of Asset Management Practice
- Implementation and Review of Policy
- Asset Management Implementation Strategy
The utility budget is a large Council budget (38%) and represents greater risks if asset management practices are not at the right level. There are a large number of water and waste water pumping stations, where the SCADA system is used for control and management. Higher The district experiences peak demand stress during holiday periods, especially the Christmas holidays, where the district is a major holiday destination.
Potential impacts of climate change and sea level rise require a long-term risk management approach. Conservation and demand management practices are applied to water and wastewater, and holistic management practices are applied to stormwater management.
Solid Waste
- Objective of the Solid Waste Asset Management Policy
- Asset Management Policy Principles
- Policy Linkages to Other Plans
- Structured Assessment of Asset Management Practice
- Implementation and Review of Policy
- Asset Management Implementation Strategy
The solid waste budget is smaller in the wider context of the Council, however the activity is significant and subject to consent. Maintaining current service levels is important to the community – reliable and consistent waste collection is a key service expectation. Stable service levels are stable, with the only request for changed service levels coming from Golden Bay.
Rivers
- Objective of the Parks and Property Asset Management Policy
- Asset Management Policy Principles
- Policy Linkages to Other Plans
- Structured Assessment of Asset Management Practice
- Implementation and Review of Policy
- Asset Management Implementation Strategy
The Rivers budget is smaller in the wider council context, but the activity is important to protect property and manage flood risk. Lower Tasman District Council's policy is to meet minimum legislative requirements or exceed requirements where deemed appropriate and cost effective through levels of service consultation.
Coastal Structures
- Objective of the Parks and Property Asset Management Policy
- Asset Management Policy Principles
- Policy Linkages to Other Plans
- Structured Assessment of Asset Management Practice
- Implementation and Review of Policy
- Asset Management Implementation Strategy
The Coastal Structures budget is smaller in the wider Council context, but the activity is important to protect property and manage the assets of harbor and other coastal structures.

Aerodromes
- Objective of the Parks and Property Asset Management Policy
- Asset Management Policy Principles
- Policy Linkages to Other Plans
- Structured Assessment of Asset Management Practice
- Implementation and Review of Policy
- Asset Management Implementation Strategy
The Airports budget is very small in the broader context of the Council, but it is an activity where there is support for.

DETAILED ANALYSIS OF ASSET GROUPS
Traffic Count 3yr cycle, counts for all roads will be completed in 2010 SAMPLE DATA ONLY.
Transportation
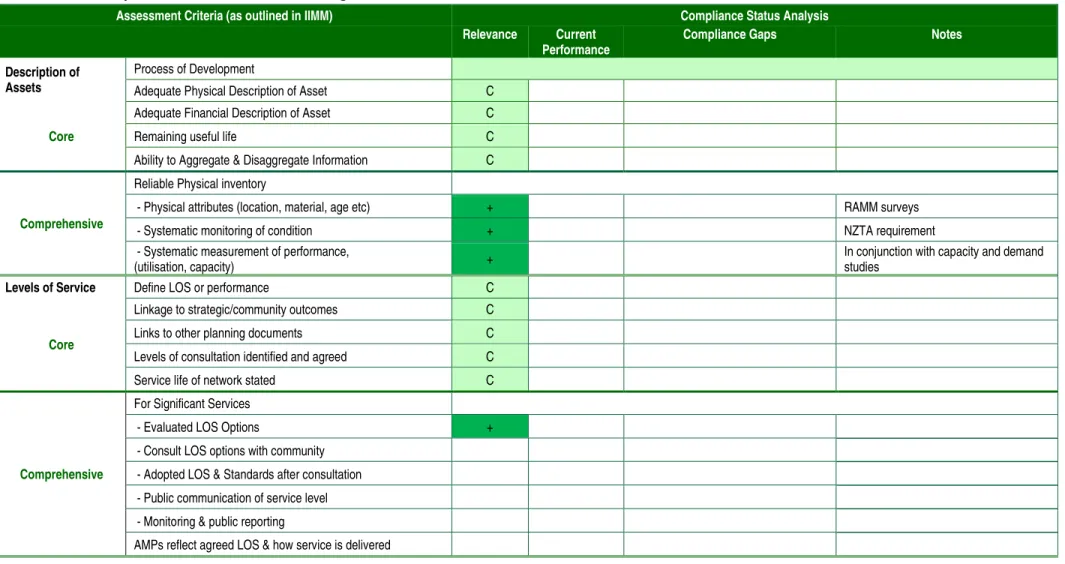
Consult LOS options with the community - Adopted LOS & Standards after consultation - Public communication of service level - Monitoring and public reporting. Translate operational, planned maintenance, renewal and new work into financial terms over the period of the strategic plan/asset life cycle. State all assumptions, including the organization's strategic plan that supports AM – linkages with other planning documents + confidence levels (as per IIMM 4.3.7).
AM plans that evolve as AM systems provide better information + AM plans are updated every 3 years together with organizations.
Utilities
Forecasts include various factors that include demand + sensitivity of asset development (Capital Works) to demand. Use predictive modeling to support long-term financial forecasts for maintenance, renewals and new capital.
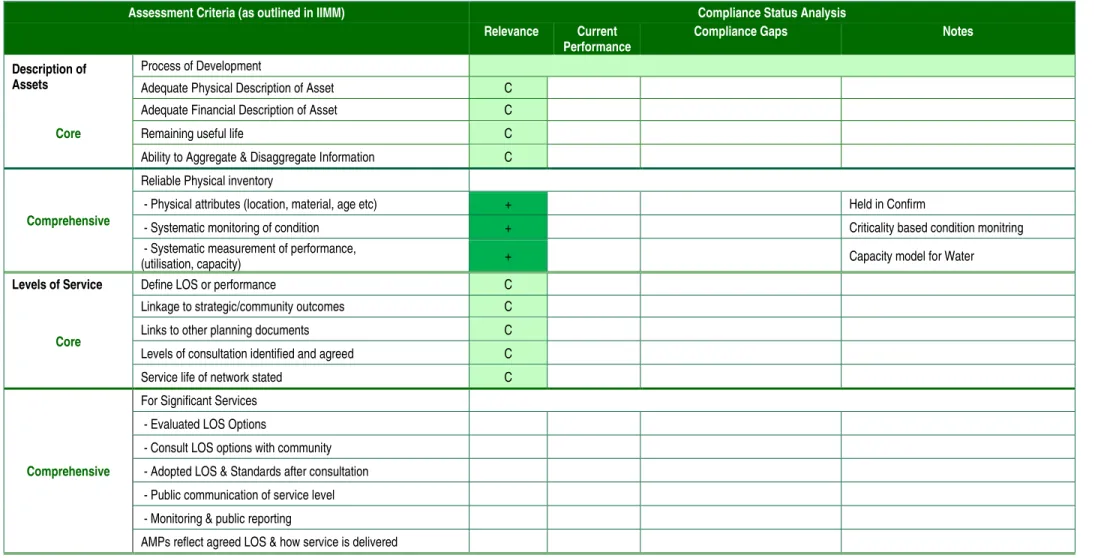
Solid Waste
Recognition and application of integrated risk principles. management to assets demonstrated + Commercial and regulatory risks require. management Apply standards and good practice in the industry. Apply agreed evaluation tools to prioritize work programs - Use predictive modeling to support long-term financial forecasts for maintenance, renewals and new capital.
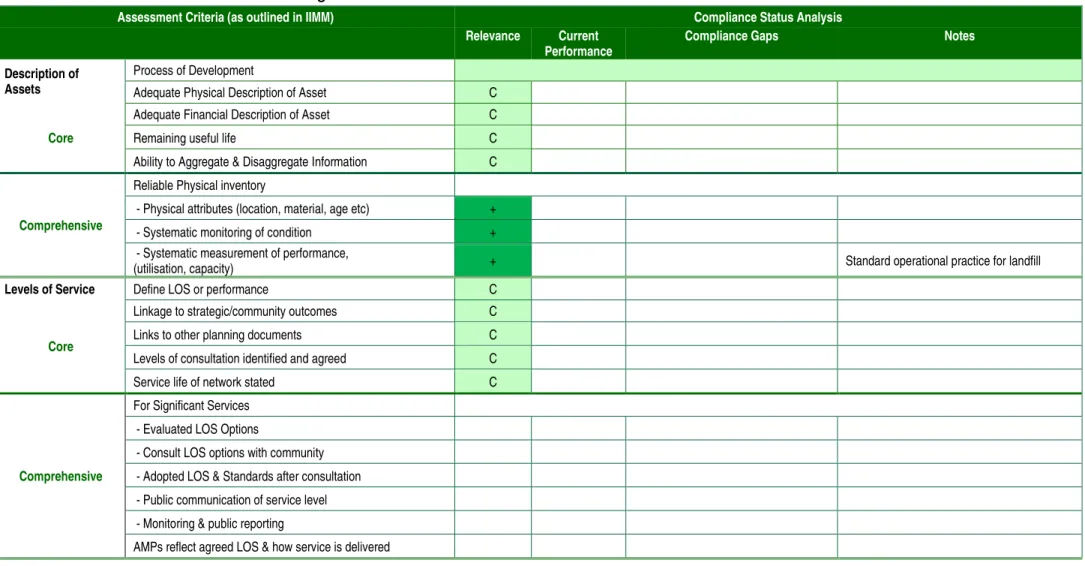
Rivers
Forecasts include several factors that include demand Sensitivity of asset development (Capital Works) to changes in demand documented.

Coastal Structures
Aerodromes