Department of Computer Science and Engineering Faculty of Natural Sciences and Information Technology Daffodil International University. We hereby declare that this project was done by us under the supervision of Tania Khatun, Assistant Professor, Department of CSE Daffodil International University. Transfer learning is a promising approach to improve the detection accuracy of rotten dragon fruit.
In this paper, a transfer learning based approach is proposed to detect rotten dragon fruit using images of dragon fruit from different locations in Bangladesh. The results of the experiments show that the proposed approach achieves an accuracy of up to 98.57% in detecting rotten dragon fruit. The results of the experiments show that the proposed approach is effective and can be used to detect rotten dragon fruit in a cost-effective manner.
INTRODUCTION
- Motivation
- Rational of Study
- Research Question
- Objective
- Expected Outcome
- Project Management and Finance
- Report Architecture
The aim of this research paper is to develop a transfer learning based approach to detect rotten dragon fruit in Bangladesh. This research paper aims to investigate the potential of transfer learning to develop a reliable system for detecting rotten dragon fruit in Bangladesh. The aim of this research paper is to analyze the potential of transfer learning to detect rotten dragon fruit in Bangladesh.
The objective of this research paper is to investigate the efficiency of transfer learning based approach to detect rotten dragon fruit. Further, the paper will propose a transfer learning based approach for the detection of rotten dragon fruit in Bangladesh. The expected outcome of this research paper is the development of a transfer learning based approach to detect rotten dragon fruit.
BACKGROUND STUDY
- Preliminaries
- Transfer Learning: Transfer learning is a machine learning technique in which knowledge from one domain is applied to another domain. It is a process of using
- Rotten: Rotten is a term used to describe food that has gone bad due to bacterial growth. Rotten food has a foul smell and has often changed in color and texture
- Fresh: Fresh is a term used to describe food that has not gone bad due to bacterial growth. Fresh food is usually free of any odor and has its original color and texture
- Related Works
- Comparative Analysis and Summary
- Scope of the Problem
- Challenges
The study also showed that transfer learning can be used to improve model accuracy by fine-tuning a pre-trained model with a small dragon fruit dataset. For example, a system was developed to classify apples, pears and oranges using transfer learning and CNN. In addition, a classification system for six citrus species was developed using transfer learning and CNN.
In conclusion, transfer learning was used to successfully develop a deep learning model for dragon fruit ripeness prediction. In addition, transfer learning has also been used to develop fruit classification systems for other fruits such as apples, pears, oranges, and citrus fruits. The scope of this research is to predict the freshness of dragon fruit in Bangladesh using transfer learning.
This research analyzes the current state of dragon fruit production in Bangladesh and the availability of resources to support the use of transfer learning. It will also explore the potential of transfer learning in predicting the freshness of dragon fruit in Bangladesh. The research will also explore the potential of transfer learning in terms of accuracy, cost and time efficiency.
In addition, this research will conduct a comparative study between transfer learning and other predictive models such as support vector machine and decision tree. Furthermore, this research will also examine the potential for transfer learning in terms of scalability, portability and reliability. Finally, this research will evaluate the performance of transfer learning in predicting the freshness of dragon fruits in Bangladesh.
Domain Knowledge: Transfer learning models require domain knowledge in order to be successful.
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
- Research Subject and Instrumentation
- Data Collection Procedure
- Statistical Analysis
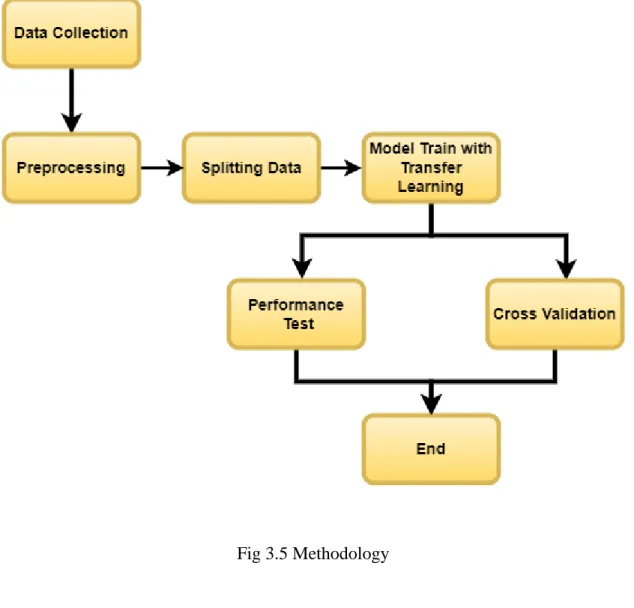
- Proposed Methodology
- Implementation Requirements
- Experimental Setup
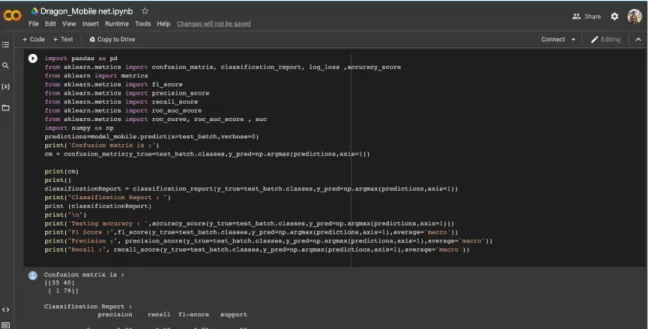
- Experimental Results & Discussion
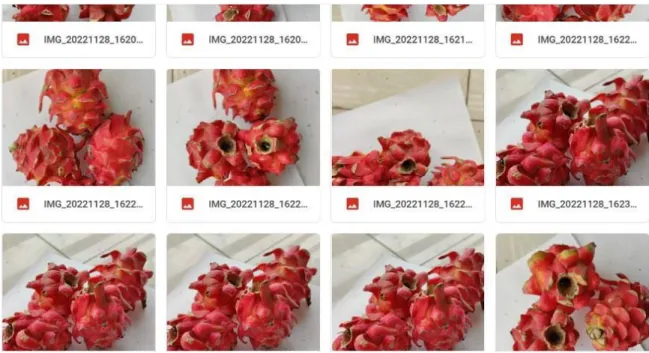
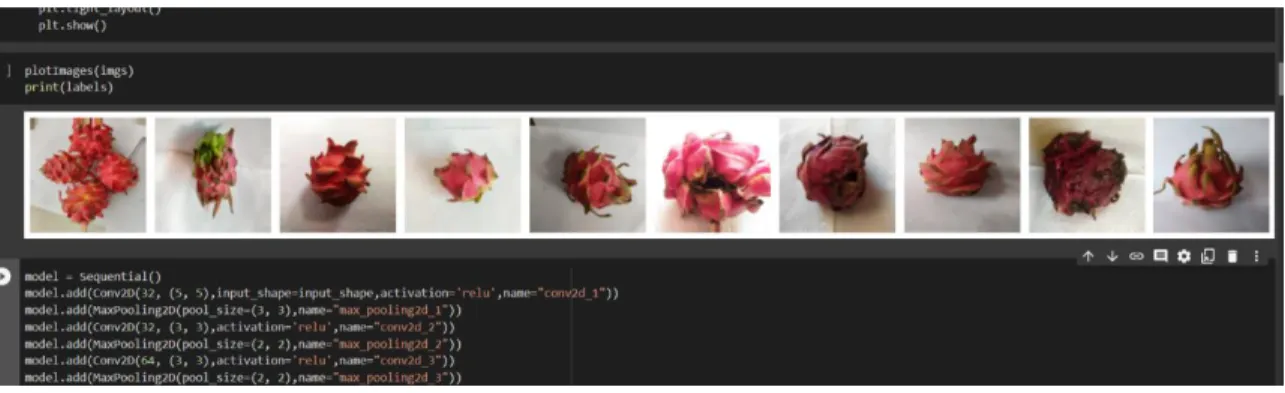
Data Collection: Collect data on the physical attributes of the dragon fruit, such as size, shape, color, texture, and weight. Visual inspection: Visually inspect the dragon fruit and rate its freshness, based on the physical attributes gathered in the previous step. The lab will take samples of the dragon fruit and analyze it for chemical and microbiological properties to determine whether the dragon fruit is fresh or rotten.
This research aimed to develop a system for detecting whether dragon fruit is rotten or fresh. The researchers used a combination of visual and chemical techniques to detect the level of ripeness and freshness of the dragon fruit. The first step in the research was to collect dragon fruit samples from local markets.
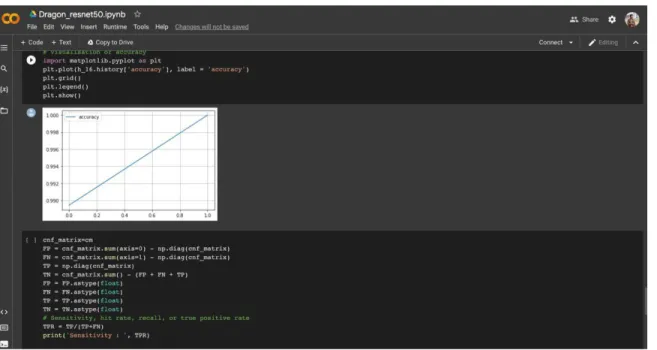
The final step in the research was to apply the transfer learning model to determine the ripeness and freshness of dragon fruit in Bangladesh. The model was applied to a randomly selected set of dragon fruit from local markets and it was found that the model was able to accurately detect the ripeness and freshness of dragon fruit. Overall, this research showed that transfer learning can be used to accurately detect the ripeness and freshness of dragon fruit in Bangladesh.
The results of this research suggest that transfer learning is a viable solution for detecting dragon fruit in Bangladesh. Furthermore, the results of this research can be used to inform future research in the use of transfer learning for detecting different types of fruits in Bangladesh. Additionally, the results can be used to provide information to farmers and other stakeholders in the agriculture sector, enabling them to better identify and manage dragon fruit in Bangladesh.
Data Collection: Collection of dragon fruit images from different sources such as market, supermarket, growers, etc. Transfer Learning: Application of transfer learning models such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) or Support Vector Machines (SVMs) to the pre-processed images of the dragon fruits to detect whether they are fresh or rotten. Documentation: Documentation of the entire process of detection of dragon fruits, rotten or fresh, using transfer learning in Bangladesh.

IMPACT ON SOCIETY, ENVIRONMENT AND SUSTAINABILITY
- Impact on Society
- Impact on Environment
- Ethical Aspects
- Sustainability Plan
In addition, the research can help farmers increase the overall quality of their crops by allowing them to detect rotten fruit early and prevent further spread of rot and contamination. In this way, the research can help reduce the environmental impact of dragon fruit production. The research can improve the efficiency of dragon fruit production in Bangladesh by reducing the excessive use of fertilizers, pesticides and other chemicals used to increase productivity.
Overall, the research can have a positive impact on the environment by reducing the amount of pollutants and food waste released into the atmosphere. Respect for human rights: Respect for human rights should be taken into account while conducting the research. The researchers should take the necessary steps to ensure that the collected data is not used for purposes other than the research.
Informed consent: Participants must receive all information regarding the study before giving their consent. Data Protection: The data collected during the study must be kept secure and confidential. Balance between benefits and risks: The research should be conducted in such a way that the benefits of the research outweigh the possible risks associated with it.
Participants must be informed of the potential risks associated with their participation in the research. Respect for cultural values: Researchers must respect the cultural values of Bangladesh such as religious beliefs and personal values while conducting research. Improved detection techniques: The development of improved techniques for detecting rotten or fresh fruit is essential for the sustainable production and consumption of dragon fruit in Bangladesh.
This may involve the use of advanced sensors and imaging technology to detect the quality of dragon fruit.
SUMMARY, CONCLUSION, RECOMMENDATION AND IMPLICATION FOR FUTURE RESEARCH
Summary of the Study
Conclusions
Implication for Further Study
Finally, research should also investigate the potential health and nutritional benefits of consuming fresh dragon fruit, as well as the possible adverse effects of consuming spoiled fruit. This could include identifying optimal storage conditions to maximize shelf life and maximizing the effects of ambient temperature, humidity and sunlight exposure on dragon fruit shelf life. In addition, research should also be conducted into the impact of different post-harvest processing methods on the shelf life of dragon fruit.
Furthermore, studies should be conducted to assess the potential of using machine learning-based approaches to detect the freshness and ripeness of dragon fruits. This could potentially enable quick and accurate detection of fresh and rotten dragon fruit. This could include studying the effects of temperature, humidity and other environmental factors on the ripening process.
In addition, the effects of storage practices, such as those used by retailers and consumers, on the quality of dragon fruit in Bangladesh can be examined. In addition, research can be conducted on the feasibility of implementing automated methods for detecting dragon fruit freshness in Bangladesh, such as machine vision-based systems.
Thiha, "Effects of Explants and Growth Regulators on In Vitro Regeneration of Dragon Fruit (Hylocereus undatus Haworth)," phdthesis, 2019. Yen, "Morphological characteristics and pollination requirement in red pitaya (Hylocereus spp.)," International Journal of Agricultural and Biosystems Engineering, vol. Panjaitan et al., "Anti-diabetic activity of the red dragon fruit peel (Hylocereus polyrhizus) in ethanol extract against diabetic rats," Pharmacognosy Journal, vol.
Chow, “Optimization of pectin production from dragon fruit peel waste: drying, extraction and characterization studies,” SN Applied Sciences , vol. Li et al., “Cold plasma treatment induces phenolic accumulation and increases antioxidant activity in fresh-cut pitaya (Hylocereus undatus) fruit,” Lwt, vol. Paw, “Effect of dragon fruit on glycemic control in prediabetes and type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis,” PloS one , vol.
Distinguishing three species of dragon fruit (Hylocereus spp.) grown in Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India using morphological, biochemical and molecular characteristics,” Scientific Reports , vol. Zulfa et al., “Effect of Red Dragon (Hylocereus polyrhizus) Extract on Membrane Lipid Peroxidation and Liver Tissue Damage Induced by Hyperlipidemia in White Rats (Rattus Norvegicus),” in 5th International Conference on Health Sciences (ICHS pp. Sanoamuang, and the other, “Fungi on dragon fruit in Loei Province, Thailand and the ability of Bipolaris cactivora to cause postharvest rot of the fruit,” Asia-Pacific Journal of Science and Technology, vol.
Bengoa, "Diseases of dragon fruit (Hylocereus species): Etiology and current management options," Crop Protection, vol. Islami, “Effect of NPK doses on yield of dragon fruit (Hylocereus costaricensis [FAC Weber] Britton & Rose) in Chittagong Hill Tracts,” American-Eurasian Journal of Agricultural & Environmental Sciences, vol.