Thus, this Social Input - Proposed National Decentralized Local Governance Policy for Bangladesh - has been drafted for the consideration of the Local Government Division (LGD), Ministry of Local Government, Rural Development and Cooperatives (MLGRD&C), Government of the People's Republic of Bangladesh. The absence of the stated policy also affects the inherent and institutional relations of the local government bodies. Thus, as part of the Management Research Report (MRR) of the MDM Program at the Asian Institute of Management (AIM), Manila, a proposed National Decentralized Local Governance Policy Framework for Bangladesh has been developed, which is actually a proposed policy for consideration by the Local Government Department ( LGD), Ministry of Local Government, Rural Development and Cooperatives (MLGRD&C), Government of the People's Republic of Bangladesh.
Anecdotal evidence, participant observations and past experiences, and studies (eg Talukdar, 2009) support that the absence of politics results in an unstable local government structure, as well as frequently changing patterns of local government power dynamics, weakening inherent institutional linkages between and/or between local government units. . Stakeholder and force field analysis to understand the set of power linkages for and against a proposed policy in order to properly formulate a policy advocacy strategy. The proposed policy framework has been formulated based on the understanding of SWOT analysis and force field analysis and on the basis of experts.
Stratum -1 Elected representatives of local government institutions Stratum -2 Civil servants of local government institutions Stratum -3 Senior officials of the Department of Local Government and the Ministry of.
Arrangement of the Working Paper
SWOT Analysis
- Initial Remarks
- Internal Analysis
- External Analysis Country Context
- Concluding Remarks
The Union Parishads, Upazila Parishads, Zilla Parishads, Municipalities and City Corporations are the local government units under this division. Helpful . to achieve the objective .. attributes of the environment Country context and social, political . as well as from the institutional perspective of local government. Main specific functions of LGD21. a) Manage all matters relating to local government and local government institutions;
This Division has framed all the nascent local government laws/laws22 that are trendy of this kind, except for some material limitations. 22 The Local Government (City Corporation) Act, 2009; The Local Government (City Corporation) (Amendment) Act, 2011; The Local Government (Pourashava) Act, 2009; The Local Government (Union Parishad) Act, 2009; The Upazila Parishad Act, 1998; The UpazilaParishad (Reinstatement of the Repealed Act and Amendment), 2009;. 23 Most of the old local government rules and regulations were drafted and/or issued by this Division.
Thus, the current structure of local government in Bangladesh (see Institutional Analysis) has been the result of a long legacy, reforms, evolution and revolution. Study29 identifies that despite a long legacy of local government in Bangladesh, until recent developments, decentralization was hardly considered a pragmatic means of achieving good governance therein. Moreover, changing pattern as well as power dynamics in the local government structure is a serious challenge to the development of a pro-poor local governance system in Bangladesh.
Even during democratic regimes, many boards/commissions for the reform of administrative and local authorities prepared reports that expressed the wishes of the government at the time. 34 Stakeholders also note that local government institutions cannot introduce a new tax or increase the rate of existing taxes or finalize the budget without government approval. The competent administrative body of the government can postpone the implementation of any activity started or even suspend any decision taken by its own subordinate department of the local government.
Finally, the local government bodies in Bangladesh operate under the control of the local government department, the Ministry of Local Government, Rural Development and Cooperatives. Perpetual resource constraints also prevent the local government bodies from delivering services assigned to them. Moreover, the local government bodies have no oversight role and function over the services provided by the government departments.
Again, despite there being a long legacy of local government in Bangladesh, until the local government institution Accelerating and.
Force-field analysis
- Initial Remarks
- Stakeholder and Force-field Matrixes
- Analysis of Key Forces
- Concluding Remarks
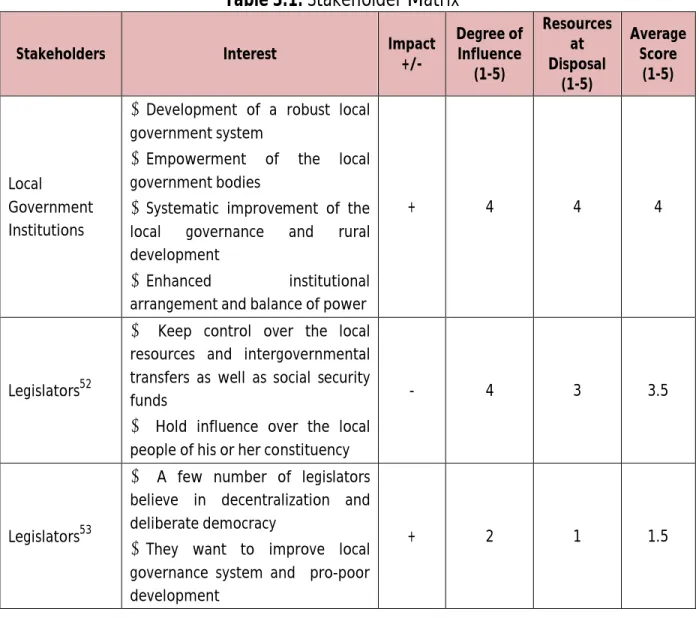
Here stakeholder matrix shows the stakeholders' interest or disinterest in the development of a robust decentralized local governance policy in Bangladesh, and their degree of influence as well as resources at their disposal, while here force field matrix demonstrates forces for the development of the said policy and forces against same. 52 Based on the in-depth interview of a legislator, the study notes that the majority of the legislators are against the development of local governance system, and thus they reject the call for a decentralized local governance policy in Bangladesh. 53Nevertheless, a significant number of legislators are in favor of the development of local governance system, and therefore advocate a decentralized local governance policy in Bangladesh.
The main opposition party and its alliance show no interest in the government formulating a decentralized local governance policy for the same reason as the government's case, as they expect to come to power, although they are not strongly opposed to it. Many small political parties have a strong interest in advancing decentralization and a system of local governance that fits their political mandate. Advocate for a nuanced system of democratic, fiscal and administrative decentralization and an improved system of local governance to meet MGD with a decentralized and deliberate democracy.
Institutions Development of a proposed decentralized local governance policy for Bangladesh and then formulation of an advocacy policy. The main forces for are local government institutions, development partners, civil society organizations, citizens, the media, local government experts and some small political parties, while the key forces against are the legislators, the government, the local government department and even the main opposition political party. 54 the survey also finds that there are few legislators who support the strengthening of the local government system, thus recognizing the importance and essence of the decentralized local government policy for Bangladesh. Importantly, media observation and participants' past experiences, particularly with UNDP, allow the study to document the attitude of the Prime Minister and the Minister of Local Government, Rural Development and Cooperatives to local governance.
In fact, historical evidence supports that during the autocratic regimes, there was a strong emphasis on decentralized local governance, but this was deliberate decentralization, intended to sabotage democracy at the central government. What is important is that research notes that the Prime Minister and the relevant Minister for local government are two powerful forces for deciding whether proposed decentralized local governance policy will be accepted or adapted to go to the Cabinet for approval. However, the result of these two-dimensional forces (i.e. forces for and against), makes the Local Government Department gradually move towards paradigm shift towards the development of local government system and local management practices.
Thus, the development of this proposed national policy of decentralized local government followed by policy advocacy strategy and implementation strategy is relevant to the Bangladeshi context. Thus, the manner and approach of a proposed decentralized local government policy for Bangladesh followed by advocacy and policy implementation strategies depend to a certain extent on this Force Field Analysis.
Decentralized Local Governance Policy Framework
- Initial Remarks
- Proposed Policy Vision
- Proposed Policy Framework Structural Framework
- Issues and Concerns Institutional Linkages
Balanced decentralization: To ensure that a nuanced move towards a balanced political, fiscal and administrative decentralization for local governance and development takes place, but the democratic decentralization is subject to immediate accommodation in all municipal institutions. Empowerment of local authorities: Ensuring that local government bodies freely exercise their powers, including those conferred on them by the national government, within the limits defined by legislation. 62Currently, there are three types of local government institutions in Bangladesh (ie Rural Local Government Institutions, Special Local Government Institutions and Urban Local Local Government Institutions).
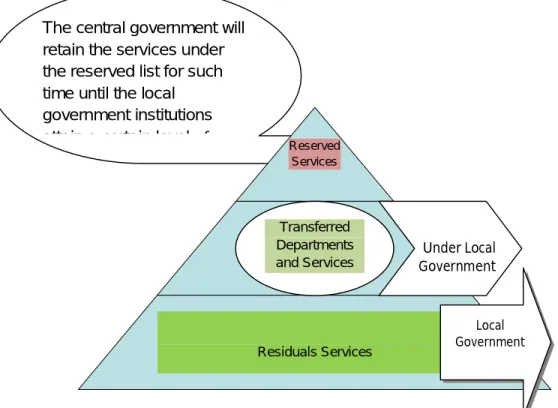
However, the Local Government Department would be downsized, with a limited number of senior officials and support staff, and a limited scope of responsibilities. The basic tasks of the LGD would be to maintain contacts with the national local government committee. However, the Local Government Engineering Department (LGED), the Department of Public Health Engineering (DPHE) and the National Institute of Local Government (NILG) will be headed by the National Local Government Commission.
The central government will keep the services under the "reserved list" for such a time until the local government institutions reach a certain level of maturity. The central government will keep the services under the reserved list for such a time until the local government institutions reach a certain level of. The local government institutions, especially Union Parishad, Upazila Parishad and Zila Parishad, are going through a deadlock and transition period.
And in Bangladesh there is an absolute absence of the legal framework for the local government's loans, but it is becoming increasingly essential here for the promotion of the fiscal decentralization. In the context of Bangladesh, the local government institutions need support to improve their planning, budgeting and financial management capacity. The recent development of GAD focuses on 'gender mainstreaming' in management and development in general, and in local government institutions in particular, so that it can strengthen local governance with a tendency to correct the gender inequalities and local poverty.
These unfair elections had resulted in unaccountable local governance that created further mistrust and suspicion between the local government and the local population. There are a number of growing concerns, e.g. lack of capacity and accountability of the local government bodies, lack of consistency in the work of the state to come forward to the local government and then to the local government. Thus, the scholars, practitioners and local elected representatives praise the need for a permanent municipal commission for years.
These commissions will have appropriate powers, functions and authority to conduct the affairs of local government institutions, including the allocation of financial resources and monitoring and oversight on behalf of the national government (adapted from GAF's Proposed Policy, 2010).
Conclusion
Nevertheless, this proposed policy prescribes one "National Independent Local Government Commission" to maintain the relationship with the central/national government and devolution of the effective local government and local government system both substantively and functionally, and eight "Regional Independent Local Government Commissions" 64 for the regional integration of local government and local governance.
Unveiling the potential of decentralization. In Decentralization, Democratic Governance and Civil Society in Comparative Perspective. A, (1981), "Government Decentralization in Comparative Perspective: Theory and Practice in Developing Countries", International Review of Administrative Sciences, 2.