Hossain's research interests are in the areas of economic and social development in the Asia-Pacific regions. His research interests are in the areas of governance and democracy, sociology, education, health and demography.
Background and Context
Rationale of the Study
Objective of the Research
Organization of the Report
2 The Local Governance Program under SHARIQUE contributes to the empowerment of local citizens to make and implement inclusive, gender-sensitive and pro-poor collective choices about their lives and livelihoods through more democratic, transparent, inclusive and effective local government systems . 4 SHARIQUE Phase III: Strengthening Good Local Governance in Bangladesh, Helvetas Swiss Inter Cooperation, Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2016.
Method
Sampling and Sample Size
A total of 282 citizens from all these UPs were interviewed using a semi-structured questionnaire (Appendix 1). A total of 46 key informant interviews (KII) and 4 group interviews were conducted to collect qualitative data.
Field Operation
Supervision
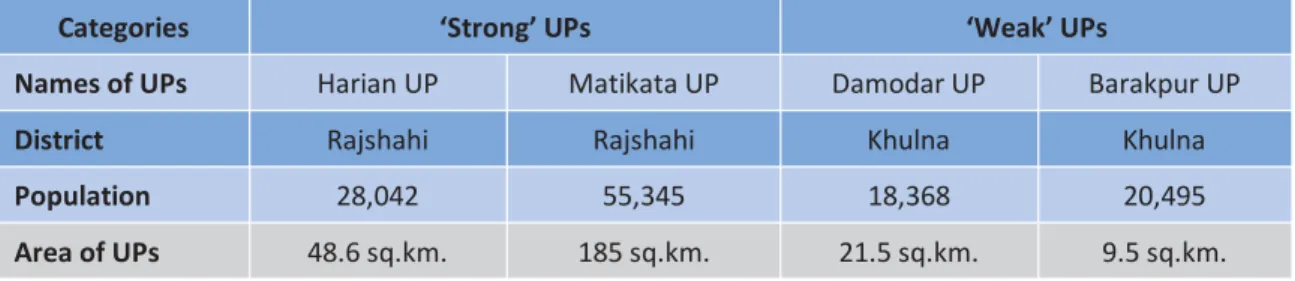
Also, the ratio between local revenues and total UP revenues is lower in weaker UPs than in stronger UPs. These two categories of UP are appropriately defined as 'strong' and 'weak' for the purpose of this study.
Quality Control Measures
Next, skilled data entry operators entered the data into the program under the close observation of a statistician/researcher from BIGD.
Analysis
Limitations
5 Ministry of Public Administration, Ministry of Health, Ministry of Agriculture, Ministry of Livestock, Ministry of Project Implementation, Ministry of Social Work, Ministry of Education, Ministry of Women Affairs, Ministry of Technology, Ministry of Secondary Education, DPHE, Ministry of Rural Development, Ministry of Environment and Forests, Ministry of Cooperatives, Ministry of Family Planning, Ministry of Fisheries, Ministry of Youth Development 6 Money raised at local level by UZPs through leasing of local resources (Haat, Ghat, Jalmahaletc). 5% of this is shared with UPs. This chapter assesses the status and distribution of income of UPs derived from various government and non-government sources.
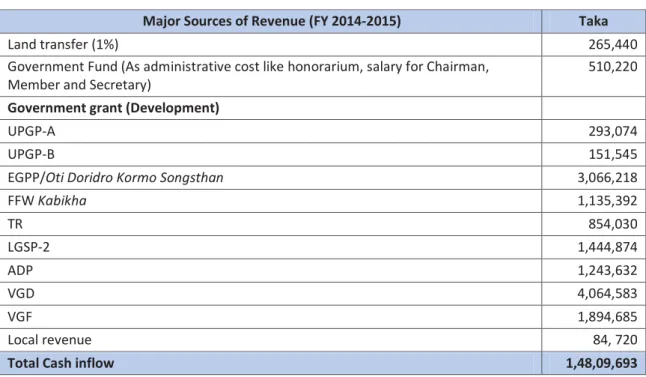
Revenue In-Flow of Union Parishad
Based on the findings, it identifies the procedural gaps in revenue collection and budget management to estimate the capacity of UPs. Finally, citizens' awareness of the functions of UPs was also measured to make inferences and observations about citizens' participation in development, their tax-paying behavior and their attitudes towards UPs.
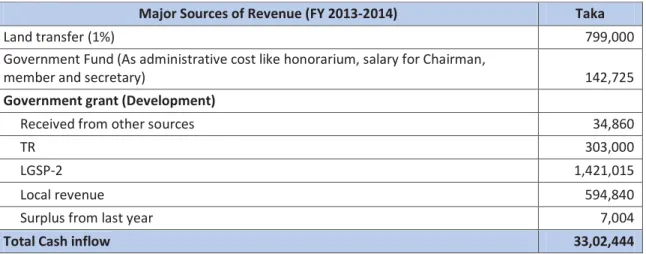
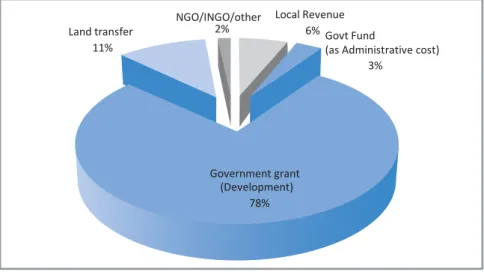
Distribution of Revenues in UPs
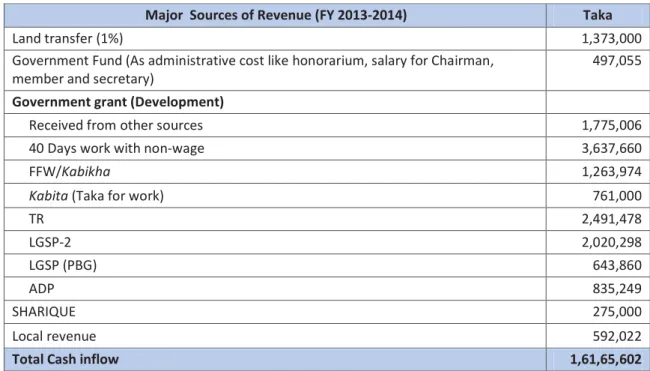
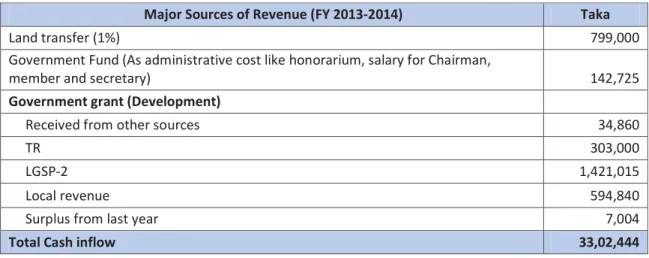
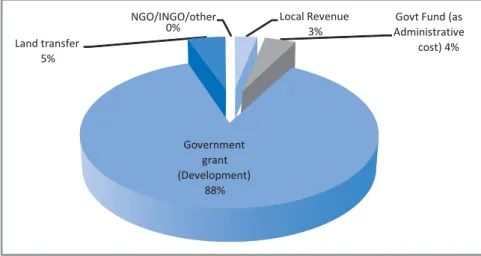
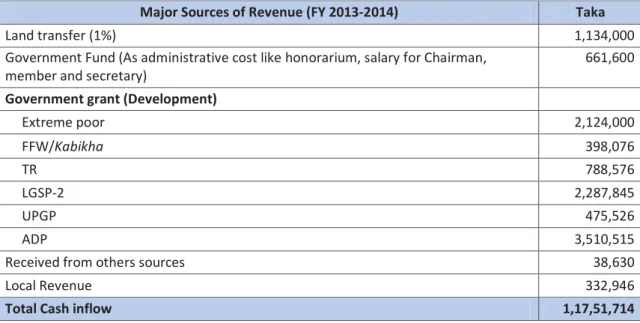
The breakdown of the main sources of income for Matikata UP from the same financial year is presented in the table below. A crucial part of the study was to take a closer look at the UPs' dependence on state subsidies.
Functions of UP and Citizens' Awareness of It
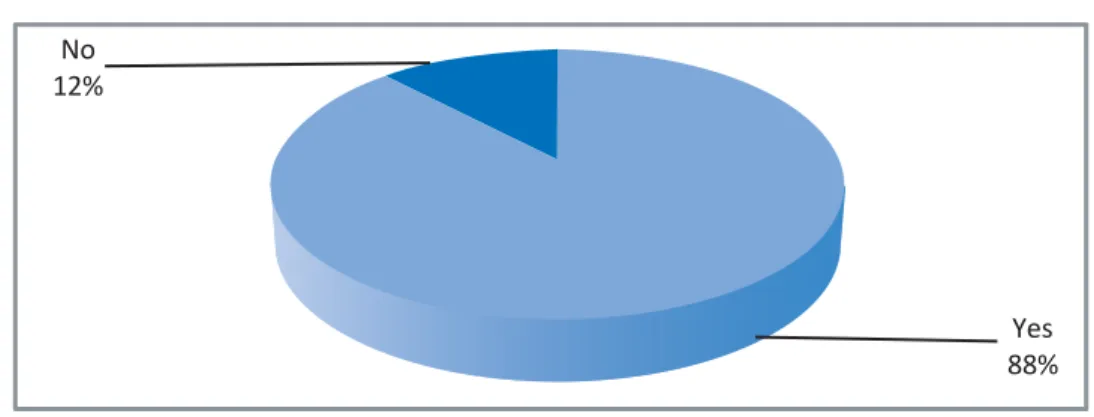
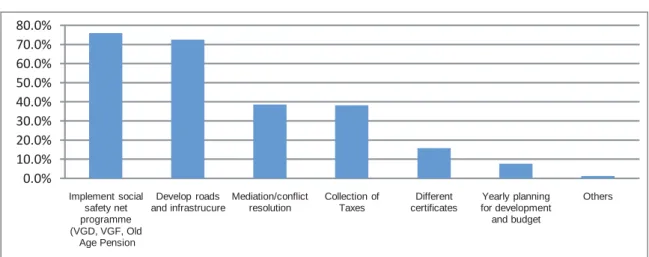
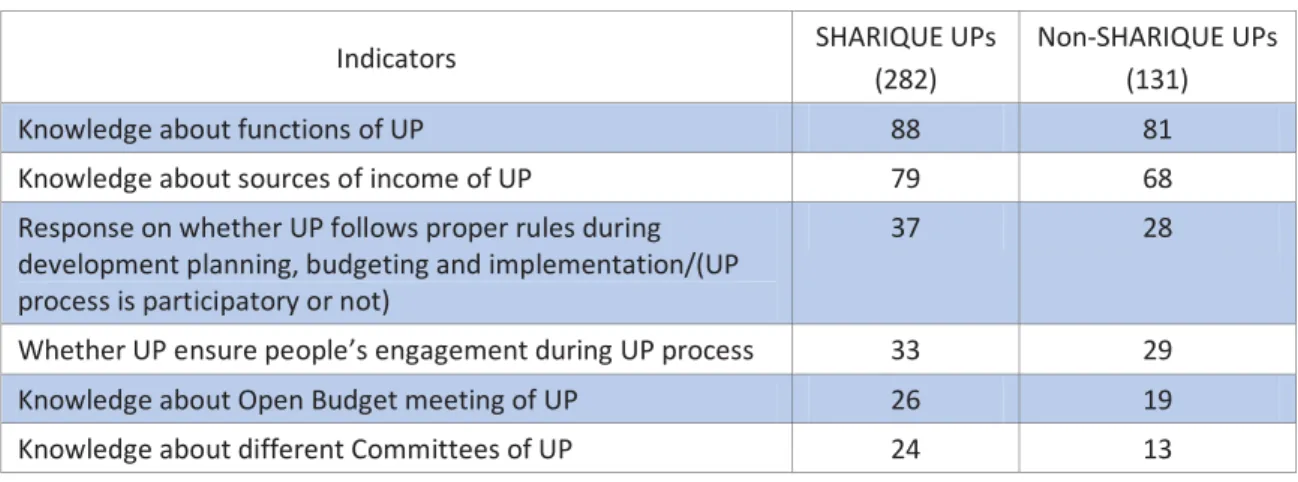
10 CARE's Journey to Advance Transparency Representation and Accountability (JATRA), 2014 Social Engagement in Budget Accountability (SEBA), Baseline Survey, 2015. Some previous studies10 also analyzed citizens' knowledge about the functions of PUs and compared with those, in this study (BIGD Income Mobilization Survey, 2015), more people answered that they know about the functions of UPs. This is due to various programmatic interventions by governments and non-governmental organizations which significantly increased citizens' awareness of functions and activities (Table-3.6).
Looking at people's perception of UP functions, the study found that the percentage of poor and less educated have higher awareness than the non-poor and more educated as shown in Table 3.7.
Constraints to Revenue-Raising in UPs
Furthermore, he identified several problems that hampered the proper functioning of standing committees in UPs, such as: (i) Lack of financial incentive schemes for members, making them uninterested in the activities of SCs, (ii) Although there is formal formation of the Standing Committees, which are not active due to the lack of sincerity of the Chairmen, (iii) Meetings of standing committees are not organized regularly, and (iv) Insufficient knowledge of the UP among its members. Lack of knowledge about how the tax money is used, the tax collection system and the functions of UPs also hinder some citizens from paying taxes. If a UP service provider or UP member is dishonest, the local citizens lose trust in the organization and refrain from participating in UP activities.” The UP Model Tax scheme assigns taxes of 0-7% to UPs that, even if fully recovered from citizens, it is insignificant to bring about general developmental changes in the UP without the help of other funding sources.
Although UPs are mainly responsible for various developmental activities, most people are not aware of the functions.
Citizens' Awareness of UPs' Revenue Sources
This chapter follows the discussion on UP revenue collection and assesses their capacity and revenue-raising potential. It discusses the sources of local revenue collection and people's awareness of them as a measure of UP's ability to nurture local governance. The chapter also explores people's perception of paying taxes by examining their willingness to pay taxes, knowledge of the tax system, government policies and benefits of paying taxes, etc.
Finally, the chapter compares SHARIQUE and non-SHARIQUE UPs and briefly introduces SHARIQUE's interventions regarding local tax transfers, UPs' capacity building in revenue collection and increasing public awareness of tax payment.
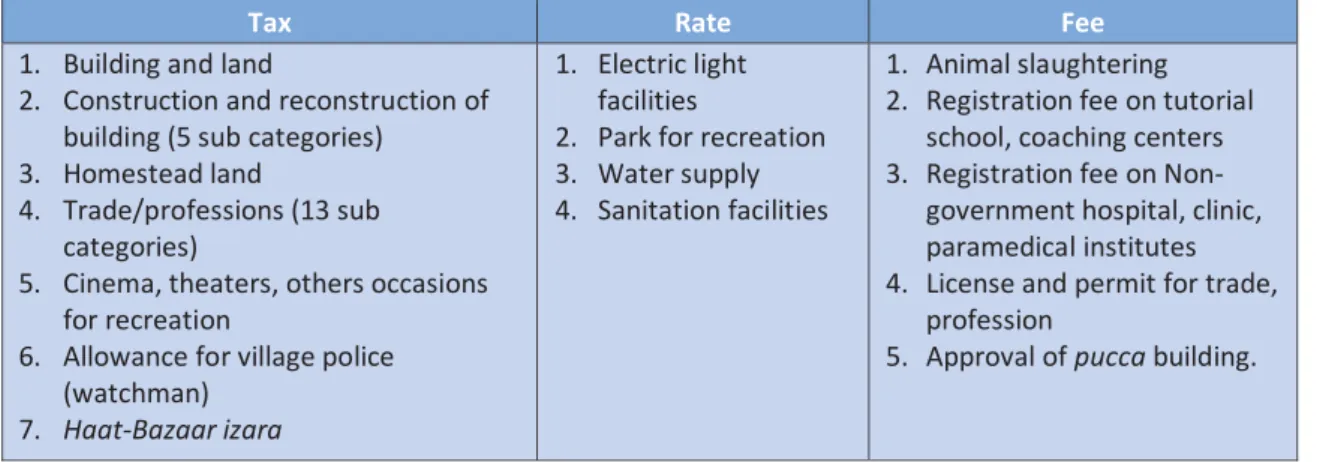
Tax Collection and Tax Payment
Willingness to Pay Taxes
Source: Authors' estimates based on BIGD Revenue Mobilization Survey, 2015 Note: Multiple responses so percentages in all options add up to more than 100.
Causes of Unwillingness to Pay Taxes
Political interference, corruption and lack of responsibility of the local body representative can be considered as the main barriers that demotivate people from paying taxes. Other forms of intimidation that deter people from paying taxes include lack of a code of conduct, illegal interactions and unfair demands from tax authorities. Similarly, lack of tax collection staff was also highlighted by some people as a reason for lower tax collection.
This finding was further substantiated by Khan (2008) who identified lack of public awareness and lack of resources in UP as major obstacles in implementing birth and death registration, electoral roll preparation and similar other research programmes.
Government Policy Regarding Tax System and Citizens' Awareness
Government Policy on Tax Collection and Assessment
On the other hand, sometimes the tax authority also has its own reasons for low tax collection. In addition, the findings show that there are some problems in the tax assessment process that hinder the overall collection of UP revenue. 2005) observed that there is no assessment list and permanent position of "tax collector" at the UP, and those who are temporarily employed for this responsibility work on a contract basis. The field visit also revealed that the tax assessment form compiled below was meant to be completed during the tax assessment process.
There are also some complications in the assessment process, resulting in low tax collection.
People's Awareness of Tax Policy, Assessment and Collection
Some landlords have e.g. several houses rented out, but they only pay property tax for one house. Similarly, a household can consist of several households (divided), but residents pay tax for a single household (figure 4.5). The proportion of the poor and less educated who answered affirmatively to the question is higher than the proportion of the non-poor and more educated.
Potentials of Local Revenue-Raising at UP level
SHARIQUE's Local Governance Programme in Bangladesh
SHARIQUE Interventions and Its Impact on Raising Local Revenue at Union Level
The analysis in this chapter shows that local revenue sources are limited, and citizens are not aware of the importance and obligation of paying taxes in general. The planning and implementation of various development projects for the benefit of the local public are the most important functions of the UP. Of the four UPs under study, only one (Matikata, Rajshahi) emphasized local revenue mobilization.
In Matikata UP, for example, a road damaged by river erosion has been repaired using local UP revenues.
Development Planning and Implementation in the UPs
This is an example of the importance of leadership and commitment of elected officials at the local level. During the investigation, some findings showed some discrepancies between the standard procedure of the law and the reality observed in the field of development project planning and implementation (Box 5.1). All the forms were fake and were only used for record keeping for future audit related issues.
Also in most cases the bidders/contractors of these projects were UP members of the respective department.
People's Awareness of Development Planning and Implementation Process of UP
Developed countries narrowed the role of central government and devolved authority to local government to provide better, accessible and affordable services to citizens" (KII with a government official, central level). When classified in terms of PCI, the percentages of the extreme poor in both "weak" and "strong" UPs are aware of participatory development planning and implementation processes are higher than the percentage above the poverty line. of the planning process of participatory development than the most educated.
In light of this finding, it seems necessary to involve the more educated and wealthy in the participatory development process in UP.
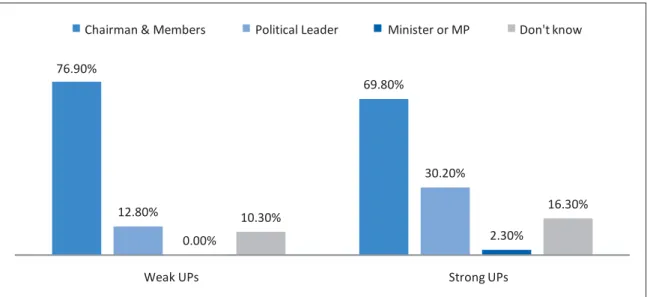
People's Awareness of UP's Governance Mechanisms
UP Committees
Open Budget Meeting
Because of its importance in establishing transparency and accountability at the UP level, the Open Budget Meeting mechanism was further explored. Awareness and participation of citizens in the UP Committee and Public Budget Meeting was also low. Therefore, more emphasis on these issues of inclusivity and good governance will be important in relation to the development process of UP.
Conclusion
Public Finance and Revenue Mobilization of Union Parishes: The Case of Four Union Parishes .. such as the establishment of committees involving the local population, meetings with citizens where their demands are assessed). This, in turn, reduces the public's willingness to pay taxes and excludes public participation in local development.
Recommendation
Measures should be taken to increase people's participation in development planning and implementation processes at the local level. Financial Resource Mobilization Performance of Rural Local Government: Case Study of Three Union Parishad in Bangladesh. Challenges of People's Participation in Local Government: A Case Study on Union Parishad Standing Committees in Bangladesh.
Financial Resource Mobilization Performance of Rural Local Government: Case Study of Three Union Parishad in Bangladesh.
Household Survey Questionnaire
Address and Location of Household Code of Respondents Code List i How far is Union Parishad from your home. In kilometers ii How much time does it take to reach Union Parishad on foot. Does your Union Paris involve community members in the development planning, budgeting and implementation process.
Interview Common Guideline
Public finance and revenue mobilization of union parishes: the case of four union parishes. 4 To what extent are UP potential from the point of view of household, non-household and other taxes?. Was there a possibility of collecting taxes in addition to those already collected from household, non-household and other sources.
Respondent Profile
List of UP Committees