MANSYURAH SADIQAH 109014000047
DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH EDUCATION
FACULTY OF TARBIYAH AND TEACHERS’ TRAINING SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
A “Skripsi”
Presented to the Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers’ Training in Partial Fulfilment
of the Requirement for the Degree of S.Pd. (S-1)
in English Language Education
By
MANSYURAH SADIQAH 109014000047
DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH EDUCATION
FACULTY OF TARBIYAH AND TEACHERS’ TRAINING
SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
English Rings a bell” Used in First Grade Junior High School Based on curriculum 2013, “skripsi” of English education at Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers’ Training of Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic University Jakarta, 2016.
Advisor: Drs. Sunardi Kartowiasastro, Dipl.Ed.
Ertin, M.A.TESOL
Keywords: Content Analysis, English Textbook, First Grade Junior High School, Curriculum 2013.
The purpose of this study is to know and describe the feasibility of content of English textbook “When English Rings a Bell” used in Junior high school, based on curriculum 2013, using the rubric assessment from BSNP, education national standard board. The result of the study is expected to help both teacher and publisher to get better information about the content of a textbook and can make an effort to fulfil the requirement of a national standard textbook if there is any lack of needed content.
The English textbook “when English Rings a Bell” contains 11 chapters as the population, and the writer use 6 chapters as samples. The writer use qualitative method specifically document analysis. The research instrument is the writer herself and the data collected from English textbook “When English Rings a Bell” for junior high school grade VII and document of curriculum 2013.
The result of this research shows that only 68.75% materials in English textbook “When English Rings a Bell” fulfil the feasibility of content requirement. 33 categories out of 48 obtain the score 4. 2 categories obtain the score 3 and 13 categories obtain score 1.
Mansyurah Sadiqah, 2016, Analisis konten buku teks bahasa Inggris “When English Rings a Bell” yang digunakan oleh sekolah menengah pertama kelas VII berdasarkan kurikulum 2013. Skripsi jurusan Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Fakultas Tarbiyah dan keguruan, Universitas islam Negeri Syarif Hidayatullah. Jakarta, 2016.
Advisor: Drs. Sunardi Kartowiasastro, Dipl.Ed.
Ertin, M.A.TESOL
Kata Kunci: Analisis konten, buku teks bahasa Inggris, sekolah menengah pertama kelas VII, kurikulum 2013.
Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk menbetahui dan mendeskripsikan kelayakan isi konten buku teks bahasa Inggris “When English Rings a Bell” yang digunakan oleh sekolah menengah pertama, kelas VII berdasarkan kurikulum 2013, dan juga untuk mengetahui jika buku teks ini memenuhi persyaratan standar kelayakan isi BSNP, badan Standar Nasiobal Pendidikan. Hasil penelitian ini di harapkan dapat membantu para guru dan penerbit buku untuk mendapatkan informasi yang lebih baik tentang konten sebuah buku teks dan dapat berusaha untuk memenuhi persyaratan buku teks berstandar nasional jika ada kekurangan isi materi yang diperlukan.
Buku bahasa Inggris “When English Rings a Bell” mengandungi 11 babsebagai polulasinya, penulis menggunakan 6 bab sebagai sampel. Penulis menggunakan metode kualitatif, spesifik analisis dokumen. Instrumen penelitian adalah penilaian dari penulis sendiri dan data di peroleh dari buku teks bahasa Inggris “When English rings a Bell” untuk sekolah menengah pertama kelas VII dan dokumen kurikulum 2013.
Hasil penelitian ini menunjukkan hanya 68.75% materi buku teks bahasa Inggris (When English Rings a Bell” memenuhi persyaratan kelayakan isi. 33 kategori mendapat nilai 4. 2 kategori mendapat nilai 3 dan 13 kategori mendapat nilai 1.
In the name of Allah, The Beneficent and The Merciful
All praises be to Allah for the blessing and guidance given to the writer for
finally completing this research paper. Peace and blessing be upon to Prophet
Muhammad SAW, his family, companion and adherence.
It is an honour that the writer could finally complete a skripsi entitled A
Content Analysis of English Textbook “When English Rings a Bell” used in First
Grade Junior High School Based on Curriculum 2013. She dedicated this skripsi
to her beloved parents and husband for being a strong pillar of support in
completing this research. Deep gratitude to both of her advisors Drs. Sunardi
Kartowisastro, Dipl.Ed and Ertin, M.A.TESOL for the guidance, patience and
motivation for the writer to accomplish this skripsi. In this occasion, the writer
would like to give the deepest gratitude and salute to:
1. Prof. Dr. Ahmad Thib Raya, M.A as the dean of Faculty of Tarbiyah and
Teachers’ Training Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic University, Jakarta.
2. The head Department of English Education, Dr. Alek, M.Pd. and secretary of
Department of English Education, Zaharil Anasy, M.Hum.
3. All lecturers in Department of English Education for the valuable knowledge,
motivation and guidance during the writer’s study.
4. Parents of the writer, Mr. Syamsuddin and Mrs. Amatul Halim for the endless
support, encouragement, sacrifices and prayers for the sake of the writers’
success.
5. Beloved husband, Nasir Ahmad for his patience, encouragement and love.
roommates.
7. Big family of UKM Bahasa-FLAT UIN Jakarta who has been great friends
and give so many wonderful experiences in university life.
8. To anyone who has contributed for the completion of the writer’s study who
cannot be mentioned one by one.
Jakarta, July 22nd 2016
Mansyurah Sadiqah
ENDORSEMENT SHEET………...ii
CERTIFICATION OF ORIGINALITY………..…..iii
ABSTRACT………..…iv
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT………..….vi
TABLE OF CONTENT………...viii
LIST OF TABLES……….…x
LIST OF APPENDICES……….……xii
CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION………..…..1
A. Background Study……….……..…. 1
B. Focus of the Research……….……...2
C. Research Question………..……….…..……2
D. Purpose of the Study……….…..……..3
E. Significance of the Study……….……..…...3
CHAPTER II: THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK……….….…….….4
A. Textbook...4
1. The Definition of Textbook………..…….…..….…4
2. The Function of Textbook……….…...5
3. How to Analyse Textbook………..…..7
4. Rubric Assessment of Textbook………...…....8
B. Curriculum………..….…22
A. Design of the Study………...26
B. Instrument of the Study………....26
C. Procedure of Analysis………...27
D. Technique of Data Analysis……….27
CHAPTER IV: RESEARCH FINDING AND INTERPRETATION….…..28
A. Research Findings………28
B. Interpretation………45
CHAPTER V: CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION………46
A. Conclusion……….…….……46
B. Suggestion……….…….…….46
1. For Teacher……….……..……...46
2. For Publisher……….………..……….46
REFERENCES……….…..47
APPENDICES……….……....49
Table 2.2 Component of feasibility of content………...13
Table 2.3 Rubric assessment for English textbook ………...18
Table 4.1 Feasibility of content chapter 1 “How Are You?” ………28
Table 4.2 Feasibility of content chapter 2 “It’s Me” ……….31
Table 4.3 Feasibility of content chapter 3 “It’s my Birthday”…………...…34
Table 4.4 Feasibility of content chapter 4 “I Love People Around Me” …..37
Table 4.5 Feasibility of content chapter 5 “How Many Pets Do You Have?” ………...39
Table 4.6 Feasibility of content chapter 6 “Let’s Listen to the Song” …….42
Table 4.7 Feasibility of content frequency tables………..44
Inggris SMP………..…..49
Appendix 2 Deskripsi Butir Instrumen 1 Penilaian Buku Teks
Pelajaran bahasa Inggris SMP……….…...51
Appendix 3 Buku Teks Bahasa Inggris “When English Rings a Bell”……..…57
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
A.Background Study
Englishhas been one of the most taught foreign languages in Indonesian
formal school. Its urgency had been justified by many programs and plans carried
out by the national education department. Despite the banishment of international
standardized school throughout the nation, English subject still remains intact as
one of the national curriculum. To fulfil the needs of learning English, there are
various textbooks available for the use of both teacher and student.
Textbook is one of the most important media for teacher as well as student.
With the aid of textbook, teacher could plan teaching material systematically and
efficiently as textbook provides aim and goal for each lesson. The teacher could
prepare and develop learning materials and class activities effectively. As for
student, textbook can help them as reference in learning so that they’re able to do
self study outside the school session.
The importance of textbook in teaching and learning process makes it
crucial for the teacher to select appropriate textbook for the student as there are
various English books published by many publishing companies. The teacher
needs to be careful in choosing the appropriate one. The content has to be in
conformity with the current curriculum as well as the aim and goal for students to
achieve.
Recently, the curriculum has been changed to curriculum 2013. This
curriculum has significant difference from the previous KTSP (School Based –
Level Curriculum)there are increases in classroom session but decreases in basic
competence or KD. Because the learning session is more to student centred,
associating, delivering, and communicating. 1 Moreover, the content of
curriculum2013 focuses more in developing student’s skill in communication and
using English or in other word productive skill as they will learn to use the
knowledge in daily life.
With the guidelines included in curriculum 2013, it is important for a
textbook used to be in conformity with the base competence,KD listed in the
current curriculum and rubric assessment from education national standard
board,BSNP. For the research, the writer is interested in analyzing the content of
textbook used in the First grade junior high school with the title “When English
Rings a Bell” published by Ministry of Education and Culture of Indonesia to find
out if it fulfils the requirement in current curriculum 2013. This textbook is
chosen because it is used by Al-Kautsar junior high school where the writer had
spent four months doing her teaching internship, or PPKT (Praktek Profesi
Keguruan Terpadu). The writer would like to make an analysis of the content of
this textbook with the title A Content Analysis of English Textbook “When English Rings a Bell” used in first grade junior high school based on curriculum 2013.
B. Focus of the Research
The research focused on the material in “When English Rings a Bell”
textbook and figure out if it comply the requirement specified in base competence
or KD (Kompetensi Dasar) of curriculum 2013
C. Research Question
The formulation of the problem stated as: Are materials in English
textbook “When English Rings a Bell” fulfil the feasibility of content requirement
specified in curriculum 2013?
1
Kementerian Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan 2013, Kurikulum 2013, Kompetensi Dasar SMP, p.4.
D. Purpose of the Study
The main purposes of the study are to find out and describe the feasibility
of content of “When English Rings a Bell” textbook based on the requirement of
the current curriculum 2013.
E. Significance of the Study
The result of the study is hoped to be useful for teacher to have new
information about the content of “When English Rings a Bell”textbook to be used
in the classroom and able to make sure that the textbook is in comply with the
current curriculum. The ministry of education is also likely to find the result of
this research useful, as if any flaws detected, they can find a way to develop and
evaluate the textbook. As the textbooks published by them are expected to be an
CHAPTER II
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
Content analysis is a method of data analysis. It concerns language
material which already exists in a finished form. One of the purposes of content
analysis is to interpret and evaluate.2
The theoretical foundation of qualitative content used in this study related
to communication science. Document is seen as a form of communication which
contains material or information intended for the reader.3
Throughout the recent debate on National examination, it was said that
students in the suburbs and inland lack the access to latest technology in education,
but they are expected to face the same exam as the students from urban areas.
What is so called equality in learning assessment; however it seems to be unfair.
But as long as the exam is truly based on the curriculum used at the moment then
the textbook plays a very important role.
A.Textbook
1. The Definition of Textbook
Textbook is a form of published printed material most commonly used as
teaching and learning media in schools or any educational institution. It is one of
the most important media in learning and teaching process as it serves as a source
and guideline to both students and teacher.
For language learning, Richards mentioned that textbooks serve as the basis for
much of the language input since learners receive and provide the content of the
lessons, the balance of skills taught and the kinds of language practice the students
2
Phillip Mayring, Qualitative Content Analysis; Theoretical Foundation, Basic procedures and Software Solution (Klagenfurt, 2014) , p. 56.
3
Ibid., p. 19.
take part in.4 This explains why at all levels of language learning textbook is still
taken as important resource among students.
On the other hand, Mudzakir concludes that a textbook can be considered as
schoolbook, course book, work book or subject book used in school or
educational institution complemented with materials for exercise as the students
reference book.5
It can be inferred that textbook is a published printed material that serve as a
source and guideline for teachers and students which contain exercises and
reference in the form of schoolbook, course book workbook or subject book.
2. The Function of Textbook
A good textbook is very crucial for both teacher and student. For teacher, it
serves as a guide for each lesson. Textbook for language learning consists of
several chapters. Each chapter will discuss different types and level of language
skill. This will help both student and teacher focus on materials they will teach or
learn. Textbook not only can provide general ideas for teacher to develop
activities suitable for every topic, but also give a brief view for student on what
they should expect for next learning session and at the same time serve as their
reference for practices.
Richards stated that in certain situation, textbook is a form of teacher
training as they give guidelines for ideas and plans on teaching format that teacher
can use. As for students textbook provides as source of contact with the language
they are learning apart from teacher’s input.6
As a resource in achieving aims and objectives that have been set in terms
of learners need, Cunningsworth listed a few roles textbook can serve as in ELT;
a. A resource for presentation material (spoken and written)
b. A source of activities for learner practice and communicative interaction
4
Jack C. Richards, The Role of Textbook in a Language program, March 2015, p. 1,(http//www.professorjackrichards.com/pdfs/role-of-textbook.pdf)
5
Mudzakir AS, Penulisan Buku Teks Yang berkualitas,March 2015,p.4, (http//www.upi.edu)
6
c. A reference source for learners on grammar, vocabulary, pronunciation,
etc.
d. A source of stimulation and ideas for classroom language activities
e. A syllabus (where it reflects learning objectives which have already been
determined)
f. A resource for self-directed or self-access work
g. A support for less experienced teachers who have yet to gain in confidence
Textbook can also be considered as teacher’s partner. The partnership
between teacher and a textbook is at its best when it shares common goals and
each side brings it special contribution. The aim of the textbook also should
closely correspond to the teacher’s aim so both can seek to meet the needs of
learners.7
It can be concluded that a textbook can help both teacher and learner to
reach their aims and adjectives in language learning, but to the extent where the
textbook serve them to reach the goals. “It is generally accepted that the role of
course book is to be at the service of teachers and learners but not to be their
master”8
3. How to Analyze Textbook
Because the textbookanalyzed by the writer is made for Indonesian student,
thus the writer will use the guidelines and instrument from BSNP to analyze the
content of “When English Rings a Bell” textbook. There are three components
that can be evaluated in a textbook assessment;
a. Feasibility of content
1. The compatibility of materials with core o
f
competenceand basecompetence
2. The accuracy of the materials
3. The learning supporting materials
7
Alan Cunningsworth, Choosing Your Coursebook (Oxford: Heinemann Publishers,1995), p. 5.
8
Ibid.
b. Feasibility of presentation
1. The technique of presentation
2. Learning presentation
3. Supporting technique of presentation
c. Feasibility of language
1. The appropriateness with learners’ development level
2. Communicative
3. Coherency and unity of concept9
For this research, the writer will only analyze the feasibility of content
because it covers the analysis of compatibility with the core of competence and
base competent of a textbook which is the most appropriate with the intended
content analysis.
1. Rubric Assessment of Textbook
The huge numbers of textbook available in the market make it crucial for
both teacher and learner to choose the right textbook based on their need. For that,
education national standard board, BSNPhave released assessment instrument
form to help teachers choosing the right textbook. In this case the textbook that
match the standard of core of competence,KI and base competence, KD Junior
High School English grade VII.
Table 2.1
Core Competence and Basic Competence of English Subject Grade VII
CORE COMPETENCE BASIC COMPETENCE
1. Respect and understand the
teaching of their religion.
Being grateful for the opportunities to learn
English language as international
communication medium.
9
Standar Penilaian Buku Teks Bahasa Inggris SMP/MTS. Pusat Kurikulum dan Perbukuan. 2006.
CORE COMPETENCE BASIC COMPETENCE
2. Respect and understand
honesty, discipline,
responsibility, caring
(tolerance, teamwork),
polite, confident in
interacting effectively with
their social and natural
environment within reach of
their association and
existence
2.1 Values polite behaviour and caringin
making interpersonal communication
with teachers and friends.
2.2 Values honesty, discipline, confidence
and responsibility in making
transactional communication with
teachers and friends.
2.3 values sense of responsibility, caring,
cooperation, and peace loving in making
functional communication
3. Understand
knowledge(facts, concepts,
and procedures) based on
their curiosity in
knowledge, technology, art,
culture related to
phenomena and real life
events.
3.1 Understand spoken texts such as
greetings, excuses, thanks, and apology
to build personal connection with other
people within school and house
surroundings.
3.2 Understand the purpose, text structure,
and language element from spoken and
written text for self introduction, brief
and simple.
3.3 Understand the purpose, text structure
and language element to name the days,
months, and time of the day, time in
numeral form, dates and years.
3.4 Understand the purpose, text structure
written text of self identity, brief and
simple.
3.5 Understand the purpose, text structure,
and language element from spoken and
written text to identify the name and
numbers of animals, things and public
buildings closely related to student’s
lives.
3.6 Understand the purpose, text structure
and language element from specific text
in the form of label and list.
3.7 Understand the purpose, text structure
and language element from spoken and
written text to identify characteristics of
a person, animals and things.
3.8 Understand the purpose, text structure
and language element from spoken and
written text to identify
behaviour/action/function of
person/animals/things.
3.9 Understand the purpose, text structure
and language element from specific text,
spoken and written in the form of
instruction, signor short notice,
warning/caution, brief and simple.
3.10 Understand the purpose, text structure
and language element from descriptive
animals and things, brief and simple.
3.11 Understand the message in a song
4. Attempting, processing, and
presenting concretely
(using, analyzing, building,
modifying, and making)
and abstract (writing,
reading, calculating,
drawing and composing) in
accordance to what have
been learned in school and
other sources which shares
the common views/theories
4.1 Composing spoken text to say and
respond to greetings, excuses, gratitude
and apology, with the correct and proper
context of language element.
4.2 Composing spoken and written text to
make and respond to self introduction,
brief and simple by taking notice of
purpose, text structure, and language
element precise and proper with the
context.
4.3 Composing spoken and written text to
name the days, months, time of the day,
time in numeral form, dates and years,
with the correct language element and
proper with context.
4.4 Composing spoken and written text to tell
the student’s origins brief and simple by
taking notice of the purpose and text
structure with the correct language
element and proper with context.
4.5 Composing spoken and written text to tell
the name of animals, things and public
buildings that closely related to student’s
daily lives with the correct language
4.6 Composing written text to make labels
and list, with the correct language
element and proper with context.
4.7 Composing spoken and written text to
identify characteristics of persons,
animals and things, with the correct
language element and proper with
context.
4.8 Composing spoken and written text to
identify behaviour/action/and function of
persons, animals, and things, with the
correct language element and proper
with context.
4.9 Composing specific text in the form of
instruction, short notice,
warning/caution, spoken and written,
brief and simple by taking notice of
purpose, text structure, the correct
language element and proper with
context.
4.10 Comprehend the meaning in instruction
text, short notice, warning/caution, in
spoken and written forms.
4.11 Composing spoken and written
descriptive text brief and simple, about
persons, animals and things by taking
notice of purpose, text structure and
with context.
4.12 Comprehend the meaning in descriptive
text, spoken and written, brief and
simple.
4.13 Comprehend the message in a song
The textbooks developed for grade VII are expected to have these criteria;
a. Developing the ability to use English language in spoken and written form for
the purpose of expanding student’sintellectual, social and emotional aspects.
b. Using proper English that correspond with language methods and
communication context. Language knowledge as complement to master
communication skills.
c. Developing the ability to communicate in English through lesson based on
students daily basic natural environment.
d. Directing to developing life skills; personal, social, academic, and vocational.
e. Developing cross cultural understanding to build friendship within local,
national and international level by expanding vision about cultural differences
to minimise misunderstanding, develop sense of appreciation, and increasing
inter-human relation quality.
f. Oriented to knowledge development and technology.10
10
Instrumen Penilaian I Buku Teks pelajaran Bahasa Inggris SMP/MTS (Badan Standar Nasional Pendidikan, Kementrian Pendidikan nasional, 2006), p.2.
Table 2.2
Components of Feasibility of Content11
Components of feasibility of content include three sub-component; uniformity of
materials with core competence and basic competence, accuracy of materials, and
supporting materials.
A. Uniformity with Core Competence and Basic Competence 1. Completeness
a. Interpersonal texts
It is a compulsory for a textbook to contain and encourage students to explore
at least brief and simple interpersonal texts related to student’s daily lives, to
give them opportunities to understand and to make expression to serve
interpersonal communication functions, spoken and written, to interact with
the students nearby circles.
b. Transactional texts
It is compulsory for a textbook to contain and encourage students to explore
at least brief and simple transactional text to give them opportunities to
ask/give things/favour/information/opinion related to the student’s daily lives
and other school subjects, spoken and written.
c. Functional texts
It is compulsory for a textbook to contain and encourage students to explore
at least brief and simple functional texts and monologues to develop their
scrutinizing, speaking, reading and writing skills about topics that related to
the students daily lives and other school subjects.
11 Ibid.
2. In Depth a. Exposure
For each text, it is compulsory for textbook to contain and encourage students
to explore various texts that relevant with their daily lives for the purpose of
getting accustoms to the texts especially its message.
b. Text Formation Rules Retention
The lessons for each text, it is compulsory for textbook to contain guidelines
so students can get explicit comprehension about three text formation rules
(social function, general structure, and linguistic features) by the time the
students already get accustom interacting about the message contain in the
texts.
c. Production
The lessons for each text, it is compulsory for textbook to contain guidelines
so the students can produce spoken/written text to achieve the social function
relevant to the texts, by taking notice of two other elements (general structure
and linguistic feature) by the time the students already get explicit
comprehension on the three text formation rules.
B Accuracy of Materials 3. Social Function
The texts given in the textbook or result of student’s exploration should be
guided to achieve social function related to the student’s daily lives.
1. Interpersonal communication; to build interpersonal connection (through interpersonal texts). The depth of each material social function at least
appropriate for the coverage of grade VII learning range.
related to the students daily lives and other school subjects, spoken and
written.
3. Functional communication; Play the role of specific function in brief functional texts and monologues related to the following types of texts;
a. Recount serves to explain personal experience such as, success story,
biography, unforgettable experience, chains of events, etc.
b. Narrative serves to entertain and teach noble values.
c. Procedure serves to give guideline in doing or making something, such
as instruction of task, manual, recipe, reminder, etc.
d. Descriptive serves to describe, identify, differentiate, offer, compliment,
criticize, etc. on things/persons/animals.
e. Report serves to explain general truth about persons/ things/ animals,
including types, definition, and common characteristics, as included in
sources of knowledge such as textbooks, encyclopaedias, etc.
4. Element and Structure of Meaning
The texts given in the textbook or result of student’s exploration should be
guided to develop the skill in thinking coherently and systematically.
a. In interpersonal and transactional texts, these elements at least covered
interactive activities such as communication initiate and response in the
form of asking and giving information/ things/favour.
b. In brief functional texts and monologues, it should at least cover elements
of meaning included in each of the following functional texts and
monologues;
1. Recount covers at least orientation and series of activities/events
2. Narrative covers at least orientation, complication, and solution.
3. Procedures cover at least steps in doing certain task, with or without
mentioning explicitly the needed items.
4. Descriptive covers at least elements in persons/ things/ animals as well
as description of each (physic, behaviour, action) that considered
necessary to be delivered to play the role of intended social function.
5. Report covers at least general characteristics of persons/ things/ animals
(physic, behaviour, action) with or without conveying explicitly general
statement in the form of definition or classification.
5. Linguistic Feature
The texts given in the textbook or result or student’s exploration should be
guided to develop communication skills with acceptable and accurate
language quality, appropriate with theongoing communicative context as well
as the type of text used in accordance to achieve intended social function.
C. Supporting Materials 6 Relevance
a. Material relevance and reference source
Teaching materials (texts, tables, illustration, appendix, etc) for each text
taken from sources that relevant with the topic discussed.
b. Up to datedness of material and sources of reference.
Teaching materials (texts, tables, illustration, appendixes, etc), taken from
the latest sources with the topic discussed.
7. Life Skills development
develop life skills such as;
a. Personal skill; know their own and other’s surplus and flaw, improving
themselves to be an independent, social, and god creation being.
b. Social skill; Cooperative, tolerant, appreciate equality of gender, peaceful,
anti-violence in communicating and interacting with other people.
c. Academic skill; search and make use of information, solving problems and
making decision in scientific task.
d. Vocational skill; possess skills, attitude and necessary capability to do
certain task/profession.
8. Diversity Insight
Texts and communicative acts motivate students to do certain things do
develop sense of diversity as follows;
a. appreciation towards multicultural and plurality in community, covering
various cultural values as well as local, national and global wisdom.
b. aware of the region potential and natural resources to promote local and
national potential and natural resources.
c. appreciation of democratic values that appropriate with the local social
culture context.
d. Comprehension of national vision to develop the love toward father land,
Table 2.3
Rubric Assessment for English Textbook12
No Item Remark
I. FEASIBILITY OF CONTENT
A MATERIALS COMPATIBILITY WITH KI AND KD
1. Material Completeness
a. Types of interpersonal texts 4 = The textbook contain brief and simple interpersonal texts, at least
95% of KI and KD materials
coverage.
1 = The textbook contain brief and
simple interpersonal texts less than
95% of KI and KD materials
coverage.
b. Types of transactional text 4 = The textbook contain brief and simple transactional texts at least
95% of KI and KD materials
coverage.
1 = The textbook contain brief and
simple transactional text less than
95% of KI and KD materials
coverage
12ibid
c. Types of functional text 4 = The textbook contain simple and brief functional texts at least 95% of
KI and KD materials coverage
1 = The textbook contain simple and
brief functional texts less than 95%
of KI and KD materials coverage.
2. Materials In-Depth
a. Exposure 4 = Each type of text includes at least 2 examples in the textbook that have
relevant social function and task for
student to find at least 2 examples of
similar texts from other sources.
1 = each type of text includes less than 2
examples in the textbook that have
relevant social function and task for
student to find less than 2 example
of similar texts from other sources.
b. Text formation rules retention
4 = Text formation rules, taught based on
3 elements; social function, element
and structure of meaning, and
linguistic feature.
1 = one from 3 elements of text
formation rule; social function,
element and structure of meaning, or
c. Production 4 = Task to produce text contain 3 text formation elements; social function,
element and structure of meaning,
and linguistic feature.
1 = One of text formation element; social
function, element and structure of
meaning or linguistic feature are not
included in the task.
B MATERIALS ACCURACY
3. Social Function 4 = At least 95% of texts are useful to achieve the exact social function.
1 = Less than 95% text are useful to
achieve the exact social function.
4 Generic structure 4 = At least 95% generic structure of text appropriate with its social function.
1 = less than 95% generic structure of
text appropriate with its social
function.
5. Linguistic feature 4 = At least 95% linguistic feature of the text appropriate with its social
function.
1 = less than 95% linguistic feature of
the text appropriate with its social
C LEARNING SUPPORTING MATERIAL 6 Up-to-Datedness
a. The relevance of materials and source of reference
4 = Overall 91% —100% teaching
material taken from relevant source
of reference.
3 = Overall 76% —90% teaching
material taken from relevant source
of reference.
2 = Overall 61% —75% teaching
material taken from relevant source
of reference.
1 = 0%—60% teaching material taken
from relevant source of reference.
b. Up-to-date material and source of reference
4 = Overall 91% —100% of sources
published in the past 4 years.
3 = Overall 76% —90% of sources
published in the past 4 years.
2 = 61% —75% of sources published in
the past 4 years.
1 = 0% —60% of sources published in
the past 4 years.
7. Life Skills Development;
- Personal
- Social
4 = Overall contain texts that contain
91% —100% life skills element.
- Academic
- Vocational
76% —90% life skills element.
2 = Overall contain texts that contain
61%—75% life skills element.
1 = Overall contain texts that contain 0%
- 60% life skills element.
8. Development Of Diversity Insight;
- Appreciation to multicultural and plural society.
- Aware of local potential and resources.
- Appreciation of democratic values.
- Comprehending the national vision.
4 = Overall contain texts that contain
91% —100% elements of diversity
insight.
3 = Overall contain texts that contain
76% —90% elements of diversity
insight.
2 = Overall contain texts that contain
61% —75% elements of diversity
insight.
1 = Overall contain texts that contain 0%
—60% elements of diversity insight.
1. Curriculum
1. Definition of Curriculum
There have been various definition of curriculum depends on the approach
to it. Allan and Francis specified five basic definition of curriculum which also
defined by other experts in curriculum studies;
a. Curriculum can be defined as a plan for achieving goals. The plan involves a
sequence of steps as wiles and Bondi proposed. Curriculum is a four step plan
b. Curriculum can be defined broadly, as dealing with learner’s experiences.
Dewey proposed that almost anything happened in or outside of school is part
of the curriculum. It can be interpreted that curriculum consists of the ongoing
experiences of children under the guidance of the school.
c. Curriculum is a system for dealing with people
d. Curriculum can be defined as a field of study with its own foundations,
knowledge domains, research, theory, principles, and specialist. Those who
adopt this definition tend to discuss curriculum in theoretical aspect instead of
practical terms.
e. Curriculum can be defined in terms of subject matter or content. This
definition emphasizes the fact and concepts of particular subject areas.13
In other source, Prof. Dr. Nana Syaodih referred to Beauchamp stating that
curriculum as a lesson plan and a system (curriculum system) which is part of
school system. As a lesson plan, curriculum includes main aim to be achieved, ,
learning activities, learning materials and timetable.14
It can be inferred that curriculum is a system in school or education
establishment involving purpose, design, implementation and assessment of
learning materials and activities.
2. Curriculum 2013
There have been frequent changes of curriculum for the past 10 years in
Indonesia. There was KBK (Competence Based Curriculum) which syllabus is
made by school and teacher. Compiled based on the characteristics of the school
in the aspect of school, teacher, and student competence.15KTSP (School
Based-Level Curriculum) which is developed from KBK itself with an addition in
13
Allan C. Ornstein, Francis P. Hunkins, Curriculum: Foundation, Principles and Issues, (U.S.A: Pearson, 2009) , p. 10.
14
Nana Syaodih Sukmadinata, Pengembangan Kurikulum:Teori dan PraktIk, (Bandung; PT Remaja Rosdakarya, 2009), p. 6.
15
Departemen pendidikan Nasional, Kurikulum Berbasis Kompetrensi (Jakarta: Pelayanan Peofesional Kurikulum 2004, 2003), p. 14.
completing the SK, competence standard, and KD, Basic competence.16and the
recent one Curriculum 2013 which was released on July 2013.
There are several development and improvement in curriculum 2013
compared to the previous one in KTSP. For the junior high school level, the
curriculum structures have been simplified due to the reducing of subject and
learning material.
Learning hours is increased to 38 hours per week with 40 minutes span for
each session. The purpose of increasing learning hours and reducing based
competence so that the teacher can develop more on the lesson and the student can
be more involved in active learning.17
Not only are there changes in curriculum 2013, but also an addition was
made. Core of competence was introduced in the new curriculum. It functions as
organising element for basic competence. Core of competence is arranged in four
interconnected groups; religious attitude, social attitude, knowledge and
knowledge application.
The cores of competence listed for English subject for junior high school are;
(1)Appreciate and understand the teachings of their religion:(2)Appreciating and understanding honesty, discipline, responsibility, social awareness (tolerance, mutual cooperation), courteous, and self confidence in interacting effectively with social environment within reach of their existence:(3)Understanding knowledge (factual, conceptual and procedural) based on their curiosity in knowledge, technology, art, culture related to phenomena and real:(4)Attempting, cultivating, and delivering in realm of concrete (use, parse, string up, modify and make) and abstract (writing, reading, calculating, drawing and composing) corresponding to what has been learned in school and other sources with similar view/theory.18
16
Departemen Pendidikan Nasional, Buku Saku Kurikulum Tingkat Satuan Pendidikan (KTSP) Sekolah Menengah Pertama (Jakarta; 2009) , p. 2.
17
Kementrian pendidikan dan Kebudayaan, Kurikulum 2013:Kompetensi Dasar SMP (Jakarta; 2013) , p. 4.
18
Kurikulum 2013: Kompetensi Dasar SMP/MTs, (Kementerian Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan, 2013), p.6.
Generally in curriculum 2013, the students are expected to develop their
potential to be a person of faith, courteous, creative, healthy, independent, tolerant,
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This chapter will elaborate on the details of research methodology which
divided into design, instrument, and procedures of the study and the technique of
data analysis.
A. Design of the Study
The design used for this study is qualitative research. More specifically as
document analysis. This method is widely applied for written or visual data with
the purpose of identifying specific characteristic or materials that are going to be
analyzed in general form of textbook, newspaper, or any other host of
documents19. The writer used the document analysis method to study the
textbook “When English Rings A bell” for Junior High School grade VII. The
characteristics and material of the textbook is tabulated according to the list of
content expected by BSNP to be included in all Grade VII English textbooks.
The writer used descriptive qualitative to analyze, interpret and report the data
provided in the textbook. From total 11 chapters in the textbook, the writer will
only analyze 6 chapters as the sample of the research.
B. Instrument of the Study
The instrument used in this study is the writer herself. In qualitative study,
the researcher is the one to decide what to observe and what to write down in
reflecting her own values, assumption and beliefs to determine the impact of the
data interpretation.20
19
Donald Ary.et al., Introduction To Research In Education, 8th Edition(Belmont : Wadsworth, 2010), p.457.
20
Donna M. Mertens, Research and Evaluation in Education and Psychology 4th Edition (USA: Sage Publication. Inc., 2015) , p. 261.
C. Procedure of Analysis
For the procedures of analysis, these steps were taken in the study:
1. Read and comprehend the data from BNSP (Badan Standar Nasional
Pendidikan) and curriculum 2013 in first grade of Junior high school English
subject. These will be the main guideline to determine the compatibility of
English textbook “when English Rings A bell” with the current curriculum.
2. Observe and scan through the content of material in the textbook “when
English Rings a Bell”.
3. The data obtained from the textbook then categorized and arranged in detailed
information to be analyzed based on the characteristic described in rubric
assessment of BNSP.
D. Technique of Data Analysis
Using the complete data collected from textbook “When English Rings A
bell”, and the rubric assessment from BNSP, the analysis was done using these
following steps:
1. Comparing the material presented in the textbook with the category of
required characteristic of an English textbook by rubric assessment from
BSNP.
2. Evaluating material in the textbook “When English Rings A Bell” by giving
score in respected category listed in the rubric assessment.
3. Interpreted the data gained from the process of evaluation.
4. Summing up the compatibility percentage of the textbook content. The writer
use the following formula to present the data forms in numbers
P = F
N× 100%
P = Percentage
F = Frequency
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH FINDING AND INTERPRETATION
In this chapter the writer presented the data collected from the textbook
analysis. The data descriptions are divided into research findings and
interpretation of data.The research findings will be presented using a score table
of feasibility of content for each chapters followed by the description for each
category on why it got its respective score.6 chapters are taken for the samples.
There are 8 categories for each chapter, with total 48 categories being
analyze. The total score finding for all 6 chapters then accumulated in frequency
table and the end result will be presented in percentage that represents the
conformity of the English textbook “When English Rings a Bell” with the
requirement from BNSP.
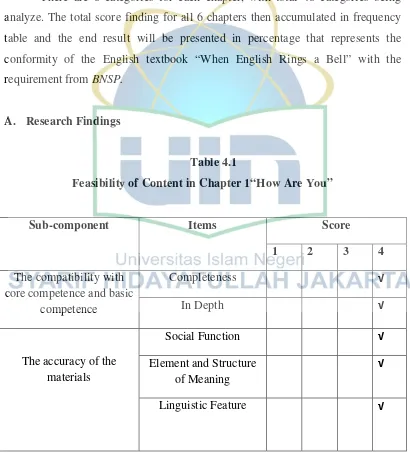
A. Research Findings
Table 4.1
Feasibility of Content in Chapter 1“How Are You”
Sub-component Items Score
1 2 3 4
The compatibility with core competence and basic
competence
Completeness √
In Depth √
The accuracy of the materials
Social Function √
Element and Structure of Meaning
√
Sub-component Items Score
Supporting Materials
Relevance √
Development of Life Skills
√
Development of Diversity Insight
√
Total 1 7
1. The Compatibility of Materials with Core Competence and Basic Competence.
a. Completeness
The materials are complete as listed in basic competence table; student is
expected to understand and able to produce spoken text such as greetings, excuses
thanks and apology to build personal connection with other people within school
and house surrounding. Several examples of interpersonal and transactional texts
of greetings as shown from page 3 to 8, expressing thanks in page 15 and 17, take
leave in page 10, and apology page 19 and 20.
b.In-depth
This chapter provide exercises for student to explore more on ways to greet
and response to inquiry. Various illustration of situation on when and who the
students are greeting as included in the exercise in page 6, exercises to ask their
classmates feelings on that day in page 9, identifying the person and place they
greet in page11, build up student critical thinking in figuring out the correct
greetings and inquiry in a dialogue in page 12 to 16. It also gives the proper
context for student exercises so they can understand and produce the text orally
1. Accuracy of Materials a. Social function
This chapter fulfilled two criteria of social function; interpersonal and
transactional communication. Students are thought to interact through the
interpersonal and transactional text by greetings with proper context of the
students surrounding, asking for favour or inquiry.
b. Element and structure of meaning
This chapter fulfilled this criterion. The interpersonal and transactional
texts covered the interactive element that encourages students to initiate
communication and response to it in the form of asking and giving
information/favour. Students are given various examples in how to produce
expression of greetings and response to greetings using simple structure of
grammar, and also the polite way to ask for favour are shown in page 17.
c. Linguistic Features
The language features are appropriate with the intended communicative
context.Students are exposed to various ways in greetings, take leave and apology
using brief and simple interpersonal and transactional texts. Students are shown
how to use the proper language use in greeting and response to greeting. The
correct context and illustration support the language in asking for favour and
apologizing as shown in page 17 and 19.
2. Supporting Materials a. Relevance
The illustration in this chapter is very accurate with the students’ daily
context. Each picture shows the correct real life situation for each type of text
learned, such as the illustration that shows student’s surrounding at school and
also their home. The dialogues use the common interaction happened in student’s
b. Life Skills Development
The aspect of life skill implemented in this chapter is social skills.
Students are taught to interact with their classmates, teachers and people around
them by exchanging and responding to greetings, student are also taught to care
for their friend by asking their feelings, offering a helping hand and apologizing
after doing something wrong.
c. Diversity insight
There are no aspects of development of diversity insight as this chapter
focus only on greetings and asking for favour or apology.
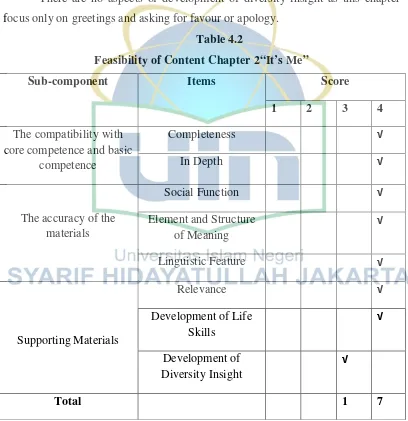
Table 4.2
Feasibility of Content Chapter 2“It’s Me”
Sub-component Items Score
1 2 3 4
The compatibility with core competence and basic
competence
Completeness √
In Depth √
1. The Compatibility of Materials with Core Competence and Basic Competence
a. Completeness
This chapter covers the requirement as stated in basic competence;
Understand the purpose and able to compose spoken and written text of self
introduction brief and simple using appropriate text structure and precise language
element within context.There are several texts that presented how to make self
introduction as shown in page 25, 28, 30, and 36 as well as how to introduce other
people in page 35.
b. In Depth
The exercise in this chapter varies; students are exposed to several
exercises on a simple way of self introduction in page 26, introducing other
people in 29 and response to inquiry of self introduction in page 31. Students are
also encouraged to make interaction with their classmates by asking their personal
detail, this is a form of transactional conversation of giving information in page 33
and 34. These are also exercises that require students to interview other people by
asking their favourite colour and food in page 34.
2. The Accuracy of Materials a. Social Functions
This chapter covers the element of interpersonal and transactional
communication. Students are exposed to explore their knowledge about
themselves and other people. Students are required to give information about
themselves as well as interviewing their classmates to obtain information about
them as instructed in the exercises in page 35.All the context are related to
students daily lives and encourage student to interact with their surroundings to
b. Element and structure of meaning
The element and structure of meaning is appropriately developed. The
students are taught to do a simple structure of self introduction before advancing
to introduce other people. The students then required to obtain information of
other people. These transactional interaction fulfil the criteria of social function.
c. Linguistic Features
The texts used in this chapter are brief and simple, and commonly used in
students daily live and serve the purpose of communication. The dialogues are
short and serve its purpose for self introduction as shown in page 27 and
introducing other people in page 29.The example of simple conversation of asking
personal details also used simple and comprehensible text as shown in dialogues
in page 30.
3. Supporting Materials a. Relevance
The chapter provide relevant illustration for each type of text. The pictures
of characters are those of students and the people of their circle; classmates,
teachers, and neighbours these illustration match well with student’s context in
their daily lives. The context of material also revolves around the student’s daily
interaction at school surrounding.
b. Life skills Development
The exercises in this chapter require students to interact with their
surroundings to obtain information in their school context by finding information
about their friends, teachers and community. The life skills developed in this
chapter are personal and social skills. Students are encourage to know their own
and other’s surplus and flaws and implement appreciation in communicating and
c. Diversity Insight
This chapter includes the appreciation to multicultural society. In the first
few pages, students were introduced to different regions in Indonesia
accompanied by illustration of certain region’s unique iconic buildings.Some of
the texts and exercises contain element of different race and culture in Indonesia.
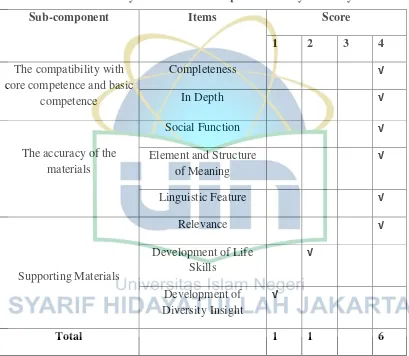
Table 4.3
Feasibility of Content in Chapter 3“It’s My Birthday”
Sub-component Items Score
1 2 3 4
The compatibility with core competence and basic
competence
Completeness √
In Depth √
3. The Compatibility of Materials with Core Competence and Basic Competence.
a. Completeness
This chapter covers the materials as proposed in the basic competence;
understand the purpose, text structure and language element, as well as composing
spoken and written text to name the days, months, and time of the day, time in
numeral form, date and years. The text include all expression listed such as
naming the name of days in pages 44 to 46, time in page 51 and 52, months in
page 56 and 57, and dates in page 58 and 60.
b. In-depth
The exercises in this chapters requires student to explore the sequence of
days and their activities in certain day as shown in page 47. Students are required
to list down their daily schedule in page 47. And to identify which day the student
do certain activities in page 48 and 49, followed by exercises to tell the time and
certain daily activities in page 53 to 55. Students then showed on how to inquiry
the date of classmate date of birth as has listed in page 59.The last exercise
courage students to explore the dates of national day’s celebrations in page 60 to
61.
4. Accuracy of Materials a. Social function
In social function, this chapter includes simple recount text and descriptive
text. Students are taught to recall personal experience of activities in certain days
and describe certain activities and events on specific dates. Most of the text is
transactional interaction in exchanging information about days, time, months and
dates.
b. Element and Structure of Meaning
The element and structure of meaning is well implemented. The students
activities followed by time. The students then exposed to naming the months and
followed by dates. Students are later required to initiate communication in order
to obtain information about them.
c. Linguistic Features
The texts used in this chapter are brief and simple; the students are guided
to explore ways of naming the day, time, months and dates and followed by
developing communication skill to inquire events of certain dates. The dialogues
are short and the language quality is accurate and appropriate for the level of VII
grader.
3. Supporting Materials a. Relevance
The chapter provide relevant illustration for each type of text. The pictures
relate to students activities at certain time and days. There’s also a picture of a
calendar to give students more information on name of the months. These
illustrations match well with student’s context in their daily lives.
b. Life Skills Development
Most of the text covers personal and academic skills. The materials cover
the information related to student’s daily activities in school and at home and
develop interaction between students to find out information about their
classmates.
c. Diversity insight
In term of diversity insight, there are few exercises that require students to
explore Indonesia historical dates. Students are exposed to historical dates as
shown in page 60 and 62, and required to explore more important national
Table 4.4
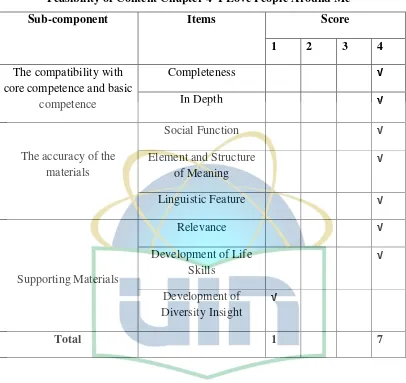
Feasibility of Content Chapter 4“I Love People Around Me”
Sub-component Items Score
1 2 3 4
The compatibility with core competence and basic
competence
Completeness √
In Depth √
The accuracy of the materials
1. The Compatibility of Materials with Core Competence and Basic Competence
a.Completeness
The materials are complete in this chapter as listed in basic competence.
The students are expected to understand the purpose, text structure and language
element to make spoken and written text of self identity and family members.
The texts cover on how to tell students personal identity as shown in page 68.
Students are also exposed on ways to describe their family members in page 70
and 74. The student also taught to identify their relation in a family tree as shown
b. In Depth
The examples of texts are detailed. There are more than 2 exercises in this
chapter. Each exercises guides the students to explore different type of ways in
introducing themselves. First the students are required to write their own identity
and personal detail in page 70, followed by describing their siblings in exercise at
page 71. Describing the rest of family members included in exercise in page 75
to77. The last two exercises, the students are taught to write their daily activities
with family members and write a letter to express love for their mother in page 80.
2. The Accuracy of Materials a. Social Functions
The chapter covers the functional communication in the form of
descriptive text. The task in this chapter specifically require student to make self
identification. The students describe themselves and their family members by
giving compliment as well to them. Later on the exercise require students to
describe their family activities as shown in page 79. The exercise in page 80 help
student to express their affection for their parents.
b. Element and structure of meaning
The structure is very systematic in this chapter. Students are first taught to
introduce themselves using simple sentence. Examples to make the sentence are
shown in page 68. The task then followed by introducing and describing family
members. This task require longer sentence and examples are given to guide the
students in page 70, followed up by describing family activities and writing a
letter in page 80.
c. Linguistic Features
The language features are appropriate for students. In this chapter the students
are required to make longer text in describing themselves and their family
surrounding and the descriptive texts are, simple but more detail in describing the
student personal identity and family members.
3. Supporting Materials a.Relevance
The illustrations used are appropriate and depict a simple family structure.
An illustration of family tree is included in page 73 to aid student in identifying
the relation within the family. Overall it represents the common family structure
of three generation.
b. Life skills Development
This chapter includes personal and social life skills. Students are taught to
get to know themselves and family members and appreciate the differences within
the family.Knowledge of their own family improve the student to be independent
and able to express affection towards family members.
c. Diversity Insight
The texts and exercises in this chapter do not include any cultural elements.
Table 4.5
Feasibility of Content Chapter 5“How Many Pets Do You Have?”
Sub-component Items Score
1 2 3 4
The compatibility with core competence and basic
competence
Completeness √
In Depth √
Sub-component Items Score
1. The Compatibility of Materials with Core Competence and Basic Competence
a. Completeness
This chapter includes the requirement stated in the basic competence;
understand the purpose, text structure and language element from spoken and
written text to identify the name and numbers of animals, things, and public
buildings closely related to student’s lives as well as able to compose spoken and
written text related to the materials. The texts cover vocabularies of names of
things in page 85. The items are related to common stationary equipment used in
the classroom by student. The things commonly found in the house are shown in
page 87 to 90. Vocabularies of animals in page 94 and 96, as well as ways to
construct the number of animals. Names of Public places are shown in page 97.
b. In Depth
There are many exercises for different types of text. Starts from naming
the objects commonly found in classroom and the number of the objects as found
in page 86. There are also exercises that require student to compose a sentence
based on the items they can identify in a certain room in page 88 to 90.Exercise to
make sentence using the information given are included in page 91 to 93, which
related to things commonly found in student’s daily lives. In page 95 to 96,
numbers of animals. And in page 97 student are given task to identify public
building commonly found in their town.
2. The Accuracy of Materials a. Social Functions
The texts used are meant for descriptive purpose by identifying things and
differentiating them with others. In this chapter, students are encouraged to
explore and identify the things commonly found in their area and able to make
description in terms of the name and numbers of things, animals and public
building commonly found in their area using the correct language element and
proper with context
b. Element and structure of meaning
The element and structure of meaning is implemented in a systematic way.
Students are given example names of things, animals, and public building. Next
the exercises require students to make sentences with the aid of illustration of
common things and animals found within their surroundings. And later compose
sentence using the simple information given. The English language level used are
simple and the difficulty increase only slightly for the level of VII grader.
c. Linguistic Features
The linguistic features are appropriate with the intended social function in
giving description of things, animals and public places. Examples of text are using
very simple forms and vocabulary and appropriate with the student daily context
in describing items.
3. Supporting Materials a. Relevance
The illustrations used are appropriate and show the things that are mostly
available at student’s surrounding within their school, such as stationary items,
pets and animals commonly kept in zoo, neighbourhood and nearby public
establishment.
b. Life skills Development
There is little life skills development element in this chapter. In the aspect
of academic skill in search and making use of information, the chapter mainly
focus on vocabulary building.
c. Diversity Insight
The texts and exercises in this chapter do not include any cultural elements.
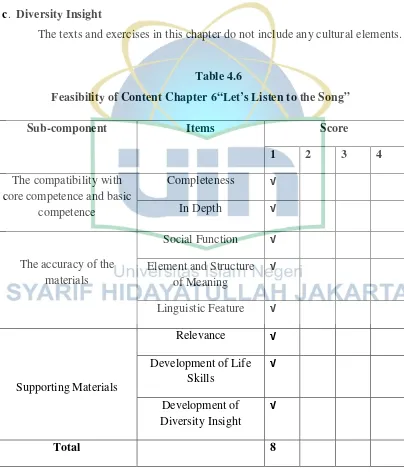
Table 4.6
Feasibility of Content Chapter 6“Let’s Listen to the Song”
Sub-component Items Score
1 2 3 4
The compatibility with core competence and basic
competence
Completeness √
In Depth √