IMPROVING STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY MASTERY THROUGH RIDDLE AT SECOND YEAR STUDENTS OF
SMP N 2 ABUNG SELATAN
By
Septia Mursanti Candra Rahman
A Script
Submitted in a Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements for S-1 Degree
In
The Language and Art Department of Teacher Training and Education Faculty
UNIVERSITY OF LAMPUNG BANDAR LAMPUNG
ABSTRACT
IMPROVING STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY MASTERY THROUGH RIDDLE AT SECOND YEAR STUDENTS OF
SMP N 2 ABUNG SELATAN
By
Septia Mursanti C. R.
Vocabulary mastery is always being an essential part of English as a foreign language. There is no doubt that vocabulary mastery plays an important role in the four language skills. The research is conducted based on the problem of the low vocabulary mastery of the second year students of SMPN 2 Abung Selatan.
The objectives of this classroom action research are to find out 1) How can the use of riddle improve students’ vocabulary mastery 2) how can the use of riddle improve students’ activity during teaching learning process. The research is conducted at SMP N 2 Abung Selatan. The subject of this research is the students of grade VIIIE in the academic year 2012/2013.
This classroom action research was conducted in three cycles; each cycles consisted of planning, action, observation and reflection.The resultsare there are three steps which should be implemented in using riddle to improve students’ vocabulary mastery, they are; introducing, knowing and practicing. By implementing those three steps, not only students vocabulary mastery improved but also students’ activity during teaching learning process.
LIST OF APPENDICES
1. Lesson plan 1... ... 74
2. Lesson plan 2... ... 78
3. Lesson plan 3... ... 82
4. Lesson plan 4... ... 86
5. Lesson plan 5.... ... 89
6. Lesson plan 6... ... 93
7. List of vocabulary score... ... 97
8. Vocabulary test 1... 98
9. Vocabularu test 2... 101
10.Vocabulary test 3... 104
11.Questonnaire.... ... 107
I. INTRODUCTION
This chapter consists of background of the problem, formulation of the research,
objectives of the research, uses of the research, scope of the research and definition of terms.
1.1 Background of the Problem
English as an international language is very important to be learned. By learning English, the students can help themselves to face their future because English is needed in facing the globalization era. It is also a top requirement for those
seeking for job because the applicant who master English whether in passive or active are more favorable than those who do not master it.
One of the most difficult and important aspect of learning a foreign language is the retention of vocabulary. Vocabulary can not be separated from the language
because vocabulary is a part of language. Vocabulary is important for learning language because of several reasons. First, the ability to understand the target language greatly depends on one’s knowledge of vocabulary. Second, vocabulary
According to the pre observation which has done by the researcher, students often
find difficulties in using a foreign language because they are lack of vocabulary and they often forget easily new vocabulary after they get the meaning from
dictionary. Sometimes in speaking class, students can not speak fluently because they are lack of vocabulary. They say only a few sentences because they can not find the appropriate vocabulary to be used in expressing their ideas. The same
problem is found in writing classes that students can not write essays easily because they are lack of vocabulary. Even though they have already learned the
strategies or techniques in writing essays, still they will find difficulties in constructing sentences. They will find difficulties in choosing and using the
appropriate vocabulary.
Vocabulary is the first step to be taught before teaching other aspects of language.
Vocabulary mastery is essential part of English as a foreign language. There is no doubt that vocabulary mastery plays an important role in the four language skills. It gives contribution to the learners to perform or practice their skills better.
Because of that reason, by mastering the vocabulary, they will be able to produce so many sentences easily either in spoken or written and to receive words in
reading and listening.
Without vocabulary nothing can be conveyed because vocabulary is the flesh of a
language. In order to be able to use the language productively, students must know certain amount of vocabulary, not only for communicating orally, but also
3
learners have a big chance to use the language directly in classroom activities.
This approach is useful in improving students’ vocabulary. Through the approach students are forced to use the language directly either in spoken or written
communication.
Vocabulary must not be neglected by everyone who learns a language. The
students need to master it in order to master the language. That’s why teaching vocabulary considered as the most important thing in the English language
teaching.
The mastery of structure of the language without adequate mastery of vocabulary could not guarantee a capability of communication in English. Vocabulary is very important to be mastered since it is an essential means for conducting
communication. Therefore, vocabulary mastery must be on the first priority in English language teaching and learning. Without mastering the vocabulary the learners will get difficulty to master the other language skills.
Unfortunately, based on the researcher’s experience when she was teaching
English course at Junior high school, she found that 9 out of 10 students are lack of vocabulary. They got difficulties in learning English. They also became passive in doing the activity in the class. It’s hard for them to express their ideas. They
Another possible problem was that the way of teaching and learning vocabulary
used by the teacher is monotonous. It made the students bored while learning language. Because of that reason, the English teacher should create the technique
or using an interesting media in teaching in order to make the students more interesting in learning English.
From the researchers’ preliminary study at the second semester of the second year students in SMP N 2 Abung Selatan, it was found that most of students are lack of
vocabulary and also low motivation in learning language. They became passive during the teaching learning process, because they could not understand the
meaning of the words. They can not get the information from the lesson. They also had low motivation in learning English. They neglected the teacher who is teaching in front of the class.
It is not an easy thing to teach English subject to the students, especially to make them mastered the vocabulary. Therefore it is important to make the students
enjoy studying English especially vocabulary by making an interesting condition in the class. So choosing appropriate technique and media in teaching vocabulary
is important in order to improve their vocabulary.
Considering the statement above, the researcher was interested to use an enjoyable
5
Riddle is excellent tools because they require students to practice a variety of
language skills in order to find a solution. Riddle requires higher level critical thinking skills, which is often needed in language learning, especially in the early
stages of language acquisition where a significant amount of time is devoted to memorization and repetition. Riddle not only asks students to think logically and creatively, but also a fun challenge to students, who will be motivated to solve the
puzzle the riddle provides.
Yuliana (2011) also has conducted a research about using riddle in improving students’ vocabulary and the result was riddle could improve students’ vocabulary
because they can easily remember the vocabulary.
One interesting feature of riddle is that they appeal to all age groups, from the
wise and experienced to the very young. Over the years the nature of riddle has changed. Riddle game require ingenuity to solving riddle, so it can make students’ more training their brain, with it students can be more motivated to learn
vocabulary.
By conducting this research, it is hoped to produce model that is effective and can be used by the teacher in using riddle game in teaching vocabulary in order to help students improve their vocabulary mastery and their participation during
teaching learning process.
could be fixed in the next cycle. Action research provides the best way to identify
the steps of using riddle in teaching vocabulary. Finally the procedures of teaching vocabulary through riddle can be developed for the improvement of
learning process based on the emphirical data collected in this research.
1.2 Formulation of the Problem
Based on the background discussed above, the writer would like to formulate the problem as follows:
1. How can the use of riddle improve students’ vocabulary mastery at second year of SMPN 2 Abung Selatan?
2. How can the use of riddle improve students’ activity during teaching learning process?
1.3 Objective of the Research
Based on the problem above, the objectives of this research are as follows: 1. To find out how the use of riddle improve students vocabulary mastery.
2. To find out how the use of riddle improve students’ activity during teaching learning process.
1.4 Uses of the Research
This research will be useful both practically and theoretically.
1. Practically
Hopefully, this research would be useful for the English teacher, students,
7
a. The teacher
Through this research, the English teacher could use the riddle as the media and also as a technique in teaching vocabulary and also could improve his or her teaching performance.
b. The students
The use of riddle in this research would make the students get
accustomed to use English as the target language. So, by using riddle,
the students could be helped to improve their vocabulary and also their learning activity during the teaching learning process.
c. The school
The result of this research could be used as a consideration for the school in order to use riddle as the media and also a technique in
teaching vocabulary. Although this media could be used only for specific lesson, but it could be used for all levels, not excepted for
intermediate level.
2. Theoretically
The result of this research produced a new method how to use riddle effectively in teaching learning process, especially in conducting the
1.5 Scope of the Research
This research is conducted in SMPN 2 Abung Selatan. The subject of this research is the second year students in class VIII E. In this Action Research, the researcher conducts two cycles. The first cycle is done based on the problems of the research
and the next cycle is done based on the result of the analysis and the reflection from the previous cycle.
Besides the students’ vocabulary mastery, the researcher also focused on students’
learning activities covered to their activities on pre – activities, while – activities, and post – activities.
1.6 Definition of Term a. Teaching Vocabulary
Teaching vocabulary means the process of giving knowledge to others the
goal of which is to improve vocabulary of the students.
b. Vocabulary Mastery
Vocabulary mastery is the ability of students to use English vocabulary in teaching learning process.
c. Riddle
II. LITERATURE REVIEW
This chapter explains about concept of vocabulary, kind of vocabulary, concept of teaching vocabulary, concept of riddle game, teaching vocabulary through riddle
game, and the advantages of using riddle game in teaching vocabulary.
2.1 Concept of Vocabulary
Vocabulary has an important role in learning language because it allows you to communicate clearly with other people. Vocabulary is a tool that must be
mastered by people to express their feelings, ideas, thought, opinion, etc in both spoken and written (Edge, 1993).
Vocabulary is a list of words which is used to build up a language. Vocabulary is a list of words usually arranged alphabetically and defined, explained, or
In learning language, students use vocabulary to communicate, share their ideas
and opinion with others. On the other hand, language is nothing without knowing the vocabulary.
Schmitt (1997) gave the definition of vocabulary as follows. Vocabulary is a basis of language which is very important to be mastered first. We cannot speak well
and understand written materials if we do not master it. Schmitt stated that no matter how successfully the sound of the foreign language is mastered, without
words to express the wider range of meanings, communication in a foreign language just cannot happen in any range of meaning.
Vocabulary is a set of lexeme including a single word, compound word, and idiom. Simple word is a single word that may not have a prefix and suffix,
example: book, pen, bag, etc (Lamb, 1963). Compound word is two or more existing words, which are simply combining. Idiom is a group of words with meaning which is different from the individual words and often difficult to
understand, for example: move on, look up, look at, look in, etc.
2.2 Kind of Vocabulary
As stated by Fries (1974:4), vocabulary can be classified into some types namely:
2.2.1 Content Words
11
Nouns are words used to identify people, places, things, and ideas. It
also word which occurs as a part of subject o a sentence or an object of a verb. Crystal (1995: 206) defines eight kind of noun as follows:
1. Adjectival Noun
Adjectival noun is an adjective that functions as a noun. The examples of adjectival noun are highlighted, 1) The other is still on
the way, 2) The poor asked any food from the rich. 2. Animate Noun
Animate noun refers to a person, animal, or other creature. This sometimes has different noun endings which make the gender clear. Examples of animate noun are: 1) The actor act perfectly, 2)
The teacher is writing in the white board. 3. Collective noun
Collective noun is a word used to define a group of objects, where the objects can be people, animals, emotions, concept or other thing. It is a noun that refers to things or people as a unit. Example:
1) The team joins the match; 2) The audience gives their applause to the singer.
4. Concrete noun
Concrete noun refers to entities which can be observed and measured. Example: 1) She holds many books. 2) My parents buy a
5. Abstract noun
Abstract noun refers to unobservable nations, such as difficulty, idea, certainty, etc. Example: I put my sister’s art up on the fridge.
6. Countable noun
Countable noun refers to individual, countable entities, such as books, houses, flowers, for example: He bought three books of
psychology. 7. Uncountable noun
Uncountable noun refers to an undifferentiated mass or notion, such as butter, water, sugar. For example: I add some sugar in his
coffee. 8. Proper noun
Proper nouns are names of specific people, place, time, occasions,
events, publications and so on. Proper nouns are not usually used with the determiners. It is also written with an initial of capital letter. The examples of proper nouns are: 1) I love Indonesia 2) I
went to a beach on Sunday 3) They watch the FIFA World Cup Championship.
b. Action done by with those things, that is: verb.
It is the words which express an action or help to make a statement.
The verb is perhaps the most important part of sentence. A verb or compound verb asserts something about the subject of the sentence and
13
predicate of a sentence and sometimes carries numbers of grammatical
categories, such as tense, aspect, and mood. There are some types of verbs. They are:
1. Auxiliary verb
Auxiliary verb is also called as helping verb. This helping verb assists the main verb in a clause to express several basic
grammatical contrasts, such as in a person, number and tense. They do not follow the same grammatical rules as main verb, which is
why they must be considered as a separate class.
Auxiliaries can be used before the word “not”. It is also put before
the subject in order to ask a question. The examples are: 1) They do not understand what he said. 2) Does she have a boyfriend? 3) Sinta does not want to meet her anymore.
2. Inchoative verb
Inchoative verb is a verb that describes a change of state. The
examples of inchoative verb are freeze, dry, burn, rise, etc. The examples in the sentences are: 1) The refrigerator freezes
everything in it. 2) The fire burns the wood.
3. Modals
Modal verbs convey a range of judgments about the likelihood of events. The function of modals is only as an auxiliary verb,
independent than those of lexical verbs. There are nine verbs in this
class: can, could, may, might, will, would, shall, should and with dare, need, ought to and used to having a very similar function. Here are the examples of using modals in sentences: 1) I will go to the beach. 2) You should obey your parents.
4. Phrasal verb
Phrasal verb is a set of verbs which demonstrate some unique
properties. It appears with what looks to be a preposition, traditionally referred to as particle. Here are the examples of phrasal verb: 1) The plane took off. 2) I am looking for my watch.
5. Regular and irregular verb
A regular verb is the verb that follows the pattern of taking –ed for the past tense and past participle or –d if the word ends in e, such as walk=walked, for example: He walked alone to school.
An irregular verb is the verb that does not take the –ed ending for the past tense and past participle forms. Some irregular verbs do
15
c. Qualities of the things, that is: adjectives.
It is the word used to qualify noun and pronoun. An adjective modifies a noun or a pronoun by describing, identifying, or quantifying words.
An adjective usually recedes the noun or the pronoun which it modifies.
In the following examples, the italic words are adjectives: 1) The small
boat foundered on the wine dark sea. 2) The back room was filled with large, yellow rain boots.
An adjective can be modified by an adverb, or by a phrase or clause
functioning as an adverb in the sentence, for example: 1) My husband knits intricately patterned mittens.
1. Possessive adjective
A possessive adjective (my, your, her, his, its, our, and their) is similar or identical to a possessive pronoun; however, it is used as
an adjective and modifies a noun or a noun phrase, as in following sentences: 1) I can’t complete my assignment because I don’t have
the text book. 2) What is your phone number?
2. Demonstrative Adjective
The demonstrative adjective this, these, that, those, and what are the identical to the demonstrative pronouns, but are used as
sentences: 1) When the librarian tripped over that cord, she dropped a pile of books. 2) This apartment needs to be fumigated.
2.2.2 Function words
Function words are those words which one is used as a means of expressing relation of grammar or structure, such as conjunction (and,
however, but), e.g.:
a. Andi is cleverer than Indah but Ronnie is not like him.(conjunction)
b. Dian and Desy have a cat.
2.2.3 Substitute words
Substitute words are those words which represent the individual things or specific action as substitutes for whole form classes of words (anybody, anyone, somebody, and someone), e.g.:
a. Everyone has left the room. b. Nobody is perfect
2.2.4. Distributed words
Distributed words are those word that distributed in use according to grammatical matter as the presence or absence of a negative, such as any, either, etc, e.g.:
17
Based on the all the kinds of vocabulary above, the writer focused on content
words that consist of noun, verb and adjective. Those three kinds of content word were considered as the most important word in the part of speech or word order.
As mentioned by Yuliana (2011) the vocabulary items for SMP students based on 2004 English Curriculum are divided into two kinds. Those are the classification of word according to the theme and class. The theme for the second year students
according to Department National Education are: Flora and Fauna, Friendship, Travel, Health, Teenage life, Recreation, Seasons.
Vocabulary items based on the theme consist of words that should be learned in
context. It is also taught in a different theme. The theme which was related to vocabulary is considered to fill the competence target. Moreover, vocabulary items are produced from genre: descriptive, narrative, recount, procedure, report,
etc. For the second grade student of SMP, genre is classified based on the semester. In thefirst semester for example, students are learning narrative text and for the second semester, students are learning descriptive text. In descriptive text,
the social functionis to describe flora and fauna, place or thing.
2.3 Concept of Teaching Vocabulary
In teaching vocabulary, the teachers have responsibility to make their teaching successful. Scoot (2007) says that there are four ways of teaching vocabulary.
1. Definitional methods include anything where a student is given a word and a definition. The students may be given a list of words and have to look
for new vocabulary words without discussing the meaning beyond the
definition. According to Nagy & Scot (1997), traditional practices of vocabulary leaning are based on the definitional approach. The focus of
this approach is to learn the meanings of the words either looking up in dictionary or glossary or by drill. It is considered the easiest and less time consuming approach to vocabulary learning. It saves time of teacher as
well the students and makes them able to study maximum words in minimum time. However, it is not a guarantee that this approach improves
comprehension of the students and increases the active vocabulary of the learner. Sometimes, learning definition does not necessarily helpful in the
integration of the knowledge. There is a need of background information for the integration of the knowledge.
2. Contextual methods of vocabulary instructions ask the students to create a meaning for a word based on the rest of sentence or paragraph. The instructional method also teaches students how to use a new vocabulary
word in the right context by writing original sentences using the new word. According to Weatherford (1990), Context Based Approach of
vocabulary learning is the most effective, and it saves lot of time of the learner that is wasted in going to dictionary again and again. Contextual evidence helps the learner to find out the meanings of the new words. It is
based on teaching the meanings of new words by having them used in different contexts surrounding the words. There are two types of context:
19
instructional context refers to sentences specifically written to introduce
the meanings of the new words. The natural context refers to text sentences written to communicate ideas of the text. To understand the
meanings of the new words, the students need to know the information related to the topic in which the words are embedded. Difficult words can also be explained by giving summary of it. For example, she speaks without break and do not give chance to anybody else to speak in the meeting. She is really a loquacious lady. In this respect, referent words, synonyms, antonyms, hyponyms, definitions, alternative and restatement help to reach at the meanings of the words. Context based approach not
only helps the reader to know the meaning of the words but also help and facilitate in the use of them. It develops independent learning habits, inculcate problem solving approach and promote active learning process.
The words that have got different meanings with the same spellings and pronunciation are very difficult to be learnt without context based approach. For example, the word pen is also used as a noun and verb, and
at the same time it has also got the meanings a shed where poultry birds are kept. In the same way, the sentence such as his fur coat was coated
meanings of the words without any context. The contextual information
helps the learner to understand the meanings of the words that have got different meanings.
3. Organizational or semantic framework instruction, students learn relationship between and among similar words. This type of instruction
includes the use of concepts maps, semantics maps, and other graphic organizer. When semantic maps are used as a vocabulary teaching
technique, the teacher chooses a central word from the text, and key ideas together with new related vocabulary words grouped and listed by
categories. During discussion of the map, students become aware of the meanings of the new words, learning new meanings for old words, and discover the relationships that hold between the various vocabulary items
and the ideas discussed and mapped (Hague, 1987; Johnson & Pearson, 1984). Semantic processing techniques such as semantic mapping are characterized by two processes: first, learners focus on the meaning of the
new words under study; second, they integrate these new words into their existing semantic system and their previous experiences (Brown & Perry,
1991; Hague, 1987). In sum, semantic mapping enables learners to understand the relationships among words by helping them use their prior knowledge since the right “interpretation of new information hinges on its
21
4. Mnemonic instructional methods make use of vital images as a way of
help students learn and remember new terminology. Instead of memorizing abstract definitions, students are encouraged the picture
something that helps them associate a word meaning. Structural methods of vocabulary instruction show students how to look at the parts of the word for clues about what the new word means. A previous study which
claims that this type of morphological word study is especially useful to the students who are learning English as an additional language (Scoot,
2007). According to Filmore and Snow (2000), structural approach of teaching vocabulary is based on the morphological analyses of the word. It
is process of breaking the words into prefixes, root and suffixes to illustrate the meanings. It is considered easy and practical approach of vocabulary building. The morphological features of the language such as
prefixes, suffixes, and root help the learner to identify the meanings. The students do not analyze the sentences to find out the meanings of the word but analyze the word to follow its meanings. Knowledge about the root
form of the word helps them to build up their vocabulary in logical and in sequenced way. After getting command over the root form of the word,
there is no more difficulty to modify it as different parts of speech and build up the vocabulary. The words that are generated by the learner can be recalled easily as compared to merely listened or read. It is, therefore,
necessary that the students must be provided opportunities to generate new words from the given exercises. For example, the students might be asked
greatly improve the vocabulary of the students. In the same way
punctuation marks also help the reader to understand the meanings of difficult words such as Full stop indicates the completion of the thought, comma indicates continuation of the thought and semi colon, colon indicate the reversal of the thought.
All of the ways above is good to teach vocabulary, but in this research the researcher used the contextual method because the researcher assumed that those
learning method helped the students to memorize the vocabulary and it was also suitable with riddle game.
2.4 Concept of Riddle Game
In teaching vocabulary, unless there is a challenging way or technique, the
students may not be interested in learning. But riddle game gave the students chance to improve the student’s vocabulary.
There are many definitions of riddle. According to Evan (1957), riddle is the nouns all refer to something baffling or confusing which is to be solved.
According to Brassell (2008) a riddle is a statement or question or phrase having a double or veiled meaning, put forth as a puzzle to be solved.
A riddle, sometimes called a "brain teaser," is usually a question that requires clever or unexpected thinking for its answer. In general conversation, someone
23
guessing the correct response. The guesser may get one or multiple guesses and
sometimes the asker gives clues, but this is not required. Riddle usually has only one correct answer, and it is commonly provided in the end, even if the guesser
does not think of it.
In general, riddle can be divided into two main sections namely enigmas and
conundrums. The enigmas are a type of a question that is presented in a metaphorical language. These can be cracked or solved only after careful
observation of the problem statement. Most of the ancient English poems had these kind of enigmas embedded within them. Conundrums are similar to enigmas
but for the fact that the answer lies hidden in the question itself and application of the concept of punning can bring out the real answer hidden within the question. The usage of different meanings with a common spelling too, can extract the
hidden truth (Rashid, 1951).
The structure of a riddle typically uses one of several techniques to create a twist,
which makes it difficult to guess. One common technique involves double meanings. If the double meaning is in the words of the question, then the language
creates intentional confusion. The asker intends one meaning and hopes that the guesser will understand the words differently. Here is an example: It has three eyes, all in a row. When the red one opens, all freeze. In this riddle, the asker intends for the guesser to understand the word “eyes” as a connotative, so the “eyes” is not as the real eyes. The eyes here are the light in traffic light, and the
According to Nation (1990:24) the characteristic of a good game are:
1. Game should be suitable in all students’ level.
2. Game should motivate students to enlarge their vocabulary.
3. The materials of game should challenge to the students.
Riddle game is appropriate with three steps in teaching vocabulary. Riddle is also
challenging for the students, because to correctly solve a riddle, students need:
to listen carefully and correctly interpret linguistic subtleties to learn to ask precise and effective questions
to precisely articulate a logical and convincing solution
Riddle requires higher level critical thinking skills, which are often needed in
language learning, especially in the early stages of language acquisition where a significant amount of time is devoted to memorization and repetition. Riddle not only ask students to think logically and creatively, but also are a fun challenge to
students, who will be motivated to solve the puzzle the riddle provides.
Wright (1984) said that riddle game provides an entertaining way for students to
identify vocabulary words, use the definition of a vocabulary word to create a riddle, for example, a riddle for the word "umbrella" might go, "When the drops start to fall, you protect me to keep dry”. Vocabulary riddle work as an oral activity for the class or as a written assignment in the form of a worksheet. Based on that statement, riddle can be used as an oral activity or as written assignment
25
2.5 Teaching Vocabulary through Riddle Game
According to Haycraft as cited by Hidayatul points out that there are many ways of presenting new vocabulary. They are:
1. Creating a context or situation from which the students can then deduce the meaning.
2. Describing, defining object and drawing if it is necessary.
3. Taking the students out and introduce words for things seen in a shop windows, or in the street.
4. Using word game. There are large varieties of these, e.g. riddle which it is useful for practicing and revising vocabulary after it has been
introduce.
Using word game is the way that the researcher chooses to play with. In teaching vocabulary, the researcher will used three stages: pre viewing, while viewing, and
post viewing.
Pre viewing
The purpose of pre viewing activity is to stimulate the student’s background knowledge or developing learner’s comprehension strategies. The activities which
would be done are:
Telling the students that they are going to play with riddle presented in English and asking them some questions to stimulate their background knowledge, for
While viewing
In this step, the riddle would be presented more. The purpose of this activity was to make the students more active and challenging in answering the riddle which
has been given by the teacher. The activities that could be done are:
First viewing is as global understanding. Give the first riddle in English, and try to solve it together and helped by the teacher. This is to make the students know how
to solve the riddle. So in solving the next riddle, it will be easier. And also ask the students to guess the topic and content.
Second viewing is presentation of language. After first viewing, ask the students
several questions to check their understanding of the context of the riddle.
Post viewing
Post viewing activities were often connected to the idea of using language that comes from the riddle. The activity that could be done are asking the students some questions about their understanding about the topic after being taught by
using riddle and having them do the vocabulary task.
2.6 Advantages of using Riddle game in teaching vocabulary
As we know that there are many techniques in teaching vocabulary and game could be one of them. Some expert says that games used for teaching vocabulary
27
1. Games bring in relaxation and fun for students, thus help them learn and
retain new words more easily.
2. Games usually involve friendly competition and they keep learners
interested.
3. Vocabulary games bring real world context into the classroom and enhance students' use of English in a flexible, communicative way. Games
are highly motivating and they give students more opportunity to express their opinions and feelings.
4. Games add diversion to the regular classroom activities," break the ice", but they are also used to introduce new ideas.
As a kind of game, the advantages of using riddle in teaching vocabulary are: 1. Students are more interested in learning the material. When they are
interested with the material, they will pay more attention to the lesson. 2. Students also feel more challenged, because to solve the riddle need a
critical thinking.
III RESEARCH METHOD
This chapter discusses about research method, research setting and subject,
population and sample, research procedure, indicators of the research, data collecting technique, and data analysis.
3.1 Research Method
This research is an Action Research. In this research, the researcher acted as a real teacher, and the English teacher as the observer, who observeed what the researcher did when conducting the research. This study was directed to develop
the teaching strategy in order to find out the solution to the classroom problem in the teaching of vocabulary.
There are four steps of classroom action research:
1. Planning the action 2. Implementing the action
29
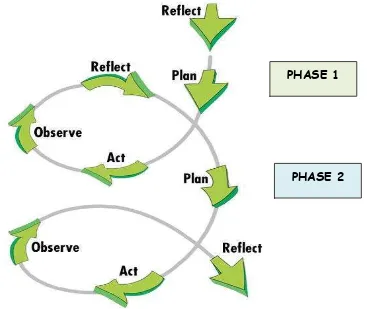
[image:34.595.132.499.119.428.2]Here is the concept of action research according to Carr & Kemmis (1986).
Figure 3.1 Carr and Kemmis’s Action Research Model (1986)
The research was begun with the planning. In this step, there were several things to plan such as the lesson plan, material and technique, instruments and the
criteria of successful. After planning those things, then the researcher continued to the acting step. This was the implementation of the things which had been made
in the planning step. While the teaching learning process was conducted in acting step, the researcher also did the observation step. This step was used to observe
the students activity during the teaching learning process. The next step was reflecting. The researcher reflected the successful of research by looking the data which had been collected in the acting and observing step. If the result was not
satisfying yet, then the researcher conducted the next cycle which was begun with the planning step again.
PHASE 1
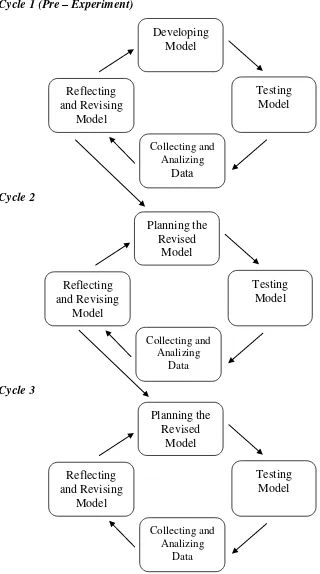
Here is the cycle of Action Research according to Setiyadi (2013).
Cycle 1 (Pre – Experiment)
Cycle 2
[image:35.595.115.435.116.690.2]Cycle 3
Figure 3.2 Cycle of Action Research according to Setiyadi (2013)
According to the figure above, the first cycle of the research was a pre – experiment and then the next cycle was the second cycle and so on. From the
31
experiment it was already found a model which was developed based on some
aspects that were suitable for teaching. After having a revised model, the researcher made preparation to teach the students using the model (in Action
Research, it was included into Planning). Then the model that had been revised was being tested for its effectiveness in learning process. Model testing here also means the action in the class (Acting/Implementing). The next step was data
collecting and analysis (Observing). It was done by observing what was going on and what problems that occured in the teaching learning process while the model
was being applied. The last step was reflection and revised the model (Reflecting). The researcher did the reflection to fix the model based on the problems occurred
and after being fixed, the model was applied in the next cycle. This process was repeated from one cycle to the next cycle until the researcher got a model which had been modified through some improvements. (Santi, 2013)
3.2Research setting and subject
This research was conducted in SMP N 2 Abung Selatan. The subject of this
research was the students of second grade of SMP N 2 Abung Selatan. The researcher acted as the real teacher, while the real teacher acted as the observer.
The problem of this class was the students were not active in teaching learning process, and also they had lowest average score than the other class.
3.3Population and Sample
Koenjaraningrat defines population as the entire object of research (1997: 115). In
sample are taken (1989: 53). In this research, the population were students of
SMPN 2 Abung Selatan. There are fourteen classes in this school, five classes of the first grade, five classes of the second grade, and four classes of the third grade.
Sample is part of population which researched. The researcher took the second grade as the sample in VIII E because as the result of pre observation, the researcher found that students in VIII E have lower ability than the other class.
3.4Research Procedure
The procedures of this study were: preliminary study, planning, action, observation, and reflection.
a. Preliminary study
Preliminary study was done to get information about the teaching learning process in the SMP N 2 Abung Selatan. The researcher met the principal
of the school to talk about the research, and the English teacher to get the information about the problem which is faced by the teacher in teaching the students, and also to get the information about the ability of the
students in learning English. After conducting the interview with the English teacher, the analysis was carried out. From the analysis, the researcher found out the student’s vocabulary competence. The data
obtained from the analysis was used to set up an action plan. b. Planning
In this case, the researcher prepared suitable model of using riddle game to improve students vocabulary mastery, designed a lesson plan, prepared
33
1. Lesson plan
The lesson plan was made by considering the standard competence, basic competence, indicators, material, teaching methods, activity and
assessment.
2. Instructional material
The material of this research was taken from the textbook which were
relevant to the topic or other resource which has been selected by the researcher.
3. Technique
The technique of this research was using riddle game. The riddle was
also the media in teaching learning process. c. Action
After arranging the planning, the researcher continued to the next step that
was action. The researcher as the teacher taught the students by using the riddle game as a technique and media. She was helped by the teacher who acted as the observer to observe the students activity. The teaching
learning activity took about 2x45 minutes. Then after the teaching learning process, the students were given questionnaires.
d. Observation
Observation was done when the teaching learning process. This was done by the English teacher as the observer. It took the same time with the
e. Reflection
The researcher was helped by the teacher to do the reflection of the result of the first cycle and made the plan for conducting the second cycle if the
result of first cycle was not satisfying enough.
3.5 Indicators of the Research
In order to see whether riddle could be used to improve student’s vocabulary in this Action Research, the researcher determined the indicators dealing with
learning process. The indicators were:
1. Learning Process
For the learning process, there was one aspect which became the focus of this research, it was, the student’s learning. The observation of student’s learning activities was done to know the activity of the students whether they were active
or not in teaching learning process. It was divided into three activities: pre – activity, while – activity, and post – activity. In the pre – activity, the researcher observed the student’s interest in following the class and responding to the topic.
In the while – activity, the researcher observed the student’s attention to the explanation of the teacher and their focus to the vocabulary which were taught,
and also their participation while doing the group works. In the post – activity, the researcher observed the students understanding about the vocabulary which were being taught by the teacher. If the students’ activity involved in the learning
process were not improved and the teaching performance was not good, the researcher would find out the problems and try to find the solution by revising the
35
2. Learning Product
The learning product of this research was not based on the KKM because as
mentioned by Setiyadi (2013) KKM which are used to be indicator of successful is not always relevant with the Action Research which was conducted by students of university. The student’s research is not always referred to objectives of
teaching which are exist in curriculum, so the researcher here just observed whether there was any improvement of students vocabulary in every cycle by
comparing the result of the test at the end of every cycle. If there was no improvement of student’s score, there would be some problems and it was used as
a reflection to revise the model for next cycle.
3.6 Data Collecting Technique
In getting the data, the researcher employed the observation, the questionnaires and vocabulary test.
1. Observation
Observation is a method of data collection in which the situation of interest is watched and the relevant facts, actions and behaviors are recorded. According to
Setiyadi (2006) the purpose of observation is to explain the situation being investigated, the activities, and people or involved in an activity and the relationship among them.
The observation here was to observe student’s participation during the teaching
2. Questionnaire
Questionnaire is a document that is used to guide what questions are to be asked
respondents and in what order, sometimes lists the alternative responses that are acceptable. In this research, the questionnaires were given to the students after teaching learning process. The purpose was to know about the student’s opinion
about their experiences after being taught using riddle. (See Appendix)
3. Vocabulary Test
In assessing students vocabulary mastery, the researcher used the multiple choices
questions which consisted of a, b, c, and d. There were 30 items of question in the vocabulary test. The questions were given at the end of each cycle. This test was used to know how far students understand the material being taught.
There are some criteria of a good test. The test should have the reliability and validity. For reliability of the test, the researcher used two raters or called
inter-rater reliability. And for the validity, the researcher used the content and construct validity to measure the validity of the test. To fulfill the content validity, the
researcher should look at the questions and analyzed whether the test had represented the whole material which would be measured. If the test had represented all the idea of the material which would be measured, the test had
fulfilled the content validity (Setiyadi, 2006). The researcher had made the vocabulary test based on the curriculum, so the researcher assumed that this test
37
which has some indicators in one aspect, for example, if the test was made to
measure vocabulary mastery, the construct validity could be measured by evaluating the questions. If the questions have measured the vocabulary mastery,
the test has fulfilled the construct validity. In this test, the researcher used the theory from Nation (2001) who said that knowing a word involves knowing its ‘form’, ‘meaning’ and ‘use’. There are three main parts of ‘form’, they are spoken, written, and word parts. While there are three main parts of ‘meaning’,
they are form and meaning, concept and references, and associations. And the last, there are four main points of ‘use’, they are grammatical, collocations, constrait
on use, register and fluency.
To test the students whether they know how the selected words are written and spelled, can be tested by a ‘dictation’; To test the students about the usage of the
selected words, the students can be asked to identify the words with the closest meanings in a multiple-choice vocabulary test; To test the students whether they know the grammatical functions, the collocations and the constraints on the use of
[image:42.595.114.512.625.746.2]the selected words, can be tested by a cloze test, or a guided writing test to elicit the relevant lexical knowledge from the students.
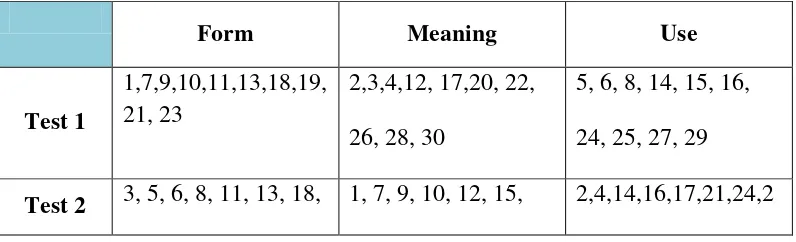
Table specification of vocabulary test
Form Meaning Use
Test 1
1,7,9,10,11,13,18,19, 21, 23
2,3,4,12, 17,20, 22, 26, 28, 30
5, 6, 8, 14, 15, 16, 24, 25, 27, 29
22, 27, 28 19, 20, 23, 30 5,26,29
Test 3
1, 5, 7, 12, 15,20,
23, 25, 27, 29
2, 4, 8, 9, 14,18, 19,
22, 24, 28
3, 6, 10, 11, 13, 16,
17, 21, 26, 30
3.6 Data Analysis
Data analysis was the process of organizing the data in order to gain regularly of the pattern and form of the research. The term interpretation could be defined as a procedure of giving meaning on the result of analytic process. Data analysis was
done to create understanding of the data and after following the certain procedure, result of the study could be presented by the researcher to the readers (Setiyadi,
2006).
In analyzing the data the researcher classified the data into two categories that were the data of learning process and learning product. Analyzing the data was done during and after collecting the data from every cycle.
1. Learning Process
In the learning process, observation was done to the students by the observer during the teaching learning process by observing the whole activities in the class and filling the observation sheets.
2. Learning product
39
compared in every cycle whether there was any improvement or not. If there was
no improvement, the researcher would analyze the problem that were faced by the students and find the solution to solve the problems. And the solution would be
applied in the next cycle.
2.1. Student’s Learning Activities
In analyzing the data from observing student’s learning activities, the researcher
did the following steps:
a. Identify the problems that occurred in learning process
The researcher identified the problem which occur while the learning process in
every cycle. The problem about students learning activities were identified in this step.
b. Making a description from the data that had been analyzed.
V CONCLUSSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS
5.1 Conclussions
Considering all the data gathered after finishing the research, which had been held in the second year of SMP N 2 Abung Selatan, some conclusion can be drawn as
follows:
1. The way to improve students’ vocabulary mastery by using riddle is by implementing the introducing, knowing, and practicing steps.
2. By implementing those three steps, the students’ activity during teaching
learning process can also improved.
5.2 Suggestions
Based on the finding, the researcher will state the suggestions as follows:
1. Having the research about using riddle in improving students’ vocabulary
mastery, the researcher suggests the English teachers to apply the media in the classroom for teaching.
70
more active. Give them instruction to increase their confidence to be
actively involved in learning.
3. When doing the group discussion, the teacher should pay attention to the students who have higher ability. The teacher should control them in order
REFERRENCES
Brassell, Danny& Furtado, Leena. Enhancing English As A Second Language
Students’ Vocabulary. (The Reading Matrix, 2008) Vol. 8, No. 1
Brown, T. S., & Perry, F. L. Jr. (1991). A comparison of three learning strategies for ESL vocabulary acquisition. TESOL Quarterly, 25(4), 655–670.
Carr, W. & Kemmis, S. (1986) Becoming Critical: education, knowledge and action research. Lewes, Falmer.
Crystal, D. 1995. The Cambridge Encyclopedia of the English Language. Australia: Cambridge University Press.
Departemen Pendidikan Nasional, Kurikulum 2004, (Jakarta: Pusat Kurikulum, Balitbang Depdiknas: 2003 iv, 88 hal, 2003) p. 33
Dorry, Gertrude Nye. Games for Second Language Learning. (New York: Mc. Braw-Hill, Inc) p:56
Edge, Julian. 1993. Essentials of English Language Teaching. London: Addison Wesley Publishing Company.
Evans, Bergen&Evans, Cornelia. 1957. A Dictionary of Contemporary American Usage. New York: Random House, Inc.
Fillmore, L. W. & Snow, C. E. (2000). What Teacher Heeds to Know about Language. Eric Special Report No: ED-99-CO-0008. Washington, D.C.
Fries, C. 1947. Teaching English as Foreign Language. Michigan: Michigan University Press.
Hidayatul, Nur. 2002. The Analysis of vocabulary Teaching Trough Puzzles. Thesis Surabaya: UNESA, p. 25.
Hornby, A. S. 1984. Oxford Advanced Learner’s Dictionary. New York: Current English University Press.
Iskandar. 2008. Penelitian Tindakan Kelas. Ciputat: Gaung Persada, h. 28 Koentjaraningrat. 1997. Metode-Metode Penelitian Masayarakat. Jakarta: PT.
72
Lamb, A. 1963. Word Studies. Ohio: South Western Publishing.
Mardalis. 1989. Metode Suatu Penelitian Proposal. Jakarta: Bumi Aksara
Mifflin, Houghton (1997). Project – Base Learning Space. [Online]. Available :
http://college.cengage.com/education/pbl/background.html. [26th of May
2013]
Naghy, W. & Scott, J. A. (2000). Scott, J.A., Noel, D.J. & Asselin, M. (2003). Vocabulary instruction throughout the day in 23 upper elementary classrooms. The Elementary school Journal, (VOL)103, 3. University of Chichago.
Nassaji, H. (2007). Schema theory and knowledge-based processes in second language reading comprehension: A need for alternative perspectives. Language Learning, 57(1), 79–113.
Nation, I. S. P. 1990. Teaching and Learning Vocabulary. Boston: Hinle and Heinle Publisher.
___________. (2001). Learning Vocabulary in Another Language. Cambridge, New York, Cambridge University Press.
Rashid, Ahmed Abdel. Teaching vocabulary using riddles. (Article: 1951)
Santi, Siti Amalina. 2013. The Implementation of EXCLUSIVE Learning Model In
Improving Students’ Speaking Skill at the First Grade of SMAN 9
Bandarlampung. Lampung: University Of Lampung
Schmitt, N. 1997. Vocabulary in Language Teaching. USA: Cambridge University Press.
Scoot, J.A. 2007. Competents of affective Vocabulary Instruction: Building word schemas. Paper presented at the International Reading Asosiation Annual Conference. Toronto : Canada.
Setiyadi, Ag. Bambang.2006. Metode Penelitian untuk Pengajaran Bahasa Asing: Pendekatan Kuantitatif dan Kualitatif. Yogyakarta: Graha Ilmu.
___________________.2013. Penelitian Tindakan Untuk Guru dan Mahasiswa (Fothcoming).
Weatherford, H.J. (1990). Techniques for Learning Vocabulary. New York: Oxford University Press.
Wright, Andrew. Betteridge, David. Buckby, Michael. (1994). Games for Language Learning.[Online]. Available:
http://www.teflgames.com/why.html. [28th of May 2013]
Yuliana, Siska. 2011. Improving Student’s Vocabulary by Using Riddles Game at the Second Grade Students of MTS Miftahul Ulum Bendung Mojokerto. Surabaya: IAIN Sunan Ampel
Uberman, A. (1998).The Use of Games For Vocabulary Presentation and Revision. Forum. Vol. 36. Page 20. [Online]. Available:
http://exchanges.state.gov/forum/vols/vol36/no1/p20.htm. [26th of May