AN ANALYSIS OF YEAR IX PRIMAGAMA
STUDENTS’ ABILITY IN MASTERING
ELLIPTIC CONSTRUCTION
A THESIS
BY
DONA MARLINA P 060721018
UNIVERSITY OF NORTH SUMATRA
FACULTY OF LETTERS
ENGLISH LITERATURE DEPARTMENT
MEDAN
Approved by the English Departement of Faculty of letter University of Sumatera Utara ( USU ) Medan as thesis for the Sarjana Sastra Examination.
Chairperson, Secretary,
AN ANALYSIS OF YEAR IX PRIMAGAMA STUDENT ABILITY IN MASTERING ELLIPTIC CONSTRUCTION
A Thesis By
Dona Marlina P Reg. no. 060721018
Supervisor, Co, Supervisor
Drs. Yulianus Harefa, M. Ed, TESOL Dra. Roma Ayuni Lubis.,MA
NIP. 131570483 NIP.132207809
Submitted to Faculty of Letters University of Sumatera Utara
In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirement for S1 in English Departement
ENGLISH DEPARTEMENT
FACULTY OF LETTERS
UNIVERSITY OF SUMATERA UTARA
MEDAN
Accepted by the Board of Examination in Partial Fulfillment of Requirement for The Degree of Sarjana Sastra from the English Departement, Faculty of Letters, University of Sumatera Utara, Medan.
The Examination is held on the faculty of Letters, University of Sumatera Utara on .
The Dean of Faculty of Letters University of Sumatera Utara
Drs. Syaifuddin, M.A. Ph.D NIP. 131284310
Board of Examiners Signature
TABLE OF CONTENTS
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
ABSTRAK
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
1.1Background of the Analysis 1.2Scope of the Analysis 1.3Problem of the Analysis 1.4Objective of the Analysis 1.5Significance of the Analysis 1.6Method of the Analysis 1.6.1 Methodology
1.6.2 The population and sample 1.6.3 The techniques
1.7Review of Related Literature
CHAPTER II
A BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF ELLIPTIC
CONSTRUCTION
2.1 Positive Elliptic Construction 2.2 Negative Elliptic Construction 2.3 Opposite Elliptic Construction
CHAPTER III
METHOD OF RESEARCH
3.1 Methodology
3.2 The population and sample
3.3 The techniques of collecting data
CHAPTER IV
ANALYSIS AND FINDINGS
4.1 Analysis
4.2
Findings
CHAPTER V CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS 5.1 Conclusions
5.2 Suggestions
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Firstly, I would like to thank the Almighty Allah SWT for the blessing and giving me an opportunity to accomplish this paper. Furthermore, I would like to express my deepest gratitude to all the people who have been around me to give support
accomplishing this paper:
1. Drs. Syaiffuddin, M.A., Ph. D. the Dean of Faculty of Letters, North Sumatera University.
2. Dra. Swesana Mardia Lubis, M. Hum, the Head of English Literature Departement.
3. My Supervisor, Drs. Yulianus Harefa, MEd TESOL, thank you for your concern and suggestion in completing this thesis.
4. My Co- supervisor Dra. Roma Ayuni Lubis, M.A, for your advice and suggestion for my thesis in order to be better.
5. All lecturers, especially in Extension Program who have thought and given me many useful knowledge during the years of my study.
6. My beloved parents, my dad H. Bahar Dullah and my mom Hj. Maimunah, thank you for you very much for all that you have given for me.
7. My dear brothers, Syahrial Syahputra, Edi antony, Bakri Zalil, and special thanks for my Manik Doni especially for borrowing me your computer.
8. My beautiful sisters, Junita, Deliani Spd and Susilawati for your caring for me. 9. My spirit friend, Sister Tati, Sister Husna and Sister Wulan who give me
10. My Classmates, especially, Usrotun Saidah, Ing – ing, Nining, Gita, Bang Samuel, Supriadi and all my friends whom could not be mentioned one by one. I wish all of us will get a success in the future and easy to get a job and also we can be a friend forever. I will never forget you my friends.
I realize that this thesis is still far from being perfect. Therefore, I welcome
constructive criticisms and suggestions. I hope this thesis will be useful for the reader.
Medan, Maret 2008
The Writer,
DONA MARLINA P
ABSTRAK
Skripsi yang berjudul “ An Analysis of Year IX Primagama Students’ Ability in Mastering Elliptic Construction ” merupakan suatu analisis tentang kemampuan siswa tahun IX dalam memahami Elliptic Construction dalam tata bahasa Inggeris. Siswa tahun IX tersebut adalah siswa dari beberapa sekolah yang ada di kota Medan yang mengikuti bimbingan belajar di Primagama Cab. Aksara yang beralamat di jln. Letda Sujono No. 108 Medan Dalam mengerjakan skripsi ini penulis menggunakan metode field research ( penelitian lapangan ) yaitu mengambil data dari siswa tahun IX yang mengikuti
ABSTRAK
Skripsi yang berjudul “ An Analysis of Year IX Primagama Students’ Ability in Mastering Elliptic Construction ” merupakan suatu analisis tentang kemampuan siswa tahun IX dalam memahami Elliptic Construction dalam tata bahasa Inggeris. Siswa tahun IX tersebut adalah siswa dari beberapa sekolah yang ada di kota Medan yang mengikuti bimbingan belajar di Primagama Cab. Aksara yang beralamat di jln. Letda Sujono No. 108 Medan Dalam mengerjakan skripsi ini penulis menggunakan metode field research ( penelitian lapangan ) yaitu mengambil data dari siswa tahun IX yang mengikuti
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
1.1 Background of the Analysis
Language is the main instrument of communication in human life. By using language, we can communicate with other person. By using language we also can convey our ideas, thought, opinion, and felling in every our life activities. Oller (1979: 7) states that language is usually to convey information about people, things, ideas, states of affair, and attitudes toward all of people in the world.
Nowadays, many people tend to study a foreign language, especially English. As we know that English holds an important part in International life as an International language. Because of that, many people are eager to speak and write English well. Most of the people in the world study English as second language in the school and support it by joining English course. Large part of students in the world study about English as they second, or foreign language.
In studying English, the most important part that the students have to understand is about grammar. Because the most important characteristic of language is the presence of grammar. As we know that, every human language has grammar indeed without
exception. Grammar is a basic skill when we study language. Lado (1970:141) states that grammatical structure is the pattern of arrangement of word. Trask (1999: 27) states that grammar is part of linguistic and linguists who specialize in the study of grammar are
which sentences are constructed; how sentences are related to each other. Another opinions by Oller, (1979: 65) states that: “The subjects’ matter of language testing research is the use and learning of language. Within educational contexts, the domain of foreign language teaching is a special case of interest.”
Troike (1976: 83) states that: “Some of our rulers for language use vary
systematically depending on pronunciation, grammar, and choice of words, gesture, and all other aspects of our linguistic behavior. A speaker’s ability to interpret and procedure appropriate styles of a language are part of his total communicative competence.”
In formal school student who learn English must learn about grammar. Because it can help the student to arrange some words, or sentence correctly if they understand how to arrange it by studying English grammar. ‘Elliptic construction’, or ‘elliptical sentence’ term is used by some writers in their grammar books, such as; Nugroho (2000: 228), Dwi (2005: 32) and Brata (2007: 87). In other English structure, or English Grammar book the writer use the term such as ‘using and + too, so, either, neither’ Schrampfer (1992: 230), ‘positive agreement too – so, negative agreement either – neither’ Dhany R. Cyssco (2003: 93), etc. Elliptic construction or elliptical sentence is one topic that the students learn in English grammar. By understanding Elliptic construction, it can help the student in speaking and writing English well.
The examples of Elliptic construction in conversation are:
1. Riri : “I want to play football this afternoon, How about you? ” Yogi : “Me too”.
Nita : “ So do I”
3. Mimi : “ My father can’t speak English.” Risa : “ Neither does My uncle ”
4. Adre : “ I rarely come to my girlfriend house.” Riyu : “I don’t either.”
5. Yuyuk : “ I can speak English fluently”. Novi : “ But I can’t”.
The examples of elliptic construction on writing are: 1. Mira wears red dress. Yuni wears red dress.
The two sentences we can combine become: Mira wears red dress and so does Yuni. or Mira wears red dress and Yuni does too.
2. Agus will not go to the cinema. Rudi will not go to the cinema. The two sentences we can combine become:
Agus will not go to the cinema and Rudi won’t either. or Agus will not go to the cinema and neither will Rudi.
In Indonesia, studying English is as important as other subject for students. They study English beginning from primary school up to university levels.
because I work there as English tutor, so it is can makes me easy to get the data from the student.
1.2 Scope of the Analysis
The topic that is going to be discussed in this thesis is about an analysis of year IX Primagama students’ ability in mastering elliptic construction, or elliptical sentence. I want to limit my analysis in order to make the discussion more focused. The subject that is to be analyzed is only about elliptic construction and the object are 30 students who are in the preparation of national examination (UN) at the testing and learning centre, Primagama Jl. Letda Sujono no.108 Medan.
1.3 Problem of the Analysis
The problem that will be analyzed in this thesis is how the ability of the year IX Primagama’s students in mastering Elliptic construction, or Elliptical sentence and in which type of Elliptic construction the student more mastering. The population is year IX who study English at Primagama. Moreover, there are three classes of year IX student in that location. The three of classes will be used as the data by giving them multiple choices questions.
1.4 Objective of the Analysis
The objectives of this research are:
1. To find out the ability of year XI Primagama students’ ability in mastering elliptic construction, or elliptical sentence.
1.5 Significance of the Analysis
I hope that the result of this research would be useful for English teacher and student. I also hope that this research could be motivating the other researchers who are interested in the same topic. I also hope that the result of the research would be useful to other people who are interested in teaching English, to describe the problems and difficulties especially toward elliptic construction or elliptical sentence. Moreover, I want try to supply solutions to that problems.
1.0Review of the Related Literature
This research is based on some linguistic theories proposed by some prominent linguists. As I have researched, there has not been any previous analysis about elliptic construction or elliptical sentence before. So for my review of the related literature I just put some of linguists’ definitions, as follows:
Widdowson (2000: 3) states that: “Testing is a universal feature of social life. Throughout history people have been put to the test to prove their capabilities or to establish their credentials”.
Stefanie (1999: 12) states that: “Grammar means something rather different it is the set of elements and rules that make up a language.”
Nugroho (2003: 228) states that:
“ Elliptical sentence adalah gabungan dua kalimat yang berbeda subyeknya tetapi predikatnya sama, digunakan untuk menghindari pengulangan. Tujuan elliptical sentence adalah untuk menyampaikan pernyataan secara sederhana dan sekaligus menghindari pengulangan unsur kalimat yang sama”.
(www. Google.com)
words in which some words have been omitted. Because of the logic, or pattern of the entire sentence, it is easy to infer what the missing words are”.
Brata ( 2004 : 87 ) states that :
“ Kalimat ellip merupakan pemendekan dari dua kalimat atau lebih dengan cara menghilangkan beberapa bagian kalimat yang memiliki kesamaan dari asalnya”. Kalimat ellip digunakan untuk menghindari adanya pengulangan kata yang sama dalam satu kalimat.
According to Free Word U ( global education is in the card ) said that :
“An elliptical sentence does not mean a sentence with an ellipsis in it. An ellipsis is three periods, symbolizing missing information. This form most often appears when using only part of a direct quote”.
“ A construction is an ordered arrangement of grammatical units forming a larger unit. Ellipsis is about the orthographic usage rules for '...' ” . ( www. yahoo.com )
From WIKIPEDIA ( the free encyclopedia ) said that :
CHAPTER II
A BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF ELLIPTIC CONSTRUCTION
In this chapter, the writer would like to discuss about elliptic contruction or elliptical sentence. There are some definition about what is elliptic contruction. An elliptical clause (a form of elliptical construction) is a clause in which some words have been omitted. (www. Ensiclopedia.com). In the grammar of a sentence, an elliptic construction is a construction that lacks an element that is, nevertheless, recoverable or inferable from the context. The elliptical construction is a sequence of words in which some words have been omitted. Because of the logic or pattern of the entire sentence, it is easy to infer what the missing words are.
An elliptical sentence does not mean a sentence with an ellipsis in it. An ellipsis is three periods, symbolizing missing information. This form most often appears when using only part of a direct quote. An elliptical sentence refers to sentences with information missing. This form does not require an ellipsis. These sentences are grammatically correct only if the necessary information to understand the sentence has been supplied previously or is clear from the context of the sentence.
Actually elliptical constructions is not only using in writing but it’s also often be used in dialogue to shorten what is being said.
For example :
Rony : “me too”.
2. Ria : “I like ice cream very much”.
Yuni : “so do I”.
3. X : “ My uncle went to Bandung last week”.
Y: “ So did my father”
4. Riri : “I had bought a new motorcycle last year”.
Yuyun : “I had too”.
5. Rika : “ I don’t want to stay here”.
Feni: “ Neither do I”.
6. X: “My mother can’t speak Frence, and how about yours?”
Y: “ My mother doesn’t either”.
7.Rio : “ My father doesn’t watch tv in the morning”.
Ria : “ My mother doesn’t either”.
8.Rika : “ She has found a lovely dress”.
Mira : “ But I haven’t”.
9. X : “ She has not a good boy friend”.
Y : “ But I have ”.
10. Rio : “ I can drive a motor cycle to around the world”.
There are three kinds of the elleptic contruction that will be discussed in this thesis :
1. Possitive elliptical contruction 2. Negative elliptical contrustion 3. Opposite elliptical construction
2. 1. Positive Elliptic
Positive elliptic is used in positive sentence to combine two positive sentences in where the sentence has the same verb and object. To make the two sentences simply we can put conjunction and add with word ‘So’ and ‘Too’.
For example:
- Mira goes to school everyday. - Rina goes to school everyday.
* The two sentences can be combine into :
- Mira goes to school everyday and so does Rina, or - Mira goes to school and Rina does too.
The important part that is must be carefully is about To be or auxiliary verb because It is always changes based on the tenses.
Explanation: From the example above ‘Mira goes to school everyday’ is as main clause and ‘so does Rina’ or ‘Rina does too’ is as next statement.
The example of elliptic construction in some tenses
The pattern is :S + V + O, + and + S + to be / Auxiliary + too
Explanation:S = subject V = verb O = object
A. Elliptical construction in Simple present tense
1. I buy a new book. She buys a new book.
* I buy a new book and so does she, or
* I buy a new book , and she does too.
2. She studies English in Primagama. He studies English in Primagama.
* She studies English in Primagama and so does he, or
* She studies English in Primagama, and he does too.
3. They are smart students in Indonesia. We are smart students in Indonesia.
* They are smart students in Indonesia and so are we, or
* They are smart student in Indonesia, and we are too.
B. Elliptical Construction in Past Tense
1. She went to Bandung last month. He went to Bandung last month. * She went to Bandung and so did he, or
2. My mother cooked some cakes yesterday.
My aunty cooked some cakes yesterday.
* My mother cooked some cakes yesterday and so did my aunty, or
* My mother cooked some cakes yesterday, and my aunty did too.
3. They saw the movie together in twenty one last nigth.
We saw the movie together in twenty one last night.
* They saw the movie together in twenty one last night and so did we, or
* They saw the movie together in twenty one last night, and we did too.
C. Elliptical construction in Present Continuous Tense
1. I am thinking about this problem now.
You are thinking about this problem now.
* I am thinking about this problem now and so are you, or
* I am thinking about this problem now, and you are too.
2. They are watching TV today. We are watching TV today.
* They are watching TV today and so are we, or
* They are watching TV today, and we are too.
3. She is preparing some books for presentation at this time.
He is preparing some books for presentation at this time.
* She is preparing some books for presentation at this time, and he is too.
D. Elliptic construction in Past continious tense
1. I was climbing Sriwijaya mountain last month.
He was climbing Sriwijaya mountain last month.
* I was climbing Sriwijaya mountain last month and so was he, or
* I was climbing Sriwijaya mountain last month, and he was too.
2. Mia was reading that novel yesterday.
Nini was reading that novel yesterday.
* Mia was reading that novel yesterday and so was she, or
* Mia was reading that novel yesterday, and she was too.
3. They were playing basketball together. We were playing basketball together.
• They were playing basketball together and so were we, or • They were playing basketball together, and we were too.
E. Elliptic construction in Present future
1. I will cut the tree tomorow. He will cut the tree tomorow.
* I will cut the tree tomorow and so will he, or
* I will cut the tree tomorow, and he will too.
2. Reza will come to your house at sevent o’clock.
* Reza will come to your house at sevent o’clock and so will she, or
* Reza will come to your house at sevent o’clock, and she will too.
3. They will breakfast with me tomorow morning.
You will breakfast with me tomorow morning.
* They will breakfast with me tomorow morning and so will you, or
* They will breakfast with me tomorow morning, and you will too.
F. Elliptic construction in Past Future tense
1. I would say sorry to you. She would say sorry to you.
* I would say sorry to you and so would she, or
* I would say sorry to you, and she would too.
2. She would bring a new magazine yesterday.
He would bring a new magazine yesterday.
* She would bring a new magazine yesterday and so would he, or
* She would bring a new magazine yesterday, and he would too.
3. They would give a doll for you. We would give a doll for you.
* They would give a doll for you and so would we, or
* They would give a doll for you, and we would too.
G. Elliptic construction with Modal auxiliary verb
* I can swim well and so cans she, or * I can swim well, and she cans too.
2. We might go to the office. I might go to the office. * We might go to the office and so might I, or * We might go to the office, and I might too.
3. You should take a medicine. She should take a medicine. * You should take a medicine and so should she, or * You should take a medicine, and she should too. 4. You must pay me more. Hari must pay me more. * You must pay me more and so must he, or * You must pay me more, and he must too. 5. Lia has to study hard. Ali has to study hard. * Lia has to study hard and so have to him, or * Lia has to study hard, and he has to too.
2. 2. Negative Elliptic
Negative elliptic is used in negative sentence to combine two negative sentences in where the sentence has the same verb and object. To make the two sentences simply we can put conjunction and add with word ‘Neither’ and ‘Either’.
For example:
- Mira doesn’t go to school today. - Rina doesn’t go to school today.
* The two sentence we can combine become :
- Mira doesn’t go to school today and Rina doesn’t either.
In elliptical construction the important part that is must be carefully is about To be or auxiliary verb because It is always changes based on the tenses.
Explanation: From the example above Mira doesn’t go to school today is as main clause and neither does Rina or Rina doesn’t either is as next statement.
The example of elliptic construction in some tenses
The pattern is :S + V + O, + and + neither + to be / auxiliary verb + S
Or
S + V + O, + and + S + to be / Auxiliary + not + either
Explanation:S = subject V = verb O = object
A.Elliptical construction in Simple present tense
1. She doesn’t study English in that course.
He doesn’t study English in that course.
* She doesn’t study English in that course, and neither does he. Or
* She doesn’t study English in that course, and he doesn’t either.
2. They are not smart students in this school.
* They are not smart students in this school, and neither are we. Or
* They are smart student in this schooland, and we aren’t either.
3. Nobody cares about my problem. Nobody cares about your problem.
* Nobody cares about my problem, and neither do you. Or
* Nobody cares about my problem, and you don’t either.
B.Elliptical Construction in Past Tense
1. She seldom went to Bandung last month.
He seldom went to Bandung last month.
* She seldom went to Bandung last month, and neither did he. Or
* She seldom went to Bandung last month, and he didn’t either.
2. They didn’t see the movie together in twenty one last nigth.
We didn’t see the movie together in twenty one last night.
• They didn’t see the movie together in twenty one last night,
and neither did we. Or
• They didn’t see the movie together in twenty one last night,
and we didn’t either.
3. Mira never made a beautiful dress yesterday.
Gusni never made a beautiful dress yesterday.
* Mira never made a beautiful dress yesterday, and Gusni didn’t either.
C. Elliptical construction in Present Continious Tense
1. I am not thinking about this problem now.
You are not thinking about this problem now.
* I am not thinking about this problem now, and neither are you. Or
* I am not thinking about this problem now, and you aren’t either.
2. They are not watching TV today. We are not watching TV today.
* They are not watching TV today, and neither are we. Or
* They are not watching TV today, and we aren’t either.
3. You are rarely cleaning my house now.
She is rarely cleaning my house now.
* You are rarely cleaning my house now, and neither is she. Or
* You are rarely cleaning my house now, and she isn’t either.
D. Elliptic construction in Past continious tense
1. Noone was climbing Sriwijaya mountain last month.
He was not climbing Sriwijaya mountain last month.
* Noone was climbing Sriwijaya mountain last month, and neither was he. Or
* Noone was climbing Sriwijaya mountain last month, and he wasn’t either.
Nini was not reading that novel yesterday.
* Mia was not reading that novel yesterday, and neither was she. Or
* Mia was not reading that novel yesterday, and she wasn’t either.
3. They were not playing basketball together.
We were not playing basketball together.
* They were not playing basketball together, and neither were we. Or
* They were not playing basketball together, and we weren’t either.
E. Elliptic construction in Present future
1. I will not cut the tree tomorow. He will not cut the tree tomorow.
* I will not cut the tree tomorow, and neither will he. Or
* I will not cut the tree tomorow, and he won’t either.
2. Reza will not come to your house at sevent o’clock.
Nila will not come to your house at sevent o’clock.
* Reza will not come to your house at sevent o’clock, and neither will she. Or
* Reza will not come to your house at sevent o’clock, and she won’t either.
3. They will not breakfast with me tomorow morning.
You will not breakfast with me tomorow morning.
* They will not breakfast with me tomorow morning, and neither will you. Or
F. Elliptic construction in Past Future tense
1. I would not say sorry to you. She would not say sorry to you.
* I would not say sorry to you, and neither would she. Or
* I would not say sorry to you, and she wouldn’t either.
2. She would not bring a new magazine last day.
He would not bring a new magazine last day.
* She would not bring a new magazine last day, and neither would he. Or
* She would not bring a new magazine last day, and he wouldn’t either.
3. They would not give a doll for you. We would not give a dool for you.
* They would not give a doll for you, and neither would we. Or
* They would not give a doll for you, and we wouldn’t either. .
G. Elliptic construction with Modal auxiliary verb
1. I never can swim well. She never can swim well. * I never can swim well, and neither can she. Or * I never can swim well, and she can’t either. 2. We might not go to the office.
I might not go to the office.
* We might not go to the office, and neither might I. Or * We might not go to the office, and I might not too.
* You should not go at the mid night, and she shouldn’t either. 4. You must not smoke here. Hari must not smoke here.
* You must not smoke here, and neither must he. Or * You must not smoke here, and he mustn’t either. 5. Lia has not to study hard. Ali has not to study hard. * Lia has not to study hard, and neither has to he. Or * Lia has not to study hard, and he has not to either.
2. 3. Opposite Elliptic
Opposite elliptic is used in two sentences that have contras meaning. Opposite sentence use to combine two sentences in where the sentence has different verb but has it object. If the first sentence has positive meaning, so the second sentence has negative one. In opposite elliptic we used conjunction “and + but” to combine that two sentences which have contras meaning.
For example:
- Mira go to school today.
- Rina doesn’t go to school today.
* The two sentence we can combine become : - Mira go to school today, but Rina doesn’t.
In elliptical construction the important part that is must be carefully is about To be or auxiliary verb because It is always changes based on the tenses.
Explanation: From the example above Mira go to school today is as main clause, but Rina doesn’t is as next statement.
The pattern is:
S + V + O, + BUT + S + to be / auxiliary
( + ) ( - ) ( - ) ( + )
Explanation :S = subject V = verb O = object
( + ) = positive sentence ( - ) = negative sentence
A. Elliptical construction in Simple present tense
1. I am not buy a new book. She buys a new book.
* I am not buy a new book, but she does.
2. She doesn’t study English in that course. He studies English in that course.
* She doesn’t study English in that course, but he does.
3. They are smart students in this school.
We are not smart students in this school.
* They are smart students in this school, but we aren’t.
B. Elliptical Construction in Past Tense
2. My mother cooked some cakes yesterday.
My aunty didn’t cook some cakes yesterday.
* My mother didn’t cook some cakes yesterday, but my aunty did.
3. They saw the movie together in twenty one last nigth.
We didn’t see the movie together in twenty one last night.
* They saw the movie together in twenty one last night, but we did.
C. Elliptical construction in Present Continious Tense
1. I am not thinking about this problem now.
You are thinking about this problem now.
* I am not thinking about this problem now, but you are. Or
2. She is preparing some books for presentation at this time.
He is not preparing some books for presentation at this time.
* She is preparing some books for presentation at this time, but he isn’t.
3. You are rarely cleaning my house now. She is cleaning my house now.
* You are rarely cleaning my house now, but she is.
D. Elliptic construction in Past continious tense
1. I was not climbing Sriwijaya mountain last month.
* I was not climbing Sriwijaya mountain last month, but he was.
2. Mia was not reading that novel yesterday.
Nini was reading that novel yesterday.
* Mia was not reading that novel yesterday, but she was.
3. They were playing basketball together.
We were not playing basketball together.
* They were playing basketball together, but we weren’t.
E. Elliptic construction in Present future
1. I will not cut the tree tomorow. He will cut the tree tomorow.
* I will not cut the tree tomorow, but he will.
2. Reza will come to your house at sevent o’clock.
Nila will not come to your house at sevent o’clock.
* Reza will come to your house at sevent o’clock, but she won’t.
3. They will breakfast with me tomorow morning.
You will not breakfast with me tomorow morning.
* They will breakfast with me tomorow morning, but you won’t.
F. Elliptic construction in Past Future tense
1. I would not say sorry to you. She would say sorry to you.
2. She would not bring a new magazine last day.
He would bring a new magazine last day.
* She would not bring a new magazine last day, but he would.
3. They would give a doll for you. We would not give a dool for you.
* They would give a doll for you, but we would.
G. Elliptic construction with Modal auxiliary verb
1. You could not smoke here. He could smoke here. * You could not smoke here, but he could.
2. They may to see your mother. She may not to see your mother. * They may to see your mother, but she may not.
3. You should not go at the mid night. She should go at the mid night. * You should not go at the mid night, but she should.
4. You must not smoke here. Hari must smoke here. * You must not smoke here, but he must.
5. Lia has not to study hard. Ali has to study hard. * Lia has not to study hard, but he has to.
THE SUMMERY OF ELLIPTIC CONSTRUCTION
1. If in the sentence use to be \ auxiliary, so we use it in next statement.
2. Nothing to be \ auxiliary is used, if verb 1 is used do or does depend on subject sentence. Verb 2 is used did.
4. There is “has” + to infinitive is used does in next statement. 5. There is “had” + object is used did in next statement.
6. If the Elliptic sentence use negative word such as, not, rarely, never, nothing, nobody, no one, seldom, etc. It means the sentence is negative sentence. Therefore, we use negative elliptic in next statement.
CHAPTER III
METHOD OF RESEARCH
3.1 Methodology
In this thesis, I apply two methods of research, they are: • Library research:
In this research, I have read some books related to the topic especially English grammar book.
• Field research:
In this research, firstly, I collect and choose the subjects. Secondly, I make a multiple choice test and give it to the student, in order to get the data of their ability in mastering Elliptic construction.
• I also used P. Harris (1969: 128) technique of data analysis :
The formula:
X’
N= _______ x 100 %
X . Y
N : the outcomes of the students’ answer
X’: the total of student’s right answer
X : the number of students
Y : the number of the test
< 50 = below average 81-100 = Average 1-1 = Good 2-1 = Very good 1-1 = Excellent
The out comes of the average level of students’ competency is obtained by applying the formula given by Hadi (2002: 37) as follows:
Σ
x
Mean : _______
N
Σx : the total score of the students
N : the number of the students
I use descriptive method to describe all the facts, which are related to the subject of analysis (about elliptical construction). The object of the analysis is year XI of
Primagama’s Student at Jl. Letda Sujono no.108 Medan.
“ Metode deskripsi dapat diartikan sebagai prosedur pemecahan masalah yang diselidiki dengan menggambarkan/melukiskan keadaan subjek/objek penelitian ( seseorang, lembaga, masyarakat,dll) pasa saat sekarang berdasarkan fakta- fakta yang tampak atau sebagaimana adanya”.(Hadi 2002: 36)
3.2 The population and sample
The word “population” may mean differently in different situation or context. Based on The Oxford Advance Learner’s Dictionary (1974 : 649), it explains that, “ population is the member of the people living in a place, country, etc or a special section of them.” According the quotation above, the population of a country is people, but the population of a research can be people, social phenomena, language, and any other things, which may be relevant to the study. In this case, population is a group of individual or item to be studied.
If we are talking about population means that talking about sample. Sample is used as an object to represent the population. It is impossible for me to take all population to be the object of this thesis. Therefore, I take same students as samples, and informants. The sample of this thesis is year IX student of Primagama on Jln. Letda Sujono No. 108 Medan.
3.3 The techniques of collecting data
In order to collect the data, I must do some steps. first, I collect my data by using observation and questionnaire. These two steps have their own advantages. By doing observation I know about the student attitude when they studying English in class, they interest and seriously or not. By giving questionnaire, I get the data based on their ability in mastering Elliptic construction. In fact, if we do a research without using any
CHAPTER IV
ANALYSIS AND FINDINGS
As it had mentioned in the first chapter, I carry on the field research. In this analysis, the data is collected from IX year of Primagama students on Jln. Letda Sujono no. 108. I had taken 30 students randomly from three classes. Each class consists of 10 students. In testing their ability, I give 30 questions.
1.0
Analysis
In this part, I will analyze of year IX Primagama students ability in mastering Elliptic Construction. The test consists of 30 items or questions. The questions are dividing in to three sections or parts. They are; Positive Elliptic question, Negative Elliptic question and Opposite Elliptic Question. The objective of the test is to find out the ability of year IX of Primagama students ability in mastering Elliptic Construction. The analysis is described as follows:
TABLE I
THE RESULT OF ANALYSIS QUESTION
I. Positive Elliptic Construction Question and the Result Number of question A B C D True answer 1 30 0 0 0 A
5 21 6 2 1 A 6 28 2 0 0 A 7 3 18 2 7 A 8 0 2 6 22 D 9 25 2 3 0 A 10 30 0 0 0 A
The result = Result of correct answer X 100% Number of student . Number of question
= 235 X 100% 1 . 10
= 78
From the table and the result above, I can know that most of the student can answer Positive Elliptic construction questions correctly. The score is 78 it is means the ability of the student in mastering Positive Elliptic Construction question is “good”.
16 8 5 3 14 D 17 0 0 0 30 D 18 0 0 0 30 D 19 0 0 2 28 D 20 0 30 0 0 B
The result = Result of correct answer X 100% Number of student . Number of question
= 231 X 100% 1 . 10
= 77
From the table and the result above, I can know that most of the student can answer Negative Elliptic construction questions correctly. The score is 77 it is means the ability of the student in mastering Negative Elliptic Construction question is “good”.
28 30 0 0 0 A 29 8 0 22 0 C 30 30 0 0 0 A
The result = Result of correct answer X 100% Number of student . Number of question
= 251 X 100% 1 . 10
= 83
4.2. Findings
TABLE II
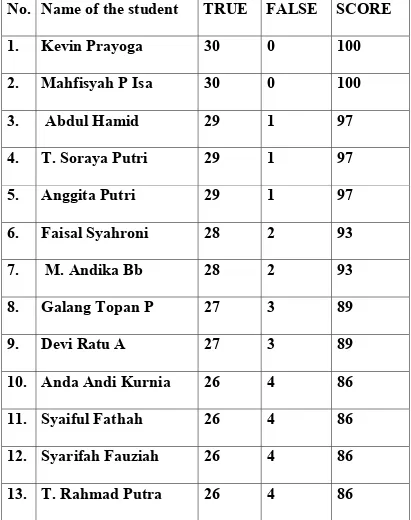
THE SCORE OF THE STUDENT
No. Name of the student
TRUE
FALSE
SCORE
1.
Kevin Prayoga
30
0
100
2.
Mahfisyah P Isa
30
0
100
3.
Abdul Hamid
29
1
97
4.
T. Soraya Putri
29
1
97
5. Anggita
Putri
29
1
97
6. Faisal
Syahroni
28
2
93
7.
M. Andika Bb
28
2
93
8. Galang
Topan
P
27
3
89
9.
Devi Ratu A
27
3
89
10. Anda Andi Kurnia
26
4
86
11. Syaiful
Fathah
26
4
86
12. Syarifah Fauziah
26
4
86
14. Guruh
A
25
5
83
15. Miftahul Khairani
25
5
83
16. Ifvhan Ramadhan
25
5
83
17. Anggi
Silvani
25
5
83
18. Astri Widya S.P
24
6
79
19. Octavia Fahrina L
24
6
79
20. Evo
Larasati
24
6
79
21. Rahmadi
Achmad
24
6
79
22. Alfi
Syahara
24
6
79
23. Hardianto
24
6
79
24. Azhari
Hidayah
21
9
69
25. Nurul
Fadillah
21
9
69
26. Habib
Islam
18
12
59
27. Melany
Sari
18
12
59
28. Husna
Dwita
18
12
59
29. Nurhabibah
15
15
50
31. TOTAL
731
169
2420
The scores of the students were converted to percentages by dividing the total scores with the number of all items and multiplying by 100% that is:
N = 731 X 100%
30.30
N = 7,31
The percentage of the whole score is 7,31%. This percentage implies that the students are able to answer Elliptic Construction question.
The outcomes of the average level of competency can be calculated as follows:
Mean =
Σ
x
N
= 2420
30
= 80,6
The average level of the students’ competency is 80,6, Therefore the competency of year IX Primagama students cab. Aksara in mastering Elliptic Construction can be categories into “Very Good.”
TABLE III
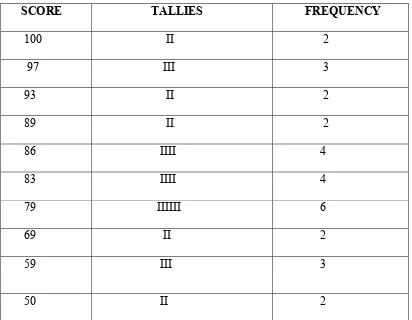
THE FREQUENCY DISTRIBUTION
SCORE TALLIES FREQUENCY
100 II 2
97 III 3
93 II 2
89 II 2
86 IIII 4
83 IIII 4
79 IIIIII 6
69 II 2
59 III 3
50 II 2
After analyzing the data, I want to describe the capability of year IX Primagama student in mastering Elliptic Construction. I will tabulate their grade and the percentage of student’s ability. Before I tabulate it, I want to write down the formula.
The capability level = The correct answer X 100% The number of questions
> 95 % A Excellent 80 % - 94 % B+ Very good
65 % - 79 % B Good
50 % - 64 % C Satisfactory
35 % - 49 % D Bad
< 35 % E Very bad
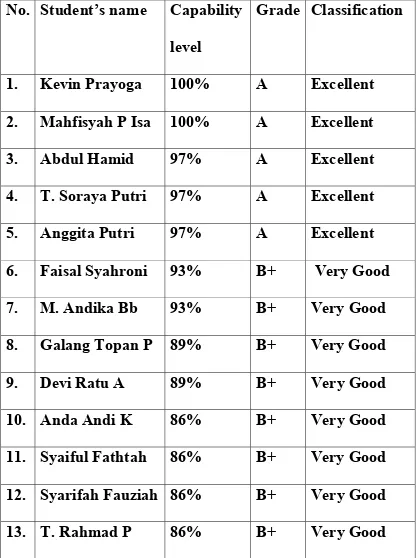
TABLE IV
THE GRADE OF THE YEAR IX STUDENT
ABILITY IN MASTERING ELLIPTIC CONSTRUCTION
No. Student’s name Capability
level
Grade Classification
1. Kevin
Prayoga 100%
A
Excellent
2.
Mahfisyah P Isa 100%
A
Excellent
3. Abdul
Hamid 97%
A
Excellent
4.
T. Soraya Putri
97%
A
Excellent
5. Anggita
Putri 97%
A
Excellent
6.
Faisal Syahroni
93%
B+
Very Good
7.
M. Andika Bb
93%
B+
Very Good
8.
Galang Topan P 89%
B+
Very Good
9.
Devi Ratu A
89%
B+
Very Good
10. Anda Andi K
86%
B+
Very Good
11. Syaiful
Fathtah 86%
B+
Very
Good
12. Syarifah Fauziah 86%
B+
Very Good
14. Guruh A
83%
B+
Very Good
15. Miftahul K
83%
B+
Very Good
16. Ifvan Ramadhan 83%
B+
Very Good
17. Anggi Silvani
83%
B+
Very Good
18. Astri Widya SP
79%
B
Good
19. Octavia Fahrina 79%
B
Good
20. Evo
Larasati
79%
B
Good
21. Rahmadi
A
79%
B
Good
22. Alfi
Syahraa
79%
B
Good
23. Hardianto
79%
B
Good
24. Azhari
H
69%
B
Good
25. Nurul
Fadhillah 69%
B
Good
26. Habib
Islam
59%
C
Satisfactory
27. Melany
Sari
59%
C
Satisfactory
28. Husna
Dwita
59%
C
Satisfactory
29. Nurhabibah
50%
C
Satisfactory
According to the capability level and the grades possessed by IX year Primagama students Cab . Aksara in 2008, I can state that:
74 % of the IX year Primagama Students have high capability in mastering Elliptic Construction. 26 % out of the IX year Primagama Student have standard capability in mastering Elliptic Construction.
CHAPTER V
CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS
5.1 Conclusions
After having analyzed the data thoroughly, I would like to take some conclusions, they are:
a. From the test that I have given to the Primagama students, the average score of year IX student is 80,6 %. Accordingly, it can be said that the ability of year IX Primagama student in mastering Elliptic Construction is very good.
b. The result of the test also shows that the process of teaching and learning English grammar is very good too at Primagama cab. Aksara. Majority of the students understand about Elliptic Construction well, it is around 80%.
c. The problem of the students is lack of vocabularies. They are not understand about the kinds of Elliptic Construction and how to use it in English sentence, especially in conversation.
5.2 Suggestions
Having seen the result of the study, I would like to offer some suggestions to be considered.
a. I expect English tutor in Primagama to improve their English teaching process especially about English grammar.
c. I hope they want to do more practice and examination, so that they get more good result in UN ( ujian nasional ) especially in English subject.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Azar, Betty Schrampfer. 1989. English Grammar. New Jersey: Prentice Hall. Inc. ---, 1992. Fundamental of English Grammar. New Jersey: Prentice Hall, Inc.
Biber, Douglas. 2002. Student Grammar of Spoken and Written English. England: Longman Group Ltd.
Dewa Brata, Paidi. 2007. Strategi Sukses UAN. Yogyakarta: Penerbit Andi. ---, 2007. Paket Pengayaan 1 Kelas 12 SMA IPS. Yogyakarta:
Penerbit Andi.
Dwi W, Elan. 2005. Modren English Grammar. Yogyakarta: Pustaka Pelajar. Hadi, Sutrisno. 2002. Statistik. Yogyakarta: Penerbit ANDI
L. Blommfield. 1995. Language / Bahasa. Jakarta: Gramedia Pustaka Utama Lado, Robert. 1970. Language Testing. London: Longman Group Ltd.
Lou, Robby. 2007. English Grammar and How to Use it. Jakarta: English Plus Series. Oller, John W. 1979. Language Test at School. London: Longman Group Ltd.
R. Cyssco, Dhanny. 2003. English Grammar Practise for TOEFL. Jakarta: Puspa Swara
Savile, Troibe Muriel. 1979. Foundation for Teaching English as a second languange. New Jersey: Prentice Hall, Inc.
Stevanie, Jennedy.1992. Language files. Columbus: The Ohio University Press. Trask, R. L. 1999. Languange the Basic. London: Routledges
www. google.com. (5th January 2008) ‘Elliptic construction’
www. yahoo.com. (10th January 2008) ‘ Analysis of Elliptic Construction’
APPENDIX 1 :
The Test Material on Elliptic Construction Given to the Year
IX Primagama’s Students.
TOPIC : Possitive Elliptic
1. Wina : “ Did you attend the meeting yesterday ?” Wike : “ Yes, I did”.
Wina : “ What about Rio ?” Wike: “ ________”.
a. so did he b. he did also c. he does to d. he was too 2. Parta : “ Did Mira go to the beach yesterday morning ?”
Budi : “ Yes, she did” . Parta : “ What about Rina ?” Budi : “ So did She”.
From the dialogue, we know that_______. a. Mira went to the beach, but Rina didn’t b. Rina went to the beach, but Mira did not. c. Both Rina and Mira went to the beach. d. Mira and Rina didn’t go to the beach. 3. Rini : “ Have you completed your homework ?”
Dita : “ Exactly, I have and you ?” Rini : “ I have too”.
From the dialogue, we know that_____.
a. Both Rini and Sita have completed their homework.
b. Not only Rini but also Sita have not completed their homework. c. Rina has not completed the homework but Rini has.
d. Sita has not completed the homework but Rini has. 4. “ we believe that this car is very expensive.”
a. So am I b. But Rani isn’t c. Neither does Rani d. Rani does too 5. Tono : “ My brother has just bought a new motorcycle”.
Parto : “ What a coincidence….!”
a. my brother has too b. also my brother c. my brother does too d. so does brother 6. Dini : “ I have just bought a new English book”. Dewi : “ what a coincidence!”
a. me too b. I don’t too c. I don’t either d. So don’t I 7. Putry could do the exam very well, and so could Ria.
Its means………
a. only Putry could do the exam very well
b. Both Putry and Ria could do the exam very well c. Both putry and Ria could not do the exam very well d. Not only Ria nor Putry could do the exam very well 8. Reni : “ Your mother like cooking”.
Dona : “ …….”.
a. my mother too b. so does my mother c. my mother did too d. neither does my mother 9. We were making a cake. They were making a cake.
The two sentences can be joined become : a. we were making a cake and so were they. b. We are making a cake and neither are they c. They were making a cake and we weren’t. d. We were making a cake and you were. 10. I am a teacher. You are a teacher.
The two sentences can be joined become : a. I am a teacher and you are too.
TOPIC : Negative Elliptic
11. Nensi : “ Did Mira go to the beach yesterday morning ?” Yuli : “No, she didn’t”.
Nensi : “ What about Rina”. Yuli : “ Neither did She”.
From the dialogue we know that_______. a. Mira went to the beach, but Rina didn’t b. Rina went to the beach, but Mira didn’t. c. Both Rina and Mira went to the beach. d. Mira and Rina didn’t go to the beach. 12. Rini : “ Have you complete your homework ?” Dita : “ Actually, I haven’t and you ?”
Rini : “ Neither I”.
From the dialogue, we know that_____.
a. Both Rini and Dita have completed their homework.
b. Not only Rini but also Dita has not completed their homework. c. Rini has not completed the homework but Dita has.
d. Dita has not completed the homework but Rini has. 13. “ We are not believe that this car is very expensive.” “______”.
a. So is Rani b. But Rani isn’t c. Neither I d. Rani does too 14. “ Did Mila phone you yesterday ?”
“ Mira didn’t phone me and _____ he”. a. Neither b. Either c. too d. so
15. Tono : “ My brother never has just bought a new motorcycle”. Parto : “ _________”.
a. my brother has too b. also my brother c. my brother does too d. my brother has either 16. “………”
a. I also sew my own clothes b. She can’t sew her own clothes c. No do I sew my own clothes d. I don’t sew my own clothes
17. Rony : “ I don’t like smoking”. Boby : “ ……” .
a. Neither don’t I b. So don’t I c. So don’t too d. I don’t either 18. Dini : “ I can not read English book well”.
Dewi : “ My young sister…………”.
a. and I do too b. I don’t too c. I don’t either d. can’t either 19. I don’t like coffee and neither does my wife.
It’s mean that…..
a. my wife like coffee b. my wife and I like coffee
c. both my wife and I like coffee d. both my wife and I dislike coffee 20. X: “ Dina and Dita haven’t returned your book .”
Y: “ ……….”
a. I haven’t too b. Neither have I c. So don’t I d. Neither haven’t I
TOPIC : Opposite Elliptic
21. Putra could do the exam very well, but Yudi couldn’t. Its means………
a. only Putra could do the exam very well
b. Either Putra or Yudi could do the exam very well c. Both putra and Yudi could not do the exam very well d. Not only Yudi nor Putra could do the exam very well 22. “ Every schools are open everyday, but…..”
a. the university aren’t either b. Neither aren’t the university c. And the university aren’t too d. on Sunday isn’t
a. Reni’s mother like cooking, but Dona’s mom doesn’t. b. Reni’s mother like cooking and so does Dona’s mother. c. Both of their mother like cooking.
d. Both of their mother dislike cooking. 24. X : “ Tiger is not able to fly.”
Y : “ Bird can fly in the sky.” The sentence mean………
a. All animals can fly. B. All animal is not able to fly. c. Tiger can not fly, but bird can d. Tiger can Fly, but bird can’t. 25. Hasan : “ I don’t think, that Maya knows anything about computers”. Angga : “ But she …….., she took a computer course last year”. a. did b. does c. know d. knows 26. Rina : “ Neti has her paper typed. What about you ?”
Wike : “ But……….”.
a. I do too b. So have I c. Neither don’t I d. I don’t 27. Chairul : “ I love Dian sastro very much”.
Rony : “ But….”.
a. I don’t love her b. I dislike her c. I love her d. You love her 28. Rudy : “She wants to go to the library”.
Ria : “But….
a. I won’t b. She wants c. I want d. She doesn’t want 29. X: “……….”
Y: “ But I can speaks English”.
a. I can’t speak English well. b. I can speak English.
c. She can’t speak English well. d. She can speak English well. 30. Riri : “She is reading book now”.
Wiwid : “He is not reading book now”. a. She is reading book now but, he isn’t. b. They are reading book now.
ANSWER KEY
POSITIVE ELLIPTIC 1. A 2. C 3. A 4. A 5. A 6. A 7. B 8. A 9. A 10. A
NEGATIVE ELLIPTIC
11. D 12. B 13. C 14. A 15. D 16. D 17. D 18. D 19. D 20. B
APPENDIX 2 :
THE FIELD RESEARCH LETTER TO GET THE
STUDENTS DATA FROM ASSOCIATE DEAN I.
APPENDIX 3 :
THE FIELD RESEARCH LETTER OBTAINED FROM THE
HEAD OF PRIMAGAMA AKSARA BRANCH.