Vol 6, No 2,
April
- Junej997
Lipid Peroxidation in IschemicStroke
109A
Study of
Lipid
Peroxidation
in
fschemic Stroke
A.K.
Sood,A.
Mahajan,
D.
Sindhu,
A.
Dua,
S. SethAbstrak
Telah dilakukan pengukuran malonil dialdehid serum
hubungan
beratny
IJmuadalah3:2.
Penen
coraonal Institute of Health Stroke Scalz.
Abstract
Serum mnlonyl dialdehyde (MDA) level, an index of lipid peroidation, was estimated in twenty
fwe cT proved ischemic stroke subjects and 25 age and sex matched healthy controls, to find oul its
cor
on with severity ord ourco^" of stroke. Mean age of strolce paticnts was al' Serum MDA lcvels 53'08+
15'01 years andmale-
s3:2.
of serum MDA levels was done by the method of placer et were found to besign
ische
c stroke paticnts compared to controls (3,33 + 0.75 lunot/L vs. 1.73 + 0'48 ltmoUL' p < 0.001 ). The levels were higher in those in whom MDA levels were estimated within 6 hours of onset of stroke, MDA levels had no coftelation with the suddenness of the stroke,with site
and ex.tent of infarction or with the severity and outcome of stroke as determined by Modified National Institute of Healthstroke Scale.Keywords : Lipi^d peroxidation, Cerebrovascul.ar accident, Ischemic strol<e, Malonyt dialdehyde
Stroke is the
third leading
cause of death afterischemic
t
e, ely
deterioration
of
polyunsaturated
fatty
acids, a processresponsible
for
theproduction
offree
radicals.
tion
are
numerous
and include hypoxia,
hyperoxia,
copper and
iron toxicity
and antioxidant
deficien_
cies."'
Imbalance
betweenperoxidant
andantioxidant
forces
in which
theformer
dominates may
bebroadly
defined
asoxidative
stress,of which
lipid
peroxidation
is an
important manifestation. Although
lipid
peroxidation affects many cellular
components,
ihe
primary
reaction sites
involve
membrané-
associatedpolyunsaturated
fatty
acids
and
protein
thiols.3
Peroxidation
of
membrane-associatedfatty
acids
andcholesterol alters
cell
membrane
fluidity and
per_meability
characteristics and
may eventually
induce
widespread membrane damage.4During
experimental
studies,Tomita
et al5 have describedetevatlon
of
lipid
peroxide
in
the
blood
of
stroke
prone
sponta.reouily
hypertensive
rats shortly
before
the
ôccurence
of
stroke.
Similarly, Kibata
et
al6 alsoobserved that
thelevels
of
free
fatty
acids
andthiobarbituric
acid
reac_tive
substances,indicative of lipid peroxidation,
werehigh
in
the serumof patients
with
stroke.Keeping the
above
facts
in
mind,
it
was planned to
study
lipid
peroxidation
byestimation of
malonyl
dial_ dehyde(MDA)
levels,
anindex
of lipid
peroxiâadon,
in
serum of patientsof ischemic
strokè and to establish Department of Neurology and Biochemistry,I
10
Sood et aI.correlation,
if
any, between serumMDA
levels
and theseverity of
neurological deficit.
MATERIALS
AND METHODS
Twenty
five
patients
of
ischemic
stroke, irrespective
of
age and sex, admitted to our institute'were includedin this
study. Another
25 healthy subjects matchedfor
age&
sex served ascontrol.
The study approved by theethical committee
of
the hospital. The criteria laid
down
by
WHOT
to
establish the
clinical
diagnosis
of
stroke were followed
and
only
CT proved
casesof
cerebral thrombosis were included.
Patientssuffering
from
TIA, AMI,
liver
and kidney
diseases,poorly
controlled Diabetes
Mellitus
and pregnant
patientswere excluded
from
the study.
All
the patiens were subjected
to
athorough physical
examination
and
investigations
like
Hb, TLC, DLC,
ESR,
urine
analysis,
blood
urea
&
sugar, serum
uric
acid,
lipids
and
electrolytes along with X-Ray
chest andEKG.
Other invesigations
like
echocardiography,
CT scan
brain
and serum
MDA
leves8
were
also studiedin all
cases soon after admission.Neurological
status of eachpatient
was assessedusing
a modified National Institute
of
Health Stroke
(MNIHS)
Scaleeat
admission and
after 3
weeks
and was correlatedwith MDA
levels.
RESULTS
Mean
ageof
stroke patients was 53.08
+
15.01 yearsand 32Vo
patients were below the
age
of 45
years.Male-female
ratio
was 3:2. Onset of stroke was suddenin
24Vo,
acute
in
567o
and
progressive
in 2OVo
of
patients.
80Voof
the patients
reached
the
hospital
within
24
hours
of
the
onset
of
stroke.
96Vopatients
presentedwith
carotid
territory
and 4Vowith
abasilar
territory
stroke.
In
the stroke
group
247oof
patientswere
hypertensive, l6Vo were
suffering from
COPD,
487o were smokers, 36Vo haddyslipoproteinemia,
I2Vowere
chronic
alcohol drinkers
and one case (47o) wasof
well controlled NIDDM.
None
of
the patients wassuffering
from
any active coronary artery disease.The severity
of
stroke
as assessedby MNIHS
scale atpresentation revealed
that 44Vopatients were
casesof
mild
stroke, 24Voof
moderately severe stroke and32%o weresuffering
from
very
severetype
of
stroke.All
the patients received need based therapy, but steroids werenot
used.
32Voof
patients
died,
40Vowere
left
with
residual deficit
and
only
28Vorccovered completely.
Med J Indones
887o
of
patients were
seento
be
suffering from
lobar
infarct
andonly
l2%o had deep seatedinfarcts.
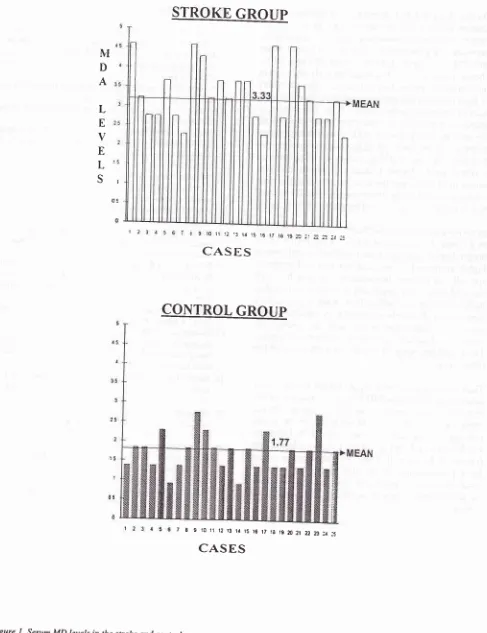
Mean serum
MDA
levels were
1.73+
0.43
pmol/L in
control group
and
it
was 3.33
+
0.75 pmol/L
in
thestroke group. The
difference was highly significant
(<
0.001). Serum
MDA
levels
were significantly
higherin those
caseswho were admitted to
thehospital
within
6 hrs compared to those who were admitted after24
hrs
of
onset
of
stroke
(3.45 + 0.8 vs
3.04
+
0.9).
MDA
levels were raisedin
all
casesof
strokeirrespec-tive of
presentation
of
stroke. The levels were
alsosimilarly
high
in
all the groups,irrespective of severity
of
stroke.
No statistically significant difference in
serum
MDA
levels was
observed
in
stroke
patientswho recovered
completely,
partialy or
died.DISCUSSION
Free oxygen radicals are
formed during normal
cellular
metabolism.
Cell
injury
associatedwith
free
radical
occurs either
in
situation
in
which the
scavengingsystem
is
overwhelmed
or in
disease statesin which
theprotective antioxidant
systemis impaired. Gotol0
suggestedthree possible mechanisms
by which
lipid
peroxide could
causevascular
damage.
High
serumlipid peroxide may
inhibit
endothelial
prostacycline
production,
may directly injure endothelial cells
or
may increase platelet
aggregation.Dzhandzhgava and
Shakarishivili
II
studiesactivity of
antioxidant
protec-tive
enzymes andfound
decreased levelscorrespond-ing
significantly
toseverity of impairment
and wereof
s can be used
for
diagnos-es.
Skochii
et
all2
and
dies
lipid
peroxidation in
patients
of ischemic stroke
and concluded
that
lipid
peroxide levels may
be used
for
evaluation
of
treat-mentefficacy
and prognosisof
the disease.Vol 6, No 2, April - June 1997 Lipid Peroxidation in Ischemic Stroke
111
STROKE GROUP
NI
D
A
L
E
V
E
L
Sa 9 l0 n i2 .3 lt i5 i6 t7 l8 19 7J 2.. r.71 a! 2i
CASES
CONTROL
GROUP
7 8 9,t0 r1 t2 13 ta 15 t6 t7 la Êæ21 z2 7J 2. :5
[image:3.595.42.529.85.718.2]CASES
rt2
Sood et al. Med J IndonesREFERENCES
1. Shatter TF. Lipid peroxidation and intracellular messengers in relation to cell injury. Agents Actions 1987;22:334-40. 2. Dillard CA, Downey JE, Tappel AL. Effect of antioxidants
on
lipid
peroxidation
of
iron loaded rats. Lipids
1984;19:127-33.
3. Freeman BA, Crapo JD. Biology of disease: free radicals and tissue injury. Lab Invest 1982;47:412-26.
4. Kagan VE.
Lipid
peroxidationin
biomembranes. Florida: CRC Press, 1988:273-3 10.5. Tomita I, Sano M, Serizawa S, Ohta K, Katou M. Fluchration of lipid peroxides and relative enzyme activities at time of stroke
in
stroke prone spontaneously hypertensive rats' Stroke 1979;10:323-6.6. Kibata M, Shimizu Y, Miyake K, et al. Alpha tocopherol and
TBA
reactive substances (TBARS)in
serum of the stroke patients at acute stage. Igaku no Ayumi 19'71;101:591-2. 7. A WHO collaborative study on stroke.Bull
World HealthOrgan 1980;58:ll3-30.
8. Placer
ZA,
CushmanLL,
JohnsonBC.
Estimationof
products
of lipid
peroxidation(Malonyl
dialdehyde) inbiochemical systems. Anal Biochem 1966;16:359-64. 9. Biller J, Love BB, Marsh EE, Jones MP, Knepper LE, Jiang
D, Adams HP Jr., Gordon
DL.
Spontaneous improvementafter
acute ischemic stroke:
A
pilot
study.
Stroke1990;21:1008- I 2.
10. Goto
U.
Lipid
peroxidesin
biology and medicine. New York: Academic Press, 1982:295-303'11. Dzhandzhgava
TG,
ShakarishiviliRR.
Activity
of
an tioxidant protective enzymes and control of lipidperoxida-tion products blood serum CSF
in
patients with ischemic brain damage. Vopr Med Khim 1992;38:33-5.12. Skochii PH, Karol HM, Tymochko MF. Characteristics of
lipid
peroxidationin
patientswith
an acute disorderof
cerebral circulation. Vrach Delo 1992;6:94-6.13. Yamasaki Y, Kogure K. Possible contribution of free radi-cals and lipid peroxidation on pathogenesis of post ischemic brain damage. Hum Cell 1992;5:341-4.
14. Santos MT, Valles
!,
Aznar J, Vilches J. Determinationof
plasma malondialdhyde like material and its clinical applica-tion in stroke patients. J Clin Patho 198O:,33:973-6. 15. Huang ZS, Lu FJ, Lee TK. Correlation between serum lipidperoxides and the lesion size
in
cerebrovascular disease. Clinica Chimica Acta 1992;17 3 :325 -30.On the other hand, Dzhandzhgava and
Shakarishivilill
studied
the
activity
of
anti-oxidant protective
en-zymes-superoxide dismutase catalase, glutathione
peroxidase
andglutathione
reductasein blood,
serumand CSF
in
patients suffering
from all
types
of
is-chemic
insult to brain
andfound
anearly
decreasein
the
activity of
antioxidant enzyme
aswell
as contentsof lipid
peroxidation products
and these patterns wereseen
to
normalise
within
14-15 days.
The
degreeof
alteration was
found to
correspond
significantly with
the
severity of impairment
and he concluded that thesepatterns
can
be used
for
diagnostic and
prognostic
po.por"r. Skochii
et
allz
in
astudy
on
89 patients
of
cerebral stroke
found
a
clear correlation
between
serum
lipid
levels
andthe severity
of
stroke
andcon-cluded
that
lipid
peroxidation may
be usedfor
evalua-tion of
treatmentefficacy
andprognosis
of the disease.In the present study, serum
MDA
levels were estimatedin
25
patients
of
ischemic
stroke at the earliest after
hospitalisation
andthey
werefound
to besignificantly
higher
compared
to
age
and sex
matched controls,
specially
in
patients hospitalised
within
6
hours of
onset
of
stroke.
No significant
difference
asfound in
the
levels in patients
with
sudden, acute orprogressive
onset stroke.
Similarly no
correlation could
beestab-lished
of
serum
MDA
levels
with
the
severity of
neurological deficit,
or with
the
outcome
of
stroke.These
findings were
in
agreementwith
those
of
theother
worker;.6'14'15Thus
we could not
detect anyprognostic
usefulnessof
determination of
serumMDA
levels inischemic
strokepatients
as assessedby their neurological
score. On theother hand, rise
in
serum
MDA
levels
in
the
strokepatients
ascompared
to
age and sex matchedcontrols
washighly significant
(p <0.001),
more soduring
first
6 hours
of
the onsetof
stroke. This
stresses therole
of
lipid
peroxidation
in
the
damage caused during
cerebral ischemic
infarction
and implies
that