DEVELOPING VISUAL MEDIA IN LINE WITH
ENGLISH THEMES FOR FIRST SEMESTER STUDENT
A “Skripsi”
Presented to the Faculty of Tarbiya and Teachers Training
In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Strata-1 (S-1)
By:
AHMAD SALIM SABITI
NIM. 102014023781
ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF TARBIYA AND TEACHERS TRAINING
SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH
STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
JAKARTA
DEVELOPING VISUAL MEDIA IN LINE WITH
ENGLISH THEMES FOR FIRST SEMESTER STUDENT
A “Skripsi”
Presented to the Faculty of Tarbiya and Teachers Training
In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Strata-1 (S-1)
By:
AHMAD SALIM SABITI
NIM. 102014023781
Approved by:
Prof. Dr. H. Muljanto Soemardi, MA.
Advisor
ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF TARBIYA AND TEACHERS TRAINING
SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH
STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
JAKARTA
LEGALIZATION OF EXAMINATION COMMITTEE
A skripsi titled
DEVELOPING VISUAL MEDIA IN LINE WITH
ENGLISH THEMES FOR FIRST SEMESTER STUDENT
was examined at
examination session of the Faculty of Tarbiya and Teachers’ Training of State Islamic
University Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta on January, 2007. This skripsi has fulfilled
the requirements for the Degree of Strata 1 (S1) at the English Education Department.
Jakarta,
January 2007
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
In the name of Allah, the Beneficent and the Merciful, all praise be to Allah Lord of the worlds, who has given mercy and blessing until the writer can accomplish his “skripsi”. Peace and Salutation be upon to the Prophet Muhammad SAW, and his household, companions and his faith forever.
This “skripsi” is presented to English Education Department, Faculty of Tarbiya and Teachers Training, Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic University Jakarta as a partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Strata -1 (S-1).
In this occasion, the writer would like to give his great appreciation, honor and gratitude to Prof. DR. H. Muljanto Soemardi, MA., as his advisor, for his time, guidance, kindness, contributions and patience in correcting and helping him in finishing this “skripsi”.
His sincere gratitude goes to:
1. Prof. DR. Dede Rosyada, MA., as the Dean of Faculty of Tarbiya and Teachers Training 2. Drs. Nasrun Mahmud, M.Pd., as the Head of English Education Department.
3. Nida Husna, M.Pd. , as the Secretary of English Education Department, and all the staff of English Education Department.
5. The writer would like to express his greatest appreciation to his beloved parents, H. Ahmad Dadih and Hj. Muiyah, for their irreplaceable encouragement and patience to motivate the writer to accomplish this “skripsi”, and also for his sister and brother.
6. The staff and officers of the libraries of UIN, AMINEF, AMCOR and National Library who have given permission to the writer to use their books.
7. Drs. H. Kuswanda, M. Pd, the Headmaster of SMP Negeri 1 Ciputat, who has given the writer a great chance to carry out the research at SMP Negeri 1 Ciputat.
8. Mrs. Marfuah, the English teacher of the seventh grade of SMP Negeri 1 Ciputat, who has helped the writer in collecting the data.
9. The writer also would like to give his greatest thanks to his best friends, Tuti, Atik, Tatu, Ade, Sultan, Dayan, Eva, Dedih, and Muflih who have supported him, shared their ideas with them and build wonderful moment together.
Finally, the writer realizes that this “skripsi” is still far from being perfect, constructive criticism and suggestion would be acceptable to make this “skripsi” better.
Jakarta, December 2006
LIST OF APPENDIXES
Page
1. Teaching Material ... 37
2. Observation Sheet ... 39
... 3. Interview Guide ... 41
4. Lesson Planning ... 45
5. Visual Media in Line with English Themes... 56
6. Question Sheet of Post-Test... 57
7. Key Answer ... 59
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
...
...
i...
TABLE OF CONTENTS
... iii
LIST OF APPENDIXES
... v
A. Background of the Study ...
1
B. Statement of the Problem ...
4
A. Objective of the Study ...
4
B.
Significance of the Study ...
5
C.
Scope of the Study ...
5
CHAPTER II
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
... 6
B.
Instructional Media ...
6
1.
Definition of Instructional Media ...
6
2.
Function of Instructional Media...
8
3.
Kinds of Instructional Media ...
11
A.
Visual Media ...
12
1.
Definition of Visual Media ...
12
2.
Kind of Visual Media and Their Effectiveness...
13
C.
English Themes ...
17
D.
Strategies in Using and Developing Visual Media
in Line with English Themes...
18
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
... 21
A. Objective of the Research ...
21
C.
.
Method of the Research ...
22
D. Teaching Procedures...
D. Data Collection ...
23
E. Data Analysis ...
24
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH FINDINGS
... 26
A.
Research Findings ...
26
1.
Description of Data ...
26
2.
Analysis of Data...
30
3.
Interpretation of Data ...
32
CHAPTER V
CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION
... 33
A.
Conclusion ... 33
B.
Suggestion ... 33
BIBLIOGRAPHY
... 35
APPENDIXES
... 37
CHAPTER I
This chapter consists of background of the study, statement of the problem, significance of the study, and scope of the study.
B.
Background of the Study
English is used as a tool of communication and it has an important role in society life, both oral and written, such as books, newspapers, magazines, television, radio, and internet. To have the ability in reading books and other written sources, people are supposed to master English. It is not easy to master English for everybody.
English is considered very important to improve knowledge and develop technology, art, and culture. English is the first foreign language, which has been taught in Junior high schools and Senior high schools in Indonesia. Since fifty years ago, in Indonesian educational system, English has been taught as subject matter in SMP and SMA. As stated in 2004 curriculum of SMP that the purpose of English teaching at SMP is the students have the ability in listening, speaking, reading, and writing skills.
There are many factors to achieve English teaching purpose. Kasbolah stated that teacher, teaching materials, media, students, curriculum and society are needed to support teaching learning process1. But to control all of the factors is not an easy process.
Prof. Dr. H. Asnawir stated that “Guru merupakan komponen pengajaran yang memegang peranan penting dan utama, karena keberhasilan proses belajar mengajar sangat ditentukan oleh
faktor guru.”2 (Teachers are one of instructional components which have a significant role because the success of teaching learning process depends on them). Therefore, the teachers are supposed to motivate the students to learn English well in class. Thus, the teachers are supposed to select and use
1
Kasihani Kasbolah.. Instructional Media for Young Learners of EFL. ELE .1995. (1): p. 68-73 2
the appropriate materials and media. They are supposed to have good and attractive techniques in teaching. One of the good techniques is using instructional media.
Instructional media are very useful in English teaching, especially for young learners. Finocchiaro stated that “media make the situation of class are more active”3. In other words, instructional media make the students more active in following the teaching learning process.
According to Brinton, in attempting to provide an overview of the range of the media available to classroom teachers’ today, it is perhaps best to stick with the traditional classification of “non technical” and “technical”4. Non technical consists of blackboards, flashcards, posters, newspapers, etc. While, technical media typically include audiotapes, videotapes, television, film, computer, language lab, etc.
In teaching learning process, especially in teaching English as a foreign language, visual media are very important because there are many differences between foreign language and native language5. One of the differences between foreign language and native language, foreign language is a language that seldom to be used in daily communication but native language is a language that used in daily communication. By using visual media, like pictures and films, the teacher can show what the pictures and films mean without showing the real thing.
By using visual media, the teacher can give information to the students clearly. On other side, the students can get and understand the information easily because the teacher displays what lesson is being discussed and they can see what the teacher means directly.
As mentioned in 2004 English Curriculum for SMP, English teachers are suggested to use some instructional media which make the teaching learning process more effective. Some instructional media are pictures, flash cards, flannel board, flip cards, charts, transparency, map, recording aids, and real objects.
3
Mary Finocchiaro. Visual Aids in teaching English as a Second Language. English Teaching Forum. 1975. Vol. XII. (34): p. 263-266
4
Marianne Celce-Muria, (ed). Teaching English as a Second or Foreign Language , 2nd edition, (USA: Heinle & Heinle Publisher, 1995), p. 457
5
The writer heard that most of SMP students assumed that English is a difficult subject. Furthermore, they are unmotivated to learn English because the class situations are very boring. They only listen to what their teacher says without knowing and understanding what the teacher means.
This fact encouraged the writer to know more whether the same problem happened at SMP Negeri 1 Ciputat. The writer is interested in describing the use of visual media in accordance with English themes that are cited in English 2004 Curriculum at SMP Negeri 1 Ciputat. He tries to conduct a research that is related to the use of visual media under the title: “DEVELOPING VISUAL MEDIA IN LINE WITH ENGLISH THEMES FOR FIRST SEMESTER STUDENTS”.
C.
Statement of the Problem
Based on the background of study above, the writer tries to conduct a research that is related with the topic of the study. Because there are many kinds of media used in English teaching, the writer only focuses on the use of visual media and how to develop it.
The formulation of this problem is “How effective are the visual media which are developed and used in English teaching at first semester of SMP Negeri 1 Ciputat?”
D.
Objective of the Study
In line with the formulation of the problems above, the objective of the study is to describe the effectiveness of the visual media that are developed and used in English teaching at first semester of SMP Negeri 1 Ciputat.
E.
Significance of the Study
The result of this study is expected to give any contribution in English teaching theoretically and practically. Theoretically, this result of the study is expected to be useful to support the previous research. Furthermore, the result of the study can be used as a reference for other researchers who are interested in conducting the same research.
Negeri 1 Ciputat about the use visual media in English teaching learning process. Information about the development and the effectiveness of visual media. The product of visual media is expected can support the student motivation in learning English.
F.
Scope of the Study
The study is limited on the use and the development of visual media in line with English themes of first semester at first semester of SMP Negeri 1 Ciputat. The visual media are only limited on pictures, flash cards, real object, and charts. The discussion of this study is limited on the kinds of visual media, the function of visual media, the student’s attitude on the use of visual media, and how to develop visual media in line with English themes.
CHAPTER II
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
This chapter consists of some theories related to instructional media, visual media, English themes, and strategies in using and developing visual media in line with English themes.
A.
Instructional Media
1. Definition of Instructional Media
Media is called as instructional media when it conveys messages which are related with instructional objectives, for example to facilitate communication6. Media is technological system for conveying messages, operating intermediately between sender (s) and receiver (s), when they are separated in space, time, or both.7
Geralch & Elly stated that “Media adalah manusia, materi atau kejadian yang membangun kondisi dan membuat siswa mampu memperoleh pengetahuan, ketrampilan serta sikap.8 (Media are person, material or event which develops a situation and make the students to get knowledge, skills and attitude).
6 Robert Heinich, et.al.,
Instructional Media and the New Technologies of Instruction,
(Canada: John Willy and Sons, Inc, 1993), p. 7
Rudy Bretz, Media for Interactive Communication, (USA: Sage Publications, 1983), p.19
8
According to Association for Education and Communication Technology (AECT) “Media adalah segala bentuk yang dipergunakan untuk suatu proses penyaluran infomasi.”9 (Media are of many forms which are used for information transfer process).
Suleiman stated that instructional media is a media which deliver information or message from a source (teacher) to receiver (student)10. He added that instructional media are intended to improve the result of study.
According to Gagne and Briggs (1975) that “Media pembelajaran meliputi alat yang secara fisik digunakan untuk menyampaikan isi materi pelajaran, yang terdiri dari antara lain buku, tape
recorder, kaset, video kamera, video recorder, film, foto, gambar dan computer11. (Instructional media consists of aids which are used physically to convey the content of the material that includes books, tape recorder, cassette, video, recorder, film, photo, pictures, and computer). In other words, media is a component source of study or idea physically which consists of instructional material in students environment in order to stimulate the students to study.
The role of media in teaching situation, according to Heinich, as supporting aid for teaching in a class. While, Rijavec stated that a message delivered through the linguistic channel, although subject to some of the same ambiguities, tends to be more precise.12
From the statements above, it can be concluded that instructional media is aids which are used to support teaching learning process. Media plays an important role in improving student’s ability. The using of media creatively will probably make the students improve their performance in study that suitable with the objectives of the teaching learning process.
2. Function of Instructional Media
Teaching aids (instructional media) are useful in teaching learning process. Finnochiaro said that the class could be more active if the media can attract student’s attention. Material aids can help
9
Prof. Dr H. Asnawir dan Drs. M. Basyiruddin Usman, M. Pd, Media Pembelajaran, (Jakarta: Ciputat Press, 2002), p. 11. Translated by the writer.
10
Amir Hamzah Suleiman,. Media Audio Visual untuk Pengajaran Penerangan dan Penyuluhan, (Jakarta: PT Gramedia, 1985), p. 2. Translated by the writer.
11
Prof. Dr. Azhar Asyad, M. A, op. cit., p. 4. Translated by the writer. 12 Maja Rijavec,
the student to communicate-that is to understand, to speak, to read, and to write English.13 Therefore, the student will give a response to an attractive thing.
The student can get their learning result better when the media integrated in learning process, and the media can facilitate learning process commonly and it’s more attractive than traditional teaching. Media can improve student’s interest, understanding and memory.
Prof. Dr. Azhar Arsyad, M. A stated that “Media berfungsi untuk tujuan instruksi di mana informasi yang terdapat dalam media itu harus melibatkan siswa baik dalam benak atau mental
apapun dalam bentuk aktifitas yang nyata sehingga pembelajaran dapat terjadi.”14 (Media is used for instructional objectives in which information in media should involve students’ participation both in mind or other mental aspects and in real activities form, so that, the learning process can be carried).
According to Prof. Dr H. Asnawir, intructional media has several functions:
1.
To help students study easily
2.
To give real experience (abstract to be more concrete)
3.
To stimulate student’s interest
4.
All of the student’s sense can be activated
5.
To attract student interest’ s in study
6.
To give theory with reality
15According to Davies, the functions of media are as follows: 1) Aids to instruction
Media serves to help the teachers and instructors to manage instruction more efficiently. Media assist teachers to communicate more effectively and take over the creating role of instruction from teacher and instructors.
2) Aids to learning
Media serves to help students learn more efficiently. Media promote understanding, assist in the transfer of training, and assist in assessment. Media can be used in assessing mastering performance. 16
13
Mary Finnochiaro, op. cit. p. 263 14
Prof. Dr. Azhar Asyad, M. A, Media Pembelajaran, op. cit., p. 21. Translated by the writer. 15
Prof. Dr H. Asnawir dan Drs. M. Basyiruddin Usman, op. cit, p. 24. 16
Levie and Lentz (1982) stated that there are four functions of instructional media:
1) Fungsi Atensi
Yaitu menarik dan mengarahkan perhatian siswa untuk berkonsentrasi kepada isi pelajaran yang ditampilkan atau menyertai teks materi pelajaran.
2) Fungsi Afektif
Yaitu media visual dapat terlihat dari tingkat kenikmatan siswa ketika belajar (atau membaca) teks yang bergambar.
3) Fungsi Kognitif
Yaitu media visual terlihat dari temuan-temuan penelitian yang mengungkapkan bahwa lambang visual atau gambar memperlancar pencapaian tujuan untuk memahami dan mengingat informasi atau pesan yang terkandung dalam gambar.
4) Fungsi Kompentaris
Yaitu media pembelajaran terlihat dari hasil penelitian bahwa media visual yang memberikan konteks untuk memahami teks membantu siswa yang lemah dalam membaca untuk mengorganisasikan informasi dalam teks dan mengingatnya kembali.17
1) Attention
It means that media should attractive and intend students’ attention to focus their concentration in understanding the presented lesson.
2) Affective
Visual media can be seen from their enjoyment in learning (or reading) some pictures texts. 3) Cognitive
Visual media as found from some research findings which stated that visual symbols or pictures can ease instruction achievements for understanding and memorizing some information or messages that is contained in the pictures.
4) Compensatory
As found from some research findings that visual media which give some contexts in understanding text, help students who have weakness in reading and to organize information in text and recall it. In other word, instructional media is used to accommodate weak students in receiving the lesson.
Furthermore, Lubis mentions some functions of visual media are to: Support understanding when the students are listening,
Put across the meaning of vocabulary, Prompt and support reading,
Provide a topic or visual focus to prompt speaking or writing, Provide a visual link between first language and second language,
17
Provide support and motivation for early reading and writing English, Provide ways around communication barriers.18
According to the functions above, it can be concluded that instructional media are very important in teaching and learning process. English teacher is supposed to use instructional media to achieve instructional objective. Therefore, the uses of instructional media are supposed to be designed and developed well. Teacher is supposed to consider some factors in using and developing instructional media to avoid any mistakes or difficulties in using it.
3. Kinds of Instructional Media
A teacher is supposed to use variety of instructional media and does not often use the same media because it can make student bored. So that, teacher is supposed to have variety of media in English teaching in order that the student can be attracted and motivated in learning English.
Generally, there are three kinds of instructional media, namely audio, visual, and audio-visual media. Audio media are a media that can be listened, visual media are a media that can be seen. Instructional media that can be seen and listened called an audio-visual media.
Finnochiaro provided some examples of visual media are blackboards, real objects, charts, picture files, flannel board, pocket chart, flash card, word card, number card, magnetic board, etc. Audio media are recording tool, tape recorder, and language lab. And audio-visual media are film, television, and instructional program.19
B.
Visual Media
Definition of Visual Media
In Oxford Learner’s Dictionary, visual media are “picture, film, video, map, etc which are used as teaching aids”20. And it can be defined as things that can be seen and used as a visual teaching and learning.
Kinds of Visual Media and Their Effectiveness Picture
18
Yusnaeni Lubis, Developing Communicate Proficiency in English As a Foreign Language,(Jakarta: Bina Rupa Aksara, 1974), p. 56
19
Mary Finnochiaro, Op. Cit. p.263-266 20
In Webster New World Dictionary of American English we can see that “picture is an imagination or likeness of an object person or scene produce on a flat surface, especially by painting, drawing or photography21.
According to Andrew Wright, “pictures are the most suitable for the revision of known language and more recombination or manipulation word, the picture are not just an aspect of method but through their representation of places, object and people they are essential part of the overall experiences.”22
[image:19.612.113.505.367.501.2]The effectiveness of visual aids in language teaching has been universally acknowledged. As Maya Rijavec said that picture is worth a thousand words. It implies that the visual channel of transmitting information is superior to the auditory.23. Often a picture will show a situation or a scene in which there are several things and persons. Suppose, for example, we have a picture of each of the following: a church, a taxi, a bus, a traffic light, a policeman, a mailbox24. As shown in figure 2.1
Figure 2.1 Pictures of activities
Flash Cards
Flash card is another example of visual media. It can be photograph, pieces of picture from magazine or newspaper. According to Suleiman pictures which is used in flash card, can be more effective if they are appropriate with these criteria as follow:
The picture should be clear, interest, quite big, and easy to be understood.
21 Noah Webster,
Webster New World Dictionary of American English,
(New York: Prentice
hall Regents 1994). p. 1089 22
Andrew Wright, Pictures for Language Learning, (Longman Group Limited, 1983), p. 3 23
Maja Rijavec,
Op. Cit.. p. 50 24
The picture should appropriate with the themes.
The picture should be authentic. Its mean that it has same condition with the real contexts. The picture should be simple. The complex pictures make the student confuse and fail in
finding the real meaning of the picture.25
The picture of flash card should be quite enough in order all the students can see clearly. The size is about 21 x 17 cm. The number of flash card to be used in vocabulary practice in the classroom is about seven to ten cards. Based on the content, they are two types of flash card. First, flash card should show one person, one action, and one object (figure 2.2). Second, it should show a situation includes some activities, people, and one object (figure 2.3). The first type can be used to give new vocabulary, drills, and exercises. And the second type can be used to describe some situations, like recreation, birthday party, in a restaurant, in the classroom, in the kitchen, and other situation. This type is also can be used to introduce some dialogues, sentences patterns drill and to stimulate the students in making composition practice.
Figure 2.2 (type 1)
Figure 2.3 (type 2)
Real Objects
Real objects are a proper media to introduce new material to the students that is used a part of learning concept about abstract vocabulary. Real object is real-life objects that enable students
25
[image:20.612.112.494.350.550.2]to make connections to their own lives. Examples include bank deposit slips and check registers for an unit on banking, or nutrition labels on food products for health unit26.
Finnochiaro assumed that students understand and retain the meaning of a word better when they have seen or have touched some object associated with it.
There several uses of real object, as follows: Uses for presenting vocabulary.
Uses for presenting new structures.
To help students get into character when acting out a dialogue or doing role-play e. g. if someone is acting of a policeman, he can be given a policeman’s helmet etc.
As props for dialogues or role-play, so if a scene is taking place in a shop, a lot of realism can be added if real money or real objects one used.
Aids for various game.27
In other word, if learning process can be improved by involving feelings, real object can facilitate learning process. Using real object will facilitate the presentation of many language items.
Charts
Another valuable aid is the charts or picture file, which should be an integral part of every classroom. An effective chart usually consists of some different graphic: pictures, cartoons, graphics, diagrams, and verbal form. The size of chart is depending on kind of picture.
It should contain at least three major types of illustration. First, pictures of persons and single objects. Second, pictures of people engaged in activities presenting the relationship between individuals and objects. Third, a series of six to ten pictures mounted on one chart of count nouns (as pieces of furniture) or mass nouns (as foods) or of sports or work activities.28
26
Jana Echevaria, et. al., Making Content Comprehensible for English Language Learners,
(USA: Allyn & Bacon, 2000), p. 27 27
Peter Hobbard, et al., A Training Course for TEFL, (New York: Oxford University Press, 1983), p. 114
28
The main function of chart is to serve ideas or difficult concepts if it is conveyed by written or oral visually29. So if there is something that can not be catch by the students in learning process, the chart can be the as the solution. Chart can also give conclusion of important points in a presentation.
As a good media, chart should be: 1. Easy to understand by the student. 2. Simple and not complicated. 3. Up to date.30
C.
English Themes
One of the objectives of teaching English at junior high school is to develop communicative competence in English both oral and written. The communicative competence consists of listening, speaking, reading, and writing.31
Learning process is leaded to gain students’ competence that can be seen from their communicative activities. For example, in speaking, students do not only focus to English themes as usual called as “talk about certain theme”. They are lead to develop communicative speaking. Themes are used as reference in developing communicative competence. Thus, themes that are related to vocabularies and grammar are considered to achieve student’s competency.
There are eight English themes for seventh grades student based on 2004 English curriculum:
self identity, school life, family life, daily needs (first semester), stories, hobbies, things around us, and
shopping (second semester).
29
Sadiman, Arief S. et al., Media Pendidikan, (Jakarta: PT Raja Grafindo Persada, 2006), p. 35. Translated by the writer.
30
Sadiman, Arief S. et al., Ibid. p. 35 31
D. Strategies in Using and Developing Visual Media in Line with English Themes
Wright suggested in how to use visual media like flash card in language teaching. Some flash cards that illustrate an action can be used to teach tenses32. For example, the teacher shows the picture of flash card and decides what to do by the person of the picture, then hide of the flash card. And then the teacher asks, ”What does she/he do?”. Picture of flash card does not need for artwork. Because the student can sees picture clearly and know it easily, those of thing it is enough about using flash card in teaching activities.
There are no definite standards or rules that can be set up for the selection of visual aids for classroom use, but there are a few criteria that can serve as guides. The teacher should consider these points:
1. The importance of the aid in attaining the objectives of the work. Is the aid essential to such class work?
2. The adaptability of the aid as compared with other aids. 3. The availability of the aid as compared with other valuable aids.
4. The efficiency of the aid from the point of view of time consumption relative to its importance. Is it economical of time both in preparation before class and in use during class? 5. The relative effectiveness of the aid as compared with other available aids.
6. The cost of the aid as compared with other aids.33
Teacher is supposed be aware that media can play a role at any or all of the four stages of the lesson, and that a variety of media might be used in these stages to complement each other and to achieve the designated teaching objective.34
I. Information and motivation stage: Getting into media
II. Input stage: Working from media Teacher presents/elicits vocabulary Teacher presents/elicits structures
32
Andrew Wright, Visual Materials for Language Teachers, (Hong Kong: Wilture Enterprise International Ltd, 1976),, 5th ed, p. 75
33
Thomas M. Risk, Principles and Practices of Teaching in Secondary School, (New York: American Book Company, 1958), 3rd ed, p. 363
34
Teacher presents/elicit functions Teacher presents/elicits content III. Focus stage: Working with media
Teacher models language items/procedures Students practice items in context
Drill Elicitation
Students manipulate language/content Note taking
Information transfer Pair work/small group work IV. Transfer stage: Working out of media
Class discussion
Student interact, using context set by media materials as a point of departure Role play
Problem-solving activity Information gap activity Game
Task-based assignment Follow-up writing assignment Sharing of personal experience Field trip
Hamalik stated that to choose and use instructional media are supposed to be suitable with the certain criteria, as follows35:
Instructional Objective Material
Methods of Teaching Needed available equipment The activities
The assessment Teacher personality Students’ competency Teaching learning process
Based on the statements above, the teachers are supposed to prepare well in using and developing visual media. They should make visual media that suitable with the instructional objective and the themes which are taught. It should be large, simple and clear size, and easy to be developed and manipulated.
35
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This chapter discusses the objective of the research, place and the time of the research, population and sample, method of the research, data collection, and data analysis.
A.
Objective of the Research
The objective of the study is to describe the effectiveness of the visual media developed and used in English teaching at first semester of SMP Negeri 1 Ciputat academic year 2006-2007. Therefore, the writer wants to prove some theories whether it is true that visual media can motivate and stimulate students in learning English.
G.
Place and Time of Research
This research is held at seventh grade of SMP Negeri 1 Ciputat, which is located on Jl Cireundeu Raya No. 2 Ciputat, with some reasons. First, this school is a place where the writer did Teaching Practice (PPKT). A teaching practice program for English department students of Islamic State University in some formal school. Second, the English teachers seldom use visual media in their teaching. Third, there is never a research that is related to the development of visual media in line with English themes of even semester. The research is held from October until November 2006.
The subject of the research is the seventh grade of SMP Negeri 1 Ciputat. The population is about 400 students in 10 classes. The writer takes class of VII-1 and VII-2 as sample of research. He takes 20 students in experiment class and 20 students in controlled class as sample.
C. Method of the Research
The writer uses experiment study. It means that the experiment is carried out in order to explore the strength of relationships between variables36. In the experiment research, there is a control which is done by the researcher accidentally to the variable. Gay stated, (in Sukardi, 2003), control is an effort on the part of researcher to remove the influence of any variable other than the independent variable
36
that effect performance on a dependent variable37. Therefore, there are two classes; experiment class
and controlled class. In experiment class, the writer used visual media in his teaching, while, in controlled class, he taught without using visual media.
H.
Teaching Procedures
To make the teaching learning process more effective, teacher is supposed to able to manage the class and use variety of teaching method. The uses of visual media are more effective to make the students are easy to understand the materials. The teacher shows the pictures, flash card, and real objects to the students. So, they get the idea easily and clearly. Then the teacher asks them to imagine what they would do with these media. It is related on unconscious knowledge (mental aspect), since they see the object and it can add their attention to the subject, the media can also illustrate each situation.
The uses of method also have essential part in teaching learning process. It is very useful to help students in understanding the material. They should use variety of method to avoid the students feel bored and lazy. Therefore, the teachers use visual media and communicative approach in teaching material based on the English themes.
In teaching English by using visual media in line with English themes, the writer does the following steps:
1. First step
The teacher shows the visual media to the students that related to the theme and ask them to mention what the visual media mean.
37
2. Second step
The teacher reads a text or dialogue to students and asks them to listen what teacher reads. And then, they are asked to find the difficult words, from the text or the dialogue and write them in their books.
3. Third step
After they write the difficult words in their books, ask for volunteers to write them on the white board, and check their spelling and pronunciation.
D. Data Collection
The data used in this study are information about the kind of visual media and their effectiveness. Collecting data is one important thing in the research, that can be determined the result of the research such as:
1. Observation
Observation is held to collect data about the use and development of visual media. The writer did three times of observation. This observation is done to know the students’ attitude in learning English by using visual media and how the teacher teaches English.
2. Interview
Interview is done to collect data from teachers. The data, which is gotten through interview, are information about the use of visual media by the English teachers and their response about the visual media that is developed by the writer.
D.
Test
The test is made by the writer. He takes the question from two books. First, “Competency based English 1” by Tony Rogers and second “Speak English First 1” by Chabib Basirun.
Both of tests are held to know their mastery of the materials at first semester. The test consists of two kinds, multiple choice and essay.
The writer gives the test to 40 students, 20 students from controlled class and 20 students from experiment class, the test consist of 15 items that related to the English themes, it is divided in two forms, and they are multiple choice and essay.
Multiple choice consists of 15 items, from number 1 to number fifteen, its score in one item is 4 (four), it means, if the students can answer the question correctly, he will get 4 scores, and if he can choose the answer of 15 items correctly, he will get 60 scores.
Essay consists of 5 items, its score in one item is 8 (eight), it means if the students can answer one item correctly, they will get 8 scores, and if they can answer 5 items correctly, they will get 40 scores.
From the description of each test above, we can see that the highest score of this test is 100 scores.
E.
Data Analysis
After getting the data either from control class and experiment class, the writer analyzes it by using statistic calculation of the t-test formula with the degree of significance 5% and 1%.
Before using t-test formula, the writer has to seek the differences of mean variables by using formula as follows:
And after getting the mean variables, the writer has to seek the standard of deviation of variable and standard error mean of variables by using formula as follows:
∑
∑
−
=
=
=
2 2 1 1 N NY
M
and
X
M
N
y
SD
and
N
x
SD
=
∑
−
−
−
=
∑
−
1 2 2 2.
1
1
1
.
2
22 1
1
=
−
−
−
−
−
=
−
The next step s seeking the standard error means difference of variables by using formula as follows:
SEM1 – M2 = M2 =
The next step is seeking the standard error mean difference of variables by using formula as follows:
Then the last is determining t-test by using formula: t0 = M1 – M2
E.
SEM
1– M
2Therefore, the writer took this formula (t-test) to calculate the data got from the research.
1
1
2 2
1
−
=
−
−
−
−
−
N
SD
SEM
and
N
SD
2 1 2
1 2
1
SEM
SEM
SEM
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH FINDINGS
This chapter presents and discusses findings of the research based on data gathered during the investigation. In line with the research findings, it discusses: (1) description of data, (2) the analysis of data, and (4) the interpretation of data.
A.
RESEARCH FINDINGS
1. Description of Data
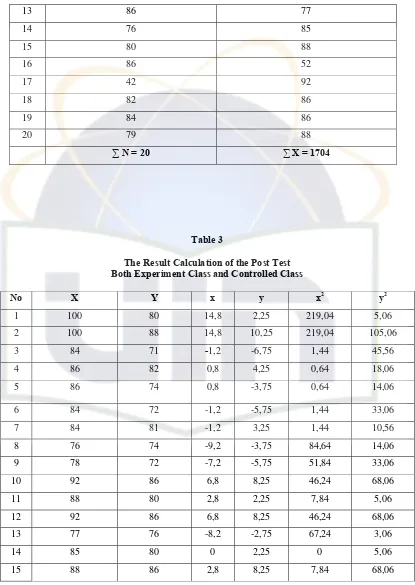
[image:30.612.114.523.342.693.2]To know the result of the experiment, the writer calculate the result of post-test of both classes, where variable X is the post-test result of the experiment class through teaching English using visual media and variable Y is the post-test of the controlled class through teaching English without using visual media.
Table 1
The Result (Score) of the Students in Controlled Class
No Pre-Test Post-Test
1 80 80
2 58 88
3 58 71
4 68 82
5 80 74
6 68 72
7 64 81
9 56 72
10 78 86
11 80 80
12 44 86
13 72 76
14 66 80
15 76 86
16 68 42
17 52 82
18 62 84
19 76 79
20 80 80
[image:31.612.116.514.110.691.2]∑ N = 20 ∑ Y = 1555
Table 2
The Result (Score) of the Students in Experiment Class
No Pre-Test Post-Test
1 80 100
2 88 100
3 71 84
4 82 86
5 74 86
6 72 84
7 81 84
8 74 76
9 72 78
10 86 92
11 80 88
13 86 77
14 76 85
15 80 88
16 86 52
17 42 92
18 82 86
19 84 86
20 79 88
[image:32.612.113.528.109.694.2]∑ N = 20 ∑ X = 1704
Table 3
The Result Calculation of the Post Test Both Experiment Class and Controlled Class
No X Y x y x2 y2
1 100 80 14,8 2,25 219,04 5,06
2 100 88 14,8 10,25 219,04 105,06
3 84 71 -1,2 -6,75 1,44 45,56
4 86 82 0,8 4,25 0,64 18,06
5 86 74 0,8 -3,75 0,64 14,06
6 84 72 -1,2 -5,75 1,44 33,06
7 84 81 -1,2 3,25 1,44 10,56
8 76 74 -9,2 -3,75 84,64 14,06
9 78 72 -7,2 -5,75 51,84 33,06
10 92 86 6,8 8,25 46,24 68,06
11 88 80 2,8 2,25 7,84 5,06
12 92 86 6,8 8,25 46,24 68,06
13 77 76 -8,2 -2,75 67,24 3,06
14 85 80 0 2,25 0 5,06
16 52 42 -33,2 -35,75 1102,24 1278,06
17 92 82 6,8 4,25 46,24 18,06
18 86 84 0,8 6,25 0,64 39,06
19 86 79 0,8 1,25 0,64 1,56
20 88 80 2,8 2,25 7,84 5,06
∑ X = 1704 ∑ Y = 1555 0 0 1913,16 1491,1
It shows that the score of both classes is on average level, means that the students achievement in learning English through using visual media in generally high, though there is a difference in minimum and maximum standard of each class, the table shows the experiment class has higher standard.
2. The Analysis of Data
From the table above, the writer gets the calculation using the following test formula: Determining Mean 1 (M1) with the formula :
M1 =
∑
X
= 1704 = 85,2 N 20Determining Mean 2 (M2) with the formula : M1 =
∑
Y
= 1555 = 77,75 N 20c. Determining the Standard of Deviation of variable 1:
SD1 =
N
x
∑
2 =20
16
,
1913
=
95
,
66
= 9, 78d. Determining the Standard of Deviation of variable 2 :
SD2 =
N
y
∑
2 =20
1
,
1491
=
74
,
555
= 8,63 e. Determining the Standard Error Mean of Variable 1 :SEM1 =
1
1−
N
SD
=1
20
78
,
9
f. Determining the Standard Error Mean of Variable 2:
SEM2 =
1
2−
N
SD
=1
20
63
,
8
−
=19
63
,
8
=
0
,
45
= 0,67g. Determining the Standard Error Mean Difference of M1 and M2:
SEM1-M2 =
2 2 2 1 M M
SE
SE
+
=
=
(
0
,
71
)
2+
(
0
,
67
)
2 =0
,
50
+
0
,
44
=
=0
,
94
= 0,96 h. Determining t0 with the formula:t0 =
2 1 2 M M
SE
SE
M
M
I−
−
=96
,
0
75
,
77
2
,
85
−
=96
.
0
45
,
7
= 7,76i. Determining t-table in significance level 5% and 1% with df: df = (N1 + N2) – 2 = (20 + 20) – 2 = 38
The writer gained t- table: S. L . 5% = 2,02
S. L . 1% = 2,7
t – score = 2,02 < 7,76 > 2,71 j. The comparison between t-score with t-table:
In the table of significance or in t-table, it can be seen from the df = 38 and on the degree of 5% and 1%, the result is 2,02 and 2,71, t-score is 7,76, so it can be concluded that t-score is higher than t-table.
Based on the data collected from the post-test gained from the experiment class taught using visual media and controlled class without using visual media showed the mean of post-test in experiment class is 85,2. While the mean scores of post-test in controlled class is 77, 75.
CHAPTER V
CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION
This chapter consists of conclusion and suggestion.
A. Conclusion
According to research findings in the previous chapter, the writer concluded that the use of visual media in English teaching is more effective than without using visual media. It can be seen from the results of statistic calculation in previous chapter. Where the value of “t0“ is higher than “tt“.
This means that developing visual media in line with English themes is effective in improving English teaching learning process.
B. Suggestion
After doing this research, the writer gives some suggestions as follows:
1. For English Teachers
a. They should motivate and stimulate students in learning English by using visual media in line with English themes based on the curriculum.
c. They should have the ability in improving the students’ language skills and developing others media.
2. For the Principal
The use of visual media is very important, so that, the
principal should provide instructional media to improve the success of
teaching learning process.
3. For Other Researchers
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Allen, Virginia French.,
Techniques in Teaching Vocabulary
, New York: Oxford
University Press, 1983.
AR, Syamsuddin and Vismaia S Damaianti.,
Metode Penelitian Pendidikan Bahasa,
Bandung: PT. Remaja Rosadakarya, 2006
Arsyad, Azhar.,
Media Pembelajaran,
Jakarta: PT. Raja Grafindo Persada, 2004.
Asnawir and Basyiruddin Usman.,
Media Pembelajaran,
Jakarta: Ciputat Press, 2002.
Bretz, Rudy.,
Media for Interactive Communication,
USA: Sage Publications, 1983.
Celce-Muria,Marianne (ed).,
Teaching English as a Second or Foreign Language
,2
ndedition, USA: Heinle & Heinle Publisher, 1995.
Davies, Ivor K,
Instructional Techniques,New York:
Mc Graw Hill, 1980.
Depdiknas,
Kurikulum 2004 Bahasa Inggris untuk SMP,
Jakarta: Depdiknas, 2003.
Echevaria, Jana., et. al.,
Making Content Comprehensible for English Language
Learners,
USA
:
Allyn & Bacon, 2000.
Finocchiaro,Mary.,
Visual Aids in Teaching English as a Second Language.
English
Teaching Forum. 1975. Vol. XII. (34)
Hamalik, Oemar.,
Media Pendidikan,
Bandung; PT. Citra Aditya Bakti, 1989.
Heinich, Robert, et.al.,
Instructional Media and the New Technologies of Instruction
,
Canada: John Willy and Sons, Inc, 1993.
Hobbard, Peter., et al.,
A Training Course for TEFL,
New York: Oxford University
Press, 1983.
Kasbolah, Kasihani.,
Instructional Media for Young Learners of EFL
. ELE .1995.
Lubis, Yusnaeni.,
Developing Communicate Proficiency in English As a Foreign
Language,
Jakarta: Bina Rupa Aksara, 1974.
M. Risk, Thomas.,
Principles and Practices of Teaching in Secondary School,
New
York: American Book Company, 1958.
Nunan, David.,
Research Methods in Language Learning,
USA: Cambridge
Univesity Press, 1992.
Richards, Jack C.,
The Language Teaching Matrix,
Cambridge: Cambridge
Unicersity Press, 1990.
Rijavec, Maja.,
Using Visual Aids Appropriately,
English Teaching
Forum
,
Vol.XXIX. No. 1 January 1991, Washington DC.
Sadiman, Arif S, et al.,
Media Pendidikan,
Jakarta: PT Raja Grafindo Persada, 2006.
Suleiman, Amir Hamzah.,
Media Audio Visual untuk Pengajaran Penerangan dan
Penyuluhan
, Jakarta: PT Gramedia, 1985.
Webster, Noah.,
Webster New World Dictionary of American English,
New York:
Prentice Hall Regents, 1994.
Wright, Andrew.,
Pictures for Language Learning,
Longman Group Limited, 1983.