A STUDY ON MANUFACTURING INFORMATION
REQUIREMENTS FOR ELECTRONICS ASSEMBLY
SOLEHA ROSSDY
UNIVERSITI TEKNIKAL MALAYSIA
MELAKA
A study on Manufacturing Information
Requirements for Electronics Assembly
Thesis submitted in accordance with the partial requirements of the Universiti
Teknikal Malaysia, Melaka for the
Bachelor of Manufacturing Engineering (Design)
By
SOLEHA BT ROSSDY
Faculty of Manufacturing Engineering
KUTKM Library (Pind.1/2005)
SULIT
TERHAD
TIDAK TERHAD
(Mengandungi maklumat yang berdarjah keselamatan atau kepentingan Malaysia yang termaktub di dalam AKTA RAHSIA RASMI 1972)
(Mengandungi maklumat TERHAD yang telah ditentukan oleh organisasi/badan di mana penyelidikan dijalankan)
(TANDATANGAN PENULIS)
* Tesis dimaksudkan sebagai tesis bagi Ijazah Doktor Falsafah dan Sarjana secara penyelidikan, atau BORANG PENGESAHAN STATUS TESIS*
JUDUL: A study on manufacturing information requirements for electronics assembly
SESI PENGAJIAN : 2006 / 2007
Saya SOLEHA BINTI ROSSDY ________________________________
mengaku membenarkan tesis (PSM/Sarjana/Doktor Falsafah) ini disimpan di
Perpustakaan Universiti Teknikal Kebangsaan Malaysia (UTeM) dengan syarat-syarat kegunaan seperti berikut:
1. Tesis adalah hak milik Universiti Teknikal Malaysia Melaka.
2. Perpustakaan Universiti Teknikal Malaysia Melaka dibenarkan membuat salinan untuk tujuan pengajian sahaja.
3. Perpustakaan dibenarkan membuat salinan tesis ini sebagai bahan pertukaran antara institusi pengajian tinggi.
4. **Sila tandakan (√)
(HURUF BESAR)
APPROVAL
This thesis submitted to the senate of UTeM and has been accepted as partial fulfilment of the requirements for the degree of Bachelor of Manufacturing Engineering (Design). The members of the supervisory committee are as follow:
………. Main Supervisor
(Mr Hafidz Fazli b Fauadi)
……… Co-Supervisor
DECLARATION
I hereby, declare this thesis entitled “A study on Manufacturing Information Requirements for Electronics Assembly” is the result of my own research
except as cited in the references.
Signature : ………. Author’s Name : Soleha bt Rossdy
ABSTRACT
In a manufacturing company, managing information is important. It is
involved of gathering data or information from the process before develop a
computerized system to store the data. Therefore, this project highlights three main
objectives, which are: to study the information requirements for underlying decision,
planning and operation for electronic assembly manufacturing, to design the
information requirements and to develop a database management system for the
assembly process. The study was conducted in an electronic factory, Cubic
Electronic Sdn Bhd (CESB). The study focuses on surface mount technology (SMT)
assembly, Manual Insert (MI) assembly and mechanical assembly (MA). For this
project, IDEF was selected as the methodology in modelling the functional and
information requirements. Microsoft Access is used to design database for the
designed model. The study has successfully achieved the objectives and may be as a
ABSTRAK
Dalam sebuah syarikat pembuatan, penyusunan data-data adalah penting. Ia
melibatkan pengumpulan data dari proses yg terlibat kemudian membangunkan satu
sistem yang meyimpan data dan boleh memanggil data jika dikehendaki. Oleh itu,
projek ini menekankan beberapa objektif di mana untuk mengkaji data-data dalam
membuat keputusan, membuat rangka kerja dan proses yg terlibat dalam pemasangan
alat elektronik di kilang yang dikaji merekabentuk data yang diperlukan dan
membangunkan sistem pangkalan data untuk proses pemasangan alat elektronik.
Kajian ini dilakukan di sebuah kilang elektronik , Cubic Electronic sdn bhd (CESB).
Fokus kajian adalah berdasarkan teknologi pemasangan surface mount technology
(SMT) dan pemasangan secara manual dan mekanikal (MIMA). Dalam projek ini,
IDEF telah dipilih sebagai kaedah dalam permodelan data. Pembangunan sistem
melibatkan penggunaan Microsoft Access dalam merekabentuk sistem pangkalan
data yang telah dianalisis. Sistem ini adalah praktikal untuk digunakan namun
beberapa batasan telah dibincangkan sebagai penambahbaikkan untuk masa akan
DEDICATION
ACKNOWLEGDEMENT
Bismillahhirrahmanirrahim,
Assalamualaikum w.b.t. and warm greeting
First of all, thank to ALLAH SWT for His blessings and for the strength given to
complete this Project Sarjana Muda (PSM) – I and II.
The author would like to thank to:
1. Mr. Muhammad Hafidz Fazli bin Md Fauadi, project supervisor for his
guidance, encouragement, wise suggestion and discussion, patience and
support in this project.
2. Mr. Zaimi Zainal as the second panel of this project and the cooperation he
gave.
3. Pn Yusnita Yusof and all the staffs in Cubic Electronics sdn bhd (CESB) for
the cooperation in sharing the information about the company.
4. Friends during Industrial Training – Nabila, Lim Pierre June and Voon for a
helpful hand and information about manufacturing assembly in CESB.
5. Yumi, from Information Technology faculty, University Technical Melaka,
Malaysia (UTeM) for knowledge gave and shared.
6. Fellow friends and housemates – for all assistance, motivation, courage and
time that we spent together.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1.3 Objectives of the Research 4
1.4 Scope of Project 4
1.5 Advantages of the project 4
1.6 Project Methodology 5
2.4.1.3 Advantages & Disadvantages of IDEF 12
2.4.2 Object Oriented 13
2.4.3.2 Entity Relationship 17
2.5 Previous Development of Information System for Electronic
Manufacturing Industry 19
2.5.1 The effects of information system infrastructure and process
improvements on supply-chain time performance 19
2.5.2 An empirical study of business processes across Internet-based
Electronic marketplaces: A supply-chain-management perspective 20
2.5.3 Business process improvement through electronic data interchanges
(EDI) systems: an empirical study 22
2.5.4 Electronic trading in the supply chain: a holistic implementation
Framework 24
2.5.5 Linking warehouse complexity to warehouse planning and control
structure an exploratory study of the use of warehouse
management information systems 25
2.5.6 Manufacturing integration strategy using MRP II and RTMs:
a case study in South China 27
2.6 Web-based Application in Manufacturing Industry 30
2.6.1Virtual factory: an integrated approach to manufacturing systems
Modeling 30
2.6.2 Product data management based on Web technology 32
2.6.3 Proton PDM 33
2.6.4 Engineering requirement management system: A PLM Strategy 34
2.6.5 Knowledge Based Engineering Practice – TATA Consultancy
Services 34
2.6.6 Mattel Tooling Development Sdn Bhd 35
CHAPTER 3.0 CUBIC ELECTRONIC Sdn. Bhd. (CESB)
3.1 Company’s background 38
3.1.2 Factory wide build up area 39
3.3 Manufacturing Process in CESB
3.3.1 Introduction 46
3.3.2 Overall Manufacturing Process 49
3.3.3 SMT Process at CESB 49
3.3.4 MIMA Manufacturing Process 57
4.2.2 Identify objectives and scope of the projects 64
4.2.3 Literature study 64
4.2.4 Define generic function and information 64
CHAPTER 5.0 SYSTEM ANALYSIS & DESIGN
5.1 Introduction 67
5.2 System Advantages
5.2.1 Functional & Information Model Advantages 68
5.2.2 Database Advantages 69
5.3 Functional Model 69
5.3.1 Sound Blaster Manufacturing (A0 Level) 70
5.3.2 Sound Blaster Manufacturing (A1 Level) 71
5.3.3 Model Layout (A1) 72
5.3.4 Surface Mount Technology, SMT (A2 Level) 73
5.3.5 Manual Insert & Assembly, MIMA (A3 Level) 78
5.3.6 Testing (A4 Level) 82
5.3.7 Packaging (A5 Level) 83
REFERENCES 102
APPENDICES A
APPENDICES B
LIST OF FIGURE
1.0 Project Methodology 5
2.0 Modelling Methodology 9
2.1 IDEF Box & Arrow Graphics 12
2.2 Object Oriented Road Map 14
2.3 An example of Yourdon system methods 15
2.4 An example of ERD (Yourdon system method) 17
2.5 Yourdon system methods, model driven methods, 1993 18
2.6 A model linking information system infrastructure, process
improvement and their interaction to supply-chain
time-based performance 20
2.7 A general supply-chain- management model 22
2.8 Research model – the relationship between EDI networks
and BPI with moderating effect of information intensity
of the industry. 24
2.9 Framework for assisting with the change towards
electronic commerce 25
2.10 WMS in relation to other management information and
technical systems 26
2.11 Integrated manufacturing system 28
2.12 IDEF design of MRP II and shop floor integration 29
2.13 Virtual factory model 31
2.14 Role of virtual factory during operations 31
2.15 An example of basic PDM data structure 32
2.16 The logical relationship of data in a PDM system 32
2.17 Product Data Management (PDM) 33
2.18 System Decomposition Diagram 36
2.19 IDEF functional model for mold making process 37
3.0 CESB Building 38
3.1 Building plan 42
3.2 Main organization in CESB 43
3.3 Manufacturing organization 43
3.4 MO1 Organization 44
3.5 MIMA Organization 45
3.6 Schematics Production MIMA/ICT 45
3.7 Process Flow in SMT 46
3.8 Process Flow in MIMA 47
3.9 Process Flow in FT 48
3.10 Process Flow in Packaging Department 48
3.11 Overall Manufacturing 49
5.0 Sound Blaster Manufacturing (A0 Level) 70
5.1 Sound Blaster Manufacturing (A1 Level) 71
5.2 Model Layout 72
5.3 Surface Mount Technology (SMT) 73
5.4 Screen Testing 74
5.5 Chip Mount 75
5.6 Integrated Circuit (IC) Mount 76
5.7 Oven 76
5.8 Testing 77
5.9 Manual Insert & Assembly (MIMA) 78
5.11 Wave Soldering 80
5.12 Mechanical Assembly 81
5.13 Visual Inspection 82
5.14 Testing 83
5.15 Packaging 84
5.16 Information Model of Sound Blaster manufacturing in CESB 85
5.17 System Flow Diagram 86
5.18 Front Page of Database System 91
5.19 Form of Production House in CESB 91
5.20 Surface Mount Technology (SMT) Form 92
5.21 Screen Printing 92
5.27 Machine used in MIMA Line 95
5.28 Wave Soldering 96
LIST OF TABLE
3.0 SMT Machine 51
3.1 Type of IC package use in CESB manufacturing 54
3.2 Product that running in each line 57
CHAPTER 1
INTRODUCTION
1.1 Introduction
The electronics sector, with it’s approximately $1 trillion world-wide market
volume, promises to create the highest employment in the 21st century – Foreign
Trade of Turkey (2004). Now, the electronics industry is no longer a branch of
manufacturing industry anymore, but rather has become a basic and prolific industry
itself developing all other industries.
Electronics industry includes the manufacture of passive components
(resistors, capacitors, and inductors), semiconductor components (discrete, integrated
circuits), printed circuit boards (single and multilayer boards) and printed wiring
assemblies.
In printed circuit board (PCB) manufacturing there are three types of boards:
1. single sided (circuits on one side only)
2. double sided (circuits on both sides)
3. multilayer (three or more circuit layers)
Board manufacturing is accomplished by producing patterns of conductive
material on a nonconductive substrate by subtractive or additive processes. (The
conductor is usually copper; the base can be pressed epoxy, Teflon, or glass.) In the
surface preparation of the base, electroless copperplating, pattern printing and
masking, electroplating, and etching.
Printed wiring assemblies consist of components attached to one or both sides of
the printed circuit board. The attachment may be by through-hole technology, in
which the ”legs” of the components are inserted through holes in the board and are
soldered in place from underneath, or by surface mount technology (SMT), in which
components are attached to the surface by solder or conductive adhesive. (The solder
is generally a tin-lead alloy.) In printed circuit boards of all types, drilled holes may
have to be copper-plated to ensure interconnections between the different copper
layers. SMT, which eliminates the drilled holes, allows much denser packing of
components, especially when components are mounted on both sides. It also offers
higher-speed performance and is gaining over through-hole technology.
1.2 Problem Background
The efficient coordination of design and production activities is a key
challenge faced by all manufacturing companies. The lead time to introduce new
products and ramp-up production has a major impact on the responsiveness of a firm
to market change and thus, its profitability.
Apart from studying the data requirements, manufacturing decision and
planning problems, this paper would discusses the benefits of an efficient Database
Management System (DBMS) in term of the improvements in production time,
engineering time and the product or process quality. Finally, future trends for DBMS
will be given.
ICT is a generic term covering computers, broadcasting, telecommunications,
data networks and smart components which are being increasingly applied in diverse
uses. It can be defined as the totality of the electronic means to collect, store, process
computer systems, data communication systems, knowledge systems, office systems
and consumer electronics.
ICT allows trade to become simpler and more streamlined, thus increasing
the value and speed of transactions. One major advantage of promoting electronic
commerce is that it can provide relatively cheap access to global markets even for
small and medium-sized enterprises in remote areas. The globalization of production
and componentization of production units through the use of ICT focuses attention
on the infrastructural and governance conditions and institutions within a country.
The expanding range of applications of information and communication
technology (ICT) which helps to increase the efficiency and flexibility of production,
marketing, financial and administrative activities for both the private and the public
sectors presents new multifaceted and important complications for governments.
These applications offer enormous opportunities to enhance the competitiveness of
industry, increase the returns from trade, attract foreign direct investment and other
forms of external capital, increase the integration of small and medium-sized
enterprises into the value chain, and enhance the service provided by the financial
sector.
Almost every aspect of society is affected by ICT. Manufacturing industry
uses ICT to control and plan production thus providing us with cheaper goods. As for
example, Computer Aided Design increases productivity of design staff and allows
costing and production scheduling to be modelled before production is undertaken.
This can be developed into Computer Aided Manufacturing where the actual
1.3 Objectives of the Research
a) To study the information requirements underlying decision, planning and
operation activities for electronics assembly task.
b) To design the information model for electronic assembly.
c) To develop a database management system (DBMS) to support electronic
assembly process
1.4 Scope of the Project
a) One electronics assembly methodology will be chosen, for example SMT
(surface mount technology).
b) The study will be conducted based on a case study company.
c) The DBMS will be a PC-based system
1.5 Advantages of the Project
The future vision of manufacturing evolution reveals the importance of
implementing integrated information systems. This system is build to provide a
measure of all production flow components in terms of design, reject, efficiency,
time, and productivity. The reports created in the database offer a complete image of
the production cycle. We can use this to identify problem occur successfully engineer
new products and re-engineer existing ones. Sharing a unique database for all
company applications is an important milestone towards implementing e
manufacturing.
The system can trace the history of any product along the assembly flow at
line, cell, or operator level. The system wills overview assembly flow, offering
reference. It can also use traceability to detect problems in the delivery chain, and
reject during assembly parts.
1.6 Project Methodology
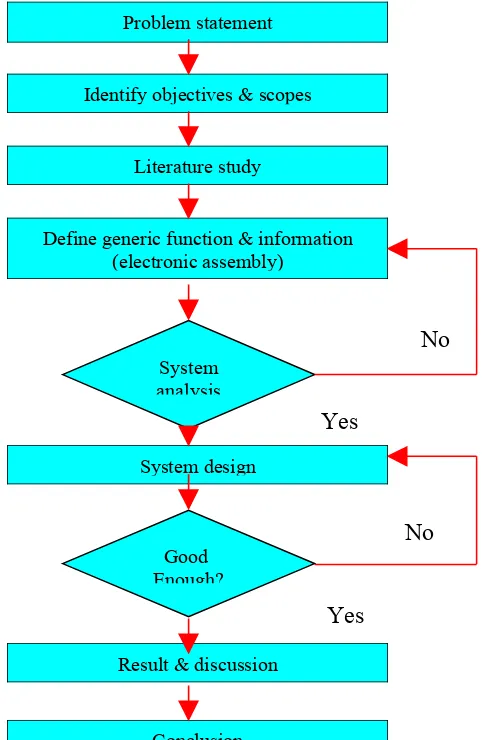
Figure 1.0 is for Project methodology, the further description will be discussed in Chapter 4.
CHAPTER 2
LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Introduction
In this chapter contain elements of the project. It describe about assembly
practices in company process flow, the information system requirement, analysis of
system methodology, previous development of information system and web based
application for electronic industries.
2.2 Electronic Assembly Process
An assembly line is a manufacturing process in which interchangeable parts
are added to a product in a sequential manner to create a finished product. The
assembly line was improved largely by Henry Ford and his engineers; Ford was also
the first to build factories around the concept. It usually consists of each worker in
control of one specific job and their work related movements are reduced to a
minimum.
In the field of electronics comprises the study and use of systems that operate
by controlling the flow of electrons (or other charge carriers) in devices such as
thermionic valves (vacuum tubes) and semiconductors. The design and construction
of electronic circuits to solve practical problems is an integral technique in the field