A ‘Skripsi’
Presented to the Faculty of Educational Sciences as a Partial Fulfillment of Requirements For Degree of S.Pd. (S-1) in English Education
By:
NICKY DWININGRUM
NIM: 1111014000081
DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH EDUCATION
THE FACULTY OF EDUCATIONAL SCIENCES
SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
JAKARTA
i
ABSTRACT
Nicky Dwiningrum, 1111014000081. “ Teaching English Pronunciation to Young Learners (A Case Study at The Sixth Grade Students of SDN 06
Ciputat)”. Skripsi of Department of English Education, Faculty of Educational Sciences Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic University Jakarta.
Advisor I : Dr. Fahriany, M.Pd.
Advisor II : Devi Yusnita, M.Pd.
Keywords : Teaching, Pronunciation, Young Learners.
The aim of this study is to describe the technique that teacher use in
teaching English pronunciation to young learners. The research method used in
this study is a case study. The instruments used in this study are observation
checklist, list of questions, and document. The sample of this study is 6c students
of SDN 06 Ciputat, Tangerang Selatan. There are three techniques of data
collection used in this study: observation, interview, and document. First,
observation is done in order to choose participants and to look the activity in the
class, whereas interview is conducted in order to have other information, and
document conducted to support data of this research. From the result of data
analysis, it is found that the teacher used two techniques in teaching English
pronunciation; drill and visual aids techniques. In drill technique the teacher used
repetition and chain drill, whereas in visual aids teacher use a realia. The fact is
the teacher does not use a realia in teaching pronunciation during four meeting.
Those techniques still effective young learners. However, this study gives
suggestion to all teachers who teach pronunciation as reference and researchers to
ii
ABSTRAK
Nicky Dwiningrum, 1111014000081. “ Teaching English Pronunciation to
Young Learners (A Case Study at Sixth Grade Students of SDN 06 Ciputat)”.
Skripsi, Jurusan Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Fakultas Ilmu Pendidikan,
Universitas Islam Negeri Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta.
Pembimbing I : Dr. Fahrianiy, M.Pd.
Pembimbing II : Devi Yusnita, M.Pd.
Kata Kunci : Teaching, Pronunciation, Young Learners
Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk mendeskripsikan tentang teknik yang
digunakan guru dalam pengajaran pengucapan Bahasa Inggris. Metode yang
digunakan pada penelitian ini adalah studi kasus. Instrument yang digunakan pada
penelitian ini adalah observasi, wawancara, dan dokument. Sample diambil dari
siswa kelas 6c yang berada di sekolah SDN 06 Ciputat, Tangerang Selatan.
Penelitian dilakukan dengan tiga teknik pengumpulan data: observasi, wawancara,
dan dokumen. Pertama, observasi dilakukan untuk menentukan partisipan dan
untuk melihat kegiatan di dalam kelas, sedangkan wawancara dilakukan sebagai
informasi pendukung, dan dokument digunakan sebagai untuk mendukung data
pada penelitian ini. Dari hasil yang didapat dari observasi, wawancara dan analisi
data ditemukan bahwa guru menggunakan dua teknik dalam pengajaran
pengucapan Bahasa Inggris. Teknik tersebut adalah drill dan visual aids. Didalam
teknik drill, guru menggunakan repetition dan chain drill, sedangkan di dalam
teknik visual aids, guru menggunakan sebuah realia. Faktanya adalah guru tidak
menggunakan realia dalam pengajaran pronunciation. Teknik tersebut masih
efektif digunakan untuk pelajar muda. Oleh karena itu, penelitian ini memberikan
saran untuk seluruh guru yang mengajar pronunciation sebagai referensi dan para
peneliti yang akan menyelidiki penelitian yang sama yaitu tentang pengajaran
v
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
In the name of Allah, the Beneficent, the Merciful
All praises be to Allah, Lord of the world, who has given the writer guidance,
strength and compassion to finish skripsi as the last assignment in her study.
Peace and blessing be upon the lovely prophet Muhammad, his families, his
companions, and his followers.
This research could not be completed without a great deal help of many people.
So, it is pleasure to acknowledge the help, support, and contribution to all of
lecturers, institution, family and friends who have contributed hence this skripsi is
processed until it becomes a complete writing.
First of all the writer would like to express her greatest appreciation and
deepest gratitude to her beloved parent, Ngadimo and Yayah Suryati, her brother,
Bagus Panuntun and her sister, Shinta Lifiani Sofyan, for their encouragement,
support and patience to motivate the writer to finish her study.
The writer also would like to express her gratitude to Dr. Fahriany, M.Pd and
Devi Yusnita, M.Pd, as the advisors for their advice, guidance, correction, and
suggesting in finishing this skripsi.
Her gratitude and honour also goes to:
1. Prof. Dr. Ahmad Thib Raya, M.A. as the dean of Faculty of Educational
Sciences State Islamic University Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta.
2. Dr. Alek, M.Pd. the Head of Department of English Education
3. Zaharil Anasy, M.Hum. the secretary of Department of English Education
4. All lecturers of English Department for their encouragment to the writer
during the study as State Islamic University Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta
5. All of the staffs and the officers of Library of Syarif Hidayatullah State
Islamic University Jakarta.
6. Dedi, S.Pd as the headmaster of SDN 06 Ciputat, who has given his
permission in doing this research.
7. Linda Eskawati, S.Pd as the English teacher at SDN 06 Ciputat, who has
vi
8. All of her friends of English Department in year 2011, especially: Selinda
Febriani, Synthia Dian Septiani, S.Pd., Yulianti Sari, Audrey Ningtyas,
Putik Delima, Nadia Karimah, S.Pd., Nurita Wulandari, S.Pd., Dara Sabila
Syarif, S.Pd., Sarah Aslamiyyah,S.Pd. , Khilda Shopia, S.Pd., and Annisa
Rantika, S.Pd., for the support, motivation, and laughts.
The writer does realize that this skripsi cannot be considered perfect without
critiques and suggestions. Therefore, it is such a pleasure for her to get critiques
and suggestions to make this skripsi would be useful for all.
Jakarta, July 2016
Nicky Dwiningrum
vii
ENDORSMENT SHEET ... iii
APPROVAL... iv
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT ... v
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... vii
LIST OF TABLE... ix
LIST OF FIGURES ... x
LIST OFAPPENDICES... xi
CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION ... 1
A. Background of Study ... 1
B. Identification of Problem ... 3
C. Limitation of Problem ... 3
D. Formulation of Study ... 4
E. Objective of Study ... 4
F. Significance of Study ... 4
CHAPTER II: THEORITICAL FRAMEWORK ... 5
A. Pronunciation ... 5
1. Nature of Pronunciation ... 5
2. Feature of Pronunciation ... 6
3. Factors that Affect in Pronunciation ... 13
4. Problem in Pronunciation ... 14
viii
1. Characteristic of Young Learners ... 20
2. Teaching English to Young Learners ... 23
C. Previous Related Studies ... 27
D. Thinking Framework ... 28
CHAPTER III: RESEARCH METHODOLOGY ... 30
A. Place and Time of Study ... 30
B. Method and Design of Study ... 30
C. Subject of The Study... 31
D. Instrument and Technique Data Collection ... 31
E. Teachnique of Data Analysis ... 31
CHAPTER IV: FINDING AND DISSCUSION ... 33
A. Data Description ... 33
B. Data Presentation ... 35
C. Discussion ... 42
CHAPTER V: CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION…... 45
A. Conclusion ... 45
B. Suggestion ... 45
REFERENCES ... 46
ix
LIST OF TABLE
1.Table 2.1 The English Consonants ... 8
2.Table 2.3 The Example of Vowel and Diphthongs ... 12
3.Table 2.4 The Characteristic of Young Learners ... 20
4. Table 4.1 The Result of Students’ Achievementt ... 41
x
2. Figure 2.2 Consonant Sounds Based on Place of Articulation 10
xi
Appendix 1 : Teacher’s Profil ... 50
Appendix 2 : Lesson plan 1 ... 51
Lesson plan 2... 54
Appendix 3 : Syllabus ... 57
Appendix 4 : Teacher’s Interview... 61
Appendix 5 : Students’ Interview ... 65
Appendix 6 : Observation Sheet ... 69
Appendix 7 : Materials... 70
Appendix 8 : Phonetic Symbol of Materials ... 85
1
This chapter discusses the general problem of the study. The writer gives
the reason why she chooses this study. The writer also presents the statements of
the problem, objective of the studies, and significance of studies.
A.Background of Study
Pronunciation is important to communicate with others, especially to speak in
English language. People can understand what you say if your pronunciation is
good. Pronunciation is the way for producing the sound of the speech. There are
three parts of pronunciation: stress, articulation, and intonation. Stress is emphasis
the syllables of a word. Articulation is the changing of the teeth, lips, and tongue
which affects the different sound produced. Intonation is rising or falling sound
when speaking.
Competence in pronunciation is related to speaking, listening, and reading. Bad
pronunciation can be bad effect to those skills. For instance, when people do not
recognize the key sounds or words from speaker in listening section, they do not
know the meaning of the words. It also happend to students, if students do not
know how to pronounce words, their partner will not understand what they speak
and feel hard for them to write the words.
According to Zhang, teaching pronunciation should be taught at primary level
because children are more effectively and quickly to learn sounds system, while
adults have difficulties in learning process because of their age.1 Students will
have some difficulties to distinguish and produce native-like sounds after puberty.
Young learners are more active than adults. They have curiosity about something
new in their live. The other reasons why better for learning pronunciation in
young age is because they have better motivation in learning language and easier
to remember the new words than the adults. Their memories are strong to
remember and easy to catch what they learn and listen around of them. Learners in
1
the 6-12 age groups are far less self-conscious than those of 13 years because this
age the ability imitates perfectly become less.2 They cannot decide what they
should learn because they tend to imitate from around of them. The one that can
be imitated is teacher. Therefore, they should give attention of something that they
teach for young learners and make it in like the standard competence for students
in young learners.
Based on standard of competence, in the first level young learners only learn
how to read and pronounce the words. They do not have the capability to
understand phrase and the meaning of sentence. Language development in young
learners is started from identification of words they get from listening and
speaking process.
Practically in Indonesia, pronunciation is not focus to be taught in elementary
school. In this level, teacher only taught vocabulary, reading, and simple
grammar. Based on the writer experience when teaching young learners, they have
difficulty to pronounce some words. It happens because they are rare in finding
and hearing the sound of the words. The other problem appeared when they find
new words and they do not how to pronounce correctly. They guessing that words
before teacher correct it. It is because there is no motivation from learners in
learning English language.
Motivation is one of factors that learners’ needed in learning English, because it can improve the learners’ enthusiasm in learning. The learners can integrate
themselves into English if the teacher supports them with an enjoyable situation
and interesting materials. For instance, teacher can use English song as a
technique in learning and teaching process. It can contribute many things to
improve learners’ capabilities, such as vocabulary, listening, and pronunciation. Learners can imitate how to pronounce well of words from English song, but the
mistake in pronounce of words still appear. The mistake of pronunciation can
cause misunderstanding and make unsuccessful in communication. Therefore, the
teacher should accompany the learners so they can aware of different sound, and
2
intonation of words.
The other problem also come from the teacher ability. Sometimes, teacher
tends to neglect some of the words. It appears because teacher is not interest of the
subject or they have doubt how to teach it. Background of teacher’s mother
tongue also can be problems in pronounce words. Sometimes, teacher’s mother
tongue is more dominant then second language. Therefore, teacher should prepare
before they teach pronunciation.
Teachers’ challenges in teaching young learners are cognitive development,
motivation, and attention. In cognitive development, learners acquire language
naturally and communicatively from situation. In motivation, teachers’ role is
important to motivate learners in learners, such as: they can select material to
which learners can relate. The last is attention. Teachers should have some
techniques that can make students focus and make learners comfort in learning so
teacher will get their attention.
Based on priliminary observation at SDN 06 Ciputat, students still bad in
pronunciation. Whereas this school have English conversation program that
students should speaking correctly. In this session, the students are demanded to
be brave to speak in public, exactly through daily conversation. Here the writer
tend to conductedthe research about “The Teaching of English Pronunciation to Young Learners (A Case Study at Sixth Grade Students of SDN 06 Ciputat)”.
B.Identification of Problem
Based on study above, the problems can be identified, as follows:
1. Teaching English at SDN 06 Ciputat does not focus to pronunciation mastery.
2. Most of students still guessing the pronunciation of the new words.
3. The teacher’s of SDN 06 Ciputat was affected by her mother tongue. It
influences the way she pronounces the new word when she teaches.
C.Limitation of Problem
Based on the identification of problem above, the writer limits study on process
of teaching English pronunciation to young learners at sixth grade of SDN 06
D.Formulation of Study
Based on the limitation of the problem above, the study will be formulated as
follows; how does the teacher teach pronunciation to young learners at the sixth
grade students of SDN 06 Ciputat?
E.Objective of Study
The objective of this study is to obtain the techniques that teacher used in
teaching pronunciation to young learners.
F. Significance of Study
The writer hoped this research could give some significance for teachers in
elementary school. Hopefully, this research can be used as a reference for the
teacher who wants to teach pronunciation and other writers who want to do
similar research in teaching pronunciation, especially for students in English
5
Learners who study English language are required to hear English
pronunciation. They demanded to reproduce the foreign words and sounds. The
writer is giving some definition to make clear understanding about pronunciation.
1. Nature of Pronunciation
There some some definition of pronunciation that might be useful to support
the writer. According to Hewings in Pronunciation Practice Activities, ―Pronunciation is components of speech that range from the individual sound that make up speech, to the way in which pitch – the rise and fall of the voice – is used
to convey meaning‖. 1
It means that component in pronunciation is intonation which will make someone easily to understand speaker’s meaning.
Ur assumed pronunciation is ―to say the sound right, to use the words to
express the appropriate meaning, or to construct their sentence in a way that
sounds acceptable‖.2 It means that people can express their feeling and convey
their meaning by using speech right.
Meanwhile ―Pronunciation is a feature of speech and spelling a feature of
writing, spelling will often have an influence on the learning of pronunciation as
the majority of learners use written texts in their studies’.3
Spelling is one of
important feature in pronunciation for students who is learning written text.
Based on Sound Concepts, pronunciation is ―an integrated system that
Martin Hewings. Pronunciation Practice Activities: A Resource Book for Teaching Engllish Pronunciation. (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2004), p. 3.
2
Penny Ur. A Course in Language Teaching : Practice and Theory. (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2009), p. 103.
3
Hewings, op. cit., p. 9. 4
Then, according to The Handbook of English Pronunciation, Pronunciation is
―central to language use in social, interactive context because pronunciation
embodies the way that the speaker and the hearer work together to establish and maintain common ground for producing and understanding each other’s
utterances‖.5
The last, based on The Cambridge Guide to Teaching English to speakers of
Other Languages, pronunciation is ―the production and perception of the
significant sounds of a particular language in order to achieve meaning in contexts
of language use‖.6
It means pronunciationis part of language that used to receptive
meaning of language.
From all definition above, the writer may conclude, pronunciation is a sound
comes from vocal cords in the form of words or sentence that become one or
important unit in the language to convey meaning from the speaker, even it was
neglected by learners.
2. Feature of Pronunciation
There are some features of pronunciation that can make the learners to avoid
being misunderstood in learning pronunciation, such as kinds of error that most
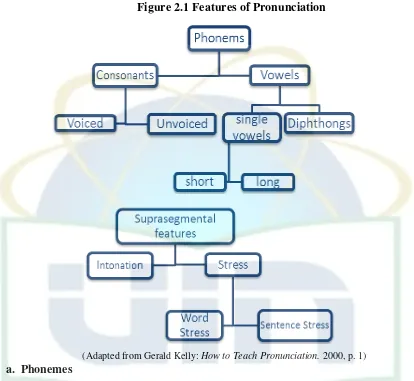
likely to interfere with communication. This figure below will show the main
feature of pronunciation. 7 There are phoneme and supra segmental. Phoneme
divide into 2 parts: consonants, that consist of voiced and unvoiced, and vowels
that consist of single vowels (short and long) and diphthong. Furthermore, supra
segmental consist of intonation and stress (word stress and sentence stress). All of
this feature will explain above.
5
Marnie Reed and John M. Levis. The Handbook of English Pronunciation: First Edition. (Oxford: John Wiley & Sons, Inc, 2015), p. 353.
6
Ronals Carter and David Nunan. The Cambridge Guide to Teaching English to Speakers of Other Language. (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2009), p. 56.
7
Figure 2.1 Features of Pronunciation
(Adapted from Gerald Kelly: How to Teach Pronunciation. 2000, p. 1)
a. Phonemes
Phonemes are the unit of sound in a specific language that has different sound
with the other language. Even people have differences in articulate sounds; we can
still describe how they produce the sounds.8 Then, phonems which makes
connection between sounds and meaning. Phonemes consist of two categories:
consonants and vowels.
1) Consonants
Consonants are a speech sound that is not vowel. In this situation, change one
consonants with another is possible to make the communication breakdown than
wrong vowel.9 There are three kinds that distinguish in conconants: voice, tongue
8
Ibid. 9
shape, and articulator.10
a. Voice: Vocal cords can be narrowed along their entire length so that they
vibrate as the air passes through them.
b. Tongue shape: extremely mobile and can take up many positions to change the
size and shape of the mouth, thus affecting sounds.
c. Articulator: Any vocal organ that takes part in the production of speech sound.
Such as: tongue, lips, etc; those that can move, and teeth, the hard palate, etc;
that remain fixed.
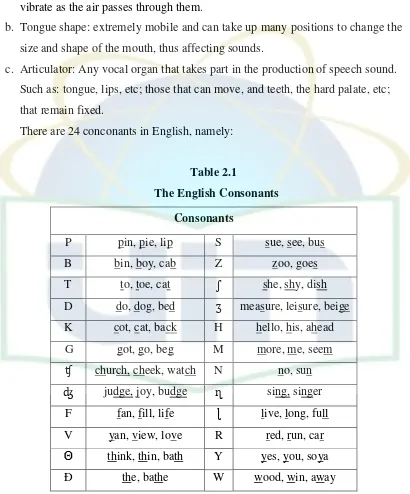
There are 24 conconants in English, namely:
Table 2.1
The English Consonants
Consonants
P pin, pie, lip S sue, see, bus
B bin, boy, cab Z zoo, goes
T to, toe, cat ʃ she, shy, dish
D do, dog, bed ʒ measure, leisure, beige
K cot, cat, back H hello, his, ahead
G got, go, beg M more, me, seem
ʧ church, cheek, watch N no, sun
ʤ judge, joy, budge ɳ sing, singer
F fan, fill, life ɭ live, long, full
V yan, view, love R red, run, car
Θ think, thin, bath Y yes, you, soya
Ð the, bathe W wood, win, away
(Adapted from Martin Hewings: Pronunciation Practice Activities: A Resource Book for Teaching Engllish Pronunciation, 2004, p. 15)
Some of consonant are use vibration when pronounce or called voiced, and the
other is not used vibration in pronounce words, called unvoiced. This is some
10
examples of voiced and unvoiced words. Examples11 :
Voiced Unvoiced
z zoo s Sue
b bill p pill
g goat k coat
From the consonants above, the unvoiced are p, t, k, f, s, ʃ, ʧ, θ, and h, and
voiced are b, d, g, ʤ, v, ð, z, ʒ, m, n, ɳ, l, r, y, and w. According to the place of
articulation, the consonant can be divided into12:
1. Bilabial : Articulation is done by bringing both lips.
e.g.: b, p, m, w
2. Labio-dental : Articlated by placing the upper teeth againts the lower lip.
e.g.: f, v
3. Dental : They are pronunced by inserting the tip of the tongue
between the teeth
e.g.: θ, ð
4. Alveolar : The tip of the tongue is raised and touches the ridge
e.g.: t, d, l, n, s, z.
5. Palato-alveolar : It produced by raising the front part of the tongue to the
palate
e.g.: ʧ, ʤ, j
6. Velar : It produced by raising the back part of the tongue to the
soft or the velum
e.g.: k, g, ɳ
7. Glottal : a narrowing causing friction but not vibration, between the
vocal cords
e.g.: h
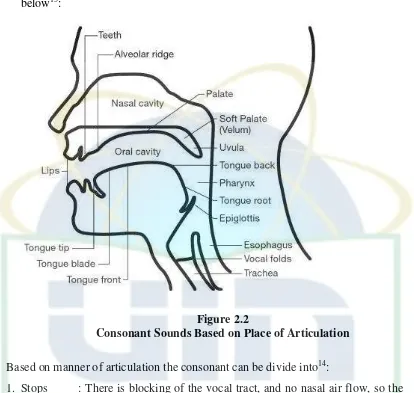
The illustration of consonant sound based on the the place of articulation is
11
Sue.F Miller. Targeting Pronunciation : The Intonation, Sound, and Rhythm of American English. (New York: Houghton Mifflin Company, 2000), p. xv.
12
below13:
Figure 2.2
Consonant Sounds Based on Place of Articulation
Based on manner of articulation the consonant can be divide into14:
1. Stops : There is blocking of the vocal tract, and no nasal air flow, so the
air flow stops completely.
e.g.: p, b, t, k, g,
2. Fricative : the consonants produced by forcing air through a narrow channel
made by placing two articulators close together.
e.g.: f, v, θ, ð, s, z, ʃ, ʒ
3. Affricates : which produced by blocking off the breath stream between the
tongue and gum ridge.
e.g.: ʧ, ʤ,
13
Felicity Cox. Australian English: Pronunciation and Transcription. (New York: Cambridge University Press, 2012), p. 26.
14
4. Nasals : which produced with a lowered velum, allowing air to escape
6. Glides : The conconant categories are usually included by semi-vowels in
functional grounds, but they are more properly treated as vowel glides.
e.g.: w, j
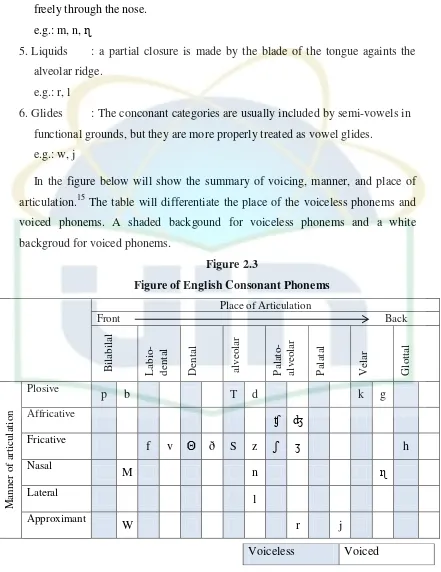
In the figure below will show the summary of voicing, manner, and place of
articulation.15 The table will differentiate the place of the voiceless phonems and
voiced phonems. A shaded backgound for voiceless phonems and a white
backgroud for voiced phonems.
Figure 2.3
Figure of English Consonant Phonems
Place of Articulation
(Adapted from Gerald Kelly: How to Teach Pronunciation. 2000, p.7)
15
Kelly, op. cit., p. 7.
2) Vowels
Vowels are speech sounds that derived by vocal cord. Vowels are
articulation that happen when a voiced airstream shaped by using the tongue and
the lips to modify all of shape of the mouth.16 The number of vowel that used in
any particular language is small but actually the possible number of vowel is
large. The linguist made some analyses of English vowels. The different number
of vowel recognized that the different symbols and combination represented of
vowels and used different term to describe them.
There are two reasons different analyses of English vowel17:
a. Different dialect have influence in system of vowel. The different dialect is not
a big problem in communication with English speakers, but it can be
noticeable.
b. The linguists have the importan of different feature, such as: physical feature.
Diphthongs are part of vowels. Diphthong is a sound that occurs by the
movement of one vowel to another. This table will show the examples of vowels
and diphthongs. 18 Examples of vowel and diphthongs:
Table 2.3
The example of vowels and diphthongs
Vowels Diphthongs
i: Bead Eı Cake
I Hit ɔı Toy
ʊ Book Aı High
u: Food ıə Beer
E Left ʊə Fewer
ə About eə Where
ɜ: Shirt əʊ Go
16
Kelly, op. cit. p. 29. 17
Kreidler, op. cit. p. 45. 18
ɔ: Call aʊ House
Æ Hat
ʌ Run
ɑ: Far
O Dog
(Adapted from Gerald Kelly: How to Teach Pronunciation, 2000, p.2)
b. Supra segmental features
Supra segmental are the characteristic of speech that used into groups of
segments or phonemes. Stress and intonation is the important feature in English.
The supra-segmental feature of stress, rhythm, and intonation are much important
for clear pronunciation than producing native – like vowels and consonants.
Meanwhile, definition of word stress is stressed syllables in words, and stressed
words in phrases, and sentences, that represented by capital letters, examples:
APple, aPartment, and underSTAND. 19 Whereas, intonation is the way to falls or
rises pitch of voice as direction of sentence.20 Based on definition about word
stress and intonation can be conclude that when someone pronunce words it must
understand about stress and intonation of words, because someone who pronounce
words with different stress and intonation, it means that words also have different
meaning.
3. Factors that Affect in Pronunciation
The native language has an important factor to pronounce English. Foreign
accents have some characteristic of sound for the native language learners. There
are 4 factors that affect in pronunciation: interference of mother tongue, learner’s
age, learner’s attitude and psychological and prior pronunciation instruction.21
a. Interference of mother tongue
Stress and intonation is become couse errors in the target language. It is
particularsound which does not exist in the native language.
b. Learner’s age
Someone who was learning second language from the child, commonly their
can pronounce like a native. Its differ with person who does not begin learning
second language until adult, they will never have a native like accent even though
they have the same aspect of language such as vocabulary or syntax. Adult
learners have limited to distinguish and produce native-like sounds.
c. Learner’s attitude and psychological
Something that can influence achievement in pronunciation is attitude of target
language learning. A good attitude can support learners to develop pronunciation
skill. A person has strong determiners of the acquisition of accurate pronunciation
of a foreign language if they have sense of identity and feeling group affiliation.
Some learners focus on their pronunciation, they often statements about how bad
their pronunciation. Sometimes, they request to correct their pronunciation if
make mistakes. A kind of achievement motivation is when the learners want to do
it well.
d. Prior pronunciation instruction
Learners should have good habit of learning correct pronunciation at the
beginning. It will influence learner’s success with current effort. When learners
failed to pronounce some words in the beginning, they will become accustomed to
their own version of pronunciation and would be more likely to mis-comprehend
when these words are not correctly pronounced.
4. Problem in Pronunciation
Pronunciation can help learners to speak English well, but when learners learn
English language they have not received much information to understand
pronunciation that needed in communication. So, some problems appear. First
problem comes from individual sound. Sound or phonems were made up by word
/kӕt/ = cat that recognisable a word. 22
That problem comes from the learners that
hard to eliminate. All the learners that have different background in first language
will have different problems, representing the contrast between the first and
second language.
Stress in words can be problem because stress can change a word’s grammatical function, for example: export, if we stress word on the second
syllable become exPORT, the function is verb. But,when we stress word on the
first syllable and become Export, the function is noun.23 The example shows the
position of the stress change the gramatical function, in this case, part of speech of
the word. It becomes the consideration when students learn English. Teacher
should make sure when learners learn new words and know where the stress of
words.
Then, learners also should be able to recognize intonation of words. There are
speech sound and intonation patterns that is not become part of speech memory
bank when English is not become first language. Usually, some of vowels and
consonants that used in English is not exist in our native language. Learners
should have strong tongue and muscle movements for the rhythm patterns in
original language in early age. They will have difficulty in pronunciation when
their memory bank does not involve the sounds or rhythm patterns of English.24
5. Teaching Pronunciation
Learning pronunciation is a very complex task. The process of learning
pronunciation can be facilitated if the task is structured. In this process, teachers’
and leaners’ role is important, both of them is involved. The teachers’ roles are
helping learners hear and make sounds. In the helping learners hear, teacher need
to check what the sounds that learners get and hear. Learners able to imitate new
sounds. But, if they cannot teachers help them to giving some sign that can help
them to make the new sound. In teaching learning process, learners only respond
what the teacher ask. If learners no take action and no try to realize their effort,
22
Jeremy Harmer. The Practice of English Language Teaching: Third Edition. (New York: Longman, 2001), p. 29.
23
Ibid., p. 32. 24
the improvement of them is minimal.
As mentioned above, teaching pronunciation have plans. First, teacher should
be aware of learners’ difficulties with particular first language groups and teacher
should prepare the activities that focus on that problems. Second, teacher checked
learners’ pronunciation weakness and give some activities that focus of that. The
last, teachers identify what part that can be used on particular area of
pronunciation. 25
The teaching of pronunciation has always been involved with different
perspective language from other language skill. The effect of first language in
relation to pronunciation is bigger in contrast with acquisition of morphology and
syntax.
6. Aims of Teaching Pronunciation
Pronunciation is one of the important things when we learn English language.
If learners have a good skill in pronunciation, they can convey their meaning
properly. Their partners also understand easily in speaking or spelling context.
Learners is not only awar of sounds and sounds feature in learning pronunciation
but also can improve their speaking ability.26
However, people in this time think that pronunce like a native is not their goals.
For example, learners who learn English, they have specific purpose, such as;
learners who want to work as telephone operators, they need to have
pronunciation that easily understood in every condition. It differs with learners
who want to be an English teacher; they will need to have pronunciation like a
native accent.
The others aims of teaching pronunciation is learners can speak clearly with
non-native or native speakers and can help to increase their confidence and
comfort level in speaking situation. A good pronunciation also improves our
performance at work if needed. 27 It will support us when we looking for job.
25
Martin Hewings, op.cit. p. 20. 26
Jeremy Harmer, op.cit. p.183. 27
7. Techniques in Teaching Pronunciation
There are some techniques that teachers can be used in teaching pronunciation.
The first technique is drilling, drilling is one of main ways of teaching
pronunciation which is practiced in classroom. Drilling is basic for teaching
pronunciation of word stress, sentence stress, and intonation. The aims of drilling
are to help the learners to get the better pronunciation and to help them to keep in
mind new items. The kinds of drillis are stated by Larsen-Freeman as follows:28
a. Backward build- up drill
This is used when long dialog is giving students trouble. The teacher breaks
down the line of dialog into several parts. The students repeat a part of the
sentence.Then, following the teacher’s clue, the students practice what they are
repeating part by part until they are able to repeat the entire line.
b. Repetition drill.
Students are asked to repeat what teacher say as accurately and as quickly as
possible. This drill is often used to teach the lines of the dialogue.
c. Chain drill
A chain drill is one-by-one, ask and answer questions of each other. The
teacher begins the chain by greeting a particular student, or asking him questions.
That student responds, and then turns to the students sitting next to him. The first
student greets or asks a question of the second student and the chain continues. A
chain drill allows some controlled communication, even though it is limited. A chain drill also gives the teacher an opportunity to check each student’s speech. d. Single- slot substitution drill
Teacher says a line, usually from the dialog. Next, the teacher says a word or a
phrase- called the cue. The students repeat the line the teacher has given them,
substituting the cue into the line in its proper place. The major purpose of this drill
is to give the students practice in finding and filling in the slots of a sentence.
e. Multiple- slot substitution drill
28
This drill is similar to the single slot substitution drill. The difference is that the
teacher gives cue phrases, on at a time that fit into different slots in the dialog line.
The students must recognize what part of speech each cue is, or at least, where it
fits into the sentence, and make any other changes, such as subject-verb
changing a statement into a question, an active sentence into passive one, or direct
speech into reported speech.
g. Question and answer drill
This drill gives students practice with answering questions. The students
should answer the teacher’s questions very quickly.
The example of exercise in drilling is teacher give stimulus by sentence to
learners then teacher asked them to repeat it until they memorize it.
Brown stated about drills as follows:29
Drills offer students an opportunity to listen and to orally repeat certain strings of language that may pose some linguistics difficulty-either phonological or grammatical. Drills are to language teaching what the pitching machine is to baseball. They offer limited practice through repetition. They allow one to focus on one element of language in a controlled activity. They can help to
establish certain psychomotor pattern (to ―loosen the tongue‖) and to associate
selected form with their appropriate context.
In pronunciation drills, chaining is one of the activities that can be used in
class. The difficulties of words and sounds in the sentence for learners can be
proved by chaining drills.30 Selected learners receives 4-10 words on separate
cards which are used to make a story then tell it in front of class. Other example is
teacher asked learners to sit in the circle then individual learners ask and the
29
H. Douglas Brown, Teaching by Principles: An Interactive Approach to Language Pedadody. (New York: Pearson Education Company, 2001), p. 272.
30
others answer. Teacher starts to drill and ask to learners then the learner answer it
then they repeat the question to their friends.
The second technique is a minimal pair. Teachers used minimal pairs in the
classroom as a process of focusing on sound that are difficult for learners. The
activity is teacher give two words whose pronunciation is different by only one
sound, such as reach and rich, bought and boat, or man and main. The aims of
minimal pairs are to help learners differentiate between similar and problematic
sounds to achieve the goal of language through listening discrimination and
spoken practice.31
The third technique is visual aids. Improvement of teacher’s description of how
sounds are produced by audio-visual aids, such as: pictures, mirrors, rods,
sound-colour chart, realia, etc. The aims of those techniques is to make learners interest
in learning pronunciation and will be more easily to understand materials.
The fourth technique is a communicative activity. All of the activities, such as:
interviews, role plays, drama, speech, and audiotaped dialog journal, is can be
used in the classroom to practice pronunciation. Meanwhile, all of those activities
are not possible done in class. Its happen because the situation and facilities is not
allow.
The last technique is reading aloud. Focusing on stress, timing, and intonation
are the part or scripts for learners in learning pronunciation. Reading aloud
technique can be involved or not in memorizing the text and it happens in the
spoken, such as: speeches, poems, plays, and dialogues. 32
B.Young Learners
Nowadays, English language becomes international language for
communication. English speakers have rapidly increased. One of the way to
improve English language skill is learning English language in the school.
Indonesia, English language is learned by the students since they were in
elementary level until high level. This means, many people realized that English
31
Marianne Celce-Murcia. et al., Teaching Pronunciation : A Reference for Teachers of English to Speakers of Other Language. (New York: Cambridge University Press, 2009), p. 8.
32
language is important and it should be taught from the early age. Early age usually
mentioned as young learners. Young learners refer to children between the ages of
seven to twelve years children approximately.33 Children in the 7-12 age group are
far less self-conscious than those of 13 years and above. But after this age the
ability imitates perfectly become less. 34
Young learners have different competence and ability in English language than
adults so the teaching English at the elementary level is urgent need and the
teacher should be trained before teach young learners. Teachers also should know
the characteristic and ability of young learners, so they can choose the best
method and classroom activities. Teacher of young learners can thrive and focus
on learning if they provide the care necessary to meet their needs.35
1. Characteristic of Young Learners
Characteristic of young learner is divided into three groups. First is under
seven years old, second is seven to twelve years old, and the last based on
children’s cognitive development. According to Pinter, he divide characteristic of
young learners into six characteristic and table below will show as follow: 36
Table 2.4
Characteristic of Young Learners
Young Learners
Children are at pre-school or in the first couple of years of
schooling
Generally, they have a holistic approach to language, which means
that they understand meaningful message but cannot analyze
language yet.
33
Caroline Nixon and Michael Tomlinson. Primary Communication Box: Speaking and Listening Activities for Younger Learners. (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2005), p. 9.
34
Arif Sari Çoban and Albina Kuç. Teaching Problematic Consonants in English to Young Learners. (An Unpublished, Turkey:Elsavier Ltd, Procedia Social and Behavioral Science 2, 2010). p. 943.
35
Caroline T, Linse and David Nunan. Practical English Language Teaching Young learners. (New York: McGraw-Hill Companies,Inc., 2005). p. 2.
36
They have lower levels of awerness about themselve as well as
about the process of learning.
They have limited reading and writing skills even in their first
language.
Generally, they are more concerned about themselves than others.
They have limited knowledge about the world.
They enjoy fantasy, imaginatin and movement.
a. Young Learners Under Seven Years Old
Young learners under seven need to learn something about world that they have
recently obtained. Piaget argued, ―The child is seen continually interacting with
the world around her/him, solving problem that are presented by the
environment‖.37
They get the new knowledge very quickly from the environment
often through direct experience and by asking curius questions. Experienced
teachers would agree that young learners like to draw attention to themselves.
According to Piaget, ―Children are not able to think abstractly, but need concrete
situations to process ideas‖.38
So, learners will interest with the contextual in
learning process.
Young learners learn about their environment through visual sense. They are
also able to use their logical reasoning and also they can use their imagination.
Sometime, it makes them feel difficult to differentiate between imagination and
fact. So, language teaching should bring real life in the classroom without relieve
children’ imagination and fantasy.
In addition, primary teachers need to know that even though young learners
have a very short attention and concentration span they are enthusiastic and
positive about learning if they are enjoying themselves and are encouraged by
teacher’s praise and support. Young learners still want to have an activity even
they do not know what and how that activity.
37
Lynne Cameron. Teaching Languages to Young Learners. (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2001), p. 2.
38
b. Young Learners Seven to Twelve Years old
In this age, children have a great progress in their physical and cognitive
development. According to Piaget, in this age children already have esperience
and they enough to do abstract problem solving.39
In addition, Vygotsky stated ―the child is an active learner in a world full of
other people; they play important roles in helping children to learn, bringing
objects and ideas to their attention‖.40
Children have a high curiousity about what
they look and hear, that was make them more active in learning.
Young learners have already created opinions about lot of things. At this age,
they do not see teacher as an authority anymore. They can make some decisions
about their own learning. They also can ask everything they want. They can
recognize the difference between reality and imagination. So, When teachers
using mother tongue in language learning, they cannot depend on the spoken word
only. Their speech should be supported by various visual aids, objects and realia.
c. Cognitive Development
That children can or cannot do at different age is connected not only to their
physical, but also to their cognitive development. The greatest part of these
changes takes place during the primary school years.The years at primary school,
learners acquire language naturally and communicatively from situation in which
the students acquire language abilities by means of acquisition rather than
learning.41
In the book Teaching Language to Young Learners, ―Piaget gives a much less
important role to language in cognitive development. It is action, rather than the
development of the first language which is fundamental to cognitive
development.‖42 His theory of cognitive development has greatly influenced the
views on teaching foreign language to children. Assimilation and accommodation
is distinguished become two ways by Piagetian psychology in development that
Sukarno. Teaching English to Young Learners and Factors to Considers in Designing the Materials. (Yogyakarta: Jurnal Ekonomi dan Pendidikan, Vol: 5, no:1, 2008). p. 59.
42
can take place as a result activity. When action takes place without any change to
the child, there is assimilation happens. Accommodation implicates the child
adapting to feature of the environment.43
Children in development builds have some developmental stages which
normally occur during the elementary school years. The first stage is the stage of
sensory-motor intelligence. It covers children from their birth to the age of two.
Primarily motor is behaviour at this stage. The last stage is preoperational though
about children two to seven years old. The language development and rapid
conceptual development is in this stage.
Piagetian viewpoint, ―a child’s thinking develops as gradual growth of knowledge and intellectual skill towards a final stage of formal, logical
thinking‖.44
2. Teaching English to Young Learners
Young learners should have fun in learning English. At the previous part is
talking about young learners and aspects of their cognitive development. In this
part will discuss about what factors that related with their learning process.
Through language, younger learners concerned with everything that they can
achieve. Therefore teachers should have pay attention to children, such as: students’ interest, activities which used, variety of lesson, and the most important is the lesson should conduct in English. According to Brown, there are five
categories which are proposed in giving some practical approaches to teaching
young learners. Those are as follows:45
a. Intellectual Development
It is closely related to what Piaget calls ‗concrete opinion‖, i.e., young learners
understand something concrete. Grammar and rules stated in abstract terms,
therefore, should be avoided but certain patterns, examples, and repetitions,
Considering that children have short attention term, it is quite useful to make
lessons become interesting, lively, and fun. Therefore, activities should be designed to capture children’s immediate interest, a lesson needs a variety of activities, a teacher needs a sense of humor, and it is badly needed to consider that
children have a lot of natural curiosity. Accordingly, the English teachers to
young learners should make sure that they interest into that curiosity whenever
possible, and teacher will there by help to maintain attention and focus children.
c. Sensory Input
In consideration of sensory input, activities should fight to get beyond the
visual and auditory modes that learners feel are usually senough for a classroom.
It means that the lessons contain physical activities, projects and hands-on
activities, sensory aids here and there, and non-verbal languages.
d. Affective Factors
Children are extremely sensitive. Therefore, the English teachers should help
their students to laugh with each other at various mistakes that they all make, be
patient and supportive to build self-confidence, and get as much oral participation
as possible from students.
e. Authentic, Meaningful Language
Children are good at sensing language that is not authentic; therefore, ―canned‖ or stilted language will likely be rejected. The language needs to be firmly
context-embedded and not context-reduced. A whole language approach is
essential. It means that if language is broken into too many bits and pieces,
students won’t see the relationship to the whole.
1) Teaching English through English
Unfortunately, not all teachers connected their lesson in the target language.
Therefore, using English in English classroom might not seem as something
natural and real. Impression that learners get from foreign language is only just a
complement in learning they do not see it as a tool of communication.
Young learners are able to produce English more than they understand. There
of words, using picture, and acting, all of those will help children to grasp the
meaning by using fun activity in class. Moreover, children have opportunity to
learn and hear English sounds in English class.
2) Choosing the Right Activity
One of the important aspects in teaching English is variety in activity. During
in teaching and learning process, teachers not only change type of activity but also
pace of the lesson. There are two varieties: first is variety of activity and second is
variety of organisation.
In the variety of activity, teacher should know the condition of class and
learners. Teacher can use a stirring or calming activity, activity at the desk or
moving activity. Teacher can stimulate learners by using games, songs, or
speaking tasks in the stirring activity. But, sometimes that activity can make
learners get too over-excited and make a noisy in the class. Besides, in the
calming activity teacher can makes some serious activity, such as: listening,
writing or colouring.
Variety of organization is talk about individual work or group work. Individual
work can use speaking task or song in class. It will make students focus to their
self. Also, learners can be less stressful than performing in front of class and they
can learn on their learning style.46 Nevertheless, using group work or pair work is
the powerful context for communication in the classroom. There is always a good
idea to demonstrate what teacher wants the children to do before the pair work
activity. Children should not be able to choose their groups because it usually
causes somebody to be left out. On the other hand, we cannot expect a pupil to
work well with someone he or she simply does not like.
3) Students’ Involvement
Students’ involvement is important method to stimulate students learning and
help them to get language quickly and effectively. They also can help teacher in
the teaching and learning process. One of the way of students is by using
presentation stage which stdents lead in, called inductive approach. On the
46
contrary, deductive approach is differing with inductive, where the presentation is
followed by examples.
Students’ understanding will be harder when they are guess something in
learning because they are not able to understand the language rule. Young learners
should be assigned such activities that make them concentrate on the task.
The activities that require high concentration and make them focus are problem
solving activities or discovery techniques. It is supported by Harmer, ―There are
good pedagogical and methodological reasons for this since the students will be
more involved and since this kind of activity invites them to use their reasoning
processes‖.47
Discovery techniques can be used for presenting any kind of new
language, for example new grammar, vocabulary or pronunciation.
Based on explanation above, not all aspect can be considered. It depends on
teacher and his/her consideration which the best activities and the best method for
his/her students. Generally it can be stated that if an activity is enjoyable, it will be
memorable.
4) Misunderstanding in Teaching Young Learners
There are two misunderstanding about teaching young learners.48 First,
teaching is straightforward. However, children have a little bit complicated view
of the world than adults. The fact is children should improve their skills to reach
their world and develop their understanding. Teachers should understand how
children learn, whether by using individual work or grouping work.
Second is, children only need to learn simple language. Sometime, children
only want to learn a simple language by using songs, numbers, and colours. In
fact, they can learn it if teacher taught it. So, children can increase their capability
in learning language. Teachers should know this condition and finding the best
way to teach them.
47
Jeremy Harmer. op.cit. p. 71. 48
C.Previous Related Studies
The first relevant study was a thesis entitled Teaching English Pronunciation
to Young Learners – Focus on Accuracy written by Adéla Králová a thesis of
University of Pardubice, which was published on 2011. The objective of the
research was the activity of pronunciation that teacher use and also for young learners’ errors in pronunciation and how to corrected it. This study used qualitative and quantitative research. The pupils at the age from nine to eleven to
attending the third, fourth, and fifth grades of a primary school are put by the
writer. Then, the result was describe by using qualitative research. 49
The second relevant study was thesis entitled Developing Pronunciation with
Young Learners written by Nad’a Tomčíková, a thesis of University of Pardubice
Faculty of Art and Philosophy (Department of English and American Studies),
which was published on 2006. The objective of the research was to a group of
young learners that was used as a basic for the research. The description of the
course and the research condition is used in the research. It was used data
collection tools and process of data analysis is explained in detail. The result is,
interpreted from the viewpoint of activities focusing on English pronunciation
development and at the same time suitable for the age group of young learners.50
The last relevant study was a journal entitled Practices and Impeding Factors
in the Teaching of English to Young Learners in the First Cycle Public Primary
Schools at Nekemte Town, Western Ethiopia, a journal of Institute of Language
Studies and Journalism, Wollega University, which was published on 2014. The
aim of the research is to examine the practice and relates impeding factors in the
teaching of English to young learners in the first cycle. The research used
observation and interview to gather relevant and proper data. The result of the
research is the study indicates that English is thought through mother tongue.51
49
Adéla Králová. Teaching English Pronunciation to Young Learners – Focus on Accuracy. (Pardubice: 2011).
50Nad’a Tomčíková
. Developing Pronunciation with Young Learners. (Pardubice:2006). 51
The distincition between the first and the second studies with the writer is the
research design. The first study combine qualitative and quantitative research. The
second use description on her/his research. Meanwhile, the write use case study
on her research. The distinction with the last study is in instrument. He/she only
used observation and interview. The writer also use that and adding
documentation.
D.Thinking Framework
After reviewing the background and theory that have been outline above, it can
be obtained thinking as follows; pronunciation affect to communication.
Pronunciation is a sound comes from vocal cords in the form of words or sentence
that become one or important unit in the language to convey meaning from the
speaker. Someone will be more easily understood with good pronunciation.
In learning pronunciation, there are important components that cannot be
abandoned; there are consonants, vowels, intonation, and stress. All of the
components will effect to meaning of words. However, in practice, not all of the
components will appear. The English pronunciation is often not in line with the
existing theories. It is caused by several factors, such as 1) interference of mother
tongue, which is learners’ first language influence their target language; 2)
learners’ age, which is adult learners have limited to distinguish and produce
native-like sounds; 3) learners’ attitude and psychological, which is attitude pf
target language learning will influence of achievement in pronunciation; 4) prior
pronunciation instruction, which means learners who have good habit of learning correct pronunciation at the beginning will influence learners’ success with current effort.
However, there is strategy in teaching pronunciation; teacher and learners
should have collaboration in teaching and learning process. Practically, effective
teaching is related to behaviors that teacher do in class. Teacher can use some
techniques to help students to learn and concern most about how to improve
students learning in pronunciation. There are five techniques that teacher can use
communicative activity, and reading aloud. The technique that easy to use for
young learners is drilling and visual aids. According Larsen, drilling divide into
7:52 1) backward build-up drill, 2) repetition drill, 3) chain drill, 4) single-slot
substitution drill, 5) multiple-slot substitution drill, 6) transformational drill, and
7) question and answer drill. Usually, teacher uses repetition and chain drill for
young learners.
52
30
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This chapter present the method and design of study, the place and time of
study, the population and sample, the instruments and techniques of collecting
data, and the techniques of data analysis.
A. Place and Time of Study
This study took place at SDN 06 Ciputat which is located at Jalan Ki hajar
Dewantara, No: 6 Ciputat, Tangerang Selatan, Banten 15411. The study was
conducted from March to April 2016.
B.
Method and Design of StudyThe objective of this study is to obtain the activities in the classroom during
teaching and learning pronunciation taking place. Therefore, the writer used
qualitative research as a method in her research. Qualitative research emphasize in
understanding some aspects of phenomenon in somewhere and produces
descriptive data in the form of written and oral words. According to Afrizal,
qualitative research defines as a research method in social science which collects
and analyzes data related to oral or written items and human actions.1 A case
study was applied in this study by the writer. The writer observed and collected
the data factually. According to Stake, Case study in qualitative research is not
methodological choice, but a choice of subject to be studied. The case is a
specific, a complex and functioning thing and it is an integrated system with some
features.2 First, the writer listed the population and chose one teacher as sample.
After that, the writer observed teaching and learning process in the classroom. All
activities during the research was recorded by using camera. Next, the writer
interviewed the teacher and the students as the informants. The interview was
started from the simple questions such as: name, background, personality, and
1
Afrizal. Metode Penelitian Kualitatif. (Jakarta: PT. Raja Grafindo. 2014). pp.21.
2
activities in the class. The last, the writer apply document analysis; teacher’s plan
and syllabus in order to support data of this research.
C.Subject of The Study
The population of this research is all teachers of SDN 06 Ciputat. The sample
of this study is an English teacher of 6C class at SDN 06 Ciputat.
D.The Instrument and Technique of Data Collecting
This study used observation, interview, and document as instruments. There
are some steps in collecting data for this study:
1. Observation
Observation is the process of individual to get the information about others by
viewing their action in the class. The tools that used in observations are: field
notes, making entries into a log or keeping a journal and also audiotapes,
videotapes, checklist, and rating scale. In this study, the writer recorded activities
in class and made some notes or field notes. The observation started from teacher’s preparation, opening, teaching and learning process, and closing.
2. Interview
Interviews are basic to finding the information to collect the data where the
person asks question to another responds. By conducting interview, the writer will
understand of an individual’s background and experience. Consecutive questions
were used by the writer based on the number which have prepared for
participants. The quetions are about teaching and learning pronunciation in class.
3. Document
Document is one of data sources which is available and accurate. The writer
used teacher’s lesson plan and syllabus as data source to analyze whether or not it
is appropriate with classroom activities.
E. Technique of Data Analysis
The writer used descriptive qualitative which is the data derived from
document, observation, and interview. All of the result was classified based on
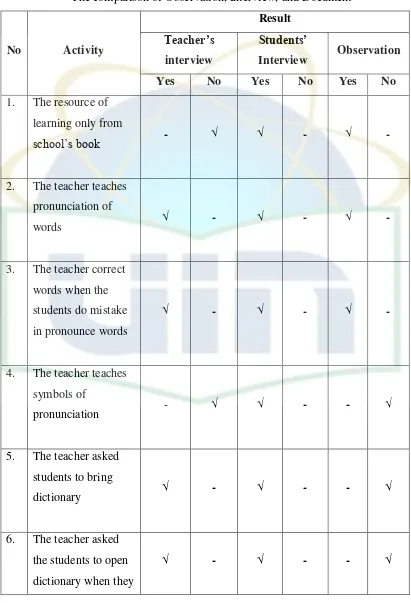
be divided because three of them related to each other.
First, the writer observed the classroom then analyzed the field note and video
recording. All the activities in the classroom were observed by the writer to see
feedback of teaching and learning process. The result of observation will notice
the technique the teacher used and the process in implementing the teachnique in
teaching pronunciation in the classroom. Afterward, the result was compared with
the interview result to supported the data of observation.
Second, the interview was done. Two students and the English teacher were
interviewed. Then, the interview was recorded and trancribed. The writer checked
and analyzed the transcription. After that, she interpreted what the informants
have informed compared the result of interview and the fact in class.
Third, lesson plan and syllabus of sixth grade students were the kinds of
documents and will be analysed by the writer. She used that to look the
compatibility of the pronunciation teaching techniques through the indicator,
whether the activity the activity already appropriate in indicator or not. After the
writer explained the data, the writer described the conclusion based on the result