Development of Leaming Object for
Engineering Courses in UTeM
Ummi Raba'ah bt Hashim
Faculty of Information and Communication Technology Universiti Teknikal Malaysia Melka (UTeM)
Melaka, Malaysia
Abstrat-This paper views e-Iearning initiative in UTeM with a focus on the development of learning object for engineering courses in UTeM. Having a learning management system called SPeL, UTeM further promote e-Iearning culture by encouraging knowledge sharing through SPeL's learning object repository. UTeM is gradually building a collection of reusable learning objects to be shared across faculties. The paper discusses the concept of learning object in UTeM context, roles of Subject Matter Expert (SME), UTeM's learning object design strategy and the development stages of learning object in UTeM. The paper further stated briely on the beneits of learning object to UTeM.
Kwors-e-leaning; leaning object; subjet mater pet; SPeL; engineering couses
I. INTRODUCTION
The advent of e-Iening has created a new educational trend among Malaysian universities. Most of the universities in Malaysia have started to utilize lening management system (LMS) as an effort to facilitate teaching and lening process. E-Leaning initiative in Universiti Teknikal Malaysia Melaka (UTeM) has stted around 2006 since it is called Kolej Universiti Teknikal Kebangsaan Malaysia (KUTKM). To ther encourage the use of e-Iening, UTeM has adopted a lening management system called SPeL (Sistem Pengurusan E-Lening). SPeL offers a blended lening solution, where conventional method is integrated with the use of virtual instructional environment to facilitate teaching and lening process. SPeL also allows collaboration between lecturers and students in the form of online discussion and content sharing. One of SPeL's mission is to promote knowledge management and knowledge sharing cultre in UTeM's community by having lecturers rom various faculties contributing to the development of leaning objects. The plan is to gradually build a repository of sharable and reusable lening objects across faculties.
There are few stages/processes involved in developing lening object in UTeM. The processes include content chunking, lening object design and development of MML (Multimedia Lesson). Various parties rom UTeM's
Aida Fazliana Abdul Kadir, Azrita Alias, Elia Erwani Hassan
Faculty of Electrical Engineering Universiti Teknikal Malaysia Melaka (UTeM)
Melka, Malaysia
community re involved in the development cycle including lecturers as SME (Subject Matter Expert), Instructional Designer, Graphic Designer, Multimedia Developer, Voice Over Talent as well as Language Editor. The roles of UTeM's academician as SME is critical throughout the leaning object development. Apart rom being a content expert, the SE also takes pt in other stages of development to ensure content quality of the leaning object. SME's involvement in the quality assurance process is crucial to ensure that the lening object being developed is reliable in content, reusable in other domain as well as ensuring that the lening object really achieves its intended leaning outcome.
II. LENNG OBJECT CONCEPT
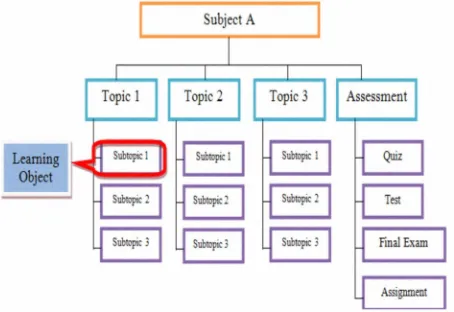
There are vrious defmitions of leaning object. Wiley [9] deined lening object as any digital resource that can be reused to support lening. Boyle [2] stated that lening object should be tied to only one lening outcome to allow reusability between disciplines where one lening object cn be used to achieve the same lening outcome in diferent disciplines. IEEE Lening Technology Standard Committee [5] defmed leaning object as a digital lening resource that facilitate a single lening objective and which may be reused in a diferent context. In UTeM context, leaning object is deined as the smallest lesson unit with a single lening outcome as shown in Figure 1.
2009 Intenational Conference on Engineering Education (ICEED 2009), December 7-8, 2009, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia In the initial stage of lening object development in
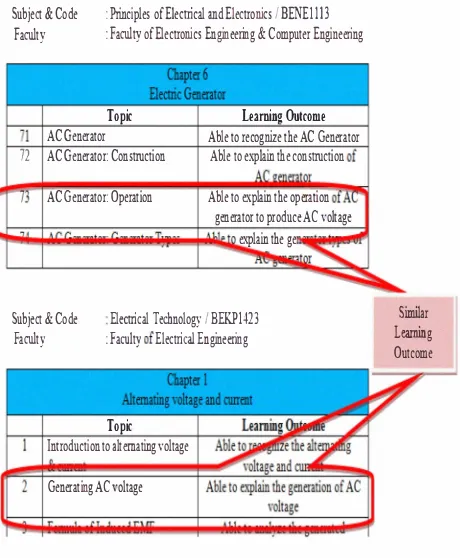
UTeM, subject is broken down to smaller topics nd urther down to smaller leaning unit called Leaning Object (LO). Figure 2 shows example of two different subjects offered by two diferent faculties which has been broken down to a list of LO for each subject. Each of the LO listed is attached to a single leaning outcome. It cn be seen that, some of the LO rom diferent subjects have similar title and share similar lening outcome. Therefore, in this case, only one LO is being developed and can be shared among common subjects.
Subject & Code Falty
: nciples of Elecical nd Electroics I BENE Illl : Falty ofElectroics Engineeing & Computer Engineeing
72 Able to recognize the AC Generator
Able to explan the constuction
Figure 2. Lening Object List
III. SUBJECT ATTER EPERT ROLES Slar Lng Outcome
Subject Matter Expert (SME) is a person who is an expert in a particular subject rea. In e-Iening environment, particularly in leaning object development, SME is someone who has speciic expertise and knowledge in certain ield such as engineering. In development process, SE is responsible to review, improve and approve technical work, to guide others, and to teach.
In UTeM context, SE refers to the lecturers who are expert in their ield and involved closely in teaching and lening activities. SEs play an important role in the development of lening object. They help to crat the lening outcomes, create content, review the content for accuracy and provide valuable feedback.
During the initial development process, SE is responsible to chunk the content of subject into smaller lening units and produce speciic leaning outcome for each unit. These lening units are known as leaning objects (LO).
Ater the process of identiying list of LOs to be developed, the SME will then work on each LO by selecting suitable content with appropriate instructional strategy for the LO. In this design stage, SME is responsible to ensure that the LO will be independent, reusable in other relevant subjects nd could promote self lening.
In the next stage of development process, SME works closely with Instructional Designer (ID) by reviewing the stoyboards produced and also the inal product, lening object in the form of Multimedia Lesson (MML), to urther improve the quality of the LO. The collaboration between SME and ID is important to enable sharing of ideas and views to achieve a reliable evaluation [4, 8].
IV. LENING OBJECT DESIGN STRATEGY
Prominent educators [6, 7] claimed that leaning is better inluenced by the instructional strategy used in the leaning materials than by the type of instructional technology used to deliver instruction.
The purpose of e-Ieaning is to promote interactive lening, self leaning and to enhance student's understanding. Hence, lening objects should be desined with appropriate instructional strategy to encourage leaning and knowledge transfer. Leaning activities crated in lening objects could encourage active processing of information and facilitate storage of information in long-term memory [6]. Since lening objects have content, context, and structure, the content of the lening objects should be presented to the lener in a clear manner, its structure adapted to the context, nd its context should relect the lening needs [ 1].
In developing mass repositoy of leaning object, time and SME prticipation is the main concen. In order to expedite nd simpliy design process, the following common instructional strategy is used in UTeM:
• Introduction (gaining leamer's attention)
• Content Presentation
• Activity (allowing the leaner to recall things they have leaned rom content presentation)
Introducion
Raone :
his unit introduce basic concpt of gnrating AC voltage. It shows how AC is gnrated using letromagntic indution nd shows simple AC wavefoms.
Leang Outcome :
At the nd of this lesson unit, you should be able to undrstnd simple men of gnrating AC volage
Assumed Pr-knowledge:
Before sttng this lesson it, you should be fir with Fraday's Law.
Figure 3. Example ofintroduction Pt in a Lening Design Document
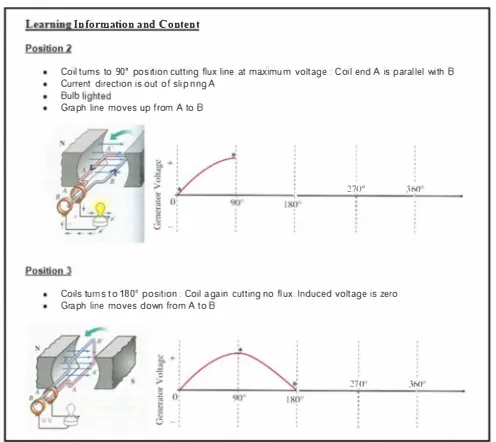
In the content section, lening information is presented using various strategy integrating various multimedia elements, for example, simulation, interactive nimation, and problem solving lesson. Lening information is being summarized (chunked) to allow faster processing of key information and encourage leners to explore nd len on their own. Example of content presentation prt in a lening design document is shown in Figure 4.
Informaion aDd Content
COil tums to 90· position cutting flux tine at m(lmum voltage COil end A IS parallel with B Current direction is out of slip ring A
Bulb
Graph line moves up from A to B
270"
Coils tuns 10 180· position: Coil again cutting no flux. Induced voltage is zero Graph line moves down from A to B
!70" 360
360"
Figure 4. Example of Content Pt in a Lening Desin Document
In the practice/interactive activity section, suitable activity is designed, allowing the leners to recall the information presented in the content section. Activities crated at the end of a lesson could promote new knowledge acquisition [4] and provide leners with a self assessment tool to self measure their achievement. Figure 5 shows an example of activity pt in a leaning design document.
Acvih'
2.0 'Iultiple Answer Ques ion
happen when the coil tm rates in a generator incr.ases?
r Voltge decreases
P Voltge ncreases
PAC Frequency ncreases
r Frequency decreases
According to 'raday·s Law, the
magnitude of the induced e.m.f is propotional to
the rate at which iL" ines re cut. herefore,
when the coil tns faster, requency nd voltage
of the AC increase.
3.0 True or False Quesion
Look at the above pictre. he coil position
indicates that mimum AC voltage is induced.
o Tue
• Flse
Figure 5. Example of Activity Pt in a Lening Design Document
v. LENNG OBJECT DEVELOPMENT PROCESS FLOW
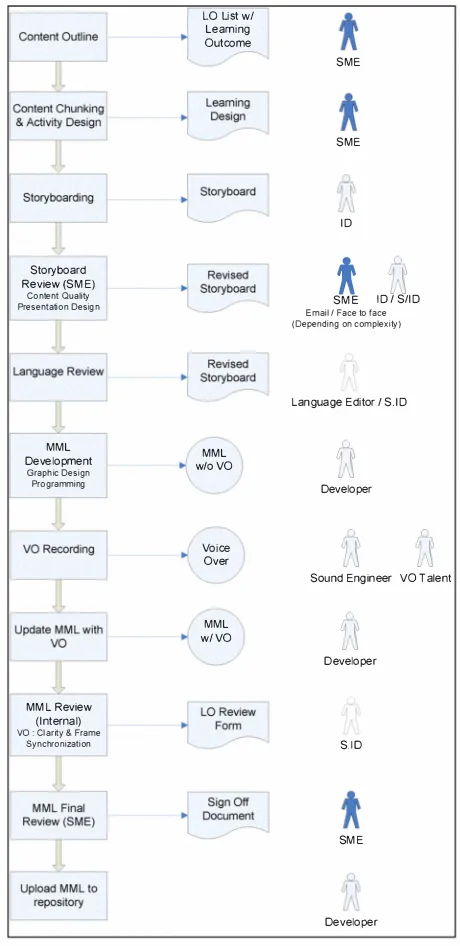
The process low chart in Figure 6 shows the process of developing engineering leaning object in UTeM. Key processes are producing lerning design, storybording and multimedia authoring (development). The process of developing LO started with lesson chunking where SME is responsible to break down their lesson/subject into independent leaning units identiied as leaning objects. The list of leaning objects will then be reined by the SME by attaching each of the leaning objects with appropriate achievable lening outcome.
The SE is also responsible to produce leaning object design document for each of the leaning object. Lening object design document is an outcome of a critical process where SME careully design and plan a suitable instructional strategy, appropriate level of content detail, engaging activities as well as attention-grabbing introduction to be included in the lening object. Normally, in common practice of instructional design, instructional designer (ID) will be responsible for all the design process, where SME is only responsible to provide content. However, in UTeM case, SME is strategically involved in part of the design process. Soon, the SME will be included in each of the development process to gradually educate them in developing their own multimedia lening object.
2009 Intenational Conference on Engineering Education (ICEED 2009), December 7-8, 2009, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia low/sequence of leaning object produced by instructional
designer (ID) based on leaning object design document. In this process, ID is responsible to plan the lesson low, layout and navigation design, placement of appropriate multimedia elements as well as producing voice over script for the multimedia lesson.
Based on the storyboard, a team of multimedia developers will then develop a ully unctional multimedia leaning object using multimedia authoring sotwre. There are many sub processes involved at this stage such as image editing, sound editing, video editing and voice over recording using vrious tools such as image editing sotware, sound and video editing sotware. Finally, the lening object is then packaged using SCORM (Sharable Content Object Reference Model) standard. SCORM standard speciy on how a lening object should be packaged to ensure reusability of the lening object.
The whole development process also includes quality assurance measures in the form of formative evaluation (evaluation conducted during the development process) and summative evaluation (evaluation of end product). Leaning object is evaluated on 3 criterias; content accuracy, presentation design and usability. Content accuracy includes review on appropriate level of content details and achievement of leaning outcome. Presentation design includes review on appropriate use of visual and auditory elements (text, graphic, animation, video, sound). Usability review includes review on progrm unctionality, clrity of instruction and clrity of media elements. Suitable criterias are used selectively in review processes at every level of development such as storyboard review and MML(Multimedia Lesson) review. Language review is another essential review conducted by appointed language editor ater the storyboarding process. The purpose of language review is to check on language accuracy of the text and voice over element in the storyboard.
The fmal product, MML, will then be uploaded to SPeL's lening object repositoy. From the repository, lecturers rom various faculties will select suitable LO to be included in their online classroom.
From the low chart, it can be shown that SE is highly involved in the whole LO development. The SE in UTeM takes part in most of the development stages rom designing and planning to review processes. The beauty and uniqueness of LO development process in UTeM lies in the strong collaboration among UTeM academician (lecturers and students). Aprt rom being SME, they also contribute as language auditor, voice over talent, designer as well as being part of the multimedia development team.
Storyboard
Sound Engineer va Talent
U
Developer
S.ID
SME
Developer
Figure 6. Lening Object Development Flow Cht
VI. BENEFIT OF LEANING OBJECT
VII. CONCLUSION
A good lening management system is meaningless without content. This paper has looked at UTeM initiative in developing a collection of lening object to ully utilize one of the most important components in SPeL, which is the lening object repositoy. The university stressed on the importnce of having a collection of lening object to promote knowledge sharing culture in UTeM. Therefore, in UTeM, instructors are encouraged to design lening objects related to their content expertise and pticipate in the lening object development process. In the development process, subject matter expert (SME) plays an important role, not only as content provider but also to ensure the overall quality of lening object. SME ensures that the lening object is creully designed to achieve desirable lening outcome. Hence, the SME cooperation is deinitely crucial to ensure the success of e-Iening in UTeM.
SPeL ofers an instructional altenative to support teaching and lening process. Aprt rom the beneits of sharable and reusable lening objects in the repository, SPeL also encourage self paced lening, collaboration and self assessment. To ully beneit rom SPeL, constraints nd limitation in implementing the system have to be overcome or reduced. Apparent problems include lack of SME paticipation, low level of e-Iening awareness as well as problems in supporting network facility (slow access to SPeL).
REFERENCES
[ 1] Ben K. D. and Permanand M. , "A Model for Evaluating Lening Objects, Proceeding of the lEE Intenational on Advanced Lening Technologies", 2004.
[2] Boyle, T., "Design principles for authoring dynamic, reusable lening object. Australian Jounal of Educational Technology, 19(1) p46-58, 2003.
[3] Edward R. Jones, "Implications of SCORM and Emerging E-Lening Standrds on Engineering Eduction", Proceedings of the 2002 ASEE Gulf-Southwest Annual Conference, The University of Louisiana t Lafayette, 2002.
[4] Erla M.," Knowledge Mangement for E-Iening based on Lening Objects: A Qualittive Focus", ITHET 6th Annual Intenational Conference, 2005.
[5] IEEE Lening Technology Standard Committee (2004) [http://ltsc.ieee.orglwgI2].
[6] Mohmed A., "Designing Lening Mterials for Successul Lening When Using Instructional Technology", Konvesyen Teknologi Pendidikan, K.Terengganu, 2005.
[7] Schramm, W., Big Media, Little Media, Beverly Hills, CA:Sage, 1977. [8] Vago, J. N. and Belfer K. A., "Learning Object Evaluation: Computer
Mediated Collaboration and inter-rater relibility", Intentional Jounal of Computers and Application, Vol. 25, No 3, 2003.