IJMsf
1Hil1i,;::i
ruDIAN
JOURruAL
OF
fiNNruNGEfiNEruT
SCIEruCE
Impact Factor
(Clf)
:
O.3?E
Volume
-
lll
Issue
-
4
bO
Ulrich's
Directory,
U5A
.C
cabell
Publishing,
USA
X
lndex
Copernicus
lnternational,
Poland
-p
Georgetown
University Library,
U5A
p
Journal5eek
=
Clobal lmpact
Factor,
Australia
October
2013
r:-
ERI'I
'-:xtr
{\
JouRNar,or
MaNacEMENTScrcxco
(IJMS)
EISSN2231.-279X
_ISSN
2249_0280 55THE
IDENTIFICATION
OF
THE
CRITICAL
SUCCESS
FACTOR
ABSTRACT
Institutions
of
Higher Education are required to develop a good business strategy,
oneof
them byutilizing advances in information technology (IT). IT processes need to be measurld to determine the
level of maturity of the implementation. Measurement of IT processes in higher education can be done
using the COBIT Framework. Higher education institutioni need
to
do an identification Brocess on Critical Success Factors (CSF)of
IT process first before doing the performance measurabie process.CSF mapping results
of IT
processesin
higher institutionsin
Salatiga, shows that the levelof
IT maturity scaleis
above 2 (repeatable) outof
5. The Highest value is on aspectsof IT
resources for frrancing theIT
investment. The lowest valueis
on aspectsof
ensuring the qualityof
the system,because the higher institutions in Salatiga do not have a specific training program
foi
users to run theapplications
of
information systems. The mapping results showed thatthl
aspects of managerial and s)'stem need to be a major concern for the head of the higher institutions in Saiatiga when these higher institutionswill
establish and develop the Academic System informationKeywords: Academic information system, Critical Success Factors, maturity level, COBIT.
4CSF)
OF
THE
ACADEMIC INFORMATION
SYSTEM
IN HIGHER
EDUCATION
USING
COBIT FRAMEWORK
VERSION
4.1
(CASE
STUDY:
HIGHER
EDUCATION
IN
SALATIGA, CENTRAL
JAVA)
Evi
Maria,
Faculty
of
Information TechnologySatya Wacana Christian University, Indonesia. Charitas
Fibriani,
Faculty
of
Information Technology Sana Wacana Christian University, Indonesia.Lina
Sinatra
Wijaya, Facultyof
Information TechnologySatya Wacana Christian
University,
Indonesia.qrnv.scholarshub.net
III,
Iuoraiv
JounNu,
or
MaN.q.cnMENT SctBNco(IJMS)
EISSN 2231-279X-
ISSN 22-19-r03ffilntroduction:
Excellent service
in
an organization has become aliability.
One of the excellent services is to satisfl'cwith
professionally qualified service competencewith
the
characteristicsof
transparency, accounrah:-q,, conditional (Tjiptono, 2001).In
orderto
improve operational efficiency and qualityof
serviceto
crinstitutions of Higher Education (PT) is also required
to
develop a good business strategy, and one of them utilizing advancesin
information technology(IT).
The useof
IT
in
higher educations should be s1'st:,considered and planned, considering that generally the institution is a non-profit organization, while the
tcrs
that the implementation of IT requires a relatively high cost (PWC, 2004, Applegate et a1.,2003).
Salatig4
in
Central Java hasfour
higher educational institutionswhich
havean
operational permL:f
establishment of study programs from the Directorate General of Higher Education (DIKTI ) and has been ac:
by the National Accreditation Board
of
Higher Education (BAN-PT).As
for targeted higher educatior-. mresearch
are
Satya Wacana Christian University (SWCU), AMA-Schoolof
Economics (stie AMA.r. -r:Academy
of
Midwifery
(AKBID
Ar-Rum), and Bhakti Nusantara-Academyof
Midwifery
(f{usantar:AKBID). The use of computers, internet technology and Information System in doing all the activities thrc'u
unit of work is a form using
IT
in these higher educational institutions. These institutions have to make < develop the service for the academic information system which is complete, accurate, current, safe,consi:iem-and relevant. This is done in order to create user loyalty, improve effectiveness and efficiency of resource use"
For
university leaders and partner,IT
management becomes oneof
the Critical Success Factor(CSI'
mr managementof
the higher educational institutions(Henderi,2010).
The complexityof
the applicatio:-;lrthese institutions makes the heads
of
the various levelsin
the institutions and stakeholders havedilr
understand, create and implement
IT
governance. This is because the higher educational institutions inhave
no
special model of the basic framework when they build the Academic Information System@lul
uur
Sembiring, 2006). As a result, the benefits obtained by the use of IT for the universities are equal
with
tl--e ,the
incurred investments. Therefore,the
university leader requiresIT
governancein
orderto
e:sur(Eachievement of the plan and the alignment between IT strategy and business strategy of the institution.
IfG*
states that the alignment process
is
done by measuring the relatedIT
process using the COBIT 4.1 (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology) .Measurement
of
IT
processesin
orderto
plan and alignmentof
business strategy usingIT
could beduu
ifl higher educational institution has already formulated and definedits
critical success factor (CSF). CSFimportant role for the progress of a company because of the demands of the business competition that r
company
to
have a clear vision and mission aswell
as practical stepsto
realize the goal. Additionzul.success factor leads the company
to
measure its working performance, whethqrit
is appropriate or r'"cr 1 2009). Seeing its importance, this researchwill
identify the critical success factor on Academic Systemb::
in higher educational institutions in Salatig4 Central Java. Results of this study are expected to provide i:nrir
leaders of the institutions in Salatiga in designing and developing the Academic System Information.
L
the resultsof
this study are expectedto
provide directionfor
the implementationof
IT
in
Higher institutions in Salatiga in order to support the achievement of the organization's vision and mission.Literature Review:
Academic Information Systems:
Academic Information System is an application used to record data from administration academic
of
ea:: ,starting from the entry (admission) to the exit (graduation).
All
university students havethe
right tt-, :e access the application. The operation of this application is important to know and masterby
the studils
they can see the financial obligations that they should pay, register the course subjects, and see the
resu:
rdstudy. (Yanuar and Maria,2012) Cotrit Framework:
Control Objective
for
Information and related Technology, abbreviated COBIT,is
designed asa
:rxriGovernance to help in understanding and managing of risks, benefits and evaluation related to IT. COBIT
!
has issued
by
the
IT
Governance Institutewhich
is
partof
ISACA
(Information SystemAudit
an:
I. Association). COBIT guidelines consist of several directives, which are Control Objectives, Audit Guice Management Guidelines. To provide information needed for companies to achieve izational goali- trm: i.c.\ JOURNALoFMANAGEMENT ScTeNco
(IJMS)
EISSN 2231.-279x-
ISSN
2249-0280 b7'
::,:s
of
COBIT describes business requirements, process orientation andIT
resource. COBIT framework" " -onsist of 34 high-level control objective, with each IT processes grouped into four major domains, namely:
:
--:rins and Organization (PO), includes strategy, tactics, and the identificationof
IT best way to make the-
'1-mum contributionto
the achievementof
the organization's business objectives. The realizationof
the-*;:35'
needsto
be
planned, communicated and managedfrom
a
varietyof
different viewpoints. The'*:-:mentation of the strategy should be accompanied by adequate infrastructure and can supportthe business
-':,'.,:ies of the organization .
-::.:isition
and Implementation(AI),
the realization of the strategy which has been set, must be accompanied"
.:propriateIT
solutions, then theseIT
solutions are conducted, implemented and integratedinto
the-:-ization's
business processes. This domain also includes changes and maintenance needed by the running,:;x.
to make sure the system life cycle is maintained.-':
;'ery&
Support, includesfulfillment
processof
theIT
service, system security, continuityof
service,::-:-:rg and education for users, and the process ofthe ongoing data.
'
I ::-.i:oring, to maintain the quality of and compliance with the applicable control, the entire IT process should".
.,lervised and assessed their feasibility regularly. This domain focuses on the issue of controls implemented,
"::tl the organization, internal and external audit and independent assurance ofthe tests carried out .' ::
-'
Success Factors (CSF) serves as a guide to management in implementing controls to IT and its processes.; j
:r
activity that can be strategic, technical, organizational, process or procedural habits. CSF is generallyr
:
"'::d with the ability and expertise and should be short, focused and action-oriented and highly affect the 'r"I
-'::.i
resourcesin
a process.In
measuring the performanceof IT
processes, COBITuses two
different"i
,;;-j;S
:
(1)Key
Goal Indicators(KGI) is
a measurement that indicates whether anIT
process has met the'
,,,i-::s
requirements needed by the management. (2) Key Performance Indicator(KPI) is
a measurement that u:'::---:l3S howwell
the performanceof IT
processesin
orderto
support the achievementof IT
goals. Keyrr"- . -:3ltce Indicator
will
provide an overview of whether a goalwill
be achieved or not. Determination of targetrr ,- -
I:::s
and performance indicators of the information system is carried out in order to control the activities soit
;riu"
:;:antee
that the goal of the IT process is achieved .'"r
:
tf rncept ofit Maturity
Model::'::it1'
Modelis
a model usedto
measure the maturity levelof IT
managementin
an
organization. This'li
:,
-r;inert
model adopted the CapabilityMaturity Model
for
software publishedby
Software Engineeringr
:--:.
Carniege Mellon University.IT
Maturity Model consistsof
five
maturity levelsof IT
management,:' ,i -,: ., g:: level 0 (non-existent), level
I
(initial), Ievel 2 (repeatable), level 3 (defined), level 4 (managed) and level:..::ized). The higher the maturity level, the better the
IT
management Process, which indirectly means more'
r.i:
--re IT support in the process of achievingthe organizational goal.)'*,,j,r'1,: q5 ReSeafCheS:
"-*
"R. (.2002) notes the failureof
implementationof
Information Technology(IT) in
Business Processof
ther'*'::.iucational
institution is not due to technical factors but becauseof
the non-technical issues thatis
ther,,,,r*'." -actor, processes and work organization. Many people become resistant
to
the implementationof
IT
in'
--' .:
: ducation (PT), so in order to overcome this condition, the role of the leader and also the IT manager arertL:rl:'-
r:
The) can managed the IT management that is needed to overcome the leadership role and encouragement;-- .:rsity and IT management which can manage the IT management
which
is focused, structured and aligned,r'
-:.: reeds of the organization. Therefore, for the leader of the institutions and the partners of the institutions ,llll
:-anagement are becoming as one of the Critical Success Factor (CSF) in the higher educational management'::-::::.
1010)'
.. ' s - : ducation has allocated large number of funds for investment in the field ofIT.
Moertini (2006) stated that'
*
::c number of students, employees (Lectures and administration staff), the amount of activity ina unit of time,
Lrr
"
.i:
:umberof
buildings and spaces,university is
categorized as a largeinstitution.
In
Indonesia, higherL-
.:. :':al institutions do not have the basic framework of specific models when making the academic Information':r'-:.
So Mutyarini and Sembiring (2006) made an architectural modelof
Academic Information System. By .,,,-.::,-a the making the architectureof
Monash University using TOGAF in orderto
achieve the Three DharmaINor.lN
Jounu,lr,
or
MINacEMENT ScrnNcr
(IJMS)
EISSN 2231-279X_[SSN,University mission. While the COBIT Control Objective Framework used in the making the -{;a:euLLu System because it fits with the characteristics of universities as a State Owned Legal Entitl. (3l.
*-[';
.the COBIT framework is not only used in architectural design
of
the information system. bui=
:mralso measures the performance of the architecture of the information System.
O'Donnell, E, (2004) found that in order to build and measure the performance of IT , we can
a::rr
j,msuch as the Information Technology Infrastructure Library
(ITIL),
ISOAEC 17799, COSO and[
,l611l[iresearch (2009) and Jusuf, Heni (2009) also uses COBIT
to
developa
modelof IT
Gcr:xrlgrluurlEducation with an argument that
COBIT
is made by using IT standards as a reference so thar:r
sul;development with the goal of the institution is guaranteed. Before the measurements is done. i:
:
sampling
of
theIT
process, then performed the translation process usingITIL,
so that the IT Ci,*ts:i obtaining the right to then measured using IT Maturity (Anugrah, 2008).Maria (201l) found that SWCU has owned
the
internal control in each level COBIT IT process ;;Emrru*il
where
the
internal control provides assurancethat
academic services are performedbr
$m!6d
procedures that have been defined. IT management has been applied in SWCU, but it has not L,eer
well-structured method and approach. Maria and Fibriani (2012) found that the implemenul-:,.
rf
Satya Wacana becomes
important
because STIBA Satya Wacana has done the managemer:i
11institution. Evaluation results show that the overall maturity level of IT implementation is ar a i r.luts d means that IT processes are running based
on
a certain pattem within the institution. The resulis:;
ltmrfound that the process of PO4, PO8, AI7, DS2, DS6,
DSl0
and ME3 is aprocess that has Lqe a1r5;compared
to
other processes, so this process should get highly prioritizedin
improvemeu
:im
processes .
Research Methodology:
This research is a qualitative descriptive study which describes the phenomenon in a way that acru,a-J an event
or
population by emphasizingthe importance of closeness to the people and the situation c:so
that
researchers gaina
clear
understandingof
reality
and
real-life
conditionsboth
q-xniliquantitatively. This study
will
make the process of identification of Critical Success Factor (CSFr -,r ntrm"rInformation System
(SI)
in Higher Education (PT) using the COBIT Framework version 4.1.This research is a case study conducted in some higher educational institution in Salatiga. The
i:
as the study have the following criteria which have an operational permit
of
the establishment c,:from the Directorate General of Higher Education
(DIKTI)
and has been accredited by the NarionulBoard
of
Higher Education(BAN-PT).
Of
determiningthe
criteriafinally we
chose1
H;Jrdrinstitution-shaped as University,
I
higher educational institution-shaped as college and2
iqm.
institutions-shaped as Academy. These higher educational institutions
are
Satya Wacana Ct: (SWCU), AMA-Schoolof
Economics (stieAMA),
Ar-Rum-Academyof
Midwifery(AKBID
+: Bhakti Nusantara -Academy of Midwifery (Nusantara Bhakti AKBID).The data used in this study consisted
of
primary and secondary data. Primary data weresfr:i.Er
interviews with the leaders
of
each institution,Unit
Technology and Information Systems is a:;
supervisor ofIl
and IT users the administrative staff, lectures and students based on the list oft-x
in accordance with the guidelines of the COBIT framework version 4.1. While the secondan'd,'mp various reports and publications relevant to the study.The phase
of
this
study include:(1)
conductinginitial
studies, conducting material searchelresearch, literature
study
and standards that support the research topic, drafting questionna::=sdocuments related
to
the
duties and functionsof
the institutions that can produce informa:l:rrstakeholders in the institutions, (2) establishing the
IT
Objectives in Higher Education and then d; of the Critical Success Factors (CSF)of
the IT Process in higher education which has the funci:rafor
the headof
the higher education managementin
implementing controlsto
IT
and itsCOBIT Framework, (3) performing the mapping
of
CSF Information technology processes at ir: Salatiga, (4) the final stage of the researchwill
be: making conclusions and suggestions fromaI
has been done.
Results and Discussion :
illiltitrtril ,
,
.ll(:iLR\.{LOFMANAGEMENTSCIENCE
(UMS)
EISSN 2281-279r_ISSN2249_0280 b9 illllrillrnlrfl-nr{r: n of Business process in Higher Education:
.llll, ll.,
:,':';i:"r:."j,::#:""1'-i'9Tll1,l?l
j,traf nro.}{es educational services to the communiry.rhe
businessl,
-
"',...1:L'i.'il::::l^'T,::j*l"to
lit:1ry"
(2 ). tvpes:it
"
*uin p.or"r.",
"rd;;;;#r,i*'i.lX'".1".'.1
,'
-:, _. -:
:;':,:
.o Jils
.l! 3 n1i* u.y;;t
;
;"r"i'r
i,lifi
l;'ffi
,tr1Xfir:"j:".'"Hl
JI";T[J;
hing, researchllil:
financial administration, cooperation and externui."lutions, and promotions .:-l::#1"':::i*'j::::"jf:'::::,*:1111*
*:
i,
",
i,r".-1,i";';;;;#'i,S)
whichis
beingrl"
H:i}#'*Y,:j:.:"0,*11t,::::11.^1,i":j,"d l1,1tl.
u,sine,s p,ocess can be carried;;:d.#:i;
_,,;llljfJ:T::^?.'3,1t:ij,ITy,
as Academicrnro,,,",io,
iil;:il;#"ffi;ffiii:",:J:;
'ti ,u*: sysrtrr, rs Known as Academlc lntormation System. Academic Information system
1;.0fi'fff:,",:.":"jffiJ:"fl:.:::t::jh:.,1q":yli*
."q,i,.a
uv
,r,. ,i"r"r,"r0.,,
"r
the higherIie
stakeholders of Higher Education ( Indrajit,
2006) arein Figure 1 below.
Supplier
I . SMQ SMI( STlr,tetc 2. DIKTtr KOPERTIS
3. Parents/Guardiatr
4. Business World 5. Co]muity
a--;;l
I Newuigherraucation ],-I / Customer \ i comp.titor ] / University st,den\
]Other Univesity | \ Business World f
'_
| \
_,
I substituts I ]Tmining comes institution
| .Certihcation Instinrtions I
[image:6.612.43.552.65.371.2]ll
Figure 1. Stakeholders in Higher Education (source:
rnaralit,
zooo;'"'i" L' : I - 'r3r needs in Higher Education
related to the need of Information- System (IS) are divided into 3 groups: (a)
ll*
--
)harma operations and higher educational managementin
tneform of the need
to
improve productivity,'' -
:-;"
and qualityof
the work, (b) informationservii
for
intemal and external interestsof
higher education,'rL
' :
-.r. ;uality r- it and decision-making.€Nsurance in the form of the need to provide data and information that is useful for doing the quality'
-
::-i
needof
information system, thearchitecture
of
Infibrmation Technology(IT)
in
Higher Education is::'1: into 3 (three) criteria, where each criteria has supported business activitiies. These Criteria and activities
::l
1' The role.of IT consists of the Academic Informatio"svri.*
activities, E-learni.,_:.^::"*?,f.,1;;t#il':;";d;,ii-1*d'3:[T-1,':H#[TfJ:l'ihfi;"";lffii;fS,HiliX1:il:"I
::.::j,:,:Tl:::":j:'::T::.,i:"'^'1'::
:*
inrormation.*d-l,ry;
;
Ailil;;;,t""H;#'h[";;,"!;;.
vrrvrqfluy Jvr YluE, J.l-*:1':;:::i'S.:r,1.ll],*:.1ccT1.and
connectivity.Ir
Security Management,poticy
and Network '-'_:ement, DC&
DRC (Data Center and Disaster Recovery Center).u*utification of
critical
success Factors(csF)
from
theit
Process at Higher Educationsin
salatiga,central
"t1t::
-'
:-ess goalsin
Higher Education were established by the headof
the institution using 4 perspective Balance'
':-'
.i
Card impact on (BSC)' the increase Goals of the financial perspective is to have good and transparent financial management so thatin profit, while goals related to the improvement of services and ensure that services
--"
'''jed
are always on timeand reliable so that the customer/user
will
get satisfaction are the goals that areset
-"':
the perspective of the customer. Goals from the internal perspectivelsa commitment to always do the repair
':-:
maintain the functions of the business processes and ensure the service given in a line with the internal policies'::r
applicable law so that the quality of sirvice is maintained. while_the goalsof
learning and growth perspective'-:
always do their innovation and dlvelop the human resources in order to become a leader in the similar business.-:- relation to the efficiency and effectiveness of the existing business processes requires the implementation of IT in
*re Higher Education' Therefore the right business strateg|
is neeJeo to achieve business goals that have been set.
Jue to the use of
I!
the business strategy defi_ned.use.s +-"gsctr
ferspective (Maria,et
a1.,2012)-r
implementation in higher education hasIT
objectives, they*.,
ful
ensuring the existinglr
services to supportwww.scholarshub.net
Vol.-
lnoLrN
JounNal
or
MIN,TcEMENT ScmNcn(IJMS)
EISSN 2231-279X-
ISSN
2249-0280 an increasein
the
qualityof
the academic program,(b)
supporting the quality improvementof
managememprograms and institutions and (c) supporting the increased cooperation with industry and other universities. In
orar
to achieve the IT objective, the control of the IT processes is carried out. The conirol of the IT processes in hi_elereducation uses COBIT framework as the basis. IT processes in higher education consists of four domains, narr3l-I
Planning and Organization (PO), Acquisition and Implementation (ary, oelirrery and Support (DS) and
Monitor;g
(ME) with a total
of
34 sub-domains. TheseIT
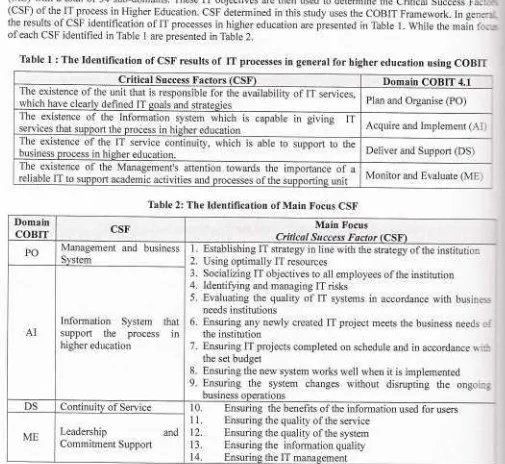
objectives are then used to detlrmine ttre Crlticat Success Factru-,*(CSF) of the IT process in Higher Education. CSF determined in this study uses the COBIT Framework. In gener:r-the results of CSF identification of IT processes in higher education are piesented in Table
l.
While the main fo,c-s of each CSF identified in TableI
are presented in Table 2.Table
I
: The Identification of CSF resultsof
IT
processes in generalfor
higher education using COBITCritical
Success f,'actors (CSF) Domain COBIT 4.1The existence of the unit that is responsible for the availability or
rr
se*icer
which have clearly defined IT goals and strategies Plan and Organise (PO)
The existence
of
the Information system whichservices that slrpport the process in higher education
is
capablein
giving ITAcquire and Implement (AI'r
The existence
of
theIT
service continuity, whichis
ableto
snpportto
thebusiness process in higher education. Deliver and Support (DS)
The existence
of
the Management's attention towardsthe
importanceof
areliable IT to support academic activities and processes of the supportins unit Monitor and Evaluate (ME't Table 2: The Identification of Main Focus CSF
Domain
COBIT CSF' Critical Success Main FocusFactor
PO Management and business System
l.
Establishing IT strategy in line with the strategy of the institution2.
Using optimally IT resources3.
Socializing IT objectives to all employees of the institution4.
Identifzing and managing IT risks5.
Evaluating the qualityof IT
systemsin
accordance with business needs institutions6.
Ensuring any newly created IT project meets the business needs t-: the institution7.
Ensuring IT projects completed on schedule and in accordancerr-ii
the set budget8.
Ensuring the new system works well when it is implemented9.
Ensuringthe
system changeswithout
disruptingthe
ongoi-n.-business oDerations
AI
that
in
Information
Systemsupport
the
processhigher education
DS Continuitv of Service Ensuring the benefits of the information used
Ensuring the quality of the service
Ensuring the quality of the system
Ensuring
the
information qualityEnsuring the IT manasement
10. 11.
12.
13.
14.
for users
ME
Leadership
andCommitment Support
From the main focus
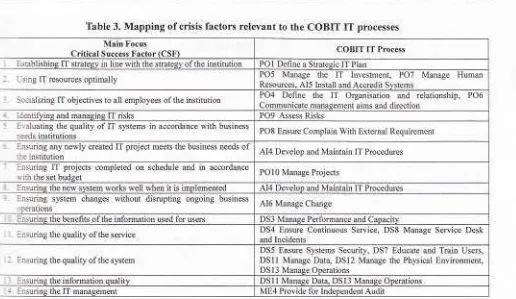
of
the CSF, the Table3
below presents the resultsof
mapping the critical factors that,:r
relevant to the COBIT IT processes. Mapping of critical factors to the COBIT IT piocesses is carried out in orde: :r measure the level of maturity
of
the internal process of IT implementation in Higher Education. The descriptior :,f the maturity level of the internal process ofIT
implementation is described urrrr,
of automic statement in qL-.,,:reach description level
of
maturity contains statements that may conclude whetheiit
is
appropriateor
nol
!m{cmostly appropriate or mostly inappropriate. Description
of
maturity level consistsof
six
leveis (0to
5)
un-'nudescribes the level
of
reliabilityof
the internal activitiesof
theIT
implementation, which are summarized :1,ISACA on consensus of many expert opinions and various best practices in the field of information technology th=i is generic and has been used as an international standard.
[image:7.612.46.551.139.603.2]I
rorlN
JouRNar.or
MaNacTMENTScrBNcr
(IJMS)
EISSN 2231-279K-ISSN 2249-0280 61Table 3. Mapping of crisis factors relevant to the COBIT
IT
processesCOBIT IT Process PO1 Define a Stratesic IT Plan
PO5 Manage the
IT
Investment, PO7 Manage HumanAI5 Install and Accredit Svstems
PO4 Define the
IT
Organisation and relationship, PO6 Communicate managelnent aims and directionPO8 Ensure Complain With External Requirement
AI4 Develop and Maintain IT Procedures
POl0 Manage Pro.lects
A14 Develop and Maintain IT Procedures
DS4 Ensure Continuous Service, DS8 Manage Service Desk
and Incidents
DS5 Ensure Systems Security, DS7 Educate and Train Users,
DS11 Manage Data, DS12 Manage the Physical Environment,
DSl3 Mana
DSll Manase Data, DS13 Manase Operations
ME4 Provide for Indeoendent Audit Main Focus
Critical Success Factor
Establishi in line with the stra of the institution
UsLng IT resources optimally
Socializing IT objectives to all employees ofthe institution Identiftins a
Evaluating the quality of IT systems in accordance with business needs institutions
Fnsuring any newly created IT project meets the business needs of
-.ne institution
Ensuring IT projects completed on schedule and in accordance
:-,ith the set bud
:nsurinq the new system works well when it is
Insuring system changes without disrupting ongoing business aDeratlons
Frsuring the benefits ofthe information used for users
:nsuring the quality of the service
-
:nsuring the quality of the systemthe information
(esults Mapping
Critical
Success Factors (CSF)from
theit
Process on Higher Education Salatiga, Central,f
lr
a:.
, ::a11. the level of maturity of information technology in higher educationin
Salatiga, Central Jav4 is above the:,":
I
(repeatable) out of 5. The Highest value is on aspects of IT resources for financing the IT investment. The:
" 3sI yalue is on aspectsof
ensuring the quality of the system, because the higher institutions in Salatiga do noti
,.
a specific training program for users to run the applications of information systems. Users use a trial and error -,:::-lach when running the application,if
it does not work (error) then userswill
ask for help from theIT
service: -:-. ider units owned by each institution.
I
-:ing
results showed that the aspects of managerial and system need to be a major concern for the head of the'
:::i
institutions in Salatiga when theywill
establish and develop Academic System Information. Whatit
meant"
:le
Managerial aspectsof
the institution is that the higher institutionsin
Salatiga need to have(l)
qualityof
''-.
-ce
management framework,(2)
a
mechanismfor
data
security systems, information,and
network--:1(mlcture, (3) standard operating procedures (SOP)
for IT
operations, (4)
mechanismsfor
supervision and*:i:sment
of IT performance, (5) The mechanism of IT management, (6) IT training and education programs on a':.-,ar
basis. While aspectsof
system, the institutions need to make a supervision system on the IT performance--:
.:r appropriate IT management system to support the business goals of the institution. -; oclusion:
-j:,:iiions
of
Higher Education are requiredto
develop a good business strategy, oneof
them by utilizing the-':, ::rces
of
information technology(IT).
Ideally the higher education business processes runin
an information,::n
(IS) using the integrated software/systems applications in the run.It
is intended that the business process .'.
:e carried out effectively and efficiently. IT Implementation in Higher Education has some objectives, they are.
::isuring
that the existingIT
services can support the increasein
the qualityof
the academic program, (b)-::lning
the quality improvement of the management programs and institutions and (c) supporting the increased,::eration with industry and other higher education. ln order to achieve IT objectives in higher education, so the
.
-l-rl
over IT processes using the COBIT framework as the basis is carried out. The measurement of IT processes-
-::er to plan and alignment of business strategy with iT, can be doneif
the higher institution has formulated and-:
::nined the Critical Success Factors (CSF) .::
napping resultsof
IT processes in higher institutions in Salatiga, shows that the level of IT maturity scale is [image:8.612.43.559.50.349.2]t21
13l t4l
INoUN JouRNal
or
MINaceMENT ScrBNcr
(IJMS)
EISSN 2231.-279X- rSSN2{q@1
above 2 (repeatable) out of 5. The Highest value is on aspects of IT resources for financing the
iT
inr e'-mm,,lowest value is on aspects
of
ensuring the quality of the system, because the higher institutions in 5s- irgp have a specific training program for users to run the applications of information systems. Mapping resrf,s that the aspectsof
managerial and system need to be a major concern for the headof
the higher iSalatiga when these higher institutions
will
establish and develop the Academic System Information.Acknowledgements:
Directorate General of Higher Education (DIKTD for funding this research on Competitive Grant
Schrrr
year 2013. References:
I1l
Anugrah, Bagus Satria.(2008).
PengukuranTingkat
KematanganTata
Kelola Teknolos
i
Menggunakan Model Kematangan COBIT di PT Bank Mandiri, Tbk. Unpublished thesis, Surahi;.u"
Applegate LM., Austin RD, McFarlan. FW. (2003). Coorporate Information Startegy and
and cases, 6th edn boston, M.A: McGraw-Hill
Curry, J. R. (2002). The Organizational Challenge: IT and Revolution in Higher Education
Henderi. (2010). Good
IT
Governance: Frameworkand
Prototypefor
Higher
Edual;mCommunication and Inovative Technology Joumal vol 3, no.2 ISSN: 1978-8282.
l5l
Indrajit, Eko. (2006). Mengukur Tingkat Kematangan Pemanfaatan Teknologi Informasi "--mrilrPendidikan (Suatu Pendekatan Kesiapan Pemegang Kepentingan/Stakeholder). Conference
:
ICT for Indonesia, Bandung: 3-4May 2006,116-120.
t6l
ISACA. (2004). COBIT Student Book. IT Governance Institute.Ul
ISACA. (2006). Integrating COBIT into theIT
Audit Process (Planning, ScopeDevelopmc:
Govemance Institute.t8l
ISACA. (2009). An Executive View of IT Governance. IT Govemance Institute.t9l
Jusuf,
Heni.
(2009).
IT
Governancepada
LayananAkademik
On-Line
di
Unii'.--r,ai
Menggunakan COBIT (Control Objectives For Information and Related Technology) r
em s
I
Seminar of Information Technology Application, Yogyakarta:20st June 2009.
Maria. (2011). Perbandingan Sistem Informasi Akademik Universitas Kristen Satya
Wac,'',
COBIT Framework, Journal of Eonomic Foccus, vol 10,
no.2hatl40-l49.ISSN
1412-3851Maria and Fibriani. (2012). Evaluasi Implementasi Teknologi Informasi di Sekolah Tinggr Baha-*. "
Satya Wacana, Salatiga Menggunakan Framework COBIT Versi 4.1. Joumal of Accountiae
'r:
Economic, vol 2, no 1 November 2012, Economic Faculty of Mercu Buana University, Yogyaka* Maria, et.,
al.
(2012). The Measurementof
Information Technology PerformanceIn
l:,a;Education Institutions
in
The Contextof
Achieving Institutional Business Goals Using COBITVersion 4.1: Case Studi Satya Wacana ChristianUniversity Salatiga. Journal
of Art,
Sci Researchers World, Vo1III,
Issue-3(3), 9-19.[13] Moertini, V.S dan Tim Program-1 PHK K-3 Unpar. (2006). Perancangan Master Plan Paagiaum
mendukung Penjaminan Mutu Perguruan Tinggi Studi Kasus: Unpar. Seminar Nasional
Perguruan Tinggi dan Sistem Pangkalan Data Pendukungnya. Bandung:22 December 2005
[14]
Mutyarini and
Sembiring. (2006).Arsitektur
Sistem InformasiUntuk Institusi
Perg::rum.Indonesia. Conference proceeding of ICT for Indonesia, Bandung: 3-4May 2006.
[15] O'donnell, E. (2004). Discussion of Director Responsibility for
IT
Govemance:A
Persp,+;::rt Intemational Journal of Accounting lnformation Systems 5: p 101-04.[16] PricewaterHouseCooper. (2004). IT Governance Global Status Report. IT Govemance
lnsi:se
[17] Suryani, Arie, Ardiyanti. (2009). Pengembangan Model IT Governance pada Organisasi Perguman T-nomt
COBIT 4.0 Domain PO dan AI. National Seminar on hformation technology, YogSrakarta: 23 Ma1 l-tlilu
[18] Tjiptono, Fandy. (2001). Strategi Pemasaran. First Edition. Andi Ofset.Yogyakarta
[9]
Yanuar and Maria. (2012). Audit Sistem Informasi Akademik Perguruan TinggiX
meneg:Domain Deliver and Support. Journal of District Accounting and Finance.vol2, no 1, Sep: t10l
[11] 112)
www.scholarshub.net
**
**