1
Information Technology
2
Learning Objectives
When you finish this chapter, you will:
Recognize major components of an electronic
computer.
Understand how the different components
work.
3
Learning Objectives
Be able to classify computers into major
categories, and identify their strengths and weaknesses.
Be able to identify and evaluate key criteria
when deciding what computers to purchase.
Know the controversy regarding the health
hazards of computers.
Recognize how to evaluate hardware so that
4
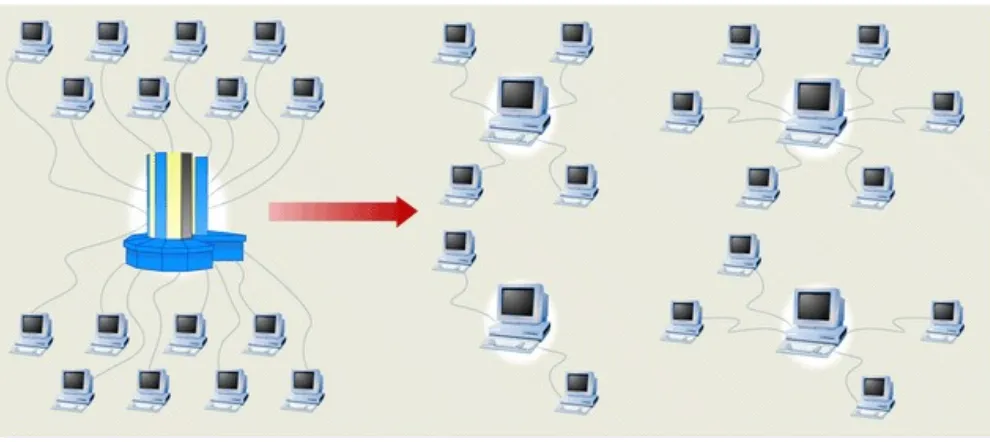
The Central Tool of Modern IS
Four Basic Functions of Computers
Accept data
Process data
Store data and instructions
5
[image:5.720.109.613.126.463.2]The Central Tool of Modern IS
6
[image:6.720.110.605.172.393.2]The Central Tool of Modern IS
7
Computers Communicating: Bits And Bytes
Computer recognizes two states: on or off
Each on or off signal represents a bit (binary digit)
Encoding Schemes
Representation of symbols by unique strings of bits
Counting Bases
Decimal system is “base 10” Binary system is “base 2”
8
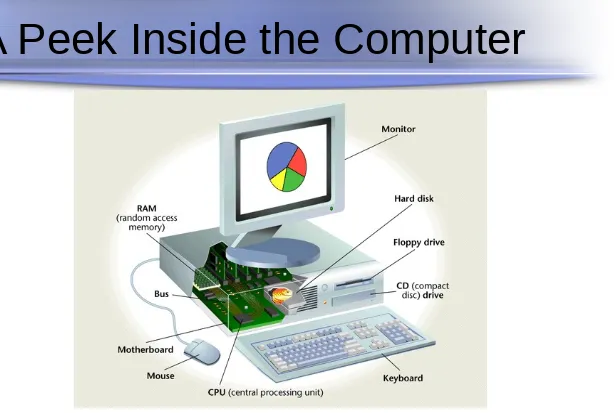
[image:8.720.65.679.42.455.2]A Peek Inside the Computer
9
A Peek Inside the Computer
The Central Processing Unit (CPU)
The brain of the computer
Microprocessor
Carries signals that execute all processing
Two Components:
Control unit
10
A Peek Inside the Computer
Microprocessor
Silicon chip embedded with transistors,
or semiconductors
11
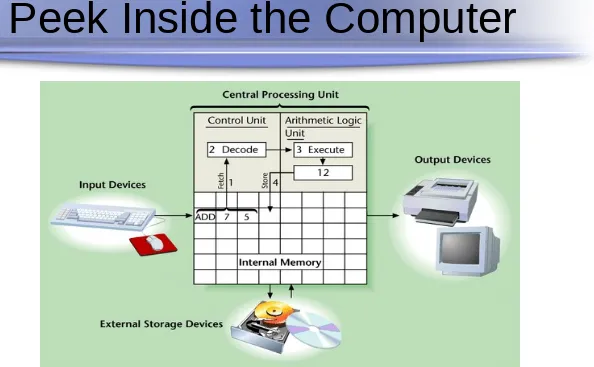
[image:11.720.74.668.63.430.2]A Peek Inside the Computer
12
A Peek Inside the Computer
Machine Cycle
CPU’s execution of four functions:
Fetch Decode Execute Store
Functions measured in small fractions of a
13
A Peek Inside the Computer
Memory
CPU Registers
Internal Memory
Random access memory (RAM) Read-only memory (ROM)
External Memory
14
A Peek Inside the Computer
Computer Power
Clock rate (measured in cycles
per second)
Amount of information the CPU
can process per second
15
Input Devices
Keyboard
Mouse, Trackball, and Track Pad
Touch Screen
Source Data Input Devices
Imaging
16
[image:16.720.37.662.42.436.2]Input Devices
17
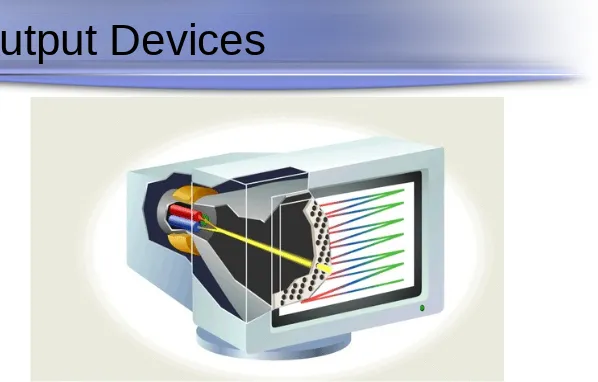
Output Devices
Soft-Copy Output Devices
Cathode-Ray Tube (CRT) Monitor
Flat-Panel Monitor
Speech Output
Hardcopy Output Devices
Nonimpact Printers (most common)
18
[image:18.720.78.676.41.423.2]Output Devices
19
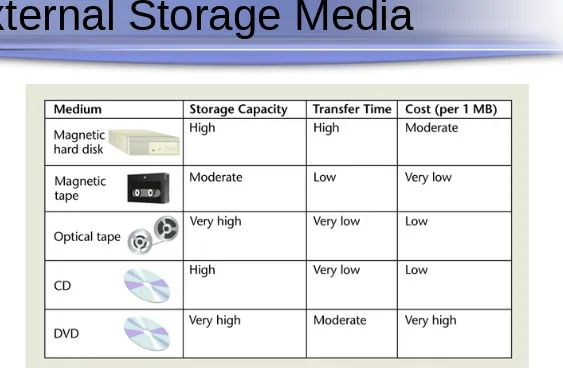
External Storage Media
Important Properties to Consider
Capacity
Speed
20
External Storage Media
Magnetic Tapes
Magnetic Disks
Optical Discs (Compact Discs)
21
External Storage Media
Business Considerations of
Storage Media
Trade-offs
Modes of Access
Sequential Access
22
[image:22.720.89.652.66.434.2]External Storage Media
23
Classification of Computers
Supercomputers
The largest, most powerful, and most expensive
Used by universities, research institutions, and large corporations
Mainframe Computers
Less powerful and less expensive than supercomputers
24
Classification of Computers
Minicomputers
Often used as the host computer in a network
of smaller computers
Priced in the tens of thousands to a few
hundred thousand dollars
Manufacturers: DEC (VAX), IBM (AS/400),
25
Classification of Computers
Compatibility
Software and peripheral devices from
one computer can be used with another computer.
In a networked environment,
computers need to communicate to share databases and other computing resources.
In addition to power and cost,
26
Considerations in
Purchasing Hardware
What should you consider when buying
hardware?
Power -- speed, size of memory, storage
capacity
Expansion and upgrade capability
Ports for external devices like printers,
hard disks, communication devices
Ergonomics: Keyboard, Monitor
Vendor reliability, warranty policy, vendor
27
Considerations in the Purchase of Hardware
Factor What to Look For
•Power Greater frequency and word size, larger
•Expandability Greater number of board slots for additional RAM
•Ports Greater number of ports for printer, external hard
disk, communication devices and other peripherals
•Ergonomics Greater comfort and safety
•Compatibility Comparability with many other computers and
peripheral devices, as swell as software packages
•Footprint Smaller area
•Support Availability of telephone and on-line support for
troubleshooting
•Warranty Longer warranty period
28
Ethical and Societal Issues
Computers May Be Hazardous to Your Health
Physical and Emotional Stress
General physical and emotional stress
Muscular-skeletal problems
Repetitive Stress Injuries (RSI)