commit to user
v
USING PICTURE SERIES TO IMPROVE STUDENTS’ WRITING ABILITY (A Classroom Action Research at the Third Grade Students of MTS NW I Kembang
Kerang in the Academic Year of 2010/2011)
THESIS
Submitted to Graduate School Sebelas Maret University
as a partial fulfillment for Getting Graduated Degree in English Education
BY
MUHAMMAD ZAINI
S890809114
ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
GRADUATE SCHOOL
SEBELAS MARET UNIVERSITY
commit to user
v
ABSTRACT
Muhammad Zaini, S890809114. 2011. Using Picture Series to improve the Students’ Writing Ability: A Classroom Action Research at the Third Grade students of MTs NW I Kembang Kerang in the Academic Year of 2010/2011. The first consultant: Prof. Dr. M. Sri Samiati T, the second consultant: Drs. H. Tarjana, MA.
Thesis, Graduate School of English Department of Sebelas Maret University Surakarta.
The research is aimed at: (1) finding whether or not picture series can improve the students’ ability in writing procedure texts; and (2) finding the strengths and the weaknesses of picture series used as media to improve the students’ ability in writing procedure texts.
This research was a classroom action research. The research was conducted from January 2011 to May 2011 at MTs NW 1 Kembang Kerang, East Lombok, West Nusa Tenggara. The subjects of the research are thirty two students of Class IX A. Based on the problem statement, the research was conducted in two cycles that consisted of planning the action, implementing the action, observing and monitoring the action, evaluating and reflecting. Picture series (PS) are a set of parallel picture showing similar scene or story that offers guidance on vocabulary, structure, and organization. Its function is to tell steps or a sequence of events based on what the students see in the picture.
There are at least five main activities involved in implementing picture series, they are: Sticking picture series on whiteboard and asking the students to describe the picture, asking the students to write based on the picture, discussing the result of all groups, making some correction to the students’ mistakes, and discussing the students’ difficulties. The data were collected quantitatively and qualitatively. To collect the quantitative data the researcher used students’ pre-test and post-test. To collect the qualitative data the researcher conducted the direct observation at the classroom, interviews, and questionnaire. Descriptive statistics and t-test of non independent variables are used to analyze quantitative data. Constant Comparative Method designed by Strauss and Glasser is used to analyze qualitative data.
commit to user
commit to user
commit to user
v
PRONOUNCEMENT
This is to certify that I myself write this thesis entitled “USING PICTURE
SERIES TO IMPROVE STUDENTS’ WRITING ABILITY” (A Classroom Action
Research at the Third Graders of MTS NW I Kembang Kerang in the Academic Year
of 2010/2011). It is not plagiarism or made by others. Anything related to other’s
work is written in quotation, the source of which is listed on the bibliography.
If then this pronouncement proves incorrect, I am ready to accept any
academic punishment, including the withdrawal or cancellation of my academic
degree.
Surakarta, June 2011
Muhammad Zaini
commit to user
v
MOTTO
Never put off till tomorrow
commit to user
v
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Praise be to Allah SWT the Almighty for the blessing, health, and inspiration
in leading his thesis to completion. The writer realizes that the accomplishment of
this thesis can not be reached without any help from others. The writer wishes to give
his sincerest gratitude to:
1. The Director of the Graduate School and Dr. Ngadiso, M.Pd the Head of
English Education Program Sebelas Maret University who have given him
opportunity and permission to conduct the research.
2. Prof. Dr. M. Sri Samiati T. and Drs. H. Tarjana, MA who have patiently and
willingly deposited their guidance and valuable advice. Without their
guidance and help, the writer can not complete this thesis.
3. His lecturers in Graduate School of English Education Department who have
given science and knowledge in various subjects during his study in the
university.
4. His parents, who always pray for him and give support to study.
5. His beloved wife, Suaebatul Aslamiah, S.Pd and his children, Rizqia and Alsa
who always give supports and encourage him.
6. The teachers, the staffs, and the students of MTs NW I Kembang Kerang who
have helped him to conduct the research. Special thanks are also addressed to
the collaborator, Shabrin, SS. for his helps given during collecting the data in
the research.
7. All of his classmates and friends for their support who can not be mentioned
commit to user
v
The writer realizes that this thesis is still far from being perfect, that is why he
always expects criticism and suggestion from the readers in order that it will get
improvement.
Surakarta, June 2011
commit to user
CHAPTER II REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE AND HYPOTHESIS
A. Review of Related Literature………..………..
4. The Curricular Objectives of Teaching Writing Skill at
SMP/MTs………
5. Assessing Writing………..
6. The Use of Picture Series in Teaching Writing………….
commit to user
c. The Weaknesses of Picture Series Used as Media……
CONCLUSION, IMPLICATION, AND SUGGESTION
commit to user
v
LIST OF TABLES
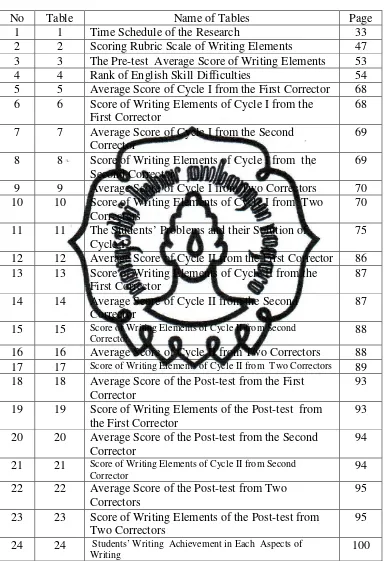
No Table Name of Tables Page
1 1 Time Schedule of the Research 33
2 2 Scoring Rubric Scale of Writing Elements 47 3 3 The Pre-test Average Score of Writing Elements 53
11 11 The Students’ Problems and their Solution of Cycle I
75
12 12 Average Score of Cycle II from the First Corrector 86 13 13 Score of Writing Elements of Cycle II from the
First Corrector
87
14 14 Average Score of Cycle II from the Second Corrector
87
15 15 Score of Writing Elements of Cycle II from Second
Corrector 88
16 16 Average Score of Cycle II from Two Correctors 88
17 17 Score of Writing Elements of Cycle II from Two Correctors 89
18 18 Average Score of the Post-test from the First Corrector
93
19 19 Score of Writing Elements of the Post-test from the First Corrector
93
20 20 Average Score of the Post-test from the Second Corrector
94
21 21 Score of Writing Elements of Cycle II from Second
Corrector
94
22 22 Average Score of the Post-test from Two Correctors
95
23 23 Score of Writing Elements of the Post-test from Two Correctors
95
24 24 Students’ Writing Achievement in Each Aspects of
commit to user
v
LIST OF FIGURES
No Figure Name of Figure Page
1 1 Steps of how to fry eggs 29
commit to user
Observation Aspects of Cycle I and Cycle II………
commit to user
CHAPTER I
1. INTRODUCTION
A. Background of Study
English as the first foreign language in Indonesia is taught starting
from the elementary school level up to university level. The general objective of
teaching English in Indonesia, based on the school based curriculum (KTSP), is
to develop students’ communicative competence of the four language skills or
aspects of teaching and learning; reading, speaking, listening, and writing.
Richard (1992: 189) states that the teaching of language skills (reading speaking,
listening, and writing) are related to each other, when a lesson involves activities
that relate listening and speaking, reading and writing, it means that listening
activity is related to spoken or oral language, and reading is related to written
language.
The purpose of learning English language in Junior High School is to
achieve the functional level. In this, the students can develop their competences in
oral or written to resolve daily problems. They are conscious of the importance
and essential of English in the global era. They can develop their comprehension
about language and culture (Depdiknas, 2006: 278).
The basic competence of writing which should be mastered by the students
in junior high school is expressing meaning by using vocabularies, grammar and
the steps of rhetorical development accurately in the forms of narrative, report,
descriptive, recount, and procedure. These should be supported by competences
namely linguistics competence, sociocultural competence, strategic competence,
commit to user
skills that have to be mastered by the students. They should be able to express
their ideas through their activities in the written form such as: They are able to
generate sentences into logical order, they are able to write supporting sentences
related to main idea, they are able to manipulate the words into understandable
and acceptable pattern of sentences, they are able to choose appropriate diction,
and they are able to arrange a procedure text which was punctuated,
well-spelled, and well-capitalized. Ideally their scores for writing should be at least 60.
The real condition found by the researcher in Class IX A students of MTs
NW I Kembang Kerang, Lombok Timur, based on the result of the students’
pre-test score 51.906, is that students of Class IX A had problem in writing, it was
indicated by: they were lack in vocabulary, the got difficulties in how to start to
write, they did not organize their writing well, the students were not able to make
grammatically correct sentences, and they are not able to arrange sentences which
was well-punctuated, well-spelled, and well-capitalized. In classroom, the
students did not enjoy the lesson, they were not active and neither creative, they
kept silent when they were asked to do the tasks in front of class, and they were
sleepy in class.
It was clear that one of the students’ difficulties is in understanding and
writing procedure texts. Therefore the writer interviewed some of the students
dealing with procedure. Some answered that they knew the procedure but some
did not. The following, is a student’s answer when the writer asked his reasons
why he got difficulties in writing a procedure text.
One of the students said (Appendix 16 d):
commit to user
sedikit dan cara merangkai kata-kata saya juga bingung grammar saya juga payah pak.
Meanwhile, another student Mhydn gave the following argument (Appendix 16
e): “Dalam menulis saya mengalami kesulitan menemukan ide, menemukan kosa
kata, cara mrangkainya, serta grammarnya”.
There are two main causes from both teachers and students. The causes
from the teacher’s side are as follows: the teachers still used traditional techniques
in which he only demanded the students’ writing product. He only gave fewer
portion of writing even though writing is a complex skill. The teachers made the
students write a text where they had to follow written language rules. He seldom
taught writing by using various techniques. The techniques used were
monotonous. He did not consider that writing was a complex skill and it needed
time to revise the contents, grammar, mechanics, and vocabulary. The causes from
the students’ side are as follows: students did not care about the lesson. If they had
homework, they did not do it at all, and they often came late to school. At home
they never studied their lesson to improve their ability. Even, they gave more
attention to look for grass for their cattle, took away passengers (ngojek), and
watched television a lot. Most of them did not want to study hard because they
considered that they would not continue their study.
Among the four language skills, writing is considered the most difficult,
and it needs an effective and interesting approach to solve it. There are many ways
to improve the students’ writing ability. Using pictures is one of the solutions to
overcome the problems. Gerngross (1992: 3) states that the uses of pictures make
communication in the foreign language class more lively, natural and stimulating.
commit to user
The use of pictures can generate the productive skills namely speaking and
writing skills.
Furthermore, Wright (2004:129) identifies some benefits of using pictures
in teaching, those are: pictures can motivate students to speak or to write. Pictures
in the picture series can create a context within which students with the
information use it in controlled practiced work. Pictures showing objects, actions,
events and relationship can cue answers to questions, substitutions, and sentence
completion. They can sponsor, stimulate, and possibly guide spoken and written
description, narration or dialogue, and they can offer information for free speaking
and writing, especially in recalling the vocabulary so that the students can express
their ideas or opinions in sentences or paragraphs easily.
Since picture series are considered to be able to help students to get
experience and stimulate students in recalling vocabularies to express their ideas
or opinions to write sentences and paragraphs even an essay, the writer proposes
to use picture series media in teaching writing, especially writing procedure texts.
B. Problem Statement
Referring to the background of the study, the problem statements are:
1. Can picture series improve the students’ ability in writing procedure texts?
2. What are the strengths and the weaknesses of picture series used as a media
to improve the students’ ability in writing procedure texts?
C. Objectives of the Study
commit to user
1. To know whether picture series can improve the students’ ability in writing
procedure texts.
2. To know the strengths and weaknesses of picture series when they are used
as media to improve the students’ ability in writing procedure texts.
D. Benefits of the Study
Hopefully, the results of the study can give some benefits:
1. To the researcher himself
The researcher can create and enhance the teaching media and use the
result of the study in the teaching-learning activities.
2. To the students
The students are interested to study hard in English subject especially in
teaching of writing and have some different interesting experiences in the
teaching- learning activities.
3. To the teachers
Teachers can select the most appropriate media to improve their students’
skill, especially writing ability.
4. To other researchers
The other researchers can develop the research based on the results and use
them as one of the references to study about writing skill.
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE AND HYPOTHESIS
A. Review of Related Literature
1. The Nature of Writing
commit to user
Writing is a process that occurs over period of time, particularly if
we take into account the some times extended periods of thinking that precede
creating an initial draft. Even “in the more immediately focused stage of
constructing a text (actually writing the words down) writer pause, think, write,
pause, think, revise and so on” (Harris, 1993: 10)
While Byrne (1997: 1) states that:
Writing can be said to be the act of forming these symbols: making marks on a flat surface of some kind. But writing is clearly much more than the production of graphic symbols, just a speech is more than the production of sounds. The symbol have to be arranged, according to certain conventions, to form word, and words have to be arranged to form sentences, although again we can be said to be “writing” if are merely making list of words, as in inventories of items such as shopping list.
Writing activity starts from producing a sequence of sentences arranged in
a particular order and linked together in certain ways. Writing can be stated as the
forming/constructing a text that minimally includes some areas of knowledge are
including grammatical and mechanical sentences, organizational structures, letter
formations, contents, and vocabulary inventories of items for expressing the
writer’s ideas .
Heaton (1975: 127) also states “that in writing the writers manipulate
words in grammatically correct sentences and link those sentences to form a piece
of writing which successfully communicates the writers’ thoughts and ideas on a
certain topic”. In short, the writers try to express their ideas in written using
grammatically correct sentences for communication purposes.
Canale and Swain in Mukminatien (1991: 134) state that “writing
minimally includes four areas of knowledge: grammatical competence, discourse,
commit to user
mentioned that writing product if it has at least four requirements. Those are:
grammatical competence, discourse, sociolinguistic competence, and strategic
competence.
Bell and Burnaby in Nunan (1998: 36) state that:
Writing is a complex cognitive activity in which the writer is demanded to demonstrate control of variables simultaneously at the sentence level-include control of content, spelling, and letter formation and the beyond of the sentence –Structure and integrated information into cohesive and coherent paragraph and text.
On the other hand a writer communicates his/her ideas by considering a
known or unknown reader who will get their meaning in the form of correct
written text. Therefore, a writer needs to know how to express the message in
written words so that can be clearly understood in communication.
Writing is an activity that supports students to analyze and synthesize their discrete knowledge about language items into a text that is acceptable in an English writing convention by using the appropriate sentence structure. Hence to be able to write students must write. (Brown, K & Hood, S. (1989).
Writing is transforming thoughts into language. It means that we need to
think about the content of our writing first and then arrange the ideas using
appropriatelanguage (e.g. grammar and vocabulary). Consequently teachers must
learn about organizational skills in writing.
Writing is not just about accuracy. It is also about having a message and
communicating it successfully to other people. To do this, teachers need to have
enough ideas, organize them well and express them in an appropriate style.
Brown (2004: 220) states that micro skills are related to imitative and
intensive types of writing task whereas macro skills are related to responsive and
extensive writing. The descriptions are as follows:
commit to user
a) Produce graphemes and orthographic patterns of English. b) Produce writing at an efficient rate of speed to suit the purpose. c) Produce an acceptable core or words and use appropriate word
order.
d) Use acceptable grammatical system (e.g. tense, agreement, pluralization), patterns, and rules.
e) Express a particular meaning in different grammatical form. f) Use cohesive devices in written discourse.
2) Macro skills:
a) Use the rhetorical forms and convention of written discourse.
b) Appropriately accomplish the communicative function of written texts according to form and purpose.
c) Convey links and connections between events, and communicate such relations as main idea, supporting idea, new information, given information, generalization, and exemplification.
d) Distinguish between literal and implied meaning when writing. e) Correctly convey culturally specific references in the context of the
written text.
f) Develop and use a battery of writing strategies, such as accurately assessing the audience’s interpretation, using pre-writing device, writing with fluency in the first draft, using paraphrase and synonyms, soliciting peer and instructor feedback, and using feedback for revising and editing.
At the micro skills, students practice specific written forms at the level of
words or sentences (grammar, vocabulary, and mechanics). On the other hand, at
the macro skills, students emphasize on content and organization. In the latter,
they express themselves using their own words, state a purpose for writing, and
specify an audience. While Hillocks in O’Malley (1996: 136) states there are at
least four types of knowledge in writing, there are:
1) Knowledge of content. In expressing it, the students conduct a memory search and call on prior knowledge and experience.
2) Procedural knowledge to organize the content, to group ideas, and to sequence the ideas in ways that match the purposes of the writing. 3) Knowledge of conventions of writing. The students must know the
discourse structures, syntactic form, and conventions of writing.
commit to user
that combine three types of knowledge just indicated in composing written piece that responds to the original purposes.
Based on the elaboration above, besides focusing on micro and macro
skills, the writer should require the range of knowledge to produce a good written
text.
b. Types of Writing
Writing can be classified into several types. Many attempts have been
made to classify writing. Harris (1993: 16) States that “the most long-established
is the four folds division of classical rhetoric exposition, argument, description
and narration”, it means that the pieces of writing are classified in relation to the
writer’s intention to form a writing and readership.
Texts can be grouped based on the purpose of arranging them. They are
intended to entertain, inform, instruct, persuade, explain, argue, and so on. They
are broadly synonymous with “texts type” forms of writing such things as posters,
brochures, pamphlets, letters, recipes, set of instructions, list labels, stories,
reports, poems, essays, play scripts, and so on. Writers set a task they need to
know some types of texts related to the teaching learning at junior high school
(SMP/MTs), those are: descriptive, report, narrative, recount, and procedure. They
will be further discussed with a focus on procedure texts.
1) Descriptive
Descriptive writing is the writing which is designed to describe persons,
places or things, moments, and theories clearly, powerfully and detailed images
in the mind to help the reader create the mental picture of what is being written
commit to user
accessed: August, 28, 2010). Descriptive writing is a kind of writing which
describes anything in written by creating the mental picture to readers. Its
structures are: identification and description, while the language features are as
follows:
a) Focuses on specific participant.
b) Uses simple present tense.
c) Uses detailed noun phrases to inform subject.
d) Uses adjectives for describing, numbering, classifying, etc.
e) Uses relating, thinking (feeling), and action verbs.
f) Uses figurative language.
2) Report
Anderson and Anderson (1999: 86) state that “an information report is a
piece of text that presents information about a subject. An information report
usually contains facts about the subject, a description and information on its
behavior and qualities parts”. Report text is a text to describe the way things are,
with reference to range of natural, man-made and social phenomena in our
environment. It tells what the phenomenon under discussion is. The generic
structures of it are: general classification, and description. While its language
features are:
a) Focuses on generic participant.
b) Uses simple present tense.
c) Uses specific language.
commit to user
3) Recount
Anderson and Anderson (1999: 16) state that “recount is a piece of text
that retells past events, usually in order in which they happened”. The purpose of
a recount is to give the audience a description of what occurred and when it
occurred. Recount tells the readers in the past, it begin by telling the readers
involved, what happened, where the event took place, and when it happened. The
generic structures of it are: orientation, series of events, and reorientation. While
its language features are:
a) Focuses on the participant
b) Uses past tense
c) Uses conjunctions and time connectives.
d) Uses adverbs and adverb phrases.
4) Narrative
Anderson and Anderson (1999: 9) state that “A narrative text type is a
piece of text which tells a story and, in doing so, entertains or informs the reader
or listener, it is related to recount text type”. The word derives from the Latin verb
narrare, "to recount", and is related to the adjective gnarus, "knowing" or
"skilled".[1] Ultimately its origin is found in the Proto-Indo-European root gnō-,
"to know".[2]
(File:
//localhost/C:/Users/MTS%20NW%20O1/Documents/Narrative%20-%20Wikipedia,%20the%20free%20encyclopedia.mht accessed: September, 24th
commit to user
A narrative is a made up story that is created in a constructive format (as a
work of speech, literature, pictures, song, motion pictures, television, video
games, theatre, musical theatre, or dance) that describes a sequence of fictional or
non-fictional events. The generic structures of it are: orientation, complication,
and solution. While the language features are as follows:
a) Focuses on specific participant
b) Uses past tense
c) Uses time connectives and conjunctions
d) Uses saying verbs
5) Procedure
Anderson and Anderson (1999: 50) state that “A procedure is a text that
shows a process in order. Its social function is to describe how something is
completely done through a sequence of series”. Procedure text is used to describe
how something is accomplished through a sequence of actions or steps. Its generic
structure is as follows: an introductory statement that gives the aim or goal, a list
of materials that will be needed for completing the procedure, a sequence of steps
in order it needs to be done, and the use of action verbs. A procedural text is used
to tell someone how to do or make something. “The type of text comes in many
forms, such as instruction manuals and recipes”(Mukarto, et al. 2007: 36). They
add that the text consists of three parts;
Title/goal : It states the goal to be achieved
List of Materials : It lists the materials needed. It often gives details on the
commit to user
Lists of equipments : It lists the equipments needed. It also often gives detail
on the size, color, numbers, shapes, quantity, etc.
Steps/Method/ Procedure: It describes steps in logical order to achieve the goal.
The steps are often marked with number (1,2,3…), letter
(a,b,c…), or bullet marks. Sometimes the steps include
caution(s) or warning(s). There are also drawings or
pictures to make the steps clear.
Procedure text is designed to describe how something is accomplished through a
sequence of actions or steps. It is also more about process than things but explain
how people perform different process in a sequence of steps. The generic
structures of procedure text are: goals, materials, and steps. The language features
of this text are as follows: focus on generalized human agents, use of simple
present tense, use of mainly temporal conjunctive relations, and use of mainly
material (action) clauses.
Based on the theories above, the writer inferred that writing is a complex
cognitive activity in which the writer is demanded to express their ideas,
experiences, knowledge, and feelings which covers content, organization,
grammar, vocabulary, and mechanics to form a piece of writing which
successfully communicates the writers’ thoughts and ideas on a certain topic.
Writing involves several sub-skills. Writing accurately involves spelling correctly,
forming letters correctly, writing legibly, punctuating correctly, using correct
layouts, choosing the right vocabulary, using grammar correctly, joining
sentences correctly in procedure texts which are used to tell someone how to do or
commit to user 2. The Teaching of Writing
The purpose of writing in principle is the expression of ideas, the conveying
of a message to the reader: so the ideas them selves should arguably be seen as the
most important aspect of writing on the other hand, “the writer needs also to pay
some attention to formal aspects: neat hand writing. Correct spelling and
punctuation as well as acceptable grammar careful selection of vocabulary”. Ur
(1996: 163).
The teaching of writing skill has been given to the students from the early
stages in Indonesia. It is officially started in the first year of junior high school,
presently it has been introduced to students at the elementary school. Yet the
students still have a lot of difficulties in expressing ideas through a written
language. That is why, during the teaching learning process, a teacher should give
more help, practices and chances to the students to explore and express their ideas.
Formally, teaching writing courses are focused on grammar or on elaborate
discussion of the theory of writing only. This condition makes the students get
sleepy and bored during the course.
commit to user
task which is often imposed on the teacher, perhaps by circumstances. This not only has psychological effect: it may also change a problem in term of content what to say.
To overcome those problems mentioned above, the English teachers need to
be aware that writing should be taught in various ways and manners so that the
students are interested in studying it. The teacher should also phase the writing
task from the simplest stage to the more complex one, so that students are not
frustrated with writing.
The 2004 Competency Based English Curriculum of Junior High School
(SMP), the program of teaching and learning English as a language aims to
develop students’ skill in listening, reading, speaking and writing. The students
are expected to achieve competencies in understanding oral written texts and to be
able to express their thoughts and ideas whether in oral written form, especially in
the forms of narrative, report, recount, descriptive, and procedure. Writing is one
of the four important skills that should be mastered by SMP students to express
their ideas, feelings, and thoughts in written.
Rivers in Mukminatien (1999: 130) states that:
Writing in language classrooms can be classified into types: (1) Writing down or notation that means imitating copying in writing activities, students are asked to copy words, phrases, sentences or paragraphs. (2) Writing in the language or writing practice, the writing activity can be in the form of writing simple dialogues, uncomplicated translation, dictation, and clone procedure. (3) Translation that refers to transferring passages or sentences from the target language and (4) Expressive writing is the expression of original ideas in the new (target) language.
It refers to the conveying of information or the expression of original ideas in a
consecutive way in the new language. Expressive writing or composition may be
commit to user
for practical purposes are writing instruction, reports, resume, concrete
description, or essential correspondence connected with everyday affairs the
ultimate goal in creative expression is to encourage some one to be more active in
developing his diction mastery and improving his grammar ability.
Huges (1996: 91) mentions five aspects of writing, they are: (1) grammar,
that is an element of writing which deals with a set of rules to have a writer
construct sentences that makes sense and acceptable in English. (2) Vocabulary, it
deals with a list of words and their meaning. (3) Mechanics that is the convention
in writing, which is related to punctuation, spelling, and capitalization. (4)
Fluency, which refers to the ease and the style of the composition. And (5) form
(organization) is the logical sequence and cohesion, or the flow of ideas being put
into written language, to make unified contribution o the whole paragraph. The
explanation of those aspects as follows:
a) Grammar
According to Fairbain and Winch (1996: 108) state that grammar is an
element of writing which deals with a set of rules to help a writer to construct
sentences that make sense and applicable in English. When a paragraph or
composition is written, grammar must be applied correctly in order to make the
writing sensible and understandable. While, Heaton (1991: 135) stating that
grammatical skill is the ability to write correct and appropriate sentences. Thus, it
can be said that if someone wants to produce an effective paragraph or
commit to user
wants to make a good writing, he or she should follow a very basic rules and
convention of grammar to construct sentences.
b) Mechanical
Heaton (1991: 135) states that mechanical skill is the ability to use those
conventions peculiar to the written language correctly. Also, Heaton (1991:
135) uses the term mechanical skill for punctuation and spelling. In line with
Fairbain and Winch (1996: 81) say that punctuation is a variety of devices that
a writer uses in order to help readers understand the meaning of peace of
writing. Furthermore, Kanar (1998: 461-461) states the marks and rules of
punctuations as follows:
1) End Punctuation Mark (. ? !)
As a good writer, one must be able to choose the most appropriate
punctuation mark to end the sentence. The period, question mark, and exclamation
point are marks of punctuation that are used most of the time. Kanar (1998: 461)
states three ways to end a sentence. They are as follows:
(a) Place a period at the end of a sentence that either makes a statement or
issues a command.
(b) Place a question mark at the end of a sentence that ask a direct question,
but place a period at the end of a statement that indirectly ask a question.
(c) Place an exclamation point at the end of a statement to indicate surprise or
intense feeling.
commit to user
Place a colon at the end of a statement if what follows is list, quotation,
explanation, or word needing special emphasis.
3) The Dash (-)
Place a dash before and after words that interrupt the flow of thought or
before words that create a dramatic effect.
4) The Hyphen
If two or more words that describe a noun function as a unit,
connect them with a hyphen.
5) The Semicolon (;)
(a) Place the semicolon between two sentences that are closely related.
(b) Place a semicolon before a conjunctive adverb that joins two
independent clauses.
(c) Use a semicolon to separate items a series if the items already contain
commas.
6) The Comma (,)
The comma, or the pause, gives reader or listeners a chance to
think about what is being said and relation of one idea to another
(a) Commas separate items in a series.
(b) Commas separate two adjectives that modified the same word if the
adjective are coordinate and belong to the same class
(c) A comma follows introductory words, phrases, and clauses.
(d) Commas come before and after interrupting words, phrases, and
commit to user
(e) A comma comes before a coordinating conjunction joining two
independent clauses.
(f) Commas set off certain ordinary material.
7) The Apostrophe (‘)
The apostrophe (‘) have two functions: to show possession and to
indicate omitted letters of number.
c) Vocabulary
Vocabulary deals with a list of words with meaning (Hornby, 1995: 1331).
The writing will be understandable if the students have a goof store of words
and are able to use words appropriately. Readers cannot understand about the
content of writing because the ideas informed would be seen through the
words used.
d) Developing Ideas
Amaudet and Barret (1990: 1- 47) state that “main ideas as topic sentences
and supporting sentences as supporting topic sentences”. In this, the topic
sentence is supported by sub topic sentence. Davis (1983: 126) defines “topic
sentence as a sentence that contains the central idea to be discussed in a single
paragraph”. Such a sentence not only announces to the reader the topic of the
sentence but also makes a definitive statement about that topic.
e) Form (Organization)
Kanar (1998: 16) states that “organization in writing means presenting the
commit to user
1) Unity
Bram (1995: 20) states that “a paragraph is said to be in good unity if it is
unified by mutually supported sentences that express one main idea of the
topic sentence only”. It means that Each of the supporting sentences should
serve to back up, clarity, explain, or prove the point in the topic sentence. In
other words, each sentence in a paragraph should relate and develop that
idea in controlling idea.
2). Coherence
Davis (1999: 126-127) states that “coherence is achieved by using words
or phrases that link the sentences together to make them coherent or stick
together, so that there is no break in the pattern of thought”. In arranging
words to be sentences or phrases, the sentences or phrases must relate to
each other, so the readers can catch an idea of the written.
3. Approaches to Teaching Writing
Attempts to teach writing, there are several approaches to hold it. Byrne
(1988: 21) states that:
Since the time when students were merely given a topic of some kind and asked to produce a ‘composition’ without further help have usually focused on some particular problematical aspect of the writing situation. Some key approaches are: focus on accuracy, focus on fluency, focus on text, and focus on purpose.
a. Focus on accuracy
Mistakes show up in written work (especially since this is usually subject
to rigorous correction) and naturally come to be regarded as a major problem. It
was assumed that students made mistakes because they were allowed to write
commit to user
the importance of control in order to eliminate them from written work. Students
are taught how to write and combine various sentence types and manipulation
exercises. Gradually the amount of control is reduced and the students are asked
to exercise meaningful choice. At a still later stage, they may be given a good deal
of guidance with language and content, but allowed some opportunities for
self-expression.
This controlled-to-free approach was very much a product of the
audio-lingual period, with its emphasis on step-by-step learning and formal correctness.
Many such schemes were carefully thought out and, although no longer
fashionable, they produced many useful ideas on how to guide writing.
b. Focus on fluency
In contrast, this approach encourages students to write as much as possible
and as quickly as possible without worrying about making mistakes. The
important thing is to get one’s ideas down on paper. In this way students feel that
they are actually writing, not merely doing ‘exercises’ of some kind; they write
what they want to write and consequently writing is an enjoyable experience.
Although this approach does not solve some of the problems which students have
when they come to write in a foreign language, it draws attention to certain points
we need to keep in mind. Many students write badly because they do not write
enough and for the same reason they feel inhibited when they pick up a pen. Most
of us write less well if we are obliged to write about something. A
fluency-approach, perhaps channeled into something like keeping a diary, can be a useful
commit to user
c. Focus on text
This approach stresses the importance of the paragraph as the basic unit of
written expression and is therefore mainly concerned to teach students how
construct and organize paragraphs. It uses a variety of techniques, singly and in
combination, such as:
- Forming paragraphs from jumbled sentences.
- Writing parallel paragraphs.
- Developing paragraphs from topic sentences (with or without cues).
Once again this approach identifies and tries to overcome one of the central
problems in writing: getting students to express themselves effectively at a level
beyond the sentence.
d. Focus on purpose
In real life, as we have seen, we normally have a reason for writing and we
write to or for somebody. These are factors which have often been neglected in
teaching and practicing writing. Yet it is easy to devise situations which allow
students to write purposefully for example, they can write to one another in the
classroom or use writing in role-play situations.
Although, like fluency writing, this approach does not solve specific
problems which students have when handling the written language, it does
motivate them to write and shows how writing is a form of communication.
commit to user
The purpose of teaching English for junior high school student is to
develop communicative competence in spoken and written form to achieve the
literacy level which can be realized through for language skills listening,
speaking, reading and writing for the junior high school graduates they are
expected to reach at the functional level, in this case, they are expected to e able to
communicate or participate in the creation of text in spoken and written in their
daily life in short, at junior high level, learners are expected to learn daily
expressions, especially fixed expressions and idioms that are needed in daily lives
to accompany their action when playing at school yards, when attending classes,
when interacting with their friends etc.
“The SMP students are expected to be able to create many kinds of
functional text and monolog in the form procedure, descriptive, recount, narrative,
and report” (Depdikbud, 2006: 278). The text created should consists of
grammatical sentences, acceptable expressions, and culturally acceptable in the
English culture. The standard competence is different for each class level in this
study, the writer focuses on the eighth grade student of SMP. In this case, the
standard competence for the eighth grade students of SMP is students are able
to express many kinds of meanings in the grammatical sentences and
acceptable expression in the written text especially in the form of narrative,
descriptive, and recount (Depdiknas, 2006: 287). It means that English texts
which created by the students must be acceptable texts, grammatically correct and
well arranged. They are also expected not to ignore grammatical patterns and the
way how the text is organized. As a result, the product of the student writing will
commit to user
5. Assessing Writing
Assessing is an integral aspect of the teaching-learning process. It happens
everyday in the classroom as a teacher continually makes judgment about the
performance of their student (Burn and Joyce, 1999: 102). Assessment plays an
important role in determining each student’s learning time.
According to Brown (2004: 4), “Assessment is an on going process that
includes a much wider aspect-whereas test is a subset of assessment which
measures a person’s ability”. In addition, “Assessment is needed by
administrators, teacher staff developers, students, and parents to determine the
appropriate instructional activities as well as monitor the students’ progress”
(O’Malley, 1996: 3). It is also essential to ensure that students meet their needs. In
other words, when students think about and reflect on their learning, they become
more active participants in the teaching and learning process. “Assessment is an
integral part of the teaching learning exile” (Brown, 2001: 420).
In relation to the teaching writing, O’ Malley and Pierce (1996:135) state
that:
Writing assessment meets at least three purposes. First, writing assessment is used for identification a program. Placement is ESL a bilingual program. Moreover, students are typically reclassified as English when they are prepared for grade level instruction. Second, writing assessment can be used to monitor student progress and determine if changes in instruction are required to meet student needs. The on going assessment of student writing enables review of student growth over time and a determination of the success of instructional approaches. The third purpose of writing assessment is accountability. Writing assessment is often conducted as part of district or statewide accountability assessment programs for all students, in some advances for high school graduation.
As stated in the previous discussion, a writer requires four types of
commit to user
These four types of knowledge used in writing have at least two implications for writing assessment. First, writing assessment should evaluate more aspects of writing then just mechanics and grammar. Second, writing assessment should capture some of the processes and complexity involved in writing so that teacher can know in which aspects of the writing process of student are having difficulty (O’Malley, 1996: 137).
In other words, writing assessment should not only look at linguistic
aspects but also look at the context in which the writing process occurs. “Writing
assessment is not an easy task, when assessing students’ writing ability, the
objective and criterions must be clear” (Brown, 2004: 218). It means that the
teacher gives a writing task after considering the objectives and the criteria to
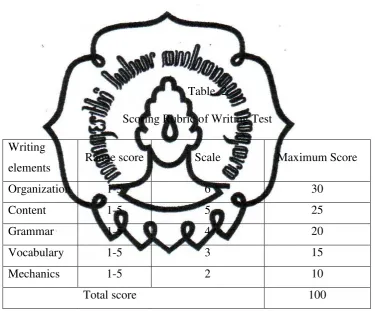
achieve the writing purposes. In scoring the students’ work, there are five
elements to score. There are organization, content, grammar, vocabulary, and
mechanics.
6. The Use of Picture Series in Teaching Writing
Raimes (1983: 36) states that picture series (PS) are a set of parallel
picture showing similar scene or story that offer guidance on vocabulary,
structure, and organization. Its function is to tell steps or a sequence of events
based on what the students see in the picture.
Picture sequence is a series of photographs dealing with one subject. It
may tell a story, present an event, describe a scene, reveal a person, or show how
to do something. A common use for a picture sequence is depicting a person
during an interview. The most successful picture sequences create several visual
images that contain emphasis and action.
commit to user
mht). A picture sequence is a group of closely related photographs that provide
the reader with only a few miscellaneous impressions of an event.
Main function of visual materials including picture in the language lesson,
is to help create situation which interest the students. Wright (1992: 16) states that
“pictures make a particularly powerful contribution to both the contents and the
process of language learning”. She also suggests that pictures can often be used to
promote productive skill like speaking and writing.
In order to use pictures effectively and efficiently, as well as achievement
at the instructional objective in language learning, teachers should be selective
and creative in determining the pictures they used in the activities they planned. A
teacher needs to consider that the size of the pictures should give adequate
visibility for which they are intended to use, whether for a large group, small
group, individual or for the whole class. Wright (1992: 17) adds that “picture can
be used to assist in stimulating the students’ inspiration”. The pictures have to be
interesting in order to hold the students attention and raise curiosity in their mind.
There are many types of pictures proposed by Wright (1992: 201) one of
them is picture series (picture sequence). Picture Series (PS) is a group of pictures
order or arranged following an event. In this case, the picture series are used to
describe how something is accomplished through a sequence of actions or steps in
writing procedure text. Raimes (1983: 28) states that pictures are valuable
resources as it provides: (1) a shared experience in the classroom (2) a need for
common language forms to use in the classroom (3) a variety of tasks (4) a focus
of interests for students. Gerngross and Puchta (1992: 21) state the preparation in
commit to user
One copy of a cut-up picture story/picture series for each group of students. The size of the groups depends on the number of picture in story/series; for example, if there are six pictures in story/series, you will need four copies for twenty-three students. In three groups each students get one picture, in the fourth group each student gets two.
Furthermore, Gerngross and Puchta (1992: 21) also propose steps in using
picture series in teaching procedure texts. The steps were as follows:
a. Write some key words of the steps on the board. Ask your students to
develop steps form the words. Have them the steps to the class.
b. Hand out the pictures. Make sure that the learners are aware of the fact that
they must not show their pictures to the others. Each student describes
his/her picture and then they decide in what order to arrange them. When
they have negotiated the order they put the pictures in a line, face down.
c. The groups usually do not finish at the same time. When the first group
has finished, the teacher goes from group to group and they quietly tell
the steps. This gives the group a chance to rehearse retelling. When all the
groups have finished, the first group tell the steps, and only then are the
pictures turned over. A discussion may follow if a group has developed a
commit to user
This is an example of picture series which might be used in the research;
Figure 1. Steps of how to fry eggs.
eggs/salt/veg.oil prepare/frying pan break/eggs
Mix/eggs pour/eggs add/salt
(Source: Taken from English on Sky 3, 2007: 18)
Furthermore, Raimes (1983: 36) states some advantages of using picture series
are:
1) The students gain an overall sense of the story and theme and can see
not only its progression but also its subtleties, drama or humor.
2) As students look through the sequence, each picture helps to clarify the
commit to user
3) The vocabulary needed to tell the whole story or describe the whole
theme can be discussed, so there will be less hesitation when the
students do the telling or describing.
4) Seeing how the story or theme ends, students can shape their oral work
more effectively, can build up to a strong climax or conclusion and can
judge how many words are needed (which is important in language
examinations in which picture composition plays a part).
5) Class time is saved by putting up pictures in advance.
B. Review on Related Research
There are some previous researches related to the use of pictures in the
teaching and learning process. Japarudin (2006) conducted a study on applying
picture series at SMP. The pictures he used were drawings which showed
sequential events, the events showed in the pictures were complete from the first
to the last event. This was for teaching writing recount paragraphs. The students
here worked in groups of four before they wrote individually. He scored the
students’ writing recount by using scoring scale, which consisted of three aspects;
content, language use, and spelling. Based on the results of that research, he found
that the teaching using picture was able to improve the students’ ability in writing
recount.
Second, Lailawati (2009) conducted a study on applying incomplete
picture series technique at MTs/SMP. Based on the results of her research, she
commit to user
students’ speaking ability as well as increasing their involvement in the teaching
and learning activities.
C. Rationale
The basic competence of writing which should be mastered by the students
in junior high school is expressing meaning by using vocabularies, grammar and
the steps of rhetorical development accurately in the forms of narrative, report,
descriptive, recount, and procedure. These should be supported by competences
namely linguistics competence, socio cultural competence, strategic competence,
and text former competence. However, the problem is that the students of Class
IX A are not able to write in English well.
The problem is indicated by they lack of vocabulary, they got difficulties
in how to start to write, they got difficulties to choose appropriate dictions, they
did not organize their writing well, they sometime lost their ideas and got stuck,
and the students were not able to make grammatically correct sentences.
The difficulties come from techniques and media were used in the
teaching-learning process. The teachers still used traditional techniques in which
he only demanded the students’ writing product. He only gave fewer portion of
writing even though writing is a complex skill. The teachers made the students
write a text where they had to follow written language rules. He seldom taught
writing by using various techniques. The techniques used were monotonous.
In teaching learning process, it is very important for the teacher to use a
appropriate media to arouse the students’ interest and it make the students easier
commit to user
communication in the foreign language class more lively, naturally, and
stimulating. It also helps the students to offer ideas to train language skill.
Besides, the vocabulary needed to write the steps or to describe the theme can be
discussed, so there will be less hesitation when the students tell, describe, and
write procedure texts.
Using picture series in teaching procedure texts can help the students to
understand the texts easily. To understand a procedure text, the students must
know about the generic structure of procedure texts that consist of: goal, material,
and steps.
Using picture series, the students can create a context within which
students with the information use it in controlled practiced work. It shows objects,
actions, events and relationship can cue answers to questions, substitutions, and
sentence completion. It also can improve the students ability in writing procedure
texts, where the procedure texts is sequence of steps and picture series is a
sequence of events or steps too.
D. Action Hypothesis
Based on the problem and the rationale of the study, the hypothesis is
formulated as follows: Picture series can improve students’ ability in writing
commit to user
school by any means of transportation because it is near the regency street. MTs
NW 1 Kembang Kerang is one of the private Islamic high schools which got A in
accreditation from Ministry Office of National Education, Institution of National
Accreditation (BAN) of West Nusa Tenggara Province.
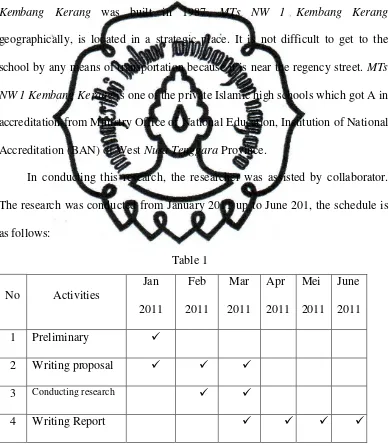
In conducting this research, the researcher was assisted by collaborator.
The research was conducted from January 2011 up to June 201, the schedule is
commit to user
Because of the limited time and finance, the research was conducted to the
students of Class IX A MTs NW 1 Kembang Kerang. Class IX A consists of 32
students and all of them are boys. Most students (90%) are from Kembang
Kerang village and 10% are from out of the village. Those who come from out
of the village, usually stay in an Islamic boarding house which is near the
school. The students come from different social and economics background.
Most of them came from poor and low social status families.
According to the previous teacher, most students did the task when the
teacher asked them although the result of their task was still far from the
teachers’ expectation. It can be seen from the result of the pre-test given. Based
on the students’ test achievement, this class is categorized into low achievers
among the other classes. In this case the researcher chooses Class IX A due to
the fact that the problem faced by this class was writing problem. They got many
difficulties in writing such as generating ideas, arranging sentences, organizing
sentences, having lack of vocabulary, and making coherence. That is why the
researcher takes a classroom action research in order to solve the problems.
C. Research Method
This research belongs to classroom action research. Action research is
known by many other names, including participatory research, collaborative
inquiry, emancipatory research, action learning, and contextural action research,
but all are variations on a theme. Put simply, action research is “learning by
doing” - a group of people identify a problem, do something to resolve it, see
commit to user
is the essence of the approach, there are other key attributes of action research
that differentiate it from common problem-solving activities engaged in
everyday.
Classroom Action Research (CAR) is a from of Self-Reflective Enquiry under taken by participants is social situation in order to improve the rational and justice of (a) their own social or educational practices (b) their understanding of these practices, and (c) the situation in which the practices are carried out. (Kemmis in Hopkin, 1993:44).
In this case, Classroom Action Research includes some aspects to do in
order to get the findings accurately.
Also Mills (2003: 5) states that “Classroom Action Research (CAR) is any
systematic inquiry conducted by teachers, researchers, principles, school
counselors, or stake holders in teaching/learning environment to gather
information about how their particular school operate, how they teach, and how
well the student learn” It encourages teachers to be reflective on their practices
in order to improve their own teaching and learning activities for the sake of
themselves and their students.
Considering the notion of CAR, the use of CAR is, therefore, inevitable
due to its appropriateness with the fundamental features of this study which
starts from focusing on solving problems in the classroom setting. An important
feature of action research is that is offers opportunities for collaborative work.
Thus, this research is conducted collaboratively in which that the researcher
cooperates with a fellow English teacher who also teaches at the same school
with the writer.
Koshy (2007: 27) states “Action Research is a cyclical process, it covers
commit to user
line with Kemmis in Hopkin (1993: 48) states that” there are some steps that
must be involved which can be described as a spiral of steps. Each step has four
stages: plan-act-observe-reflect”. Action Research is efforts to overcome
education problems and to improve the education quality done by the teachers
and others related to their reflections upon the effect of those actions.
It can be concluded that an action research in this study means the
systematic study of attempts to improve the teaching and learning process in
order that the English learners’ achievement are satisfactory.
The research procedure summarized as figured in (figure. 2) the figure of
the Classroom Action Research procedure is adapted from Kemmis and Taggart
in Hopkin (1993: 48).
commit to user
Adapted from Kemmis and Taggart in Hopkin (1993: 48)
D. Research Procedure
Joko Nurkamto, (2009) states the procedures of the Classroom Action
Research (CAR) can be illustrated are as follows;
PR FF PS GP A1 O1 R1 RP …
Where PR : Preliminary Reflection
FF : Fact Finding
PS : Problem Statement
GP : General Planning
A1 : Action 1
O1 : Observation 1
R1 : Reflection
RP : Revised plan
… : A2,O2, P2
The description of each step of the procedure can be seen on the following
commit to user
1. Preliminary Reflection
This research was started by making an observation. This was done in
January 2011. During the observation, the researcher found that students faced
problems in writing. There were some indications which showed their poor ability
in writing for instance: the students did not organize their writing well, their ideas
were not coherence, they did not use tense in the right context, they had lack of
vocabulary, diction and their understanding of mechanics was low.
2. Fact Finding Analysis
Based on the preliminary research, the researcher found that the students’
writing ability was still far from what is expected. From the result of the students’
writing, the average score was 53,51. There were only 12,50% or 4 students who
got scores more than 60, and 87,50 % or 28 students were failed. They got scores
below the passing grade (the minimum adequacy criteria is 60). Most of them
could not pass the passing grade It means that the students’ writing ability in
English lesson for the ninth grade was low.
3. Problem Statement
Based on the identification and the analysis of the problem the researcher
formulates the problem to solve. The formulation of the problem is accompanied
by the causes. In this study, the researcher formulated that the problem was the
students’ difficulties in writing. There were two causes of the students’ problems
in writing. First, teachers still used traditional approach in which they only
commit to user
whereas writing is a complex activity. Second, students could not organize their
ideas well, use right grammar, chose appropriate vocabulary, and use punctuation
correctly.
4. General Planning
Based in the fact finding analysis above, the researcher applied media
picture series to solve the problems’ in teaching writing. There were some steps
that the researcher did; Building Knowledge of the Field (BKOF), Modeling of
the Text (MOT), Join Construction on the Text (JKOT), and Independent
Construction of the Text (ICOT). These steps can lead the students to write
through some stages in the writing process including pre-writing, writing,
revising, and editing. Each stage must be followed by the students in order that
they can create a good written text. By doing so, it is hoped that it could solve the
students’ problems. The stages facilitated the students with interesting teaching
strategy and media in order to facilitate them to write. Furthermore, in the phase
the researcher prepares the material and media, sets the criteria of success and
prepares the research instrument.
a. Preparing the lesson plan
Preparing the lesson plan is very important in order to make the teaching
learning process run well. It covers standard competency, basic competency,
indicators, learning objectives, instructional media and strategy, teaching and
learning materials, teaching and learning activities, source of learning and the