COLLOCATION ACQUISITION: AN INVESTIGATION OF
INDONESIAN EFL LEARNERS’ COLLOCATIONAL ERRORS IN
THEIR WRITING
A Research Paper
Submitted to Department of English Education of FPBS UPI in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
By:
Aidiana Fatimataz Zahro 1009083
DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH EDUCATION
FACULTY OF LANGUAGE AND LITERATURE EDUCATION INDONESIA UNIVERSITY OF EDUCATION
Collocation Acquisition: An
Investigation of Indonesian EFL
Learners’ Collocational Errors i
n
Their Writing
Oleh
Aidiana Fatimataz Zahro
Sebuah skripsi yang diajukan untuk memenuhi salah satu syarat memperoleh gelar Sarjana pada Fakultas Pendidikan Bahasa dan Sastra
© Aidiana Fatimataz Zahro 2015 Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia
Februari 2015
Hak Cipta dilindungi undang-undang.
AIDIANA FATIMATAZ ZAHRO (1009083)
COLLOCATION ACQUISITION: AN INVESTIGATION OF
INDONESIAN EFL LEARNERS’ COLLOCATIONAL ERRORS IN
THEIR WRITING
Approved by:
Supervisor
Prof. Fuad Abdul Hamied, M.A., Ph. D NIP. 195008211974121001
Head of Department of English Education Faculty of Language and Literature Education
Indonesia University of Education
Aidiana Fatimataz Zahro, 2015
Collocation Acquisition: An Investigation Of Indonesian Efl Learners’ Collocational Errors In Their Writing Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu
ABSTRACT
Collocations play essential roles in learners’ language competence. However, for the learners of English as a foreign language (EFL), collocations are considered challenging as they still have problems with collocations despite a large number of vocabularies they have in English (Phoocharoensil, 2011). The present study aimed at investigating Indonesian EFL learners’ collocational errors in their writing and the learning strategies they employ in their acquisition of English collocations. This study employed a descriptive qualitative method. An error analysis was used to investigate the nature of collocational errors the learners made in their writing and an interview was conducted to explore some possible sources of errors and the learning strategies the learners apply. The results of the students’ essay analysis revealed that they committed colocational errors in their writing, including grammatical and lexical collocations. It was also revealed that lexical collocations are more problematic for EFL learners than grammatical collocations. The results of the interview indicated that the learners’ errors were due to various reasons, such as lack of collocational knowledge and ignorance of the rule. In addition, the learning strategies the learners applied in their collocation learning were also found to play major roles in their error making. These include first language transfer, synonymy, literal translation, overgeneralization, and resourcing. It is then suggested that collocations should be given special attention in vocabulary teaching. Additionally, language teachers need to know what learning strategy works and does not work well to assist the students’ collocation learning more effectively.
ABSTRAK
Kolokasi berperan penting dalam kemampuan berbahasa pembelajar. Namun, bagi pembelajar bahasa Inggris sebagai bahasa asing (EFL), kolokasi dianggap sukar karena mereka masih mengalami masalah meskipun telah memiliki pembendaharaan kata yang banyak dalam bahasa Inggris (Phoocharoensil, 2011). Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk meneliti kesalahan kolokasi pembelajar EFL Indonesia dalam tulisan mereka, serta strategi belajar yang mereka gunakan dalam akuisisi kolokasi bahasa Inggris. Penelitian ini menggunakan metode deskriptif kualitatif. Error Analysis digunakan untuk mengetahui bentuk kesalahan kolokasi yang pembelajar buat dalam tulisan mereka, dan wawancara dilakukan untuk mengetahui penyebab kesalahan serta strategi belajar yang mereka terapkan. Hasil analisis esai siswa menunjukkan bahwa mereka melakukan kesalahan kolokasi dalam tulisan mereka, yang meliputi kolokasi gramatikal dan leksikal. Selain itu, ditemukan juga bahwa kolokasi leksikal lebih problematik bagi pembelajar EFL daripada kolokasi gramatikal. Hasil wawancara menunjukkan bahwa kesalahan tersebut disebabkan oleh berbagai alasan, seperti rendahnya pengetahuan kolokasi dan ketidaktahuan akan aturan. Selain itu, strategi belajar yang pembelajar terapkan dalam pembelajaran kolokasi mereka juga berperan besar sebagai penyebab kesalahan mereka. Strategi tersebut meliputi first language transfer, synonymy, literal translation, overgeneralization, dan resourcing. Oleh karena itu, kolokasi perlu mendapatkan perhatian khusus dalam pengajaran kosa kata. Selain itu, guru bahasa perlu mengetahui mana strategi belajar yang efektif dan yang tidak agar dapat membantu siswa belajar kolokasi dengan lebih efektif.
Aidiana Fatimataz Zahro, 2015
Collocation Acquisition: An Investigation Of Indonesian Efl Learners’ Collocational Errors In Their Writing Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu
TABLE OF CONTENTS
STATEMENT OF AUTHORIZATION ... ii
PREFACE ... iii
2.1.1. Definition of collocation ... 6
2.1.2. Classification of collocation ... 7
2.1.2.1. Grammatical collocation ... 8
2.1.2.2. Lexical collocation ... 9
2.1.3. The Importance of collocation ... 10
2.2. Language Learning Strategies ... 12
2.3. Error Analysis ... 15
2.3.1. Differences between errors and mistakes ... 16
2.3.2. Classification of error ... 17
2.3.4. Criticisms of error analysis ... 19
2.4. Previous Studies on Collocation ... 20
2.5. Concluding Remark ... 23
CHAPTER 3 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY ... 24
3.1. Research Design ... 24
3.2. Research Site ... 25
3.2.1. Setting ... 25
3.2.2. Participants ... 25
3.3. Data Collection... 26
3.3.1 Documentation of students’ essays... 26
3.3.2. Interview ... 26
3.4. Data Analysis ... 27
3.4.1. Identification of collocational errors from the students’ essays ... 27
3.4.2. Transcription of interview data ... 29
3.5. Concluding Remark ... 29
CHAPTER 4 FINDINGS AND DISCUSSIONS ... 30
4.1 Findings ... 30
4.1.1 Students’ essay analysis ... 30
4.2 Discussion ... 32
4.2.1. The results of the students’ essay analysis ... 32
4.2.1.1. Errors in the production of grammatical collocations ... 32
4.2.1.2. Errors in the production of lexical collocations ... 34
4.2.2. The results of the students’ interview ... 38
4.2.2.1. Students’ knowledge and opinion about collocations ... 38
4.2.2.2. Students’ problems and their causes in using English collocations ... 39
4.2.2.3. Students’ strategies in learning English collocations ... 42
4.2.2.3.1. First language transfer ... 43
4.2.2.3.2. Overgeneralization... 44
Aidiana Fatimataz Zahro, 2015
Collocation Acquisition: An Investigation Of Indonesian Efl Learners’ Collocational Errors In Their Writing Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu
4.2.2.3.4. Resourcing ... 46
4.2.2.3.5. Literal translation ... 47
4.2.2.3.6. Substitution ... 47
4.4 Concluding Remark ... 49
CHAPTER 5 CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS ... 50
5.1 Conclusions ... 50
5.2 Suggestions ... 51
REFERENCES ... 53
LIST OF TABLES
Table 2.1 Typical Combinations of Grammatical Collocation Based on the
Classification Proposed by Benson et al. (2010) and Their Examples ... 9
Table 2.2 Typical Combinations of Lexical Collocation Based on Classification Proposed by Benson et al. (2010) and Their Examples ... 10
Table 3.1 Framework for Classifying Types of Collocational Errors ... 28
Table 4.1 Distribution of Collocational Deviations in the Students’ Essays ... 31
Table C1 Examples of Collocational Deviations in the Students' Essays 1 ... 86
Aidiana Fatimataz Zahro, 2015
Collocation Acquisition: An Investigation Of Indonesian Efl Learners’ Collocational Errors In Their Writing Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu
LIST OF APPENDICES
A. Instruments ... 60
1. Writing Prompts ... 61
2. Interview Guideline ... 62
B. Some Examples of Students’ Writing ... 64
C. Examples of Collocational Errors from the Students’ Writing ... 85
D. Transcript of Interview ... 97
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
This chapter presents a brief introduction of the research, including background, research questions, aim of the research, scope of research, significance of the research, clarification of terms, and organization of the paper.
1.1. Background
One of the most important aspects in learning a language is learning the vocabulary of the language and its appropriate use, including collocations, how words occur together with other words (Woolard, 2005, p. 6). It has been widely known that collocation plays essential roles in language use as it helps the learners to communicate effectively, especially in writing. In addition, it is believed that collocational proficiency leads the learners to achieve native-like competence and fluency (Farrokh, 2012). However, collocation is considered quite challenging, particularly for non-native speakers. Collocation is not simply putting words together, because words cannot be combined freely or randomly into phrases and sentences (Pecina, 2005; Dzierżanowska, cited in Martyńska, 2004). Therefore, a great attention should be paid to this matter.
2
in which the learners rely heavily on their mother tongue in their acquisition of English collocations. Additionally, some researchers have also discovered that EFL learners depend on certain learning strategies which also contribute to the
learners’ errors, such as synonymy, and overgeneralization, (e.g. Phoocharoensil, 2011; Li, 2005; Darvishi, 2011) etc.
However, most of previous studies mentioned above focused on the nature of collocational errors and on learners with high proficiency as they only focused on college students (e.g. Phoocharoensil, 2011; Darvishi, 2011; Parastuti, et al., 2009; Li, 2005, Hama, 2010, Ridha & Al-Riyahi, 2011). Also, there have not
been many studies examining learners’ errors in their interlanguage with regard to collocation learning, particularly in Indonesian context. Focusing on Indonesian
EFL high school students’ collocational errors in their interlanguage, this study
attempts to investigate the nature of collocational errors made by the learners, with regard to the learning strategies they use to produce English collocations in their writing. It is expected that the results of this study will give a contribution to pedagogical implication in which the teachers can provide the students with appropriate ways in teaching English collocation. It is also expected that the early identification of collocational errors and the learning strategies the EFL learners
apply will give contribution to prevent the learners’ language from being fossilized.
1.2. Research Questions
As mentioned in the previous explanation, this study attempts to answer the following questions:
a. What are the collocational errors Indonesian EFL learners made in their writing?
b. What are the learning strategies on which Indonesian learners depend in their English collocation learning?
3
1.3. The Aims of the Research
Relevant to the research questions, this research is aimed to meet the following purposes:
a. To investigate the collocational errors found in Indonesian EFL learners’ writing.
b. To investigate the learning strategies, on which Indonesian EFL learners depend, in their English collocation learning.
1.4. Scope of the Research
This research concerns the analysis of collocational errors found in Indonesian
EFL learners’ writing as well as the learning strategies, on which they depend, in their English collocation learning. About 35 twelfth grade students at a senior high school in Bandung will be involved in order to collect the data for this research.
1.5. Significance of the Research
As this research aims at investigating collocational errors made by Indonesian EFL learners in their writing as well as the learning strategies on which they depend in their acquisition of English collocation, it is expected that the results of the study give significance in some areas, such as theory and practices.
Theoretically, this research will enrich English literature, particularly on collocational errors made by EFL learners and the learning studies they apply in their acquisition of English collocation. In addition, it is expected that the results of this research can be a reference for other researchers studying the topic.
4
the early identification of collocational errors and the learning strategies the EFL
learners apply will give contributions to prevent the learners’ language from being
fossilized.
1.6. Clarification of Terms
In order to avoid misunderstanding, several terms are clarified as follows:
a. Collocation is a combination of words that often occur together in natural text with greater than random frequency (McCarthy and O’Dell, 2005, p. 6; Mccarten, 2007, p. 5; Chapelle & Hunston, 2009, p. 317).
b. Error is inappropriate utterance which results from learners’ lack of L2 knowledge (Saville-Troike, 2006, p. 188). In this study, error is referred to any deviation of collocations the students produce in their writing.
c. Interlanguage is intermediate states or interim grammars of learners’ language as it moves toward the target L2 (Saville-Troike, 2006, p. 190).
In other words, it is the state in which the learners’ language system is
between the native and target language. In this study, the term
interlanguage is used to refer to the learners’ language.
d. Learning strategies refer to the behavior and techniques that individuals apply in their efforts to learn L2 (Saville-Troike, 2006). In this study, learning strategies are certain ways or techniques the students apply in their attempt to produce English collocations, such as synonymy, L1 transfer, and overgeneralization.
1.7. Organization of the Paper
This paper is organized into five chapters: Chapter 1: Introduction
5
research, significance of the research, clarification of terms, and organization of the paper.
Chapter 2: Literature Review
This chapter elaborates some theories relevant to this research, including collocation, error analysis, and learning strategies in collocation acquisition. In addition, some relevant studies on the topic are reviewed.
Chapter 3: Research Methodology
This chapter explains the methodological aspects applied in this research. It includes research design, research site and participant, data collection and data analysis.
Chapter 4: Findings and Discussion
This chapter presents and discusses the results of the research. Additionally, the interpretation of the findings is provided in this chapter.
Chapter 5: Conclusions and Suggestions
This chapter presents the conclusion and suggestions of the research. The conclusion section is based on the findings and discussion in the previous chapter. Meanwhile, the suggestions are addressed to future research on related topic. 1.8. Concluding Remark
Aidiana Fatimataz Zahro, 2015
Collocation Acquisition: An Investigation Of Indonesian Efl Learners’ Collocational Errors In Their Writing Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu
CHAPTER 3
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This chapter explains the methodological aspects applied in this research. It includes research design, research site and participant, data collection and data analysis. Research design elaborates the method employed in this research, including its principles and characteristics. The research site and participants emphasize the place where the research takes place and the participant involved. The data collection presents the data types and data collection techniques. The data analysis elaborates the procedure for analyzing the data.
3.1. Research Design
This study employed a descriptive qualitative design embracing the characteristic of a case study approach. A case study, according to Yin, cited in Malik &
Hamied (2014), is “an empirical inquiry about a contemporary phenomenon or a case set within the real -world context- especially when the boundaries between
phenomenon and context are not clearly evident” (p. 259). Similarly, it is defined as “a method of studying social phenomena through the thorough analysis of an
individual case” (Theordorson & Theordorson, Ibid, p. 259). A case can comprise
an instance of an individual, a role, a small group, an organization, a program, and community (Malik & Hamied, 2014, p. 259; Fraenkel et al., 2011, p. 434).
In the present study, since the main purpose was to understand a case in depth, this approach was chosen, as it provides an intensive description and analysis of a single case (Fraenkel, et al., 2011; Griffee, 2012). Also, this approach was considered relevant as the present study addressed a descriptive
question about „what the nature of collocational errors made by Indonesian EFL learners in their writing is‟ and „what the learning strategies applied by the
learners in their collocation are‟.
25
proven to make a big contribution to the study of SLA (Saville-Troike, 2006, p. 40). It provides a broad range of possible explanations for researchers to use to account for errors (Gass & Selinker, 2008, p. 103). As for classifying the collocations produced by the students, this study used framework Benson et al. (2010). Oxford Collocation Dictionary for Students of English (2002), BBI Dictionary of English Word Combinations (Benson et al., 2010) and online Longman Collocation Dictionary and Thesaurus) were referred to in order to determine the accuracy of collocations and to provide suggestions for correction. However, it is important to note that error analysis was used as a methodology for dealing with data, rather than a theory of acquisition (Cook, in Hasbun, 2007). Therefore, this study also conducted an interview as another data collection method. A focus group interview was conducted to identify possible factors responsible for the occurrence of the learners‟ errors which seem to be influenced by the learning strategies the students rely on.
3.2. Research Site 3.2.1. Setting
This research was conducted at a public Senior High School in Bandung. The place was chosen because the school authorities allowed the researcher to conduct this study in their school. Besides, the researcher has been familiar with the situation and the condition of the school. The familiarity with the situation and the condition gave more feasibility to conduct the research.
3.2.2. Participants
26
Aidiana Fatimataz Zahro, 2015
Collocation Acquisition: An Investigation Of Indonesian Efl Learners’ Collocational Errors In Their Writing Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu
3.3. Data Collection
This research used two techniques to collect the data: documentation of students‟ essays and interview.
3.3.1. Documentation of students’ essays
Documentation of students‟ essays was chosen as a technique to collect data for documents can be a valuable source of information in helping researchers to understand central phenomena in qualitative studies (Creswell, 2012, p. 223). Also, they provide the advantage of being in the language and words of participants, who have usually given thoughtful attention to them (Ibid).
Therefore, authentic data from the students‟ language can be obtained in order to
answer the first research question, which is to find out the nature of collocational errors the students made in their writing.
In the present study, the participants were asked to write essays in class within 80 minutes. The essays were argumentative essays written under two different topics, (see Appendix A), and were collected on two different occasions. Before completing the task, the participants were informed that the essays would never be assessed based on grammatical accuracy, therefore, the student could be more relaxed enough to naturally produce linguistic data that represent their collocation competence (Phoocharoensil, 2011). A total of 60 texts were selected
from the students‟ essays to analyze and identify the collocational errors. Then,
Oxford Collocation Dictionary for Students of English (2002), BBI Dictionary of English Word Combinations (Benson et al., 2010) and online Longman Collocation Dictionary and Thesaurus) were referred to in order to determine the accuracy of collocations and to provide suggestions for correction.
3.3.2. Interview
27
explore the participants‟ perception of difficulty in collocation as well as to identify the major source of collocational errors the students made in their writing. Moreover, a focus group interview was applied in this study. This approach was used to collect shared understanding and views from specific people (Creswell, 2012 p. 218) about the major source of collocational errors the students made in their writing. In addition, a focus group interview was advantageous for the interviewees as well as for the interviewer. For the interviewees, it gave them more comfort and courage to answer the questions from the interviewer as some of them might be hesitant or reluctant to provide the information in any type of interview (Ibid). Also, it lets them share understanding and opinion related to the subject matter, and therefore avoided time-consuming compared to the one-on-one interview (Ibid). Thus, conducting a focus group interview was useful for both interviewees and interviewer.
Besides a focus group interview, semi-structured interview was conducted in this study. This type was chosen as it has a flexible and fluid structure compared to structure interview. Moreover, Bahasa Indonesia was used to ease the process of the interview, as the students found it more comfortable with Bahasa Indonesia than English. Furthermore, the use Bahasa Indonesia also helped the students understand the questions and express their opinion better.
3.4. Data Analysis
The data analysis in this research is divided into two sections: identification of the collocational errors from the students‟ essays and transcription of interview data. Each section is explained below.
3.4.1. Identification of collocational errors from the students’ essays
28
Aidiana Fatimataz Zahro, 2015
Collocation Acquisition: An Investigation Of Indonesian Efl Learners’ Collocational Errors In Their Writing Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu
online Longman Collocation Dictionary and Thesaurus) were referred to in order to determine the accuracy of collocations and to provide suggestions for correction. Moreover, for certain collocations which were not found in those dictionaries, Google and some other online dictionaries were used as references. Then the errors were described into specific linguistic elements and categorized according to the classifications of collocations proposed by Benson et al. (2010), as shown in Table 3.1. After that, the errors found were quantified based on their categories. Finally, the findings were analyzed and interpreted by explaining the collocational errors in relation to the learning strategies the students applied (data collected from interviews) in order to find out some possible factors contributing to the occurrence of the collocational errors.
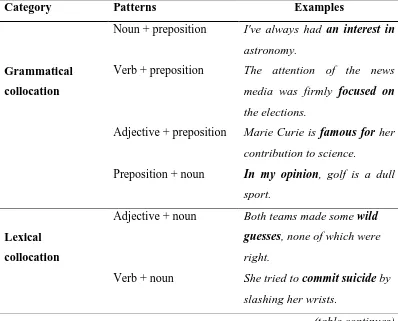
Table 3.1
Framework for Classifying Types of Collocational Errors
Category Patterns Examples
Adjective + preposition Marie Curie is famous for her contribution to science.
Preposition + noun In my opinion, golf is a dull sport.
Lexical collocation
Adjective + noun Both teams made some wild guesses, none of which were
right.
Verb + noun She tried to commit suicide by slashing her wrists.
29
Category Patterns Examples
Lexical collocation
Noun + verb Hatred flared up inside her. Adverb + adjective This principle is clear and
absolutely fundamental.
Verb + adverb All the instruments were functioning normally.
Adverb + verb The disease is potentially fatal. (Adapted from Benson et al. 2010)
3.4.2. Transcription of interview data
To best represent the dynamic nature of the living conversation during the interview, a transcription was done (Malik & Hamied, 2014, p. 207). Transcription is the process of converting audio tape recordings or field notes into text data (Ibid, p. 220). In the present study, the interview recording was transcribed to best represent the information supplied by the participants and to
ease the data analysis. Pseudonyms were used to ensure the participants‟
confidentiality in reporting the data (Ibid, p. 207). The data were then categorized according to the interview questions. After that, the data were categorized and interpreted to find out some possible factors contributing to collocational errors. Finally, the data was presented and explained in accordance with the previous data
of the students‟ collocational errors.
3.5. Concluding Remark
Aidiana Fatimataz Zahro, 2015
Collocation Acquisition: An Investigation Of Indonesian Efl Learners’ Collocational Errors In Their Writing Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu
CHAPTER 5
CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS
This chapter presents the conclusions and recommendations of the study. This chapter is divided into two sections: conclusions and suggestions. The conclusions of this study are based on the findings and the discussion in the previous chapter. Meanwhile, the suggestions provide some pedagogical concerns and recommendations for further research on a related topic.
5.1. Conclusions
This study has investigated collocational errors made by Indonesian EFL learners in their acquisition of English collocations. This study aimed at investigating the nature of collocational errors as well the learning strategies employed by the eleventh grade students of one senior high school in Bandung in their writing.
The data from the analysis of the students’ writing products indicated that
51
collocation were also found to be the source of errors the students made. These include first language transfer, overgeneralization, synonymy, and literal translation. These findings confirmed previous studies (e.g. Phoocharoensil, 2011; Li, 2005; Darvishi, 2011). Regarding resourcing or rereading strategy, it was considered beneficial in the learners’ collocation learning, even though it might also be problematic when the learners neglected the language rules. As for substitution, this strategy was preferable when they found difficulties in the production of collocations. As the results, errors could not be identified from the learners as they avoid making errors.
5.2. Suggestions
In accordance with the findings, discussions and the conclusions of the study, some recommendations are proposed for pedagogical concerns and for future studies in related topic.
As mentioned earlier that collocation plays an important role in leading learners to achieve language proficiency and fluency, it is essential for language teachers to r a i s e t h e l e a r n e r s ’ a w a r e n e s s o f c o l l o c a t i o n a s m a n y o f t h e m s t i l l h a v e
v e r y l i m i t e d k n o w l e d g e o f c o l l o c a t i o n s .
Thus, in teaching new vocabulary to the students, the teacher should not only focus on its meaning and example, but also on its possible collocations. Because, k n o w i n g a w o r d i n v o l v e s k n o w i n g w h a t
w o r d s i t t y p i c a l l y o c c u r s w i t h ( N a t i o n ,
52
Aidiana Fatimataz Zahro, 2015
Collocation Acquisition: An Investigation Of Indonesian Efl Learners’ Collocational Errors In Their Writing Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu
work well. Thus, the teachers can help the students learn collocations more effectively.
Regarding future research, some recommendations are offered here. Since the present study only focused on collocational errors found in the learners’ writing products, it is suggested that further research would be conducted to
investigate the learners’ errors in speaking product in order to obtain a more
detailed picture of the learners’ collocational competence. In addition, a deeper
analysis of the error types should be done. These include errors which only occur in earlier stages of acquisition, those which take longer time to be corrected, and those which are persistent over time, which therefore tend to become fossilized despite pedagogic interventions. Furthermore, further research can be carried out in the form of an experimental design to explore some appropriate and pleasant ways or teaching methods to assist the students increase their collocational competence in accordance with learning strategies the students apply.
53
REFERENCES
Baker, M. (1992). In other words: A coursebook on translation. London: Routledge.
Benson, M., Benson, E., & Ilson, R. (2010), The BBI combinatory dictionary of English: Your guide to collocations and grammar (3rd ed.). Amsterdam: John Benjamins.
Bloom, M. (2008). Second language composition in independent settings:
Supporting the writing process with cognitive strategies. In Stella Hurd &
Tim Lewis (Eds.), Language learning strategies in independent settings.
(pp. 103-118). Bristol, UK: Multilingual Matters.
Cambridge Advanced Learner's Dictionary (3rd ed.)
Chapelle, C. A., & Hunston, S. (Eds.). (2009). Learning vocabulary in another language. United Kingdon: Cambridge University Press.
Collin Dictionary Online, at
http://www.collinsdictionary.com/dictionary/english/stay-at-home
Corder, S. P. (1981). Error analysis and interlanguage. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Cohen, A. D. (2011). Second language learner strategies. In Hinkel, Eli (Ed.), Handbook of research in second language teaching and learning, Volume II. (pp. 681-698). New York: Routledge. Retrieved from http://en.bookfi.org/book/1380225
Creswell, J. W. (2012). Educational research: Planning, conducting, and evaluating quantitative and qualitative research (4th ed.). Boston: Pearson. Darvishi, S. (2011). The investigation of collocational errors in university
54
Aidiana Fatimataz Zahro, 2015
Collocation Acquisition: An Investigation Of Indonesian Efl Learners’ Collocational Errors In Their Writing Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu
Education, Research and Innovation, 18, 52-56. Retrieved from http://www.ipedr.com/vol18/12-ICERI2011-R10018.pdf
Dulay, H., Burt, M., & Krashen, S. (1982). Language two. Oxford: Oxford
University Press. Retrieved from
http://dl.lux.bookfi.org/genesis/827000/07bd60561cafe2e21e99a4bb0e721 222/_as/%5BHeidi_C_Dulay%5D_Language_two(BookFi.org).pdf
Erdogan, V. (2005). Contribution of error analysis to foreign language teaching. Journal of the Faculty of Education, 1(2), 261-270. Retrieved from http://www.turkofni.org/files/contribution_of_error_analysis_to_foreign_l anguage_teaching-vac_de_erdo_an-mers_n_un__2005.pdf
Farrokh, P. (2012). Raising awareness of collocation in ESL/EFL classrooms. Journal of Studies in Education, vol. 2(3), 55-74. Retrieved from http://www.macrothink.org/journal/index.php/jse/article/download/1615/1 525
Fauziati, E. (2009). Interlanguage errors in English textbooks for junior high school students in Surakarta. Retrieved from http://journal.teflin.org/index.php/teflin/article/viewfile/71/208
Firth, J. R. (1957). Papers in linguistics 1934 – 1951. London: Oxford University Press.
Fraenkel, J. R., Wallen, N. E., & Hyun, H. H. (2012). How to design and evaluate research in education (8th ed.). Boston, MA: McGraw Hill.
Gao, X. 2010. Strategic language learning: The role of agency and context. Bristol: Multilingual Matters. Retrieved from http://en.bookfi.org
55
Griffee, D. T. (2012). An introduction to second language research methods: Design and data. United States of America: TESL-EJ Publication. Retrieved from http://www.tesl-ej.org/pdf/ej60/sl_research_methods.pdf Hama, H. Q. (2010). Major sources of collocational errors made by EFL learners
at Koya University. Bilkent University. A Thesis. Retrieved from http://www.thesis.bilkent.edu.tr/0003969.pdf
Hasbún, H. L. (2007). Fossilization and acquisition: A study of learner language. Filología y Lingüística XXXIII (1), 113-129. Retrieved from http://revistas.ucr.ac.cr/index.php/filyling/article/download/4280/4104 Hong, A. L., Rahim, H. A., Hua, T. K., & Salehuddin, K. (2011). Collocations in
Malaysian English learners’ writing: A corpus-based error analysis. The
Southeast Asian Journal of English Language Studies. 17, 31-44. Retrieved from http://journalarticle.ukm.my/3043/1/6-Ang_Leng_Hong_et_al.pdf
Hori, M. (2004). Investigating Dickens’ style: A collocational analysis. New
York: Palgrave Macmillan. Retrieved from
http://en.bookfi.org/book/1082763
Larsen-Freeman, D., & Long, M. H. (1992). An introduction to second language acquisition. United Kingdom: Longman.
Li, C.C. (2005). A study of collocational error types in ESL/EFL college learners’ writing. A Thesis in Applied English. Retrieved from http://ethesys.lib.mcu.edu.tw/ETD-db/ETD-search/getfile?URN=etd-0730105-205237&filename=etd-0730105-205237.pdf
56
Aidiana Fatimataz Zahro, 2015
Collocation Acquisition: An Investigation Of Indonesian Efl Learners’ Collocational Errors In Their Writing Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu
Longman Collocation Dictionary and Thesaurus (Online)
Longman Dictionary of Comtemporary English Online, at http://www.ldoceonline.com/dictionary/homebody
Macaro, E. (2001). Learning strategies in foreign and second language classrooms. New York: Continuum. Retrieved from http://en.bookfi.org/book/1270791
Malik, R.S. & Hamied, F.A. (2014). Research methods: A guide for first time researchers. Bandung: UPI Press.
Martyńska, M. (2004). Do English language learners know collocations?. Vol. XI,
1-12. Retrieved from
http://www.staff.amu.edu.pl/~inveling/pdf/malgorzata_martynska_inve11. pdf
McCarthy, M., & O’Dell, F. (2005). English collocations in use. Cambridge.
Retrieved from http://bookos.org/book/708583/3a2d09
Merriam-Webster's Learner's Dictionary Online, at http://www.learnersdictionary.com/definition/homebody
Miyakoshi, T. (2009). Investigating ESL learners’ lexical collocations: The acquisition of verb + noun collocations by Japanese learners of English. A
Dissertation. Retrieved from
http://www.ling.hawaii.edu/graduate/dissertations/TomokoMiyakoshiFinal .pdf
57
Morelle, R. (2014). Solar wind ‘triggers lightning on Earth’. Retrieved from http://www.bbc.com/news/science-environment-27406358
Mortensen, P. (1997). Laser beam triggers lightning strike during Japanese experiment. Retrieved from http://www.esdjournal.com/articles/lightn.htm
Nesselhauf, N. (2005). Collocations in a learner corpus. Amsterdam: John Benjamin Publishing Company. Retrieved from http://en.bookfi.org/book/746926
Nation, I.S.P. (2000). Learning vocabulary in another language. Cambridge:
Cambridge University Press. Retrieved from
http://en.bookfi.org/book/1364147
Oxford collocations dictionary for students of English. (2002). Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Oxford Dictionary Online, at
http://www.oxforddictionaries.com/definition/english/homebody?searchDi ctCode=all
Parastuti, A., Said, M., & Wurjantoro, W. (2009). The negative transfers of English collocations written by the students of Gunadarma University.
Retrieved from
http://www.gunadarma.ac.id/library/articles/graduate/letters/2009/Artikel_ 10604015.pdf
Pecina, P. (2005). An extensive empirical study of collocation extraction methods. Proceedings of the ACL Student Research Workshop, 13-18. Retrieved from http://www.aclweb.org/anthology/P05-2003
58
Aidiana Fatimataz Zahro, 2015
Collocation Acquisition: An Investigation Of Indonesian Efl Learners’ Collocational Errors In Their Writing Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu
Ridha, A. N. S., & Al-Riyahi, A. A. (2011). Lexical collocational errors in the writings of Iraqi EFL learners. Journal of the Colledge of Arts, 58, 24-51. Retrieved from http://www.iasj.net/iasj?func=fulltext&aId=58096
Said, M. (2011). Negative transfer of Indonesian collocations into English and implication for teaching English as a foreign language. 6(2). Retrieved
from
http://ejournal.uin-malang.ac.id/index.php/humbud/article/download/1458/2545
Samra, N. A. (2003). An analysis of errors in Arabic speakers’ English writings. Retrieved from http://abisamra03.tripod.com/nada/languageacq-erroranalysis.html
Saville-Troike, M. (2006). Introducing second language acquisition. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Schmitt, N. (2000). Vocabulary in language teaching. Cambridge: Cambridge
University Press.
Sun's activity triggers lightning strikes. (n.d). Retrieved from http://www.theguardian.com/science/2014/may/15/sun-lightning-strikes-earth-solar-wind
Woolard, G. (2005). Key word for fluency: Intermediated collocation practice.