SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
for
Van der Waals Effects between Hydrogen and First-Row Atoms in
Molecular Mechanics (MM3/MM4)
Norman L. Allinger and Kathleen A. Durkin
Table I. Interaction energy (kcal/mole) data in the head-to-head methane-methane
3.50 6.9856 7.1205 10.877 10.637 4.00 0.8369 1.0725 1.5087 1.5572
4.20 0.5158 0.5637
4.40 0.0790 0.1180
4.60 -0.1574 -0.0602 -0.0922 -0.0623 4.80 -0.1812 -0.1025 -0.1437 -0.1213 4.90 -0.1788 -0.1077 -0.1482 -0.1288 5.00 -0.1715 -0.1071 -0.1453 -0.1285 5.50 -0.1151 -0.0750 -0.0979 -0.0893 7.00 -0.0341 -0.0162 -0.0210 -0.0193
a Geometries were optimized at MP2/6-31G**. Energies are relative to the isolated energy of methane and which was -40.3937707 at MP2/6-311++G (2d,2p) (x 2 for the dimer). b This is relative to the isolated energy of methane which was 0.2157 kcal/mole by MM4 and 0.0 kcal/mole by MM3 (x 2 for the dimer). The MM3/4 H is atom type 5. The C-H bond length in MM3/4 is 1.07Å and 1.09Å at MP2/6-31G**.
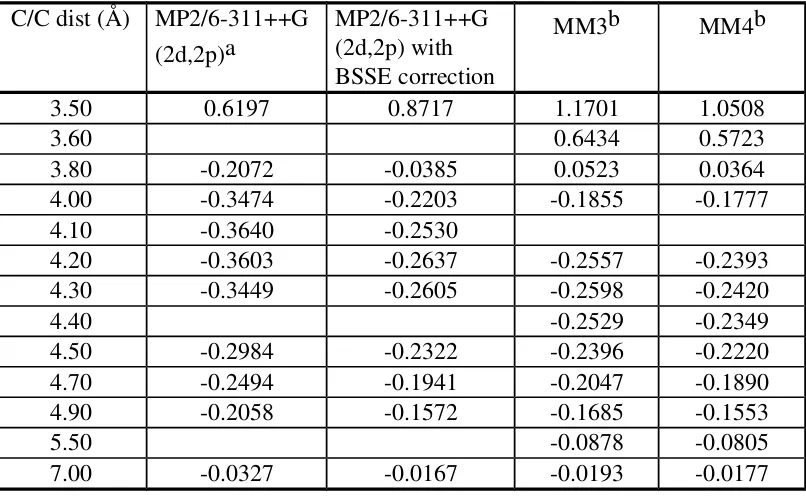
Table II. Interaction energy (kcal/mole) data in the head-to-tail methane-methane system.
3.50 0.6197 0.8717 1.1701 1.0508
3.60 0.6434 0.5723
3.80 -0.2072 -0.0385 0.0523 0.0364 4.00 -0.3474 -0.2203 -0.1855 -0.1777 4.10 -0.3640 -0.2530
4.20 -0.3603 -0.2637 -0.2557 -0.2393 4.30 -0.3449 -0.2605 -0.2598 -0.2420
4.40 -0.2529 -0.2349
4.50 -0.2984 -0.2322 -0.2396 -0.2220 4.70 -0.2494 -0.1941 -0.2047 -0.1890 4.90 -0.2058 -0.1572 -0.1685 -0.1553
5.50 -0.0878 -0.0805
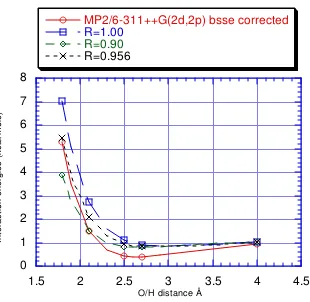
Table III. Interaction energies (kcal/mole) in the methane-dimethyl ether system.
O/H
dist (Å) MM4 a MM3 HF/6-31G**b MP2/6-31G** BSSE correctedc HF/6-31G** BSSE corrected MP2/6-31G** 1.8 5.1890 5.8873 5.9401 2.9031 6.6349 4.8162 1.9 3.4134 3.9187 3.7245 1.1582 4.4009 2.9175 2.0 2.1620 2.5216 2.1962 0.0020
2.1 1.2939 1.5448 1.1571 -0.7402 1.7563 0.7390 2.2 0.7021 0.8728 0.4593 -1.1958
2.3 0.3067 0.4190 -0.0025 -1.4533 0.5593 -0.1658 2.4 0.0492 0.1194 -0.3008 -1.5744
2.488 -0.4661 -1.6029 0.0772 -0.4620
2.5 -0.1127 -0.0723 -0.4823 -1.6025 0.0592 -0.4706 2.6 -0.2092 -0.1895 -0.5876 -1.5683 -0.0595 -0.5151 2.7 -0.2616 -0.2562 -0.6382 -1.4935 -0.1296 -0.5221 2.8 -0.2849 -0.2889 -0.6517 -1.3921 -0.1678 -0.5065 2.9 -0.2894 -0.2995 -0.6414 -1.2743 -0.1775 -0.4791 4.0 -0.1278 -0.1257 -0.1238 -0.2125 -0.0875 -0.1534 a This is relative to the isolated energies of methane and dimethyl ether which were 0.2157 and 0.9239 kcal/mole respectively by MM4. By MM3, these were 0.0 and 2.3040 kcal/mole respectively.
b All geometries were optimized at MP2/6-31G**. The interaction energies are relative to isolated methane and dimethyl ether. The HF energies are -40.2016949 and -154.0030263 Hartrees, respectively. The MP2 energies are -40.3646259 and -154.5518256 Hartrees. c Corrections were applied by counterpoise method.
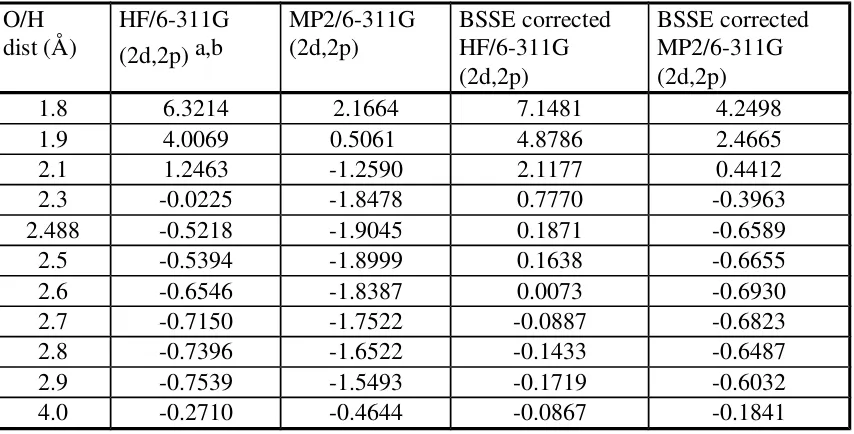
Table IV. Interaction energy (kcal/mole) data in the methane-dimethyl ether system. O/H
dist (Å) HF/6-311G (2d,2p) a,b MP2/6-311G (2d,2p) BSSE corrected HF/6-311G (2d,2p)
BSSE corrected MP2/6-311G (2d,2p)
1.8 6.3214 2.1664 7.1481 4.2498
a This is relative to the isolated energies of methane and dimethyl ether which were -40.2120991 and -154.1146257 Hartrees, respectively, at the HF level. The isolated energies at MP2 were -40.3934864 and -154.6584773 Hartrees, respectively.
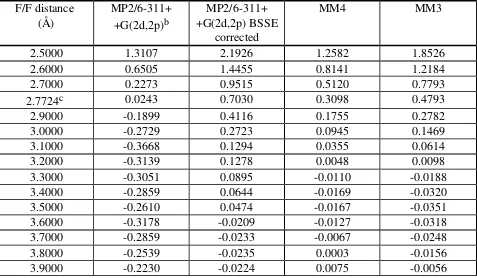
Table IXa. Fluoromethane dimer interaction energy (kcal/mole) for the head-on orientation.a F/F distance
(Å) MP2/6-311++G(2d,2p)b +G(2d,2p) BSSEMP2/6-311+
corrected
MM4 MM3
2.5000 1.6552 2.4180 1.5696 1.9584
2.6000 1.2525 1.9347 1.2374 1.4982
2.7000 1.0095 1.6129 1.0059 1.1776
2.8372c 0.8099 1.3297 0.8435 0.9541
2.9000 0.7523 1.2371 0.7286 0.7978
3.0000 0.6883 1.1225 0.6461 0.6880
3.1000 0.6421 1.0368 0.5858 0.6100
3.2000 0.6121 0.9666 0.5405 0.5539
0.5055 0.5127 0.4774 0.4815
3.5000 0.5615 0.8136 0.4542 0.4573
0.4342 0.4376 0.4165 0.4210 0.4005 0.4066 0.3857 0.3937
4.0000 0.5127 0.6401 0.3719 0.3817
0.3123 0.3306
5.0000 0.3958 0.4117 0.2645 0.2881
Table IXb. Fluoromethane dimer interaction energy (kcal/mole) for the 90° orientation.a
F/F distance
(Å) MP2/6-311++G(2d,2p)b +G(2d,2p) BSSEMP2/6-311+
corrected
MM4 MM3
2.5000 1.3107 2.1926 1.2582 1.8526
2.6000 0.6505 1.4455 0.8141 1.2184
2.7000 0.2273 0.9515 0.5120 0.7793
4.0000 -0.1273 0.0186 0.0145 0.0045
4.5000 0.0413 0.0465
5.0000 -0.0183 0.0245 0.0543 0.0700
a The isolated energies of fluoromethane were 0.0815 and 0.0497 kcal/mole by MM3 and
MM4, respectively. The isolated energy at MP2/6-311++G(2d,2p) was -139.4827432 Hartrees. Each isolated energy was doubled to account for the dimer energy at infinite separation and this value was used to calculate the interaction energies.
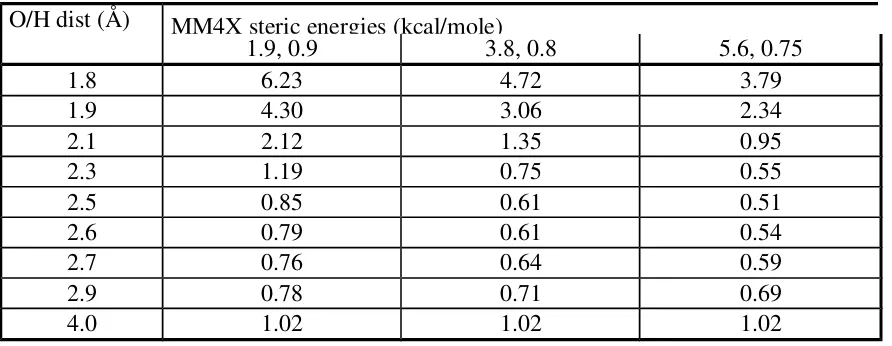
Table XI. MM4X vs. Gaussian data in methane-dimethyl ether interactions. O/H dist (Å) MM4X steric energies (kcal/mole)
1.9, 0.9 3.8, 0.8 5.6, 0.75
1.8 6.23 4.72 3.79
1.9 4.30 3.06 2.34
2.1 2.12 1.35 0.95
2.3 1.19 0.75 0.55
2.5 0.85 0.61 0.51
2.6 0.79 0.61 0.54
2.7 0.76 0.64 0.59
2.9 0.78 0.71 0.69
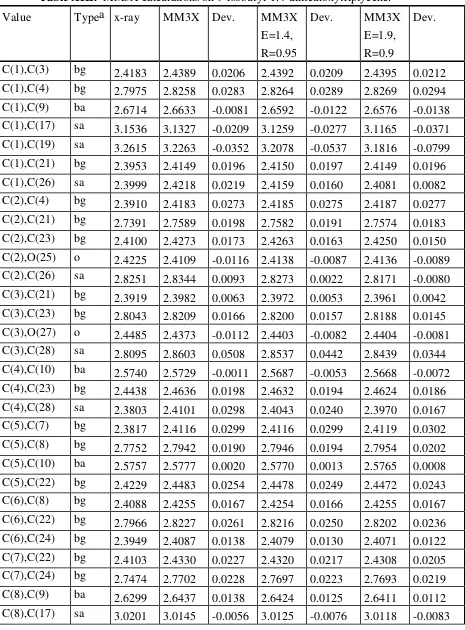
Table XIII. MM3X calculations on 9-isobutyl-1.4-dimethoxytriptycene. Value Typea x-ray MM3X Dev. MM3X
E=1.4,
C(14),C(16) bg 2.4021 2.4211 0.0190 2.4210 0.0189 2.4211 0.0190 C(17),C(19) ss 2.6393 2.6451 0.0058 2.6404 0.0011 2.6336 -0.0057 C(17),C(20) ss 2.5085 2.5404 0.0319 2.5409 0.0324 2.5410 0.0325 C(17),C(22) sa 2.5844 2.5637 -0.0207 2.5614 -0.0230 2.5586 -0.0258 C(17),C(23) sa 2.6429 2.6220 -0.0209 2.6172 -0.0257 2.6097 -0.0332 C(17),O(25) o 2.7883 2.8107 0.0224 2.8047 0.0164 2.7950 0.0067 C(18),C(22) sa 3.2468 3.2106 -0.0362 3.2028 -0.0440 3.1920 -0.0548 C(18),C(23) sa 3.4368 3.4066 -0.0302 3.3949 -0.0419 3.3791 -0.0577 C(18),O(25) o 3.0803 3.1475 0.0672 3.1323 0.0520 3.1118 0.0315 C(19),C(20) aa 2.5159 2.5193 0.0034 2.5204 0.0045 2.5215 0.0056 C(19),C(22) sa 3.4199 3.4249 0.0050 3.3976 -0.0223 3.3654 -0.0545 C(19),C(23) sa 3.2560 3.2056 -0.0504 3.1822 -0.0738 3.1514 -0.1046 C(19),O(25) o 3.0165 3.0651 0.0486 3.0552 0.0387 3.0390 0.0225 C(20),O(25) o 3.3326 3.4182 0.0856 3.3864 0.0538 3.3475 0.0149 C(21),C(22) aa 2.8226 2.8333 0.0107 2.8338 0.0112 2.8334 0.0108 C(21),C(24) aa 2.4339 2.4283 -0.0056 2.4279 -0.0060 2.4278 -0.0061 C(21),O(27) o 2.3542 2.3638 0.0096 2.3595 0.0053 2.3577 0.0035 C(22),C(23) aa 2.5120 2.5202 0.0082 2.5194 0.0074 2.5177 0.0057 C(23),C(24) aa 2.8546 2.8635 0.0089 2.8638 0.0092 2.8623 0.0077 C(23),O(25) o 2.3792 2.3926 0.0134 2.3891 0.0099 2.3883 0.0091
RMS
Deviation 0.025995 0.024297 0.025713
a Type bg is a beta or gamma interaction across a phenyl ring. Type ba is a bridge carbon to aromatic carbon interaction. Type sa is a saturated (except bridge) carbon to aromatic carbon interaction. Type o is an interaction involving oxygen. Type ss is a saturated carbon to saturated carbon interaction. Type aa is an aromatic carbon to aromatic carbon
0
Insert for Kathy’s paper
While the scaling factors for the O/H interactions seem certain enough as long as the
hydrogen is an ordinary hydrogen attached carbon (an alkane hydrogen), and the oxygen is
an ordinary ether oxygen (alkane type). However, in the triptycene case, we are looking at
an oxygen attached to an aromatic ring. Such an oxygen is well known to be an electron
donor into the pi system. This means that the electron density of that oxygen will be less
than in the case of an aliphatic oxygen, and the effective nuclear charge at oxygen in this
system will be higher than the effective nuclear charge for an isolated oxygen atom. Both of
these effects tend to reduce the van der Waals repulsion between oxygen and anything else.
The first of these simply reduces the electron density, which is the principle source of the
repulsion. The second of these means that the nucleus attracts the electrons more than
normally, and pulls the electron cloud even closer to the nucleus.
We have in our parameterization to this point simply used the aliphatic oxygen
numbers for the oxygen in the triptycene system. But actually, the van der Waals radius of