735
Identification
of
Acid-Based
Concept
Understanding Using the Assessment of A
Two-Tier Multiple Choice Diagnostic Instrument
*1
Lisa Ariyanti Pohan and
2Syahwin
1
Departement of Chemistry Education, Faculty of Teacher Training and Education, University of Islamic North Sumatera, Indonesia;
2Departement of Physics Education, Faculty of Teacher Training and Education,
University of Islamic North Sumatera, Indonesia;
*
Corresponding author: [email protected]
Abstract
Mastery of concepts in chemistry lessons it is important to note, by teachers of chemistry. Therefore, this study was aimed to evaluate the concept of understanding acid -base using a multiple-choice assessment type two tier. So that teachers are able to measure the students ' understanding about the mastery of acid-base concept as reference materials for teachers to continue to correct the learning in the classroom. A number of 15 items about the concept of acid-base was designed using multiple choice two tier test tested to 11th graders in the even semester. The method used in this study using descriptive qualitative. The research was conducted in senior high school 19 Medan with population 159. The sampling technique was done by random sampling. Data analysis technique used description of data obtained from result of student answer. The results of the data analysis obtained as amount as 47% or there are seven items which answered correctly in the first tier with the lowest category, 47% or there are seven items which answered correctly in both tiers with medium category, and only one question answered correctly on both tiers with high category. Percentage of students' understanding of the concept of acid-base using two tier diagnostic tests is 35 people or 47% in the low category, 40 persons or 53% in the medium category, while the higher category is 0%.
Keywords: identification, chemistry assessment, two-tier tests, acids and bases concept.
Introduction
Learning acquires a complete concept, broad, and deep is often overlooked in the learning process in the classroom due to the school administrators, students and teachers shackled with a standard test system of graduation. These tests usually only emphasize basic cognition at low-level and not pay attention to the importance of a deeper understanding (Windschitl, 2002).
736 Acid-base material in chemistry is one of the principals of the study of that important to master students because this material into the basic concepts to learn advanced chemical materials such as acid-base reactions, acid-base titration, etc. On the basic material of the acid base chemistry at the high school level curriculum studied three models of acid-base is most commonly taught in high school that is the model of the Arrhenius, Bronsted-Lowry, and Lewis. Of the three modes of acid-base each defines an acid and a acid-base in different ways, but in fact this model is not contradictory in the essence of the basic behavior of acid base. For example, HCl is an acid according to the Arrhenius model. Similarly, according to the Bronsted-Lowry model and Lewis model, things that are not possible when there is one defined as acid compounds according to one model and defined a base according to another model. The occurrence of acid base model differences because the experts see the basic behavior of acid-base from different points of view, but actually does not contradiction between one and the other. The second model expanded the definition of the first models and the third model is the expansion of the definition of the second model. So, comprehend some models of acid-base became a challenge for students and sometimes cause confusion as if going contradiction between one model with other models.
To know the students' understanding level against the concepts of chemistry can be done by asking the questions directly the nature of investigation for students with a model interview, but this practice takes a long time. Educational researchers need a practical assessment to assess students ' mastery of the concept is to use multiple choice tests that can capture data quickly and effectively, and efficiently. Multiple choice test covers some item selection that originally only evaluates the content knowledge regardless of the reasons behind the choice of responses student (Duncan & Johnstone, 1973).
Literature Review
Concept Learning
The subject matter of chemistry is laden with concepts that the concrete as well as abstract. Studying the chemistry, the foundations should be built on a correct understanding of chemical concepts because of the concepts is the Foundation of thinking early to study chemistry. What is a concept? What is a concept? A concept is an object, a symbol, or events that have the characteristics, attributes, or have certain important traits that become its identity. A concept is real structure or representation category that makes people able to recognize an example and is not an example, though an example and not an example has many attributes that are similar (Dahar, 2006).
Students develop their views on scientific concepts and phenomena based on their sensory experience, cultural background, colleagues, mass media as well as learning in class (Chandrasegaran, Treagust & Mocerino, 2008). There is a tendency for students to be satisfied with their own conception due to it is already embedded in their mentation's nature and supported by their life experiences (Chandrasegaran, Treagust & Mocerino, 2008).
737 A Concept attainment model that was initiated by Bruner is the basic operational structure embedded mental model of students learning when understanding new concepts. Then, B. Joyce and M. Weil translate their theory in the form of concept attainment learning models where teachers and students work together to develop, examine, modify, and draw conclusions from collectively formulated assumptions, based on work findings in the field.
1. Understanding of Acid-Base Concept
The acid-base material is known as one of the difficult chemistry subject since it involves some prerequisite materials as an introduction to deeply understanding the acid-base material such as: chemical equilibrium, chemical reactions, stoichiometry, matter properties, and solutions (Artdej, Ratanaroutai, Coll, & Thongpanchang, 2010).
Investigation of the students' understanding about the acid-base concept had been done by chemical education practitioners. Kala, Yemen and Ayas (2013) detected misunderstandings of students in understanding the concept of pH and pOH. They understand that pH is associated with acid while pH is associated with the base. It is also found a different understanding about the categorization of methanol properties. One student determines methanol as a base because in water, it can be dissociated into an OH group. The other students also assume that methanol is acidic because the breaking C-H bond can contribute protons (Wan, 2014).
2. Two-tier Multiple Choice
There are many methods evaluate students' conceptual understanding, i.e., multiple choice, interview, and concept maps. Each of methods has advantages and disadvantages. Multiple choice tests are often chosen to assess students' understanding of the science class because it is easy to apply. However, multiple-choice tests have some limitations in determining whether a student gives the correct answer to his or her understanding or simply guessing and speculation so it becomes difficult to investigate students' reasoning abilities. On the other hand, the interview can provide more detailed information to find out the reason of the students in choosing the answer so that the teacher can find out whether the concept owned by the students is in accordance with the scientific reasons. However, this method requires a long time to interview with many students to generalize their alternative conception. As well as concept maps, the use of concept maps in the assessment process takes a long time to train students using concept maps and interpretations (Artdej, Ratanaroutai, Coll & Thongpanchang, 2010).
Since the two techniques mentioned above have some limitations for practical use in the classroom, it is developed two-tier multiple-choice types to identify alternative conceptions of students (Treagust, 1986; Treagust, 1995). Treagust (1988) argues that identifying student concepts using multiple choice two tier assessment tools can develop students' scientific concepts.
738 Treagust & Chandrasegaran, 2012), and electrochemistry (Rahayu, Treagust, Chandrasegaran, Kita & Ibnu, 2011).
Research Method
The research method used in this research is descriptive qualitative method. This method is a research method that describes and analyzes understanding level diagnostic data of the concept of acid base using multiple choice two-tier instruments.
The study was conducted at SMAN 19 Medan Labuhan, Medan city in the even semester of the academic year 2016/2017. The population involved in this study was 159 11th grade students. Sampling of population members was done randomly because there were no strata of the population. Techniques of random sampling can be done because the population is homogeneous, Sugiyono (2001). Sample size taken on the opinion of Surakhmad (1994), if the population size is equal to or more than 1000, the sample size is expected to be at least 15% of the population size by following the formula:
S = 15% +
(50% - 15%)
Where: S = Sample n = Population
The instrument used in this study is multiple choice two-tier. Items were designed using chemistry syllabus of senior high school in Indonesian. A total of 15 questions were designed after the questions were examined by teachers who have been certified and experienced to teach at least 5 years using the format of review questions. Then, validated qualitatively using three approaches are: content validity, criterion validity, construct validity (construct validity), Popham (1995).
Data analysis technique used description of data obtained from result of student answer. Furthermore, the data obtained from the test results were processed by searching for presentation and analyzed descriptively, e.g.: if the score obtained is 25-50 (lowest category), score 51-75 (medium category), and score 76-100 (highest category) Sudijono, 2009). The scoring guidelines used in the study using the Two-tier Multiple Choice instrument refers to the scoring guidelines of Bayrak (2013) have been adapted, presented in Table 1.
Table 1. Assessment criteria
Option Score
Option is correct and reason is correct Option is correct but reason is incorrect Option is incorrect but reason is correct Option is incorrect and reason is incorrect
2 1 0 0
739 experimental data, 2) Identifying the characteristic of acid and base solutions with various indicators, 3) Explaining the meaning of acid strength and summarizing the pH measurement results from several acid and base solutions of equal concentration, 4) Explaining the application of acid-base concepts in life. The following sample is acid base concept questions with multiple choice two-tier in table 2.
Table 2. A sample question an acids and bases diagnostic test two tier
Tier A sample three-tier question
First tier
Second tier
1) Every compound containing H is an acidic compound, such as HCN, HNO3, HCl, NH3, CH3COOH, H2SO4
a. True b. False Reason:
a. Acid is a substance that when dissolved in water produces H+ ions according to Arrhenius.
b. CH3COOH is a base because it contains OH-.
c. NH3 is not acid, but base, according to Lewis because it
has electron pair
d. NH3 is the only compound containing H in its structure which is alkaline
Results and Discussion
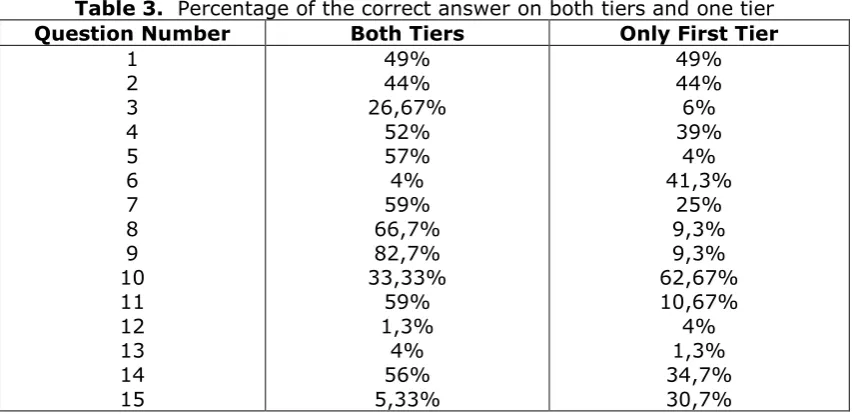
The results of the assessment toward students 'conceptual understanding using multiple choice two tier assessment are described from the percentage of students' correct answers on both tier and the first tier. Afterward, it is ranked from highest to lowest by category score. The percentages of correct answers were given by the students on both the tiers and one tier of the given test was described in following table 3.
Table 3. Percentage of the correct answer on both tiers and one tier
Question Number Both Tiers Only First Tier
1
740 there is still confusion about this test model. Acquisition score of student concept comprehension can be seen in table 4 as follows:
Table 4. Percentage of students' concept comprehension level
Criteria Percentage
High 0%
Medium 53%
Low 47%
From table 4 above, it can be seen that none of the students gained the level of understanding in the high category. While in the medium category, there are 40 students from 75 students or 53% who are at the level of medium understanding and there are 35 students or 47% who are at the level of low understanding.
The following are submitted some questions very low of acquisition correct answers of students on both tiers and first tier, e.g. 3.4, 12, 13 and 15.
Table 5. The question of item number 3
Tier A sample three-tier question
First tier
Second tier
3) H2PO4-is a base specie
a. True b. False Reason:
a. H2PO4- produces H+ ion when dissolved in water
b. H2PO4 -
is base and cannot be explained by Arrhenius theory c. H2PO4-is base because accepts proton from H2O explained
by Bronsted Lowry theory
d. H2PO4- is base because negative charged
The question number three, students answered correctly on both tiers is 26,67% and on the first tier 6%. The acquisition of students’ answer on this number is very low. This is due to the understanding of the acid base concept Bronsted Lowry has not been comprehensive, all this time in learning, teachers just give an ordinary example like HCl which conjugate base is Cl-. But, when given the example HS-, is it acid or base this species according to Bronsted Lowry acid? Then, the students are still confused to answer it. Actually, the answer can be acid or can be base depend on whether HS- receives protons or gives protons. If HS-accepts proton, it will be base, conjugate acid is H2S but, if HS- donates proton, it will be acid, conjugate base
is S2-. To embed students' understanding of the concept of conjugate acid base, it is necessary to have many variations of complex questions and not too easy.
Table 6. The question of item number 6
Tier A sample three-tier question
First tier
Second tier
6) Reaction Na2O and SO3 involves reaction of oxide ion is O2– from
solid Na2O and gas SO3. Then, Na2O is base and SO3is acid:
a. True b. False Reason:
a. Na2O and SO3 is acid because containing oxygen as main
element in acid substance according to Lavoiser
b. Na2O is base because containing Na is alkaline and SO3is
acid because containing S.
c. Na2O is basic because it donates electron and SO3 is acidic
741 d. Na2O is acidic because it donates electron and SO is basic
because it receives electron based on Lewis theory.
The question number six, students answered correctly on both tiers is just 4% and on the first tier 41,3%. The acquisition of students’ answer on this number is very low, although there is 41,3% answered correctly on the first tier. This question asks about the mastery of Lewis acid concept. The mastery of the Lewis acid concept in senior high school level is still not profound, sometimes just enough to know definition, but not Lewis acid base reaction. Learning Lewis's acid-base concept needs to be prepared with the mastery of Lewis notation writing because the concept of Lewis acid base involves the transfer of electrons.
Table 7. The question of item number 12 and 13 Tier A sample three-tier question
First tier
Second tier
12)Among the following compound : HClO4 0,2 M ; HCl 0,02 M ;
CH3COOH 0,2 M (Ka = 1,8 x 10-5) which have the lowest pH is
HCl a. True b. False Reason:
a. CH3COOH 0,2 M because it is acid weakest
b. HCl 0,02 M because the concentration is the lowest c. HClO4 0,2 M is strong acid and its concentration is more
concentrated than HCl d. Another reason: First tier
Second tier
13)Concentration of H+ ion in following substances: HF, HCl, HCN, HBr are same
a. True b. False Reason:
a. Those are equally acid group valence one b. In water ionized to be H+ ion valence one
c. It is only HCl which is different concentration H+ ion because only HCl which is strong acid
d. HF and HCN are weak acid and not completely ionized in water, so that concentration H+ ion was determined by acid ionization constant.
The question number twelve, students answered correctly on both tiers is just 1,3% and on the first tier 4%. The question number thirteen, students answered correctly on both tiers is just 4% and on the first tier 1,3%. The question number twelve and
thirteen verify students’ understanding about acid strength and conclude pH
measurement result of several acid-base solution which are the same concentration. In this concept, student mastery of the concept is still very low.
Table 8. The question of item number 15 Tier A sample three-tier question
First tier
Second tier
15)When the soil condition is too acidic and do not support for plant growth. So, the chemicals used to improve soil conditions are to add lime CaO.
a. True b. False Reason :
742 acidity
c. The acid conditions in the soil cannot be converted into base d. CaO is oxide base element.
The question number fifteen, students answered correctly on both tiers is just 1.3% and on the first tier 4%. This question verifies students’ understanding about application of acid-base concept in life. Concept acquisition of this question is still low.
The overall percentage of students' understanding of acid base concepts using two tier diagnostic tests is 35 people or 47% in low category, 40 persons or 53% medium category, while high category 0%. This shows that the ability of students to understand the basic concept of acid base is still low in SMA 19 Medan Labuhan. This could be due to students not so interested in chemistry lessons because the nature of the chemistry lessons does require students' thinking skills, seriousness, and thoroughness. In addition, the two-tier model is a new problem model so students are not familiar with the assessment model.
Conclusions
Multiple choice two tier is a multiple-choice test of the latest model that function to overcome the weakness of the usual multiple choice. While the interview model assessment system takes a long time in its application. Multiple choice two-tier is the development of new test models to obtain concept information that has been obtained by students and alternative concepts that students have. For the application of two tier instruments, students are not accustomed to using multiple choice models of tier type and need time to train students to get used to them. It can be seen from the results of the score of students score as much as 47% are low understanding level and 53% are medium understanding level. While in the high category none of the students was in the high understanding level.
References
Artdej, R., Ratanaroutai, T., Coll, K.R., & Thongpanchang, T. (2010). Thai Grade 11
students’ alternative conceptions for acid-base chemistry. Research in Science &
Technogical Education, 28, 167-183
Ausubel D.P. (1968). Educational psychology: a cognitive view, Holt, Rinehart and Winston, New York.
Bayrak, B. K. (2013). Using two-tier to identify primary students’ conceptual understanding and alternative conception in acid base. Mevlana International Journal of Education, 3, 19-26
Chandrasegaran, A. L., Treagust, D. F., & Mocerino, M. (2007). The development of a two-tier multiple-choice diagnostic instrument for evaluating secondary school students’ ability to describe and explain chemical reactions using multiple levels of representation. Chemistry Education Research and Practice, 8(3), 293-307. Chandrasegaran, A. L., Treagust, D. F., & Mocerino, M. (2008). An evaluation of a
teaching intervention to promote students’ ability to use multiple levels of representation when describing and explaining chemical reactions. Research in Science Education, 38(2), 237-248.
Dahar,W.R. (2006). Teori-teori belajar & pembelajaran. Jakarta: Penerbit Erlangga. Damanhuri, M.I.M., Treagust, F.D, Won, M., & Chandrasegaran, L.A. (2015). High
school students’ understanding of acid-base concepts: an ongoing challenge for
teachers. International Journal of Environmental and Science Education, 11(1), 9-27
Dindar, C.A., & Geban, O. (2011). Development of a three-tier test to assess high
school students’ understanding of acids and bases. Procedia Social Behavioral
743 Duncan I.M. & Johnstone A.H., (1973), The mole concept. Education in Chemistry,
10, 213-214.
Geary, D.C. (1995). Reflection of evolution and culture in children’s cognition: Implications for mathematical development and instruction. American Psychologist, 50, 24 - 37
Haslam F. & Treagust D. F. (1987) Diagnosing secondary students’ misconceptions of photosynthesis and respiration in plants using a two-tier multiple choice instrument. Journal of Biological Education, 21, 203-211.
Jones, L.J. & Hilaire, S.R. (2014). Concept learning in undergraduate classroom: A case study in religious studies. International Journal of Instruction, 7, 66-72 Kala, N., Yaman, F., & Ayas, A. (2013). The effectiveness of Predict-Observe-Explain
technique in probing students’ understanding about acid-base chemistry: A case for the concepts of pH, pOH and strength. International Journal of Science and Mathematics Education, 11(1), 555-574.
Odom, A.L. & Barrow, L.H. (1995). The development and application of a two-tier diagnostic test measuring college biology students’ understanding of diffusion and osmosis following a course of study. Journal of Research in Science Teaching, 32(1), 45-61.
Rahayu, S., Treagust, D. F., Chandrasegaran, A. L., Kita, M, & Ibnu, S. (2011). Assessment of electrochemical concepts: A comparative study involving senior-high school students in Indonesia and Japan. Research in Science & Technological Education, 29(2), 169-188.
Sia, D.T., Treagust, D. F., & Chandrasegaran, A. L. (2012). High school sudents’ proficiency and confidence levels in displaying their understanding of basic electrolysis concepts. International Journal of Science and Mathematics Education, 10, 1325-1345
Schunk, H.D.(2012). Teori-teori pembelajaran (6th ed.). Yogyakarta: Pustaka Pelajar.
Sudjana, N. (2009). Penilaian hasil proses belajar mengajar. Bandung: PT. Remaja Rosdakarya.
Sugiyono (2001). Statistika untuk penelitian. Bandung: Alfabeta
Sudijono, A. (2009). Pengantar Statistik Pendidikan. Jakarta: Rajawali Pers.
Tan, D. K-C. & Treagust, D. F. (1999). Evaluating students’ understanding of chemical bonding. School Science Review, 81, 75–83.
Tan, K. C. D., Goh, N. K., Chia, L. S., & Treagust, D. F. (2002). Development and application of a two-tier multiple choice diagnostic instrument to assess high school students’ understanding of inorganic chemistry qualitative analysis. Journal of Research in Science Teaching, 39(4), 283-301.
Treagust, D.F. (1986). Evaluating students' misconceptions by means of diagnostic multiple choice items. Research in Science Education, 16,199-207.
Treagust, D. F. (1988). Development and use of diagnostic tests to evaluate students' misconceptions in science, International Journal of Science Education, 10, 159-169.
Treagust, D. F. (1995). Diagnostic assessment of students’ science knowledge. In S. M. Glynn and R. Duit (Eds.), Learning in science in the schools: Research reforming practice (pp. 327-346), Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Treagust, D. F. & Chandrasegaran, A. L. (2007). The Taiwan national science concept learning study in an international perspective. International Journal of
Science Education, 29(4), 391–403.
Tyson, L., Treagust, D. F. & Bucat, R. B. (1999). The complexity of teaching and learning chemical equilibrium. Journal of Chemical Education, 35, 1031–1055. Windschitl, M. (2002). Framing Constructivism in practice as the negotiation of
744 Wan, J.Y. (2014). Assessing College Students’ Understanding of Acid Base Chemistry
Concepts (doctoral thesis). Retrieved from