BAB
7
Cahaya dan Optik
Light and Optics
Konsep PENTING
IMPORTANT concepts
7
BIDANG
PEMBELAJARAN
BA
B
APAKAH ITU CAHAYA DAN OPTIK? WHAT ARE LIGHT AND OPTICS?
Cahaya membolehkan kita melihat. Optik mengkaji ciri-ciri cahaya termasuk interaksinya dengan jirim dan pembinaan peralatan yang menggunakan atau mengesan cahaya.
Light enables us to see. Optics studies the properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the constructions of instruments that use or detect it.
TEMA 3: Tenaga dan Kelestarian Hidup
Ciri imej bagi jarak objek yang berbeza
The characteristics of image for objects with difference distances
Pembentukan imej akhir oleh peralatan optik Final image formation by optical instruments
Aplikasi kanta dalam peralatan optik
The application of lenses in optical instruments
Kanta cembung dan kanta cekung
Convex and concave lenses
Gambar rajah sinar The ray diagrams
Peralatan optik Optical instruments
Model teleskop ringkas The model of simple telescope
CAHAYA DAN OPTIK LIGHT AND
OPTICS
Titik fokus kanta cembung dan kanta cekung
The focal points of convex and concave lenses
NOTA BESTARI
Kanta Cembung dan Kanta Cekung
1. Kanta cembung (kanta penumpu) menumpukan sinar-sinar cahaya yang melaluinya.
2. Kanta cekung (kanta pencapah) mencapahkan sinar-sinar cahaya yang melaluinya.
3. Imej yang dibentuk oleh kanta cembung bergantung pada jarak objek dari kanta itu.
4. Ciri-ciri imej yang dibentuk oleh suatu kanta cembung adalah
(a) maya atau nyata (b) tegak atau songsang (c) dikecilkan atau dibesarkan
Jenis Imej dan Maklumat daripada Rajah Sinar
1. Imej nyata ialah imej yang dapat terbentuk pada skrin manakala imej maya ialah imej yang tidak dapat terbentuk pada skrin.
2. Maklumat daripada rajah sinar:
(a) Jarak objek ialah jarak antara objek dengan pusat optik manakala jarak imej ialah jarak antara imej dengan pusat optik.
(b) Titik fokus ialah titik tumpuan sinaran cahaya manakala panjang fokus ialah jarak antara pusat optik dengan titik fokus.
(c) Paksi utama ialah garis yang menerusi pusat optik kanta.
(d) Pusat optik ialah titik tengah kanta.
Pembentukan Imej oleh Kanta Cekung dan Kanta Cembung
1. Kanta cekung mencapahkan sinar-sinar cahaya. Ciri-ciri imej yang terbentuk adalah maya, tegak dan dikecilkan.
2. Imej yang terbentuk oleh kanta cembung bergantung pada jarak objek.
Jarak objek Ciri-ciri imej Alat optik Lebih
daripada 2F Nyata, songsang dan dikecilkan
Kamera Di 2F Nyata, songsang
dan sama saiz dengan objek
Mesin fotostat
Di antara F
dengan 2F Nyata, songsang dan dibesarkan
Projektor slaid dan projektor transparensi Di F Imej terbentuk di infiniti Lampu sorot Kurang
daripada F Maya, tegak dan dibesarkan
Kanta pembesar
Alatan Optik
Kanta digunakan pada peralatan harian seperti kamera, telefon pintar, projektor LCD, cermin mata, kanta pembesar dan CCTV.
Convex and Concave Lenses
1. Convex lenses (converging glases) converge light rays that passes through it.
2. Concave lenses (diverging glasses) diverge light rays that passes through it.
3. The image formed by a convex lens depends on the distance of the object (object distance) from the lens. 4. The characteristics of the image formed by a convex
lens are
(a) virtual or real (b) upright or inverted (c) diminished or magnified
Types of Images and Information on Ray Diagrams
1. A real image is an image that can be formed on a screen where a virtual image is an image that cannot be formed on a screen.
2. Information on a ray diagram:
(a) The object distance is the distance between the object and the optical centre while the image distance is the distance between the images and the optical centre.
(b) The focal point is the point where light rays converge while the focal length is the distance between the optical centre and the focal point (c) The principal axis is a line through the optical
centre of the lens.
(d) The optical centre is the midpoint of the lens.
Image Formation by Concave Lenses and Convex Lenses
1. A concave lens diverges light rays. Characteristics of an image formed are virtual, upright and diminished. 2. An image formed by a convex lens depends on the
object distance. Object
distance Characteristics of the image Optical instrument More
than 2F Real, inverted and diminished (smaller) Camera At 2F Real, inverted and the
same size as the object Photocopy machine Between
F and 2F Real, inverted and magnified Slide projector and overhead projector At F Image is formed at
infinity Spotlight
Less
than F Virtual, upright and magnified Magnifying glass
Optical Instruments
Lenses are used on everyday devices such as cameras, smartphones, LCD projectors, glasses,
magnifying glasses and CCTV. Nota Grafik
BAB
Tarikh:
EKSPERIMEN
INKUIRI
Penemuan Inkuiri PBD7.1
Standard Kandungan7.1 Pembentukan imej oleh kanta
Kanta cembung dan kanta cekung
Convex and concave lenses
Mengkaji ciri-ciri imej yang terbentuk oleh kanta cembung dan kanta cekung bagi objek jauh
To study the characteristics of an image formed by a convex lens and a concave lens for a distant object
Kanta cembung, kanta cekung, pemegang kanta, skrin, pembaris meter Convex lens, concave lens, lens holder, screen, metre rule
1 Sediakan susunan radas seperti yang ditunjukkan dalam rajah.
Set up the apparatus as shown in the diagram.
2 Laraskan skrin sehingga suatu imej yang tajam terbentuk pada skrin. Adjust the screen until a sharp image is
formed on the screen.
3 Rekod pemerhatian anda tentang ciri-ciri imej yang terbentuk.
Record your observation on the characteristics of the image formed. 4 Ulang langkah 2 dan 3 dengan
menggunakan kanta cekung.
Repeat steps 2 and 3 by using a concave lens.
1 Berdasarkan pemerhatian anda, nyatakan ciri-ciri imej yang dibentuk oleh kanta cembung dan kanta cekung bagi objek jauh. TP2
Based on your observation, state the characteristics of the images formed by a convex lens and a concave lens for a distant object.
(a) Kanta cembung/Convex lens:
Nyata, songsang, dikecilkan/Real, inverted, diminished
(b) Kanta cekung/Concave lens:
Maya, tegak, dikecilkan/Virtual, upright, diminished
2 Nyatakan titik tumpuan sinar cahaya yang memberikan imej yang paling tajam. State the point where light rays converge that gives the sharpest image. TP1 Titik fokus/Focal point.
Kanta cembung dan kanta cekung masing-masing menumpu dan mencapahkan
sinar-sinar cahaya yang melaluinya.
Convex and concave lenses converge and diverge respectively light rays that passes through them.
Tujuan Bahan dan Radas Prosedur Pemerhatian Ciri-ciri imej
Characteristics of the image
Jenis kanta
Type of lenses
Cembung
Convex ConcaveCekung
1 Bolehkah imej terbentuk pada skrin? Can an image be formed on the screen?
Boleh
Yes
Tidak boleh
No 2 Adakah imej tegak atau songsang?
Is the image upright or inverted?
Songsang
Inverted
Tegak
Upright 3 Bandingkan saiz imej dengan saiz objek
Compare the size of the image with the size of the object
Lebih kecil/Mengecil
Smaller/Diminished Lebih kecil/MengecilSmaller/Diminished
Perbincangan Kesimpulan Tingkap Window Skrin Screen Pemegang kanta Lens holder Kanta cembung Convex lens
BAB
7
Buku teks m/s 202 – 209Tarikh:
EKSPERIMEN
INKUIRI
PenemuanInkuiri
PBD
7.2
Panjang fokus kanta cembung
The focal length of a convex lens2002 BHG. C, S1(a) & (b) 2008 BHG. A, S2 2009 BHG. C, S10
Menentukan panjang fokus kanta cembung K1PP1
To determine the focal length of a convex lens
Pembaris meter, skrin putih, kanta cembung tebal dan nipis, pemegang kanta K1PP4
Metre rule, white screen, thick and thin convex lenses, lens holder
Kanta cembung
Convex lens
Pemegang kanta
Lens holder
Sinar cahaya dari objek jauh
Light rays from a distant object Skrin Screen
Pembaris meter/Metre rule Panjang fokus/Focal length
K2PP4 1 Sediakan susunan radas seperti yang ditunjukkan dalam rajah.
Set up the apparatus as shown in the diagram.
2 Letakkan satu kanta cembung tebal pada pemegang kanta. Place a thick convex lens on a lens holder.
3 Letakkan kanta cembung itu di hadapan satu skrin putih. Place the convex lens in front of a white screen.
4 Arahkan kanta itu pada suatu objek jauh./Direct the lens at a distant object. 5 Laraskan skrin supaya satu imej yang tajam terbentuk.
Adjust the screen so that a sharp image is formed. 6 Ukur jarak antara kanta cembung dengan skrin (imej).
Measure the distance between the convex lens and the screen (image). 7 Ulang langkah 2 hingga 6 dengan menggunakan kanta cembung nipis.
Repeat steps 2 to 6 by using a thin convex lens.
(Jawapan murid/Student’s answer) 1 Nyatakan satu inferens berdasarkan pemerhatian bagi aktiviti ini. TP2
State one inference based on the observation for this activity.
Kanta cembung yang lebih tebal mempunyai panjang fokus yang lebih pendek . The thicker convex lens has a shorter focal length.
2 Nyatakan hubungan antara ketebalan kanta cembung dengan panjang fokusnya. TP2
State the relationship between the thickness of the convex lens and its focal length. Semakin tebal kanta cembung, semakin pendek panjang fokusnya.
The thicker the convex lens, the shorter its focal length.
Kanta cembung tebal mempunyai panjang fokus yang pendek manakala kanta cembung nipis mempunyai panjang fokus yang panjang .
A thick convex lens has a short focal length while a thin convex lens has a long focal length.
Tujuan Bahan dan Radas Prosedur
Ketebalan kanta cembung
Thickness of the convex lens Panjang fokus (cm)Focal length (cm)
Kanta cembung tebal/Thick convex lens 15
Kanta cembung nipis/Thin convex lens 20
Keputusan Perbincangan Kesimpulan Praktis Kendiri
BAB
7
Buku teks m/s 202 – 209Tarikh:
AKTIVITI
PERBINCANGAN
MasteriPBD
7.3
Gambar rajah sinar bagi kanta cembung dan kanta cekung
The ray diagrams for convex and concave lenses1 Label bahagian-bahagian gambar rajah sinar bagi kanta cembung dan kanta cekung. TP1
Label the parts of the ray diagrams for a convex lens and a concave lens. Paksi kanta Axis of lens Titik fokus Focal point Pusat optik Optical centre Panjang fokus Focal length Paksi utama Principle axis F F (b) (c) (d) (a) Paksi utama Principle axis Paksi kanta Axis of lense Panjang fokus Focal length Titik fokus Focal point
Kanta cembung/Convex lens
F F (b) (c) (a) Pusat optik Optical centre Paksi utama Principle axis Panjang fokus Focal length Kanta cekung/Concave lens
2 Rajah di bawah menunjukkan suatu aktiviti untuk mengkaji pembentukan imej oleh kanta cekung. The diagram below shows an activity to study the formation of an image by a concave lens.
Video
2F F F 2F
(c) Nyatakan tiga ciri imej yang terbentuk./State three characteristics of the image formed. TP1 Maya, tegak dan dikecilkan/Virtual, upright and diminished
2013 BHG. C, S11(b)(iii) & (iv)
3 Lukiskan gambar rajah sinar bagi imej yang terbentuk oleh kanta cembung bagi jarak objek yang berbeza. Ukur saiz imej dan nyatakan ciri-ciri imej serta alatan optik yang mengaplikasikan prinsip itu./Draw ray diagrams for the images formed by convex lenses at different object distances. Measure the size of the images and state the characteristics and the optical instruments that apply the principles.
TP2
(* Saiz objek/Object size = 1 cm, F = Titik fokus/Focal point)
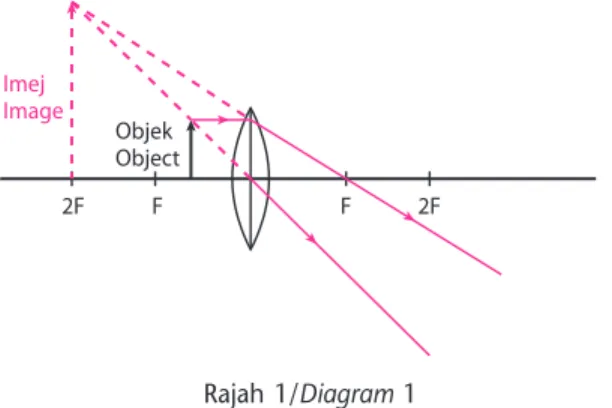
(a) Objek terletak lebih daripada 2F/Object is positioned at more than 2F
(i) Saiz imej/Image size
= 0.6 cm
(ii) Ciri-ciri imej:
Characteristics of the image
Nyata, songsang dan dikecilkan
Real, inverted and diminished (iii) Alatan optik:
Optical instrument: Kamera/Camera objek object 2F F F 2F imej image
(a) Lengkapkan rajah di sebelah untuk menun jukkan pembentukan imej. TP3/KBAT
Complete the diagram on the left to show the formation of the image.
(b) Ukur dan tulis/Measure and write down TP3/KBAT (i) saiz imej/the size of the image,
0.4 ± 0.1 cm
(ii) jarak imej/the distance of the image.
1.1 ± 0.1 cm
Buku teks m/s 202 – 209
BAB
(b) Objek terletak di 2F/Object is positioned at 2F
(i) Saiz imej/Image size
= 1.0 cm
(ii) Ciri-ciri imej:
Characteristics of image:
Nyata, songsang dan sama saiz seperti objek/Real, inverted
and same size as the object (iii) Alatan optik
Optical instrument:
Mesin fotostat
Photocopy machine (c) Objek terletak antara F dengan 2F/Object is positioned between F and 2F
(i) Saiz imej/Image size
= 2.0 cm
(ii) Ciri-ciri imej:
Characteristics of image:
Nyata, songsang dan dibesarkan
Real, inverted and magnified (iii) Alatan optik
Optical instrument:
Projektor slaid/Slide projector
(d) Objek terletak di F/Object is positioned at F
(i) Imej terbentuk di
infiniti
Image is formed at infinity (ii) Ciri-ciri imej:
Characteristics of image
Maya, tegak dan dibesarkan
Virtual, upright and magnified (iii) Alatan optik
Optical instrument:
Lampu sorot/Spotlight
(e) Objek terletak kurang daripada F/Object is positioned at less than F
(i) Saiz imej/Image size
= 3.0 cm
(ii) Ciri-ciri imej:
Characteristics of image
Maya, tegak dan dibesarkan
Virtual, upright and magnified (iii) Alatan optik
Optical instrument: Kanta pembesar Magnifying glass Objek Object 2F F F 2F imej image Objek Object 2F 2F F F imej image Objek Object 2F 2F F F Objek Object 2F 2F F F imej image Praktis Kendiri
BAB
7
Berdasarkan alatan optik dan gambar rajah sinar (jika ada) yang diberikan, jawab soalan-soalan yang berikut./Based on the given optical instrumens and ray diagrams (if any), answer the following questions. TP2
1 Mikroskop/Microscope
Kaji rajah sinar bagi pembentukan imej oleh mikroskop di atas dan jawab soalan-soalan yang berikut. Study the ray diagram for the formation of the image by the microscope above and answer the following questions.
(a) Tandakan ( ✓ ) kanta yang mempunyai jarak fokus yang lebih panjang. Tick ( ✓ ) the lens which has a longer focal length.
✓ Kanta mata
Eyepiece Kanta objekObjective lens
(b) Tandakan ( ✓ ) ciri-ciri imej akhir yang terbentuk, seperti yang diperhatikan oleh pemerhati. Tick ( ✓ ) the characteristics of the final image formed, as seen by an observer.
✓ Dibesarkan
Magnified ✓ SongsangInverted NyataReal DikecilkanDiminished ✓ MayaVirtual 2 Teleskop/Telescope
Kaji rajah sinar bagi pembentukan imej oleh teleskop di atas dan jawab soalan-soalan yang berikut. Study the ray diagram for the formation of the image by the telescope above and answer the following questions.
(a) Tandakan ( ✓ ) kanta yang mempunyai panjang fokus yang lebih panjang. Tick ( ✓ ) the lens which has a longer focal length.
Kanta mata/Eyepiece ✓ Kanta objek/Objective lens
(b) Tandakan ( ✓ ) ciri-ciri imej akhir yang terbentuk, seperti yang diperhatikan oleh pemerhati. Tick ( ✓ ) the characteristics of the final image formed, as seen by an observer.
✓ Dibesarkan
Magnified ✓ SongsangInverted NyataReal DikecilkanDiminished ✓ MayaVirtual
Tarikh:
AKTIVITI
PERBINCANGAN
7.4
Standard Kandungan 7.2 Peralatan optikPeralatan optik
Optical instruments Kontekstual
PBD Objek Object Imej akhir Final image Kanta objek Objective lens Kanta mata Eyepiece Pemerhati Observer Fo Fo Fe Fe
Fo= Titik fokus kanta objek
Focal point of objective lens
Fe= Titik fokus kanta mata
Focal point of eyepiece
Pemerhati Observer Imej akhir Final image Kanta objek Objective lens Sinar cahaya dari objek jauh
Light rays from distant object Kanta mata Eyepiece Fe Fe Fo
Fo = Titik fokus kanta objek
Focal point of objective lens
Fe = Titik fokus kanta mata
Focal point of eyepiece
Buku teks m/s 210 – 215
BAB
Tarikh:
AKTIVITI
PERBINCANGAN
KontekstualPBD
7.5
Aplikasi kanta dalam peralatan optik
Application of lenses in optical instrumentsLengkapkan ruang tentang aplikasi kanta dalam peralatan optik. TP2
Complete the spaces about the application of lenses in optical instruments. Membetulkan
Corrects MemfokusFocuses PengawasanSurveillance MemantauMonitor MemaparkanDisplay KedudukanPosition DibesarkanEnlarges 1 Kamera dan kamera telefon pintar
Camera and smartphone camera
Memfokus cahaya yang terpantul dari suatu objek. Focuses the light reflected from an object.
2 Spectacles
Cermin mata
Membetulkan kecacatan penglihatan mata.
Corrects the eye defects.
3 Televisyen litar tertutup
Closed circuit television, CCTV
Membolehkan penggunaan kamera video untuk
memantau harta benda.
Allows the use of videos cameras to monitor the property.
4 Kanta pembesar
Magnifying glass
Membesarkan imej objek. Enlarges the image of an object 5 Kamera perisik Spy camera Terutamanya digunakan untuk aktiviti pengawasan .
Mainly used for
surveillance activities. 6 Projektor LCD dan slaid
LCD and slide projectors
Memaparkan video, gambar atau data komputer pada layar atau permukaan rata yang lain.
Display video, images or computer data on a screen or other flat surface.
7 Mesin fotostat
Photocopy machine
Membuat salinan dokumen berbeza saiz dengan menyelaraskan
kedudukan kanta,
Make copies of documents of different sizes by adjusting the position of the lens,
8 Projektor transparensi
Overhead projector
Menggunakan cahaya untuk mempamerkan gambar yang
dibesarkan pada skrin.
Uses light to project an enlarged image on a screen.
Buku teks m/s 210 – 215
BAB
Kertas 1
PRAKTIS PENGUKUHAN 7
SPM
Arahan: Setiap soalan diikuti oleh empat pilihan jawapan, A, B, C dan D. Pilih jawapan yang terbaik. Instructions: Each question is followed by four options A, B, C and D. Choose the best answer.
1 Rajah 1 menunjukkan pem ben tukan imej oleh kanta cembung. Antara kedudukan objek A, B, C dan D, yang manakah akan menghasilkan imej yang lebih kecil daripada objek?
Diagram 1 shows the formation of an image by a convex lens. At which position, A, B, C or D, should the object be placed to produce an image that is smaller than the object?
B C D
2F F F 2F
A
Rajah 1/Diagram 1
KLON SPM2010/2013
2 Rajah 2 menunjukkan satu gambar rajah sinar.
Diagram 2 shows a ray diagram.
Rajah 2/Diagram 2
Antara yang berikut, yang mana kah merupakan ciriciri imej yang terbentuk?
Which of the following are the characteristics of the image formed?
A Nyata dan tegak Real and upright
B Maya dan tegak Virtual and upright
C Nyata dan songsang Real and inverted
D Nyata dan lebih kecil dari pada objek
Real and smaller than the object KLON SPM2000/2012
3 Berikut menunjukkan ciriciri imej yang terbentuk oleh suatu objek. KBAT Objek Object 2F 2F F F
The following shows the characteristics of an image formed by an object.
• Maya/Virtual • Tegak/Upright
• Dikecilkan/Diminished
Apakah objek itu? What is the object?
A Cermin satah Plane mirror B Prisma Prism C Kanta cembung Convex lens D Kanta cekung Concave lens
4 Antara yang berikut, yang manakah kedudukan objek untuk membolehkan suatu kanta cembung bertindak sebagai kanta pembesar?
Which of the following is the position of the object to enable a convex lens to act as a magnifying glass?
A Kurang daripada panjang fokus
Less than the focal length
B Sama dengan panjang fokus The same as the focal length
C Dua kali panjang fokus Twice the focal length
D Antara panjang fokus dengan dua kali panjang fokus
Between the focal length and twice the focal length
KLON SPM2004/2007
5 Rajah 3 menunjukkan su sunan radas untuk mengkaji pembentukan imej oleh kanta cembung.
Diagram 3 shows the arrangement of apparatus to study the formation of image by a convex lens.
Rajah 3/Diagram 3
Antara kedudukan A, B, C, dan D, di manakah suatu objek perlu diletak untuk membolehkan projektor slaid berfungsi?
At which of the positions, A, B, C or D, should an object be placed to enable a slide projector to function?
6 Imej yang terbentuk pada skrin putih dalam Rajah 4 adalah nyata, songsang, dan mengecil. The image formed on the white screen in Diagram 4 is real, inverted and diminished.
Rajah 4/Diagram 4
Apakah yang berlaku pada imej pada skrin jika lilin dialihkan ke kedudukan X?
What happens to the image on the screen if the candle is moved to position X?
A Imej menjadi lebih besar. The image becomes bigger.
B Imej menjadi lebih kecil. The image becomes smaller.
C Imej maya dan tegak terbentuk.
The image formed is virtual and upright.
D Tiada imej terbentuk pada skrin.
No image is formed on the screen. Kanta cembung Convex lens 2F F A B C D X Skrinputih White screen F 2F
BAB
7
Kertas 2
Arahan: Jawab semua soalan. Instructions: Answer all the questions.
Bahagian B/Section B
1 Rajah 1 menunjukkan aktiviti untuk mengkaji pembentukan imej oleh suatu kanta cembung.
Diagram 1 shows an activity to study the formation of an image by a convex lens. KLON SPM2006 BHG. A, S2
Rajah 1/Diagram 1
(a) Lukiskan rajah sinar bagi pembentukan imej pada Rajah 1.
Draw the ray diagram for the formation of the image in Diagram 1. [2 markah/2 marks] (b) Ukur jarak imej./Measure the distance of the image.
2.1 ± 0.1 cm
[1 markah/1 mark] (c) Nyatakan tiga ciri imej yang terbentuk./State three characteristics of the image formed.
Maya, tegak dan lebih besar daripada objek/ Virtual, upright and larger than the object
[3 markah/3 marks] (d) Nyatakan satu alatan optik yang objeknya diletakkan pada kedudukan seperti yang
ditunjukkan dalam Rajah 1.
State one optical instrument whose object is located at the position as shown in Diagram 1.
Kanta pembesar/Magnifying glass
[1 markah/1 mark]
Bahagian C/Section C
2 Kaji pernyataan berikut./Study the following statement.
Cermin mata orang tua mempunyai panjang fokus yang lebih pendek daripada cermin mata seorang dewasa yang rabun dekat. Hal ini demikian kerana kanta cermin mata mereka mempunyai ketebalan yang berbeza. The spectacles of old people have shorter focal lengths than those of an adult who is long-sighted. This is because the lenses in their spectacles have a different thickness.
(a) Nyatakan satu pernyataan masalah daripada maklumat di atas.
State one problem statement from the above information. [1 markah/1 mark] (b) Cadangkan satu hipotesis untuk menyiasat pernyataan di atas.
Suggest one hypothesis to investigate the above statement. [1 markah/1 mark] (c) Berdasarkan pernyataan yang diberi, reka bentuk satu eksperimen makmal untuk menguji hipotesis anda
dengan menggunakan kanta pelbagai ketebalan.
Based on the given statement, design a laboratory experiment to test your hypothesis by using lenses with different thickness.
Huraian anda harus mengandungi aspekaspek berikut: Your description should include the following aspects:
(i) Tujuan eksperimen/Aim of the experiment [1 markah/1 mark] (ii) Mengenal pasti pemboleh ubah/Identification of variables [2 markah/2 marks] (iii) Prosedur atau kaedah/Procedure or method [4 markah/4 marks] (iv) Penjadualan data/Tabulation of data [1 markah/1 mark]
2F F F 2F Objek Object Imej Image Praktis SPM