10/17/2016
Daftar Isi
http://widyasaripress.com/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=774:daftarisi&catid=92:vol18no1jurnalmaret2016&Itemid=2
1/2
Widya Sari Press
cari...
Daftar Isi
Ditulis oleh Administrator Jumat, 22 April 2016 07:02
Widya Sari
Jurnal Ilmiah Pendidikan, Sejarah dan Sosial Budaya
(Kerjasama Widya Sari Press Salatiga dengan Progdi Sejarah FKIP, UKSW, Salatiga)www.widyasaripress.com
Vol. 18 No. 1, Maret 2016
Hubungan Antara Motivasi Belajar Dengan Hasil Belajar Matematika 1 7 Siswa Kelas VIII SMP Negeri 2 Tuntang Tahun Ajaran 2015/2016 Anita Sari, Sutriyono, Tri Nova Hasti Yunianta
Upaya Meningkatkan Hasil Belajar PKn Materi Keutuhan 8 15 Negara Kesatuan Republik Indonesia Melalui Model Pembelajaran
Problem Based Learning Pada Siswa Kelas 5 Sekolah Dasar Negeri 02 Paseban Kecamatan Jumapolo Kabupaten Karanganyar
Semester I Tahun Pelajaran 2015/2016 Rohtri Rahayu
Peningkatan Aktivitas Dan Hasil Belajar Siswa Materi Gaya 16 25 Melalui Permainan Loop Cards Pada Siswa Kelas V SD Negeri Sukoharjo 04 Semester II Tahun Pelajaran 2013/2014
Sri Haryani
Pengaruh Bahasa Gaul (Prokem) Terhadap Keberadaan Bahasa Indonesia 26 39 Untuk Meningkatkan Kemampuan Asertif Pada Anak Kelompok B Semester 2 TK Desa Nguter 02 Kecamatan Nguter Tahun Pelajaran 2014/2015 Dwi Supraptiwi
Penerapan Teknik Jigsaw Dalam Meningkatkan Kemampuan Menulis Puisi 40 48 Bagi Siswa Kelas V Semester I Sekolah Dasar Kedungjeruk
Tahun Ajaran 2014/2015 Hartono
Peningkatan Kemampuan Mengarang Melalui Model Pembelajaran 49 57 Picture and Picture Siswa Kelas IV SD Negeri Dalangan 01
Semester II Tahun Pelajaran 2014/2015 Ismadi
Upaya Peningkatan Ketrampilan Guru 58 65
Dalam Membuka Dan Menutup Pembelajaran Bagi Guru SD Negeri I Senggrong Kecamatan Andong Kabupaten Boyolali Melalui Supervisi Klinis
Pada Semester I Tahun Ajaran 2015/2016 Endah Sarwati
Upaya Meningkatkan Pembelajaran Pendidikan Kewarganegaraan 66 71 Melalui Penerapan Model Pembelajaran Cooperative Script Kelas IV SD Negeri Mertan 01 Semester I Tahun Pelajaran 2015/2016
10/17/2016
FROM COMMON READING TO CREATIVE READING
http://widyasaripress.com/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=756:fromcommonreadingtocreativereading&catid=92:vol18no1jurnal… 1/4
Widya Sari Press
cari...
FROM COMMON READING TO CREATIVE READING
Ditulis oleh Administrator Jumat, 22 April 2016 06:52
FROM COMMON READING TO CREATIVE READING:
AN ICTBASED ELL MODEL DEVELOPMENT
Mozes Kurniawan Faculty of Teacher Training and Education Satya Wacana Christian University ABSTRAKJurnal ini mengkaji mengenai kendalakendala yang dihadapi guru dan siswa dalam Pembelajaran Bahasa Inggris (ELL) terkait dengan penggunaan TIK, peran teknologi animasi dalam meningkatkan pemahaman siswa terhadap bacaan berbahasa Inggris dan pengembangan model pembelajaran kreatif inovatif integrasi antara materi bacaan dalam ELL dan teknologi animasi. Metode penelitian yang digunakan yaitu Research and Development (R&D) dengan pendekatan studi kasus di SMP Kristen Satya Wacana (Laboratorium) Salatiga sebagai sekolah berteknologi mutakhir. Responden penelitian ini sebanyak 36 orang terdiri dari seorang kepala sekolah, lima orang guru Bahasa Inggris dan 30 siswa. Sebagai sekolah dengan predikat �berteknologi mutakhir�, SMP Lab Salatiga tentunya perlu menerapkan pembelajaran Bahasa Inggris berbasis TIK dengan maksimal. Namun, kenyataannya masih banyak kendala yang dihadapi oleh guru dan siswa terkait dengan penggunaan TIK dalam materi bacaan ELL, kendalakendala penggunaan teknologi dalam pembelajaran, model pembelajaran yang belum kreatif inovatif, dan kompetensi guru dalam menggunakan TIK yang masih kurang. Oleh karena itu, jurnal ini dibuat melalui beberapa tahapan Penelitian dan Pengembangan Borg & Gall (1989) guna mengembangkan model pembelajaran ELL berbasis TIK yang bernama Creative Reading. Kata Kunci: Creative Reading, Model Pembelajaran, Strategi Membaca Pemahaman Bacaan, Pembelajaran Bahasa Inggris INTRODUCTION Globalization is, recently, marked by the development of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) (Zhu, 2003 in Sims et al., 2011) that can help humans to do their activities in almost all aspects of life. ICT plays important role in economic world, politic secment, social life and also education. The implementation of ICT in education is not a new thing. Indonesia, particularly, implements ICT in education addressed to improve the way educational practitioners provide, develop and optimatize educational resourses in order to gain a high quality of education. The development of technology, basically, brings additional values in producing a better education compare to decades before where technology has not been implemented. In a research journal, Munir (2009:2) stated that ICT in education was defined as three things, such as: 1) ICT as a Tools, a hardware used to support teaching learning process; 2) ICT as a Content, technology used within teaching learning materials as additional values for the content of them; 3) ICT as a Program Application, program applications used in tecahing learning process and used to create ICT as a Content. In this journal, ICT as a Content becomes the major point to discuss apart from the other two. ICT as a Content is a way where teaching learning process can be combined by additional materials like computer system or results of program appliction in designing teaching learning materials, the inovation of computer usage to make teachers teach students easily and to make students access teachers� material fast without any difficulties. In line with the previous statement, Bhvard (2009:2) brought the idea that technology provided various options that can be used not only to make education more interesting but also to make it effective, eficient and productive in developing students� skill and ability. One of the technologies is animation which is a motion effect from pictures that can be added by sound and accessed by using television, computer and other digital tools (Webopedia, 2013). This kind of technology is so widely spread and enthused until this 21st century. Education is also using this kind of technology as a compliment in developing teaching
materials. This technology can be applied in many subjects or courses like Mathematics, Physics, Art, English Language and etc. This journal is discussing technological issues in English Language education especially in reading comprehension which usually uses convetional system (using too much handout, work sheets, supporting paperbased instruments) as its problematic teaching learning method.
Knuth & Jones (1991, in Chapel Hill, 2013) stated that reading is a basic language skill whose difficulty is quite high so there appears an idea to integrate animation technology in English reading comprehension. The integration is expected to improve students� reading comprehension and become foundation of a creative innovative learning model development. In reading comprehension, students may find some problems such as: difficulties in understanding text, the improper use of reading strategies, insufficient teacher guidance to have a good reading habit, etc (Biancarosa & Griffith, 2012:142143). Here, animation technology can play an important role in improving students� English reading comprehension through attractive creative presentation.
In one hand, this kind of technology brings positive contribution to students� English reading comprehension. In the other hand, teachers still get confused of what to do in managing teaching material integrated with animation technolog. They find it difficult since the material development management in some schools have not been optimally developed (Adman, 2005).
10/17/2016
FROM COMMON READING TO CREATIVE READING
http://widyasaripress.com/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=756:fromcommonreadingtocreativereading&catid=92:vol18no1jurnal… 2/4
In other word, teachers need to know, create and implement a creative innovatve learning model in order to have a understandable teaching/education so the aims of the course will be achieved. This background brings an idea of ICTbased English Language Learning (ELL) model development. This journal used Sekolah Menengah Pertama (SMP) Kristen Satya Wacana (Laboratorium) it will later be stated as SMP Lab Salatiga as the object of research. This junior high school was known as a school using ICT since 1985 and the first junior high school in Salatiga that implemented sophisticated technology, i.e. 30 units of personal computer with Intel Processor (the most uptodate processor in its time). By knowing that facts, preresearch was conducted to check and gather additional information related to the use of ICT in ELL. Then, by having a sufficient background data, a learning model will be developed to help teachers to have a creative innovative English reading comprehension lesson.The result of preresearch stated that from two high school (junior and senior) under Satya Wacana Christian University Foundation, there were a big difference of ICT usage by teachers in ELL. In one academic year (two semesters) there were 21 studentteachers teaching English in those schools but only 9 studentteachers (42.9%) that used technology in ELL. The other 57.1% were still using conventional learning model and most of them were studentteacher in SMP Lab. From that background, this journal takes some research question guiding this research, such as: 1) In what extents, teachers find difficulties in ELL related to the use of ICT? 2) What are the roles of animation technology in improving English reading comprehension? 3) What learning model does SMP Lab�s ELL need? The main purpose of this journal is to develop a creative attractive learning model in ELL (reading comprehension).
ANIMATION TECHNOLOGY FOR EDUCATION
The term �technology� refers to the use of animation to make human activities easier in economic, social, media and educational area. Lee (2013), simply, stated that animation is a way to make movement objects. The idea of animation is also as a picture movement created from sequences of inanimate position and made alive by arranging the position in such a movement. Animation technology consists of animation clips which made by cutting film into shorter pieces whose duration is not more than 10 minutes (Stiviani & Hayati, 2011). Though animation can be seen from the arrangement of drawings as briefly outlined above, but also it can be such an animated movement of scratch/painting called by cartoon. There are also some aspects to understand related to the animation technology such as: users (those who use the technology), visual effect (pictures presented by the technology) and suggestion effect (intersting and attracting point from the technology usage). In education field, learning presented with pictures and cartoons (graphics or cinema) will enhance the understanding and knowledge of each word associated with pictures or cartoons. This happens because the animation can be a creative media and attract the attention of students. Besides, the animation will help students in improving personal understanding (Setiawan, 2011) and that is flexible (Agina, 2013). It is also supported by the results of research by Agina (2013), in International Journals, Oracle Think Quest, stated that students used animation technology in teaching learning process captures the lessons much more quickly. LEARNING MODEL DEVELOPMENT IN ENGLISH READING COMPREHENSION As noted earlier that animation technology in education really brings good in the various fields of knowledge/lessons. Similarly, in the ELL particularly on reading comprehension, animation technology has a special role. Agina (2013) stated the merits of the application of technology in learning.
�Interactive learning with liveaction animation, simulation, video, audio, graphics, �. keep learners interested and reinforces skills. Because it is exciting, challenging, and fun to use, it encourages learners to return to � again and again and again over! ...�
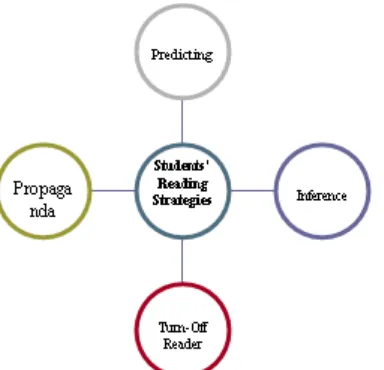
However, in understanding a reading passage, especially in English, there are problems that may occur. Hidayat (2009) and Widyaiswara (No Year) similarly states that there are many obstacles that often happens to students in reading comprehension, like students� behavior like students� passive, fear of exploring ideas, ignoring the lesson, etc as what Ling (2004) stated. �My students often told me that they refused to participate in classroom activities because they were afraid ... �. Students can behave as one of them because of the conventional learning system where teachers use many papers, ask students to read and answer questions from the reading given without any ice breakers such as games, stories, supporting pictures and/or animation that makes students feel comfortable with the material provided. Cultural differences, environmental conditions and psychological condition of students also influence the process of students' understanding of the material presented. In other words, there are three categories of general constraints. Teachers and their incompetence, students with learning model given by teacher and infrastructure management in teaching learning process. Actually, these obstacles can be overcome by students with strategies they have but when students are faced with the conventional learning systems too intensively, they can not develop their strategies well. Students are able to do 1) Predicting and Anticipating, by predicting the sense of every word and reading in general; 2) Inference, by reading the whole passage and then take a conclusion; 3) TurnOff Reader, which is skipping strategy in reading that keep the meaning intact in reading process; and 4) Propaganda Technique, in which students directed their understanding on specific things that students want to know from the literature that exists (Kristono & Sensenig, 2010). Such strategies can be developed if there is an integration between animation technology that gives a clue to develop students� background knowledge and students� critical thinking. Some aspects of English reading comprehension presented in ELL process are text type, language feature, vocabulary and question following the readings. Those aspects may be influenced by problems if students� reading strategies are not developed well. Therefore, in this journal, a learning model is developed associated with those strategies in learning and the ways in which organized and thought well to answer the purpose or intent of ELL (Widdiharto, 2004). The integration between English reading materials and animation technology later called by Creative Reading learning model. METHOD This Journal uses Research and Development (R&D) method. This method explores potentials and problems as the basis for the development of a learning model and then through several stages there will be a hypothetical model that can be used as an alternative in developiing a better learning to achieve the goal of education. This research uses stages one Research Analysis up to seven Revision of Final Product (Borg & Gall, 1989). The approach used is a case study in which the issues were investigated regarding the predicate of SMP Lab Salatiga as a hightech school that exclusively be the object of the research.
In general, the design of the study in this journal is the stage from the problem faced by students, that were about to look for a solution through teaching learning management, as shown in Figure 2 combined with stages of research and development by Borg & Gall (1989).
In this paper there are 36 people as the respondents where 30 people are students (S), 5 teachers (teachers/T, studentteacher/ST) and the principal in SMP Lab Salatiga. Then, through the respondents, the data can be obtained by using several insrumens like: OpenEnded Questionnaire for students, Focused Group Discussion (FGD) for teachers, studentteacher and principals, and SemiStructured Interview for deepening further data. Analysis is made by Coding/Categorization.
10/17/2016
FROM COMMON READING TO CREATIVE READING
http://widyasaripress.com/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=756:fromcommonreadingtocreativereading&catid=92:vol18no1jurnal… 3/4
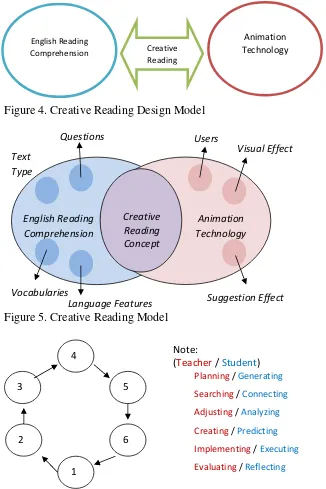
Creative Reading learning model, a Preliminary Product Development (stage three) as presented in Figure 4 which is the initial model prior to process validation, revision and testing. The model was then validated by two practitioners as R&D�s stage four before the field test. The practitioners are experts in fields related to the production of model design. Lany Kristono, M.Hum is a practitioner in the field of English who have been teaching in reading comprehension for years. While, Michael Bezaleel Wenas, S.Kom, M.Cs is practitioner who develop knowledge in the field of technology particularly in multimedia and animation. Both are active lecturer at the Satya Wacana Christian University Salatiga which validates the design of existing models. The validation discovered several weaknesses. In general, the weaknesses were concised into one big ideas about the understanding of the model design that was less clear. It was not clear enough because there was no actual parts to understand by the user in designing teaching learning process using this model. Therefore, the Creative Reading model changed into more detail (stage five Revision of the Prototype) as presented in Figure 5 and it was ready to be tested in the main field. RESULT AND DISCUSSION In accordance with the results of the data collection from 30 students, it was known that the frequency of the use of technology in SMP Lab was still unstable or not all the teachers in the English course (are able to) use animation technology, particularly in supporting students' reading comprehension. Those 28 (93.3%) out of 30 students stated that the use of ICT in ELL was only sometimes two to five times a month compare to the whole facetofface meeting per month. One (3:33%) student said that teacher rarely below two times a month used ICT and another one (3:33%) said often more than five times a month. Those statement was supported by the opinion of some students regarding the reliability (English teacher expertise) in technology in the delivery of lessons. "... sometimes there are teachers who can not" (S7)... not all use it ... there is also a proficient (S14)... � "... having idea to use it but I can not make by my own, I usually copy and paste. The time management is also not good ...� (T1) Factors affecting the frequency of technology usage was also the unqualified teachers in using the type of technology. Because the process of preparation to the delivery of learning can be creatively designed by the teachers according to the theme and standard of facilities and infrastructure, learning tends to be done according to the capabilities and reliability of the teachers. Thus, there was some factors affecting the frequency in term of teacher�s age, learning model usage and capability of using ICT in ELL. FROM COMMON READING TO CREATIVE READING It is known that in English reading comprehension found many obstacles in terms of teachers and their competence. SMP Lab�s teachers were indicated not having optimum competence in the use of animation technology in ELL. Students with learning model applied also found some difficulties because students tend to get bored, sleepy and lose their interest in the material presented by conventional learning systems. From conventional learning systems, it was obtained various constraints faced by students which if they ignored them, it would interfere their achievement of learning objectives that exist. Such exposure was derived from observation of the application of the conventional learning systems in English reading comprehension before the technology was applied in student reading materials.Then, Creative Reading learning model was tried by integrating reading materials and animations into ELL (particularly in English reading comprehension). After the model tried in the main field (stage six Main Field Test), there was found that difference between students who read with conventional learning model and those with Creative Reading models existed. Students with conventional learning models tend to have constraints that far more than those who read with animation technology. Students felt comfortable when they learned English using animation technology. They could develop their understandng of the text given by using reading strategies they have supported with clues from tthe animated pictures in the reading passage. They also did not get bored, sleepy but were awake and anthusiastic.
� ... sometimes I imagined how the plot will be. So, It was easy for me to understand... by using animation, I felt so anthusiastic and it was effective because the animated pictures (design) will attract students and they will develop their imagination...� (S2)
However, after applying Creative Reading learning model, a confusion experienced by teachers was found in understanding the model especially in applying the model from teaching preparation until the learning process. Some student teachers who want to develop learning material with such model did not understand how to get started building the creative material. Some them also asked the stages in applying Creative Reading model into ELL. From those confusion and statement of evaluation, there was an input to revise the previous model that has been established in which the model contained only the concept of integrating ELL materials (including its components) and animation technology (including its components).
After product trial, i.e. Creative Reading model in ELL process, it was revised (stage seven Revision of theFinal Product) by adding some stages in deploying the model into teaching learning process. It was found from problems of the research that in applying learning model, there were several steps to run. Those stages are divided into two such as teachers preparation steps and students� learning steps.
For teachers, there are six stages in the preparation of teaching materials related to the Creative Reading model. First, planning, where teachers plan what are to be taught, what objectives to be achieved in the learning sessions. Second, searching, a stage where teachers find material or adopted suitable teaching material that exixt. The third stage is adjusting, where teachers adjust the material obtained in accordance with the concepts and learning models that exist. Next is creating teaching material. Having created the teaching material, teachers are now able to apply (implementing) it in ELL. The last stage is evaluating, where the teaching materials that have been used for teaching evaluated to find error and/or any improper things. Then, the stages continues from one to six into a cycle.
For students, there are also six stages in learning process where Creative Reading was applied. First, generating their background knowledge (knowledge that exixted) to understand the reading that is integrated with animation as a clue, stimulate their attention and interest to read. Furthermore, linking them with the knowledge of the existing readings to gain understanding. Once they are able to connect their knowledge, they start to analyze whether their understanding obtained are correct in accordance with the true meaning of the passage. The next stage is predicting. Students are, then, executing what they have learned. Here, students predict their learning outcomes. It will be a good learning input for students to reflect. The last stage is reflecting, where students recall the learning process from the very begining until they have understood the material presented. This reflection is used to develop students� self learning for what they have not been achieved. Similarly, this stages continues as a cycle.
From cycle of stages encountered in the implementation of Creative Reading learning models, a model which previously formed added by those stages of teaching and learning becomes a new Creative Reading revised from previous models. Figure 7 is the revised Creative Reading model after product trial
CONCLUSSION
From the research above, there are some points as the conclussion. Those are stated as follows:
1. In English Language Learning (ELL) especially in English reading comprehension, there were some obstacles found by
10/17/2016
FROM COMMON READING TO CREATIVE READING
http://widyasaripress.com/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=756:fromcommonreadingtocreativereading&catid=92:vol18no1jurnal… 4/4
habit. For teacher, they still used conventional learning model where hand out are given too much, many work sheets and they do not give attraction to the student, they do not master technology (technology is potential to attract students). Those extents brings difficulties in ELL related to the use of ICT.2. Animation Technology plays important role in ELL process. Beside becoming an attractive learning source, it can stimulate
students reading strategy. Students are able to improve their strategies such as: Predicting and Anticipating, Inference, TurnOff Reader, and Propaganda Technique in understanding reading passage.
3. Creative Reading learning model are developed by integrating English reading comprehension aspects such as: text type,
language feature, vocabulary and question following the readings and animation technology whose aspects are users (those who use technology), visual effect (pictures presented by the technology) and suggestion effect (intersting and attracting point from the technology usage). The model, then, revised by adding stages of teacher teaching from Planning, Searching, Adjusting, Creating, Implementing and Evaluating and stages of students learning such as: Generating, Connecting, Analyzing, Predicting, Executing and Reflecting
REFERENCE
Adman. 2005. Manajemen Pendidikan Nasional: Strategi dan Upaya menghadapi Tantangan Globalisasi melalui Pendidikan. Jurnal Edukatif UPI. Vol.1, No.1, 2005.
Agina, A. M. 2013. Animation in Education Oracle Think Quest: Education Foundation. Retrieved from:
http://library.thinkquest.org/05aug/00066/content_education.html
Bhavard, R. 2009. Audiovideo Aids in Teaching English. English Language Teaching Weekly. Issue No.6.
Biancarosa, G. & Griffith, G.G. 2012. Technology Tools to Support Reading in the Digital Age. The Future of Children Journal, Vol. 22, No. 2.
Borg, W., & Gall, M. (1989). Educational research: An introduction (5th ed.). White Plains, NY: Longman
Hidayat. 2009. Identifikasi Hambatan Perkembangan Belajar Dan Pembelajarannya. FIP: Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia Hill, Chapel. 2013. Reading Comprehension: Helping Learners Focus on Meaning. UNC: Tutor training SCALE. Human
Development Report. Retrieved from: www.dif.mp.gov.in/mphdr%5CChap1_E_2007.pdf?
Knuth, R. A. & Jones, B. F. 1991. What does research say about reading? Retrieved from:
http://www.ncrel.org/sdrs/areas/stw_esys/str_read.html
Kristono, L. & Sensenig, V. 2010. Critical Reading: Unit 9. Satya Wacana Christian University: pp 17
Lee, J. H. 2013. History of Animation: Presentation. Seoul National University. Retrieved from:
http://mrl.snu.ac.kr/courses/CourseAnimation/notes/HistoryOfAnimation.pdf.
Ling, Y. W. 2004. How can I improve the students� selfconfidence in our classroom activities in order to enhance their learning? Retrieved from: http://www.actionresearch.net/living/moira/Ling%20Yiwen.htm
Munir. 2009. Kontribusi Teknologi Informasi dan Komunikasi (TIK) dalam Pendidikan Di Era Globalisasi Pendidikan Indonesia. Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia.
Setiawan, D. 2011. Animation in Language Learning. Information and Communication Technology Journal
Sims, D. D. et al. 2011. Academic Reading Module: Globalization and language learning. SWCU: Faculty of Language and Literature.
Stiviani, R. & Hayati, N. 2011. Using Animation Clip to Improve the Listening Ability of the Eight Graders of SMP Negri 21 Malang. State University of Malang.
Webopedia. 2013. Definition of Animation. Retrieved from: http://www.webopedia.com/TERM/A/animation.html. Widdiharto, R. 2004. ModelModel Pembelajaran. Yogyakarta: PPPG Diknas.
�
Widyaiswara, J. . Efektifitas Pembelajaran Tuntas. Medan: Balai Diklat Kemenag
Figure in
Widya Sari Journal (Vol18. No1. Maret 2016)
- Mozes Kurniawan:
Figure 1. SMP Lab Students’ Reading Strategies (Kristono & Sensenig, 2010)
[image:9.595.87.452.329.751.2]Figure 2. Research Design in SMP Kristen Satya Wacana Salatiga
Figure 4. Creative Reading Design Model
[image:10.595.78.398.586.728.2]Figure 5. Creative Reading Model
Figure 6. Stages of Teachers Teaching and Students Learning from preparation to evaluation
Figure 7. Creative Reading Learning Model
English Reading
Comprehension
Animation
Technology
Creative
Reading
English Reading
Comprehension
Animation
Technology
Creative
Reading
Concept
Text
Type
Questions
Vocabularies
Language Features
Visual Effect
Suggestion Effect
Users
4
2
6
1
5
3
Note:
(
Teacher
/
Student
)
Planning
/
Generating
Searching
/
Connecting
Adjusting
/
Analyzing
Creating
/
Predicting
Implementing
/
Executing