New asset accounting features
Fixed asset accounting based on universal journal
After new asset accounting migration, previous year reporting is
possible due to compatibility views.
We have an option of assigning the depreciation is to accounting
principle.
Here we can segregate the accumulated depreciation and depreciation
asset wise, but it is not happening now in classic asset accounting.
Simplified chart of depreciation, only one depreciation area per
valuation is necessary, no delta depreciation areas required for parallel
valuation, but which is happening now in classic asset accounting.
Flexible account determination and no more FI-AA reconciliation is
required.
Posting to different periods possible, but beginning /end of the FY need
to be equal.
New transactions for accounting principle, depreciation area specific
documents.
The beauty of new asset accounting is always systems will posts the
separate documents per each accounting principle, like ledger specific
document in new GL.
Depreciation postings will happen each asset wise.
The traditional asset tables like ANEK, ANEP, ANEA, ANLP & ANLC
now replaced with ACDOCA and ANEK table data will be replaced with BKPF;
we will call ACDOCA as a universal journal table.
In new asset accounting technical clearing account acts as a zero
balance clearing account in new GL and it is a offsetting account.
In new asset accounting after posting the document, the display
document in FB03 contains the special tab of Asset accounting display, once
you click on this document it will give you the accounting principle wise posted
accounting document, here the technical clearing account will acts as a
offsetting account in both the accounting principles.
In AW01N transaction you have hierarchical views for both
accounting principles and we can differentiate the same.
The AFAB depreciation screen modified completely and you
can give the company code range in AFAB screen, accounting
principle specific we can run the depreciation.
In the classic asset account, system won’t allow you to post
any depreciation if you have errors in depreciation run, but now in
new asset accounting, you can exclude the errors and can execute
the depreciation for other assets, like cost estimate for materials in
CK40N.
Former IMG activity reset posted depreciation is obsolete
due to redesign of depreciation run.
AT THE TIME OF POSTING SIMULATE ASSET
ACCOUNTING WILL APPEAR
WE CAN SEE THE DOCUMENT POSTED WITH LEDGER
GROUPWISE
AT DEPRECIATION RUN-WE GET ACCOUNTING
PRINCIPLE-RUN DEPRECIATION ACCOUNTING
PRINCIPLEWISE
NOT GIVEN REPEAT/RESTART/UNPLANNED POSTING
RUN
AT THE TIME OF ASSET TRANSFER WE CAN GIVE
ACCOUNTING PRINCIPLE AND DEPRECIATION AREA. IF
WE DO NOT GIVE SEPARATELY IT TAKES ALL LEDGERS
i.e., LEADING AND NON-LEADING LEDGERS.
AT THE TIME OF ASSET SCRAPPING WE CAN GIVE
ACCOUNTING PRINCIPLE AND DEPRECIATION AREA. IF
WE DO NOT GIVE SEPARATELY IT TAKES ALL LEDGERS
i.e., LEADING AND NON-LEADING LEDGERS.
CAPITAL WORK IN PROGRESS-LINE ITEM
SETTLEMENT-WE HAVE TO SELECT ASSET LINE ITEMS AND
TECHNICAL CLEARING ACCOUNT LINE ITEMS
Financial Accounting (New) -> Asset Accounting (New) ->
General Valuation -> Depreciation Areas -> Define Depreciation
Area for Quantity Update
Quantity updates in real time is possible for depreciation areas
other than 01. This function is especially relevant in case of
collective low-Value assets. Currently the system uses
depreciation area 01 for updating quantities unless we have
configured different depreciation area for the same.
Smoothing is no more relevant (and available) any more
For representing parallel accounting in New asset
accounting, you have two scenario’s as mentioned below.
Using Parallel ledgers: The Ledger approach
Using Additional accounts: The Accounts approach
Ledger approach:
2.
The depreciation areas have equal status. Separate
documents are posted for each accounting principle or
valuation.
3.
For each accounting principle or valuation, the system
posts the correct values in real time. The values that are
posted are full values and not delta values.
4.
For each valuation, there is always just one
depreciation area that posts to the general ledger in real
time and manages APC. For this leading depreciation area,
choose the posting option
Area Posts in Realtime
. This
applies both for the leading valuation and for all parallel
valuations. You can choose which of these depreciation
areas, which post to the general ledger, posts to the leading
ledger.
5.
One or more depreciation areas represent a valuation.
You must assign an accounting principle uniquely to all
depreciation of a valuation. For each valuation, the
accounting principle has to be assigned to a separate ledger
group. The ledgers of these ledger groups are
not
allowed to
overlap.
6.
Differences in values in each accounting principle: You
can enter documents that are valid only for a certain
accounting principle or valuation. To do so, when entering
the business transaction, you can restrict the posting to the
accounting principle or to one or more depreciation areas.
start dates and end dates of the fiscal year variants must be
the same.) If the dates of FY are different then AA MCT need
to be enhanced accordingly.
8.
Within an asset class, it is possible to make a simple
assignment of different G/L accounts (such as, reconciliation
accounts for APC and value adjustments) for each valuation.
9.
If you have defined parallel currencies in new General
Ledger Accounting, and you want to use these currencies in
new Asset Accounting, you are required to create – for the
leading valuation and the parallel valuations – the necessary
depreciation areas for each currency.
10.
Managing quantities: In the standard system,
depreciation area 01 is intended for the quantity update. If
needed, you can specify a different depreciation area for the
quantity update. However, this has to be a depreciation area
that posts to the general ledger. The quantity – if it is to be
managed on the asset – is updated in the asset master
record only when a posting is made to this different
depreciation area.
Different Fiscal Year Variants:
variant is assigned. The system then derives the period from
the posting date. The depreciation, however, is determined
as before using the fiscal year variant of the depreciation
area of the posting.
Accounts Approach:
1.
You represent different valuations on different accounts
within the same general ledger. This means that you have to
create the same set of accounts again for each parallel
valuation.
2.
Separate documents are posted for each accounting
principle or valuation.
3.
For each accounting principle or valuation, the system
posts the correct values in real time. The values that are
posted are always full values and
not
delta values.
4.
For each valuation, there is always just one
depreciation area that posts to the general ledger in real
time and manages APC. The following applies for these
posting depreciation areas:
1.
For the leading valuation, choose the posting
For the parallel valuations, choose the posting option
Area
Prerequisites for new asset accounting:
1.Enterprise Business function activation
EA-FIN is required for FI-AA (new) and
FIN_AA_parallel_val under Enterprise
Business functions.
2.For every additional currency type
defined on the company code a
corresponding depreciation area need to
be set up.
SAVE
5.ASSIGN ACCOUNTING PRINCIPLE TO LEDGER GROUPS
7.copy/delete depreciation areas
Select area 15-select details button
save
8. Assignment of chart of depreciation to company code –error
Transfer apc values-by default for deprn area 35-01 will appear.
Remove 01-then enter
NOTE: THE SAME WAY WE HAVE TO DO FOR TRANSFER
DEPRECIATION VALUES
code-10.specify account determination
12.Define number range interval
14.Define screen layout for asset master data
IN SCREEN LAYOUT WE SPECIFY COST CENTER REQUIRED FOR
ASSET MASTER CREATION.
14.Determine Depreciation areas in the asset class (oayz)
16.CREATION OF GL MASTERS
350001-ASSET SALE ACCOUNT-NON-OPERATING INCOME
350002-PROFIT ON ASSET SALE-NONOPERATING INCOME
450001-LOSS ON ASSET SALE-NONOPERATING EXPENSES
450002-LOSS DUE TO SCRAPPING-NONOPERATING
EXPENSES
400500-DEPRECIATION-OPERATING EXPENSES-COST
ELEMENT CATEGORY 1
17.CREATION OF TECHNICAL CLEARING ACCOUNT
FS00
CREATE 200010-TECHNICAL CLEARING-RECONCILIATION ACCOUNT
FOR ACCOUNT TYPE-ASSETS
COPY A/C 200000 AND CREATE TECHNICAL CLEARING ACCOUNT
–AO90
POSTING OF
TRANSACTION-ASSET 1-0 DR
1000000 TECHNICAL CLEARING A/C-200010
TO VENDOR
SAP NOTE:TO ENABLE PARALLEL POSTINGS TO DIFFERENT LEDGERS
SYSTEM USES A TECHNICAL CLEARING ACCOUNT FOR ASSET
ACQUISITIONS. THIS IS REQUIRED FOR A TECHNICAL PURPOSE AND
THE BALANCE OF THIS ACCOUNT IS ALWAYS ZERO AFTER EACH
POSTING. THE TECHNICAL CLEARING ACCOUNT MUST BE A
RECONCILIATION ACCOUNT FOR ASSETS AND IT CAN NOT BE USED
IN ACCOUNT DETERMINATION FOR ASSET ACCOUNTING.
20.specify document type for posting of depreciation
21
.specify intervals and posting rules
22.SPECIFY ACCOUNT ASSIGNMENT TYPES FOR ACCOUNT
ASSIGNMENT OBJECTS
23.SPECIFY ROUNDING OF NET BOOK VALUE AND/OR DEPRECIATION
24.DEPRECIATION KEYS CREATION
25.TO MAKE COST CENTER FIELD OPTIONAL ENTRY FIELD FOR
FIELD STATUS GROUP G067
OBC4
ERROR MESSAGE WHILE POSTING:
RUN PARALLEL
VALUATION-SOLUTION:
26.Migrate Chart of depreciation
SPRO->FINANCIAL >ASSET
ACCOUNTING->MIGRATION ASSET ACCOUNTING (NEW) -> MIGRATION
(CLASSIC) TO NEW ASSET ACCOUNTING-> MIGRATION FOR
NEW ASSET ACCOUNTING-> MIGRATE CHART OF
SELECT UPDATE RUN AND EXECUTE
27.WHEN NEW PACKAGE IS GIVEN IT GIVES AN ERRO
MESSAGE –CHART OF DEPRECIATION 0DE NOT ASSIGNED
TO COMPANY CODE 003.
GO TO ASSIGN CHART OF DEPRECIATION TO COMPANY
CODE
28. ACTIVATE ASSET ACCOUNTING NEW
By default in preparation radio button will be selected.
INDIAN INCOME TAX DEPRECIATION IN SIMPLE
FINANCE-1.ACTIVATE BUSINESS FUNCTION
2.CHECK COUNTRY SPECIFIC SETTINGS
3.COPY REFERENCE CHART OF DEPRECIAN/DEPRECIATION AREAS
EC08
ALREADY COMPLETED
4.ASSIGN CHART OF DEPRECIATION TO COMPANY CODE
OAOB
ALREADY COMPLETED
5.SPECIFY ACCOUNT DETERMINATION
6.CREATE SCREEN LAYOUT RULES
7.DEFINE NUMBER RANGE INTERVAL
8.DEFINE SCREEN LAYOUT FOR ASSET MASTER DATA
ALREADY COMPLETED
9.DEFINE SCREEN LAYOUT FOR ASSET DEPRECIATION AREAS
ALREADY COMPLETED
10.DEFINE ASSET CLASSES
11.SPECIFYING TAB LAYOUT FOR ASSET MASTER RECORD
12.ASSIGN TAB LAYOUTS TO ASSET CLASSES
13.DEFINING DEPRECIATION AREAS
3.INCOME TAX DEPRECIATION CALCULATION REPORT
END USER AREA:
1.MAIN ASSET MASTER CREATION
AS01
1-0
2.MAIN ASSET PURCHASE POSTING
F-90
3.TO VIEW EACH SUB-ASSETWISE YEARWISE VALUES
4.DEPRECIATION RUN
CHANGES
EHP6
SIMPLE FINANCE
ACCOUNTING PRINCIPLE
NOT AVAILABLE
AVAILABLE
REPEAT/RESTART/
UNPLANNED POSTING RUN
AVAILABLE
NOT AVAILABLE
DETAIL LOG/TOTAL LOG
NOT AVAILABLE
AVAILABLE
5.ASSET TRANSFER
ACCOUNTING PRINCIPLE LEVEL
ASSET TRANSFER IN ONE STEP
METHOD-i) DEFINE SCREEN LAYOUT FOR ASSET DEPRECIATION AREAS
AO21
ii)DETERMINE DEPRECIATION AREAS IN THE ASSET CLASS
OAYZ
iii)CREATION OF PROFIT CENTER STEEL1 FOR BANGALORE
SEGMENT
KE51
iv)CREATION OF COST CENTER FOR BANGALORE
KS01
v)ASSET TRANSFER IN ONE STEP METHOD
ABUMN
OTHER CHANGES IN ASSET
ACCOUNTING-OLD CODES
NEW CODES
AB01
AB01L
ABAK
ABAKL
ABST
ABSTL
Different fiscal year variants for leading ledger and
non-leading ledger:
1.Define accounting principle
2.Define non-leading ledger 1 and 2
Leading ledger-apr to march
Non-leading ledger 1-jan to dec
Non-leading ledger 2-apr to march
3) Create a ledger group containing of both non-leading
ledgers: different FY and the one from the step before
marking this as representative
4) Assign this ledger group to the parallel valuated
depreciation area
We are already using new G/L and are on EhP7. Now we
want to activate new asset accounting. Some company
codes use a different fiscal year defined in a non-leading
ledger. To handle this there's a workaround described in
SAP note 2220152:
a) Assign company code to an additional
non-leading-ledger assigned to the same fiscal year variant as the
leading ledger
b) Create a ledger group containing of both non-leading
ledgers: different FY and the one from the step before
marking this as representative
STEPS REQUIRED: sap note no. 2220152
1.Define Accounting principle
X1-indian accounting standards
X2-IFRS
2.Define settings for ledgers and currency types
0L-leading ledger-fiscal year variant v3
X1-non-leading ledger1-fiscal year variant k4-accounting
Principle-x2
X2-non-leading ledger1-fiscal year variant v3-accounting
Principle-x2
3.Define ledger group
For ledger group
x3-Assign
ledgers-X2-select representative ledger check box
X1-deselect non-representative ledger check box
4.Assign accounting principle to ledger groups
Accounting principle ledger group
X1 0L
X2 X3
SAP S/4HANA Finance
Fiscal Year variant in Company
Code have different end
oadb-settings.png
Hi All,
We are in the process of migrating to S/4HANA and got an error while running the
pre-migration check program RASFIN_MIGR_PRECHECK. The error is "Fiscal
Year variant in Company Code XXXX have different end dates". We are using
New GL and have created non-leading ledgers are per local requirements.
The Fiscal year variant (FYV) of the leading ledger does differ from the fiscal year
variant of the non-leading ledgers. Hence we are getting the issue during the
migration check.
We found SAP notes "2220152 - Ledger approach and Asset Accounting (new):
Non-calendar fiscal year variant for parallel valuation" and "844029 - Inconsistent
fiscal year variant with ledgers in the NewGL" which talks about creation of
additional ledgers and ledger groups to resolve the issue.
Our queries are as follows:
1. Is the solution specified under notes 844029 and 2220152 are the only
solutions available or are there are any solution which can be evaluated?
2. Suppose the solution available under the above notes is the only solution, and
we have the current setup
Main ledger: 0L (FYV X1)
Non leading ledger: L1 (FYV Z6)
Ledger Group Z1: L1 and L2 and make L2 as the representative ledger
We assign the new ledger group Z1 under parallel valuation in OADB to the local
depreciation area. Our question is, prior to the change the local depreciation
postings were happening as per the local FYV Z6, since ledger L1 was assigned
to it. After the configuration change the local depreciation postings will happen as
per
which FYV,
since it has now been assigned to the ledger group Z1, where
the representative ledger is L2?
Additional ledger constrain in
New asset accounting for S4
HANA
Hi Friend,
My company is in Hana on cloud and we are planning to go for S/4 HANA Finance ( Simple finance) next year July. For S/4 Hana Finance we have to move to new asset accounting from classic asset accounting. According we have decided to move with the ledger approach with new asset accounting.
My client is a UK based company with legal entities spread across the countries. For legal reporting we follow the April to March reporting period for all company codes but for local reporting we have to abide by country specific tax requirement. For example countries Russia and Mexico the leading ledger(0L) is maintained in April to March fiscal year but for local report Jan to December fiscal year is maintained.
Hence at the time of migration of Chart of depreciation ( one of the step post installation of Simple finance alias SFin 1503 alias S/4 Hana Finance) , system gives a error message start and end end of the leading and non leading ledger is not same. As with new asset accounting there will be real time posting in both the books (i.e leading and non leading ledger) . SAP has recently introduced a note with more clarity on the topic. The SLO service mentioned in the note is a work around to abide by the issue of asset accounting rather can completely solving.
SAP note 2220152 - Ledger approach and Asset Accounting (new): Non-calendar fiscal year variant for parallel valuation
Good to have your view on the same as we are stuck. Regards
Shikha
Tags:
2 replies
Vikash Kumar Tulsyan replied December 01, 2015 at 19:20 PM Hi Shikha,
You can perform the steps outlined in the note 2220152 and issue will be resolved. Unless you have different start and end date between 0L and Non leading ledger you need not have to go with SLO service.
Defined a ledger group and assign a ledger (create a dummy one) which has the same fiscal year variant as leading ledger and add the non leading ledger and assign this ledger group to your parallel depreciation area and issue will be resolved.
Shikha Gupta replied
December 02, 2015 at 11:45 AM Hi Vikash,
The reason we are stopping is because for Russia legal entity we have a different fiscal year in leading and non leading ledger.
Current scenario
To fix we need to create additional ledger Z1 with fiscal year as April to Mar (same as
per leading) and make that as representative ledger and assign in the ledger group
with the old non - leading Ledger
Ledger
This entire configuration needs to be done before the simple finance installation as SAP suggest to populate values in the new Z1 Ledgers before the table structure changes in S/4 Hana Finance.
But the bottleneck is SAP suggests an SLO service which in simple term is Table update is not sure to resolve this. This is a work around for asset accounting to work.
Also the source ledger for Z1 to copy values cannot be Z2 ledger as the fiscal year variant for them is not same neither it cant be 0L Ledger due to local statutory reporting posting made only in non leading ledger. This becomes a stop stopper for S4 Hana Finance.
Regards Shikha
SAP note 2220152 – Ledger approach and Asset Accounting (new): Non-calendar fiscal year variant for parallel valuation
Regards Eugene
like
(0)1.
Abhay ParekhSeptember 19, 2016 at 10:51 am
Thanks for sharing the document… It will help a lot in HANA implementation but one thing i would like that why SAP has not allowed to get LSMW,BDC for ABLDT.. Don’t you think it wierd thing?? D
like
(0)Thanks for encouraging words.
Yes there is no LSMW or BDC for ABLDT which is bit weird. Regards
Eugene
like
(0)Subsequent implementation of an additional ledger
Hello,
We are already using new G/L and are on EhP7. Now we
want to activate new asset accounting. Some company
codes use a different fiscal year defined in a non-leading
ledger. To handle this there's a workaround described in
SAP note 2220152:
a) Assign company code to an additional
non-leading-ledger assigned to the same fiscal year variant as the
leading ledger
b) Create a ledger group containing of both non-leading
ledgers: different FY and the one from the step before
marking this as representative
c) Assign this ledger group to the parallel valuated
depreciation area
STEPS REQUIRED:
The current version of note 2220152 dated Dec 2015
states the following:
"Existing customers must ensure that correct values exist
in the new
representative ledger L2 . In addition, a migration of the
data (with
migration and the absolutely necessary SLO migration
service, see
www.service.sap.com/glmig
."
If we follow this recommendation we face tremendous
challenges for our new asset accounting implementation.
Furthermore we plan at a later point to switch to S/4HANA
which is baed on new asset accounting.
Now, knowing that this ledger assignment (step A above)
is only a techical prerequisite done to enable the config of
New Asset Accounting the data in the additional ledger is
irrelevant and will never be analyzed or used.
Could anybody share some experiences or insights if we
really need to go that route and perform a new G/L
migration with the connected effort, time and cost? What
would happen if we don't do that? I have worked on New
asset accounting last year, implemented this in a sandbox
w/o any migration. The handful asset tests we performed
were alright.
Thanks,
JoachimJoachim Nerreter
January 28, 2016 at 11:35 AM
0 Likes Helpful Answer
by
Sanil Bhandari
Sanil Bhandari
Ajay Maheshwari SAP Trainer
Ajay Maheshwari SAP Trainer
Ajay Maheshwari SAP Trainer
13 replies
Helpful Answer
Sanil Bhandari replied
January 12, 2016 at 17:06 PM
We are in the process of migration to S/4 HANA Finance
1503 edition. We had a similar situation where our leading
ledger had fiscal year from April to March and non leading
ledger had a fiscal year from Jan to Dec or June to July
depending on the geography. We have used a technical
ledger with the same fiscal year as leading ledger to allow
the transactions to go through.
However, local GAAP reporting still remains a challenge
for non leading ledger since the above solution only allows
the transactions to be posted for assets, but if i want to
look at a block of assets for local GAAP the reports do not
work. We are developing a custom report to tide over that.
SAP also has an additional tool, where a dummy company
code is created and data migrated to the dummy company
code for reporting. But you will have to check with the SLO
or LT team within SAP for the same as there is additional
license fee involved.
New Asset Accounting in itself is mandatory for S/4 HANA
Finance and you will have to activate the same during
migration. Given my exp, it is easier to develop based on
ACDOCA rather than Suite on HANA. So unless there is
pressing business requirement for new asset accounting
functionality, you may want to do this as a part of your S/4
HANA Finance Journey.
Thanks & Regards
Sanil Bhandari 0 likes
Joachim Nerreter replied
January 12, 2016 at 18:24 PM
Hello Sanil,
you don't face any issues with that "technical" ledger which you have only to allow postings to go through?
Because this was exactly my question.
However, you recommend not to implement New Asset Accounting at this point of time but rather at the same time the migration to S/4HANA takes place. I would have expected that the S/4HANA Finance (formerly known as Simple Finance) would be easier if New Asset accounting is already in place. Initially we planned to go-live with S/4HANA Finance in one step: SoH, new asset accounting and activation of Simple Finance. We found that transfer prices are not supported as of now and reduced the scope to SoH. The idea would be to further minimize the risk and effort by decoupling New Asset accounting activation and the Simple Finance add-on activation. Any comments on that? You wrote: "However, local GAAP reporting still remains a challenge for non leading ledger since the above solution only allows the transactions to be posted for assets, but if i want to look at a block of assets for local GAAP the reports do not work. We are
developing a custom report to tide over that."
Can you explain that and let me know what you mean? I don't fully understand. Thank you,
Joachim 0 likes
Helpful Answer
Sanil Bhandari replied
January 13, 2016 at 10:13 AM
Hi
We have 240+ Company Codes with almost 100+ Company codes having this issue. We have not faced any technical issues yet and we are in Integration testing 3 phase of the S/4 HANA Finance Project.
I believe the New Asset Accounting should be activated with S/4 HANA Finance transformation since there are fundamental changes on the accounting itself for assets and it is easier to go in for this kind of changes in terms of user adoption and changes. Secondly, my suggested change of a technical ledger works in New GL, however, standard Asset Reports still report based on the fiscal year of leading ledger. In our case the leading ledger is from April to March and multiple markets have fiscal years from June -July or Jan -Dec. So in such a case, we are developing a custom report and such a report works much more easily on ACDOCA rather than on the new GL Tables. So unless it is a very pressing business requirement which is addressed by New Asset Accounting, I would rather prefer to go as a one step for New Asset Accounting plus S/4 HANA Finance.
Hope that answers your questions. Regards
Joachim Nerreter replied
January 13, 2016 at 11:51 AM
Hello Sanil,
Wow, a huge number of company codes, is this in a single instance? We have > 150 company codes within one instance/SAP system. A few of them need this "technical" ledger because they are using different FY. Some already use different FY. I can cinform what you are saying as this is not new to us: the asset reports are always based on the FY of the company, no matter what depreciation area you use - with same of different FY. I take it that's no issue for accountants since they live with that w/o complaining. I understand that you are still implementing S/4 HANA Finance so you haven't seen the "technical" ledger in a live system - and can tell if that's an issue or not. Correct? I opened a message to SAP to ask if the migration scenarion is really necessary... Thanks,
Joachim 0 likes
Joachim Nerreter replied
January 19, 2016 at 09:06 AM
Hello Sanil,
I'm coming back to the question if an additional ledger causes issues when not migrated properly with General Ledger migration scenario 7.
I opened an incident to SAP raising this questions. The answer that I received said that SAP itself can't give an comprehensive answer. Issues would arise after the assignment of additional ledgers: while reversing or clearing documents that have been posted before the assignment. In addition currency calculation could be an issue. We're free to test this and maybe we can live with that.
However, I tested this: assigned an additional ledger, reversed and cleared documents w/o any issue.
Additionally I've seen that in the config where you add additional ledgers a pop-up appears asking whether the company is productive and telling that you then need to use General Ledger migration Services.
Ajay Maheshwari SAP Trainer replied
January 19, 2016 at 10:28 AM
Hi Joachim
I know this approach works, but cant recommend that..
With our limited knowledge about the system design, we can foresee upto some extent. If something goes adverse, SAP wont support you. So, that's the only flip side
If you wanna go ahead, I would suggest also do YE Close activities, GL Balance C/F on Ledgers, etc. test everything that you would do in the live system
I align with Sanil that it is better to activate New AA in Simple Finance.. Because AA in SFIN has further changed over and above EhP7... So, no point in doing it twice
Regards Ajay M
0 likes
Joachim Nerreter replied
January 19, 2016 at 12:21 PM
Hi Ajay,
So you are saying adding the subsequent ledger w/o G/L migration works. The down side is that if an issue arises SAP wouldn't be forthcoming in the support. That makes sense seeing the hint in the note and in the config. So either test it soundly and take the risk or use the SAP G/L migration scenario 7. The latter would be the safest I take it. I haven't done a G/L migration service project yet. Do you have any idea what the cost might be (100$, 1000$ or 10000$, or more). The impact of adding a subsequent ledger isn't that high, it's not a complete new G/L implementation.
Any experience with G/L migration service?
Ok, I understand Sanil's and your point regarding the timing with S/4HANA being on the horizon.
Ajay Maheshwari SAP Trainer replied
January 19, 2016 at 12:26 PM
Hi Joachim
No idea about the cost involved.. But this scenario should be an easier one
Fyi.. I read one SAP note long back, which offers a correction program.. That program basically populates a ledger with the historical data, by deleting the present transaction data
Though SAP says it must be used only for correction purpose, am not sure if it can work for you.. Again it is a Q of taking risk
Regards Ajay M 0 likes
Joachim Nerreter replied
January 19, 2016 at 12:45 PM
Thank you Ajay for your help. You don't happen to know the number of this note? 0 likes
Helpful Answer
Ajay Maheshwari SAP Trainer replied
January 19, 2016 at 12:58 PM
Hi Joachim
Am a lazy guy, but you made me search finally Program: FAGL_DELETE_RELOAD_LEDGERS
However, note 1340411 - EURO: FAGL_DELETE_RELOAD_LEDGERS, says this must be used only for Currency Conversion cases and not as a utility to correct corrupt docs Rgds
Ajay M 0 likes
Joachim Nerreter replied
January 21, 2016 at 09:26 AM
Thanks, Ajay.
Regarding my original question I got a reply from NewGLMigration@sap.com.
They told me at length that SAP strongly recommends to use the G/L migration service to add the and populate consistently the additional ledger. Also in order not to jeopardize the support and warranty. Costs are from 10,000 to 30,000 Euro based on the migration scenario used. Scenario 7 would be in the lower region. The migration date would be the start of our next fiscal year (July 1).
Any thoughts? Thanks, Joachim
0 likes
Ajay Maheshwari SAP Trainer replied
January 21, 2016 at 09:43 AM
Hi Joachim
I think you can club both. They are not mutually exclusive
but since you have access to SAP New GL Migration team, better to ask them Br, Ajay M
0 likes
Aleksey Tkachenko replied
January 28, 2016 at 11:35 AM
Hi,
I wouldn't recommend to perform 2 these project in parallel. 0 likes
S4HANA Finance: New Asset Accounting – Simplified.
S/4 HANA- New Asset Accounting – Considering Key Aspects
This blog is focused on New Asset accounting for ledger approach in
multiple currency environment. New Asset Accounting is the only
Asset Accounting solution available in S/4 HANA, classic Asset
Accounting is not available any more.
I have covered following key topics within S/4 HANA New Asset
Accounting keeping in view various questions coming in from
different customers/partners on this key innovation step taken
within Finance as part of S/4 HANA simplification and we need to
be very clear on this new requirement before starting the new or
conversion S/4 HANA project.
1. Pre-requisite Business Functions
2. Data Structure Changes in Asset Accounting
3. New FI-AA-Integration with the Universal Journal Entry
4. Asset Accounting Parallel Valuation
5. Key Configuration Consideration in Ledger Approach
6. Why will use a technical clearing GL account
7. New Asset Accounting Posting Logic
8. FI-AA Legacy Data Transfer
9. Adjusting chart of Depreciation Prior to Conversion
10. Installing SFIN in Conversion/Migration Scenario
1. Pre-requisite Business Functions
Activate the following Business Functions
ENTERPRISE_EXTENSIONS – EA-FIN
ENTERPRISE_BUSINESS_FUNCTIONS – FIN_AA_PARALLEL_VAL
2. Data Structure Changes in Asset Accounting
Actual data of ANEK, ANEP, ANEA, ANLP, ANLC is now stored in table
ACDOCA. ANEK data is stored in BKPF.
Compatibility views FAAV_<TABLENAME> (for example, FAAV_ANEK)
are provided in order to reproduce the old structures.
Statistical data (for example, for tax purposes) previously stored in
ANEP, ANEA, ANLP, ANLC is now stored in table FAAT_DOC_IT
Plan data previously stored in ANLP and ANLC is now stored in
FAAT_PLAN_VALUES
Classic Asset Accounting is mostly transformed automatically into the
New Asset Accounting by executing mandatory migration steps related
to Asset Accounting.
Posting to different periods possible (restriction: beginning/end of FY
needs to be equal) refer OSS note 1951069/ 2220152
3. New FI-AA-Integration with the Universal Journal Entry
Asset Accounting is based on the universal journal entry. This means there is no longer any redundant data store, General Ledger Accounting and Asset Accounting are reconciled Key changes are listed below: –
There is no separate balance carry forward needed in asset
accounting, the general balance carry forward transaction of FI
(FAGLGVTR) transfers asset accounting balances by default.
The program Fixed Assets-Fiscal Year Change (RAJAWE00)
transaction AJRW is no longer has to be performed at fiscal year
change
Planned values are available in real time. Changes to master data and
transaction data are constantly included
The most current planned depreciation values will be calculated
automatically for the new year after performing the balance carry
forward. The depreciation run posts the pre-calculated planned values.
The Selection screen is simplified as the “reasons for posting run”
(planned depreciation run, repeat, restart, unplanned posting run) are
no longer relevant.
Errors with individual assets do not necessarily need to be corrected
before period-end closing; period-end closing can still be performed.
You have to make sure that all assets are corrected by the end of the
year only so that depreciation can be posted completely.
All APC changes in Asset Accounting are posted to the general ledger
in real time. Periodical APC postings are therefore no longer supported.
Transaction types with restriction to depreciation areas are removed in
new Asset Accounting and you can set the obsolete indicator in the
definition of the transaction that were restricted to depreciation areas in
the classic asset accounting.
4. Asset Accounting Parallel Valuation
Very Important part of new Asset accounting is parallel valuation in
multicurrency environment.
The leading valuation can be recorded in any depreciation area. It is no
longer necessary to use depreciation area 01 for this. The system now
posts both the actual values of the leading valuation and the values of
parallel valuation in real time. This means the posting of delta values
has been replaced; as a result, the delta depreciation areas are no
longer required.
5. Key Configuration Consideration in Ledger Approach
We need to answer some basic question before configuring new asset accounting in S4 Hana environment as this would determine the required minimum depreciation areas to align the FI with Asset Accounting. i.e.
Required Valuation Approach
How Many Ledgers (Leading + Non Leading) exists or to be
configured.
What all currencies are used in each of the ledgers.
For
Example:-In this Example we have one com code which has 2 ledgers 0L & N1 & these 2 ledgers having 3 currencies i.e 10,30 & 40 as shown below.
Above mapping is to ensure and establish link between depreciation area/accounting principal and Currency
Explaining with ledger approach example. From release 1503 i.e initial version of SAP Finance add on version in S4 Hana a new table ACDOCA is introduced which stores the asset values also per ledger /per currency on real time basis & no need to have any reconciliation between Finance and Asset accounting and to do so it is must to follow the guidelines while setting up depreciation areas & respective currencies, which I have tried to explain with an example as given below: –
Ledger & currency setting has to be done in New GL in the following
SPRO node.
Financial Accounting (New)–> Financial Accounting Global Settings (New)–> Ledgers–> Ledger –> Define Settings for Ledgers and Currency Types
Define Depreciation Areas
Specify Depreciation Area Type
Specify Transfer of APC Values
Specify Transfer of Depreciation Terms
In this activity, you specify how the depreciation terms for a depreciation area are adopted from another depreciation area. You can specify if the adoption of values is optional or mandatory. If you specify an optional transfer, then you can change the proposed depreciation terms in the dependent areas in the asset master record. In the case of a mandatory transfer, you cannot maintain any depreciation terms in the asset master record. In this way, you can ensure that depreciation is uniform in certain depreciation areas.
Define Depreciation Areas for Foreign Currencies
For every additional currency type defined on the company code a corresponding depreciation area needs to be set up.
depreciation area ( Here leading valuation depreciation area will derive currency from com code currency)
Specify the Use of Parallel Currencies
Here we need to specify the Currency type for each for the Depreciation area which will align FI Currency type with Asset Depreciation areas & accordingly will be updated in ACDOCA.
With this setting its ensured that all currency types are aligned with respective
depreciation area and asset values are getting updated parallel to Financial accounting per currency.
6. Why will use a technical clearing GL account
Architecture has been changed in the way that we now post in asset accounting for each valuation a separate document. So we perform on the asset part accounting principle specific postings. Technically we perform ledger-groups specific postings.
On the operational part (accounts receivable, accounts payable) the value is always the same for each accounting principle. So for the operational part we have to perform postings which are valid for all accounting principles. Technically we perform postings without specifying the ledger-group.
To split the business process in an operational and a valuating document there was a need to establish the “technical clearing account” for integrated asset acquisition.
For each valuating part (asset posting with capitalization of the asset), the system generates a separate document that is valid only for the given accounting
principle. This document is also posted against the technical clearing account for integrated asset acquisitions. From a technical perspective, the system generates ledger-group-specific documents.
Define account “Technical clearing account” for integrated asset
acquisition.
Specify Alternative Document Type for Accounting Principle-Specific
Documents
Here Operational document type will have original document used during entry & while generating accounting principal wise separate document it would be document type AA.
7. New Asset Accounting Posting Logic
The Operational Entry Document posts to a technical clearing account. The Operational Entry Document does not update the asset values; the asset data is only used to perform checks.
Asset Acquisitions Operational Document
Asset Acquisitions Accounting Principal (LOCA) specific Document
Universal Table updated with respective ledger (0L & N1) and
currencies.
Correction Asset Acquisition value in specific GAAP
Use Transaction code AB01L
8. FI-AA Legacy Data Transfer
You post the transfer values using transaction ABLDT; in doing so, a
universal journal entry is posted for the fixed asset.
If wrong transfer values were posted, you must reverse the journal
entry and then recreate it.
You can use transaction AS92 to change master data; transaction
AS93 to display master data; and transaction AS94 to create sub
numbers for the Asset master record.
Time of Legacy Asset Transfer
The transfer date is the cut-off date for the transfer of legacy data. The transfer will only include data up to this point in time. There are two possible scenarios.
The transfer date can be the end of the last closed fiscal year.
The transfer date can be in the fiscal year. This is called
“transfer during the fiscal year.
Scenario 1: Transfer Date is the End of the Last Closed Fiscal Year:
In this case, you do not need to include any posted depreciation or transactions in the transfer of legacy data. You only need to transfer master data and the cumulative values as of the end of the last closed fiscal year.
Scenario 2: Transfer During the Fiscal Year
Along with the general master data, and the cumulative values from the start of the fiscal year (time period A), you must also transfer the following values.
Depreciation during the transfer year and Transactions during the
transfer year
Include the depreciation posted in the legacy system since the end of
the last closed fiscal year up to the date of transfer (time period B).
Any asset transactions in your legacy system that have a value date
after the transfer date, but before the date of the physical transfer of
data (time period C), need to be posted separately in the Asset
Accounting component in any case.
year:-Case: Legacy asset is acquired in previous year 01.01.2015 and taken over into simple finance system in mid-year of current year (30.04.2017)
Specify Transfer Date/Last Closed Fiscal Year (V_T093C_08)
Specify Last Period Posted in Prv. System (Transf. During FY)
(OAYC)
Step 2:- ABLDT to update Legacy Original Acquisition Value/
Accumulated Depreciation and current year Depreciation
Posted.
Step 4: Verify Legacy posted Value
9. Adjusting Chart of Depreciation prior to Conversion
For the leading valuation of the ledger approach and accounts
approach and for parallel valuations of the ledger approach its must
that the parallel currencies in the leading ledger in General Ledger
Accounting and in the depreciation areas in Asset Accounting must be
the same as explained one example above with ledger approach
scenario.
Using the migration program available under Migration Tools, you can
automatically adjust the parameters in your charts of depreciation. If
error messages appear stating that automatic adjustment is not
possible, you have to adjust the charts of depreciation manually.
If until now you have been using parallel currencies in General Ledger
Accounting, but you have not implemented the corresponding parallel
currency areas in Asset Accounting for all depreciation areas, you must
implement these areas in a separate project before you install SAP
Simple Finance. In such a project, you must first perform the
preparatory steps for creating depreciation areas in Customizing; you
must then determine the new values for each fixed asset for a newly
created depreciation area.
For company codes that are assigned to the same chart of
depreciation, these company codes are not allowed to differ in number
and type from the parallel currencies used in General Ledger
Accounting.
Even if you migrate to SAP Accounting powered by SAP HANA from a
system (e.g. EHP7) having FI-AA (new) already active, you still must
migrate every active chart of depreciation.
10. Installing SFIN in Conversion/Migration Scenario
complete period-end closing directly before you install SAP Simple Finance and some of the important point you must consider w.r.t New Asset Accounting. (for detail you may refer conversion guide)
To check if the prerequisites outlined are met, you have to check using
the program for preliminary checks RASFIN_MIGR_PRECHECK. You
import the current version of this program using SAP Note 1939592,
before you install SAP Simple Finance in your system. Perform this
check in all of your systems – in the Customizing system as well as in
the downstream systems (test system and production system).
If until now you updated transactions in parallel valuations with different
fiscal year variants and want to continue using this update, then you
must implement a new representative ledger using the SAP General
Ledger Migration Service before you install SAP Simple Finance. For
more information about alternative fiscal year variants with parallel
valuation, see SAP Note 2220152 Information published on SAP site.
You must have performed periodic APC posting (RAPERB2000)
completely; the timestamp must be current.
Execute the periodic depreciation posting run (RAPOST2000).
Run the program for recalculating depreciation (transaction AFAR).
Reconcile your general ledger with the Asset Accounting subsidiary
ledger, both for your leading valuation and for parallel valuations.
The migration must take place at a time when only one fiscal year is
open in Asset Accounting.
You can check which fiscal year is closed in your company code in
Customizing for Asset Accounting (New) under Preparations for Going
Live à Tools à Reset Year-End Closing.
Ensure that no further postings are made in your system after running
period end transactions before installing S4 Hana Simple Finance
hence lock the users.
Perform a backup before installing SFIN
As soon as you have installed SAP Simple Finance, you can no longer
post in Asset Accounting. To ensure that migration is successful, it is
essential that you make sure that the prerequisites are met and a
complete period-end closing was performed before you install SAP
Simple Finance. Posting for new Asset Accounting is only possible
again after you have completed the migration fully and successfully.
After completing the migration, make sure that no fiscal year that is
before the migration is reopened in Asset Accounting.
Thanks a lot
Ajeet Agarwal
venkatakasi Reddy Polu Aug 24, 2016 9:36 AM
Hello Ravi,
Regards Kasi Reddy
Like (0)
o
Ravi Chirivella Aug 24, 2016 9:58 AM (in response to venkatakasi Reddy Polu)
Hi kasi,
As per the current system settings
once you select the check box
Smoothing, In one financial year
system will distributes the delta
depreciation value to other open
periods equally, other wise, the
whole delta value will post in the
immediate period, but in New asset
accounting this change is
incorporated in the coding level so
that, the setting is obsolete.
Regards,
RaviLike (1)
venkatakasi Reddy Polu Aug 25, 2016 6:19 PM
Hello Ravi,
In Simple Finance Can we use different
Fiscal Year Variants for Different
Accounting Principles and Ledgers?
Regards Kasi Reddy Like (0)
o
Hello,
find some hint in SAP help
I have marked relevant text, see screenshot.
br erwin
Link SAP Help: FI-AA
New Asset Accounting: Ledger Approach and Accounts Approach - SAP Simple Finance Add-On for SAP Business Suite powered b…
Like (1)
venkatakasi Reddy Polu Aug 26, 2016 12:00 PM (in response to Erwin Leitner)
thank u Erwin for ur information. Like (0)
o
venkatakasi Reddy Polu Aug 26, 2016 12:01 PM (in response to venkatakasi Reddy Polu)
ACCOUNTS APPROACH VS LEDGER APPROACH:
Difference between Ledger and Accounts Approach in
SFIN
I would like to understand the difference between Ledger
Approach and Accounts Approach in SFIN. where i can
see which approach they are using in our current system
.is there any configuration steps are involved.
if possible could you brief us with certain examples or
Business scenarios where we can use different
approaches.
Aleksey Tkachenko
Aug 8, 2016 4:29 PM
(in response to
Lal Maheswararao Dara)
Hi, first of all you can check in IMG Financial Accounting
Financial Accounting Global Settings
(New)-Ledger-Define Settings for Journal Entry Ledger. you can
choose/assign which approach do you use wise
combination Ledger/Company code... But this config more
'informal' then required.
How posting flow to FI you need to check automatic
postings config, e.g. in FI-AA AO90, config for FAGL_FCV
and so on.
Accounting Global Settings (New)-Ledgers-Parallel
Accounting
o
Al
How to Set Up Parallel Asset
Accounting in SAP S/4HANA
Finance with Differing Fiscal Year
Variants
Posted on10/07/2017
by Ajay Maheshwari,
SAP FI/CO and SAP S/4HANA Solution Architect Kavita Agarwal,
SAP FI/CO and SAP S/4HANA Solution Architect
February 02, 2017
Learn how to set up the new Asset Accounting
functionality (FI-AA) in SAP S/4HANA Finance in a
parallel reporting scenario with differing fiscal year
variants.
Learning Objectives
Reading this article, you will learn:
How the real-time integration between General
Ledger Accounting (FI-GL) and Asset Accounting
(FI-AA) in SAP S/4HANA forces a different kind of
setup for the ledgers
Key Concept
The unified data model and real-time
integration between General Ledger Accounting (FI-GL)
and Asset Accounting (FI-AA) force the fiscal year variants
from the leading and non-leading ledgers onto the
depreciation areas.
Accounting (FI-AA). It offers many benefits to users,
especially the real-time reconciled ledgers (the
main ledger and asset sub-ledger).
However, the new features of SAP S/4HANA
Finance also significantly change how the new
FI-AA module must be set up in a parallel reporting
scenario (for example, local reporting and group
reporting, where the local company and parent
companies follow different reporting periods).
Consider a scenario that represents a practical
real-life scenario for many organizations. ABC Inc.
USA follows International Financial Reporting
Standards (IFRS) reporting standards and Jan-Dec
as the fiscal reporting period. It has a subsidiary
company in India (represented by company code
9999 in our example) that has to follow Apr-Mar as
the fiscal reporting period to comply with local
laws. As such, company code 9999 follows parallel
accounting in SAP S/4HANA Finance, using a ledger
approach.
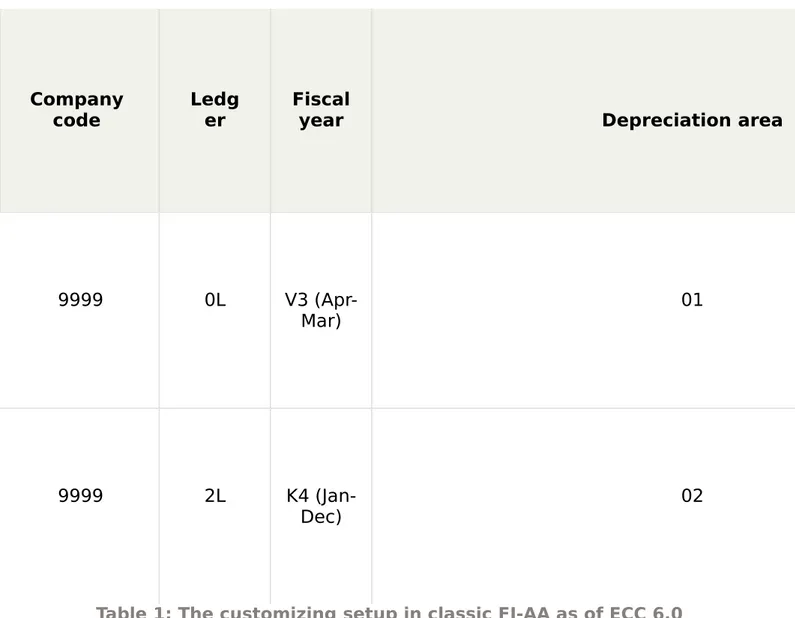
Setting Up the Scenario in Classic FI-AA as of ECC
6.0
Company
code
Ledg
er
Fiscal
year
Depreciation area
9999
0L
V3
(Apr-Mar)
01
9999
2L
K4
(Jan-Dec)
02
Table 1: The customizing setup in classic FI-AA as of ECC 6.0
In our scenario, you would assign the leading ledger (0L)
and a non-leading ledger (2L), with fiscal year variants as
V3 and K4, respectively, to the company code 9999. (The
steps for this configuration in ECC are not part of the
scope of this article). Using the ledger 0L, company code
9999 would be reporting as per local laws (i.e., Apr-Mar)
and with the ledger 2L, it would report as per the group
reporting norms (i.e., Jan-Dec).
The leading ledger 0L is assigned to the Depreciation Area
01 and the non-leading ledger 2L is assigned to the
start and end date must be same for all depreciation areas
in asset accounting.
Asset Accounting (New) in S4 HANA
Finance
New Asset accounting is available in ECC6.0 EHP7 (optional)
and S4 HANA Finance (Mandatory)
In New asset accounting, you can handle parallel accounting
using depreciation areas.
For representing parallel accounting in New asset
accounting, you have two scenario’s as mentioned below.
Using Parallel ledgers: The Ledger approach
Using Additional accounts: The Accounts approach
Ledger approach:
11.
Different accounting principles or valuation are mapped
in separate ledgers, as in new General ledger accounting. In
general, the same accounts are used in the ledgers.
13.
For each accounting principle or valuation, the system
posts the correct values in real time. The values that are
posted are full values and not delta values.
14.
For each valuation, there is always just one
depreciation area that posts to the general ledger in real
time and manages APC. For this leading depreciation area,
choose the posting option
Area Posts in Realtime
. This
applies both for the leading valuation and for all parallel
valuations. You can choose which of these depreciation
areas, which post to the general ledger, posts to the leading
ledger.
15.
One or more depreciation areas represent a valuation.
You must assign an accounting principle uniquely to all
depreciation of a valuation. For each valuation, the
accounting principle has to be assigned to a separate ledger
group. The ledgers of these ledger groups are
not
allowed to
overlap.
16.
Differences in values in each accounting principle: You
can enter documents that are valid only for a certain
accounting principle or valuation. To do so, when entering
the business transaction, you can restrict the posting to the
accounting principle or to one or more depreciation areas.
18.
Within an asset class, it is possible to make a simple
assignment of different G/L accounts (such as, reconciliation
accounts for APC and value adjustments) for each valuation.
19.
If you have defined parallel currencies in new General
Ledger Accounting, and you want to use these currencies in
new Asset Accounting, you are required to create – for the
leading valuation and the parallel valuations – the necessary
depreciation areas for each currency.
20.
Managing quantities: In the standard system,
depreciation area 01 is intended for the quantity update. If
needed, you can specify a different depreciation area for the
quantity update. However, this has to be a depreciation area
that posts to the general ledger. The quantity – if it is to be
managed on the asset – is updated in the asset master
record only when a posting is made to this different
depreciation area.
Different Fiscal Year Variants:
as before using the fiscal year variant of the depreciation
area of the posting.
Accounts Approach:
5.
You represent different valuations on different accounts
within the same general ledger. This means that you have to
create the same set of accounts again for each parallel
valuation.
6.
Separate documents are posted for each accounting
principle or valuation.
7.
For each accounting principle or valuation, the system
posts the correct values in real time. The values that are
posted are always full values and
not
delta values.
8.
For each valuation, there is always just one
depreciation area that posts to the general ledger in real
time and manages APC. The following applies for these
posting depreciation areas:
1.
For the leading valuation, choose the posting
option
Area Posts in Realtime
.
2.
For the parallel valuations, choose the posting
option
Area Posts APC Immediately, Depreciation
Periodically
.
You can choose which of these depreciation areas that post
to the general ledger represent the leading valuation.
receive the posting option
Area Posts in Realtime
for the
leading valuation or
Area Posts APC Immediately,
Depreciation
Per
iodically
for parallel valuations.
2.
One or more depreciation areas represent a valuation.
You must assign an accounting principle uniquely to all
depreciation areas of a valuation. For each valuation, the
accounting principle has to be assigned to a separate ledger
group. These ledger groups must
always
contain the leading
ledger as the representative ledger.
3.
If you have defined parallel currencies in new General
Ledger Accounting, and you want to use these currencies in
new Asset Accounting, you are required to create a
depreciation area for each currency for the leading
valuation. However, this is not mandatory for the parallel
valuations.
4.
Differences in values in each accounting principle: You
can enter documents that are valid only for a certain
In New asset accounting, you can handle parallel
accounting using depreciation areas.
For representing parallel accounting in New asset
accounting, you have two scenario’s as mentioned below.
Using Parallel ledgers: The Ledger approach