An Error Analysis on the Use of Conjunction in Students’ Writing
at English Education Department of Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta
A Skripsi
Submitted to the Faculty of Language Education In a Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
For the Degree of Sarjana Pendidikan
Evita Menur Fauziah
20120540083
English Education Department Faculty of Language Education Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta
i
An Error Analysis on the Use of Conjunction in Students’ Writing
at English Education Department of Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta
A Skripsi
Submitted to the Faculty of Language Education In a Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
For the Degree of Sarjana Pendidikan
Evita Menur Fauziah
20120540083
English Education Department Faculty of Language Education Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta
iv
blessing, health, strength and love, so that I can finish my skripsi writing.
Greatest thankful goes to my family who always love and support me in
every joy and sorrow of life. Thank you Papa and Mama who never complained,
even though you were tired of working, educating and raising your children. Also,
thank you for always pray for me Ma, Pa. Being a good person when I live far
from you, studying hard in the university, and finishing this skripsi is a little gift
from me to you. No exception, thanks to my brother and my sisters, Bayu, Ayu,
and Cynthia who always pray for me.
I would like to express my gratitude to Mr. Dr. Suryanto as my supervisor.
Thank you for always guiding, helping, and encouraging me to finish my skripsi. I
have learned many things from you and I wish all the knowledge that you gave
will be useful for me and others. Thank you for taught me not only about the
lesson, but also you have taught me that in order to achieve something we need
persistence, patience and process. Every advice and experience that you gave to
me will be a valuable lesson for me.
I also want to say my thanks to all the Lecturers of English Education
Department of Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta, who taught me many
things that will be useful for me in the future. I want to give my thanks to Mr.
vi
Statement of Authenticity... iii
Acknowledgement ... iv
Table of Contents ... vi
List of Tables ... ix
List of Figures ... x
List of Appendices ... xi
Abstract ... 1
Chapter One ... 3
Introduction ... 3
Background of the Study ... 3
Identification of the Problem ... 6
Limitation of the Study ... 7
Research Questions of the Study... 8
Purposes of the Study ... 8
Significance of the Study ... 8
Outline of the Study ... 9
vii
The Definition of Writing ... 10
The Process of Writing ... 11
Aspect of Writing ... 12
Conjunction ... 16
Types of Conjunction ... 16
An Error Analysis on the Use of Conjunction ... 20
Error ... 20
Error Analysis ... 20
Types of Error on the Use of conjunction ... 21
Review of Previous Study ... 24
Conceptual Framework... 25
Chapter Three ... 28
Methodology... 28
Research Design ... 28
Population and Sample ... 29
Data Collection Method ... 30
Validity ... 30
viii
Findings and Discussion ... 34
Findings ... 34
The student common error on the use of conjunction in students’ writing ... 34
The types of error occur most frequently on the use of conjunction in student writing ... 37
Discussion ... 42
The student common error on the use of conjunction in students’ writing ... 42
The types of error occur most frequently on the use of conjunction in student writing ... 48
Chapter Five ... 57
Conclusion and Recommendation ... 57
Conclusion ... 57
Recommendation ... 58
References ... 60
ix
Table 3. Total of conjunctions but, and, or, because, so ... 35
Table 4. Error on the use of conjunction in sentence ... 36
Table 5. Misuse on the use of conjunctions but, and, or, because, so ... 38
Table 6. Unnecessary addition on the use of conjunctions but, and, or, because,
so ... 39
Table 7. Omission on the use of conjunctions but, and, or, because, so ... 40
Table 8. Redundant repetition on the use of conjunctions but, and, or, because,
so ... 41
Abstract
Conjunction is a word for connecting words, phrases, clauses, or sentences.
Conjunction is used to make a sentence which having the cohesion and coherence
in text. The absence of the right conjunction will result in having illogical
meaning, and the message tends to be vague. Because of the important role of
conjunctions in the writing process, this study aims to reveal the students’
common errors on the use of conjunction in their writing, and investigate types of
errors that occur most frequently in students’ writing.
The researcher limited the problem in this study that is only discussed about an
error analysis on the use of adversative (but), additive (and, or), and causal
(because, so) in students’ writing. This research used quantitative research
methodology, and to be more specific the researcher used error analysis as a
method. This research took place in English Education Department of Universitas
Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta with the respondent from students in academic year
2015/2016. To collect the data the researcher used document analyses. There were
140 recount texts that were analyzed by the researcher. The researcher also used
SPSS to analyze the data.
The result of this research showed that from the most to the least frequent
common errors on the use of conjunction in students’ writing were conjunction
and, followed by but, so, because, and or. Also, from the most to the least
frequent types of error that occured in the texts were misuse of conjunction,
Chapter One
Introduction
This chapter presents several parts. They are background of the study,
identification of the problem, limitation of the study, formulation of the study,
purpose of the study, significance of the study, and outline of the study.
Background of the Study
Writing is one of the four skills that should be owned in learning English.
According to Husain, Hanif, Asif, and Rehman (2013) “Writing is an outward
expression of what is going in the writer's mind” (p. 832). When studying English,
of course, writing skill becomes one of the competencies that should be mastered
by students in inside and outside the classroom. The more frequent the students
practice writing skill both inside and outside the classroom, the better writing skill
the students posses, because this skill can be better mastered by a lot of practices
(Melyane & Kurniasih, 2014).
In writing we need a group of words to be a sentence. A sentence is a set
of connected words that reveals a whole idea (Sanford, 1979). Sentences are
divided into four types; simple sentence, compound sentence, complex sentence,
and compound-complex sentence (Oshima & Hogue, 1998). A simple sentence
consists of one clause. “A clause is a group of words containing a subject and a
verb” (Phillips, 2001, p. 209). However, compound, complex, and
found a sentence with two or more clauses, then it needs a conjunction between
them to make a correct sentence.
Conjunction is one of the parts of speech. A conjunction has a meaning
that is a word for connecting other words or groups of words (Sanford, 1979;
Warriner, 1982; Forlini, 1983). A conjunction is recognized as a word that is used
to connect words, phrases, and clauses within a sentence (Melyane & Kurniasih,
2014). According to Warriner (1982) conjunction is classified into three types
namely coordination conjunction, correlative conjunction, and subordination
conjunction. While Warriner (1982) divided conjunction into three types, Halliday
and Hasan (1976) categorized conjunction into four types that are additive,
adversative, temporal, and causal. These four types of conjunction have different
function in writing.
Nace (1983) stated, “Conjunction works like cements between bricks” (p.
73). We can assume that cements are conjunction and bricks are grammatical
structure. So, the function of conjunction is combining grammatical structures
(Klammer &Schulz, 1992) to make a well-formed sentence. “In writing
comprehension, one cannot simply create a good writing text without the use of
conjunction” (Melyane & Kurniasih, 2014, p. 2). Beside that, conjunctions are
used to make a sentence have the cohesion and coherence in text. Hence without
the right use of conjunction, the sentence would not have logical meaning and the
Hamed (2014) analyzed the use of conjunction in argumentative essay of
fourth-year undergraduate learners of English at Omar Al-Mukhtar University in
Libya. The result of the study showed that students of English as Foreign
Language (EFL) made many errors when they use conjunction in writing. The
Libyan EFL students have difficulty in using the conjunction on the other hand,
but, in fact, and, furthermore, moreover, so, and because. The finding showed that
adversative conjunction is the most difficult conjunction for learners, followed by
conjunction additive and causal.
As a student of English Education Department (EED) of Universitas
Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta (UMY), it is important to have a good ability in
writing. The student must learn, understand, and master the grammar to be able to
write well. Writing will not be separated from the use of conjunctions because by
using right conjunctions the writer can make a good sentence that is easy to be
understood by readers. So, the use of conjunction has a very important role, and
students of EED of UMY should master how to use it.
Based on researches by Blaz (1966), Faustino (1971), Floresheim (1972),
Kimizuka (1968), Robinson (1970), and Waymire (1965) as cited in Tomiyama
(1979) it was revealed that “Articles and connectors are two highly frequent
categories of grammatical errors made by students of several different language
backgrounds” (p. 2). It turns out that the conjunction constitutes one of the parts
of speech that student encountered errors when they used it. This problem needs
more attentions and also we should find the way to solve it. Therefore we require
also necessary to look for ways to overcome the problems of the students in the
use of conjunction. Unfortunately, the research about an error analysis on the use
of conjunction in student writing has not been done in EED of UMY.
Based on the above background, the researcher was interested in
conducting the research about an error analysis on the use of conjunction in
students’ writing. This research wants to finding out the students’ common errors
on the use of conjunction in writing, and also the types of errors that most
frequently occur on the use of conjunction in students’ writing,
Identification of the Problem
Based on the background of the research that has been described above,
this research aims to analyze errors on the use of conjunction in students’ writing
at EED of UMY. As we know in Indonesia people learn English as a foreign
language, and every day we use Indonesian language to communicate each other.
It makes learning English more difficult, because we are not accustomed to using
it either spoken or written. Also, there are four skills that should be owned by the
learner in learning English, and writing is one of the four skills that most difficult
for them (Nacira, 2010).
The writing skill is the one of abilities that is difficult to master by
students. One of the difficulties in writing lies on the use of conjunctions
(Melyane & Kurniasih, 2014). Students sometimes overuse, misuse, and use
unnecessary conjunction in their writing (Ong, 2011). Error in using conjunction
(Hamed, 2014, p. 117). Whereas without a proper conjunction student cannot
make a well-formed sentence. Also, conjunction determines whether their writing
is interconnected or not. This is why conjunction is important to be mastered by
the students. To investigate the students’ mastery on the use of conjunction, it is
essential to carry out the research on the use of conjunction. Therefore, the
research on an error analysis on the use of conjunction in student writing should
be conducted in English Education Department of Universitas Muhammadiyah
Yogyakarta.
Limitation of the Study
In order to make the problem in this research not too wide, it is necessary
to decide the problem limitation. There are four types of conjunctions namely
additive, adversative, causal, and temporal (Halliday & Hasan, 1976), but the
researcher limited the problem in this study that is only discussed about an error
analysis on the use of adversative (but), additive (and, or), and causal (because,
so) in students’ writing. The researcher did not choose temporal conjunction,
because temporal conjunction (then, next, after that) is easy to use and the
learners seldom make error in using it (Hamed, 2014).
The researcher chose adversative, additive, and casual for the study
because based on the research by Hamed (2014) students often commit errors in
these three types of conjunction including adversative, additive and causal. Beside
that, based on the researcher’s observation, conjunctions and, or, but, so, and
Research Questions of the Study
According to background of the study, identification of the problem and limitation
of the study, then the research questions of the study can be state as follows:
1. What are the students’ common errors on the use of conjunction in
students’ writing?
2. Which types of errors occur most frequently on the use of conjunction in
students’ writing?
Purposes of the Study
The purpose of this study is:
1. To find out the students’ common errors on the use of conjunction in their
writing.
2. To find out types of errors occur most frequently on the use of conjunction
in students’ writing.
Significance of the Study
This research will have several benefits as follow:
For the learners. This research will be useful to make the learners understand the common error and the types of error on the use of conjunction in
writing. After knowing about error in conjunction, hopefully the learners will
learn more about conjunction. Also learner will be more careful when using
For the lecturer. This research will be useful for the lecturers to find out the errors in using conjunction and types of conjunctions’ error that occur most
frequently in students’ writing. The presence of this research can be a reminder to
the lecturers that there are many students who do not understand how to use
conjunction properly. After the lecturers know about the error that their students
made in writing, then the lecturers are expected to give more explanation when
teaching writing especially in teaching about conjunction.
For the next researcher. The benefit for the next researcher is that the data in this study can be a reference for other researchers that would investigate
the same thing in the future. Beside that, the presence of this research hopefully
can help other researchers who want to conduct a research about the use of the
conjunction such as helping the researcher in finding book or journal’s source.
Outline of the Study
This skripsi consists of five chapters. The first chapter is introduction
consisting of background of the study, identification of the problem, limitation of
the study, research questions of the study, purposes of the study, significance of
the study, and outline of the study. The second chapter describes about literature
review. In this part there are several topics that will be discussed. The topic
consists of writing, conjunction, and an error analysis. Then the third chapter
explains the research method that is used to collect and analyze the data in this
study. The fourth chapter presents the finding and discussion of this study.
Chapter Two
Literature Review
In this section, the researcher discusses the existing literatures that are
related to the topic of this study. The topic consists of writing, conjunction, and an
error analysis on the use of conjunction.
Writing
In this section, the researcher would explain three parts. The first part the
researcher will explain about the definition of writing. The second part is about
the process of writing. The last one is the aspect of writing.
The definition of writing. Having a good writing skill is very important nowadays. This skill is needed in various kinds of academic activities that should
be owned by a student. Especially in language learning, writing is a way to master
a language. Writing is not same as talking. How to arrange words into sentences,
and arrange sentence becomes a whole paragraph to deliver a message in a piece
of written work is a difficult thing to do, and all of it needs skill and lots of
practices.
Writing is a complex process even when writing in native language, and
writing in a second language or foreign language turns out to have a higher level
of difficulty (Sarfraz, 2011; Heydari & Bagheri, 2012). “In L1 writing, the
learners can perform with least hesitation and with few possibilities of errors and
p. 832). The differences in language and sentence structure become a major factor
of the difficulties in writing. That is why among the four skills of language,
writing is counted as one of the most difficult skills to master (Ong, 2011).
According to Nacira (2010), “Writing is a form of expression and
communication which enables learners to communicate ideas, feelings, and
different attitudes in a written mode” (p. 14). Writing is like transferring the ideas
and feelings from mind that wants to be conveyed to others in a written form.
Writing is also a part of the communication, but not delivered verbally.
The process of writing. “In terms of ESL and EFL instruction, writing
helps student learn” (Sattaayatham & Ratanapinyowong, 2008, p. 19). In school,
writing is used to explore student ability in a written task, with this ability student
can pass the course (Brown, 2000). To pass the course of course student needs to
learn how to write well. To make a good writing, learners should implement some
step in writing process.
According to Scrivener (2005) writing involves some mental processes.
Those are to think, to prepare, to rehearse, to make a mistake and to find the
alternative or solution. The other processes in writing are planning, drafting,
revising, and editing (Harmer, 2007). Writing takes a long process. To make a
good piece of writing, of course it is not easy. Therefore the writer must follow
the process in writing step by step, so that their writing will be good in the end.
First step in writing is planning, in this section the writer should prepare
brainstorming. The second step is drafting, th is section focuses on writing freely
without noticing the grammar. The third step is revising. At this stage, the writer
should review their work. They have to check their ideas and find out the errors.
The last step is editing. After the writers conduct planning, drafting, and revising,
they should re-read and focus on tidying their writing like grammar, spelling,
punctuation, and etc, to produce a final version of their written work.
Aspect of writing. There are some aspects in writing. Those aspects are macro and micro skills, mechanical components of writing, cohesion and
coherence (Nurjanah, 2012; Ferdiyana, 2014). The aspects of writing are
elaborated as follow:
Macro and micro skill. The first aspect of writing is macro and micro
components. Brown (2007) mentioned some aspects of micro skill in writing. He
said that macro skill consists of “Produce graphemes and orthographic pattern of
English” (p. 399). Grapheme is the smallest unit of a writing system. Grapheme
consists of a letter of the alphabet, numbers, punctuations, symbols (alphabet of
Chinese, Japanese, or Korean), or other signs that are used to write. Meanwhile,
orthographic pattern is the right way to write a system of writing the language.
Orthographic consists of rules of spelling, hyphenation, capitalization, word
breaks, emphasis, and punctuation.
Furthermore, he mentions the other aspects of micro skill that is “Produce
writing at an efficient rate of speed to suit the purpose” (p. 399). Writing needs an
efficient speed and time, so that the purpose of writing can be achieved. For
aspect that he mentions is “Produce an acceptable core of words and using
appropriate word order patterns” (p. 399). In writing activity especially academic
writing, students are required to write formally that uses appropriate words and
patterns.
He also mentions, “Use acceptable grammatical systems (e.g, tense,
agreement, patterns, and rules) patterns, and rules” (p. 399). A writing that can be
understood by the reader is writing that uses correct grammar (e.g, tenses,
agreement, patterns, and rules). Writing using correct grammar is in accordance
with the rules of writing to make the message that the writer wants to convey can
be delivered appropriately. The last aspects of micro skills that he mentioned is
“Express a particular meaning in different grammatical forms” (p. 399). A word
can have many forms. For example, the word ‘compete’ which is a verb, it could
be a ‘competition’ which is a noun.
Brown (2007) also mentioned some aspects of macro skill in writing. The
first aspect that he mentioned is “Use cohesive devices in written discourse” (p.
399). Writing cannot be separated from the cohesion or linking word. Cohesion
uses for linking between two sentences, phrase, or clauses, so that the sentence
has a logical meaning. Halliday and Hasan (1976) divided cohesion into five
types, reference, substitution, ellipsis, conjunction, and lexical cohesion. The
other aspect that he mentioned is “Use the rhetorical forms and conventions of
written discourse” (p. 399). Rhetorical form in writing is the technique of using
well-structured language. There are four common rhetorical forms: narration,
Furthermore, he mentions the other aspect of micro skill that
“Appropriately accomplish the communicative functions of written texts
according to form and purpose” (p. 399). Writing is one of communication form.
To convey what the writer think or feel can be done by writing. Every written text
must have a goal. There are many goals in writing in accordance with the written
form to be made. For example, narrative text aims to telling a story or an event to
the reader. Besides that, he also mentioned that in writing the writer tries to
“Convey links and connections between events, and communicate such relations
as main idea, supporting idea, new information, given information, generalization,
and exemplification” (p.399).
The next aspect is “Distinguishing between literal and implied meanings
when writing” (p. 399). Literal meaning is a sentence written explicitly. For
example, I hate that ugly shoe. Meanwhile, the implied meaning is a sentence
written implicitly. For example, Maybe you should wear other shoes. The other
aspect that he mentioned is “Correctly convey culturally specific references in the
context of the written text” (p. 399). Culturally specific reference is a word or
phrase that has meaning for one group, but has no meaning in the other group. In
writing a second language this is often occurs. The differences of culturally
specific references must be considered well in writing. For example, British
usually use the term ‘cab’, while American uses the term ‘taxi’. The last aspect
that Brown mentioned is “Developing and using a battery of writing strategies,
such as accurately assessing the audience’s interpretation, using pre-writing
soliciting peer and instructor feedback, and using feedback for revising and
editing” (p. 399).
In conclusion, micro skills include things that are the most basic and
easiest to write, such as mechanical component of writing, and macro skills
include things that are more difficult to write like creating text that has a goal and
arranged in a well-structured.
Mechanical component of writing. The second aspect is mechanical
components of writing. Harmer (2004) mentioned some mechanical components,
such as handwriting, spelling, punctuation, and construction of well-performed
sentences, paragraphs and texts. To make a good writing of course, the writer
should put components in writing into their writing. The writer that use proper
spelling, punctuation, and use construction of well-performed sentences,
paragraphs and texts, then their writing would be good.
Cohesion and coherence. The third aspect of writing is cohesion and
coherence. Halliday and Hasan (1976) define cohesion as the “relations of
meaning that exist within the text” and “it occurs when the interpretation of some
elements in the discourse is dependent on that of another” (p. 4). It means that the
use of cohesion is like a linking between sentence with other sentences, or
paragraph with other paragraphs, so that the text will have an understandable
meaning to the reader. Haliday and Hasan (1976) divided cohesion into five
categories those are reference, substitution, ellipsis, conjunction, and lexical
The other aspect of writing is coherence. Coherence means “to stick
together” (Sattaayatham & Ratanapinyowong, 2008, p. 21). It means when writing
a text, the previous sentence is always interconnected with the next sentence. In
line with Sattaayatham & Ratanapinyowong, Harmer (2004) stated that coherence
is an element of the writing that made phrase and sentence related to each other. If
the text has coherence the reader would be able to understand about the writer’s
purpose and what the writer’s think about.
Conjunction
In this section, the researcher would explain two parts. The first part is
about the definition of conjunction. The second part is about the types of
conjunction. In this part the researcher would explain four types of conjunction;
those are additive, adversative, causal, and temporal.
The definition of conjunction. A conjunction is a word for connecting two or more words (Sanford, 1979). This statement is in line with Setyawan
(2013) who said that “Conjunctions are words function to relate words, phrases, or
sentences that can be classified into coordinating conjunctions, correlative
conjunctions, and subordinating conjunctions” (p. 13). According to Raimes
(1992) conjunction is ways to connect two clauses by using a comma followed by
one of connecting word in order to be aligned sentences. Conjunction takes an
important role in the writing. Without conjunction, the meaning of the text will be
not logic.
Klammer & Schulz, 1992). However, this research will use the types of
conjunction in taxonomy of cohesion by Halliday and Hasan (1976), they divided
cohesion into five types. They are reference, ellipsis, substitution, lexical
cohesion and conjunction. Conjunction is also divided into four types. They are
additive, adversative, causal, and temporal (Halliday & Hasan, 1967). The
researcher takes the types of conjunction from Halliday and Hasan (1976) because
they provided the complete theory about conjunction in English and it is very
detailed.
Actually there are four types of conjunction, but in this study the
researcher limited the types of conjunctions that will be studied. They are
additive, adversative, and causal. The researcher chose adversative, additive, and
casual to be the focus of this the study because based on the research conducted
by Hamed (2014) students often commit errors in these three types of conjunction
namely adversative, additive and causal. Beside that, the researcher did not choose
temporal conjunction, because temporal conjunction (then, next, after that) is easy
to use and the learners seldom make error in using temporal conjunction (Hamed,
2014).
Additive. Additive is used for linking units of semantic similarity. The
additives emphasize the key points or add relevant new information to the
previous sentence. Additive consist of and and or. “The conjunction and links
words or phrases that are similar in sense, or go together in some other ways”
(Seaton & Mew, 2000, p. 232). For the example, Daniel is playing a piano, and
(Seaton & Mew, 2000, p. 232). For the example, I am still thinking to buy this
dress, or other person will buy it. From the example, we can see that there are
similarities in semantic and also relevant information between two clauses.
Beside that, conjunction not only links a whole sentence, but also can
connect phrases. Conjunction and, but, or, and nor can connect noun phrases,
adjective phrases, verb phrases, and prepositional phrases (Raimes, 1990). The
example of how to connect conjunction between phrases (Raimes, 1990, p. 246) is
[image:30.595.94.516.332.734.2]presented below.
Figure 1
Conjunction connecting phrases
Noun phrases
It has a fireplace and moldings. (two items)
It has a fireplace, moldings, and a view. (three items)
Adjective phrases
It always looks neat and tidy. (two items)
It always looks neat, tidy, and cheerful. (three items)
Verb phrases
They probably contemplate life and have drinks before dinner. (two items)
themselves as civilized. (three items)
Prepositional phrases
She works in the kitchen and in the bedroom. (two items)
She works in the kitchen, in the bedroom, and on the pool. (three items)
Adversatives. Adversative is used to indicate information that mark
correction, contrast, and opposite to the sentence mention previously. One of
conjunction that included in adversative is but. “Conjunction but is use to link
words that have different or contrasting meaning” (Seaton & Mew, 2000, p. 232).
For the example: Diana’s hair is short, but Ana’s hair is long. From the example,
we can see that there are contrastive between two clauses.
Causal. Causal is used to express result, reason, or purpose. This
sub-conjunction consists of because and so. “Conjunction so is used to express a
result” (Eastwood, 1994, p. 326). For example: Harry told a sad story, so Julie
cried. Meanwhile conjunction because is called as conjunction of reason, and
conjunction because is used to say why something happens, why somebody does
something, or why you are suggesting something” (Seaton & Mew, 2000, p. 235).
For the example, I go to library because I want to read a book.
Temporal. Temporal used to connect two sentences with sequential,
simultaneous, or preceding relation in the text. It consists of then, next, after that,
the vegetable. Temporal conjunction indicates sequent in the sentences. Usually
temporal conjunction can be found in a procedure text.
An Error Analysis on the use of Conjunction
In this section, the researcher would explain three parts. The first part is
about error. The second part is about error analysis. The last one is about types of
error on the use of conjunction.
Error. In language learning, a student does not always use correct English when they do the writing task. Sometime they make a mistake and error in
writing. Mistake and error are different things in second language acquisition.
According to Brown (2000) a mistake is “a failure to utilize a known system
correctly”, meanwhile an error “reflects the competence of the learner” (p. 257). It
means when the students made a mistake they know where their faults are,
whereas when the students made an error they do not know their fault.
According to Harmer (2007) error is a mistake made by students, and they
can not correct their mistake by themselves, also they need other help to solve
their problem. Error is a mistake committed by students, because they don’t know
what correct is (Ellis, 2000). An error happens because student’s lack of
knowledge about the target language.
Error analysis. The most significant theories of second language
acquisition is Error Analysis (Sawalmeh, 2013). The term of Error Analysis (EA)
was first introduced by S. P. Corder (1967) and it makes him called as the ‘Father
focuses on the error learners made” (Sawalmeh, 2013, p. 2). Similarly, Rustipa
(2011) said that Error Analysis is a type of study that investigated the amount of
error that happens in linguistic area. According to Hourani (2008), error analysis
is an important supply of information about students’ errors to the teacher so that
the teachers can correct their student’s error as well increase their competence of
teaching. Error analysis is a study that discusses about finding student’s errors in
linguistic area.
According to Corder (1981) an error analysis has two functions:
theoretical and practical. “The theoretical aspect of error analysis is a part of
methodology of investigating the language learning process. Meanwhile, the
practical aspect of error analysis is its function in guiding the remedial action we
must take to correct an unsatisfactory state of affairs for learners or teachers”
(Corder, 1981, p.27). When we want to find out the error made by learners, then
we need an error analysis. From that method we can find the solution to overcome
the error that learners made.
Types of error on the use of conjunction. Conjunction plays an important role in English language production. If the writers make an error in
using conjunction, the message they try to convey will give misunderstanding to
the readers. And also, the readers will feel the difficulty to comprehend the text
(Ong, 2011). So, the writers should use conjunction appropriately to make the
This research classified the error in conjunction based on Ong (2011) he
said that there are four types of errors including misuse, unnecessary addition,
omission, and redundant repetition. Misuse happens when the writers used a
conjunction wrongly in the text. Unnecessary addition happens when a
conjunction is used unnecessarily in the text. Omission happens when a
conjunction is expected in the text but the writers did not write there. Redundant
repetition occurs if the writers write a conjunction more than once in the text, so
the conjunction can be deleted or replaced by other words.
Misuse. The use of a conjunction in text classified as misuse if the writers
used a particular conjunction in the text wrongly. For the example, “The
professors are almost the Doctors and [but] the Master postgraduates only can be
assistants” (Ong, 2011, p. 53). The use of conjunction and on the sentence above
is used wrongly. That sentence consists of two clauses connected with
conjunction, and the sentence shows the contrast between the status of the
professor and the master postgraduate. However, the writers uses additive
conjunction and which marks semantic similarity, instead of adversative
conjunction but which marks a contrast that will be suitable for linking that
sentence above.
Unnecessary addition. The use of a conjunction in text classified as
unnecessary addition if the writers used a particular conjunction unnecessary in
the text. For the example, “The government should do its best to punish violators.
So, the government should increase the fine. The government is the only one
The use of conjunction so on the sentence above is an additional conjunction that
is not needed. Conjunction so is used to connect the results or purpose between
two clauses or sentences, but on the text above there is no explanation about result
or purpose after the sentence that uses the conjunction so. The use of so in the text
confuse the readers, so it should be deleted in order to become a correct sentence.
Also, according to Davis, Minihan, Small, and Yitbarek (2007), it is better not
start a sentence with conjunction and, but, or, and so. We can use also or in
addition instead and, use however instead but, use otherwise instead or, and use
as a result or consequently instead so to begin the sentence.
Omission. The use of a conjunction in text classified as omission if the
writer does not use the conjunction that is expected in the text. For the example,
“Shall we watch television go for walk play football?” (Seaton and Mew, 2000, p.
238). That sentence is difficult to comprehended because the sentence is lacking
punctuation comma and a conjunction or. The sentence states a choice, and it
needed a conjunction or to connect the words on the sentence. If the writer write
the sentence like this, Shall we watch television, go for walk, or play football?,
then the sentence will be correct and easy to comprehend.
Redundant repetition. The use of a conjunction in text classified as
redundant repetition if the writer uses the same conjunction more than once in the
text. The use of conjunction like that is not appropriate and one of two
conjunctions should be deleted or replaced by other words. For the example,
“When I back home from in the mall, I met her she called my name “Laras”, and I
than once conjunction and in one sentence. It makes the sentence structure not
correct, so we need delete one of conjunction and from the sentence.
Review of Previous Study
Ong (2011) investigates the use of cohesive devices in expository
composition written by Chinese EFL learners who were learning in a university of
Singapore. The result shows that the participants had a most difficulty in using
reference cohesion, followed by conjunction and lexical cohesion. For
conjunction, the result shows that the greatest difficulty is using additive,
followed by adversative, and then causal or temporal.
Shan-ling (2012) studied error analysis and related theory, and focused on
the cause and the types of the error in student’ writing. The result shows that there
are some errors in students’ writing. The errors include text error and error in
discourse. Text error consists of error in vocabulary, error in collocation, error in
grammar, and error in syntax. In the part of conjunction, the result show that
Chinese learners made errors in using because and so. Chinese learners usually
using so and because in one sentence. The use of because and so in one sentence
is not proper sentence structure in English.
Hamed (2014) analyzed the use of conjunction in argumentative essays of
the fourth-year undergraduate learners of English at Omar Al-Mukhtar University
in Libya. The result of the study showed that students of English as foreign
language made many errors when they use conjunction in writing. The Libyan
fact, and, furthermore, moreover, so and because. The finding shows that
adversative conjunction is the most difficult conjunction for learners in Lybia,
followed by additive and causal.
Melyane and Kurniasih (2014) investigated the use of conjunction in
recount text of student’s writing assignment of tenth graders of SMA N 19
Surabaya. The aim of this study is to find the errors of conjunction usage and the
causes of error that students made based on Richard’s theory (1974). The result
shows that conjunction and, but and because are conjunction’s error that occur
most frequently. The type of error that most frequently occur is omission and
addition. Also the cause of error that happened is because incomplete application
of rules, ignorance of rule restrictions, and over-generalization.
Conceptual Framework
Based on the existing literatures that are related to the topic of this study,
the researcher provides the conceptual framework about an error analysis on the
use of conjunction in student writing.
Writing is a skill that hard to master by English learners. Even a native
learner feels writing is ability that is very difficult to master. Writing can be
defined as an activity to produce a written work. In school, this ability is required
to pass the course. There are some aspects in writing like macro and micro skill,
mechanical component of writing, cohesion, and coherence. In writing, there are
some processes that should be done by a writer. They are planning, drafting,
Conjunction is a word to connect two clauses to make a good sentence.
Conjunction is required to determine whether the text have a good cohesion and
coherence. Conjunction is divided into four types covering additive, adversative,
causal, and temporal.
In the field of Second Language Acquisition (SLA), there is a theory about
an error analysis. This theory appeared because in learning English student always
made an error in using target language. Error is defined as a mistake that cannot
be corrected by students. So, the teacher needs an error analysis to find the way to
Figure 2
Chapter Three
Research Methodology
This chapter presents the methodology of this study, and discusses how
this study was conducted. It consists of four parts, namely research design,
population and sample, data collection method, and data analysis. In the research
design, the researcher explains the design and some reasons of choosing the
design. Next, in the population and sample, the researcher explains the population
and the number of samples, and the sampling technique used for this study. In the
data collection method, the researcher explains the way to gather the data. The last
is data analysis. In this part, the researcher reveals some steps in analyzing the
data.
Research Design
This research adopted a quantitative research method. “In quantitative
research, the investigator identifies a research problem based on trends in the field
or on the need to explain why something occurs” (Creswell, 2012, p.13).
Quantitative research was a research on phenomena using measurement of
quantity or amount (Kothari, 2004). A quantitative research method was suitable
for this research because the researcher wanted to calculate the common errors
and error types of the use of conjunction that most frequently occur in students’
writing.
To be more specific, this research used an error analysis as a method
language learning process” (Corder, 1981, p. 27). The purposes of this study were
to find out the students’ common errors and the types of errors which most
frequently occurred in the use of conjunction in students’ writing. This study is
important because it can discover the students’ errors in using conjunction, and
research on the issue has not been conducted yet at the English Education
Department (EED) of Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta (UMY).
Population and Sample
“Population is a group of individuals who have the same characteristic”
(Creswell, 2012, p. 142). In this study, the population was all students of the EED
of UMY in academic year 2015/2016. There were several reasons of choosing the
students of batch 2015 of the EED of UMY. Firstly, they were in the first year in
learning English. It was assumed that they had problems in using conjunction.
Secondly, the researcher could have easy access to collect the data because the
researcher studied at the EED of UMY.
The total number of students who enrolled at the EED of UMY in
academic year 2015/2016 was 140 students. The researcher used total sampling to
select research respondents. Total sampling is a sampling technique if the number
of population and sample that were used in the study is equal (Sugiyono, 2009).
Thus, all students of the EED of UMY enrolling in academic year 2015/2016
Data Collection Method
To collect the data, the researcher used document analysis. The researcher
collected the data by collecting students’ writing assignment with the lecturer’s
permission. The data were taken from Academic Reading and Writing subject.
The researcher took one of the final writing assignments that the genre was
recount text. There were 140 recount texts of students’ writing assignment and
each text consisted of 20 sentences. The documents were collected to measure the
errors that students made in the use of conjunction.
Validity
Validity is the main key in successful research and it determines the worth
of a piece of research (Cohen, Manion, & Morrison, 2005). The researcher
checked the validity of the data by proofreading. First, the researcher retyped what
respondents wrote on their writing assignment. Then, the proofreader read the
documents of respondents’ original worksheets and the documents that the
researcher retyped. This method was conducted to ensure that the data of
respondents’ writing assignment were exactly the same as what the researcher
wrote.
To ensure the validity of the data, the researcher also used expert
judgment. The expert judgment was carried out by the researcher’s supervisor. All
of errors that were found in the respondents’ writing assignment were discussed
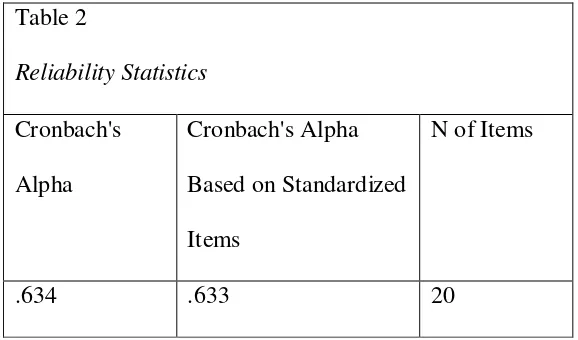
Reliability
According to Cohen, Manion, and Morrison (2005), “Reliability is
essentially a synonym for consistency and replicability over time, over
instruments and over groups of respondents” (p. 117). This research reliability is
important to reveal whether or not the instrument used by the researcher can be
[image:43.595.107.516.277.420.2]trusted. Sekaran (2000) classified three criteria of reliability.
Table 1
The criteria of reliability
0.8-1.0 Good
0,6-0,799 Moderate
< 0,6 Not good
Based on the table above, the researcher applied Cronbach’s alpha in
SPSS to measure the reliability. The result of reliability instrument fell off in
0,633. The table of Cronbach’s alpha is presented below.
Table 2
Reliability Statistics
Cronbach's
Alpha
Cronbach's Alpha
Based on Standardized
Items
N of Items
[image:43.595.106.395.501.671.2]Data Analysis
To analyze the data, the researcher used Corder’s (1967) method of error
analysis. There were three steps. Firstly, the researcher took samples from the
respondents. Secondly, the researcher read all the respondents’ worksheets, and
identified the errors. Thirdly, the researcher analyzed and classified the errors.
After collecting data, the researcher read all of the respondents’
worksheets. There were 140 recount texts that consisted of 2800 sentences. After
read all the worksheets, the researcher identified the errors found in respondents’
worksheet based on errors in the use of conjunction but, and, or, because, and so.
The identified error sentences were typed in Microsoft Word and the researcher
made lists of errors in the use of conjunction but, and, or because, and so. Then,
the researcher analyzed all of the identified error sentences. After the researcher
re-read and analyzed all of the error sentences, the researcher deleted some
sentences, which did not have errors in the use of conjunction, from the list and
left the rest sentences that had errors. Last, the researcher classified the errors into
four types, namely misuse, unnecessary addition, omission, and redundant
repetition.
In this study, the researcher used a statistical analysis program, SPSS, to
process the data. After all of the data were collected, the researcher analyzed the
data using descriptive statistics. According to Creswell (2012), “descriptive
statistics indicates general tendencies in the data (mean, mode, median), the
spread of scores (variance, standard deviation, and range), or a comparison of how
components of descriptive statistic are mean, mode, and median used to answer
the research questions. Creswell (2012) stated mean is an average score of the
data, median is the middle of a position of scores, and mode is the numbers that
Chapter Four
Findings and Discussion
This chapter presents the answers of two research questions. The first
research question is “What are the students’ common errors in the use of
conjunction in students’ writing?”. The second research question is “Which types
of errors occur most frequently in the use of conjunction in students’ writing?”.
The discussion of the findings is also presented in this chapter.
Findings
In this section, the researcher presents the findings of the research. This
heading will explain two parts. The first part is about the students’ common errors
in the use of conjunction in students’ writing. The second part is the types of error
that occurred from the most to the least frequently in the use of conjunction in
students’ writing.
The students’common errors on the use of conjunction in students’ writing. The researcher categorized conjunction based on Halliday and Hasan (1976). Haliday and Hasan (1976) said that there are four types of conjunction,
namely adversative, additive, causal, and temporal. However, the researcher only
studied conjunction but included in adversative conjunction, and, and or included
in additive conjunction, as well as because and so included in causal conjunction.
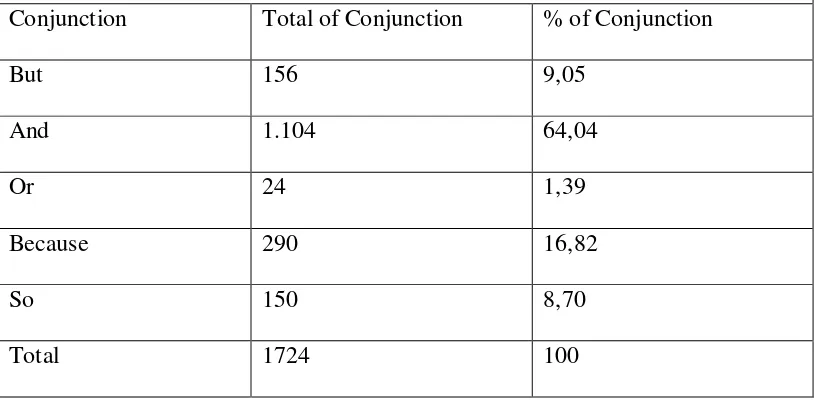
Based on the data analysis, it can be seen in table 3 about the frequency of
conjunction used in the text by students of the EED of UMY in academic year
Table 3
Total of Conjunction but, and, or, because, so in the text
Conjunction Total of Conjunction % of Conjunction
But 156 9,05
And 1.104 64,04
Or 24 1,39
Because 290 16,82
So 150 8,70
Total 1724 100
Based on the table 3, there were 1.724 conjunctions that consist of but,
and, or, because, and so. There were 156 conjunctions but (9,05%), 1104
conjunctions and (64,04%), 24 conjunctions or (1,39%), 290 conjunctions
because (16,82%), and 150 conjunctions so (8,70%) that were used by students in
the texts. The result showed that the most to the least frequent used conjunctions
in students’ writing respectively were and, because, but, so, and or.
Based on the findings, the frequency of using conjunction and was the
most commonly used in the text. The number of conjunction and was the highest
among the other conjunctions because the researcher used recount text on this
study. If the researcher used other genres such as argumentative text, compare and
contrast text, or procedure text, the possibility of the frequency of conjunction use
Table 4
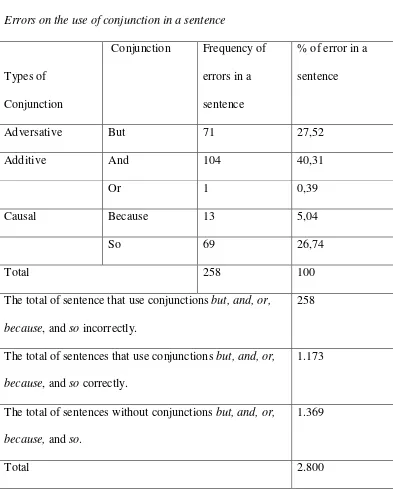
Errors on the use of conjunction in a sentence
Types of
Conjunction
Conjunction Frequency of
errors in a
sentence
% of error in a
sentence
Adversative But 71 27,52
Additive And 104 40,31
Or 1 0,39
Causal Because 13 5,04
So 69 26,74
Total 258 100
The total of sentence that use conjunctions but, and, or,
because, and so incorrectly.
258
The total of sentences that use conjunctions but, and, or,
because, and so correctly.
1.173
The total of sentences without conjunctions but, and, or,
because, and so.
1.369
Total 2.800
Based on table 4, of 2800 sentences there were 258 error sentences in the
use of conjunctions but, and, or, because, and so. There were 1369 sentences that
were written without conjunctions but, and, or, because, and so. Meanwhile, there
and so correctly in the texts. The data showed there were 71 error sentences
(27,52%) in using conjunction but, 104 error sentences (40,31%) in using
conjunction and, 1 error sentence (0,39%) in using conjunction or, 13 error
sentences (5,04%) in using conjunction because, and 69 error sentences (26,74%)
in using conjunction so. The data revealed that the most to the least frequent
common errors in the use of conjunctions in students’ writing was respectively
conjunction and, but, so, because, and or.
The types of error occur most frequently on the use of conjunction in students’ writing
The researcher categorized the types of errors made by the students of the
EED of UMY in academic year 2015/2016 when using conjunction in writing
based on research by Ong (2011) written in chapter two (p. 21-23). Ong (2011)
divided errors into four types, namely misuse, unnecessary addition, omission,
and redundant repetition.
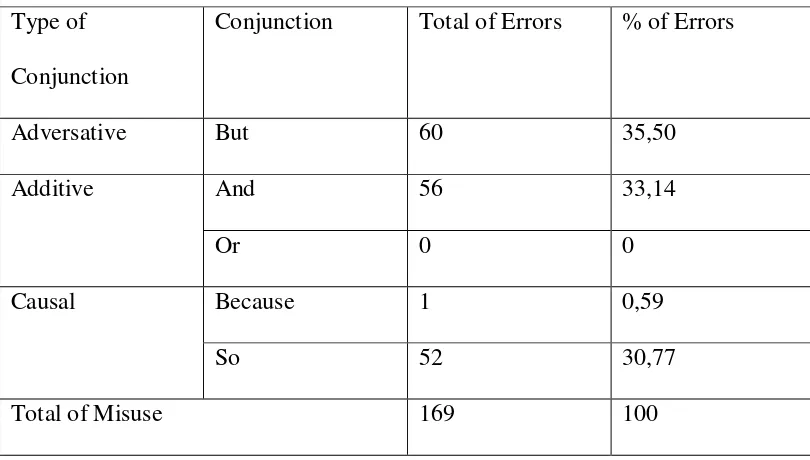
Table 5
Misuse on the use of conjunctions but, and, or, because, so
Type of
Conjunction
Conjunction Total of Errors % of Errors
Adversative But 60 35,50
Additive And 56 33,14
Or 0 0
Causal Because 1 0,59
So 52 30,77
Total of Misuse 169 100
Based on the table 5, the result showed there were 169 misuses in
conjunction. There were 60 sentences misusing conjunction but (33,50%), 56
sentences misusing conjunction and (33,14%), 1 sentence misusing conjunction
because (0,59%), and 52 sentences misusing conjunction so (30,77%). The data
reported that conjunction and was the most frequent misuse.
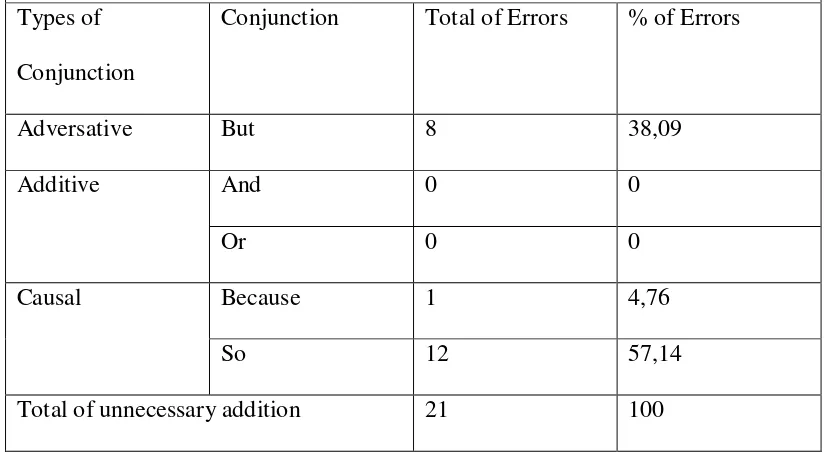
Unnecessary addition. The second type of errors in conjunction is
unnecessary addition. The result of this error type is presented in the table below.
Table 6
Unnecessary addition on the use of conjunctions but, and, or, because, so
Types of
Conjunction
Conjunction Total of Errors % of Errors
Adversative But 8 38,09
Additive And 0 0
Or 0 0
Causal Because 1 4,76
So 12 57,14
Total of unnecessary addition 21 100
From the table 6, 21 sentences were included in the unnecessary addition.
There were 8 unnecessary addition sentences that used conjunction but (38,09%),
1 unnecessary addition sentence that used conjunction because (4,76%), and 12
unnecessary addition sentences that used conjunction so (57,14%). It can be
concluded that the use of conjunction so is the most frequent error in unnecessary
addition type.
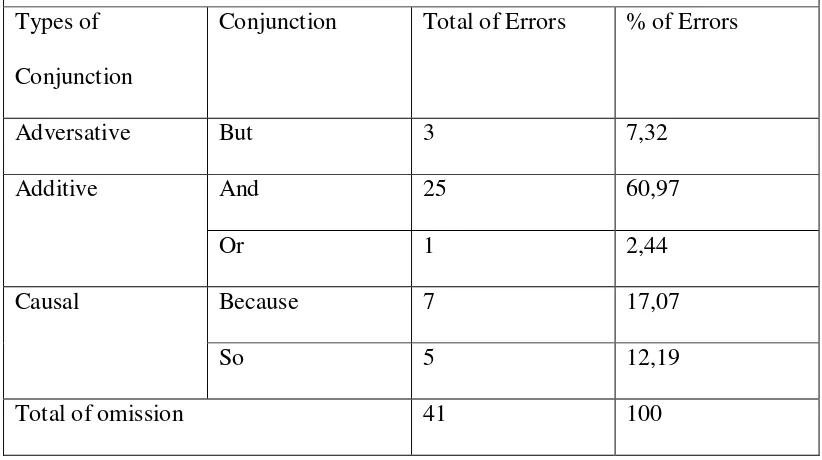
Table 7
Omission on the use of conjunctions but, and, or, because, so
Types of
Conjunction
Conjunction Total of Errors % of Errors
Adversative But 3 7,32
Additive And 25 60,97
Or 1 2,44
Causal Because 7 17,07
So 5 12,19
Total of omission 41 100
It can be seen from table 7 that 41 sentences were included in the omission
type. There are 3 omission sentences that used conjunction but (7,32%), 25
omission sentences that used conjunction and (60,97%), 1 omission sentence that
used conjunction or (2,44%), 7 omission sentences that used conjunction because
(17,07%) and 5 omission sentences that used conjunction so (12,19%). As the
result, conjunction and is the most frequent error in omission type.
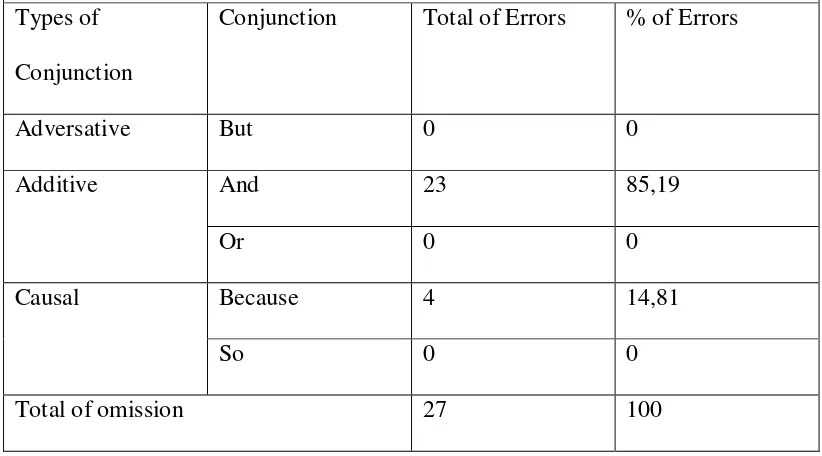
Table 8
Redundant repetition on the use of conjunctions but, and, or, because, so
Types of
Conjunction
Conjunction Total of Errors % of Errors
Adversative But 0 0
Additive And 23 85,19
Or 0 0
Causal Because 4 14,81
So 0 0
Total of omission 27 100
It can be seen from table 8 that 27 sentences were included in conjunction
types. There were 23 redundant repetition sentences that used conjunction and
(85,19%), and 4 redundant repetition sentences that used conjunction because
(14,81%). The finding showed that conjunction and is the most frequent error in
redundant repetition type.
Based on the presented data of each error type, the results of all types of
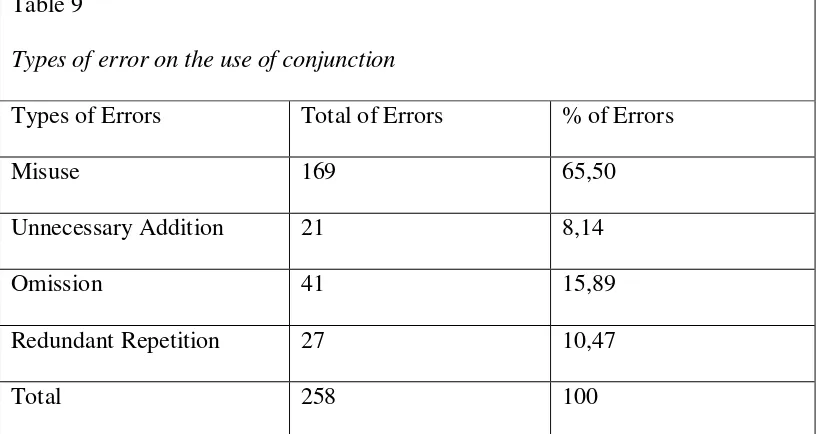
Table 9
Types of error on the use of conjunction
Types of Errors Total of Errors % of Errors
Misuse 169 65,50
Unnecessary Addition 21 8,14
Omission 41 15,89
Redundant Repetition 27 10,47
Total 258 100
Based on table 9, there were 169 sentences (65,50%) of misuse type, 21
sentences (8,14%) of unnecessary addition type, 41 sentences (15,89%) of
omission type, and 27 sentences (10,47%) of redundant repetition type. the data
showed that types of error occurring most frequently in the text were respectively
misuse, omission, redundant repetition, and unnecessary addition.
Discussion
The students’ common errors on the use of conjunction in students’
writing. Based on the results, there were many errors on the use of conjunction that were found. Errors on using conjunction that were found in the students’
writing assignment would be analyzed by using error analysis. The researcher
read all of examined documents. There were many errors in the use of adversative
conjunction (but), additive conjunction (and, or), and causal conjunction
The use of adversative conjunction. One of that adversative conjunctions examined by the researcher is but. The results showed that students made
mistakes in using conjunction but when they wrote. The inappropriate use of
conjunction but was showed in 71 sentences (27,52%).
Error in the use of conjunction “but”. This research found out that
students of the EED of UMY still made errors in using conjunction but when they
wrote. For example, “She should arrived Jogja in the morning because she went in
evening. But because of far away and stagnation effect of holiday” (Respondent
14). The respondents who wrote that sentence used the conjunction but want to
show the contrastive relation between the sentences. However, he used
conjunction but in the text incorrectly. He added conjunction because right after
he used conjunction but. “Conjunction but uses to link words that have different
or contrasting meaning” (Seaton & Mew, 2000, p. 232); otherwise, conjunction
because included in causal conjunction is used to express a result, reason, or
purpose (Halliday & Hasan, 1967). The use of conjunction but in the sentence is
improper because of the use of the conjunction because after the conjunction but.
It made the sentence confusing, whether the sentence showed contrast relation or a
reason.
Based on the findings, the researcher found out that most of respondents
used two conjunctions to link two clauses. For instance, “Although I felt so tired
but I enjoyed my trip” (Respondent 93). The respondent used two conjunctions to
link two clauses in the text. The use of conjunction in the sentence is
connect two clauses by using a comma followed by one of the connecting words
in order to be aligned sentences. The respondents should delete conjunction but in
the sentence to make the sentence correct.
The other error in the use of conjunction was that students often used
conjunction but to begin a sentence. Meanwhile, Davis, Minihan, Small, and
Yitbarek (2007) said that students should not start a sentence with conjunction
and, but, or, and so. For example, “They went to Jogja by car and they left on
Friday. But, there was traffic jam on the trip” (Respondent 70). The research
findings showed that many respondents used conjunction but, and, or, and so to
begin a sentence even though they used a correct conjunction in the text.
However, they wrote the conjunction but, and, or, and so to begin the sentence,
and it was not appropriate based on Davis, Minihan, Small, and Yitbarek (2007).
If they used coma instead of full stop before the conjunction but, it would be
correct.
The use of additive conjunction. There are two additive conjunctions
which are and and or examined in this research. The results showed that students
made mistakes in using conjunction and and or when they wrote. The
inappropriate use of conjunction and was showed in 104 sentences (40,31%) and
the incorrect use of conjunction or was revealed in 1 sentence error (0,39%).
Error on the use of conjunction “and”. The findings showed that most of respondents used conjunction to begin a sentence. For example, “And then after
subuh prayer, I drank a cup of coffe. And I went to the kitchen, I called my
conjunction because he began a sentence with conjunction and. For instance,
“And we build a tent, it's almost take 25 minutes. And didn't forgot to make a fire
camp to keep warm” (Respondent 60). It is line with the theory of Davis, et al.
(2007) that a sentence should not begin with conjunction and, but, or, and so.
This research also found out that students of the EED of UMY did not use
conjunction and to link the word, clause, or sentence. For example, “After that
stand by for walk around beach, Lawang sewu, tembarang, simpang” (Respondent
48). The sentence was error because the respondent did not use conjunction to link
word tembarang and simpang. It was in line with Raimes (1990) saying that
conjunction and, but, or, and nor can connect noun phrases, adjective phrases,
verb phrases, and prepositional phrases. To make a correct sentence using
conjunction and to connect two noun phrases, the sentence should be “After that
stand by for walk around beach, Lawang sewu, Tembarang, and Simpang”.
Error on the use of conjunction “or”. After analyzing the error on the use
of conjunction or in students’ writing assignment, the researcher found one error
on the use of conjunction or. “I did not go to Mall, Market, or the Historical Site
and the other place because I was save my money” (Respondent 32). The
respondent used conjunction or in the text inappropriately. There were three noun
phrases in the sentence that should be linked by conjunction. The sentence
showed the choice among four places so that conjunction or to link the noun
phrases was necessary. It was in line with Seaton and Mew (2000) saying that
conjunction or is used to express a choice. However, the respondent used
between the third and fourth noun. To make a correct sentence, the respondent
should change conjunction and and put conjunction or between the third and
fourth noun. It was supported by Raimes (1990) saying that conjunction or can
connect noun phrases. If there are two or more noun phrases, the conjunction
between the last two noun phrases should exist.
The use of causal conjunction. This research examined two adversative
conjunctions, namely because and so. The findings showed that students made
mistakes in using the use of conjunction because and so when they wrote. The
inappropriate use of conjunction because was showed in 13 sentences (5,04%)
and the incorrect use of conjunction so was revealed in 69 sentences (26,74%).
Error on the use of conjunction “because”. This research found out that
most of error in using conjunction because is because the respondent did not use
conjunction to connect two clauses when it needed. “There was any problem to
met him, he asked me to met at night” (Respondent 68). The first clause told that
there was a problem to meet the respondent’s friend, and the second clause told
the reason why the respondent cannot meet his friend was because his friend
wanted to meet him at night. The conjunction because was necessary to connect
those two clauses so that the relation of the clauses would be clear.
The other respondents also made the same errors in the use of conjunction
because. For instance, “At the time, my nephew come from solo to my house, she
want holiday in Jogja” (Respondent 140). The first clause of the sentence told that
the respondent’s nephew who came to his house from Solo, and the second clause
conjunction because was necessary to connect those two clauses because Seaton
and Mew (2000) said that “Conjunction because is called as conjunction of
reason, and conjunction because is used to say why something happens, why
somebody does something, or why you are suggesting something” (p. 235).
Besides, this research also found that a respondent forgot to use a
conjunction to link two clauses and they also used the same conjunction in one
sentence. “I felt so happy to worked here because almost all of the crew who still
young, because they are AMPTA student” (Respondent 25). It can be seen that
the respondent used conjunction because twice in the sentence. The first clause
told that the respondent was happy working at his work place, and the second
clause told that he gave a reason why he was happy. To link the first and the
second clause, he used conjunction because, However, after he linked those two
clauses, he added the other conjunction because in the sentence. The use of two
conjunctions was not appropriate and one of two conjunctions should be replaced
by another conjunction (Ong, 2011).
Error on the use of conjunction “so”. This research found the most
dominant error on using conjunction so is because the respondents used
conjunction so to begin the sentence. Meanwhile it clearly stated by Davis,
Minihan, Small, and Yitbarek (2007) not to start a sentence with conjunction and,
but, or, and so. If there is a sentence begin with conjunction so, then it will be
error. For the example, “The location was on the top of the hill. So all of us gave a
little extra try to got on the top” (Respondent 19). Same problems happened on
the sentence with conjunction so. “We also took some pictures with tourist from
another country. So, I can practice my English to the tourist” (Respondent 30).
Another error in the use of conjunction so was also found in this research
because the respondent used conjunction so in correctly. For example, “Last week
it was a new year eve, so I didn’t went anywhere” (Respondent 120). The
sentence, in fact, was not about purpose relation that the conjunction is so, but the
sentence actually showed contrast relation between two clauses. It is in line with
the statement of Seaton and Mew (2000) that “conjunction but is used to link
words that have different or contrasting meaning” (p. 232). Thus, to make the
sentence