A "Skripsi"
Presented to the Faculty ofTarbiyah and Teachers' Training
in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Strata
1
(Bachelor of Arts) in English Language EducationBy:
SUCI ANGGRAENI
NI:tvi: 103014026975
., '""'
.
X?,
r>
'L
:
|ウ[ゥセ@
·::"
J\o. lmhdz .·b
l0
-.o.:i.,.=.L
0?
kfa:-;ifil"<;:;J ; ... -.. -. ....-DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH EDUCATION
FACULTY OF TARBIYAH AND TEACHERS' TRAINING
SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
A Skripsi
Presented to the Faculty ofTarbiyah and Teachers' Training
in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Strata 1
By:
SUCI ANGGRAENI
103014026975
Approved by Adviser:
Dr. DIDIK SANTOSO, M.Pd
NIP :
150 270 348
DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH EDUCATION
FACULTY OF TARBIYAH AND TEACHERS' TRAINING
SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
Training certifies that the 'skripsi' (scientific paper) entitled "TEACHING
QUESTION TAGS THROUGH PICTURES (A Pre Experimental Study at
the Second Year Students ofSMP Al Mubarak Ciledug)", written by Suci
Anggraeni, student's registration number 103014026975, was examined by the
committee on December, 5th 2008, and was declared to have passed and,
therefore, fulfilled one of the requirements for the acedemic title of S.Pd.
(Bachelor of Arts) in English Language Education at the Department of English
Education.
Jakarta, December, 5th 2008
EXAMINATION COMMITTEE
CHAIRMAN : Ors. Syauki, M.Pd
NIP.150 246 289
(
SECRETARY: Neneng Sunengsih, S.Pd. ( )
NIP.150 293 236
' Y _
EXAMINERS: 1. Ors. H. A. Munir Sonhadji,
mNe、セェ@
,NIP.150 050 682 .
2. Dr. M. Farkhan, M.Pd
NIP.150 299 480
Acknowledged by:
(
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... .iii
CHAPTER I : INTRODUCTION v A. Background of the Study ... ! B. Identification of the Problem
セ@
... 3C. Limitation of the Problem ... 3
D. Fonnulation of the Problem.' ... 4
E. Significance of the Study ... .4
CHAPTER II : THEORETICAL FRAME,VORK A. Theoretical Description ... 5
1. Question Tags ... 5
a. Definition of Question Tags ... 6
b. Pattern and Function of Question Tags ... 7
2. Pictures ... 11
a. Definition of Pictures ... 11
b. Kind and Type of Pictures ... 12
c. Design of Teaching through Pictures ... 14
d. Procedure of Pictures ... 15
e. Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Pictures ... 17
B. Conceptual Framework ... 18
C. Hypothesis ... 19
a. Conceptual Definition ... 21
b. Operational Definition ... 21
c. Specification ... 22
6. Analysis ofData ... 22
B. Research Findings 1. Description ofData ... 24
2. Discussion ... 32
CHAPTER IV : Conclusion and Suggestion A. Conclusion ... 33
B. Suggestion ... 33
BIBLIOGRAPHY ... .35
Lord of the world who has bestowed upon the writer in completing this
"Skripsi". Peace and Blessing upon our prophet Muhammad SAW, his
families, his companion and his followers.
This "skripsi" is presented to the Department of English Education Faculty ofTarbiyah and Teachers' Training SyarifHidayatullah State Islamic University Jakarta as partial fulfillment of the requirement for the degree of S.Pd (Bachelor of Arts) in English language education.
The writer would like to thank to Dr. Didik Santoso, M.Pd as her adviser. Thank you very much for your guidance, correction, and also your valuable time to guide the writer until she finished her paper.
The writer also would like to thank to the most special person in her life, her husband always encourages her in every situation with his full heart and love (Fambudi Irrnansyah). Her parents (Kasiman and Sariyah), her sisters (Novi and Umi) and also her lovely daughter (Khilyatin), have given their support during her studying and her writing "skripsi". Thank you for your kindness.
Alhamdulillah, the writer has finished this "skripsi". Absolutely, it is not an effort by herself alone, there are many "hands" help her. In this occasion, she presents great honor to:
1. All lecturers who have taught her in this English Department, for giving new . knowledge and advices in facing life.
2. Drs. Syauki M.Pd., the head of English Department.
3. Mrs. Neneng Sunengsih S.Pd., the secretary of English Department.
4. Pro£ Dr. Dede Rosyada, MA., as a dean ofTarbiyah Faculty and Teachers' Training.
May Allah, the Almighty bless them all, Amin.
Finally, the writer realizes that this "skripsi" is far from being perfect,
therefore it is really a pleasure to receive suggestion and critic from everyone for
better writing.
Jakarta, November 2008.
The writer
A. Background of the Study
Language is a way of expressing ideas, feelings using movements,
symbols, and sound1• And English is one of an international language and it is
widely used and studied all over the world. As we know English is not only used
in writing but also in speaking as a means of communication. In teaching language especially English as a foreign language, one thing that the learner
must study at the first time they learn English is about grammar. To be able to
speak and write English well and fluently, the learner should master grammar
perfectly in written & spoken, they can not write and speak English without
knowing grammar.
To teach grammar as a mean for communication, the students are not
only to be obliged to understand the knowledge of grammar but also they have
to use it in a real communication. Teaching for communication means teaching
student to do things through language
セ、@
mastering the grammatical structurenecessary to achieve that end. Consciousness of correct grammatical forms and
the way the forms are used is necessary to facilitate communication. It is the
support system for all communication though we may be concentrating in our
teaching. As Eskey (1983) points out with exasperation: " we used to believe
that if students learned the form, communication would somehow take care of
itself. Now we seem to believe that if students somehow learn to communicate,
mastery of the forms will take care ofitself"2•
Learning in order to communicate is now commonplace, recent trends in
teaching English programs show the growing concern among educators for the
importance of communicative approach as applied in teaching English. Through
1
communicative approach, students are supposed to have communicative
competence using English.
Learning a language is not a matter, of acquiring a set of rules and
bQilding up a large vocabulary. The teacher's efforts should not be directed at
informing her student about a language, but at enabling them to use it. A
student mastery of a language is ultimately measured by how well he can use it,
not by how much he knows about
it.
In this respect learning a language hasmuch common with learning musical instrument. The drills and exercises a
student does have one end in sight: to enable him to become a skilled performer.
A student who has learnt a lot of grammar but who cannot use a language is in
the position of a pianist who has learnt a lot about harmony but cannot play the
piano. The student's command of a language will therefore be judged not by
how much he knows, but how well he can perform in pub!ic3•
Acquiring a new language is not easy tc do. The fact shows that many
stUdents who study English as a foreign language for many years are unable to
apply English. So we cannot say that the students who have studied English for
several years are automatically able to use it. Mackey said: "Every year millions
of people start learning a second language but very few succeeded in mastering
it. Why is this so? The first and obvious reason is that the learner of the second
language has had experience with another language"4•
The statements above show that grammar keeps an important role in
communication. But, when the student learns a second or a foreign language
they will meet a method or an approach that it cannot be separated from their
process in learning language. And basically a method or an approach will be
often influenced by a view or a theory of language, for example, if a method is
based on the assumption, it will be different from a method based on the
on the teacher, the imagination, her creativity and the condition of the class, a certain problem can be solved with the various techniques5•
In fact, methods or technique are important to improve the students' comprehension about grammar. Therefore the teacher can use methods or techniques that are suitable and interesting to the students. The teacher can organize material with some techniques so that it is easier to understand. The explanation and examples should be sufficient activities to reinforce the understanding. The picture can be use in teaching language, individual pictures may be used for introducing and memorizing.
The pictures can direct the students to communicate. The picture can create students more active to learn and to understand about question tags. Using pictures in teaching question tags is effective helpful in teaching learning process. Because learning question tags is more complicated and there is separate tag for each sentence pattern. Therefore the teacher uses the picture to make easy her explanation and the students become easy in understanding English.
Based on the statement above, the writer is going to make a research about teaching question tags using pictures at second grade of SMP AL Mubarak Ciledug Tangerang.
B. Identification of the Problem
There are many problems that can be identified in relation to question tags:
• How do the students use question tags? • Do the students difficult to use question tags?
• Can pictures teaching influence the ability to use question tags? • How to teach question tags by using pictures?
C. Limitation of the Problem
To avoid misunderstanding in interpreting the problem, it is necessary to
make the limitation of the problem. The writer limits the problem as follows:
1. Question Tags is a part of English subject taught in the second year students
of SMP AL Mubarak Ciledug.
2. Picture is a technique that writer makes a research in this paper.
D. Formulation of the Problem
Based on background of the study, the writer formulates her problem as
follows: " Is there any difference between the Students' Pre-test Scores and the
Students' Post-test Scores in Teaching Question Tags through Pictures ? "
E The Organization of the Paper
This research paper has four chapters:
The first chapter is introduction, which consists of background of study,
identification of the problem, limitation of the problem, formulation of the
problem, significance of study. The second chapter is theoretical framework,
which consists of three parts. Part one is theoretical description, which covers
two parts. Part a is question tags, which consists definition of question tags,
pattern and function of question tags. Part b is pictures, which consists definition
of pictures, kinds and type of pictures, design of teaching through pictures,
procedure of teaching through pictures, advantages and disadvantages of
pictures. Part two is conceptual framework and Part three is hypothesis.
The third chapter consists of two parts. Part A is Research Methodology
which consists objective of study, place and time, population and sample,
method of research, instrument of research consists of conceptual definition,
operational definition, specification. And the last of chapter three is analysis of
data. Part B is research finding which consists data description and discussion.
A. Theoretical Description
1. Question Tags
A question tag is a grammatical structure in which a declarative
statement or an imperative is turned into a question by adding an
interrogative fragment (the "tag").
In most languages, question tags are more common in colloquial
spoken usage than in formal written usage. They can be an indicator of
politeness, emphasis, or irony. They may suggest confidence or lack of
confidence; they may be confrontational or tentative. Some examples
showing the wide variety of structure possible in English are:
• She doesn't really want that, does she?
• You'd better stop now, hadn't you?
Standard English question tags, on the other hand, are constructed
for every sentence, therefore quite variable: have I? did you? won't we?
etc. This is also found
in
the Celtic languages. A question tag need not have the grammatical form of a question (will you?); an adverb oradverbial may serve the purpose instead: right? all right? surely? OK? eh?
German often uses oder? ("or") and ja? ("yes") as question tags. 6
a. Definition of Question Tags
A question tag is a question added at the end of a sentence. Speaker use question tags chiefly to make sure their information is correct to seek agreement. 7
According to Jean Paningkas; question tags are short yes I no questions added to statements. They are conversation forms and seldom occur in writing except in reported speech. Sometimes question tags are used just to keep the conversation going; other times the speaker is not absolutely sure of his statement and he is asking for confirmation. The two different situations are reflected in the intonation. 8
A question tag is a statement with a short question attached at the end. People usually use question tags to ask for clarification or to confirm information they think is true. The subject of a tag is always a pronoun. Question tags use the same auxiliary verbs as yes I no questions.9
A question tag is rather like a 'reply question' : it is made up of auxiliary verb
+
personal pronoun. It is used at the end if a sentence, to ask for confirmation of something we are not sure about, or to ask for agreement 10Question tags are also yes-no questions, but the special form into which they are put shows which of these two answers is actually expected. These alternatives for yes-no questions consist of two parts. The first part makes a statement; the second part asks the question that expects agreement with the statement. The second part contains the
7 Betty Schrampfer Azar, Understanding and Using English Grammar for
Communication 2nd Edition, (USA:: Prentice Hall.Inc., 1989), p. 390
8 Jean Paningkas, Rapid Review of English Grammar 2'" Edition, (New Delhi: Prentice
regular question auxiliary plus the personal pronoun that stands for the subject. 11
Based on the explanation above, the writer can conclude that " Question tag is a question or yes-no question which is put at the end of a statement and made up of auxiliary verb + personal pronoun, to ask for clarification, to confirm information or to make sure that information is correct".
b. Pattern and Function of Question T::gs
1) Pattern of Question Tags
Many languages have just one tag which is added to all statement. English is more complicated. There is separate tag for each sentence pattern. Observe the following facts about conversation questions:
• When the statement is affirmative, the question is negative, when the statement is negative, the question is affirmative.
He likes apples, doesn't he? She doesn't like apples, does she?
• When the verb in the statement is a single form of be, the verb in the question is the same form.
Taxes fill< high in college town, aren't they? That's right, isn't it?
• When the verb in the statement in a single of any verb except be, the verb in the question is the same form.
You live in an apartment, don't you? Miller lives in an apartment, doesn't he?
• In most other cases, the verb in the question is the first auxiliary of
the verb phrase.
You've owned this house quite a while, haven't you?
It will be six years soon, won't it?
• When the verb phrase in the statement is made with used to or have
to, the verb in the question is do.
They didn't have to pray property エセNク・ウ@ then, did they?
• Statements made about one's self with the verb be are generally
made in the negative, due to the lack of a contraction of
am
+
not.
If the statement is affirmative, the full form must be used in thequestion. Though it sounds a bit pedantic, it is certainly quite
acceptable.
I'm not late, am I?
I'm not going to see you again, am I?
I'm going to see you again, am I not?12
According to Betty Schrampfer Azar in her book, she gives simple pattern
of question tags that would make students understanding clearly.
a) Jack can come, can't he?
b). Fred can't come, can he?
A tag question is a question added at
the end of a sentence. Speakers use
tag questions chiefly to make sure
their information is correct or to seek
agreement.
Affirmative Sentence + Negative Tag セ@ Affirmative Answer Expected
Mary is here,
+
Y o.u like tea,
+
isn't she?
don't you?
Yes, she is.
Negative Sentence + Affirmative Tag - - Negative Answer Expected
Mary isn't here, + is she?
You don't like tea, + do you?
They haven't left, + have they?
b) Thisffhat is your book, isn't it?
Theseffhose are yours, aren't they?
they
-
--No, she isn't.
No, I don't.
No, they haven't.
The tag pronoun for this/that
=
it The tag pronoun for these/those =c) There is a meeting tonight, isn't there? In sentences with there +be, there is
d) Everything is okay, isn't it?
e) Everyone took the test, didn't they?
f) Nothing is wrong, is it?
used in the tag.
Personal pronouns are used to refer
to
indicate pronouns. They is usually
used in a tag to refer to everyone,
everybody, someone, somebody, no
one, no body.
Sentence with negative words take
g) Nobody called on the phone, did they? Affirmative.
h) You've never been there, have you?
i) I am supposed to be here, am I not?
j) I am supposed to be here, aren't I?
In(j): am I not? Is formal English.
In(k): aren't I? Is common in spoken
En ... 1! 'h 13
2) Function of Question Tags
Question tags are normally used to ask for confirmation of what
has just been said. Question tags have some functions, they are14;
a) If we simply wish to ask for confirmation concerning something we already feel sure of, falling intonation is used. The purpose of this is
usually just to elicit a reaction from the other person.
It's a nice day, isn't it?
...
...You don't live in London, do you?
b) If, on the other hand, we are not sure whether what we are saying is correct, rising intonation is used. In this case the question tag helps to
form a more genuine question.
...
/ "
Sheila's met you before, hasn't she?
...
/ "
He didn't pay, did he?
c) There is also another type of question tag. These are not normally
'questions' at all, but are used to express emotional reaction of some
kind. They may indicate feelings like: anger, worry, interest. In these
cases a rising intonation is normally used.
...
/ "
Anger : So he's late again, is he?
...
/ "
Worry
: She's safe now, is she?...
/ "
2. Pictures
Visual aids is one of the teaching aids that can be used for presentation, practice and testing. We can show things that can not be explained in simple word.
Picture plays an important role as an alternative teaching aids in teaching English. The teacher gives a picture, then she asks the students about it Picture is easy to be found by all people. Through picture the students can practice to develop their ideas.
The use of picture is an excellent technique to help students understand various aspect of foreign language. The picture has motivated the students, made the subject clearer to understand, and illustrated the general idea of an object reaction which is particular to a culture. It can help to develop various other needed skills such as visual discrimination, attention to detail, and extension of concepts.
Pictures are versatile and useful resources for teaching aspects of grammar that require a structure meaning match. Interesting or entertaining pictures motivate students to responds in ways that more routine teaching aids, such as textbook or a sentence on the board, can not Pictures can also be used in various configurations to enhance learning and practice.15
a. Definition of Pictures
In Oxford advanced learner's dictionary, "picture is a painting, drawing, sketch, especially as a work of art.16
through their representation of places, object and people they are an essential part of the overall experience3.17
In Webster's New World Dictionary of American English, "Picture is an imagination or likeness of an object person or scene on a flat surface, especially by painting, drawing or photography".18
According to the definitions above, the writer can assume that "Picture is a painting, a drawing, an imagination or likeness of an object person or scene on flat surface, which might be used more effectively to develop and sustain motivation in producing positive attitude toward English and to reach or reinforce language skill ".
b. Kinds and Type of Pictures
There are many pictures that we can see in life, according to William Frances Mackey, there are some different kinds of pictures nan1ely:
• Thematic Pictures
Thematic pictures are those used simply to illustrate a theme or a text. Their use in getting meaning across can only be incidental to their function as illustrations. It most often came in the form of crowded scenes, illustrating a single tlieme, etc. Although they usually do not give the meaning of everything, it is likely that the meaning of a certain percentage of items, especially that of the concrete nouns, is conveyed through the picture.
• Mnemonic Pictures
Mnemonic pictures are those designed to remind the learner of certain words or sentences. They may be pictures of situations, presented simultaneously with sentences about these situations, and used later to remind the learner of these sentences. They may
represent situations broken up into sequences and presented in a
short comic-strip technique.
• Semantic Pictures
Semantic pictures are those whose sole function is to get a specific
meaning across. If the pictures are all intentionally semantic, that
is, if they are exclusively a me:ms of teaching, we may examine
them for the amount of meaning they teach and for their effiCiency
in teaching it.19
As language teachers we use a variety of teaching aids to explain
language meaning and construction, engage students in a topic, or as the
basis of a whole activity. Teacher has always used pictures or graphics
whether drawn, taken from books, newspapers and magazines, or
photographs to facilitate learning. Pictures can be in the form of;
• Flashcards ( smallish cards which we can hold up for our students to
see)
• Large wall pictures ( big enough for everyone to see details )
• Cue cards (small cards which students use in pair or group work)
• Photographs or illustrations ( typically in a textbook)
• Teacher also draw pictures on the board to help with explanation and
language work. 20
According to Andrew Wright, there are some designs of pictures as
their shapes:
• Wall charts
Wall charts illustrate aspects of a topic. On one chart use may be made
• Wall pictures
Wall pictures represent subjects containing a mass of information.
These may be composite wall pictures, meant by publisher to be used
for language work, or cultural information pictures.
• Wall Posters
Wall posters illustrate a limited bit of information. They are used in
advertising and propaganda. In language teaching they may be used to represent single actions or objects, they may also be part of a sequence
of pictures.
• Flash cards
Cards printed with words and or pictures which can handled easily by
the teacher. 21
c. Design of Pictures
1) Objective of using pictures are:
• Pictures can motivate the students and make them want to pay
attention and want to take a part.
• Pictures can stimulate and provide information to be referred to in
conversation, discussion and storytelling.
• Pictures contribute to the context in which the language is being
used. They bring the world into the classroom.
• Pictures can move students' right brain to interest the objective that
teacher wants to give.
2) Type of learning and teaching activity is:
Functional communication activities include such tasks as learners
comparing sets of pictures and noting similarities and differences;
working out a likely sequence of events in a set of pictures;
behind a screen to another learner and giving instructions on how to draw a picture or shape.
3) Teacher roles
The teacher has two main roles: the first role is to facilitate the communication process between all-participants in the classroom. The second roles is to act as an independent participant within the learning-teaching group.
4) Learner roles
The role of learner as negotiator-between the self, the learning process, and the object of learning-emerges from and interacts with the role of joint negotiator within the group and within the classroom procedures
and activities. 22
d. Procedure of Pictures
The teaching procedures are as follows: 1) Motivation
Teacher greets the students
Teacher asks the students about their condition Teacher asks the actual news and gives the comment Teacher gives the pre-test with pictures
2) Presentation
Teacher tells the topic and asks the background of it to the students Teacher explains the method that will be used
Teacher explains about question tags and shows the pictures a) The Materials
b) TheRules
• When the statement is affirmative, the question is negative,
when the statement is negative, the question is affirmative.
He likes apples, doesn't he?
She doesn't like apples, does she?
• When the verb in the statement is a single form of be, the verb
in the question is the same form.
Taxes セ@ high in college town, aren't they? That's right, isn't it?
• When the verb in the statement in a single of any verb except
be, the verb in the question is the same form.
You live in an apartment, don't you?
Miller lives in an apartment, doesn't he?
Six years ago the Allens lived in an apartment, didn't they?
• In most other cases, the verb in the question is the first
auxiliary of the verb phrase.
You've owned this house quite a while, haven't you?
Teacher asks to the students to give the example of question tags with
to be or auxiliary verb.
Teacher calls the students one by one to write down the pattern of
question tags on the white board.
Teacher corrects the students' writing on the white board.
Teacher asks the students' their trouble about question tags.
Teacher gives questions and gives the reward for the correct answer.
3) Evaluation
Teacher gives an activity by answering the teacher's question while
they are studying as a process to get the result of scoring. At the last
meeting the students were given an exercise of the post-test for taking
e. Advantages and disadvantages of using Pictures
Advantages of using Pictures
Pictures of all kinds can be used in multiplicity of ways, as the
following examples show:
• Drills
With lower level students a traditional use for pictures especially
flashcards. Flashcards are particularly useful for 'drilling' grammar
items for cueing different sentences, or practicing vocabulary.
• (Communication) games
Pictures are extremely useful for a variety of communication activities,
especially where they have a game like feel, such as describe and draw
activities.
• Understanding
One of the most appropriate uses for pictures is for the presenting and
checking of meaning of the word.
• Ornamentation
Pictures of various kinds are often used to make work more appealing.
• Prediction
The pictures are useful for getting students to predict what is coming
next in a lesson.
• Discussion
Pictures can stimulate questions such as: What is it showing? How
does it make you feel? How much would you pay for the picture?23
According to Jeremy Harmer in another of his book, even in an
increasingly technological age, there is still good value to be had from
pictures of all shapes and sizes.
• Pictures can come from a variety of sources: drawings, magazines,
• Teachers can use pictures as prompts for controlled language work as an alternative to holding up objects.24
Disadvantages of using Pictures
Using picture as a teaching aids can give advantages for teacher and students. besides it also can give disadvantages for them. It is difficult
Lo make a picture explains an abstract condition, and the teacher has to prepare himself to make a picture or to find a good picture. Because the students do not always know how to read pictures and the pictures often limits student's interpretation.
According to Asnawir and Basyiruddin the disadvantages of using picture in teaching are:
• Sizes and distances are often distorted, because the back students can not see the picture clearly
• Understanding about pictures un complete, because lack of color in some pictures and person's behavior
• Students do not always know how to read pictures and sometime they have different means.25
B Conceptual Framework
According to the discussion above, the writer assumed that: pictures are very useful resources for teaching grammar especially question tags that require a structure-meaning match. In this paper the writer use the picture to make easier her explanation about question tags to the students. The pictures can create students more active to speak and to write, also to understand about question tags.
Pictures help students understanding various aspects of foreign languages. The pictures have motivated the students, made the subjects they
are dealing with clearer, and illustrated the general idea and forms of an object or action which are particular. However, a central aim of the teacher is to help the students develop skill and confidence in searching for meaning themselves.Although question tags are difficult and very complicated, but pictures make them easier and interesting.
C Hypothesis
I. The experimental hypothesis (Ha): there is significant difference between the students' pre-test scores and the students' post-test scores in teaching question tags through pictures at the second year students of SMP Al Mubarak Ciledug.
2. The null hypothesis (Ho): there is no significant difference between the students' pre-test scores and the students' post-test scores in teaching question tags through pictures at the second year students of SMP Al
A. Research Methodology
1. Objective of the Study
The writer hopes that this paper will be of a great help to her and to other people. The objective of the study in a foreign language is to find out whether or no significant difference between the students' pre-test scores and the students' post-test scores in teaching question tags through pictures.
2. Place and Time
The research took place at SMP AL Mubarak' located in Ciledug Tangerang. This research began by observation on February 171\ 2008.
She held a research by 。セーイ・@ experimental study to the capability of students' knowledge about question tags through pictures. Pre-test and post-test used in the classroom.
3. Population and Sample
4. Method of the Research
The method of research used in this study is a pre experimental
research and supported by library study for collecting and analysing
sources about teaching question tags through pictures .
5. Instrument of the Research
a. Conceptual Definition
Based on the explanation in the second chapter, the writer can
conclude that:
"Question Tag is a question or yes-no question which is put at
the end of a statement and made up of auxiliary verb
+
personalpronoun, to ask for clarification, to confirm information or to make
sure that information is true".
b. Operational Definition
Question tags are scores that the students obtain after they
c. Specification
No Dimension Element Sub Element
1 Question Tags 1. Preceded by to be 1. 1. Present
1.1.1. To Be Is 1.1.2. To Be Are 1.1.3. To Be Am 1.2. Past
1.2.1. Was 1.2.2. Were
2. Preceded by 2.1. Present
auxiliary verb 2.1.1. do
2.1.2. does 2.1.3. have 2.1.4. has 2.2. Past
2.2.1. did 2.2.2. had Total
-6. Analysis of Data
The writer uses the formula to compare the two samples that have a
relationship each other:
MD
to=
-SEMD
MD Mean of differences; the average score from the differences gained
scores, between X and Y variables, which are calculated with
formula;
MD=---N
L
D The total score between X and Y variables. D is gained with theformula: D = X - Y
N Number of cases
SDo The standard deviation from the differences between scores ofX
and Y variables, which is gained with the fonnula:
JLD
2- (LD)
2
sdッセ@
N N
SEMo The standard error from mean of differences which gained with the
formula:
SDo
B. Research Findings 1. Description of Data
a. The Pre Test Scores of Question Tags
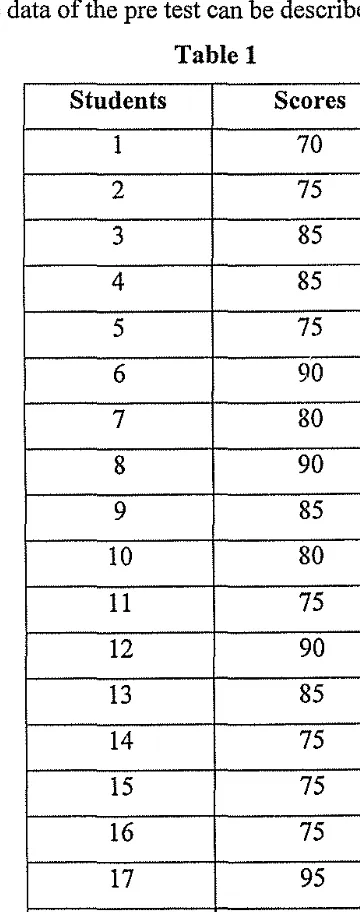
[image:31.595.151.331.253.709.2]After analysing the data of the students pre test, it shows that the highest score is 95 and the lowest score is 65. The mean scores of the students is 80.75. The median scores is 80 and the deviation standard is 7.46. The data of the pre test can be described in table 1.
Table 1
Students Scores
1 70
2 75
3
854 85
5 75
6 90
7 80
8 90
9 85
10 80
11 75
12 90
13 85
14 75
15 75
16 75
17 95
18 85
19 80
From the table above, the writer concludes that : Mean : Mx =
l::y
N
Median : 7 = 2n
+
1 7-1 =2n2n=6 n=3 Median: 80
Standard deviation:
sdク]セ@
N
セ@
20
セ]@
=
7.46
b. The Post Test Scores of Question Tags
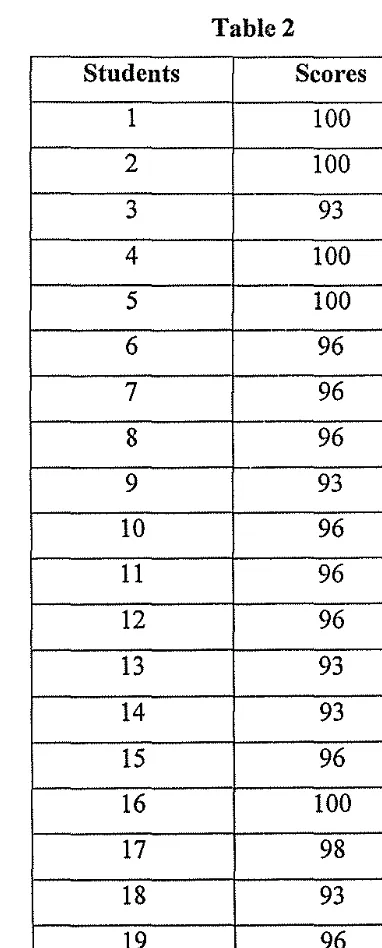
After analysing the data of the students pre test, it shows that the
highest score is 100 and the lowest score is 93. The mean scores of the
students is 96.75. The median scores is 96 and the deviation standard is
2.74. The data of the post test can be described in table 2.
[image:33.595.163.354.226.700.2]Table2
Students Scores
1 100
2 100
3 93
4 100
5 100
6 96
7 96
8 96
9 93
10 96
11 96
12 96
13
9314 93
15 96
16 100
17 98
18 93
19 96
20 100
From the table above, the writer concludes that :
Mean: My=
LY
=N
Median : 4 = 2n
+
1 4-1=2n2n = 3
n = 1.5
Median: 96
Standard deviation:
sdケ]セ@
N
セ@
20
= 2.74
c. The Comparison between Pre Test Scores and Post Test Scores of Question Tags
The next table below is the average score for each test that is analysing students' question tags through pictures ( variable X I pre-test ) and (variable YI post-test).
Students Pre-test Post-test D n2
(X) (Y) (Y-X) (Y-X) 2
1
70
100
30
900
2
75
100
25
625
3
85
93
8
64
4
85
100
15
225
5
75
100
25
625
6
90
96
6
36
7
80
96
16
256
8
90
96
6
36
9
85
93
8
64
10
80
96
16
256
11
75
96
11121
12
90
96
6
36
13
85
93
8
64
14
75
93
18
324
15
75
96
19
361
16
75
100
25
625
17
95
98
3
9
18
85
93
8
64
19
80
96
16
256
20
65
100
35
1225
From the table above, the writer looks for the mean and median of each variable. Based on the result calculation, the writer got the result of mean of X variable 80.75 and mean of variable Y is 96. 75. The median of variable X is 80 and median of variable Y is 96. And the standard deviation of variable X is 7.46 and standard deviation of variable Y is 2.74.
Then the writer tried to find out the standard deviation with the formula as follows26:
J
I
D' - (I
D ) 'N
N
J
6174 - (304) 220 20
=J
308.7 ( 15.2) 2·J
308.7 - 231.04ᄋᄋᄋセ@
According to the data in table 3 above, the writer tried to calculate the mean of differences (MD) between variable X and Y with formula:
2:D
MD=-N
304 MD=
-20
= 15.2
After gaining the result of sdッセ@ 8,81 the writer calculated the standard error from mean differences (SEMO) between variable X and Y : SEMo = SDD
.JN-I
8.81
]セ]]@
.)20-1
8.81
- ../19
8.81
-4.36 =2.02
The last procedure of the calculation is determining the result of to: to= MD
SEMO
= 15.2
2.02
It includes that the result to= 7.25. The following step in
completing the result of this research, the writer tried to find out the
degree of freedom df with the formula as follows:
df= N-1
= 20-1
=
19According to the table above, dfat significance level of0,05 and
0,01 are:
0,05 =to : tt = 7.25 > 2.09
0,01 =to : tt = 7.25 > 2.84
It can be concluded that t observation (to) is higher than t table (tt).
d. Test Hypothesis
• The experimental hypothesis (Ha) : there is significant difference
between the students' pre-test scores and the students' post-test
scores in teaching question tags through pictures at the second year
students of SMP Al Mubarak Ciledug.
• The null hypothesis (Ho): there is no significant difference
between the students' pre-test scores and the students' post-test
scores in teaching question tags through pictures at the second year
students of SMP Al Mubarak Ciledug.
2. Discussion
It is obtained that the t observation (to)= 7.25 and t table (tt) =2.09 on
the significance level of 0,05. Therefore to > tt this means that the
research hypothesis is accepted and the null hypothesis is rejected. So
the hypothesis of the research is empirically tested. This means that
• Marianne Celce Murcia and Sharon Hilles stated that " Pictures are versatile and useful resources for teaching aspects of grammar that require a structure-meaning match, and several areas of grammar for which pictures constitute particularly effective resources ,m, Pictures can be used in all phases of grammar lesson. Interesting or entertaining pictures motivate stL1dents to respond in ways that more routine teaching aids. Although they can be used to advantage at all levels of proficiency, they are especially useful with beginning and low-intermediate learners, who sometimes have trouble understanding long or complicated verbal cues.
• Andrew Wright also said that "Pictures can be used to illustrate a number of examples of each one of the structure. Although the sentences refer to the picture, there is little importance given to
. 1 1 . . ,,2s
meanmg, t 1e emp rns1s 1s on structure .
• According to Jeremy Harmer, he said that " Pictures of all kinds can be used in a multiplicity of ways, as the example show that flashcards are particularly used for 'drilling' grammar items, for cueing different sentences, or practising vocabulary ".29
• S. Pit Corder said: "Everything belonging to or brought into the classroom, animate or animated, is a potential visual aids-teacher, boys, girls, pets, plants, clothes, furniture, materials, objects; everything that anyone is seen to do all are potential visual aids. 30
27 Marianne Celce Murcia and Sharon Hilles, Techniques and Resources in Teaching
Grammar, (England: Oxford University Press, 1988), p. 73
28 Andrew Wright, Pictures for language learning, (Longman Group Ltd, 1983), p. 3 29 Jeremy Hanner, The Practice of English language Teaching 3"1
A Conclusion
CHAPTER IV
CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION
Based on the students' achievement of the research stated that most of students often get difficulties in studying grammar when they learn English. The writer concludes that the students' post-test scores in question tags through pictures are higher than the students' pre-test scores that do not use the pictures. From the difficulties that happened, most of students do not know the correct question tags. So the writer used the pictures as an alternative way to help students to understand better in the use of question tags in their studying.
The result by using the pictures, the students who got the difficulties were lower than before. From the calculation in the previous chapter stated that the value of"to" is higher than "tt". It means that to= 7.25 indicate that there is a significant difference between the results of teaching question tags through pictures and without pictures. The students could improve their knowledge ab'out question tags by using the pictures. Teaching learning activities in question tags is very important to choose the suitable media to improve students' skill. So, by using pictures the subject will be easy to understand.
B Suggestion
The writer has some suggestions in relation to this paper. It is suggested to the teacher that:
3. To make the students' more enthusiastically, it is better to use the colorful pictures and it will be more creative pictures.
4. The students are more practice and practice to improve their question tags wherever and whenever by using ari alternative resources to express their imagination and to get more ideas and information. 5. The English teacher should be creative and chooses a suitable
technique in teaching learning process, especially in teaching question tags that often confuse students.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Alexander, L G. Practice and Progress. London: Longman Group Ltd., 1975
Asnawir, Prof. Dr. H., and Drs.M. Basyiruddin Usman M. Pd. Media Pembelqjaran, Jakarta: Ciputat Press, June 2002
Azar, Betty Schrampfer. Understanding and Using English Grammar for Communication 2nd Edition., USA:: Prentice Hall.Inc., 1989
Darley, W. L. English Language Teaching. Oxford University Press, 1962
Frank, Marcella. Modern English a Practical Reference Guide. New Jersey: Prentice Hall, Inc., 1972
Freeman, Diane Larsen. Techniques and Principies in Language Teaching. New York : Oxford University Press, 1986
Harmer, Jeremy. How To Teach English. England: Pearson Education Limited, 1998
Harmer, Jeremy. The Practice of English Language Teaching 3rd Edition.
England: Pearson Education Limited, 2001
Homby, A S . Oxford Advanced Learner's dictionary of current English.
Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2000
Kim, Elaine and Darcy Jack. Interactions I Grammar 4th Edition. New York:
Mackey, W. F.
Language Teaching Analysis.
USA: Indiana University Press, 1965Murcia, Marianne Ce!ce, and Sharon Hilles.
Techniques and Resources in
Teaching Grammar.
England: Oxford University Press, 1988Paningkas, Jean.
Rapid Review of English Grammar
2"dEdition.
New Delhi: Prentice Hall of India private Limited, 1982Parkes, Geoff et. al,
101 Myths about the English Language,
England Books, 1989.Richard, C Jack and Theodore S. Rodgers.
Approaches and Methods in
Language Teaching.
New York: Cambridge University Press, 1986Soemardi, Muljanto.
Pengajaran Bahasa Asing Sebuah Tinjauan dari Segi
Metodologi.
Jakarta: bulan bintang, 1975Sudijono, Anas, Drs.
Pengantar Statistik Pendidikan.
Jakarta: PT Raja Grafindo Persada, 1997Swarn, Michael.
Practical English Usage.
Oxford University Press, 1983Wright, Andrew.
Pictures for Language Learning.
Longman Group Limited, 1983Wright, Andrew.
Visual Materials for the Language Teacher.
Longman Group Limited, 1976AJ,>pendix 1
RENCANAPELAKSANAANPENGAJARAN
Nana Sekolah : SMP AL Mubarak Mata pelajaran : Bahasa Inggris Ke las : VIII.I I 2
Waktu : 2 x40 Menit
Terna : Structure
Subtema : Question Tags Part one Tahun Pelajaran : 2007 -2008
I. STANDAR KOMPETENSI
Berkomunikasi secara lisan dan tertulis dengan menggunakan ragam bahasa yang sesuai dengan lancar dan akurat dalan1 wacana interaksional atau monolog.
II. KOMPETENSI DASAR
Mengungkapkan makna dalam bentuk teks tulis fungsional pendek
sederhana dengan menggunakan ragam bahasa tulis secara akurat, lancar dan berterima untuk berinteraksi dengan lingkungan sekitar.
III. INDIKATOR
Siswa mampu memahami question tags
IV. MATER! DAN URAIAN MATER!
QUESTION TAGS
Question tags are short questions put at the end of a statement. We use them, not to ask for information, but for confirmation of or agreement to our statement. Ex: He can drive\, can't he?
Complete list of auxiliary verb:
be am is are was were
have has had may might do
does did shall should am to
need dare will would can could
must have to used to
We can form question tags with an auxiliary verb and a personal pronoun (I, you, he, it, etc.). a question tag has the same auxiliary verb as in the statement. If there is no auxiliary verb
in
1.he statement, we use do, does or did accordingly.Ex: She is sleeping, isn't she? He came too late, didn't he?
Statement Statement+ Tag Question Notes
Tony came from Italy. Tony came from Italy, didn't he? Sometimes you He has three children. He has three children, hasn't he? think
He is very old now. He is very old now, isn't he? something is Rene wasn't born here. Rene wasn't born here, was she? tJ.ue, but you're She can't speak Italian. She can't speak Italian, can she? not sure. To She moved here. She moved here, didn't she? make sure, use
V. SUMBER DAN MEDIA PEMBELAJARAN
1. Sumber Pcmbelajaran:
)> Text book: Firmansyah, Diyati, Stepping More for Junior High
School I Madrasah Tsanawiyah Grade VIII, CV. Regine, 2006
)> LKS Bahasa Inggris
)> Handout
)> Kurikulum Bahasa Inggris
2.
Media:)> Flash card and wall picture )> Large picture
)> Realia
VI. METODE & STRATEGI PEMBELAJARAN
Strategi : Explanation
Metode : Two Ways Communication
VII. SKENARIO PEMBELAJARAN
NO
7.1
7.2
KEGIATAN
Pendahuluan
7.1.1. Salam dan tegur sapa 7 .1.2. Guru mengabsen
7.1.3. Guru memberikan motivasi Kegiatan Pokok
7.2.l. Guru memberi penjelasan tentang
question tags dengan menggunakan gambar 7.2.2. Guru memberikan langkah-langkah
retorika kalimat question tags
7.2.3. Siswa memilihjawaban yang tepat dari
WAKTU
10 menit
7.2.4. Siswa membuat pemyataan question tags yang sesuai dengan gambar
7.3 Penutup 20 menit
7 .3 .1. Guru memberikan kesmpatan kepada siswa untuk mengungkapkan hambatan-hambatan yang dialami selama proses pembelajaran 7 .3 .2. Guru membantu siswa dalam menyimpulkan
pokok pembelajaran
7.3.3. Guru memberikan kegiatan tindak lanjut berupa pekerjaan rumah
VIII. PENILAIAN
a. Penilaian proses
b. Penilaian hasil
c. Instrumen
: Dilakukan pada saat proses KBM structure and grammar
: Diambil darijawaban siswa yang diberi nilai pada test
Appendix2
RENCANAPELAKSANAANPENGAJARAN
Nana Sekolah : SMP AL Mubarak Mata pelajaran : Bahasa Inggris
Kelas : VIII.I I 2
W aktu : 2 x 40 Menit
Terna : Structure
Subtema : Question Tags Part two Tahun Pelajaran : 2007 - 2008
I.STANDAR KOMPETENSI
Berkomunikasi secara lisan dan tertulis dengan menggunakan ragam bahasa , yang sesuai dengan lancar dan akurat dalam wacana interaksional atau
monolog.
11.KOMPETENSI DASAR
Membuat statement atau pemyataan dalam sebuah teks berbentuk question tag pendek sederhana dengan menggunakan ragam bahasa tulis secara akurat, lancar dan berterima untuk berinteraksi dengan lingkungan sekitar.
111.INDIKATOR
Siswa mampu membuat question tag disetiap statement sesuai dengan gambar
Siswa mampu membedakan question tags itu berbentuk present atau past tense melalui gambar
IV. MATERI DAN URAIAN MATERI
QUESTION TAGS
A positive statement is followed by a negative statement by a positive question tags.
Ex: He likes apples, doesn't he? She doesn't like apples, does she? He never complains, does he?
Affirmative Sentence
+
Negative Tag___,.. Affirmative Answer ExpectedMary is here,
+
You like tea, +isn't she?
don't you?
--Yes, she is. Yes, I do.
Negative Sentence
+
Affirmative Tag --1>- Negative Answer ExpectedMary isn't here,
+
is she? -+ No, she isn't.You don't like tea,
+
do you?-
No, I don't.They haven't left,
+
have they?-
No, they haven't.Ifwe are sure of what we are asking and we don't expect an answer, the voice goes down (falling intonation). Ifwe are not sure and we expect an answer, the voice goes up (rising intonation).
Ex: She is ugly, isn't she? (sure)
She is a secretary, isn't she? (not sure)
V SUMBER DAN MEDIA PEMBELAJARAN
1. Sumber Pembelajaran:
セ@ Text book: Firmansyah, Diyati, Stepping More for Junior High School I Madrasah Tsanawiyah Grade VIII, CV. Regine, 2006
セ@ LKS Bahasa Inggris
セ@ Handout
セ@ Kurikulurn Bahasa Inggris
2.
Media:セ@ Flash card and wall picture
セ@ Large picture
セ@ Reali a
VI. METODE & STRATEGI PEMBELAJARAN
Strategi : Explanation
Metode : Two Ways Communication
VII. SKENARIO PEMBELAJARAN
NO
7.1
7.2
KEG IATAN
Pendahuluan
7 .1.1. Salam dan tegur sapa 7.1.2. Gum mengabsen
7 .1.3. Gum memberikan motivasi Kegiatan Pokok
7.2.1. Gum memberi penjelasan tentang
question tags dengan menggunakan gambar 7.2.2. Gum memberikan langkah-langkah
retorika kalimat question tags
7 .2.3. Siswa memilih jawaban yang tepat dari
セpZエゥhョ@ nP:rt::tnv::iRn セ・ウQQ。ゥ@ denQat1 rrambar
WAKTU
10 menit
7.2.4. Siswa membuat pemyataan question tags yang sesuai dengan gambar
7.4 Penutup 20 menit
7 .3 .1. Guru memberikan kesmpatan kepada siswa untuk mengungkapkan hambatan-hambatan yang dialami selama proses pembelajaran 7.3.2. Guru membantu siswa dalam menyimpulkan
pokok pembelajaran
7.3.3. Guru memberikan kegiatan tindak lanjut berupa pekerjaan rumah
VIII. PENILAIAN
a. Penilaian proses : Dilakukan pada saat proses KBM structure and grammar
b. Penilaian hasil : Diambil dari jawaban siswa yang diberi nilai pada test
"
1. She is looking at herself in the minor, ... ?
A. does she? B. is she?
セゥウョGエ@ she? D. doesn't she?
2. Rifa'i has cut his hand,. ... ?
A. hasn't he?
B. do they? C. doesn't he'? D. has he?
3. Khilya didn't write a letter,. ... ?
A. didn't she? B. did he? C. doesn't she? D. did she?
4. Faqih gives a bunch of flower to khilya, ... ?
A. does he? B. doesn't he? C. is he? D. did she?
5. Romy and Yuli are getting manied, ... ?
D. didn't she?
7. Inem wasn't washing her clothes, ... ?
A. was he? B. wasn't he? C. was she? D. did she?
8. Parjo likes cleaning his car,. ... ?
A. is he? B. doesn't he? C. don't they? D. does she?
9. She isn't ironing the clothes,. ... ?
A. is he? B. does she? C. isn't she? D. is she?
10. Brian finishes his homework, ... ?
2.
You have a big breakfast this morning, .... ? b. don't we?3.
I'm not allergic to cats, .... ? c. don't you?4.
We hardly finish doing this test, .... ? d. haven't you?5.
He had dinner at 6.00, .... ? e. aren't they?6. They are journalists, ... ? f. am I?
7.
You study very hard, .... ? g. aren't I?8.
The boys were not hurt, .... ? h. hadn't he?9.
I am tall, ... ? i. isn't she?JO. She is in France at the moment, ... ? j. don't they
r.
Faqih gives a bunch of flower to khilya, ... ?A. does he? ;:;i;(doesn't he?
C. is he? D. did she?
2. Romy and Yuli are getting married, ... ?
A. don't they? B. are you?
C. aren't you? D. aren't they?
3. He helped his wife in the kitchen, ... ?
A. didn't he? B. don't he? C. is he? D. didn't she?
4. She is looking at herself in the mirror, ... ?
A. does she? B. is she? C. isn't she?
D. doesn't she?
5. Rifa'i has cut his hand, ... ?
A. hasn't he?
B. do they? C. doesn't he?
D. did she?
7. Brian finishes his homework,. ... ?
A. does he? B. doesn't he? C. doesn't she? D. is he?
8. She isn't ironing the clothes,. ... ?
A. is he? B. does she? C. isn't she? D. is she?
9. Parjo likes cleaning his car,. ... ?
A. is he? B. doesn't he? C. don't they? D. does she?
10. Inem wasn't washing her clothes, ... ?
2.
You study very hard, .... ? b. aren't I?J.
The boys were not hurt, .... ? c. hadn't he?4.
I am tall,. .... ? d. isn't she?5.
She is in France at the moment,. .... ? e. don't they 6. They play football in the yard,. ... ? f. were they?7.
You have a big breakfast this morning, .... ? g. don\ we?8.
I'm not allergic to cats,. ... ? h. don't you?9.
We hardly finish doing this test, .... ? i. haven't you?10. He had dinner at 6.00,. ... ? j. aren't they?
1.
c
2. A 3. D 4. B 5. D 6. A 7.c
8. B 9. D10. B
PartB
I. J 2. D
3. F
4. B 5. H
6. E
7.
c
8. A 9. G
10. I
1. B
2. D 3. A 4.
c
5. D 6. D 7. B 8. D 9. B 10.c
Part B
I. J
Jawablah Pertanyaan Dibawah ini Menurut Pendapat Anda
! ! !
1. Buku apa yang anda pakai untuk belajar bahasa inggris?
2. Kesulitan apa yang anda hadapi ketika belajar bahasa inggris?
3. Apakah anda culmp berminat terhadap bahasa inggris?
4. Factor apa yang mcnunjang anda agar dapat mcmahami bahasa inggris dengan baik clan benar?
5. Kesulitan apa yang sering anda hadapi ketika anda belajar bahasa inggris?
6. Menurut kamu penting ga sih mempelajari question taq dalam bahasa inggris?alasannya?
7. Seberapa sering kamu diberikan latihan bahasa inggris dikelas?
10. Kita telab sama - sama menggunakan metode demonstrasi dan metode komunikatif dalam beberapa kali pertemuan, bagaimana pendapat kalian tentang metode komunikatif?
11. Apakab mctode komunikatifmcmbantu kalian dalam mcmabami question taq?
12. Scjaubmana metodc ini memberi perbedaan dalam pembelajaran babasa inggris anda dibandingkan mctode sebelumnya?
13. Dari basil test ini, bagaimanakab perbandingan basil test semester ini dengan test sebelumnya, apakab mengalami perubaban?
14. Apa tujuan anda mempelajari inggris?
Ketua Jurusan Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris Drs. Syauki, M.Pd
Di
Tempat
Assalamualaikum Wr. Wb.
Semoga kesejahteraan tercurahkan kepada bapak I ibu dan selalu sukses dalam menjalankan aktifitas sehari - hari amin.
Mengingat akan berakhirnya masa studi saya di tingkat strata 1 ( satu ), maka saya yang bertanda tangan di bawah ini :
Nama : Suci Anggraeni
Nim :
103014026975
Fak I Jurusan : Ilmu Tarbiyah da11 Keguruan I PBI Semester : X
Bermaksud mengajukan skripsi denganjudul "ANALYSIS ON USING PICTURES IN PRACTICING QUESTION TAGS (An Experimental Study at SMP Al -Mubarok Pondok Aren Jombang Ciledug of Eight Grade)"
Sebagai bahan pertimbangan bagi Bapak I Ibu bersama ini saya lampirkan : 1. Outline
2. Abstraksi
3. Daftar Pustaka Sementara
Demikianlah pengajuan judul skripsi saya, atas segala kerendahan hati dan pe1iimbangan yang matang semoga judul skripsi ini dapat diterima, atas ke1jasama dan dnktmgan moralnya saya ucapkan terima kasih
Wassalamualaikum Wr. Wb
セセ@
ヲ・セ@
セイN@
Otd.1[,,
セエゥ@
r.fon
1M Pd .
t01·
GNEセPX@
Jakarta,
17
Juni2008
PemohonTclp. : (62-21) 7443328, 7401925, Fax. (62-21) · 13
Janda Nomor 951Ciputut15412, Indonesia Enwil : [email protected]
Ii< cywp•llllm rn wtGBGGNNNLLNNNNョQGWイGyャャᆱャGャャャャGャャセイ」jャャZエエjャ\Q\セZ[ZMN[cZQLッエlMLLN⦅NNNNNNNNNL⦅セvAAGsGoG@ MNLLMュセ@ ;,' 'V GzGwwセBBMセMュオ QキッNイョャャAGGoGGBM セ@
Nomor Lamp. Ha I'
, -·· L I
. Un. 01/F.1/KM.01.3/ /":
: Abstraksi!Outline ·
. : BIMBINGAN SKRIPSI
' Kepada Yth:
Dr. Didik Santoso, M.Pd Pembimbing Skripsi
12008
Fakultas llmu Tmbiyc1l1 <Jan Keguruan UIN Syarif Hidayatullcih
Jakarta.
Assalamu'alaikurn w1: wb.
Jakarta, 25 Juni 2008
Dengan ini diharapkan kesediaan Saudara untuk menjadi Pembimbing 1/11
(materiiteknis) penulisan skripsi mahasiswa:
Nam a NIM Jurusan Semester Judul Skripsi Suci Anggraeni 103014026975
Pendidikan Bahasa lnggris
x
Analysis on using pie-lures in practicing question tags (an experimental study at SMP al-Mubarak Ciledug of Eight grade)
Judul tersebut telah disetujui oleh Jurusan yang bersangkutan pada tanggal 17 Juni 2008 abstrak/outline terlampir dapat melakukan perubahan redaksional pada judul tersebut. Apabila perubahan substansial dianggap perlu, mohon pembimbing menghubungi jurusan terlebih dahulu.
Bimbingan skripsi ini diharapkan selesai dalam waktu 6 (enam) bulan, dan dapat diperpanjang selac1a 6 bulan berikutnya tanpa surat perpanjangan .
Alas perhatian dan kerja sama Saudara, kami ucapkan terima kas·1h.
Wassa!arnu'a/aikurn wr.wb.
Tembusan:
Ketua Jurusan Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris Drs. Syauki, M.Pd
Di Tempat
Assalamualaikum W r. Wb.
Semoga kesejahteraan tercurahkan kepada bapak I ibu dan selalu sukses dalam menjalankan aktifitas sehari - hari arnin.
Selanjutnya saya yang bertancla tangan di bawah ini :
Nama : Suci Anggraeni
Nim : 103014026975
Fak I Jurusan : Ilmu Tarbiyah dan Keguruan I PBI Semester : XI
Dengan ini saya mengajukan perubahan judul skripsi, yang berjudul:
"ANALYSIS ON USING PICTURES IN PRACTING QUESTION TAGS AN EXPERIMENTAL STUDY AT SMP AL MUBARAK CILEDUG OF EIGHT GRADE"
Menjadi:
" TEACHING QUESTION TAGS THROUGH PICTURES : A PRE
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY AT THE SECOND YEAR OF SMP AL MUBARAK CILEDUG"
Dernikianlah surat permohonan 1111 saya ajukan. semoga Bapak berkenan
menyetujuinya. Atas perhatiannya saya ucapkan terima kasih Wassalamualaikum Wr. Wb
Wassalamualaikum
Dosen Pembimbing
Dr. Didik Santoso. M.Pd NIP. 150 270 348
Jakarta, 6 September 2008 Pemohon
JL. Raya Ciledug - Jornbang, No. lE., Fondok !iacang Timur, Pondok Aren Tangerang - Ban ten 15";'..!11 Tclp. (021) 71158912
SURA 1' kEfERANGAN
Nomor : 030 I K.SMP I AM I SK IV I 2008\' ang bertanda tangan dibawah menerangkan bahwa :
••
llll, Kepala SMP Almubarak Pondok Aren - Tangerang
Nama
NIM
Jenis Kelamin
Pekerjaan
SUCl ANGGRAENl
103014026975Perempuan
Mahasiswa Fakultas llmu Tarbiyah dan Keguruan UIN Syarif Hidayfttuilah, Jakarta
Jurusan : Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris Semester X
'felah melaksanakan observasi terhadap siswa - siswl Kelas 8 SMP Almubarak pada tanggal 19 Mei s/d 24 Mei 2008, sehubungan dengan tugas penyelesaian Skripsi