Aldy S. Rambe dkk. Profil Penderita Trauma Kapitis...
Majalah Kedokteran Nusantara Volume 41 y No. 4 y Desember 2008
239
The Effect of Honey and Uncaria on The Prevention of Post Laparotomy
Intraperitoneal Adhesions in Rats
Pane Y. S., Martina S. J., Tri W., Ichwan M., Lelo, A.
Department of Pharmacology and Therapeutic, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, Indonesia
number and the volume of IPA. The data observed were analyzed by one way ANOVA with level of significant P<0.05. Result: IPA occurred in all animals of study group I and III (6/6), but it was much less in the group II (2/6). The number of IPA formed in group I (1.33±0.52) and group III (1.33±0.52) were significantly (P<0.05) greater than group II (0.33±0.52). The volume of IPA in group I (0.23±0.24 ml) and group II (0.09±0.15 ml) were statistically (P<0.05) less than group III (0.61±0.43 ml). Conclusion: The present study demonstrated that honey could reduce the incidence, the number and the volume of IPA, while uncaria appears enhancing the volume of IPA.
Keywords: intraperitoneal adhesions, post laparotomy, honey, uncaria
Abstrak: Latar Belakang: Adhesi intraperitoneum pasca laparotomi (AIP) selalu diikuti dengan peningkatan morbiditas dan mortalitas. Anti inflamasi non-steroid telah digunakan untuk mencegah terjadinya AIP. Madu dan uncaria (gambir) secara turun temurun telah digunakan sebagai obat anti radang. Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk melihat efek madu dan uncaria pada pembentukan AIP pada tikus. Metoda: 18 ekor tikus Sprague Dawley (berat badan: 150-200 gram) dibagi dalam 3 kelompok (n=6), yaitu: (I) Kelompok kontrol 1 cc aquadest sebagai plasebo, (II) madu (1 g/kgbb), dan (III) uncaria (10 mg/kgbb). Masing-masing kelompok diberi obat 2 kali sehari selama 3 hari segera setelah dilaparotomi. Pada hari ke-10, masing-masing tikus dibunuh untuk dilakukan laparotomi ulang dan selanjutnya melihat adanya kejadian, jumlah dan volume AIP. Data dianalisis dengan menggunakan ANOVA, dimana suatu perbedaan dinyatakan bermakna, bila P<0,05. Hasil: AIP didapati pada seluruh hewan percobaan kelompok I dan III (6/6), dan kelompok III kejadiannya lebih sedikit (2/6). Rerata jumlah AIP pada kelompok I (1,33 ± 0,52) dan kelompok III (1,33 ± 0,52), lebih banyak (P<0,05) bila dibanding dengan kelompok II (0,33 ± 0,52). Volume AIP pada kelompok I (0,23 ± 0,24 ml) dan kelompok II (0,09 ± 0,15 ml) lebih sedikit (P<0,05) lebih sedikit dibanding kelompok III (0,61±0,43 ml).
Kesimpulan: Penelitian ini menunjukkan bahwa madu dapat mengurangi kejadian, jumlah dan volume dari AIP, sebaliknya uncaria tampaknya meningkatkan volume AIP.
Kata kunci: adhesi intraperitoneum, pasca laparotomi, madu, uncaria
INTRODUCTION
Intraperitoneal adhesions (IPA) might occur in patient post laparotomy (67-93%)
and post pelvic surgery (97%) 1,2.
, that could
increased morbidity and mortality 3,4
. IPA are
the major causes of intestinal obstruction and secondary infertility. IPA is fibrous tissue that connected to abdomen wall with various organs in cavum abdomen (ex. intestine,utery,
etc.)5
Karangan Asli
Majalah Kedokteran Nusantara Volume 41 y No. 4 y Desember 2008 240
In order to prevent postoperative IPA,
many adjuvants have been used in animal
models and in the clinical trials 6
. Non
steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs),
which inhibit prostaglandin production, have
been shown to decrease adhesion formation
7-10
. The formation of IPA can be prevented
after administering NSAIDs, i.e: nimesulide3
,
diclofenac11,12
, meloxicam 13
, ketorolac11,13,14
,
and celecoxib12
.
Traditional medicines which have anti-inflammatory action such as temulawak
(Curcuma xanthorrhiza)11
and sambiloto
(Andrographis paniculata)13
have been demonstrated to be able preventing the formation of IPA. Honey and uncaria are other traditional agents have been studied and
used as anti inflammatory agents15,16
. In the present study, we investigated the effect of honey and uncaria on the formation of IPA in rat.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Eighteen Sprague Dawley rats, weighing
150–200 g,were used in the present study. All
rats wereobserved for several days to ascertain
their health before study conducted. All
procedures were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of the Universitas Sumatera Utara.
Before surgery, rats were randomly assigned into three groups (n=6), i.e. group I control group received 1 cc aquadest as placebo, group II received honey (1 g/kgbw), and group III received uncaria (10 mg/kgbw). All rats recovered without incident after surgery and resumed preoperative physical
activity and feeding patterns postoperatively.
Each drug was orally administered twice daily for three consecutive days post laparotomy.
Under an ether anesthesion,the abdomen was
shaved and prepared with a povidone iodine
solution. Using sterile technique, a 5 cm
vertical midline incision was done. Care was
taken to avoid gross bleeding from injured
sites. Handling of other tissues was
minimized.The incision was closed in a single
layer, excluding the peritoneum, with a
running 3–0 monofilament delayed absorbable suture and interrupted suture to skin. The total operative time was less than 10 min. On day 10, each rat was killed by deep general
anesthesion and then re-laparotomy with vertical paramedial incision.
The data observed (i.e. the incidence, the number and the volume of IPA) were analyzed by one-way ANOVA with the level
of significance was set at P < 0.05.
RESULTS
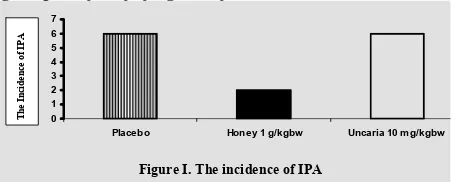
During the study period there was no one of rats died. We found that the incidence IPA occurred in all animals of study group I and III (6/6), but it was much less in the group II (2/6) (Figure I).
Figure I. The incidence of IPA 0
Placebo Honey 1 g/kgbw Uncaria 10 m g/kgbw
Th
The average of number of IPA formed in group I receiving aquadest as placebo (1.33±0.52) and group III receiving uncaria (1.33±0.52) were significantly (P<0.05) greater than group II receiving honey (0.33±0.52) (Figure II).
Figure II. The average of number of IPA
0 0.5 1 1.5
Placebo Honey 1 gr/kgbw Uncaria 10 m g/kgbw
Th
The volume of IPA in group I (0.23±0.24 ml) and group II (0.09±0.15 ml) were statistically (P<0.05) less than group III (0.61±0.43 ml) (Figure III).
Figure III. The average of volume of IPA
0
Placebo Honey 1 gr/kgbw Uncaria 10 m g/bw
Th
Pane Y. S. dkk. The Effect of Honey...
Majalah Kedokteran Nusantara Volume 41 y No. 4 y Desember 2008
241
An inflammation is the initial response to peritoneal injury that leads to extravasations
of serum and cellular elements. The site of
peritoneal injury is coveredpredominantly by
polymorphonuclear cells entangled in fibrin strands, which are soon outnumbered by
macrophages. When normal fibrinolysis
occurs, islands of mesothelial cells proliferate throughout the injury site and completely
cover the defect within 4–5 days 17
. It was therefore in the present study the drugs treated administered for 3 days only. It has
been found that various inflammatory
mediators such as prostaglandins (PGF2 and
PGE 2) might play an important role in the
process of adhesion formation18,19
. Ibuprofen the inhibitor of prostaglandin formation
appearedto significantly inhibit the formation
of adhesions as compared with that in
untreated control animals7
.
During peritoneal repair, the cellular
events appear to becoordinated at least in part
by cytokines. The antibodies to IL-6 20
,
tumour necrosis factor- (TNF- ) and
interleukin-1 (IL-1)21
reduce postoperative adhesion formation. It has been demonstrated that COX-2 expression is highly induced by a
number of cytokines,including IL-1, TNF- ,
and other stimuli associated with
inflammation and growth22
. Nimesulide at
therapeutic concentrations is a potent
inhibitor of IL-6 production 23
. Inhibitor effect
of nimesulide on TNF- production mayalso
contribute to its anti-inflammatory properties. In this study, it was demonstrated a
significant reduction in postoperative IPA
formations in rats treated with honey administration, but uncaria appears enhancing the volume of IPA. How come uncaria appears to enhance IPA?
Pane et al. (2007) demonstrated that celecoxib an selective COX-2 inhibitor has different effect on the formation of IPA. Compared to the low dose of celecoxib (1.4 mg/kgbw), the high dose of celecoxib (7 mg/kgbw) may enhance the incidence (5/5; 100% vs 0/5; 0%), the number (1,40±0,55 vs 0,20±0,45), and the volume of IPA (0,53±0,22 ml vs 0,06±0,13 ml).
It was reported previously that high dose celecoxib will stimulate the activity of
NF-kB24
, which may then stimulate TNF- . It means the high dose of celecoxib has no anti-inflammatory action but has an antioxidant
action. It appears that uncaria has similar action as occurred with celecoxib.
The antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of uncaria have been assessed in vitro. Uncaria has potency for inhibiting tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) synthesis; this cytokine is a key mediator of chronic inflammatory processes such as arthritis. An important finding was that TNF-alpha production was effectively suppressed at much lower concentrations of uncaria than were needed to produce antioxidant effects. Previous research has shown that TNF-alpha is a worthwhile therapeutic target, but it is not known whether the beneficial effects of uncaria are due to TNF-alpha inhibition alone. In addition, prostaglandin E2 production was significantly reduced by uncaria, suggesting that cyclooxygenase-2 expression was
inhibited16
.
Insummary, based on the experimental
results, it is suggested that honey could reduce the incidence of IPA, while uncaria enhancing the volume of IPA. Findings should be evaluated further in other experimental animal models and human trials.
REFERENCES
1. Menzies, D., and Ellis, H. Intestinal
obstruction from adhesion: How big is the
problem? Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 72.
1990. p 60-63.
2. Diamond, M. P., Daniell, J. F., and Johns,
D. A., Postoperative development after operative laparoscopy: Evaluation at early
second-look procedures. Fertil. Steril. 55.
1991. p 700.
3. Guvenal, T., Cetin, A., Ozdemir, H.,
Yanar, O., and Kaya, T. Prevention of postoperative adhesion formation in rat uterine horm model by nimesulide: a
selective COX-2 inhibitor. Hum. Reprod.
16. 2001. p 1732.
4. Hanafi, B. Pencegahan Adhesi
Intraperitonium Paska Bedah. Bandung. 2001. p 9-11.
5. Diamond, M. P. and Schwartz, L. B.
Prevention adhesion development.
Karangan Asli
Majalah Kedokteran Nusantara Volume 41 y No. 4 y Desember 2008 242
6. DeCherney, A. H. and diZerega, G. S.
Clinical problem of intraperitoneal postsurgical adhesion formation following general surgery and the use of adhesion
prevention barriers. Surg. Clin. North.
Am., 77. 1997. p 671–88.
7. Siegler, A.M., Kontopoulos, V. and
Wang, C.F. Prevention of postoperative adhesions in rabbits with ibuprofen, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agent.
Fertil. Steril. 34. 1980. p 46 –49.
8. Cofer, K. F., Himebaugh, K. S., Gauvin,
J. M. and Hurd, W. W. Inhibition of adhesion reformation in the rabbit model by meclofenamate: an inhibitor of both prostaglandin and leukotriene production.
Fertil. Steril. 62. 1994. p 1262 –65.
9. Rodgers, K. E., Girgis, W., Campeau, J.
D. and diZerega, G. S. Reduction of adhesion formation by intraperitoneal administration of anti-inflammatory
peptide 2. J. Invest. Surg. 10. 1997. p 31–
36.
10. Rodgers, K. E., Girgis, W., St Amand, K.
et al. Reduction of adhesion formation by intraperitoneal administration of various
anti-inflammatory agents. J. Invest. Surg.
11. 1998. p 327–339.
11. Mustafa. et al. Natrium diklofenak dan
Kombinasi Kurkuminoid minyak atsiri Temulawak Sebagai anti-adhesi Intraperitoneal Pascalaparotomi pada tikus. Sekolah Pascasarjana, Universitas Sumatera Utara. 2005. p 56-65.
12. Pane Y. S. et al. Efek Peningkatan Dosis
Celecoxib dalam Upaya Pencegahan Adhesi Intraperitoneum Pascalaparotomi pada Tikus. Sekolah Pascasarjana, Universitas Sumatera Utara. 2005. p 80-90.
13. Darwin. et al. Efek Meloksikam dan
Ekstrak sambiloto terhadap adhesi Intraperitoneum Pascalaparotomi pada Tikus. Sekolah Pascasarjana, Universitas Sumatera Utara. 2005. p 40-56.
14. Zahari. Ketorolac Ability in Inhibiting
Post Operative Intraperitoneal Adhesion in Wistar Mice Model. Surgical Departement of Faculty of Medicine of Andalas University, Djamil General Hospital, Padang. 2002. p 34-52.
15. Imhof M. et al. Propolis may have a role
as an Alternative Treatment for Chronic
Vaginal Infection. Int. J. Gynaecol.
Obstet. 89. 2005. p 127-132.
16. Piscoya J. et al. Safety and Effectiveness of
cat’s claw in osteoarthritis. Inflammation
Research. 50. 2001. p 442-48.
17. Raftery, A. T. Regeneration of parietal
and visceral peritoneum: an electron
microscopical study. J. Anat. 115. 1973. p
375 –392.
18. Golan, A., Bernstein, T., Wexler, S. et al.
The effect of prostaglandins and aspirin— an inhibitor of prostaglandin synthesis—
on adhesion formation in rats. Hum.
Reprod. 6. 1991. p 251 –254.
19. Golan, A., Maymon, R., Winograd, I. and
Bukovsky, I. Prevention of post-surgical adhesion formation using aspirin in a
rodent model: a preliminary report. Hum.
Reprod. 10. 1995. p 1797 –1800.
20. Saba, A. A., Kaidi, A. A., Godziachvili, V.
et al. Effects of interleukin-6 and its neutralizing antibodies on peritoneal adhesion formation and wound healing.
Am. Surg. 62. 1996. p 569 –572.
21. Kaidi, A. A., Nazzal, M., Gurchumelidze,
T. et al. Preoperative administration of antibodies against tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-factor-alpha) and interleukin-1 (IL-1) and their impact on peritoneal
adhesion formation. Am. Surg. 61. 1995.
p 569–572.
22. Crofford, L. J. COX-1 and COX-2 tissue
expression: implications and predictions.
J. Rheumatol. 24. 1997. p 15 –19.
23. Henrotin, Y. E., Labasse, A. H., Simonis,
P. E. et al. Effects of nimesulide and
sodium diclofenac on interleukin-6, interleukin-8, proteoglycans and prostaglandin E2 production by human
articular chondrocytes in vitro. Clin. Exp.
Rheumatol. 17. 1999. p 151–160.
24. Niederberger. et al. Celecoxib loses its
anti-inflammatory efficacy at high doses
through activation of NF-κB. FASEB J.