Home
Volumes
Submit Paper
Manuscript Status Author Guidelines Editorial Board
Technical Board
Indexing and Abstracting Subscribe to JATIT Contact Us
FeedBack | Links | Contact Us | Site Map
Welcome to Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology
Editorial Board
EDITOR IN CHIEF
Prof. Niaz Ahmad
FCE, MOE, Islamabad, PAKISTAN
EDITORIAL BOARD
Dr. CHRISTEL BAIER
Faculty of Computer Science, Institute for Theoretical Computer
Science, Technical University Dresden, GERMANY.
Dr. YUSUF PISAN
Department of Software Engineering, Faculty of Information
Technology, University of Technology, Sydney, AUSTRALIA.
Dr. YUXIN MAO
School Of Computer & Information Engineering Zhejiang Gongshang
University, CHINA
Dr. MUHAMMAD SHER
Faculty of Basic and Applied Sciences, Department of Computer
Science, International Islamic University, Islamabad. PAKISTAN.
Dr. ZARINA SHUKUR
Computer Science Dept., Fakulti Teknologi dan Sains Maklumat,
University Kebangsaan Malaysia, 43600 Bangi, MALAYSIA.
Dr. NOR AZAN MAT ZIN
Department of Information Science, Faculty of Information Science &
Technology, National University of Malaysia (UKM) 43600 UKM BANGI,
MALAYSIA.
Dr. KHAIRUDDIN BIN OMAR
Faculty of Information Science and Technology, Universiti Kebangsaan
Malysia, 43600 Bangi Selangor Darul-Ehsan, MALYSIA.
Dr. TENGKU MOHD. BIN TENGKU SEMBOK
Faculty of Information Science and Technology Universiti Kebangsaan,
Malaysia, 43600 Bangi Selangor Darul-Ehsan, MALYSIA.
Dr PRABHAT K. MAHANTI
Department of Computer Science and Applied Statistics (CSAS),
Hazen Hall Room 311, University of New Brunswick, Saint John, New
Brunswick, CANADA.
Dr. R. PONALAGUSAMY
Department of Mathematics, National Institute of Technology,
Tiruchirappalli, Tamil Nadu, INDIA.
Dr. NITIN UPADHYAY
Computer Science & Information Systems Group, Birla Institute of
Editorial Board -Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Techn...
http://www.jatit.org/Editorial_Board.php
Technology and Science (BITS), Pilani-Goa Campus, NH-17B Bypass
Road, ZuariNagar, Goa, INDIA.
Dr. A. SERMET ANAGN
Eskisehir Osmangazi University, Industrial Engineering Department,
Bademlik Campus, 26030 Eskisehir, TURKEY.
Dr. YACINE LAFIFI
Department of Computer Science, University of Guelma, BP 401,
Guelma 24000, ALGERIA.
Dr. CHRISTOS GRECOS
School of Computing, Engineering and Physical Sciences, University of
Central Lancashire, Preston PR1 2E, UNITED
KINGDOM.Dr. JAYANTHI RANJAN
Institute of Management Technology, Raj Nagar, Ghaziabad, Uttar
Pradesh, INDIA
Dr. ADEL M. ALIMI
National Engineering School of Sfax (ENIS), University of SFAX,
TUNISIA
Dr. SIKANDAR HAYAT KHIYAL
Department of Computer Science, Fatima Jinnah Women University,
Rawalpindi, PAKISTAN
Dr. ADEL MERABET
Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering, Dalhousie
University, Halifax, CANADA
DR. HEMRAJ SAINI
CE&IT Department, Higher Institute of Electronics, Bani Walid. LIBYA
Dr. MAUMITA BHATTACHARYA
SOBIT, Charles Sturt University, Albury - 2640, NSW, AUSTRALIA
Dr. SEIFEDINE KADRY
Lebanese International University, LEBONON
Dr. AIJUAN DONG
Department of Computer Science, Hood College Frederick, MD 21701.
USA
Dr. S.S.RIAZ AHAMED
Mohamed Sathak Engineering College, Kilakarai, & Sathak Institute of
Technology, Ramanathapuram , Tamilnadu, INDIA
Dr. ZURIATI AHMAD ZUKARNAIN
University Putra Malaysia, MALAYSIA
Dr. CHELLALI BENACHAIBA
University of Bechar, ALGERIA
Dr. MOHD NAZRI ISMAIL
University of Kuala Lumpur (UniKL) MALYSIA
Dr. VITUS SAI WA LAM
The University of Hong Kong, CHINA
Dr. WITCHA CHIMPHLEE
Suan Dusit Rajabhat University, Bangkok, THAILAND
Editorial Board -Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Techn...
http://www.jatit.org/Editorial_Board.php
Dr. SIDDHIVINAYAK KULKARNI
University of Ballarat, Ballarat, AUSTRALIA
Dr. S. KARTHIKEYAN
Caledonian College of Engineering, OMAN
Dr. DRAGAN R. MILIVOJEVI
Ć
Mining and Metallurgy Institute Bor Zeleni bulevar 35, 19210 Bor,
SERBIA
Dr. ABDUL AZIZ
Professor of Computer Science, University of Central Punjab,
PAKISTAN
Dr.P.DANANJAYAN
Professor, Department of ECE, PEC, Puducherry, INDIA.
Dr. E. SREENIVASA REDDY
Principal - Vasireddy Venkatadri Institute of Technology, Guntur, A.P.,
INDIA
Dr. SANTOSH DHONDOPANT KHAMITKAR
Ramanand Teerth Marathwada University, Nanded. Maharashtra
431605, INDIA
Dr. M. IQBAL SARIPAN
(MIEEE, MInstP, Member IAENG, GradBEM)
Dept. of Computer and Communication Systems Engineering, Faculty
of Engineering, Universiti Putra MALAYSIA
Dr. E. SREENIVASA REDDY
Principal - Vasireddy Venkatadri Institute of Technology, Guntur, A.P.,
INDIA
SHAHBAZ GHAYYUR
Faculty of Basic and Applied Sciences, Department of Computer
Science and Software Engineering, International Islamic University,
Islamabad. PAKISTAN.
Dr. T.C.MANJUNATH,
Professor & Head of the Dept.,Electronicis & Communication Engg.
Dept,
New Horizon College of Engg.,Bangalore-560087, Karnataka, INDIA.
Dr. Nacer eddine ZAROUR
LIRE Laboratory, Computer Science Departement, University Mentouri
of Constantine (UMC)
Dr. RIKTESH SRIVASTAVA
Assistant Professor, Information Systems, Skyline University College
P O Box 1797, Sharjah, UAE
Dr. Mohd ZAINAL ABIDIN AB KADIR,
PhD, MIEEE
Centre of Excellence on Lightning Protection (CELP)
Dept. of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Faculty of Engineering,
UPM, Selangor, MALAYSIA
Dr. OUSMANE THIARE
Gaston Berger University, Department of Computer Science, UFR
S.A.T
BP 234 Saint-Louis, SENEGAL
Dr. SIDDHIVINAYAK KULKARNI
Graduate School of Information Technology and Mathematics
University of Ballart AUSTRALIA
Editorial Board -Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Techn...
http://www.jatit.org/Editorial_Board.php
Dr. BONNY BANERJEE
Senior Scientist Audigence, FL, USA, The Ohio State University,
Columbus, OH, USA
Dr. NICKOLAS S. SAPIDIS
Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Western
Macedonia
Kozani GR-50100, GREECE.
Dr. NAZRI BIN MOHD NAWI
Software Engineering Department, Faculty of Science Computer
Information Technology, Universiti Tun Hussein Onn
MALAYSIA
Dr. JOHN BABALOLA OLADOSU
Ladoke Akintola University of Technology, Ogbomoso, NIGERIA
Dr. ABDELLAH IDRISSI
Department of Computer Science, Faculty of Science, Mohammed V
University - Agdal, Rabat, MOROCCO
Dr. AMIT CHAUDHRY
University Institute of Engineering and Technology, Panjab University,
Sector-25, Chandigarh, INDIA
Dr. ASHRAF IMAM
Aligarh Muslim University, Aligarh-INDIA
Dr. MUHAMMAD UMER KHAN
Department of Mechatronics, Faculty of Engineering, Air University,
Islamabad. PAKISTAN
Dr. MOHAMMED ALI HUSSAIN
Dept. of Computer Science & Engineering, Sri Sai Madhavi Institute of
Science & Technology, Mallampudi,
Rajahmundry, A.P, INDIA
Dr. KHALID USMANI
Department of Computer Science, Arid Agriculture University,
Rawalpindi, PAKISTAN.
Dr. GUFRAN AHAMD ANSARI
Qassim University, College of Computer Science, Ministry of Higher
Education, Qassim University, KINGDOM OF SAUDI ARABIA
Dr. Defa Hu
School of Information, Hunan University of Commerce, Changsha
410205, Hunan, P. R. of CHINA
MANAGING EDITORS
Saleha Samar
(
managing_editor at jatit.org
)
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology
Shahzad A. Khan
(
publisher at jatit.org
)
Lecturer IMCB, FDE Islamabad.
(
Managing Editor/Linguist & In-charge Publishing
)
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology
**You can join the elite panel of JATIT as member technical editorial
Editorial Board -Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Techn...
http://www.jatit.org/Editorial_Board.php
jatit.org Publishing Policy Review Process Code of Ethics
board if you hold a PhD in computing and have at-least 10
publications in International Journals/Conferences. Please drop your
CV at
managing_editor at jatit.org
. Members lists and requests are
reviewed at the end of every year in regional advisory panel meeting.
Editorial Board -Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Techn...
http://www.jatit.org/Editorial_Board.php
Home
Volumes
Submit Paper
Manuscript Status Author Guidelines Editorial Board
Indexing and Abstracting Subscribe to JATIT Contact Us
Frequency :
MONTHLY
FeedBack | Contact Us |Links | Site Map
Welcome to Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology
Submit Paper / Call for Papers
Journal receives papers in continuous flow and we will consider articles from a wide range of Information Technology disciplines
encompassing the most basic research to the most innovative technologies. Please submit your papers
electronically to our submission system at http://jatit.org /submit_paper.php in an MSWord, Pdf or compatible format so that they may be evaluated for publication in the upcoming issue. This journal uses a blinded review process; please remember to include all your personal
identifiable information in the manuscript before
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology
January 2014 | Vol. 59 No. 2
Title: A NOVEL APPROACH TO GENERATE TEST CASES FOR COMPOSITION & SELECTION OF WEB SERVICES BASED ON MUTATION TESTING
Author: ASHOK KUMAR. P.S, KAARTHICK .B, GOPAL KRISHNA. C
submitting it for review, we will edit the necessary information at our side. Submissions to JATIT should be full research / review papers (properly indicated below main title).
Full Text
Title: CORRECTION POSITION OF COORDINATES FROM DATA GPS LOGGER IN GOOGLE MAPS BY USING LAGRANGE INTERPOLATION METHOD
Author: NGAKAN MADE SATRYA WIBAWA, I MADE SUKARSA, I KETUT ADI PURNAWAN
Abstract: Development of navigation technologies increase rapidly. People need a GPS to indicate a location or street. The accuracy of the GPS position is often less precise. This problem is used as a discussion of issues in the design of GIS to fix the GPS coordinates to the coordinates of the path using interpolation polinom lagrange method. This study uses PL/SQL to MySQL engine to perform the calculations haversine formula and interpolation polinom lagrange. Coordinates improvements value obtained from the results of these calculations.
Keywords: GPS, GIS, PL/SQL, Correction Coordinate, Interpolation Polinom Lagrange
Source: Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology January 2014 -- Vol. 59. No. 2 -- 2014
Full Text
Title: COMPARATIVE STUDY OF DATA MINING MODEL FOR CREDIT CARD APPLICATION SCORING IN BANK
Author: EVARISTUS DIDIK MADYATMADJA, MEDIANA ARYUNI
Abstract: The growth of credit card application needs to be balanced with the anticipation of bad credit risk because it does not use security collateral as warranty. The usage of credit scoring can be used to help the credit risk analysis in determining the applicant's eligibility. Data mining has been proven as a valuable tool for credit scoring. The aim of this research is to design a data mining model for credit scoring in bank in order to support and improve the performance of the credit analyst job. The proposed model applies classification using Naïve Bayes and ID3 algorithm. The accuracy of Naïve Bayes classifier is 82% and ID3 is 76%. So we can conclude that Naïve Bayes classifier has better accuracy than ID3 classifier.
Keywords: Credit Scoring, Data Mining, Credit Card, Bank, Naïve Bayes, ID3, Classification
Source: Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology January 2014 -- Vol. 59. No. 2 -- 2014
Full Text
Title: MULTI-LEVEL TRUST ARCHITECTURE FOR MOBILE ADHOC NETWORKS BASED ON CONTEXT-AWARE
Author: A.RAJESH, DR. N. MOHAN KUMAR
Abstract: Mobile ad hoc networks (MANETs) are not favorable to centralized trust architecture and literature review provides several security framework and solutions for trust management. However, there is no unified architecture for MANET to exploit deployed security models based on trust. This study presents compelling trust architecture in which a trust based security model is superimposed with three trust models such as a low-level trust model, a medium-level trust model, and a high-level trust model based on context-aware security. The low-level trust model meets the necessary security requirements using direct observations. The medium-level trust model ensures medium security level using direct observations and recommendation messages. The high-level trust model provides a highly secured system with high complexity and computational cost. The proposed work is formulated based on the application context to determine the trust-level in geographic routing protocol. The proposed trust is fully distributed and application context dependent and dynamic in nature. The proposed multi-level trust model is integrated with Position based Opportunistic Routing (POR) Protocol that selects the trusted next hop in the routing path. The correctness of the proposed scheme is analyzed using network simulator (NS-2). Proposed work increases packet deliver ratio and throughput significantly.
Keywords: Mobile Ad Hoc Networks, Geographical Routing, Trust Management, Context-aware Trust, Trust based Security
Source: Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology January 2014 -- Vol. 59. No. 2 -- 2014
Full Text
Title: INVESTIGATION OF SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINE CLASSIFIER FOR OPINION MINING
Author: K.SARASWATHI, Dr. A.TAMILARASI
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology - January ...
http://www.jatit.org/volumes/Vol59No2/fiftyninth_2_2014.php
Abstract: Complicated text understanding technology which extracts opinion, and sentiment analysis is called opinion mining. Building systems to collect/examine opinions about a product in blog posts, comments, and reviews/tweets is sentiment analysis. Product reviews are the focus of existing work on review mining and summarization. This study focuses on movie reviews, investigating opinion classification of online movie reviews based on opinion/corpus words used regularly in reviewed documents.
Keywords: Opinion Mining, Classification Accuracy, Sentiment analysis, Movie reviews, Support Vector Machine, Bagging
Source: Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology January 2014 -- Vol. 59. No. 2 -- 2014
Full Text
Title: A ROBUST METHOD FOR DIGITAL IMAGES WATERMARKING BASED ON COMBINATION OF SVD, DWT AND DCT USING OPTIMAL BLOCK
Author: MOHAMED RADOUANE, TARIK BOUJIHA, ROCHDI MESSOUSSI, RAJA TOUAHNI
Abstract: With the growth of the Internet, development of digital media technologies and computer network, the change and the protection of copyright have become very important. To protect multimedia data against illegal recording and retransmission, the integration of a signal (digital signature, watermark) has become an obligation without modifying quality of the original image, the goal of this operation is to identify the owner and protect his intellectual property. Digital watermarking has been proposed as a solution to solving the copyright problem by introducing invisible data (watermark) into original image. In this paper, we propose a robust method for digital images watermarking. This method is achieved by searching the optimal block that can be used to insert the watermark in original image by modifying the singular value decomposition (SVD) in DWT (discrete wavelet transform) combined with DCT (Discrete Cosine Transform) . The experimental results show that this imperceptible method combines the advantage of three transformations to ensure robustness against most attacks.
Keywords: Watermarking, DWT, SVD, DCT, Entropy
Source: Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology January 2014 -- Vol. 59. No. 2 -- 2014
Full Text
Title: FUZZY VAULT FUSION BASED MULTIMODAL BIOMETRIC HUMAN RECOGNITION SYSTEM WITH FINGERPRINT AND EAR
Author: R.VINOTHKANNA, Dr.AMITABH WAHI
Author: G. Thippa Reddy, K. Sudheer, K Rajesh, K. Lakshmanna
Abstract: Cloud computing is rapidly gaining popularity. However, like any new system, cloud computing is facing some significant challenges. The most significant challenge faced by cloud adopters is related to legal compliance, security controls, privacy and trust. This paper proposes a novel security management framework by employing data mining to detect, contain and prevent attacks on cloud computing systems. Given that the security frameworks and related controls on cloud computing are still evolving, this research may prove to be a useful piece of contribution in enhancing the theoretical foundation established by existing studies.
Keywords: Cloud Computing, Data Mining, Security-as-a-service, OPNET, Positivism and the Interpretivism
Source: Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology January 2014 -- Vol. 59. No. 2 -- 2014
Full Text
Title: A MULTI-AGENT BASED DISTRIBUTED INTRUSION PREVENTION SYSTEM AGAINST DDOS FLOODING ATTACKS
Author: A. SAIDI, A. KARTIT, M. EL MARRAKI
Abstract: Denial of service (DoS) attacks is a simple and very annoying type of intrusions. This kind of attacks attempts to make unreachable at least a service of equipment like it can stagnate the whole of a network. To launch a DoS attack, we have, nowadays, often tools to succeed. Some of these tools try to send a compromised network load to corrupt their targets by flooding it with SYN, UDP or ICMP packets [1],[2]. Our paper describes the conception of a multi-agent-based intrusion prevention system (IPS) that can apprehend these flooding attempts in a distributed way.
Keywords: DoS Attacks, Intrusion Prevention, Multi-agent System, Distributed System
Source: Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology January 2014 -- Vol. 59. No. 2 -- 2014
Full Text
Title: FORECASTING EARNINGS PER SHARE FOR COMPANIES IN IT SECTOR USING MARKOV PROCESS MODEL
Author: M.P. RAJAKUMAR , V. SHANTHI
maturity.
Keywords: Audit of Information System, IT Governance, COBIT, Maturity Level, ITIL
Source: Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology January 2014 -- Vol. 59. No. 2 -- 2014
Full Text
Title: ENERGY EFFICIENT INTRUSION DETECTION SYSTEM FOR WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORK USING NEURAL NETWORK
Author: SYEDA GAUHAR FATIMA,Dr.SYED ABDUL SATTAR, Dr.K ANITHA SHEELA
Abstract: In wireless sensor network (WSN), the existing intrusion detection techniques rarely consider energy consumption for judging the node state. Also there is need for increased detection rate. Hence in this paper, we propose an energy efficient intrusion detection system for WSN. Initially the nodes deployed in the network are analyzed for malicious activity based on their residual energy. If the energy consumption of a node is greater than a predicted threshold, it is considered as malicious and the packets emerging from these nodes are said to be abnormal. The abnormal packets are passed through the Back Propagation Network (BPN) to analyze the data misinterpretation. In case, the output of BPN is found to be abnormal, then the attack detection is confirmed and attack type is estimated. By simulation results, we show that the proposed technique is more energy efficient.
Keywords: WSN, Intrusion Detection, Wnergy Efficient, Neural Network
Source: Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology January 2014 -- Vol. 59. No. 2 -- 2014
Full Text
Title: A NOVEL APPROACH FOR MITIGATION OF HARMONICS AND INTERHARMONICS IN VARIABLE FREQUENCY DRIVES
Author: PROF.VIJAYAKUMAR.A, DR.MAHENDRA BABU. T.K
Abstract: Interharmonics are non-integer multiples of the fundamental frequency that causes several undesirable effects. Variable frequency drives are main sources of interharmonics. Also interharmonics are generated when the inverter load is unbalanced or the inverter is operating in overmodulation. In this study, adjustable speed drive employing diode bridge rectifier and voltage source inverter with load unbalance is considered. Propogation of interharmonics in the supply side due to load unbalance is analysed and a novel method for mitiating interharmonics is proposed. The proposed method employs an active filter in supply side which is simulated using PSIM . With the proposed active filter the compensation effectiveness is significantly improved and allows the elimination of passive filters thereby reducing cost and space required.
Keywords: Interharmonics, Power Quality, Adjustable Speed Drive, Active Filter, Interharmonics Mitigation
Source: Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology January 2014 -- Vol. 59. No. 2 -- 2014
Full Text
Title: MAPPING THE RESEARCH PRODUCTIVITY OF BANARAS HINDU UNIVERSITY: A SCIENTOMETRIC STUDY
Author: R. BALASUBRAMANI, R. PARAMESWARAN
Title: EXPLOITING IPV6 ROUTING HEADERS TYPE 0/2 IN DIFFERENT IP WIRELESS NETWORKS: ATTACK SCENARIO & ANALYSIS
Author: BASSAM NAJI AL-TAMIMI, RAHMAT BUDIARTO, MOHD. ADIB OMAR, KAMAL M. ALHENDAWI
Keywords: Content-based image retrieval, Computed Tomography, Coif let wavelets, Particle Swarm Optimization, Genetic algorithm, Support Vector Machine
Source: Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology January 2014 -- Vol. 59. No. 2 -- 2014
Full Text
Title: SOLVING MAXIMAL COVERING PROBLEM USING PARTITIONED INTELLIGENT FISH ALGORITHM
Author: AMIN JULA, ELANKOVAN SUNDARARAJAN, NARJES KHATOON NASERI, REZA ABIAT
Abstract: NP-Complete optimization problems are a well-known and widely used set of problems which surveyed and researched in the field of soft computing. Nowadays, because of the acceptable rate of achieving optimal or near-optimal solutions of the mentioned issues, using of nature-inspired algorithms are increasingly considered. One of the familiar problems in the field of NP problems is Maximal Covering Problem which has various applications of pure mathematics to determine the location of mobile network antennas or police stations. In this paper, we introduced a heuristic algorithm called Partitioned Artificial Intelligent Fish Algorithm which using artificial fish-search algorithm, logical partitioning of the search space of this algorithm to several sub-space and change in motor functions in fishes, deals with the suitable, innovative and fast solution of maximal covering problem. The results of implementing this algorithm and comparing it with the performance of some the best known algorithms for solving NP problems will be represented by a very good performance of the proposed algorithm.
Keywords: Artificial Fish Algorithm, Maximal Covering Problem, NP-hard problem
Source: Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology January 2014 -- Vol. 59. No. 2 -- 2014
Full Text
Title: E-BANJAR BALI, POPULATION CENSUS MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM OF BANJAR IN BALI BY USING FAMILY TREE METHOD AND BALINESE CULTURE LAW
Author: I GUSTI BAGUS ARI PINATIH, A.A. KOMPIANG OKA SUDANA, I KETUT ADI PURNAWAN
Abstract: This paper describes how population census in Balinese traditional village i.e. banjar are managed. This kind of information system is known as e-Banjar Bali. A case study was conducted in Banjar Padang Tegal Tengah, a banjar in Ubud, Bali regarding to the information system. This population information system uses website as its basis. The study was done to find an easier population census management. Managing family tree, calculating total population, indigenous and non-indigenous people, active and non-active population, natality and mortality are inclusive in the census. Additional feature included as a part of this information system is management upon banjar organizational data and information spreading among the society. This particular information system is expected to minimize the use of paper or manual execution of population census.
Keywords: Banjar, Population, Management, Family Tree, Balinese Culture Law
Source: Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology January 2014 -- Vol. 59. No. 2 -- 2014
Full Text
Title: BASIP A VIRTUAL MACHINE PLACEMENT TECHNIQUE TO REDUCE ENERGY CONSUMPTION IN CLOUD DATA CENTRE
Author: AJITH SINGH. N, M. HEMALATHA
Abstract: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) in cloud computing provides Infrastructure as a service for the demand of user from small instance to large instance in pay per use model. The services include like computer resource, networking and data storage. An API (Application Programming Interface) is used to access the infrastructure and a dashboard to control the server and to create and manage different Virtual Machines in the cloud data centre. Multiple cloud users access the service simultaneously. Due to continuous access of the services, a deadlock can happen, and it may lead to a system crash, although cloud computing is designed to overcome such problem, a proper Virtual Machine Placement Technique is needed for implementation to rule out such incidences. Deadlock can occur in cloud computing as the system is inherited from distributed computing and virtualization. A Virtual Machine Placement Technique known as BASIP is proposed to overcome the issue of deadlock by using a banker algorithm with Stochastic Integer Programming. Further, the proposed algorithm is being simulated with hundreds of servers and thousands of virtual machines. The proposed algorithm was simulated with different overload detection and VM selection algorithm. The BASIP algorithm is experimented with 800 servers with 1024 Virtual Machines. From the experimental results, BASIP algorithm reduces energy significantly.
Keywords: Virtual Machine, Cloud Computing, Live Migration, Bankers and Stochastic Integer Programming, Deadlock Avoidance, Resource Allocation, Energy, Cloud Data Centre, Minimum Utilization Rank, Polynomial Regression, BASIP
Source: Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology January 2014 -- Vol. 59. No. 2 -- 2014
Full Text
Title: PERFORMANCE OF MIMO MC-CDMA SYSTEM WITH CHANNEL ESTIMATION AND MMSE EQUALIZATION
Author: N. TAMILARASAN, L. NITHYANANDAN
the same row and the second stage is forming a vertical chain that includes all chain heads. The mechanism for selecting the heads in each row is sequentially chosen with all the heads belong to the same column. In the second stage, the node with maximum residual energy amongst the chain heads will be the main head that functions as a gateway to the base station. Simulation results show that TSCP outperforms CCM and CCBRP in overall energy conservation, network lifetime and stability.
Keywords: Wireless Sensor Network, TSCP, CCM, CCBRP, Chain Protocol
Source: Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology January 2014 -- Vol. 59. No. 2 -- 2014
Full Text
Title: A NEW DENSITY BASED PROBABILISTIC COUNTER SCHEME FOR SOLVING BROADCAST STORM IN MOBILE AD HOC NETWORKS
Author: A. SENTHIL KUMAR, K.S. RAMASWAMI
counted a significant field of research over the past decade. Thus, we present an inclusive review and present classification on the current routing sensor protocols, which are particularly designed for wireless sensor networks. We emphasize the main motivation behind the development of each routing protocol category and clarify the operation of different protocols in detail related to energy issues, with emphasis on their advantages and disadvantages. Moreover, the current multipath routing approach is broadly used in wireless sensor networks in order to improve network performance such as load balancing, reliability, fault tolerance, bandwidth aggregation and QoS Improvement. Therefore, in this paper we highlight the notion of the multipath routing approach and its essential challenges, additionally the basic motivations for utilizing this technique in wireless sensor networks. In addition, we contrast and review the state-of-the-art multipath routing protocols that based on energy aware method, fault tolerance and QoS multipath routing. At the end of this paper, a characterized comparison has been forwarded on these methods based on the analysis outcome.
Keywords: Wireless Sensor Networks, Routing Protocols, Energy Efficiency, Fault Tolerance, Qos, Multipath Routing
Source: Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology January 2014 -- Vol. 59. No. 2 -- 2014
Full Text
Title: A STUDY OF TSUNAMI MODEL FOR PROPAGATION OF OCEANIC WAVES
Author: E.SYED MOHAMED, S.RAJASEKARAN
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology
20thJanuary 2014. Vol. 59 No.2
© 2005 - 2014 JATIT & LLS. All rights reserved.
ISSN: 1992-8645 www.jatit.org E-ISSN: 1817-3195
411
E-BANJAR BALI, POPULATION CENSUS MANAGEMENT
INFORMATION SYSTEM OF BANJAR IN BALI
BY USING FAMILY TREE METHOD
AND BALINESE CULTURE LAW
1
I GUSTI BAGUS ARI PINATIH,
2A.A. KOMPIANG OKA SUDANA,
3
I KETUT ADI PURNAWAN,
1,2,3
Department of Information Technology, Udayana University, Bali, 80119
E-mail:
1gba.pinatih@gmail.com
2
agungokas@hotmail.com
3dosenadi@yahoo.com
ABSTRACT
This paper describes how population census in Balinese traditional village i.e.
banjar
are managed. This
kind of information system is known as
e-Banjar Bali
. A case study was conducted in
Banjar Padang
Tegal Tengah
, a
banjar
in Ubud, Bali regarding to the information system. This population information
system uses website as its basis. The study was done to find an easier population census management.
Managing family tree, calculating total population, indigenous and indigenous people, active and
non-active population, natality and mortality are inclusive in the census. Additional feature included as a part of
this information system is management upon
banjar
organizational
data and information spreading among
the society. This particular information system is expected to minimize the use of paper or manual
execution of population census.
Keywords:
Banjar, Population, Management, Family Tree, Balinese Culture Law
1.
INTRODUCTION
Balinese culture is widely known in the world. Its
traditional customs, cultures, and arts become a
unique trait for Bali Island itself. The other unique
trait is the way how Balinese manage its population.
Balinese societies live in a special system called
banjar
.
Banjar
is an administrative division under
the governance of sub-district or village in Bali
Province, Indonesia.[1]
Banjar
is a term to refer to a unity of society
bounded by law which governs the region borders
in controlling and ruling local society needs – based
on its local customs that has been acknowledged
and respected by Indonesian government.[6]
Banjar
is ruled by a traditional village. Traditional
village is governed by sub-district. Each sub-district
might consist of some traditional villages. Every
traditional village might have several
banjar
.
Figure 1: Scheme Of Banjar In Bali
Population management in Bali is totally different
from other area in Indonesia because of the
existence of
banjar
itself. The differentiation of
societies that appears in two resident statuses –
penduduk dinas
and
penduduk adat
– is the
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology
20thJanuary 2014. Vol. 59 No.2
© 2005 - 2014 JATIT & LLS. All rights reserved.
ISSN: 1992-8645 www.jatit.org E-ISSN: 1817-3195
412
Penduduk adat
refers to a person who possesses
traditional or indigenous status based on the local
custom in their neighborhood.[12]
Penduduk dinas
and
penduduk adat
were formed
because there are two types of living status in Bali
i.e.
banjar dinas
and
banjar adat. Banjar dinas
is a
compulsory social organization which should be
possessed by every people in particular
banjar
– as
national administrative affairs managed in
banjar
dinas
.[7]
Banjar adat
refers to
banjar
status living
– that i.e. owned by indigenous people – where any
traditional affairs (mortality,
odalan
, and marriage)
and other
banjar
local affairs are usually taking
place.[5]
A family in
banjar
area is often illustrated with a
tree and its branches that grow over time. Thus, this
system is called lineage or family tree. This family
tree will have more branches as new members
enters. Then, relationships among the members of a
family should be clearly defined so that personal
identity can be known completely. This is in line
with the purpose of calculating population.
At one banjar in the population, those cases have
certainly occurred as marriage, divorce, death, birth,
natives and immigrants, community organizations,
and dissemination of relevant information on
population.
Population data collection during years are
addressed by using the book (manual data
collection). The data entry by using this type is very
simple to use but would be inefficient for data
processing and dissemination of population
information.
Figure 1: Population And Activities Archieve Of Banjar Padang Tegal Tengah Ubud 2013
Over the development period, in the
banjar
population census has been put on Ms. Office
Excel. Data processing is handled by the software.
But, not everyone can operate and use the existing
formulas on the software.
Figure 2: Population Data Of Banjar Padang Tegal Tengah Ubud 2013 Using Ms. Excel
Figure 3: Population Data Of Banjar Padang Tegal Tengah Ubud 2013 Based On Employment And
Education
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology
20thJanuary 2014. Vol. 59 No.2
© 2005 - 2014 JATIT & LLS. All rights reserved.
ISSN: 1992-8645 www.jatit.org E-ISSN: 1817-3195
413
Some cases that can be managed by this population
census management information system are
patriarch,
matriarch,
divorce,
non-indigenous
inhabitant, indigenous inhabitant, natality and
mortality, society organization, as well as newest
information spreading (e.g. current
banjar
activity,
announcement, documentation, and any other
information that can be delivered through internet).
The boundary’s problem of this case study is on a
scale of population census only on one
banjar
.
2.
METHODOLOGY
Methodology used in this research was family tree
method and combine with interview method
towards the head of
banjar
Padang Tegal Tengah
Ubud. This interview is used to collect
informations
about Balinese culture law. So, methodology used
in this research is combination between family tree
and Balinese culture law (based on interview with
head of
banjar
)
2.1
Family Tree Method
Family tree is a term used to describe lineage
showing the line of descent from an ancestor to a
person or a family which has a connection towards
other people being his wife or relatives.[2] The
lineage then describes the relationships among
members of a family vertically and horizontally by
mentioning the name of the family.[2]
Figure 4: An Example of a Family Tree
Famiy tree makes the drawing of lineage and
observing the descendents, head of household, and
inheritors easier.[2] An example above shows that
after Mr. Edy and Mrs.
Luna getting
married, they
have two sons and a daughter. Furthermore, in this
case, Mr. Edy is the head of the household (looking
at the husband line or patrilineal system).
Meanwhile, his wife and his children are the
members of the family. As all of his children got
married, there will be three new families. This
situation continues on and on.
Residential system in Bali is similar to the family
tree system mentioned previously but it is in a
slightly different version of the traditional one.
Seeing this case, this research was done in
banjar
Adat Padang Tegal Tengah Ubud Bali. For
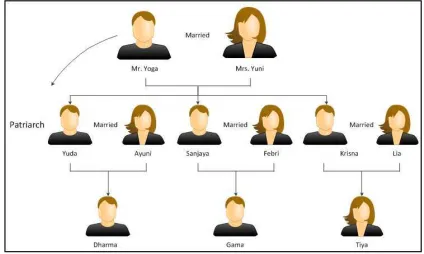
example, Mr. Yoga and Mrs. Yuni got married.
They have three sons. Mr. Yoga was the head of the
household.
Figure 5: An Example of Family Tree Method
These three sons then got married and have their
own wife and children. Since their parents were not
productive and active anymore – due to age factor –
then the first son had to be responsible for the
family. Therefore, the first son in Mr. Yoga’s
family took the responsibility as the head of the
household. Mr. Yoga, Mrs. Yuni, Sanjaya, and
Krisna were now under Yuda’s responsibility.[9]
Figure 6: Example Of Family Tree, The Changing Of The Head Of Household In Bali
To make it clearer, an example of family tree
system is portrayed in the following case. It can be
seen in figure 5.
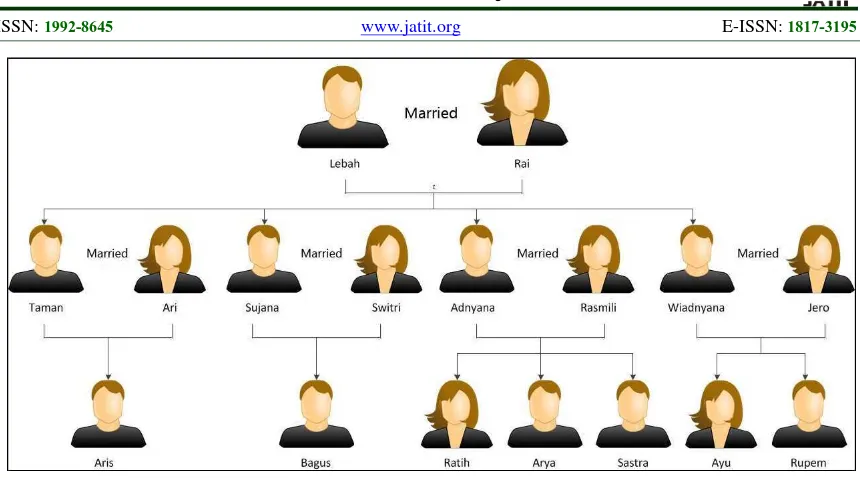
A house for a big family consists of a couple of old
man and woman. They have four sons. Each of
their sons has got married. All of them already have
their own children. The situation can be described
as follows:
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology
20thJanuary 2014. Vol. 59 No.2
© 2005 - 2014 JATIT & LLS. All rights reserved.
ISSN: 1992-8645 www.jatit.org E-ISSN: 1817-3195
414
Figure 7: Example of Family Tree (In Detail)
In detail, Mr. Lebah has:
a.
A wife
b.
Four sons
c.
Four daughters-in-law
d.
Seven grandchildren
If we see it from the child’s side (i.e. Taman), it can
be said that he has:
a.
A father and a mother
b.
A wife
c.
A child
d.
Three brothers
e.
Three sisters-in-law
f.
Four nephew and two niece
This continuity happens until a lineage of a family
appeared. A datum or a person must be related to
his/her own family. For instance, Lebah’s data
should have detailed descend data. This specific
condition is also for Lebah’s descend data – i.e. his
son’s data.
The details will be explained in the following
design and architecture part.
2.2 Interview with the Leader of the Banjar
An interview with the leader of the
Banjar
was
conducted in order to get necessary data for the
research. Besides, any other factor concerned in this
research was custom-based regulation in managing
the population itself. The leader of the
banjar
is
known as
Kelihan Banjar
in Balinese. He and his
partners have important roles in leading the
banjar
adat
affairs such as information spreading,
population management, local customs affairs
(
ngaben
, religious ceremony, etc.), and other
activities that can enhance the
banjar
identity as
well as appreciate values exist in the society.
Another interview also was conducted with the
leader of ST and PKK. The leader of ST (
Sekeha
Teruna
or an organization of non-marriade people
in banjar) is considered as the most mature
youngster in leading the youth in that
banjar
.
Activities that are done by ST such as celebrating
banjar
anniversary,
taking
parts
in
many
competitions, and creating other youth events.
On the other side, PKK (
Pemberdayaan dan
Kesejahteraan Keluarga
or an organization
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology
20thJanuary 2014. Vol. 59 No.2
© 2005 - 2014 JATIT & LLS. All rights reserved.
ISSN: 1992-8645 www.jatit.org E-ISSN: 1817-3195
415
wealthy as well as law enforcement and
environmentally literate.
Then,
those
points
were
investigated
and
implemented towards the information system by the
researchers.
3. SYSTEM OVERVIEW
This part clarifies (1) design and system feature, (2)
application of family tree, (3) marriage and divorce
in Bali, as well as (4)
banjar
organizer features.
3.1 Design and System Feature
e-
Banjar
Bali is a web-based application. Its
information takes place in online form so it can be
accessed anytime and anywhere. In addition,
information can be exchanged among the residents,
administrators, and village organizers without any
space and time boundaries. For instance, when
there is important information wanted to be
delivered by
Kelihan Banjar
, he can directly gives
instructions to the system. Meanwhile, the
administrators and members of the system will get
the instruction and they will do it immediately. The
user gives information in a form of personal data
such as KTP (ID card) and SIM (driving license)
scan to the system to complete their own identity.
Moreover, the admin will insert news, population
and other necessary information to the system that
the others can easily access. Obviously, all data will
run in the load and saved in and to the database.
Figure 8: Form of Interaction in e-Banjar Bali System
The design of e-
Banjar
Bali population census
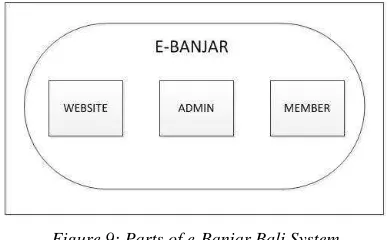
management information system is divided into
three parts namely (1) website page, (2)
administrator page, and (3) member page. Website
page is a page consists of important information
related to
banjar
which will always be updated by
the administrator. [3]
Administrator page refers to a page which is used
by the administrator to manage the population and
other necessary data which is related to
banjar
itself. The administrator has a right to manage this
information system – this is certainly in accordance
with the leader of
banjar
’s permission and
agreement.
Furthermore, member page is defined as a page for
all members of
banjar
. Each member has their own
username and password. They do not have the
rights to change any existed
data which inputted
from the registration process. But, all members can
see
the information and data stored in the system
alongwith
their
digital
document
uploaded
previously such as KTP, SIM, certificate of birth,
certificate of marriage, diforce, and so on.
Figure 9: Parts of e-Banjar Bali System
Each resident must register themselves to the leader
of
banjar
to get their username and password. The
username and password
will be used to log in to the
member page. As the registration process finished,
population data is automatically inputted by the
administrator. Figure 8 shows an example of
marital case where new resident should be
registered.
Figure 10: Member Sign Up
Most of the activities in this information system are
done in the administrator page. Some features that
could be controlled in the administration page of
this information system are mentioned as follows:
a.
In-
banjar
marital case
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology
20thJanuary 2014. Vol. 59 No.2
© 2005 - 2014 JATIT & LLS. All rights reserved.
ISSN: 1992-8645 www.jatit.org E-ISSN: 1817-3195
416
g.
Mortality case
h.
Natality case
i.
Non-indigenous resident case
j.
Temporary resident case
k.
Facility of ST organizational management
l.
Facility of PKK organizational management
m.
News management facility and data master
n.
Data archive
o.
Facility of
Banjar
leader
p.
Banjar
activities record.
q.
Report
This information system focuses more on the
population census management. The other part of
this application is ST organizational management
PKK organization, and information broadcasting to
banjar
members.
3.2 Family Tree Application
Family tree can be figured in many ways such as
branches – so it will look like a tree. Giving
numbers on chapter and sub-chapter is the other
way that can be done to describe family tree.
Chapter and sub-chapter numbering is used to make
application of this system easier. One to another
data will be related.[9] See the following example
for the illustration of case in Figure 5.
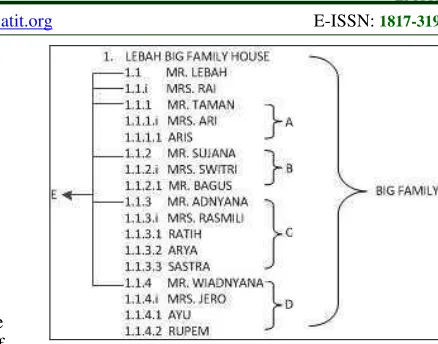
1.
LEBAH’S BIG FAMILY
1.1
MR. LEBAH
1.1.I MRS. RAI
1.1.1 MR. TAMAN
1.1.1.i MRS. ARI
1.1.1.1 ARIS
1.1.2 MR. SUJANA
1.1.2.i MRS. SWITRI
1.1.2.1 MR. BAGUS
1.1.3 MR. ADNYANA
1.1.3.i MRS. RASMILI
1.1.3.1 RATIH
1.1.3.2 ARYA
1.1.3.3 SASTRA
1.1.4 MR. WIADNYANA
1.1.4.i MRS. JERO
1.1.4.1 AYU
1.1.4.2 RUPEM
According to Figure 5, chapter and sub-chapter
numbering is used in describing a family tree. Each
small family then put into some categorization.
These small families later will create bigger family
in the same house.
Figure 11: A Family Tree using Numbering System
Figure Description:
A.
Mr. Taman’s family consists of his wife
(Mrs. Ari) and his only child (Aris).
B.
Mr. Sujana’s family consists of his wife
(Mrs. Switri) and his only child (Bagus).
C.
Mr. Adnyana’s family consists of his wife
(Mrs. Rasmili) and his three children
(Ratih, Arya, dan Sastra).
D.
Mr. Wiadnyana’s family consists of his
wife (Mrs. Jero) and his two children (Ayu
dan Rupem).
E.
Mr. Lebah’s family consists of his wife
(Mrs. Rai) and his four children (Mr.
Taman, Mr. Sujana, Mr. Adnyana, dan Mr.
Wiadnyana).
A house might consist of one or more head of the
household. There will come a time when the
inactive old head of household
is replaced by the
next generation. For example, Mr. Lebah and Mrs
Rai are getting old and not very active anymore.
Later on, Mr. Lebah and Mrs. Rai status of head of
household
is taken by Mr. Taman. In short, Mr.
Lebah and Mrs. Rai will be Mr. Taman – who is the
oldest son in the family – responsibility.
3.3 Marriage and Divorce Status
Marriage
in
the
system
falls
into
three
categories[10]:
a.
In-
banjar
marriage
This type of marriage involves outside-
banjar
resident that get into the
banjar
itself. Thus, the
number of
banjar
resident will rise: the
outside-banjar
resident gets married with one of the
adat
resident in that
banjar
.
b.
Intra-
banjar
marriage
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology
20thJanuary 2014. Vol. 59 No.2
© 2005 - 2014 JATIT & LLS. All rights reserved.
ISSN: 1992-8645 www.jatit.org E-ISSN: 1817-3195
417
But, there will be changing status of both the
groom and the bride from single to married.
c.
Out-
banjar
marriage
Out-
banjar
marriage is the opposite of in-
banjar
marriage. There will be number of inhabitants
added to
banjar
in-
banjar
marriage. In contrary,
in out-
banjar
marriage, the total population will
decrease. The married resident data will be
saved as an archive since s/he does not belong
to the
banjar
anymore.
Divorce cases in e-
Banjar
Bali system also has its
own regulation implemented based on the local
custom. When a couple decided to divorce and
went back to their old home, both of them will not
be considered as the ones who possess relationships
towards their family anymore. Thus, there must be
someone who accepts him/her. They could be
his/her uncle, aunt, father, or anyone under the
same lineage.[11]
3.4 Banjar Organizer
Banjar
organizers such as
kelihan banjar
or
banjar
secretary hold the authorities to control and solve
every problem exist related to
banjar
local
custom
.
[12]
For instance,
magebagan
– an event where every
male is ought to do night watch in relation to death
ceremony – should be arranged by
banjar
organizers. This event usually takes place for three
days or more, depends on the decision made by the
family whose member is dead. Therefore, in this
system, there will be turns for every head of
household to come and do the night watch
for the
first night, the second night, and so forth.
The turns made is sent to every head of household.
As a result, they will receive their night watch
schedule notification on their member page.
3.5 Dinas and Temporary Resident
Dinas
resident are the one who do not have the
responsibility to get involved in the local custom
affairs. They are usually originated from other
regions, whether in the same island or outside the
island, own a house and live in the
banjar
.[8] They
only take responsibility in the
dinas
affairs. This is
totally different from the indigenous residents who
possess two resident statuses,
adat
and
dinas
.
Moreover, temporary residents are people who live
temporarily in a place i.e.
banjar.
They might be
originated from the island or outside the island. The
examples of temporary inhabitants are lodging house
occupant, tourists who spend their vacation for
certain period of time, and other temporary living
inhabitants.[8]
These two types of resident should be statistically
recorded by the
banjar
so that there will be
dangerous condition took place (e.g. case of illegal
inhabitants who tend to commit crimes).
4. IMPLEMENTATION
The research stages were done by taking some
examples of census population such as population
statistic and the application of family tree method.
This system was created using some software (e.g.
PHP, Javascript, and MySQL).
4.1
Results of the Experiment
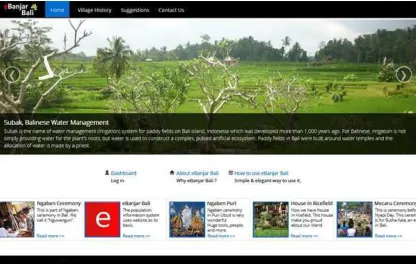
e-Banjar Bali homepage give people information
about whats new in his area. All new information
are here online.
Figure 12: e-Banjar Bali Homepage
Sample of
used data
was taken from population
data in 2013 – where the total population of
banjar
Padang Tegal Tengah Ubud was 429 people. The
population statistic is shown in a form of column
chart.
Figure 13: Total Population Graph
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology
20thJanuary 2014. Vol. 59 No.2
© 2005 - 2014 JATIT & LLS. All rights reserved.
ISSN: 1992-8645 www.jatit.org E-ISSN: 1817-3195
418
Based on the data, there are 218 males and 211 females.Figure 14: Total Population Graph by Sex
The next experiment was done to see the population
statistic based on marital status: (1) married, (2)
unmarried, (3) widower, or (4) widow.
Figure 15: Total Population Graph by Sex
According to the graph, there are 181 unmarried persons, 4 widowers, 11 widows, and 233 married persons.
Resident list was provided in a form of table that
contains common information. When a datum is
chosen, there will be detailed information shown.
Figure 16: List of Population
A datum was taken from A.A. GD. Raka Puja to see the members of his family.
Figure 17: An Example of Family Members
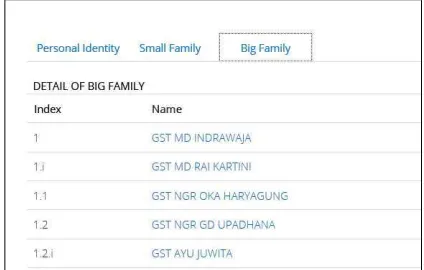
This is one example of family tree in this system.
This is family tree of Gst Md Indrawaja.
Figure 18: Family Tree in e-Banjar Bali
This is one example of marriage, marriage to the
Banjar (Banjar). This is the input form of
In-Marriage process. Only in admin page.
Figure 19: In-Banjar Marriage Input Form
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology
20thJanuary 2014. Vol. 59 No.2
© 2005 - 2014 JATIT & LLS. All rights reserved.
ISSN: 1992-8645 www.jatit.org E-ISSN: 1817-3195
419
Figure 20: An Example of Family MembersFigure 21: Write a News in Admin Area
4.2
Discussion
The objective of this information system is to help
the society in the rural area, especially Balinese
banjar
residents, in the process of population
census. This system is based on PHP, Javascript,
and MySQL so that it can be implemented online
and every resident has the opportunity to access it
anywhere and anytime.
Every resident will get their own username and
password that can be used to access system or log
in. Connected to the member page, the residents
will be able to see the information about themselves
as well as their family, population statistic, other
resident
information,
and
organizational
information exists.
The system will manifest as an easier way for the
society in getting to know each other. Also, it will
help the village organizers in getting reports from
the society. To be expected on the future, citizens
know each other more, care about the information,
as well as the discipline of the population census.
The comparison of data collection methods with the
book, Ms. Excel, with e-Banjar Bali is as follows;
Table 1: Comparison Population Cencus (E-Banjar Bali, Book, And Ms. Excel.)
Features
*
1
2
The
dissemination
of
information is much faster
√
-
-
Anytime and anywhere could
be
accessed
by
banjar’s
administrator, the committee of
the
banjar
and the whole
banjar’s
population
√
-
-
Online
√
-
-
The work efficiency of data
cencus
√
-
√
Information
among
people
each other in order to be more
knowing the fellow members
of the
banjar
√
-
-
A faster report
√
-
√
Critical idea and suggestion
from people to
banjar
√
-
-
Notification
of
news
or
messages for people (residents)
online
√
-
-
Easy to use
√
√
-
Note:
* : Population cencus with e-Banjar Bali
1 : Population cencus with book
2 : Population cencus with Ms. Excel
5.
CONCLUSION
In this paper, the way to count the
banjar
resident
in Bali was explained. Some experiments have been
conducted in this system. Conclusions of this
research can be formulated as follows:
a.
Population census management in a region can
be done easily. For instance, a resume of the
whole population census can be seen from the
population graph.
b.
Population data is organized based on patriarch
system. Head of household
possesses family
member which is then known as family tree.
c.
Manual population census, where books are
usually involved in, is now can be changed into
computerized one and online. Thus, population
census works can be finished efficiently.
d.
Technology
implementation
towards
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology
20thJanuary 2014. Vol. 59 No.2
© 2005 - 2014 JATIT & LLS. All rights reserved.
ISSN: 1992-8645 www.jatit.org E-ISSN: 1817-3195
420
REFERENCES
[1] Christina Gantini, Josef Prijotomo, and
Yuswadi Saliya, "Guna dan Fungsi pada
Arsitektur Bale Banjar Adat di Denpasar,
Bali", Temu Ilmiah IPLBI. 2012.
[2] Bagan Silsilah. Available at :
http://id.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bagan_silsilah
.
[3] A.Vijayaraj and P.DineshKumar, "Design and
Implementation of Census Data Collection
System Using PDA", International Journal of
Computer Applications, Vol. 9, No.9, 2010.
[4] I Ketut Sudantra, “Pengaturan Penduduk
Pendatang dalam Awig-Awig Desa Pakraman”,
Udayana University. 2006.
[5] Dr. Ir. Nyoman Utari Vipriyanti, MSi, "Banjar
Adat
and
Local
Wisdom:
Community
Management for Public Space Sustainability in
Bali Province", IASC. 2008.
[6] Rusian Wiryadi, “Banjar - the smallest parts in
the community system of Bali”, 2013.
Available
at:
http://www.ubudcommunity.com/en/articles/ba
linese-culture/item/203-banjar-the-smallest-parts-in-the-community-system-of-bali
[7] Banjar, Basic Building Block of Balinese
Society. Avaiable at :
http://id.indo.com/featured_article/banjar.html
[8] I Nyoman Artayasa, "Pengaturan Penduduk
Pendatang
oleh
Desa
Pekraman",
Mahasaraswati University, Denpasar. 2012.
Available
at:
http://inayasa.blogspot.com/2012/09/pengatura
n-penduduk-pendatang-oleh-desa.html
[9] Putu Ayu Juliastini, “Rancang Bangun Sistem
Silsilah Keluarga Berbasis Tree Berdasarkan
Hukum Adat Bali”, Electrical Engineering,
Udayana University. 2012.
[10] Anom, B. Perkawinan Menurut Adat Agama
Hindhu. Denpasar. 2010
[11]I Gede Panetje. “Aneka Catatan Tentang
Hukum Adat Bali”. Denpasar. 1986.