WELCOME MESSAGE
CONFERENCE ORGANIZATION
LIST OF PAPERS
LIST OF PAPERS
KEYNOTE
Impact of Electromagnetic Fields on Current Ratings
and Cable Systems
H. Orton (Convener) (Canada); P. Maioli (Secretary) (Italy),
H. Brakelmann (Germany); J. Bremnes (Norway); F. Lesur (France);
J. Orella Saenz (Spain); J. Smit (The Netherlands)
ID 12
Design of Snubber Circuit and PI Control to Achieve Load Independent Output
Voltage in Micro Smart Home System
Didi Istardi, Andy Triwinarko
ID 13
Economic Cost Study of Photovoltaic Solar System for Hotel in Nusa
Lembongan
I.A.D. Giriantari, I.N.S. Kumara, D.A. Santiari
ID 14
Elimination of Sympathetic Inrush Currents in Transformers Connected in
Parallel
Kartik P Basu, Naeem M Hanoon
ID 18
Investigation and Modelling of Sympathetic Inrush Due to Transformer
Energization
LIST OF PAPERS
ID 19
Load Fl
ow and Supply Security Analysis of Power System in Tiga Nusa;
Before and After the Application of 20kV Submarine Cable
Dayu Giriantari, I W. Sukerayasa, Y.M.A. Prawira
ID 20
The Design of Web Based Academic Information System in Universitas Sains
dan Teknologi Jayapura
Marla S.S. Pieter, Evanita V. Manullang
ID 21
Implementation Dedicated Sensing Receiver (DSR) in 3G - WiFi Offload
Setiyo Budiyanto, Muhammad Asvial, Dadang Gunawan
ID 22
Website Content Management Analysis of eGovernment in Bali Province
According to the Ministry of Communications and Information Guide (KOMINFO)
Gerson Feoh, Linawati, Ni Made Ary Esta Dewi Wirastuti
ID 23
Server Log Monitoring Based On Running Services
LIST OF PAPERS
ID 31
Performance Analysis of Packet Scheduling Algorithm for Video Service in
Downlink LTE
Ida Nurcahyani, I Wayan Mustika, and Selo
ID 35
Study on Feasible Solution of Power Control in Cognitive Radio Networks
Norma Amalia, I Wayan Mustika, and Selo
ID 42
Visualization of Indonesian Translation of Quran Index
Suwanto Raharjo, Khabib Mustofa
ID 43
A Review : Identification of Avian Influenza Environmental Risk Factor using
Remote Sensing Image and GIS
M. A. Padmasari, Linawati, N.M.A.E.D. Wirastuti
ID 44
Modelling and Numerical Simulation of Multiple One Way Gears Wave Energy
Converter to Generate Electricity
LIST OF PAPERS
ID 61
Comparison between RC Detector and High Frequency Current Transformer in
Measuring Partial Discharge in Liquid Insulation
Suwarno, Aulia
ID 62
Unidirectional Motion Estimation Technique With Full Search Algorithm For Frame
Rate Up-Conversion Video
I Made Oka Widyantara, Ni Putu Widya Yuniari, Linawati
ID 63
Modeling and Detection of High Impedance Faults
Huwei Wu, B.T. Phung, Daming Zhang, Jichao Chen
ID 75
Effect of the Distance of Partial Discharge Sensor to Partial Discharge Source on
the Attenuation of Partial Discharge induced Electromagnetic Wave in Gas Insulated
Switchgear
Umar Khayam, Zahrina Hafizhah
ID 77
New Designed Bowtie Antenna with Middle Sliced Modification as UHF Sensor for
Partial Discharge Measurement
LIST OF PAPERS
ID 78
Demand and Thermal Aware Approach for Greener IaaS-Cloud Data-Centers
Nazi Tabatabaei Yazdi, Chan Huah Yong
ID 85
DC Motor Speed Control with Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) Method of Infrared
Remote Control Base on Microcontroller ATmega16
Putu Raka Agung, Syamsul Huda, I Wayan Arta Wijaya
ID 86
Microhydro Powerplant for Rural Area in Bali to Generate Green and Sustainable
Electricity
ORGANIZING COMMITTEE
General Chair:
Ida Ayu Dwi Giriantari
Co-Chair:
W. G. Ariastina
General Secretary:
N. M. A. E. Dewi Wirastuti
Publication:
I M. Arsa Suyadnya
Secretariat:
I. B. Alit Swamardika
Finance:
N. Budiastra
I W. Sukerayasa
Sponsorship:
I M. Oka Widyantara
Local Program:
I N. Satya Kumara
I N. Setiawan
TECHNICAL PROGRAM COMMITTEE
Linawati, Ph.D (Indonesia – Chair)
Prof. A Min Tjoa (Austria)
Prof. Hugh Outhred (Australia)
Dr. Toan Phung (Australia)
Prof. Syed Islam (Australia)
Dr. Maria Retnanestri (Australia)
H. E. Orton (Canada)
Prof. Uwe Rehling (Germany)
Prof. Tsuyoshi Usagawa (Japan)
Prof. Wei-Chung Teng (Taiwan)
Prof. Emmanouil M. Tentzeris (USA)
Yoga Divayana, Ph.D (Indonesia)
Prof. Ontoseno Penangsang (Indonesia)
Dr. Yoyon K. Suprapto (Indonesia)
Prof. Suwarno (Indonesia)
Dr. Tumiran (Indonesia)
Dr. Lukito Edi Nugroho (Indonesia)
Prof. Rudy Setiabudi (Indonesia)
Prof. Dadang Gunawan (Indonesia)
Dr. Hermawan (Indonesia)
Prof. Gamantyo Hendrantoro (Indonesia)
Prof. Rukmi Sari Hartati (Indonesia)
Prof. Suprapta Winaya (Indonesia)
Prof. M. Ashari (Indonesia)
Dr. Asvial (Indonesia)
Dr. I Wayan Mustika (Indonesia)
Dr. Nyoman Gunantara (Indonesia)
Dr. Agus Dharma (Indonesia)
Dr. Made Sudarma (Indonesia)
Dr. I M. Yulistya Negara (Indonesia)
Dr. Wayan Nata Septiadi (Indonesia)
Unidirectional Motion Estimation Technique With
Full Search Algorithm For Frame Rate
Up-Conversion Video
I Made Oka Widyantara, Ni Putu Widya Yuniari, Linawati
Department Of Electrical Engineering Udayana University
Denpasar-Bali, Indonesia
[email protected], widyayuniari2010@gmail@com, [email protected]
Abstract—FRUC is a technique of inserting a new frame (frame intermediate) into a sequence of original video aiming at increasing frame rate. This technique is used in the process on video signal to overcome the limitation bandwidth transmission and temporal resolution. FRUC algorithm applies Motion Compensation Interpolation (MCI) technique. MCI technique relies on a process which is known Motion Estimation. Motion Estimation process is implemented by using a method searching. This technique is aim to get frame intermediate on FRUC algorithm as accurate as possible with low complexity. This research also aim to realize the FRUC algorithm with the application of Unidirectional motion estimation technique by the method of Full Search.
This research is conducted to obtain the performance of Unidirectional motion estimation technique with Full Search method in inserting frame intermediate. Experiment and analysis is implemented with frame rate ratio 1:2. Full Search method consist of two methods, there is Exhaustive Search and Half Pixel.
By comparing complexity Full Search on search area ±7 and ±15 pixel based on computation time it is revealed that Exhaustive Search method has lower complexity compare to Half Pixel method for insertion frame intermediate on FRUC algorithm.
Keywords: FRUC, Motion Compensation Interpolation, Motion Estimation, Full Search Method
I. INTRODUCTION
Multimedia service which is adapting digital based technology video has become a daily human needs. Many digital technology devices which support different format and usually needed to convert a format and frame rate. For instance film which is produce in 24 frame per second (fps) but on TV is displayed with 30 fps. There will be motion and voices that is well visually perceived if displayed 30 fps. The
technique which is adapted is called Frame Rate Up Conversion Video (FRUC). FRUC is a technique inserting a new frame (frame intermediate) into a sequences original video to increase frame rate. This application is used in processing video signal in order to overcome limitation of transmission bandwidth and to increase temporal resolution. FRUC algorithm applies Motion Compensation Interpolation (MCI) method. MCI technique relies on a process which is known Motion Estimation (ME). ME process for MCI algorithm on FRUC is aiming to predict frame position as motion vector (mv) which is nowadays is relying on reference frame. The obtaining mv will be stored in decoder as an information used for generate frame intermediate.
There is ME algorithm which is implemented to FRUC. This ME method is done only on the based on backward direction [1-3] which is uses a previous frame as a reference frame by copying mv from previous frame to become mv for frame intermediate. However, this method produces poor video motion. In order to overcome this sort coming a technique which is implemented linear combination technique that is reference frame application on both side that is backward and forward directions to give inform in inserting frame intermediate.
Choi et al [4] purposed MCI method using Bilateral ME technique. However this technique has a high complexity. To reduce this complexity, Zhang et al [5] has purposed Unidirectional method for FRUC algorithm. Algorithm of [1-3], [4-5] uses motion estimation with full search method with one pixel accuracy which is known as Exhaustive Search (ES) by adopting block based video coding. ES will search block candidate on every block position in reference frame by determining searching window[6]. Many researches has been done in order to obtain the most accurate frame intermediate with equality similar to original frame. There is searching method which is development of Exhaustive Search method that is a Full Search with a half pixel accuracy. This paper purpose an application of motion estimation technique with Full Search on FRUC algorithm. The target is to produce frame intermediate which is inserted on decoder in order to get the most accurate frame from the original video sequence.
ISBN : 978-1-4799-6126-9 Bali, 5 - 7 November 2014 ICSGTEIS 2014
-82-II. REVIEW
A. FRAME RATE UP CONVERSION VIDEO (FRUC)
Increasing the frame rate, i.e. up-conversion, is done to enhance the visual experience of video with low frame rate. Video at 30 frames per second (fps) is clearly smoother than video at 20 FPS, especially for video with much motion. Up-conversion is performed by adding new frames to a video from existing ones, as figure 1 illustrates.
Figure 1 Mechanism Of FRUC [6]
B. MOTION COMPENSATION INTERPOLATION FOR
FRUC
FRUC method with MCI technique uses two consecutive decoded frame as reference. In this research use MCI technique with an Unidirectional ME algorithm. Consider two consecutive decoded frames ft-1 dan ft+1 Let ft be the
intermediate frame, i.e., the frame to be interpolated. It can be modeled as
ft(x,y)= 1
2
1
− t
f
(x-2
1
Δx,y-2
1
Δy) +ft+1(x +
2
1
Δx, y +2
1
Δy) +ηt(x,y) (1)
Where (x, y) and (Δx,Δy) are pixel location and
unidirectional mv, respectively. In this research to get Δx and Δy based on Full Search Method.
The best of mv for generate frame intermédiate is the
lowest mean value from substract forward and backward side. Therefore
Δv = (Δx,Δy) = arg
y xΔ Δ ,
min
ρ(ft-1, ft+1; Δx, Δy) (2)where ρ() is a proper distance function. For unidirectional ME, such as forward prediction, ρ() can be defined as
ρ(ft-1, ft+1; Δx, Δy) =
|
,y Gx
Σ
∈ ft-1(x,y)- ft+1(x+Δx, y+Δy)| (3)ρ() for backward prediction can be defined as
ρ(ft-1, ft+1; Δx, Δy) =
|
,y Gx
Σ
∈ ft+1(x,y) - ft-1(x+Δx, y+Δy)| (4)Where G is a pixel group, usually an image block.
C. FULL SEARCH METHOD
Full Search involves finding a best match for a reference block against all possible block locations within a specified search window. In this research there is two FS methods, can be defined as Exhaustive Search and Half Pixel.
1. EXHAUSTIVE SEARCHMETHOD
Exhaustive Search by adopting block based video coding. ES will search block candidate on every block position in reference frame by determining searching window[6]. In this research location of searching for Exhaustive Search can be processed by raster order technique,as figure 2 illustrates.
Figure 2 Exhaustive Search Method With Raster Order[6]
ES with raster order technique can be defined as
1. Limit of search area is – p until p within search range area.
2. Find location with one pixel step size as figure 2.
3. Find the lowest value of Mean Absolute Difference (MAD) from all location of search range area.
2. HALF PIXEL SEARCH METHOD
Half Pixel method can be implemented with calculate a half intensity value from mean value of integer pixel with close position. Half Pixel model inserts new candidate from Exhaustive Search process, as figure 3 illustrates.
Figure 3 Model Of Half Pixel Method [7]
Based on figure 3, to get value of frame position with half pixel can be defined as
1 = (A+B+1) / 2
2= (A+C+1)/ 2 (5) 3= (A+B+C+D+1) / 4
III. IMPLEMENTATION
FRUC mechanism in this research is implemented seen in figure 4 below with unidirectional ME by implementing Exhaustive Search which is compared with Half
D C
A 1 B
3 2
Ket : : Position of integer pixel : Position of half pixel
ISBN : 978-1-4799-6126-9 Bali, 5 - 7 November 2014 ICSGTEIS 2014
-83-Pixel search method. Therefor accuracy is known from its method in frame intermediate insertion.
Figure 4 Model Implementation of FRUC [6]
Quality frame intermediate which is produced from FRUC algorithm with Unidirectional ME that uses Exhaustive Search and Half Pixel will be analyzed based on distorsion of frame can be defined as Peak To Peak Signal To Noise Ratio (PSNR). PSNR is an objective measurement often used an a relative measurement of a frame estimation to reference frame. In this study a frame resulted from estimation in decoder on FRUC algorithm by Exhaustive Search method and Half Pixel method is compared sequence frame with the frame from original video sequence. PSNR is formulated is below.
(
)
⎥⎥ ⎥ ⎥ ⎦ ⎤ ⎢ ⎢ ⎢ ⎢ ⎣ ⎡ − =∑∑
i j prc ref i j Y i jY N PSNR 2 2 10 ) , ( ) , ( 1 255 log 10
(6) QCIF with 176 × 144 pixel format of frame video is
used,therefor MSE can be defined as.
(
)
{
}
175 143 2
0 0
1 , ˆ( , )
176 144i i
MSE X i j X i j
= =
= −
×
∑∑
(7)
Where X(i,j) is a pixel coordinate within frame from original
sequence and
X i j
ˆ ( , )
is a pixel coordinate within frame intermediate.A. COMPARISON SCHENARIO OF FRAME DISTORSION
Performance method of Exhaustive Search and Half Pixel in inserting frame intermediate will be analyzed by evaluating PSNR output and compare with PSNR the original frame which is assumed store in buffer and finally the performance is known. Distorsion frame is calculated from PSNR measure based on equation 6. The test condition is applied in this result.
• Video test: Foreman and Hall Monitor. This sequences
showed different type on show content. That is high movement (Foreman) and slow movement (Hall Monitor).
(a) (b)
Figure 5 Example Frame Of Video Sequence (a)Foreman dan (b)Hall Monitor
• Number of frame for each sequence: Foreman video test =
400 frame and Hall Monitor video test = 300 frame.
• Spatial dan temporal : Format test video used QCIF (176
x 144 piksel) with frame rate 30 fps. Comparison number of frame which is used on FRUC 1:2.
• Block size : 8 x 8 pixel with search range ±7 and ±15
pixel by vertical and horizontal.
B. COMPARISON SCHENARIO OF COMPENSATION TIME
Compensation time is a period needed by search method to get the best vector motion candidate in order to have a finished frame reconstruction process. This compensation time is affected by candidate search mv computations. The more computation is perform the more time is needed with shows the complexity in inserting frame intermediate. A search method is consider efficient when it’s able to preserve compensate time which is needed. In order to get efficient compensation time the research uses equation 9 below[8].
%
100
*
)
1
(
rb rat
t
Efficiency
=
−
(8)Where:
tra = mean of compensation time search method which is
purposed
trb= mean of compensation time search comparing method
IV. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
A. PSNR ANALYSIS METHOD OF FULL SEARCH
In figure 6 and 7 shows trace PSNR of Exhaustive Search and Half Pixel on search area ±7 and ±15 pixel by using Foreman video test.
Figure 6 Comparison PSNR Of Exhaustive Search and Half Pixel On Search Area ±7 Pixel By Using Foreman Video Test.
ISBN : 978-1-4799-6126-9 Bali, 5 - 7 November 2014 ICSGTEIS 2014
-84-Figure 7 Comparison PSNR Of Exhaustive Search and Half Pixel On Search Area ±15 Pixel By Using Foreman Video Test
Based on PSNR trace in figure 6 and 7 it can be showed that trend from Full Search method is fluctuated. It because of many movement produced by Foreman video characteristic. In general based on mean PSNR value resulted from foreman video test, it known that performance of Half Pixel search method is better in inserting frame intermediate in comparison to Exhaustive Search. This result came from mean PSNR value for searching area ±7 and ±15 from Half Pixel search is higher than Exhaustive Search (0,13 and 0,02 dB consecutively).
Specifically it can be shown that baseline of object movement when there is not much movement, Exhaustive Search method has better performance than Half Pixel method. As PSNR value of insert frame intermediate the 2th up to 12th
of Exhaustive Search was higher than Half Pixel. It is because that the accuracy increment on baseline movement is not necessary and therefore it is not affectedly when applied. Moreover on insertion frame intermediate 268th up 332 th, the
performance of Exhaustive is better than Half Pixel because on 267th up to 333th frame sequence when object movement
start to occur with background change. The accuracy increment of Half Pixel is unable to maximally perform. Figure 8 and 9 showed test video Hall monitor, trace PSNR of Exhaustive Search and Half Pixel on the search area ±7 and ±15.
Figure 8 and 9 below showed that trend of trace PSNR comparison of Full Search was almost linear. This is an accordance to Hall Monitor characteristic small movement. Generally with Half Pixel search method, mean PSNR value on search area ±7 and ±15 using Hall Monitor video test has produced lower than Exhaustive Search (1,41 and 1,14 dB consecutively). However mean PSNR value accomplish by Half Pixel search method can be maintain when search area is increase from ±7 to ±15 (34,13 dB). This finding showed that Half Pixel is not effective it is used on video with low movement as in Hall Monitor.
Figure 8 Comparison PSNR Of Exhaustive Search and Half Pixel On Search Area ±7 Pixel By Using Hall Monitor Video Test.
Figure 9 Comparison PSNR Of Exhaustive Search and Half Pixel On Search Area ±15 Pixel By Using Hall Monitor Video Test.
B. COMPLEXITY ANALYSIS OF FULL SEARCH METHOD
Complexity analysis in this study is obtain based on time computation defined as the period needed in by compensation process on every frame intermediate from its search method. Compensation process is computation done by search method to get the best mv candidate until from reconstruction process finished. Therefore, the more computation is done by the search method will have an impact to the necessary period is needed. Before stepping to analyze to comparative algorithm complexity we will describe comparative algorithm computations that have latter complexity itself. Meanwhile Half Pixel search method increases the accuracy from the Exhaustive Search process. Does number of steps of Exhaustive Search and Half Pixel will be equal.
For search range ±7 pixel with Exhaustive Search
method, block size condition k= N x N pixel, and frame size = M x M pixel, therefore :
• Number of candidate mv = (2p +1)2
• Number of computation for each block = (2p + 1)2 N2 • Number of computation for each frame = (2p + 1)2
N2 x M2/N2 = M2 (2p + 1)2
Whereas for search range ±7 pixel with Half Pixel
method, block size condition k= N x N pixel, and frame size = M x M pixel, therefore :
• Number of candidate mv = ((2*(2p +1)-1)2
• Number of computation for each block = ((2*(2p
+1)-1)2 N2
• Number of computation for each frame = ((2*(2p
+1)-1)2 N2 x M2/N2 = M2 (2p + 1)2
For search range ±7 pixel with Exhaustive Search
method, block size condition k= 8x8 pixel, and frame size = 176 x 144 pixel, therefore :
• Number of candidate mv= (2p +1)2 = (2.7 + 1)2 =
225
• Number of computation for each block = (2p + 1)2 N2
= 225x 64 = 14.400
• Number of computation for each frame = M2 (2p +
1)2 = 225x176x144= 5.702.400
For search range ±7 pixel with Half Pixel method, block
size condition k= 8x8 pixel, and frame size = 176 x 144 pixel, therefore :
ISBN : 978-1-4799-6126-9 Bali, 5 - 7 November 2014 ICSGTEIS 2014
-85-• Number of candidate mv = ((2*2p +1)-1)2 = ((2*14 +
1)-1)2 = 841
• Number of computation for each block = ((2*2p
+1)-1)2 N2 = 841 x 64 = 53.824
• Number of computation for each frame = M2((2*2p
+1)-1)2 = 841 x 25344 = 21.314.304
Half Pixel search method produced accuracy increment by a half of pixel and therefore computations by Half Pixel search method is more than Exhaustive Search method. Using the above formula it can be determine number of mv candidate that is number a computations in one block and computations in one frame in search area ±7 and ±15 it can be shown in table I below.
Tabel I Calculation Of Computation Full Search Method
Metode Pencarian Ukuran daerah pencarian Jumlah Kandidat MV Jumlah Komputasi
Per blok Per frame
Exhaustive Search
7 225 14400 5.702.400
15 961 61.504 24.355.584 Half Pixel 7 841 53.824 21.314.304 15 3721 238.144 94.305.024
Table I shows that Exhaustive Search and Half Pixel algorithm is very much affected by search area size. Search area size will affect number of mv vector candidate in which the bigger the search area size the more candidate mv can be produced. It is because that the wider search area it will result in increase of number of test point. Based on calculation above computation it is generally can be analyzed that time needed for compensation process on search area ±7 and ±15 from Half Pixel search method was higher than Exhaustive Search. This because Half Pixel search method carry out search process with increment of accuracy by Half Pixel from Exhaustive Search process. This analysis is supported by value of compensation trace time which is obtained from simulation Foreman video test is shown in figure 10 and 11 below.
.
Figure 10 Comparison Compensation Time Of Exhaustive Search and Half Pixel Method On Search Area ±7 Pixel By Using Foreman
Video Test.
Figure 10 shows that compensation time needed by Half Pixel search method is 2,37 s which is greater than Exhaustive Search method. In order to increase search area size (±15 as shown by figure 11) average of compensation time needed by Half Pixel 11,8 was higher than Exhaustive Search method. It is revealed that complexity of Exhausted Search method is lower than Half Pixel search method. Figure 11 and 12 below
shows trace compensation time that is required by its method with hall monitor video test.
Figure 11 Comparison Compensation Time Of Exhaustive Search and Half Pixel Method On Search Area ±15Pixel By Using
Foreman Video Test
Trace compensation time which is obtained from simulation Hall Monitor video test is shown in figure 12 and 13 below.
Figure 12 Comparison Compensation Time Of Exhaustive Search and Half Pixel Method On Search Area ±7 Pixel By Using Hall
Monitor Video Test
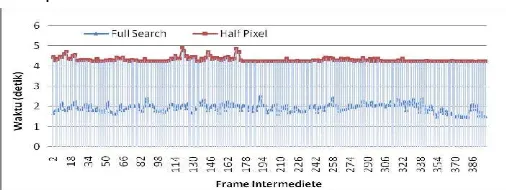
Based on graph in figure 12 it is revealed that average of time needed by Half Pixel method was 5,27s higher than Exhaustive Search method. In order to increase search area (±15 as shown by figure 13). It revealed that average time that is needed by Half Pixel was 20,01 s higher than Exhaustive Search method. This is because of process Half Pixel computation is more frequent which is accuracy increment by Half Pixel than Exhaustive Search method which is have an impact on compensation time needed.
Figure 13 Comparison Compensation Time Of Exhaustive Search and Half Pixel Method On Search Area ±15 Pixel By Using Hall
Monitor Video Test
Based on the above explanation its concluded that size of search area affects compensation time needed by Full Search Method. The wider search area, the higher compensation time is required. In order compare to Full Search method on the search area ±7 and ±15, Exhaustive Search method is lower than Half Pixel search method.
ISBN : 978-1-4799-6126-9 Bali, 5 - 7 November 2014 ICSGTEIS 2014
-86-V. RESULTS AND CONCLUSION
It is concluded that Half Pixel method with the accuracy increment by Exhaustive Search method is more effective and better performance for inserting frame intermediate on FRUC while is implemented on video with high motion characteristic. By comparing complexity Full Search by on search area ±7 and ±15 based on computation time it is revealed that Exhaustive Search method has lower complexity compare to Half Pixel method for insertion frame intermediate on FRUC algorithm.
.
REFERENCES
[1] A. Vetro, Y.K. Chen H. Sun, and S. Y. Kung, ”Frame-rate up-conversion using transmitted true motion vectors,” in Proc. IEEE Workshop Multimedia Signal Process., Dec. 1998, vol. 2, pp. 622-627.
[2] G.D. Haan, P.W.A.C. Biezen, H. Huijgen, and O. A. Ojo, ”True-motion estimation with 3-D recursive search block matching,” IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol., vol. 3, no. 5, pp. 368-379, Oct. 1993.
[3] C.C. Cheng, W.L. Hwang, Z. Shen, and T. Xia, ”Advanced motion compensation techniques for blocking artifacts reduction in 3-D video coding sistems,” in Proc. ICIP, Sep. 2005, vol. 3, pp. 89-92. [4] B.D. Choi, J.W. Han, C.S. Kim, and S. J. Ko,
”Motion-compensated frame interpolation using bilateral motion estimation and adaptive overlapped block motion compensation,” IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol.,vol. 17, no. 4, pp.407-416, Apr. 2007.
[5] L. Zhang, C. Wang, W. Zhang, and Y. P. Tan, “Frame Rate Up-Conversion With Edge-Weighted Motion Estimation and Trilateral Interpolation,“ IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol.,vol. 20, no. 6, pp. 886-893, June. 2010.
[6] J. Jostell, A. Isberg, , “Frame Rate Up-Conversion Using High Definition Remote Video Surveillance,” Technical Report,” Dept. Of Computer Science and Engineering, Chalmers University Of Technology Sweden, Apr. 2012.
[7]
Flierl, M, Bernd Girod. 2007. “Half-Pel Accurate MotionCompensated Orthogonal Video Transform.” IEEE
DCC. Max Planck Center For Visual Computing and Communication Stanford University.
[8] Gwo Long Li, Mei Juan Chen, Hung Ju Li, Ching Ting Hsu. 2005. “Efficient Search And Mode Prediction For Motion Estimation in H.264/AVC, “ IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst., vol. 6, hal. 5481-5484.
.
ISBN : 978-1-4799-6126-9 Bali, 5 - 7 November 2014 ICSGTEIS 2014