Adventure Game as Learning Media for Introducing
Music Interval and Ear Training to Kids
Muhammad Ilham Rizqyawan
Faculty of Engineering and Computer ScienceUNIKOM Bandung, Indonesia [email protected]
Abstract— Interval plays a major role in music theory so that almost every musician must recognize musical intervals. On the other hand, interval can not be separated from relative pitch, an ability to recognize interval by ear. A common problem in learning music theory and ear training is that it can be boring, less fun and less challenging to students. Therefore, Game-Based Learning (GBL) is proposed in this study as a learning media for musical interval and ear training. An experiment with pre-test and post-test is conducted, and as a treatment, an adventure game with proposed approach was built. Pre-test and post-test includes both theoretical and relative pitch test. Theoretical test is written test with multiple choices of theoretical questions about learning material presented on each stage. Relative pitch test were conducted by playing a random musical interval and asked the student to guess what interval is it. The result is the game could give an improvement in theoretical test score by 79.22% and 19.23% in relative pitch test.
Keywords—Educational Game, Music Interval, Ear Training
I. INTRODUCTION
Interval plays a major role in music theory so that almost every musician must recognize musical intervals[1]. Garry Willis said in his book that when you listen to music, you're listening to intervals[2]. When musician learning about interval, it can not be separated from relative pitch. Relative pitch is an ability to recognize a note based on a note that's been played before as a reference. In other word, relative pitch is related to recognize the distance between notes, which is called interval. Ear training, a training for improving one's relative pitch, is so important that it is said more important than performing, conducting, or even more than practicing an instrument[3]. Most valuable asset for painter is their vision in order to recognize color, composition, shapes, balance, etc. The same is applied to musician, the most valuable asset that a musician can have is their well-developed ear[2]. But a common problem in learning music theory and ear training is that it can be boring, less fun and less challenging to students. So Game-Based Learning (GBL) is proposed in this study as a learning media for musical interval and ear training.
Since at least mid 60s, games has been discussed in popular press and academic journals for its learning potential[4]. Nowadays, game has been recognized as a high potential learning approach. It's proven by the many studies on
it applied on various fields, such as natural science[5], healthcare education[6], computer science[7, 8, 9], and Foreign Language[10]. It can be applied as a learning media for elementary school students [11], as well as higher education students [8, 12]. In order to make an effective game-based learning, a suitable approach needs to be designed so it won't be a merely another way of presenting the learning material [13], especially, since there's a special type of training required in this study (ear training).
Consequently, in this study, an educational game is proposed by integrating three sub-level-stages design as the gaming scenario. To evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed approach, the following research questions are investigated: How much improvement in knowledge shown after student learn musical interval with the proposed game approach? How much improvement in relative pitch shown after student training their ear with the proposed game approach?
II. GAME DESIGN
In this study, an adventure game was developed by integrating three sub-level-stages design as the gaming scenario. The game was developed using Adobe Flash Builder with ActionScript 3 as the programming language. The three sub-level-stages are learning stage, theoretical quiz stage, and ear training stage. Fig. 1 shows the structure of the game and fig. 2 shows flow of the game.
Figure 1 Game Structure
2015 International Conference on Automation, Cognitive Science, Optics, Micro Electro-Mechanical System, and Information Technology (ICACOMIT), Bandung, Indonesia, October 29–30, 2015
Figure 2 Game flow
The game consists of 5 levels and each level consists of three sub-level-stages. Learning stage is implemented in platformer style of game. The scenario is the game character needs to pass through the enemies and obstacles to the exit door which will take him to the next stage, but the door is blocked by some kind of barrier. The player required to earn all of the learning material boxes as a key to unlock the barrier so they can go to the next stage. Each stage consists of five materials, and each material consists of a title, picture, descriptive text, and an example sound of the material. Fig. 3 shows the learning stage implemented in game.
After the player unlocks the barrier, they need to unlock the key by entering the password of the door. Here comes the theoretical quiz. To get the password, the player needs to match the answer letters with the sequence of question given. The question is based on the material learning appeared in the previous stage. Fig. 4 shows the quiz stage in the game.
Figure 3 Learning Stage
Figure 4 Quiz Stage
The last stage on every level is the ear training stage. After the player successfully unlocks the exit door, they continue on the journey and faced with another obstacle. They faced with a wall with multi-door. Only one of these doors is the true door and the rest of it is a trap door. In order to know which door is the true door, the clue is given. The system plays an interval notes and the player needs to guess what interval that's been played. The answer option is labelled on each door and the player has to choose based on their answer. Fig. 5 shows ear training stage in the game.
III. EXPERIMENT
The study was conducted in an elementary school in West Java, Indonesia. The subject consisting of a fifth and six grader at an age of 9 - 12 years old. The total of subject participated in the experiment was 40 students, both male and female students, with the criteria of minimum computer skill (can do browsing), familiar with video games, and have a healthy hearing.
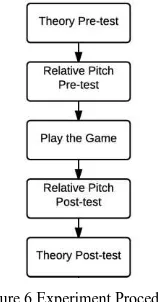
At the beginning of experiment, the students asked to do a pre-test to determine their initial knowledge and relative pitch score. After they finished playing the game, they asked to do a post-test. The theoretical pre-test and post-test consist of a multiple-choice questions, and the relative pitch pre-test and post-test use the ear training stages (in the separate mini game form) of the game. The experiment procedure can be seen at Fig. 6.
Figure 6 Experiment Procedure
Pre-test and post-test includes both theoretical and relative pitch test. Theoretical test is written test with multiple choices of theoretical questions about learning material presented on each stage. Relative pitch test were conducted by playing a random musical interval and asked the student to guess what interval is it. While theoretical test is used to determine the level of understanding of the student about the theory, relative pitch test is used to know the sensitivity of ear of the student to differentiate about musical interval just by hearing it.
IV.RESULT
One of main research question in this study is whether the student who play the game with proposed approach can improve their score both in theoretical and relative pitch test or not. In order to examine the result of the experiment, the result of pre-test and post-test, both from the theoretical and relative pitch test were collected, calculated and analyzed.
A. Pre-test and Post-test Score
In order to examine the result of the experiment, the result of pre-test and post-test, both from the theoretical and relative pitch test were collected, calculated and analyzed. The result of the experiment can be seen in table 1.
TABLE 1 PRE-TEST AND POST-TEST SCORE
Student Theory Score Relative Pitch Score Pre-test Post-test Pre-test Post-test
1 20 60 60 80 score, and α is pre-test score. The pretest average score, post-test average score, and percentage of improvement of both theoretical and relative pitch test can be seen at Table 2.
(1)
TABLE 2 PRE-TEST AND POST-TEST RESULT
The pre-test average score for theoretical test is 38.5. With post-test average score jumps to 69, the improvement in theoretical test score is 79.22%. It’s such a relatively high improvement on the theoretical test. On the other hand, the pre-test average score for relative pitch test is 52 and the post-test average score is 62. The improvement is lower than theoretical test at 19.23%.
V. CONCLUSION
After the conducted experiment, we can see that the game could give an improvement in theoretical test score by 79.22% and 19.23% in relative pitch test. One thing to note is the in-game instruction, as several students have some difficulty in through the Bandung Technical Implementation Unit for Instrumentation Development (Deputy for Scientific Services) funded by Indonesian Institute of Sciences, Indonesia.
References
[1] P. Pavlik, Jr., H. Hua, J. Williams and G. Bidelman. 'Modeling and optimizing forgetting and spacing effects during musical interval training'. 2013.
[2] G. Willis. 'Ultimate ear training for guitar & bass'. Milwaukee: Hal Leonard Corporation, 1998, pp. 3-4.
[3] T. Crist, 'Ear training Page', ARKANSAS STATE
UNIVERSITY. [Online]. Available:
http://www.clt.astate.edu/tcrist/eartraining.htm. [Accessed: 21- Aug- 2015].
[4] R. Van Eck, 'Building intelligent learning games', Games and simulations in online learning research & development frameworks, pp. 271–307, 2006.
[5] G. Hwang, L. Yang and S. Wang, 'A concept map-embedded educational computer game for improving students' learning performance in natural science courses', Computers & Education, vol. 69, pp. 121-130, 2013.
[6] J. Torrente, B. Borro-Escribano, M. Freire, A. del Blanco, E. Marchiori, I. Martinez-Ortiz, P. Moreno-Ger
and B. Fernandez-Manjon, 'Development of Game-Like Simulations for Procedural Knowledge in Healthcare Education', IEEE Trans. Learning Technology, vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 69-82, 2014.
[7] A. Serrano-Laguna, J. Torrente, B. Manero and B. Fernandez-Manjon, 'A game engine to learn computer science languages', 2014 IEEE Frontiers in Education Conference (FIE) Proceedings, 2014.
[8] A. Basawapatna, K. Koh and A. Repenning, 'Using scalable game design to teach computer science from middle school to graduate school', Proceedings of the fifteenth annual conference on Innovation and technology in computer science education - ITiCSE '10, 2010.
[9] M. Papastergiou, 'Digital Game-Based Learning in high school Computer Science education: Impact on educational effectiveness and student motivation', Computers & Education, vol. 52, no. 1, pp. 1-12, 2009.
[10] Li Cai, Fangyu Liu and Zhihong Liang, 'The research and application of education game design model in teaching Chinese as a Foreign Language', 2010 IEEE International Conference on Progress in Informatics and Computing, pp. 1241 - 1245, 2010.
[11] Chen-Shu Wang, Chia-Chen Liu and Yu-Chieh Li, 'A game-based learning content design framework for the elementary school children education', The 16th North-East Asia Symposium on Nano, Information Technology and Reliability, pp. 53-57, 2011.
[12] W. Watson, C. Mong and C. Harris, 'A case study of the in-class use of a video game for teaching high school history', Computers & Education, vol. 56, no. 2, pp. 466-474, 2011.
[13] G. Hwang, H. Sung, C. Hung, I. Huang and C. Tsai, 'Development of a personalized educational computer game based on students’ learning styles', Education Tech Research Dev, vol. 60, no. 4, pp. 623-638, 2012.