fSBN NO
:9794984574
Proceeding
of
1"
International
Conference
on
Rehabilitation
and
Maintenance
in
Civil
Engineering
(
ICRMCE
)
2l-22
march
zt}grsbloo
Indonesia
dJ*o\
.$/ol*:
r*'{}'J
Sehlas
llrret
Linircnity(uNstub)
ifirililryofPublto
Wotuhemdr
Edited
by
:
Kusno
Adi
Sambowo
Sholihin As'ad
Ary
Setytwan
S.A.
Kristiawan
Setiono
Syaf
i
Yuseph
llluslih
in
ollrbontion
with
:Advisors
Chairman
Co-Chairman
Member
Dr.
Ary
Setyawan,
Fajar S
Handayani,
I'IIT
Edy Purwanto,
MT
Endah
Safiti, MT
Setiono, MSc
Dr.
S.A.
Kristiawan,
Djoko
Sarwono,
MT
Djumari,
MT
Dr. Kusno
Adi
Sambowo.
Dr.
Eng. Syafei
Solichin,
MT
.Yusep
Muslich,
MT
Ir. Siti
Qomariyah,
MSc
Pungki
Pramesti,
MT
Senot
Sangaji,
MT
Bambang Setiawan,
MT
Wibowo, DEA
Sunarmasto,
MT
Ministry
of Public
Works
Indonesia's
Hasto Agoeng
Sapoetro,
SIMT.
Ir. Agus
Sutopo,
MT
Bambang
Ari
Amarto,
STNugroho Wuritomo,
ST.,MT.
Anjar Pramularsih,
STDra.
Sri
Musri Ambarukmi, MT
Dra.
Nurul
FuadiYah
Muhadl
S.Sos,M.Pd
Indrawan,
SE,M.Pd
Organizing
Committee
Dean
Faculty of Engineering,
Uni.
SebelasMaret
Dean
Faculty of Engineering,
Uni. Chulalongkorn
Head of Pusbiktek
Ministry
of Public
Work, lndonesia
Head of Post Graduate Program in Rehabilitation
and Maintenance
Civil
Eng.
Uni.
SebelasMaret
Head of
Civil
Engineering Dept.
Uni.
SebelasMaret
Dr. Sholihin As'ad
Dr. Agus
P.Rahmadi
Sttrdents College Committee
Reki
Arbianto
Gopta
Andhika
Pratama
Annisa
Kusumawti
Ariesita Putri
PDina Rachmayati
Irma Trianawati Y
Ratna
Dwiyani
N
Ferdian Agung
N
Awaludin
FAryanto
Setyo
Purnomo Y
Muhammad
Agus
F.Samuri
Saptadhi Sampurno
Istiqomah
Nur'IJbaY
Meirawati
Dwi
JaYd
Akhyaarul Umam AzzaqY
Sony
Irawan
Nugroho
RaharP
Committee
Umar Effendi, SH
Rumadi
Kambali
Preface
The objective
of
the
l't
International conferenceof
Rehabilitation and Maintenance inCivil
Engineering(rcRMcE)
is to
provide theforum
andto
initiate
a networkfor
the engineers, academicians, government agencies and practitionersin
exchanging the ideas and experiences, technological advancement and innovation related to rehabilitation and maintenance incivil
engineering.This event has been responded positively
by
the engineers, academicians, governmentsagency and practitioners. Since
its
first
announcementon last
SeptembJr 200g, the organizing committee has received92
abstractsfrom
nine countries -andfinally
66full
papers could be presented in this conference proceeding.The topics
of
papers are divided into fifteen groupsof
sub-theme. Those are (a) Special experiences on building and infrastructure rehabilitation and maintenance, (b) Advanced Technology onBuilding
and Infrastructure Rehabilitation Technique, (c). Assessmentof
Building
and Infrastructure Perfonnance, (d) Assessnr€ntof Builiing
anA InfrastructurePerformance
Related
to
Natural
Hazard,
(e)
Smart
Material
-for
Building
and Infrastructures Repair (Including Material Development forBuilding
and Infrastructures),(f)
Building
and
Infrastructure Damage Assessment,(g) Building
and
InfrastructureMaintenance
Strategy, (h)Testing
and
Inspection,
(i)
Restoration,
preservation,Rehabilitation and Maintenance
of
HistoricBuilding,
(i).
Management onBuilding
and Infrastructure Maintenance,(k)
Building
and Infrastructure ServiceLife
Modeling, (n) Code on building and infrastructure rehabilitation and maintenance (o) Others.This
eventis
organizedby
the
Departmentof
Civil
Engineeringof
Sebelas MaretUniversity (UNS-Solo), School
of
Rehabilitation and Maintenancein
lnfrastructureof
Post Graduate Program
of
Civil
Engineering, Sebelas Maret University (UNS-Solo) andthe
Minisry
of
Public Works
of
Republic lndonesia
with the
supporting panner Karlsruhe Instituteof
Technology(KIT),
Indonesian Societyfor
Building
Maintenance(HAPBI) and University of Chulalongkorn.
On behalf
of
the organizing committeeI
wouldlike
to thank the institution parfirers, the speakers and the paper contributors, the sponsors, the media partners,all
the committee members, theCivil
Engineering Service (CES) and the Associationof
Civil
Engineering students (HMS) of sebelas Maretuniversity
(uNS-Solo) for their great support.Solo,
2l't
March 2009.Dr. Sholihin As'ad
Chairman of the Organizing Committee of
Table
of
Contents
A. Special Experiences on
Building
andInfrastructure
Rehabilitation
and MaintenanceA1. Port Pier Condition Survey and Maintenance
of SepangarBayOilTerminal,
KotaKinabalu....
...1
A2. Rehabilitation and Rearrangementof
the Old InsuranceBuildingin
OmarAlmuktarStreet
Benghazi-Libya.
...11
43.
Retrofitting of School Building to protect schoolchildren
fromEarthquake..
...19
,A.4. Rehabilitation of Buildings in The City of Manokwari
and Samarinda Indonesia..
..
...25
A5. Deformation Behavior of Main Dike of Sidoarjo Mud
volcano...
...31
B. Advanced Technology on
Building
andInfrastructure
Rehabilitation
TechniqueB 1. Cunent Practices on Cement Rendering in
Australia
. ... ...39 83. comparison BetweenZd and 3d computer Modeling for FrexuralRehabilitation of Steel structures with
Hm-cfrp
and steersheet.
...49B12. Numerical Study on rhe Effects of Hm-Cfrp End Cutting
Shapes for Flexural Rehabilitation of Steel
Structtres..
...58B 13. Introduction
of
Repairing and Joining Methods for Simply-SupportedPrestressed Bridges Using
Link
Slab.
.......66
814. Utilization of Fibre Admixture in Improving the Geotechnical Propertiesof Volcanic
Soil....
...74
C. Assessment of
building
andinfrastructure
performanceCl.
Box Beams Subjected to Combined Load, Snapping and StrengtheningbyExternalPrestressing...
...81C2.
A
Comparative Study of Models for Confinement of Concreteby Welded Wire
Mesh
. .. . .. . ..90C5.
A
Study of Fiber Contribution to GenerateDuctility
of Lightweight
Concrete...
...101C7. The Influence of Roughness Base Apron Toward the
Icngth
of
HydraulicJump.
...109C9. Durability
of
Lightweight Aggregate Concrete Panelfor Modular Housing Consruction.. .
...
...119Cl
l.
Reconstruction of Reinforcement Modelling for Prevent the Early Failureof
Deep Beam ReinforcedConcrete.
. ....127Cl4.Influence
of Confinement Modifications onAxial
Capacityof
Reinforced ConcreteColumn.
.. . .. ..I45
c15. strenght Assessement of a Heritage Brick Masonry schoolBuilding
AgainstEarthquake
...151
Cl6.
Plastic Shrinkage Crack Analysis in One Way Reinforced Concrete Slabs ;Artificial
Neural Network(ANNs).
...163C19. Comparison
of
the New Zipper Brace System Behaviorwith
Inverted V-Brace in Elastic Z.ane in Simple Steel Frames Using the Finite Element Method...168D. Assessment of
Building
andInfrastructure
Performance Related toNafural Hazard
D1. Earthquake
Vulnerabilityof
Residential Houses in YogyakartaCity.
...I75
D3. Seismic Evaluation with Pushover Analysis on Assesment of 7-StoryInegularBuilding....
...183
D4. Influence of Reinforced Concrete Column Section Dimensions
on Pushover Capacity of 4-Story School
Building.
...190
D6. Fire Resistance Requirement in Medium Size Room
Study the Effect of Ventilation Scenarios and Compartment
Boundaries
...198 E. SmartMaterial for
Building
andInfrastructures Repair (Including
Material
Development
for
Building
andInfrastructures)
El.
The Potentials of Geopolymer for Rapid-Set High-Strength Cementin Concrete
Repair.
...204
EL.TheAdvantage
of
Nylon Mesh for Beam Confinement Smart Materialfor Beam
Repair.
""""208
B[.
The Influence of Accelerator Content against Shotcrete Compressive Strengttr,Absorption and Porosity as Structure
Reinforcement.
"
'213 E5. Resistance to Chloride Penetration of Blended Concrete ContainingRice Husk Ash:
A
Review...
""""'2I8
E6. Study Of Using Lime And Recycled Asphalt Pavement In Stabilizing Soil... ---...225
E8. Beach Sand in
Mortar...
""230
E10. Effects of
AntiOxidants
on Ageing of Asphalt Cement andMixes.
-,240
El1.
Evaluation of Porous AsphaltMix
Properties Subjected toAgeing
...247El4.
Different Methods of Cruing in Concrete Technology, Maintenanceand
Strengthen...
"
"252E15. Different Percentage of Bagass and Hair of Goat in Concrete Slab Application,
PSC Reduction and
Strengthen.
""257
E16. The Behavior of Clay
Brick
Masonry Wall with Glass FiberReinforced Polymer
Strengthening...
"
'262 E17. Use of Flowable High Strength Mortar as a Repair Material:.
F.
Buitding
andInfrastructure
Damage AssessmentFl.
The Damage Assessment of Weirs Along the 10-km Reach of River Tanggekand The Proposed Rehabilitation
Method.
...286
F2. Structural Damage Assessment of a Shear Building under
Earthquake
Excitations
...296
F3. Damage Detection of Frame
Structures.
....302
F4.
A
Case Study of Structural Assessment of Steel Stnrcnre Subjected to Differential Settlement of Foundation.G.
Building
andInfrastructure
Maintenance StrategyGl.
Analysis of Faulty Designs Causing Construction Defects on Public School Building in lndonesia and Its Relationshipswith Rehabilitation
Priorities.
...321G3. Maintenance Strategy:
A
Case Study in the Defect Typesand Maintenance Management System of Hostel
Buildings.
....330 G4. Effectof
Decentralisation on Maintenance Road Ranking Criteriaat Badung Regency of
Bali.
...340
G5. Evaluation
of
Decentralized Communal Wastewater Treatment in Yogyakarta...346 H. Testing and InspectionHl
. The Measurement of Water Content of GranulerSoil UsingA
Gypsum Block. . . ..355H2. The Benefit
If
Gypsum Block for Measuring Soil WaterContent.
...359 H3. Karst Material Characteristics and Geotechnical Assessment on Constructionof Bribin Underground River
Barrag.
...366
H4. Hydraulic Fracturing Test on the Clay Core ofRockfill
Damon Various Fine Contents..
..
...374
J. Management on
Building
andInfrastructure
MaintenanceJl.
A
Study on Quality Cost Awareness inCivil
Engineering Rehabilihation andMaintenance Programmes
(A
Case Study on Malaysia Construction Industry)...382J2. Preliminary Study on Building Maintenance and Operation Contract..
...
....391J4.
Minimizing
WaterDeficit
Using Three Risk Indices on Existing Irrigation WaterManagement...
...401
J6. The Farmer's Participation in the Maintenance of Inigation
Network
to Support the Sustainabilityof
the lrrigation System (Case Study in The Irrigation Areaof
Bondoyudo)...
...407J7. Highway Maintenance:
A
Case Study in the Defect Types and MaintenanceK. Building
andInfrastructure
ServiceLife Modeling
Kl.
ServiceLife
Prediction of Partial Pre-stressed Concrete Structures in a MarineEnvironment
....423K3. Quantifying the Reliability of Limited Site lnvestigations on the Design of Pile
Foundations...
...430
N.
Code onBuilding
andInfrastructure
Rehabilitation
and MaintenanceNl.
A National Standard for Seismic Rehabilitation of Existing BuildingsWhy We Do Not Have It To
Date?...
...438O.
Other
Swot Analysis of Small Scale Contractor:
A
Surakarta CaseStudy
...448
II\IVITED
SPBAKERSRepair of Architectural Concrete And Concrete Monuments : Harald S.
Miiller,
EdgarBohner
&
MichaelVoge1...
...452Assessment and Repair/Strengthening of
A
Settlement Damaged OfficeBuilding
:ld lntematlonal Contercnca on Fehabllltatlon and Malntenance In Clvlt Englnecrlng (|CRMCE)
Solo,21.22 March 2mO
ISBN No.979,4984574
THE INFLUENCE OF
ROUGHNESS
BASE APRON TOWARD
THE LENGTH
OF
HYDRAULIC JUMP
Cahyono'lkhsan
r),solichin
2)Civil Engineering Dept, Sebetas Maret lJniversityl)
E m a i t : ca hv o n o L97.! ? va.h.oo -?
? rll . _ _ ^ 2 )
Civil Engineering Dept, Sebelas Maret Universi1r Email : sol'tchin-S73l 3 @yahoo'com
Abstract
The important thing that should be noted in planning a design of spillway building is erosion
that happens in the bottom of spillway becausl of ttreihydrautic lump' To avoid this' commonly
in the downstream of aam is eiuipped by apron. However, rarely the apron is lgsigned P holg the total length of hydru"fi":ttitpd""auie ii needs a very big cost' Therefore' it is a need to set
a jump contol equipment , ifti.tt
it
used to shorten the intervals between jumps' This researchwas trying to study the characteristics of hydraulic jump happening above the apron, which has a roughness uur",
op."i"tiy
"uout the hyhraulic
jirmp and Lnogy reduction.The method that
was used in this research was laborato.y
"^p"ti-In"ntul by using
a flume to make the flow circularion.
To
raise tfre fryarautic jump, ihere wasa
spillway modelin
which-in
itsdownstream *as equipp-ed uy
"pton.
ttt"
bur" of theapron was covered by the roughness
elements with
its threl
form variations, which were ion*tant triangle prisms' -balls andd;lt-.C"n"lusion
from me anatysis that the using of the roughness element was effective toshorten the length of fryAruufic jump anO the red'uction of energy' The using of roughness element in form ot"onrlrrt
ri*ir"
piir*,
the most effective to shorten the length of hydraulic jump and reductionoi"n"rgy
-*tti"tt*".
2123%. This was based on that the roughnesselement in form or
"or,rtuJ"ttiangle
prisms has the biggest roughness parameter value (k)' which is 0.08630.
Keyword: apron, hydraulic jump, roughness parameter
1.
BACKGROUNDFlow
denaturing
fiom flow
superkritisbecomes
flow
subkritis
to
cause
thehappening of hydraulic jump. This condition
ot."d:n
met
at leg
PelimPah
becausetransformation of dip of passage basis that is sudden.
The
happeningof
hydraulic jump always is accompanied with turbulensi which is hign, dynamiC speed and the increasingof
watei eOdy causing causes the happeningof
erosionoi
grinder alongside placeof
the happeningoi
hop' To prevent the happening of-grinder resulted fromby
hydraulicjYtp'
utu-utlyin
going
downstream pelimpah is equiped [bY] coven floor or aPronThis
researchaim
to
know how
influenceform and roughness height (k) apron basis to
hydraulic
jump
length and kehilanpnanof
dissociation
energy
of
diatomic
is
gonedownstream
tbyl
pelimpah'
This
eliteexpected earns
ii
of
benefit to expansionof
theory
in
hydraulics areaespeciilly
about hydraulic jump and can give consideration in exploitingof
hydraulicjump
as dissociatlon"n"rgy
o1 diatomic absorber causingis
got solut-ibnof
makingof
efficient and effectivedissociation
energy
of
diatomic
absorberbuilding
Ranga Raju
(
1986) phrases big head at partof pate;upstream pelimpah yields.big speed (
in ionsequence
of flow
superkritis) acurate under thsbuilding. While flow part ofit
(the downstream becomesflow
subkritis becausesloping
dip
in
passagebasis
hereinafter't r hterndhn4f GoqtFwrcg..pn Refiaburdbn
anC:lldoHrange In QlvllrElt€f nerlng' QGRTGE) qeb, 2l'U March ?00e
IS-BN N9..97H98{57'4
Losing
of
head can be becauseof
boundaryfriction
(
boundary
friction) and
f,orm resistance ( form resistance).Utomo
(
20M)
performs[a]
research aboutusage effectivity
of
stilling basin typefV
in damping excessive dissociation energyof
diatomic at part of downstream with addition
of baffle piers bobrbentuk always with three
kinds
of
surface shape bebeda. Resultof
research shows
baffle piers
with form
of
basin
is
which
most effectivein
lesseninghydraulic
jump
length,yields
olakan andbreaks biggest
dissociation
energy
of
diatomic.
Hager
(
1992) phrasesif
element pengotrol like baffleblock ( collision tooth) outspread isof all
tbyl
passagebasis place
of
thehappening
ef
hop, hence reference the thingcan a hydraulic jumphappened is on the basis
of passage with element of roughness
Flow Discard
Number
of
fluids flowing
through cross-section of flow every one set of time called asflow debit is given [by] notation Q. Charged
flow
mgasuredin
fluid
volume every setof
time, Inveterate
unit is
usediq
practice is meter cubic per second ( m /s) or other unit (liter/detih liter/menit etcetera).
In ideal
fluid
where not happened frictionof
speed of flow V is same is every [by] point at
cross-section. For nantre passage like regulus, speed
of flow
is
calculated based on plane speed-
plane taken away
from
by
realkecepata profile.
Open Channel.
Open
flow
hardly
influencedby
groundaCceleration
of
gravity, on that account flow characteristics at open jetting can be studiedby
the wayof
comparing inertia force withgravitational
force
working
for
the
flow'-omparison between both this forces called
as Bilangan Froude ( Fr) and expressed with:
: Number Froude'
: Flow mean velocity
: Gravitational force
: Depth hidraulik
Hydraulic jump
Hydraulic
jump
happenedin
the
eventof
transformation
of flow
super-kritis becomesflow
sub-kritis. Conditionof
like
this oftenmet in
passage
basis
experiencing transformationof
dip
suddenlylike
the onehappened at leg a pelimpah. Hydraulic jump would always
in
following turbulensi which is high, dynamic speed and the increasingof
water eddy.In Chow
(
1989) mentioned that a hydraulicjump
will
be formedat
passageif
numberfroude
flow
(
Fr),
depth upriver hopd
anddepth
in
going downstreamd
hopto
fulfill
equation of continuitY following
,-L=
Vdt+8Fr2
-r)
...(z)
d" / L'
Energy
lossEnergy loss at hydraulic
jump is
differencebetween
specific
energies
happened athydraulic
jump staninf
points
(
El)
andhydraulic jump end point
(
E2). Simply can be formulated as follows:gp=(d,
,d,)t
...(3)
4di2
Roughness
Parameter
Rajaritnam
introduceshigh
formula
of
roughness ( k) that is
k=k,
/dr
k,
: High equivalen of roughnessd
|
: DePth aPProach to elementof
roughnessFigurel. Hidraulik Jump In Rugged Passage Basis
Pr=l
,l
sd
(1)
Fr v
g
d
ld lntematlona! Conlerunce on Rehabllltatlon and llalntonance In Clvll Englnerlng 0CRllCE)
src/,o,21-2. March2009
ISBN No.979{98457-4
d2
dL
If
d2ldr was function of from value Froude (Fr)
hencevalue
k
can
be
searched with equation of continuity=
Fr +0,41(Fr
-
1)exp(-6k)
...(4)2.
RESEARCH
METHODOLOGIES
In this research applied method eksperimental
that
is
by
the
way
of
performing
[a]experiment
activity
in
laboraturiumto
get data wanted. After performing [a] activityof
eksperimentalthen
data result
of
theexperiment diolah for then is done analysis to result of eksperimental.
In
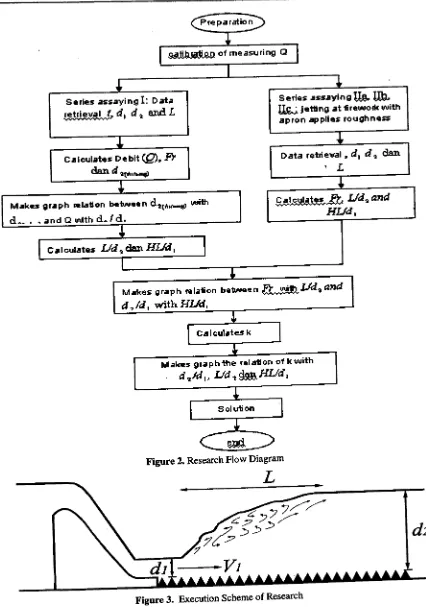
skematis researchpath as seen at Fig.2.
Executidn of Assaying at model is done with
measuring
water
face
height
upriverhydraulic
jump
(
d
),
water face height in going dpwnstream hydraulic jump(
d
)
andhydraulic jump length (
Irvator
skapula). Tobe more sharpness presented in Fig. 3
1r
hrndonC
Conblucaoof,#|lra$on
and llalntenmcsln GMI Englneelng {CRMCE)
W,21-2. March2009
ISBN No.379-49&457{ .
reparation
Sffib.tefiP-D of measuring Q
Series assayins
IIg'
I[a'
IIE ; lettng et f rewod( witheplon aPPlies roughness
Se ries assaying
I:
Data1gti3yal*t
d,
d,
andt
Data rettieval
'
dr
di
darr,L
Celculates Debit
(ff,
Fr
fu
d.t.,,''p
gEIgs^;$*.,{U.
ud'and
Mrkrs
greph ntation betnreend.t".*.C
*ifr
d^-. .and(ltithd-td.
Caf cufater
IJd 2&fi
HLId IMakes graph
elaton
betnreen f*r**$ti,hJ'/d" andd,/d,
v'it]'l.HUd,
fuf
[image:11.542.44.470.64.671.2]"L"t
dJd),
graph IJdaQAfl''HUdlthe relalion of k raithFigure 2. Research Flow Diagram
L
dt
Execution Scheme of Research
dz
Figure 3.
idtntematlonalconf eronc!onRehqb-lllltloil
"no
riiiit"iiii"'m
crtrr Enelneerlns $.cRl'igFl
5olo,21'22 March 20o9
ISBN No.979-{98-{574
3.
ANALYSIS AND SOLUTION3.
1
Result Of Calibrationof
Measuring Instrument of
Debit'
lCalibration of measuring instrument ^of Debit
it
Aon" by comparing debit result of read at hvdraulic bench with debit result of gaugmg;iil;;;ting
it
obtained an equation of.""ii""iry
whici
applicable to calculate levelof
debit closing truth' First pacel:
assumeittui
guugingJr
o"uit
at
flume
by
ustng;;;a;d
"l'tino"t
is
correctness' Becausewater
accornodated measurableof
its(thevolume causing
is
assumed correctness'*frit"
."uturin!
instrumentis
charging atr,nit"tri"
unknJwn bench are there damlee;*;;;.- D;"
and result
of
calculation calibrationof
measuring instrumentof
debitpresented at Tabel 1'
of instrumen! o:!!9!!!
Tablel.Data@
bration 0.9 8 0.9 6 0.0017 7 0.0018 5 8.6 10 5.55 5.55 5.811.8 2 1.8 0 1.6 o 0.99 1.8 o 1.09 1.1 0 1.1 0 0.0016 7 0.0016 4
8.5 10 5.81 6.32 5.81
1.8 0 1.8 0 1.8 ,) 1.10 1.1 0 1.1 2 0.0015 8 0.0016 3
8.4 10 6.84 6.06 6.06 1.8 0 1.8 0 1.8 2 1.8 4 1.19 t.20 1.1 :) 1.1 6 0.0015 2 0.0015 1 8.3 10 6.84 6.04 6.84
1.8 4
t.2
5 r.2 5 0.0014 3 0.0014 88.2 10 6.58 7.O9 '7.35 1.8 2 1.8 2 1.8 2 1.8 2 r.25
t.2
5 1.4 5 0.0013 6 0.0013 78.1
t0
7.35 7.35 7.35 1.80
l.u
0 1.8
I
1.80l
2 t.45t.4
5 1.4 5 0.0012 3 0.0012 58.0
ro
|
7.37 8.38 8.64L6 2 1.8 2 1.8 2 1.61 1.4 5 1.4
)
0.0011 3 0.0012I
7.9
r0
I
8.64 8.90 8.901.6 2 1.8 ?, 1.61 1.6 5 1.6 5 0.0010 5 0.0011 1
7.i lrolg'+t
9.4r 9.671d tntematlonal Conferencs on Rehabllltatlon and Malntenance In Clvll Englneerlng QCRMCE)
Solo,21-22 March 2009
ISBN No. .979{98-4574
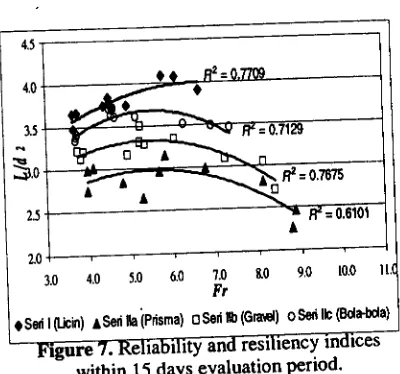
Result of calculation at Tabel 1 presented in
the form of graPh like at Fig. 4.
o(mo
o(xllt
!
oort
o0t1E, oor2
omlo oqrn
".(In omlo oqrt2 Gd)14 (Idn6
(Id)18 oq},l)
QHTbottc Bcnch (llld)
figo""
-
4. Graph Result Of Calibration ofMeaswing Instrument of Debit
beginning of hop ( d ) and depth in hop final
(
d
I
fufnffs Persamaan(
23)' To know the conOdon hence need to be searched value dwith data input d and Fr kedalam Persamaan
(
if).
n"tuit of
calculationd
hereinafter incomparing
to
valued
resultof
gauging to know itsdhe correlation' Result of calculationtf,""
it
presented in the formof
graph relationbetween d z{ni*ns1 with
d
rrurr, at Fig' 5Fie. 4 showing relation between debit result
oi?oO
at hyJraulic bench with measurablea"Ui, u, flume. Second connection charged
the
is
linear,this
thing
shows measurlnginr*rn"n
of
debit
to
hydraulic
benchapplicable to measure
flow
debit happened'ljii"*
equationof
a line
Y
=
0'919X + 0,-000,b.ruut"
axis of the ordinate as debittrupp"*O at flume, and axis of the abscis as
i"liri"turt
of gauging of deviceat hydraulic Uenctr hence-the
equationof
continutty;;;;;t
Q
=
0,91e
x
Q
+
o'ooo2' At
lui*iution-rt"t"inafter, flow
debit!ryn"1"0
ai
countaUte flumeby
entering debit value reaa UV deviceat
hydraulic benchto
the equation of continuitY'3.2 Running Model
3.2.1
SeriesI
S"ti
f
tnat
is flow
applies apron- without
element of roughness' To know level ot rtow
["Uii"t
flume,-beforehand is measured debit;; ;
hYdraulicbench'
Flow debit
atlnAtuufi.
Uenctr(
Q)
gotten by comparingUetween water volumes
with
the
durattonir"onnuirr*te
time ( VoUt)' I-evel Of Flow JeUitat
flume
(
Q)
obtainedby
enteringvalue
Q
kedalamiquation
of
continuity;;;
-frorn
calibration
of
measuringinr*t"n
of debit that is Q =0919
I
Q*
6:ooot.By
using water depth data.in
the*glitr"I
fr
nopi
dr ) resuli of gauging andqil"liir
"alcuiot-iott,
countable level
of
fL;
tpt"d ( V
)
and Froude number(
Fr) beginning of hoP.il"tnyitoulic
jumP
will-be
joT:o
*
[image:13.546.263.475.90.724.2];;age
if
Froudi number ( Fr)' dePth in theFigure 5. GraPhs relation between
[image:13.546.33.228.112.281.2]d zeitunil with d r,urr,
Figure.5.
indicating that relation betweendl*^u
with drr*,,
has correlation value(
n
)u."of
good that is 0'9875' This-thing isLenuniukan
that
data
yielded ^{:".'
;iluj,*
-p"tiu*oun -SeriI
in
laboraturiumfulfills
( 23). To know relation between
dzldt
with Q
hence resultof
calculationufro
i,
Presentedin
the form
of
graPh relation between Q with d /d 'c) 75 I !
{
m 65Ft2 = 0,9875
65 ^ o""""o 15
9
a
s
to
@betweenflowdebit(
Q) with
dz/dl
Fie.
6
that ever greater chargedflow
(
Q);"il ;;lt"
J
ia
*outd
smaller' .Value;;;;t
J"uit
t
Q)
and water dePthil
loP;fi;ii
Jiu,
u'*ving
of
seriesI
"p!tl:9,-"'
l;;;";
criterion
at
break even assayrnghereinafter
1n Intematlonal Confettnce on Rehabllttatlon
"no li'aini"nance
ln ctvtl Englneerlng 1t-cR.MgFl
5olo.21-22 March 2o09
ISBN No'979-498-457'4
3.2.2
SeriesII
in"
Rstayingof
Seriestr
that is pangaliranofpfi".
aproi
equipedwith by
element oftiigrtn"tt.
Assaying
of
Series
II
isconsisted:
essaying of Series
IIA
: applies elementof
roughn"it of triangular prism always'
e*?vi"g
ofSerieJIIB
: applies elementof
roughness gravel.n*?vi"g
oT SeriesIIC
: applies elementof
spheres roughness.3.2.3
llydraulic jump
LelSth-{lalysis
.Hop length data from result of this assaymg
"*p."tt"?
in
a
graph,with
Froude-number
abicissa
(
Fr)
and
its
the
ordinate
isairn"ntioni"ss
ratio
of
IJdz
'
Result
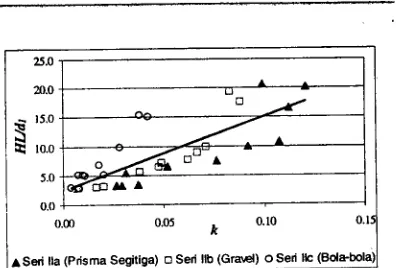
ofcalculation is presented in the form of graph relation between Fr with Ud2like
Assaying of Series
II
yields value d. which.isr*uii"t
lompared to at this Pengujian SeriI
Hal in
becauseat
Pengujian SeriII
waterno*ing
from pelimpah direct tofill
basin ( dale) formed by elementof
roughness' as ai"tuit
uutu"d
smaller causing yields valuestretch
Fr
larger
ones
comparedto
atPengujian Seri I.
3.2.4
EnergY loss AnalYsisnn"tgy
loss-at
hydraulic jump-
(
HL) .oun-aUt" basedon
differenceof
specific energy between starting pointses and hop"nO
i6in,.
Result of calculation of each
jetting series presented in the form of graph
;;i;;i;t
betweenHIJdI
with
dz/dr
like at Fig.8,9,
1045 I
I
4.0 J
J.) '
i"
-Jt.u ,5 2!
11
82=0.709tu
E-N
r ff=0'6101
A
3.0
43
5.0
60
ki
&0 e0
100 IO Sai | (lj;in) r Sai h ierismal o Sod lb (Grad)
o S€d llc (8d+bda)
within 15 daYs evaluation Period'
25,O
20,o l5,o
q
i
r0,o5'O
0'o
V = 31?21r'13.24 /''
----T
F
4.o 6,0 8'O lo'o t
dzldt
Fisure 8. Graphs relation between HUd with
-
d /d atPengujian Seri Iia
25p
20.o
- l5.O
!
rop5.o
Y ' 2'7@9\'11'12
-
--4 t @t'' oo6,0 I'O lo'o &/dt
flg"*
fO. Graph relation between HI-/dt with d2 /d1 at Pengujian Seri II cFig.
7
indicating that elementof
roughness,o"p*guiion sJri
u
either SeriIIa'
IIB
and"fr"
nJdonrut
shorthydraulic jump
$gP'
This thing
is
knowablefrom
valuelJo
'*tt"t
,rn'ott"t valuelJd
hence hydrauliciuto
ftn*ft
increasingly dwarf' However.alli"etfttion
curve formed from graph relatton;;i;;;;F
andt/d
has correlation value ( Ri-
"
*"f
small
(
less
than 0'85)'
This.onOi
ion
indicatesthat
hydraulic
jltp
i""g,ii
Oirfi"ult to be determined with visuali""i*uitt*ce.
element of Roughness is inln"
fot
of
triangular prism always mosteffective
in
cutting
short hydraulic. lump length(
Levator skapula) because navlng value L/dz smallest 'dz /dr at Pengujian Seri II b
[image:14.540.55.255.317.504.2]ld lntematlona! Conterence on Rehabllitation and Malntenance In Clvll Englneering (ICRMCE)
Solo,21-22 March 20og ISBN No. .97$498-457-4
Graph relation between HL/dr with dz /dr at
all of
assaying series yields linear equationof
continuity and regression curve gradientas follows:
Table
2.
linear EquationOf
Continuities andregression curve gradient
at'
graph relationResult of calculation value k ploted at graph, with axis of the abscis as d /d and axis of the
ordinate
as value
k,
causingis
obtained graph like like at Fig. 11, 12, 13Table
39
indicating
that
element
of
roughness is in the form of triangular prism
always
most
effective
in
damPing dissociation energyof
diatomic' This thing from biggest linear regression curve gradient value.Gvel
percentageof
dampingof
dissociation energyof
diatomicat
apron applies element of roughness compared to at [image:15.549.278.478.119.540.2]upion without
element
of
roughness (Figure 11. Graphs relation between k with d2 /d1
at Pengujian Seri IIa ( triangular prism roughness)
4.O 6.0 a'o loo
dz/dt
Figure 12. Graphs relation between k with dz /dr at Pengujia-n Seri IIb ( roughness gravel)
4,O 6.0 8'O lo'o
dz/dt smooth) countable as follows
Vo
damping
of
dissociationdiatomic at
IIa
=21,23 VoVo
damping
of
dissociationdiatomic at
IIb
=
15,51 VoVo
damPingof
dissociation diatomic atIIc
= 8,33 VoFigure 13. Graphs relation between k with dz /dr
at Pengujian Seri IIc ( spheres roughness)
In general graph relation betwee4 between
k
wifi
az/d
menunjukanthat
bver greaterorr"rr"d
d2t$
hence valuek
also ever sreater. Remembers value dz/dr
which isEult
g."*"t
showsflow
debit value that is smaltEr(
like
shownto
Gambar 43) henceuufu"
f
-would
be
ever
greaterif
small relative flow debit.To look for cupola line ( trendline) at.graph
,"iution between
k
with
d/d
at assayingof
-S;;in
is applied [by] approach of logarithm
curve. Based
on
perhitungnan appllespiogt"t
Microsoft Office Excel is obtainedenergy of
energy of
energy of
Element
of
Roughnessis
in
the
form
of
triangular
prism
always
can
dam.n fl9wdisso-ciation energy of diatomic equal to that
is
21,23 Vo comparedto
without
using element of roughness3.2.5 Roughness Parameter Analysis ( k)
If
dz
/dr
was function
of
from
Froudenutb",
( Fr) hence value k can be searchedwith equation of continuitY:
)
uz
= Fr
+o,4!(Fr-
l)exP(-6k)
dr
=2,5754x
=2,7899x
tr.I22
[image:15.549.52.262.142.661.2] [image:15.549.50.259.156.369.2]ld lntematlonal Conlerence on Rehabllltallon and Maintenance In Clvll Englneerlng (CRMCE)
Solo,21-22 March 2009
ISBN No.979.498.457-4
Tabel
3.
Persamaan graph logarithm curve relation betweenk
with d /d at assaying Seriy = 0,1 l96ln(x)
-
0,1624 y = 0,0973ln(x)-
0,1360tbyl
logarithm
curve
with
equationof
continuity of like presented at tables of 311.
Value k at each element of roughness can be
searched
by
entering value d2/dr
kedalam equation of continuity of logarithm curve.Following presented example
of
calculationvalue
k
at
each elementof
roughness toassess
(dzldr)=8'
Value
k
at
elementof
triangular prism roughnes=
0,1 196Ln(8)-
0,1624 = 0,08630 Value k at element of roughness gravel=0,O973Ln(8)-0,1360
=0,06632
Value
k
at elementof
spheres roughness = 0,0515Ln(8)-0,0771
=O'02999 Result of perhitungna is upper indicating that element of roughness of triangular prism hasbiggest
k
value
that
is
0,08630'
Butlogarithm curve at element
of
roughnessof
tri-angular prism has correlation value(
R2 ) smali that is 0,8447. This thing is caused by at elementof
roughnessof
triangular prism happened turbulensiwhich
is
big so
thatdifficult to determine depth is initial by hop (
dr ).
Relation between valuek
with
value l-ldzandvisible HI-/dratFig
14 and 154.O
3.5
$
a.oa<
LO
o.0o o.o5
ft 0'lo 0 l
a S€ri lla (Pdsma Ssgltlga) o Sed ltb (GEEI) o S€rl llc
a-f
Z-_^_
-o^H
o"
^ [image:16.543.265.463.48.182.2]{or
t
Figure 15. Graphs relation between k with HU d1
After all
data plotedat
graph, then pulledlinear
regression
curve.
Drawing
310indicating
that
is
ever
greater assessedk
value L/dz smaller meaning length hidraulikhop increasingly dwarf,
while
Gambar 311menunjukan that ever greater assessed k ever greater
HL/dr
value
meaning dampingof
ever greater dissociation energy of diatomic.4. CONCLUSION
AI\D
RECOMMENDATION
4.1. Conclusion
Based on data analysis and solution, can be
taken conclusion as follows:
1.
Result
of
calibration
of
measuring instrumentof
debit indicates that relation between debit resultof
read at hydraulic bench with measurable debit at flume haslinear equation
of a
line
Y
=
0819X
+0,0002 with correlation value ( R2 ) a real
good
that
is
0,9816.This
thing
meansmeasuring instrument
of
debit
athydraulic bench applicable
to
measureflow debit.
2.
The
hYdraulic
jumP
length
withcomparison
ratio
value
of
Udz
which smailer and can damp bigger dissociation energyof
diatomic ditunjukan with valueIilJdr
larger ones. Elamen roughness is in the form of triangular prism always most effectivein
cutting short hydraulic jump length and damps dissociation energyof
diatomic 21,23 bigger Vo.3.
Level
of
valuek
for
each elementof
roughness can
be
searchedby
enteringvalue
d2 ldt
kedalam equation
of
continuity as follows:
[image:16.543.39.247.143.265.2]assi tla (Prisma Segiliga) o Seri llb (Gratd) o Sed lh
figure 14. Graphs relation between k with Udz
[image:16.543.40.247.603.704.2]ld lntematlonal Conference on Rehabllltatlon and Malntenance In Clvll Englneerlng (ICRMCE)
Solo,21-22 March 2009
ISBN No. .979-498'457'4
Seri IIa (hisma segitiga) Y = 0,1 l96ln(x)
-o,l6vl
Seri trb (gravel) y = 0,0973ln(x)
-0.1360
Seri trc (bola-bola) y = 0,0515ln(x)
-o.o77l5.
Negm,A.M, 2W1
OPtimnl RaushenedIzngth
of
Prismatic Stillinp
Basins' ConferencesICI{E
Articles,
Warsawa Poland6. Raju,
K.G'R.,
1986,
Aliran
MeIaIuiSaluran Terbuka, Erlangga, Jakarta
7.
Sosrodarsono, S. dan Takeda,K,
1977'Bendungan TYPe lJrugan,
PradnYaParamita, Jakarta
8.
Triatmodjo Bambang, 1993, HidrolikaII'
Beta Offset, YogYakarta9.
Utomo,B.W.T,
2O04, Pengaruh Bentuk dan Letak Buffle Piers Menerus Terhad'apPaniang'
Loncat
Air,
Skripsi'
JurusanTeknik Sipil Fakultas Teknik Universitas
Sebelas Maret, Surakarta
lO.Veraineta,
D.H,
2004,
PengaruhKekasaran
Dasar
Saluran
TerhadaPKecepatan
Aliran'
Pad'aModel
Saluran Terbuka, Skripsi, JurusanTeknik
SipilFakultas
Teknik
Universitas
SebelasMaret, Surakarta Element of Roughness of triangular prism
has biggest roughness parameter that is 0,08630 for dz /dr = 8.
4.
Ever greater assessedk
hence value L/dzwould
smaller
meaning
hoP
lengthincreasinglY
dwarf,
sedangakan
isassessing
HIJdr
would be
ever greatermeaning damPing
of
ever
greaterdissociation energy of diatomic'
4.2. Recommendation
This
researchhas
somethings
requiring attention that at the next research is got [by]better result, therefore
at this
opportunity compiler gives suggestion some suggestionsas follows:
1.
Be
betterif
research hereinafter applies open channel model with scale larger ones toglt
result which more closing is field state'L
N""Ot
existenceof
further
research toknow
distance influence between elementgibbosities of roughness to hop length'.
i.
NoOt
existenceof
further research withmodelling scale
that
resultof
research in laboratory earns in application in field'5. REFERENCE
1.
Atmaja,I.T.,
2003, Efektivita,s-Ukuran Blok Halang pada Kolatn Olak Type IV'
Skripsi, Juruian
Teknik Sipil
FakultasTeknik
Universitas Sebelas
Maret'Surakarta
2. Chow,V.T.,
lgg2,
Hirolika
Saluran Te rbuka, Erlangga, Jakarta3.
Hager,W.H.,
1992,Energy
DissipatorsAnd Hyd'raulic Jutnp, Kluwer Academic
Publ ishers, Netherlands
4.
Hinge,G.A.
andB'K'
Awaghade'- -
' ReductionIn
l*ngth
of
Stilling Basin by Provid.ing Depressionin
The Horizontal Aprbn