ABSTRACT
Sari, Vinencia Lefrianita Cendana. (2015).
A Study on the Use of Articles in
Students’ Written Projects of Critical Reading and Writing I Class.
Yogyakarta:
English Language Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University.
Writing is one of the important skills in learning English. Through writing,
students learn to make good sentences with correct English grammar. It is common to
see grammatical errors in writing because grammar has many parts that the students
must understand and master. The use of articles in English grammar seems simple but
complicated because of the various kinds of nouns following the article itself.
Non-native speakers of English must be consistent whether to use
a
or
an
and
the
in their
writings.
Based on this issue, the researcher focused on analyzing the errors in the use
of articles made by 10 students in Critical Reading and Writing I Class E academic
year 2014/2015 in the English Language Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma
University. There are two research problems in this research: (a) What errors in the
use of articles are found in students’ written projects of Critical Reading and Writing
I Class? (b) What are the causes of errors in the use of articles in students’ written
projects of Critical Reading and Writing I Class? This research has two objectives: (a)
to find out what errors in the use of articles found in students’ written projects of
Critical Reading and Writing I Class are, (b) to find out the causes of errors in the use
of articles in students’ written projects of Critical Reading and Writing I Class are.
Document analysis was the method in this research. There were three
instruments: human, document, and interview. Human instrument was the primary
instrument, document was the second instrument and interview was the third
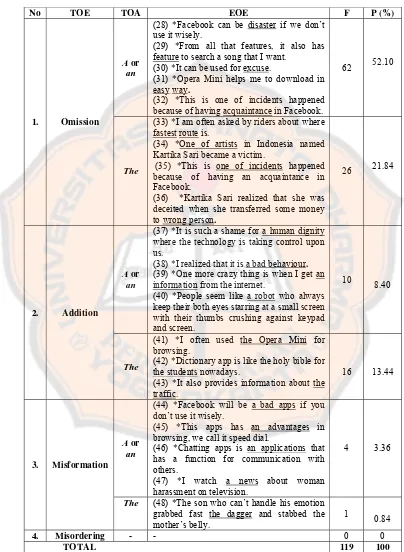
instrument. The errors found in students’ written projects were classified into four
types of error by Dulay, Burt and Krashen (1982): omission of a
or
an (62 times,
52.10 %) followed by the omission of
the
(26 times, 21.84 %), the addition of
the
(16
times, 13.44 %), the addition of
a
or
an
(10 times, 8.40 %), misformation of
a
or
an
(4 times, 3.36 %), misformation of
the
(1 time, 0.84 %) and misordering of
a
,
an
, and
the
(0 time, 0 %). The researcher used the theory from Brown (2000), who classified
context of learning and Norrish (1983), who classified carelessness, first language
interference, translation, and error as a part of creativity as the causes of errors.
The researcher gives recommendations for English teachers, students, and
future researchers. For English teachers, it is better to give brief and detail
explanation about the use of articles to the students. For students, it is better to
deepen their understanding about the basic rules of articles and practice themselves a
lot. For future researchers, it is better to classify the causes of errors deeper based on
the types of errors and modify the instruments or the participants.
ABSTRAK
Sari, Vinencia Lefrianita Cendana. (2015). A Study on the Use of Articles in
Students’ Written Projects of Critical Reading and Writing I Class. Yogyakarta:
English Language Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University.
Menulis adalah salah satu kemampuan penting dalam Bahasa Inggris.
Menulis memberi kesempatan bagi penulis untuk menerapkan struktur bahasa
dengan tepat. Eror dalam menulis sering ditemukan karena penulis harus
mempelajari dan menguasai struktur Bahasa Inggris. Penggunaan
articles
dalam
Bahasa Inggris terlihat mudah namun rumit karena terdapat banyak bentuk kata
benda yang mengikuti
articles
tersebut.
Penutur bahasa selain Bahasa Inggris
harus
konsisten dalam menggunakan
a
atau
an
dan
the
dalam tulisan mereka.
Menanggapi hal tesebut, peneliti menganalisis eror pada penggunaan
articles
oleh 10 mahasiswa di kelas
Critical Reading and Writing I.
Terdapat dua
permasalahan dalam penelitian ini
:
(a) Apa saja eror pada penggunaan
articles
yang
ditemukan dalam tulisan mahasiswa di kelas
Critical Reading and Writing I
? (b) Apa
penyebab eror pada penggunaan
articles
dalam tulisan mahasiswa di kelas
Critical
Reading and Writing I
? Penelitian ini memiliki dua tujuan: (a) Untuk mengetahui
apa saja eror pada penggunaan
articles
yang ditemukan dalam tulisan mahasiswa di
kelas
Critical Reading and Writing I
, (b) Untuk mengetahui penyebab terjadinya
eror pada penggunaan
articles
dalam tulisan mahasiswa di kelas
Critical Reading
and Writing I.
Document analysis merupakan metode dalam penelitian ini.
Terdapat tiga
instrumen dalam metode ini
: human, document,
dan
interview. Human
sebagai
instrument utama,
document
sebagai instrument kedua, dan
interview
sebagai
instrument ketiga. Eror yang ditemukan dalam penelitian ini dibagi menjadi empat
tipe sesuai dengan teori yang dikemukakan oleh Dulay, Burt dan Krashen (1982)
: the
omission of a or an (62
kali
, 52.10 %),
diikuti
the omission of the (26
kali
, 21.84%),
the addition of the (16
kali
, 13.44 %), the addition of a or an (10
kali
, 8.40 %),
misformation of a or an (4
kali
, 3.36 %), misformation of the (1
kali
, 0.84 %),
dan
misodering of a,an
dan
the (0 kali, 0 %)
. Untuk menjawab permasalahan kedua,
peneliti menggunakan teori yang dikemukakan oleh Brown (2000) tentang
context of
learning
dan Norrish (1983) tentang
carelessness, error as a part of creativity, first
language interference,
dan
translation
sebagai faktor-faktor penyebab eror.
Peneliti memberi rekomendasi bagi para guru Bahasa Inggris, para
mahasiswa, dan para peneliti selanjutnya. Para guru Bahasa Inggris menjelaskan
dengan rinci penggunaan articles kepada mahasiswa. Para mahasiswa lebih
memahami penggunaan articles dan banyak berlatih. Para peneliti selanjutnya
mengklasifikasi penyebab eror sesuai dengan tipe eror yang ditemukan. dan
memodifikasi instrument atau subjek yang dipilih.
A STUDY ON THE USE OF ARTICLES
IN STUDENTS’ WRITTEN PROJECTS OF
CRITICAL READING AND WRITING I CLASS
A
SARJANA PENDIDIKAN
THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
to Obtain the
Sarjana Pendidikan
Degree
in English Language Education
By
Vinencia Lefrianita Cendana Sari
Student Number: 101214046
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM
DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION
FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY
YOGYAKARTA
i
A STUDY ON THE USE OF ARTICLES
IN STUDENTS’ WRITTEN PROJECTS OF
CRITICAL READING AND WRITING I CLASS
A
SARJANA PENDIDIKAN
THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
to Obtain the
Sarjana Pendidikan
Degree
in English Language Education
By
Vinencia Lefrianita Cendana Sari
Student Number: 101214046
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM
DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION
FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY
YOGYAKARTA
ASarjana pendidikan Thesis on
A
STUI}Y
ON
I'HE
USE
OF'ARTICLES
IN STUDENTS'WRITTEN
PROJI,CTS
OF'CRITICAL
READING AND
WRITING
I
CLASS
Approved by
ffiq
ffi
X*d
tff
,$'"
P
lriltFt
Is
t#
Advisor
Chairperson
Secretary
Mernber Member Member
A Sarjun* Pendidikan Thesis on
A
STUI}Y
ON
THE
USE
OF
ARTICLES
IN
STUDENTS'WRITTE1Y
PROJECTS OF
CRITICAL
READIT{G AND
WRITI}{G
I
CLASS
By
Vinencia Lefrianita Cendana Sari Student Number: 1Al.214046
Defended before the Board of Examiners
on January 21,2015
and Declared Acceptable Board of Examiners
: P. Kuswandono, PII.D.
:Drs. Barli Bram, M.Ed., Ph.D" : Drs. Y. B. Gunawan, M.A.
: Ch. Lhaksrnita Anandari, S.Pd., Ed.M. : Drs. Barli Bram, M.Ed., Ph.D.
Yogyakarta, January 21, 701 5 Dharma University
ffi
W
./ .{{r'-rif
iv
FIND YOUR PASSION,
AND LIVE IT!
This thesis is dedicated to:
My beloved parents, Bapak Marianus Mochtar Modesir and
Ibu Wellybrorda N. Lawalu
My beloved brother, Ch. Gloria Lefriana C. Agung Modesir
STATEMENT
OFWORI('S ORIGINALITY
I
honestly declare that this thesis, whichI
have written, does not contain the work or partsof
thework
of
other people, except those citedin
the
quotations and the references, as a scientific paper should.Yogyakarta, January 21, 2074 The Writer
LEMBAR PERNYATAAN
PERSETUJUANPUBLIKASI KARYA
ILMIAH
UNTUK KEPENTINGAN AKADEMIS
Yang bertanda tangan di bawah ini, saya mahasiswa Universitas Sanata Dharma:
Nama
: Vinencia Lefrianita Cendana SariNomorMahasiswa
:101214046Demi
pengembanganilmu
pengetahuan, saya memberikan Universitas Sanata Dharma karya ihniah saya yang berjudul:kepada Perpustakaan
A
STUDY
ON
THE
USE
OF
ARTICLES
IN
STUDENTS'
WRITTEN
PROJECTS
OF
CRTTICAL READING AND
WRITING
I
CLASS
besefia perangkat yang diperlukan
(bila
ada). Dengan demikian saya memberikankepada Perpustakaan Universitas Sanata Dharma hak untuk menyimpan, mengalihkan
dalam bentuk
media
lain,
mengelolanyadalam bentuk
pangkalan
data,mendistribusikan secara terbatas, dan mempublikasikannya
di
Internet atau medialain
untuk
keperluan akademistanpa
perlu
meminta
Ljin
dari
saya
maupunmemberikan
royalti
kepada saya selama tetap mencantumkan nama saya sebagaipenulis.
Demikian pernyataan ini yang saya buat dengan sebenarnya.
Dibuat di Yogyakarta
Pada tangg al
2l
I anuai 201 5Yang menyatakan
(Vinencia Lefri anita Cendana S ari)
vii
ABSTRACT
Sari, Vinencia Lefrianita Cendana. (2015).
A Study on the Use of Articles in
Students’ Written Projects of Critical Reading and Writing I Class.
Yogyakarta:
English Language Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University.
Writing is one of the important skills in learning English. Through writing,
students learn to make good sentences with correct English grammar. It is common to
see grammatical errors in writing because grammar has many parts that the students
must understand and master. The use of articles in English grammar seems simple but
complicated because of the various kinds of nouns following the article itself.
Non-native speakers of English must be consistent whether to use
a
or
an
and
the
in their
writings.
Based on this issue, the researcher focused on analyzing the errors in the use
of articles made by 10 students in Critical Reading and Writing I Class E academic
year 2014/2015 in the English Language Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma
University. There are two research problems in this research: (a) What errors in the
use of articles are found in students’ written projects of Critical Reading and Writing
I Class? (b) What are the causes of errors in the use of articles in students’ written
projects of Critical Reading and Writing I Class? This research has two objectives: (a)
to find out what errors in the use of articles found in students’ written projects of
Critical Reading and Writing I Class are, (b) to find out the causes of errors in the use
of articles in students’ written projects of Critical Reading and Writing I Class are.
Document analysis was the method in this research. There were three
instruments: human, document, and interview. Human instrument was the primary
instrument, document was the second instrument and interview was the third
instrument. The errors found in students’ written projects were classified into four
types of error by Dulay, Burt and Krashen (1982): omission of a
or
an (62 times,
52.10 %) followed by the omission of
the
(26 times, 21.84 %), the addition of
the
(16
times, 13.44 %), the addition of
a
or
an
(10 times, 8.40 %), misformation of
a
or
an
(4 times, 3.36 %), misformation of
the
(1 time, 0.84 %) and misordering of
a
,
an
, and
the
(0 time, 0 %). The researcher used the theory from Brown (2000), who classified
context of learning and Norrish (1983), who classified carelessness, first language
interference, translation, and error as a part of creativity as the causes of errors.
The researcher gives recommendations for English teachers, students, and
future researchers. For English teachers, it is better to give brief and detail
explanation about the use of articles to the students. For students, it is better to
deepen their understanding about the basic rules of articles and practice themselves a
lot. For future researchers, it is better to classify the causes of errors deeper based on
the types of errors and modify the instruments or the participants.
viii
ABSTRAK
Sari, Vinencia Lefrianita Cendana. (2015). A Study on the Use of Articles in
Students’ Written Projects of Critical Reading and Writing I Class. Yogyakarta:
English Language Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University.
Menulis adalah salah satu kemampuan penting dalam Bahasa Inggris.
Menulis memberi kesempatan bagi penulis untuk menerapkan struktur bahasa
dengan tepat. Eror dalam menulis sering ditemukan karena penulis harus
mempelajari dan menguasai struktur Bahasa Inggris. Penggunaan
articles
dalam
Bahasa Inggris terlihat mudah namun rumit karena terdapat banyak bentuk kata
benda yang mengikuti
articles
tersebut.
Penutur bahasa selain Bahasa Inggris
harus
konsisten dalam menggunakan
a
atau
an
dan
the
dalam tulisan mereka.
Menanggapi hal tesebut, peneliti menganalisis eror pada penggunaan
articles
oleh 10 mahasiswa di kelas
Critical Reading and Writing I.
Terdapat dua
permasalahan dalam penelitian ini
:
(a) Apa saja eror pada penggunaan
articles
yang
ditemukan dalam tulisan mahasiswa di kelas
Critical Reading and Writing I
? (b) Apa
penyebab eror pada penggunaan
articles
dalam tulisan mahasiswa di kelas
Critical
Reading and Writing I
? Penelitian ini memiliki dua tujuan: (a) Untuk mengetahui
apa saja eror pada penggunaan
articles
yang ditemukan dalam tulisan mahasiswa di
kelas
Critical Reading and Writing I
, (b) Untuk mengetahui penyebab terjadinya
eror pada penggunaan
articles
dalam tulisan mahasiswa di kelas
Critical Reading
and Writing I.
Document analysis merupakan metode dalam penelitian ini.
Terdapat tiga
instrumen dalam metode ini
: human, document,
dan
interview. Human
sebagai
instrument utama,
document
sebagai instrument kedua, dan
interview
sebagai
instrument ketiga. Eror yang ditemukan dalam penelitian ini dibagi menjadi empat
tipe sesuai dengan teori yang dikemukakan oleh Dulay, Burt dan Krashen (1982)
: the
omission of a or an (62
kali
, 52.10 %),
diikuti
the omission of the (26
kali
, 21.84%),
the addition of the (16
kali
, 13.44 %), the addition of a or an (10
kali
, 8.40 %),
misformation of a or an (4
kali
, 3.36 %), misformation of the (1
kali
, 0.84 %),
dan
misodering of a,an
dan
the (0 kali, 0 %)
. Untuk menjawab permasalahan kedua,
peneliti menggunakan teori yang dikemukakan oleh Brown (2000) tentang
context of
learning
dan Norrish (1983) tentang
carelessness, error as a part of creativity, first
language interference,
dan
translation
sebagai faktor-faktor penyebab eror.
Peneliti memberi rekomendasi bagi para guru Bahasa Inggris, para
mahasiswa, dan para peneliti selanjutnya. Para guru Bahasa Inggris menjelaskan
dengan rinci penggunaan articles kepada mahasiswa. Para mahasiswa lebih
memahami penggunaan articles dan banyak berlatih. Para peneliti selanjutnya
mengklasifikasi penyebab eror sesuai dengan tipe eror yang ditemukan. dan
memodifikasi instrument atau subjek yang dipilih.
ix
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Thanks be to God, who always gives His blessings in my life so that I could
still be alive and be healthy in finishing my thesis writing. He guides me through all
of learning processes, happiness, sadness, experiences, and precious time I have got
in PBI Sanata Dharma. I also thank Jesus Christ and Mother Mary, who are always
with me whenever and wherever I am.
My deepest gratitude goes to my thesis advisor, Drs. Barli Bram, M.Ed.,
Ph.D., for giving his time, advice, guidance, correction, and support so that I could
finish my thesis writing well. I would like to thank Caecilia Tutyandari M.Pd., as
my academic advisor and Truly Almendo Pasaribu, S.S., M.A., who allowed me to
use her class as the subject of this research. I would also like to thank the third
semester students in Critical Reading and Writing I Class E academic year
2014/2015, who contributed their writing as my thesis data and participated during
the interview process.
x
My special gratitude goes to PSM Cantus Firmus, especially my lovely
coach, brother, and friend,
Pak
Pancasona Adji (
Pak
Mbong), who trusts me to be
one of the members in PSM Cantus Firmus. I am grateful for the lessons, the
precious opportunities and the unforgettable experiences so that I could express my
self, increase my ability, and become a better person. I am also grateful for the
support, suggestions, and love from my brothers and sisters in PSM Cantus Firmus
especially
Uli, Detha, Ria, Laras, There, Ully, Fanny, Vera, Arta,
Mbak
Ichan,
Mbak
Lintang,
Mas
Yogis,
Mas
Louis, Adit, and Paul. I am really happy and proud
to be a part of this family. I would also like to thank my new friends from UKM
Grisadha especially Witta, Riri, and Resa, who have been supporting me until now.
My best gratitude belongs to my best friends, Lina, Nova, Regita, Memei,
Wara, and Okis, who always support and be with me until I finish my study in PBI. I
am grateful for all the togetherness, happiness, sadness, love, and unforgettable
experiences that I had during my study in this study program. Finally, I thank all
people and friends whom I cannot mention here one by one. Their support, love and
prayers help me finishing my study. God always bless them all.
xi
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page
TITLE PAGE ………...
i
APPROVAL PAGES ………...
ii
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY ………
v
PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI
... vi
ABSTRACT ...
vii
ABSTRAK
... viii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ...
ix
TABLE OF CONTENTS ……….
xi
LIST OF TABLES ...
xv
LIST OF APPENDICES ...
xvi
xii
1. English Grammar Theories……….
a. Theory of Count- Non-count Nouns ………..
1) Count Nouns ……….
2) Non-count Nouns ………...
2. Theory of Articles ………..…………
a. The Origin of Articles
...
b. The Types of Articles ...
1)
A
...
2)
An
...
3)
The
...
4)
Zero Article or
∅
.
…...…………..……….……..
3. Theory of Errors ………....……....….
a. Definition of Errors and Mistakes ...……...
b. Error Analysis ...
b. Types of Errors ...
1) A Linguistic Taxonomy ………...
2) A Surface Taxonomy ...
c. Causes of Errors ………...
1) Context of Learning………..….………
2) Carelessness...
3) First Language Interference ………..………
4) Translation ………
5) Error as a Part of Language Creativity ...………
B.
Theoretical Framework ………
xiii
CHAPTER III. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
A.
Research Method ……….
B.
Research Setting ………..
C.
Research Participants ………...
D.
Instrument and Data Gathering ………
1.
Human Instrument ………..…...
2.
Document ……….………..
3.
Interview ………...
E.
Data Analysis Technique ……….
F.
Research Procedure ………..
1.
Preparation ...
2.
Data Gathering ...
3.
Data Analysis ...
4.
Report of The Analysis ...
29
30
30
31
31
31
32
32
33
34
34
35
35
CHAPTER IV. RESEARCH RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
A.
Students’ Errors ….………...
1.
The Omission of
A
or
An
………
2.
The Omission of
The
………..
3.
The Addition of
A
or
An
……….
4.
The Addition of
The
………...
5.
Misformation of
A
or
An
……….
6.
Misformation of
The
………...
xiv
B.
The Causes of Errors ………...……….
1.
Data Presentation of the Causes of Errors in the
Use of Articles ....…….……….…….
2.
Discussion of the Causes of Errors in the Use of
Articles ………...………
54
55
55
CHAPTER V. CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS
A.
Conclusions………...
B.
Recommendations ………....
62
64
REFERENCES ………
APPENDICES ……….
xv
LIST OF TABLES
Page
Table 2.1 Table 2.1 Four Groups of Non-count Nouns ………...
Table 2.2 The Use of
A
………
Table 2.3 The Use of
An
………..
Table 2.4 The Use of
The
………
Table 2.5 Exceptions on the Use of
The
……….
Table 2.6 The Use of ∅ ………...
Table 2.7 A Sample Linguistic Category Taxonomy ………..
Table 2.8 The Classification of Errors ………..………...
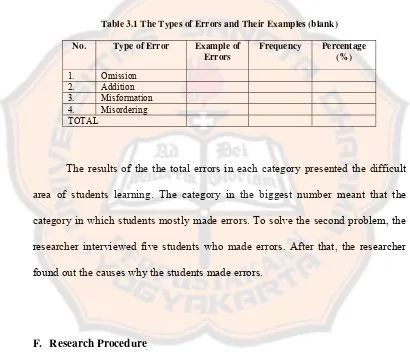
Table 3.1 The Types of Errors and Their Examples (blank) ………...
Table 4.1 The Types of Errors ………..……...
xvi
LIST OF APPENDICES
Page
Appendix A:
Surat Ijin Penelitian
………..….…..
69
Appendix B: Students’ Written Projects ………
70
Appendix C: The Interview Blue Print ……….……….…
84
Appendix D: The Interview Guideline …….………..
85
Appendix E: Summary of Interview Results ……….….
87
Appendix F: The Interview Transcripts ……….………
89
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
In this chapter, there are six main sections, namely the research
background, research problems, problem limitation, research objectives, research
benefits and definition of terms. The research background deals with the reason
chosen with the topic. The research problem describes the problems to be
analyzed in this study. The problem limitation focuses on the limitation or the
problem in this research. The research objectives deal with the aims of the
research. The research benefits describe the benefits of conducting the research
for the researcher, students, English teachers, and also further studies. Finally, the
definition of terms explains several terms that are important for this research.
A. Research Background
Nowadays, English is viewed as one of the important languages in the
world. It is because English is used by almost all of the people as the international
language. In English there are four skills to be learnt: listening, speaking, reading
and writing. One of them is writing skill. In writing, students express themselves
and share what they think. According to Tiedt (1989: 2), writing is one way of
expressing what we think. We can express and deliver all of our thoughts through
writing. Therefore, writing skills should grow along with learning and thinking in
the classroom (1989: 3). Tiedt (1989: 6) also states that writing is not easy. In
writing something, the ideas are generated. This part becomes difficult because we
need to think harder to deliver our thoughts. The problems appeared when writing
are facing the spelling, mechanics, and the time needed to write each word (Tiedt,
1989: 6).
The students of Critical Reading and Writing I Class in the English
Language Education Study Program are prepared to their next writing classes;
Critical Reading and Writing II, Academic Essay Writing and Thesis Writing
subjects in the fourth, fifth and eighth semester. Because of that, they have to take
Critical Reading and Writing I course first. Based on Panduan Akademik Program
Studi Bahasa Inggris (2011) Critical Reading and Writing I course as a
project-based class is designed to give students practice to write responses critically project-based
on the given texts or passages. As a critical class, the students of this class have to
write responses critically by using good English grammar. Good English grammar
will lead them to the success of this class instead of having good and critical
responses to the passages given.
In this class, they have to explore their ideas well in order to become a
good writer. Dawe and Dornan (1984: 9) say that one of the secrets of becoming a
good writer is to discover the personal method of nudging and teasing experience
and ideas into words. In other words, to become good writers the students have to
use their own way to express their ideas. In order to write correctly, students need
to become familiar with basic grammatical patterns of English (McKAY, 1985:
xviii). Based on the researcher’s experiences in previous writing classes, the use
some written projects, the researcher needed carefulness. The researcher realized
that she made a lot of errors in her writing especially in using articles in English.
It is often difficult to decide whether an English noun needs an article
before it, and, if so, which article (a or an or the) to use. The main things to
consider when choosing an article are whether or not the noun is countable, and
whether it is definite (Writing Centre Learning Guide The University of Adelaide,
2014). After studying articles for years, many non-native speakers of English find
it challenging to use articles, especially in formal academic writing in English.
This kind of writing in general uses more nouns than other types of writing, and
every noun requires a decision about articles (Biber, Conrad, & Leech, 2002).
Learners nowadays still have problems in using a or an and the.
According to Sharpling in the University of Warwick (2013), articles a or an and
the are difficult to use because sometimes language do not have the same concept
of ‘countable’ and ‘uncountable’ nouns as in English; there is a tendency to add
articles in English where they are not required. For example, the is often used
wrongly when the noun has the general reference. It is also difficult because some
people regard the rules of article use as virtually ‘unteachable’; using articles is
such a subtle process that only native speakers can fully grasp how articles
operate. This means that even expert speakers will still make mistakes with
articles.
Non-native speakers of English must constantly think about whether to use
a or an, the, or . Making an appropriate choice—that is, a choice that does not
complicated (Center for Writing University of Minnesota, 2014). It is simple to
use an article, what makes it complicated for learners is the various kind of nouns
following the article. The examples are:
(1)He killed a woman.
(2)He killed the woman.
Two examples above show different conditions. In example (1), someone
killed a woman who is not recognized by the readers. A woman in example (1)
may refer to any woman in the world. Both the speaker and the listener do not
know who exactly that woman is. Besides, in example (2), someone killed the
woman. The speaker uses the because the listener knows which specific woman
the speaker is talking about. Therefore, article the is used when both the speaker
and the listener are thinking about the same specific thing (Azar, 2009: 118).
Because the problem in the use of articles still exists, it is important to
have a research about this issue. The errors made by the third semester students in
Critical Reading and Writing I Class in the use of articles a or an and the can
define the ability of the students whether or not they can make good responses
using good English grammar. Besides, the students of this class will realize and
B. Research Problems
Considering previous explanation, there are two problems to be solved in
this research:
1. What errors in the use of articles are found in students’ written projects of
Critical Reading and Writing I Class?
2. What are the causes of errors in the use of articles in students’ written projects
of Critical Reading and Writing I Class?
C. Problem Limitation
Considering the limitation of time and resources, the researcher limits to
conduct the research for third semester students who have taken Critical Reading
and Writing I Class in 2014 of the odd semester. The researcher randomly chooses
10 written projects made by 10 students in Critical Reading and Writing I Class E.
This study focuses on the errors in the use of articles a or an and the in students’
written projects so that the researcher does not explain any further analysis on the
other issues.
D. Research Objectives
The study is conducted in order to:
1. Find out what errors in the use of articles found in students’ written projects of
Critical Reading and Writing I Class are.
2. Find out the causes of errors in the use of articles in students’ written projects
E. Research Benefits
This study is expected to bring beneficial results for the researcher,
students, English teachers, and also further studies.
1. Researcher
It is useful for the researcher to know the article errors in students’ written
projects of Critical Reading and Writing I Class. This study can help the
researcher to deepen the understanding of article errors and the factors causing the
students in making those errors and also to be more careful in using articles.
2. Students
This research is expected to help students to understand the basic rules of
English articles, to know better the use of articles, to improve their knowledge
about the use of articles and to avoid them in making errors in the use of articles
in the future.
3. English teachers
The findings of this research can be the references for English teachers to
know the article errors in students written projects. Hopefully, by reading this
study, the English teachers can overcome students’ errors and difficulties in using
articles and find an effective teaching strategy to help the students to avoid
4. Further Studies
This research is expected to be the references for future researchers in
conducting the relevant studies related to the use of articles in students’ written
projects.
F. Definition of Terms
In this section, the researcher will define the keywords specifically used in
the study. It is used in order to clarify the concepts and avoid misinterpretation.
1. Errors
Errors usually appeared in learning English. According to Dulay, Burt, and
Krashen (1982: 138), errors are the flawed side of learner speech or writing. A
learner may make errors in some parts of conversation in a language. It is because
a learner deviates from the rules of language. Therefore, Dulay, Burt, and Krashen
(1982: 138) state that people cannot learn language without first systematically
committing errors. In writing, students tend to make errors because they assume
that their work is correct. These errors commonly happen when students write
some sentences in the Critical Reading and Writing I Class.
2. Critical Reading and Writing I
Critical Reading and Writing I is the first subject that encourages students
to write critically. Based on Panduan Akademik Program Studi Bahasa Inggris
(2011), Critical Reading and Writing I course is designed as a project-based class
to give students practice to write responses critically based on the given texts or
In this course, reading and writing skills are integrated. The students are
expected to do the activities well. Students may take this course if they have
passed Basic Reading I, Basic Reading II, Basic Writing, and Paragraph Writing.
3. Articles
Leech and Svartvik (1975: 237) state that the articles are a subclass of the
determiners. Determiners are words which specify the range of reference of a
noun in various ways, e.g. by making it definite (the book), indefinite (a book), or
by indicating quantity (many books) (p. 268). In this case, articles make the
reference of a noun to be definite or indefinite as their name implied.
4. Students’ Written Projects
Students’ written projects are taken from the first written projects in
Critical Reading and Writing I Class. The topic of the students’ written projects is
technology. The written projects tell about comparison and contrast in using
technology. It consists of introduction, two or three main paragraphs, and
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
In this chapter, the review of the theoretical writing will be presented.
There are two sections in this chapter namely the theoretical description and
theoretical framework. The theoretical description consists of theory explanations
supporting this research. Meanwhile, the theoretical framework synthesizes the
theory explanations in the previous part. The theoretical framework discusses all
theories stated in the theoretical description as the basis to analyze students’
article errors and the causes of errors.
A. Theoretical Description
This section presents some theories related to the research: the English
grammar theories, theory of articles, and theory of errors.
1. English Grammar Theories
Veit (1986: 6) states that grammar is a person’s subconscious language
knowledge. We use our English grammar whenever we speak or write English or
understand someone else’s speech or writing. However, Heffernan and Lincoln
(1990: 6) state that grammar of the language is the set of rules by which its
sentences are made. Discussing grammar will lead us to the structure of the
sentences.
The main reason we study grammar is that we human beings are curious
and want to learn more about ourselves (Veit, 1986: 2). The study of how we
create language can provide important insights into the nature of our minds and
the way we think. It can help us understand better what it means to be human
(Veit, 1986: 2).
Studying about grammar has practical benefits. Using the conscious
grammatical knowledge can help us to understand what we are doing and allow us
to make some choices. The knowledge of grammar can also give us a tool to
analyze our writing and a vocabulary to discuss it (Veit, 1986: 2). Studying
grammar is valuable and important in writing (Veit, 1986: 254). It is because by
studying grammar help us to understand how we have written, to think critically
about what we have done, and also to consider other choices that might have
presented ourselves. Conscious grammatical knowledge allows us for this analysis
and provides vocabulary for communicating about it (Veit, 1986: 256). Therefore,
this subchapter explains a theory supporting this research: theory of count- non
count nouns.
a. Theory of Count- Non-count Nouns
Azar (2009: 109) mentions two kinds of noun based on the countability of
the nouns: count and non-count nouns. Count noun is divided into two groups:
singular and plural. The examples of singular noun are an apple, a book and a boy.
Besides, examples of plural noun are apples, books, and boys. Thus, non- count
noun is divided into four groups: a group of things e.g. food or furniture,
phenomena of nature e.g. snow, sunshine, wind, or fire, masses of particles e.g.
Based on their countability, Azar (2009: 109) divides nouns into two
groups: count and non-count nouns.
1) Count Nouns
Azar (2009: 109) states a count noun is an item that can be counted. Count
noun can be still divided into singular if the noun is single or the quantity of the
item is only one. The examples of singular noun are an apple or a boy. The use of
articles a and an here is important because it shows that the item is singular.
Meanwhile, apples and boys are classified into plural nouns. In the plural form,
the items are more than one so that the form takes a final ‘–s’ or ’-es’. Plural
nouns have another form which is called irregular plural form. The examples are
‘child’ becomes ‘children’ or ‘fish’ becomes ‘fish’.
2) Non-count Nouns
Azar (2009: 110) states non-count nouns are nouns that cannot be counted.
[image:30.612.105.508.218.631.2]The examples of non-count nouns are written in Table 2.1 below.
Table 2.1 Four Groups of Non-count Nouns
Number Groups Examples
1. A group of things Food, furniture 2. Phenomena of nature Snow, sunshine, wind, or fire 3. Masses of particles Salt, sugar, or coffee 4. An abstract concept Fun, information, advice, or news
In other words, based on their countability, nouns are divided into two
classified as the singular and plural nouns. Meanwhile, non-count nouns are
classified into nouns representing a whole group of thing, phenomena in nature,
whole masses, and abstract concepts.
2. Theory of Articles
According to Azar (2009: 114), there are three types of articles: a, an, and
the. Those three articles are used in different conditions which mainly depend on
the nouns after the articles. Nonetheless, there is also a condition when a noun
does not need any article. Azar (2009: 114) uses the symbol ∅ to help the students
in visualizing such condition. Meanwhile, a, an, the, and ∅ are used in different
conditions. It will be explained on the next subchapters.
a. The Origin of Articles
Articles are important in English. It is stated by Berry (1994: vi) that
articles give structural information. Articles tell that a noun is following in the
sentence. Changing one article for another can often cause misunderstanding. For
example, ‘I like English’ (the language), when someone means ‘I like the English’
(the people).
According to Azar (2009: 114), there are three articles in English: a and an
which are called the indefinite article and the which is called the definite article.
The was developed from a word which has much the same meaning as the
demonstrative that. That is more emphatic in pointing something out and a and an
155) give further explanation about one, sometimes when one is in the sense of a
single unit or item one cannot be substituted for the indefinite article without
changing the meaning.
Leech and Svartvik (1975: 237) state that the articles are a subclass of the
determiners. Determiners are words which specify the range of reference of a
noun in various ways, e.g. by making it definite (the book), indefinite (a book), or
by indicating quantity (many books) (p. 268). In this case, articles make the
reference of a noun to be definite or indefinite as their name implied.
b. The Types of Articles
After knowing the origin of articles, it is important to know the differences
among the articles. This subchapter represents four types of articles: a, an, the,
and zero article or ∅.
1) A
Article a is basically used for singular nouns which begin with consonant
sounds. Besides, article an is used if the nouns begin with vowels or diphthong
sounds. The explanation of article an will be presented in the next discussion
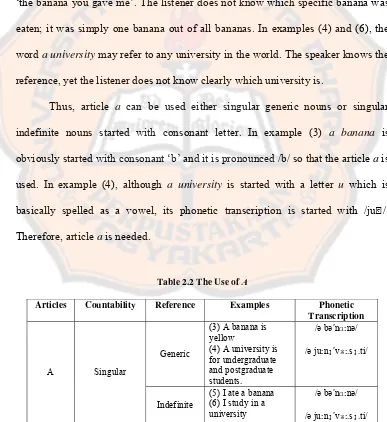
[image:32.612.101.511.238.515.2]while the detailed use of a is provided in Table 2.2.
Table 2.2 shows the use of article a before (1) singular generic nouns and
(2) singular indefinite nouns as the examples (3), (4), (5), and (6). Those singular
generic and indefinite nouns are begun with consonant. Azar (2009: 114) uses
things. It is not a specific, real, concrete thing, but rather a symbol of a whole
group. Therefore a banana in examples (3) and (5) represent all bananas in the
world, not a specific banana.
Meanwhile, an indefinite noun is an actual thing (not a symbol), but it is
not specifically identified. In example (5), the speaker is simply saying that she or
he ate one banana. The speaker is not referring to ‘this banana’ or ‘that banana’ or
‘the banana you gave me’. The listener does not know which specific banana was
eaten; it was simply one banana out of all bananas. In examples (4) and (6), the
word a university may refer to any university in the world. The speaker knows the
reference, yet the listener does not know clearly which university is.
Thus, article a can be used either singular generic nouns or singular
indefinite nouns started with consonant letter. In example (3) a banana is
obviously started with consonant ‘b’ and it is pronounced /b/ so that the article a is
used. In example (4), although a university is started with a letter u which is
basically spelled as a vowel, its phonetic transcription is started with /ju/.
[image:33.612.117.504.267.689.2]Therefore, article a is needed.
Table 2.2 The Use of A
Articles Countability Reference Examples Phonetic Transcription
A Singular Generic
(3) A banana is yellow
(4) A university is for undergraduate and postgraduate students.
/ə bən :nə/ /ə ju:nɪvɜ:.sɪ.ti/ Indefinite
(5) I ate a banana (6) I study in a university
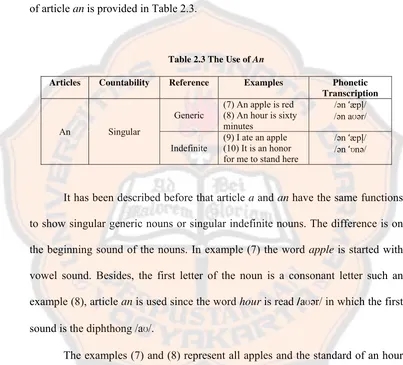
2) An
Article an has the same functions with article a, but it is used in the
beginning of nouns which have a special sound. The information related to the use
[image:34.612.103.506.183.548.2]of article an is provided in Table 2.3.
Table 2.3 The Use of An
Articles Countability Reference Examples Phonetic Transcription
An Singular Generic
(7) An apple is red (8) An hour is sixty minutes
/ən æpl/ /ən aʊər/ Indefinite
(9) I ate an apple (10) It is an honor for me to stand here
/ən æpl/ /ən nə/
It has been described before that article a and an have the same functions
to show singular generic nouns or singular indefinite nouns. The difference is on
the beginning sound of the nouns. In example (7) the word apple is started with
vowel sound. Besides, the first letter of the noun is a consonant letter such an
example (8), article an is used since the word hour is read /aʊər/ in which the first sound is the diphthong /aʊ/.
The examples (7) and (8) represent all apples and the standard of an hour
in the world. Generic noun does not refer to a specific thing, but to a class of
things. Meanwhile, those words in examples (9) and (10) use articles an as the
3) The
Different from the previous articles, the is not affected by the first sound
of the nouns. The use of the is usually influenced by the reference of the nouns.
[image:35.612.102.510.206.594.2]The example and the detailed of the is provided in Table 2.4.
Table 2.4 The Use of The
Articles Countability Reference Examples
The
Singular
Definite
(11) Thank you for the umbrella Plural (12) Thank you for the bananas Noun-count (13) Thank you for the fruit.
Table 2.4 shows that the countability and the first sound of a noun do not
affect the use of the. It is supported in examples (11), (12), and (13). In example
(11) the word umbrella is a singular noun and it is started with vowel sound. On
the other hand, in example (12), the word bananas is plural and started with
consonant sound. All the examples (11), (12), and (13) show that the speaker uses
the in front of the words umbrella, bananas, and fruit. The speaker uses the
because the listener knows which specific umbrella, banana, and fruit the speaker
is talking about. Therefore, article the is used when both the speaker and the
listener are thinking about the same specific thing.
There is also an exception in using the. Azar (2009: 118) states that the is
used for several singular generic count noun such as species of animals,
inventions, and musical instruments. The exceptions in the use of the are provided
Table 2.5 Exceptions on the Use of The
No Classifications Examples
1 Species of animals (14) The elephant is the largest land mammal. 2 Inventions (15) Who invented the refrigerator?
3 Musical Instruments (16) I’d like to learn to play the piano.
4) Zero Article or ∅
Zero article or ∅ is a state when a noun does not need any article. It is generally used for plural and noun-count generic nouns. Table 2.6 shows detail
information related to this article.
Table 2.6 The Use of ∅
Articles Countability Reference Examples
∅ Plural
Generic (17) ∅Bananas are yellow. Noun-count (18) ∅ Fruit is good for you.
∅ is used for plural and noun-count generic nouns. Example (17) shows the example of plural generic nouns. To refer to a class of noun, in addition to use
a singular noun identified by a or an, a plural noun can also be used, as shown in
example (17). Meanwhile, the other use of ∅ is that is followed by noun-count generic noun, such as fruit in example (18).
Each article is used with different kinds of nouns. The nouns are
distinguished by three different criteria: the countability, the reference, and the
first sound of a noun. First, article a is used with singular generic and indefinite
nouns started with consonant sounds. Second, article an is used for singular
article the is used for definite noun. Fourth, zero article or ∅ is used for plural and
noun-count nouns.
3. Theory of Errors
The following discussion covers the definition of errors and mistakes,
error analysis, types of errors, and causes of errors.
a. Definition of Errors and Mistakes
Dulay, Burt, and Krashen (1982: 138) state that errors are the flawed side
of learner speech or writing. A learner may make errors in some parts of
conversation in a language. It is because a learner deviates from the rules of
language. Therefore, Dulay, Burt, and Krashen (1982: 138) state that people
cannot learn language without first systematically committing errors. They
provide two major purposes of studying learners’ errors. First, it provides data
from which inferences about the nature of the language learning process can be
made. Second, it helps the teachers to understand students’ difficulties and
students’ ability to communicate effectively (Dulay, Burt, and Krashen, 1982:
138).
Besides, Norrish (1983: 7) has a statement about the definition of an error.
It is a systematic deviation when a learner has not learnt something and
consistently ‘gets it wrong’. This means when a learner of English as a second or
foreign language makes an error systematically, it is because he has not learnt the
Dulay, Burt, and Krashen (1982: 138) also state the most common errors
made by the students. They are:
1. Omitting grammatical morphemes – the items that do not contribute to the
meaning of sentences.
2. Double marking – a semantic feature when only one marker is required.
3. Regularizing rules – for examples as in womans for women.
4. Using archiforms – one form in place of several.
5. Using two or more forms in random alternation – the use of each only under
certain conditions.
6. Misordering – misplacing items that may be correctly placed in more than one
place in the sentence.
In addition, errors are different from mistakes. Brown (2000: 217)
mentions that mistakes and errors are technically two different phenomena. A
mistake refers to a performance error that is a ‘slip’, in that it is a failure to use a
known system correctly. Everyone can make mistakes, even the native speakers of
a language. James (1998: 83) also states that an error cannot be self-corrected
while mistakes can be self- corrected if the deviation is pointed out to the writer.
b. Error Analysis
According to Gass and Selinker (1994: 67), error analysis is “a type of
linguistic analysis that focuses on the errors learners make”. The analysts describe
that the comparison made is between the errors a learner makes in producing the
is the study of the errors that learners make in their speech and writing (Ellis &
Barkhuizen, 2005: 51).
Identification, description and explanation of errors are stated in the error
analysis. As mentioned by Ellis and Barkhuizen (2005: 58), identification of error
involves a comparison between what the learner has produced and what a native
speaker would produce in the same context. Description of errors involves
specifying how the forms produced by the learner differ from those produced by
the learner’s native speaker counterparts. It focuses on the surface properties of
learner utterances (Ellis & Barkhuizen, 2005: 60). Thus, explanation of errors as
stated by Ellis and Barkhuizen (2005: 62) involves determining the source of the
error in order to account for why it was made.
c. Types of Errors
In this subchapter, the researcher classifies the errors made by the learners
into two taxonomies suggested by Dulay, Burt, and Krashen (1982: 147), those
are a linguistic taxonomy and surface structure taxonomy.
1) A Linguistic Taxonomy
The linguistic items that are affected by an error are used to be the base of
error taxonomies. Linguistics category taxonomies classify errors according to
both the language component and the linguistic constituents (Dulay, Burt, &
Krashen, 1982: 146). The components of the language are phonology, syntax and
constituents are the elements that comprise each language component. Dulay,
Burt, and Krashen (1982: 147) also describe that many researchers use the
linguistic category taxonomy as a reporting tool that organizes the collected
errors.
Dulay, Burt and Krashen (1982: 147) give examples about the taxonomy
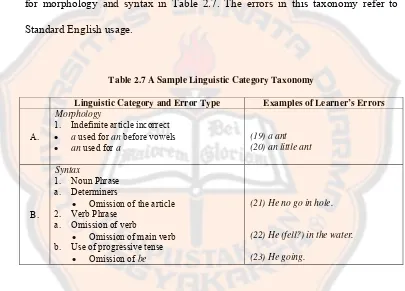
for morphology and syntax in Table 2.7. The errors in this taxonomy refer to
[image:40.612.108.513.240.531.2]Standard English usage.
Table 2.7 A Sample Linguistic Category Taxonomy
Linguistic Category and Error Type Examples of Learner’s Errors
A.
Morphology
1. Indefinite article incorrect
• a used for an before vowels
• an used for a
(19) a ant (20) an little ant
B.
Syntax
1. Noun Phrase a. Determiners
• Omission of the article 2. Verb Phrase
a. Omission of verb
• Omission of main verb b. Use of progressive tense
• Omission of be
(21) He no go in hole.
(22) He (fell?) in the water.
(23) He going.
Table 2.7 shows the error types based on a linguistic category and also
some examples related to learner’s errors. In examples (19) and (20), indefinite
articles are incorrect. The words a ant should be corrected into an ant, and the
words an little ant should be corrected into a little ant since a is followed by
2) A Surface Taxonomy
Dulay, Burt, and Krashen (1982: 150) also state another type of error
classification named Surface Strategy Taxonomy. This taxonomy highlights the
ways surface structures are altered. Surface Strategy Taxonomy concentrates on
the ways in which surface structures are changed. Using this taxonomy, Dulay,
Burt, and Krashen (1982: 150) divide errors into the following categories:
omission, addition, misformation, and misordering. Those error classifications
[image:41.612.106.507.240.542.2]would be described further in Table 2.8.
Table 2.8 The Classification of Errors
No Category Description Examples
1 Omission
The nonexistence of an item that must be appeared in a good utterance.
(24) She singing. 2 Addition
The presence of an item that must not appear in a well-structured utterance.
(25) She is sings well. 3 Misformation A substitution of the morpheme
or structure used in utterances.
(26) The plane flied to Budapest.
4 Misordering
The incorrect placement of a morpheme or a group of morphemes in an utterance.
(27) Why mother is crying?
Omission means that an item which must be present in a well-formed
utterance is absent. There is an evidence that grammatical morphemes (e.g. noun
and verb inflections, articles, prepositions) are omitted more often than content
morphemes which carry the meaning (Dulay, Burt, & Krashen, 1982: 154-155). It
is illustrated in the incomplete sentence in example (24). The sentence in example
(24) needs a linking verb is since it is a present continuous tense sentence. The
Addition is the second category of Surface Strategy Taxonomy and also
the opposite of omission. The presence of an extra item which had not be present
in a well formed utterance was characteristic for additions (Dulay, Burt, &
Krashen, 1982: 156). They divide them into three categories: double markings,
regularization, and simple addition, which contain the rest of additions (Dulay,
Burt, and Krashen, 1982: 156-158). The sentence She is sings well in example
(25) shows that there is an addition of linking verb is in a simple present tense
sentence. She sings well is the correct sentence.
Misformation is the third category of error. It refers to “the use of the
wrong fom of the morpheme or structure” (Dulay, Burt, & Krashen, 1982: 158).
When learners commit misformation errors, they use incorrect form of a language
item in making a sentence. Example (26) is the illustration of misformation error.
The learner should use flew instead of flied to construct the correct sentence.
Therefore, the correct sentence should be the plane flew to Budapest.
After discussing about three categories of errors, misordering comes as the
fourth category of errors. Misordering is indicated by incorrect placement of a
morpheme or a group of morpheme. Example (27) emphasizes the misordering
error. Is should be put before mother. Therefore, the correct form of the example
is why is mother crying?
d. Causes of Errors
The errors made by the students in writing their projects commonly
five causes of errors that commonly influence the students in learning the foreign
language. Those are context of learning, carelessness, first language interference,
translation, and error as a part of language creativity.
1) Context of Learning
According to Brown (2000: 226), context of learning is the source of error
which refers to the classroom with its teacher and materials in the case of school
learning. The teacher or the text book can lead the learner to make false concepts
about the language. The errors made by the students because the teacher misleads
the explanation, presents the structure or word in a textbook incorrectly, and also
because of a pattern that was memorized by the students in a drill but improperly
contextualized (Brown, 2000: 226). The errors made are because the teacher
provides incorrect information by giving misleading definition, word, or
grammatical generalization.
2) Carelessness
Carelessness is often closely related to lack of motivation (Norrish, 1983:
7). The analyst argues that some teachers will admit that it is not always the
student’s fault if he loses interest; perhaps the materials or the style of
presentation do not suit him. Lack of motivation can lead the students to make
errors because they are not motivated to read their writings and tend to think that
3) First Language Interference
According to Norrish (1983: 22), learning a language (a mother tongue or
a foreign language) is a matter of habit formation. The learner’s utterances are
thought to be gradually ‘shaped’ towards those of the language he learns. Mother
tongue leads in turn to repetitions of the utterances and the subsequent formation
of linguistic habits.
Besides, according to Ellis (1985: 22), interference is the result of what is
called proactive inhibition which concerns with the way in which previous
learning prevents or inhibits the learning of new habits. Therefore, first language
interference is essentially a set of habits. When we try to learn new habits, the old
habits will interfere with the new ones.
4) Translation
Norrish (1983: 26) states that translating word by word using idiomatic
expressions in the learner’s first language is another factor in making errors in his
or her writing. It can happen in a typical situation when a learner has been asked
to communicate something, in this case in writing, but he is aware that he does not
know the appropriate expression or structure. He may even be unaware that an
appropriate one exists. Consequently, as he wants to communicate his ideas, he
will fall back on the language system in which he is familiar, namely his mother
5) Error as a Part of Language Creativity
According to Norrish (1983: 34-35), language creativity is a natural
activity of human who interacts with his environment in the laudable attempt to
make sense of it and to form it to his own ends. Learners who are limited in their
opportunities in listening to examples of the target language tend to form
hypothetical rules about the new language. Norrish (1983) states that learners
need to create new utterances, but with limited experience of the target language,
they may make mistakes. For example, ‘emergent visit’. It should be ‘emergency
visit’. The process leading to the error is clearly a creative one.
There are two types of creativity in language use (Norrish, 1983: 35-36).
First, the ability in the learner to use the parts of the language that he has learnt in
order to say something that he may not have heard before. The learner is drawing
certain conclusions about how the language behaves by using the evidence of
what he has seen in the target language. Second, the term of ‘creative arts’ means
creating works of literature in a language other than their own. For example,
Joseph Conrad whose first language was Polish, he wrote novels in English.
B. Theoretical Framework
The second part of this chapter discusses the theoretical framework that
contains the description of the theories to solve the research problems. The
description is related to English grammar theory: count and non-count nouns,
Actually, this research is frequently related to articles which are classified
as determiners of nouns and as the main subject of the study. In order to find out
students’ errors in the use of articles, the researcher needs to classify different
types and the rules using articles. To solve the first research problem, the
researcher employs theory of English grammar: count and non-count nouns,
theory of articles proposed by Azar (2009) and theory of types of errors
mentioned by Dulay, Burt, and Krashen (1982). The classifications of errors
stated by Dulay, Burt, and Krashen (1982) i.e. omission, addition, misformation
and misordering are types of errors based on Surface Strategy Taxonomy. All of
the students’ errors will be classified based on the theory.
Dealing with the definition of error, the researcher agrees with Dulay,
Burt, and Krashen (1982: 138), who state that errors are the flawed side of learner
speech or writing. A learner may make errors in some parts of conversation in a
language. It is because a learner deviates from the rules of language. Errors can
appear in writing process because the students do not learn the correct form of
grammar. Besides, the researcher also agrees that errors and mistakes are
different. It is stated by Brown (2000: 217) who mentions that mistakes and errors
are two different phenomena. A mistake refers to a performance error that is a
‘slip’, in that it is a failure to use a known system correctly. While James (1998:
83) also states that an error cannot be self-corrected while mistakes can be self-
corrected if the deviation is pointed out to the writer.
To solve the second research problem the researcher agrees with Brown
influence the students in learning the foreign language i.e. context of learning,
carelessness, first language interference, translation, and error as a part of
language creativity. These five causes of errors will be used in interview process
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
In this chapter, there are six main sections namely the research method,
research setting, research participants or subjects, instruments and data gathering
technique, data analysis technique, and research procedure.
A. Research Method
In this section, the definition of the type of research chosen was presented.
Since this research explored the use of articles a or an and the in students’ written
projects as the major focus for investigation and interpretation, this research used
qualitative research in the methodology. According to Creswell (2003: 17), in
qualitative research, the researchers collected the data on an instrument or test.
Therefore, the researcher would explain what instruments were used in the
instrument and data gathering technique.
The researcher used qualitative in order to understand the participants
through visiting the context and gathering information personally. The researcher
would make an interpretation of things found, and an interpretation shaped by the
researcher’s own experiences and backgrounds (Creswell, 2003: 9). This research
later provided an explanation of errors which were made by students in their
writing. The kind of method was called document analysis. Document analysis
was considered as the activity of analyzing the document. In order to classify the
errors, the researcher collected the students’ written projects. Then, the researcher
analyzed each written project carefully to find the errors and classified them
correctly. The results of the classification would be used to solve the first research
problem “What errors in the use of articles are found in students’ written projects
of Critical Reading and Writing I Class?” Moreover, this study provided an
explanation of how errors come about. This description concerned the second
research problem “What are the causes of errors in the use of articles in students’
written projects of Critical Reading and Writing I Class?”
B. Research Setting
This section informed when and where the research was conducted. The
researcher conducted this research in Critical Reading and Writing I Class E of the
English Language Education Study Program academic year 2014/ 2015. Then, the
researcher conducted the research from September until October 2014.
C. Research Participants
The participants of the research were the ten students from third semester
in the English Language Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma University
in academic year 2014/2015. The researcher took students’ first projects from
Critical Reading and Writing I Class E. By taking specific participants, it was
was taken from the students in Critical Reading and Writing I Class, who
represented the abilities of all Critical Reading and Writing I students.
D. Instrument and Data Gathering Technique
In order to solve the two research problems, this research provided three
kinds of instrument i.e. human instrument, document, and interview. The three
kinds of instrument were used to convey that data and information obtained were
reliable and valid.
1. Human Instrument
In this research, the researcher was classified as human instrument who
became the primary instrument. It was because the researcher obtained the data,
read the students’ written projects, interviewed, made interactions with the
participants and recorded the information in journals.
2. Document
Document had an important role in this research. It was because the data
was taken from ten students’ written projects as their first projects. It was used to
classify the article errors made by the students. By using document, the researcher
second instrument in this research because the document had been written by the
participants who had experience with the phenomenon under the study directly.
3. Interview
Interview was the third instrument in this research. Interview was used to
help the researcher to understand participants’ experiences. The researcher would
use semi structured interview where the researcher formulated the questions
related to the topic. The researcher could modify the format or questions during
the interview process (Ary, Jacobs, & Sorensen, 2010: 438). In this interview, the
researcher interviewed the same participants in Critical Reading and Writing I
Class E.
By using interview, the researcher would be easier in analyzing the data
beside of using documents. The interview was conducted in Bahasa Indonesia
since it was students’ native language. It would help the students in understanding
the questions and in giving the answers.
E. Data Analysis Technique
Surface description was used in this research because it involved
explanation of errors in students’ writing. The researcher referred to the Surface
Strategy Taxonomy propos