A THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain theSarjana PendidikanDegree
in English Language Education
By Fl. Juliani
Student Number: 051214139
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY YOGYAKARTA
i
TEACHERS’ PERCEPTION ON THE USE OF PICTURES
IN TEACHING ENGLISH TO YOUNG LEARNERS
A THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain theSarjana PendidikanDegree
in English Language Education
By Fl. Juliani
Student Number: 051214139
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION
FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY
ii A Thesis on
TEACHERS’ PERCEPTION ON THE USE OF PICTURES
IN TEACHING ENGLISH TO YOUNG LEARNERS
By Fl. Juliani
Student Number: 051214139
Approved by:
Major sponsor
iii A Thesis on
TEACHERS’ PERCEPTION ON THE USE OF PICTURES
IN TEACHING ENGLISH TO YOUNG LEARNERS
By Fl. Juliani
Student Number: 051214139
Defended before the Board of Examiners on September 20th, 2010
And Declared Acceptable
Board of Examiners
Chairperson : C. Tutyandari, S.Pd., M.Pd. ______________
Secretary : Made Frida Yulia, S.Pd., M.Pd. ______________
Member : Christina Kristiyani, S.Pd., M.Pd. ______________
Member : C. Sih Prabandari, S.Pd., M.Hum. ______________
Member : Drs. Y.B. Gunawan, MA. ______________
Yogyakarta, September 20th, 2010
Faculty of Teachers Training and Education Sanata Dharma University
Dean,
iv
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY
I honestly declare that this thesis, which I have written, does not contain the work or parts of the work of other people, except those cited in the quotations and the references, as a scientific paper should
Yogyakarta, 20thSeptember 2010 The Writer
v
LEMBAR PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI KARYA ILMIAH UNTUK KEPENTINGAN AKADEMIS
Yang bertanda tangan dibawah ini, saya mahasiswa Universitas Sanata Dharma:
Nama : Fl. Juliani
Nomor Mahasiswa : 051214139
Demi pengembangan ilmu penegtahuan, saya memberikan kepda Perpustakaan Universaitas Sanata Dharma karya ilmiah saya yang berjudul:
TEACHERS’ PERCEPTION ON THE USE OF PICTURES IN TEACHING ENGLISH TO YOUNG LEARNERS
beserta perangkat yang diperlukan (bila ada). Dengan demikian saya memberikan kepada Perpustakaan Universitas Sanata Dharma hak untuk menyimpan, mengalihkan dalam bentuk media lain, mengelolanya dalam bentuk pangkalan data, mendistribusikan secara terbatas, dan mempublikasikannya di internet atau media lain untuk kepentingan akademis tanpa perlu meminta ijin dari saya maupun memberikan royalti kepada saya selama tetap mencantumkan nama saya sebagai penulis.
Demikian pernyataan ini yang saya buat dengan sebenarnya.
Dibuat di Yogyakarta
Pada tanggal: 20 September 2010 Yang menyatakan
vi ABSTRACT
Juliani, Fl. (2010).Teachers’ Perception on the Use of Pictures in Teaching English to Young Learners. Yogyakarta: English Language Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University.
There are a lot of factors that influence the teaching process. Media became one of them. The appropriate media would facilitate learning and help the teachers in teaching. However, the teachers’ perception on the use of certain media influences the behavior and the motivation of the teachers in teaching and finally will affect the teaching and learning process. Picture is one of media used by teachers in teaching to young learners. Because of those reasons, the researcher was interested to seek and explore the teachers’ perception on the use of pictures in teaching English to young learners. There were two research questions in this study: 1) What are the teachers’ perception on the use of pictures in teaching English to young learners? 2) What are teachers’ recommendations the use of pictures in teaching English to young learners?
To answer the problem formulation, the researcher conducted a survey research. The respondents were 20 young learners’ teachers around Yogyakarta and Klaten who graduated from English Education Study Program and had experiences in teaching children at least for six months. The researcher used two instruments in this research. They were questionnaire and interview. The questionnaire consisted of 20 close-ended questions and 1 open-ended question whereas there were 8 questions in the interview. The researcher applied Likert scale to measure the teachers’ attitude toward the questions. The interview was conducted to verify the questionnaire result and to dig out more information.
The findings showed that all the teachers who participated in this research had positive perception toward the use of pictures in teaching English to young learners. All the teachers said that pictures were effective media in teaching to young learners because it was suitable with the concrete cognitive level of children. The teachers also admitted that both the teachers and the students obtained positive outcomes from using pictures in teaching English to young learners. Besides, the teachers became more confident and motivated in teaching because their students enjoyed learning using pictures.
vii ABSTRAK
Juliani, Fl. (2010).Teachers’ Perception on the Use of Pictures in Teaching English to Young Learners. Yogyakarta: Fakultas Keguruan dan Ilmu Pendidikan , Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Ada banyak faktor yang memepengaruhi proses pembelajaran. Salah satunya adalah media pembelajaran. Media yang tepat akan memfasilitasi belajar dan membantu guru dalam mengajar. Akan tetapi, persepsi guru terhadap media tertentu mempengaruhi tingkah laku dan motivasi guru dalam mengajar dan pada akhirnya akan mempengaruhi proses belajar dan mengajar. Gambar adalah salah satu media yang digunakan oleh guru dalam pembelajaran bahasa Inggris untuk anak-anak. Karena alasan tersebut, peneliti tertarik untuk mencari dan menyelidiki persepsi guru terhadap penggunaan gambar dalam pembelajaran bahasa Inggris untuk anak-anak. Ada dua rumusan masalah yang dikaji dalam penelitian ini: 1) Bagaimana persepsi para guru terhadap penggunaan gambar dalam pembelajaran bahasa Inggris untuk anak-anak? 2) Saran-saran apa saja yang para guru berikan terhadap penggunaan gambar dalam pembelajaran bahasa Inggris untuk anak-anak?
Untuk menjawab rumusan masalah tersebut, peneliti menggunakan penelitian survei. Para responden adalah 20 guru anak-anak yang berada disekitar daerah Yogyakarta dan Klaten yang menamatkan pendidikan S1 nya di jurusan Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris dan memiliki pengalaman mengajar behasa Inggris untuk anak-anak paling sedikit selama 6 bulan. Peneliti menggunakan dua instrumen dalam penelitian ini, yaitu kuesioner dan wawancara. Kuesioner terdiri dari 20 pertanyaan tipe terutup dan 1 pertanyaan tipe terbuka sedangkan wawancara terdiri dari 8 pertanyaan. Peneliti menggunakan skala Likert untuk mengukur tingkah laku para guru terhadap pernyataan-pernyataan pada kuesioner. Selanjutnya, wawancara dilakukan untuk membuktikan hasil kuesioner dan untuk menggali informasi yang lebih banyak.
Hasil penelitian menunjukkan bahwa semua guru yang berpartisipasi dalam penelitian ini memiliki persepsi positif terhadap penggunaan gambar dalam pembelajaran bahasa Inggris untuk anak-anak. Hampir semua guru mengakui bahwa gambar adalah media yang efektif untuk anak karena sesuai dengan tingkat kognitif anak yang konkret. Para guru juga mengakui bahwa baik para guru maupun para murid mendapat hasil yang positif dari menggunakan gambar. Selain itu, para guru menjadi lebih percaya diri dan termotivasi dalam mengajar karena murid mereka menyukai proses belajar dengan menggunakan gambar.
viii
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
First of all, I would like to thankJesus Christfor giving everything which is
the best for me. Jesus is my truly savior because He gave me what I needed instead of
what I wanted. Therefore, I could pass all the obstacles and pressure in finishing my
thesis. Anyway, there were so many people who gave contributions during the
process of writing this thesis and this is the best time to express my deepest gratitude
to them all.
I would like to say my deepest gratitude to my major sponsor, Christina
Kristiyani, S.Pd .,M.Pd., for her patient, support, guidance, understanding, and
corrections that enable me to finish this thesis. I would also like to thank all the
educators in English Education Program for giving me knowledge and support and
for helping me to be a better student. I am lucky to be their student.
My gratitude also goes to all the young learners’ teachers who became my
respondents in this research. I cannot mention them all, but I sincerely thank them for
their willingness and their time in helping me finishing my research. Without their
help and valuable information, this research could not be done well.
I would also like to express my deepest gratitude to my beloved parents for
their support, prayers and loving, so that I could get through all the obstacles. I would
also like to thank my brothers and sisters for their prayers, support and patience
ix
My gratitude also goes to someone special, Guntur Andy Saputra, for his
loving, patience, support and prayers. I thank him for giving me encouragement and
happiness and for helping me passed through difficult moment during I wrote this
thesis. I would also thank all my friends, especially Novi for her help, Andre and
Putu Verdi for giving corrections on my thesis, Esti for helping me finding some
respondents, Mba Ratih for helping me and give me support, Funy, Gendis, Dea,
Pram, Wiwin, Dion, Marshel, Sedik, Lidya, Sherly, Christine and all students of
PBI 2005 for giving me happiness and support every time I need.
Further, I would also thank anyone whose name cannot be mentioned all for
giving me encouragements and prayers. I believe God will bless you all.
x
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page
TITLE PAGE……….... i
APPROVAL PAGES………... ii
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY……… iv
LEMBAR PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI KARYA ILMIAH UNTUK KEPENTINGAN AKADEMIS v ABSTRACT……….. vi
ABSTRAK………. vii
AKNOWLEDGMENTS……….. viii
TABLE OF CONTENTS………. x
LIST OF TABLE………... xiii
LIST OF APPENDICES……….. xiv
CHAPTER I. INTRODUCTION………. 1
A. Research Background……… 1
B. Problem Formulation………. 5
C. Problem Limitation……… 5
D. Research Objectives……….. 6
E. Research Benefits……….. 6
F. Definition of Terms………... 7
CHAPTER II. RIVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE………... 9
A. Theoretical Description……….. 9
1. Pictures……… 9
xi
b. Criteria for Good Pictures………... 11
2. Young Learners………... 13
a. The Definition of Young Learners……….. 13
b. The Cognitive Development of Young Learners……… 13
c. The Learning Strategies of Young Learners………... 16
d. Teaching English to Young Learners……….. 18
3. Perception and Perception Process……….. 21
B. Theoretical Framework……….. 23
CHAPTER III. METHODOLOGY………. 26
A. Research Method………... 26
B. Research Participants………. 27
C. Research Instruments………. 27
D. Data Gathering Technique………. 29
E. Data Analysis Technique………... 31
F. Research Procedure………... 35
CHAPTER IV. RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION……… 36
A. Teachers’ Perception on the Use of Pictures in Teching English to Young Learners………. 36
1. Teachers’ Perception on the Use of Pictures in Teaching English to Young Learners Based on the Questionnaire………... 37
2. Teachers’ Perception on the Use of Pictures in Teaching English to Young Learners Based on the Interview………... 43
3. Discussion ………... 46
xii
Pictures in Teaching English to Young Learners Based on the
Questionnaire………... 49
2. Teachers Recommendation to Improve and to Maximize the Use of Pictures in Teaching English to Young Learners Based on the Interview……….. 52
3. Discussion……… 53
CHAPTER V. CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS………... 56
A. Conclusions………. 56
1. Teachers’ Perception on the Use of Pictures in Teaching English to Young Learners………... 56
2. Teachers Recommendation to Improve and to Maximize the Use of Pictures in Teaching English to Young Learners……… 57
B. Suggestions……… 58
REFERENCES……….. 60
xiii
LIST OF TABLE
Page
xiv
LIST OF APPENDICES
Page
APPENDIX 1 The Questionnaire Sheet……….. 64
APPENDIX 2 Interview List………... 67
APPENDIX 3 Blueprint of Questionnaire Result (Close-ended
Questions) ………... 68
1 CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
This chapter provides the research background of the study which presents the
background information of selecting the subject matter, presents the motivation why
the researcher wants to do the research on the subject matter, and the goals of
conducting this research.
A. Research Background
In this globalization era it is not strange to hear people communicate using
English as their foreign language though it is not their first language. English as an
International language has also influenced our education. The Instructional Program
Guideline of the English syllabus states that English is the first foreign language in
Indonesia and it is considered as an important language to develop science,
technology, art and culture to maintain a relationship with other countries
(Depdikbud, 1994:1).
The 1994 curriculum states that the goal of teaching English to elementary
school students is to motivate or to encourage the students to be more ready and
knowledge, skills and experiences in English before they enter the higher level of
study which put them at the higher level of difficulties (Depdikbud, 1994:1).
Being considered that English is needed to be learnt, the government
constructed a curriculum which introduced English to the Elementary students of the
fourth to the sixth grades. Furthermore, in order to improve our education, the
government created a new curriculum in 2006, called School Based Curriculum
(SBC).In this curriculum, English has a position as the local content subject which is
expected to help the students to recognize themselves, their culture and other people’s
culture, to help the students to be able to express their ideas and feeling, participate in
the society and to help the students to use their analytic and imaginative ability
(Karsidi, 2007).
Nowadays, this improvement can be observed clearly. One of the changes is
that English is not only introduced to the elementary students of grade four as the
1994 curriculum stated but also to the earlier ages. It is not strange if we can find
easily schools which introduce English to the first or second graders. This means that
English teachers should deal with younger learners in which it is not easy and
sometimes it arise problems. This situation creates an awareness that we have to learn
and recognize their characteristics wisely.
Further, according to Hurlock (1978), there is a big difference between
children of five can do and children of ten can do, some children develop early and
some children later (Hurlock, 1978). Therefore, it is important to understand clearly
adaptable and ready to explore new methods in promoting learning by seeing the
learning situation from a child’s point of view (Anning, 1998) . From this point, it can
be concluded that learners’s characteristics become a fundamental consideration to
determine the teaching and learning process. In this case, the pupils are the children
of elementary school at the age of seven to ten who usually want to make sense out of
things, find how things work, gain competence and control over themselves (Smith,
1982)
One of the characteristics that should be considered is children cognitive level
which also determines the way they receive information. According to Piaget’s
periodization of cognitive development, children are included in the concrete
operational which begins at age 7 to 11 years old (Clarke, 1985: 308). Faw (1980)
also supports Piaget’s theory that he categorizes children in this age into the
concreteness period in which children can solve problems that can be experienced in
concrete ways (Marjito, 1997). This theory has been investigated by Wasiati (1995:
xi-xii) in her thesis on “Picture test for English beginner: design and validity”. She
stated that the use of picture test is related to and suitable for children cognitive
development according to Piaget’s division (Wasiati, 1995). It can be seen that the
existence of picture can accommodate children in understanding things. As Nelson
(1989) quoted from Marjito’s (1997) said that by using picture drawing, it can
eliminate the necessity for the students to translate from his native language into his
second language so that pictures and text altogether enable the students to attain a
Besides, some efforts on the use of picture in language teaching have been
made by several experts in the field which show the advantages of using pictures in
teaching process. L Bening Perwitasukci (1991) has done her investigation on the use
of pictures in language teaching in 1991. She used pictures to teach English
conversation. In her research she concludes that pictures help students focus their
attention and avoid boredom. With pictures, teachers can provide students with an
interesting atmosphere in the classroom (Perwitasukci, 1991).The same situation can
also be found in some schools such as SD Putra Bangsa Klaten. The teachers there
used pictures in teaching and learning activities in order to help them when they
explain things and it seemed that the pictures as the media help them in the teaching
and learning process.
From the previous researchers and the observation, it is obvious that the
existence of pictures in language teaching and learning is important. The presence of
picture in teaching and learning can be effective media in the teaching process.
According to Vygotsky (1978), teachers work actively in improving children
development in learning. Therefore, both the role of teachers and the role of students
in the teaching and learning process are important. Those previous studies that have
been done by Wasiati and Perwitasukci were investigated in order to see the role of
pictures in teaching from students’ point of view. In this research, the researcher
wants to seek out the perception of young learners’ teachers on the use of pictures in
teaching English and some recommendations to improve and to maximize the use of
the use of pictures will influence their behavior and will finally influence the teaching
and learning process.
B. Problem Formulation
From our discussion on the background of the study, the researcher wants to
address two research questions, they are as follows.
1. What are the teachers’ perceptions on the use of pictures in teaching English
to young learners?
2. What are the teachers’ recommendations to improve and maximize the use of
picture in teaching English to young learners?
C. Problem Limitation
The discussion of the teachers’ perception on the use of pictures in teaching
English to young learners is needed to be limited to make the study possible to be
investigated in-depth. The researcher focuses on digging and exploring any
information related to the teachers’ perception, including opinion attitude and feeling
on the use of pictures in the teaching and learning activities and the possible
recommendations to improve and to maximize the use of pictures in teaching English
to young learners.
Furthermore, the study focuses on the perception of the young learners’
teachers from some schools around Yogyakarta and Klaten. Additionally, the young
learners are the group of children in the age of 7-9 years old or students in the first
grade to third grade of elementary school. The researcher chose this age in order to
seek out Piaget’s theory that is children’s cognitive level in the age of 7-11 includes
in concrete level. Therefore, in order to dig richer data, the researcher chose the
young learners’ teachers who teach English for the first grade to the third grade of
elementary school.
D. Research Objectives
This study is formulated to answer the research questions that are teachers’
perceptions on the use of pictures in teaching English to young learners and the
recommendation to improve and to maximize the use of pictures in teaching English
to young learners. Therefore, the researcher tends to investigate and to explore
teacher’s perception on the use of pictures in teaching English to young learners.
E. Research Benefits
The findings of this research are expected to give positive contribution to
these following people.
1. The Young Learners’ Teachers
This research provides clear information about perceptions of the teachers in
using picture in teaching English to young learner. It is hoped that the information
also expects that after knowing the result, the other young learners’ teachers who use
pictures will get some beneficial recommendation from this research.
2. The other researchers
Hopefully, the result of this research will give stimulation for the other
researchers who have interest in investigating related studies. Moreover, it is also
expected that the information of the teachers’ perception in the use of picture in
teaching English to young learners will enrich their knowledge.
F. Definition of Terms
There are several terms that need to be clarified related to the research. The
terms are as follows.
1. Perception
This study explores teacher perception on the use of pictures in teaching
English to young learners. Suparinah (1986) defines perception as an active process
in which a person views a stimulus together with his experiences, motivation, and
attitude (Suparinah, 1986). According to Kemp and Smellie, perception is the process
whereby one becomes aware of the world around oneself (Kemp and Smellie, 1989).
They defined perception as a cognitive process in which a person views information
and environment through listening, seeing, smelling, feeling, and thinking. They also
describe perception as a unique interpretation toward particular phenomenon.
Based on definitions above, in this research, perception deals with the way
2. Picture
Duffy and Walter (1985: 249) define picture as some hand-made images that
relate, however, distantly to the appearance or structure of real or image things. On
the other hand, Heinich (1982:84) has a simpler description about picture. He defines
picture as photographic representation of people, places, things that are usually taken
from books, catalogues, and study prints or magazines.
The pictures in this study deal with the images related to the appearance of
real image things, made by the teachers or taken from books which are used in pre
activity, main activity and post activity in the classroom.
3. Young learners
According to Suyanto (2007), young learners are elementary students in the
age of 6-12 years old. They have learned English since they are at the age of 6-12
years old. They are also known as beginners when they learn English in this age.
Another description of young learners is given by Smith (1982:16). He divided the
young learners into two levels, namely, the primary grade and the intermediate grade.
The primary grade is the level of students in the first three years in elementary school,
whereas the intermediate grade is the level of the students in the last three years in
elementary school.
In this research, the researcher tends to use the definition of young learners in
9 CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
In this chapter, the writer would like to provide theoretical description and
theoretical framework of this study. The theoretical description discusses some
theories related to this research whereas the theoretical framework discusses major
relevant theories which help in answering the reaserch questions.
A. Theoretical Description
In this part, the researcher would like to describe some underlying theories
related to the study. They are the theory of pictures, the theory of young learners, and
the theory of perception.
1. Pictures
In this part, the researcher would desrcribe the theory of pictures in Teaching
and learning process and the criteria of good pictures
a. Pictures in Teaching and Learning Process
Pictures are widely used in teaching and learning process. As Heinich (1982)
states that concrete experiences facilitate learning and the acquisition, retention, and
usability of abstract symbols. Further, he says that pictures as instructional media not
only provide necessary concrete experiences, but also help students to integrate their
Rawntree (1990) in his book entitledTeaching through Self Instructionstates
ten possible functions of pictures in teaching and learning process. First, pictures can
be used as decoration. It is used in order to relieve the monotony of solid print.
Almost any kind of pictures can serve the reader a visual break that helps them to be
motivated to carry on reading. Second, the use of pictures is amusement in which
some pictures, cartoons in particular, can more deliberately motivate the reader by
humanizing the subject and showing its lighter side. Therefore, readers can highlight
a key point and make it memorable. Third, pictures can be used to show expression in
which readers can convey an emotion and feeling expressively. Thus, photographs
might be used to involve the reader in some situation of conflict or confrontation.
Forth, pictures can be used as persuasion in which pictures can persuade readers
towards a change of attitude. Fifth, pictures can be used as illustration. Sixth, pictures
can be used as description. The picture is meant to convey a necessary understanding
that could not be conveyed in words alone. It shows what something looks like.
Seventh, pictures can be used as explanation in which pictures describe what thing
looks like. They show how they work, or how they can be operated. Eighth, pictures
can be used as simplification in which pictures offers us a means of simplifying
reality. Ninth, pictures can help us in quantification in which we need to consider
quantities, compare sizes, and recognize changing proportions, thus pictures often
help the learner present the data pictorially. The last, pictures can be used in problem
solving in which pictures can create a problem or question to learners (Rawntree,
In addition to what Rawntree describes about the functions of pictures,
Hamalik (1994) states similar reasons of using pictures in teaching. First, pictures are
concrete. Students can see clearly the item being discussed through a picture. Second,
pictures overcome the time and space. For example, the teacher can bring Eiffel tower
to the class through pictures. Third, pictures can overcome the human senses
limitations. For example, we can see small materials clearly through a picture. Fourth,
pictures can be used to explain a problem. Fifth, pictures are cheap and are easily
gotten. Sixth, pictures are easily used both for individuals or a group of students.
b. Criteria for Good Pictures
To achieve the objectives of learning through pictures, the pictures that are
used must be good. There are some requirements that must be fulfilled of good
pictures. Newby (2000) in his book entitled Instructional Technology for Teaching
and Learning states some criterias of good pictures. First, use pictures that can
illustrate the ideas. Second, use simple pictures. Third, use harmonious colors.
Trisisca (1999) formulates the criteria of good pictures. They are as follow.
1. Simple
The first consideration in selecting pictures is that the pictures should be
simple. Using complex and too much details pictures may cause confusion for the
children. It will be suitable to select simple pictures as far as they can clarify the
2. Having no ambiguity
The sources of pictures are abundant but not all of them can be used in
teaching and learning process. Many of them have ambiguity. For example, there is a
picture of a boy who is sitting and holding a book. It is difficult to decide whether the
point is studying or reading. Therefore, we have to use pictures that can illustrate the
ideas clearly.
3. Must be in accordance with the students’ level of proficiency
Teachers should be selective in choosing the pictures which is in accordance
to the students’ level of proficiency. If the teachers select the pictures which are
difficult and not appropriate with the students characteristic, the students will feel
frustrate and bored in learning.
4. The size of the pictures depends on the class
The purpose of this consideration is to enable each student to see the pictures
clearly. If the students cannot see the pictures clearly, they might misinterpret the
pictures and might get bored easily because the pictures do not attract their attention.
5. The pictures must be related to the topic taught
The pictures are used to help the teachers deliver the topic discussion.
Therefore, the pictures should be related to the topic discussion in order to avoid
2. Young Learners
In this part, the researcher would describe the theories of young learners,
including the definition of young learners, the cognitive development of young
learners, the learning strategies of young learners, and the teaching English to young
learners.
a. The Definition of Young Learners
Acording to Suyanto (2007) young learners are the elementary students in the
age of 6-12 years old. They can be categorized into two groups, namely, younger
group in which the students are in the age of 6-8 years old and older group in which
the students are in the age of 9-12 years old. Based on the grade level, they also can
be put into two groups. They are lower classes and upper classes. The lower classes
are including students from grade 1, 2, and 3, whereas the upper classes include
students from grade 4, 5 and 6 (Suyanto, 2007). Additionally, Smith (1982: 16) also
categorize into two different levels: the first three years are called the primary grade
whereas the last three years are called intermediate grade.
b. The Cognitive Development of Young Learners
The young learners of this study are about 6-8 years old. According to Piaget’s
periodization of cognitive development, they are included in the concrete operational
which begins at age 7 to 11years old (Clarke, 1985: 308). The term concrete deals
with the fact that child can reason only about touchable objects, such as milk and
manipulates information for some purpose. It is also an integral part of an organized
network of related thinking.
Faw (1980), as quotes from Marjito (1997: 20) states the characteristics of
middle childhood’s cognitive development. They are as follows.
1. Concreteness: initially the world of middle childhood is still concrete. Problems
that can be solved are those that can be experienced in concrete ways
2. Egocentrism: children in the middle childhood no longer view the world from
their own unique vantage point. They have capability to realize that others
perceive the world differently. As the children become older, they may even
seek out an understanding of other perspectives in order to appreciate more
fully the problems.
3. Centration: children in the middle childhood can consider more than aspects of
a problem at the same time and their attention are not dominated by the
perceptual characteristics of a stimulus array. In essence, they can look from
one tree to another rather than focusing on the biggest tree. Thus, they can see
the forest as well as the individual trees.
4. Attention to transition as well as states: an important acquisition in the
cognition of middle childhood is the ability to conceptualize both the states
through which one moves in getting from one situation to another and the
process that allows for those changes to take place.
5. Reversibility: the understanding of the concept of reversibility is one critical
between states as well as the states themselves. In addition, to the symbolizing
the transition from state one to state two, the child can symbolically represent
the reverse transition, which returns things to their original state (Marjito,
1997:20)
Clarke (1985: 320) explains three important aspects in the concrete
operational development. First is reversibility. It refers to a major advance of concrete
operational thinking. Children in this stage can realize that milk poured from one
glass to another can be poured back again. They can perform inversion. It means that
children can recognize that the effect of one manipulation can be reversed by
applying the opposite. Second, is decenter. Decentering is focusing on and
coordinating two or more dimensions for example height and width. Children at this
stage recognize reciprocity – that one dimension, go beyond the narrowness of the
glass, may make up for or compensate for its other dimension, height. Third is the
ability to put manipulation of objects in symbolic form. In this period, children are
able mentally to represent and remember events and objects in symbolic forms.
From the quotations above, it is clearly stated that children in the middle
childhood can solve more than one problem at a time. In addition, Siegler (1991: 37)
adds that although children in concrete operational have capability in solving
problems, sometimes children find difficulties in certain types of abstract reasoning.
Consequently, the presence of concrete object such as picture will help them to
c. The Learning Strategies of Young Learners
The way of children learning strategies will be different from adult learners.
According to Anning (1991), behaviorism gives strong influence to our views on how
children learn language. They said that the view lead us to see children as a blank
slate who learned by giving reaction passively to different kinds of stimuli and also
positive and negative feedback they received. In contrary, Piaget said that children
are actively constructing his or her own thinking by acting upon the physical and
social environment. Children learning strategies are influenced by their physical and
their environment. Accordingly, it will be difficult to teach children if they are not
ready yet to learn (Anning, 1991). Hence, it can be accepted that Piaget thought that
the role of language and the role of adults did not influence the way children learn
something.
As Vygotsky (1978) said as the contrary of Piaget theory that the role of the
adult and language in children’s learning are very important. There is a difference of
both theories Piaget and Vygotsky. Piaget believes that children learn through his or
her own individual action and exploration, whereas Vygotsky believes that adults/
teachers work actively to improve children development in learning (Vygotsky,
1978).
According to Anning (1998), in the early 1990’s most British teachers of the
young learners believe some theories as follows.
1. Children develop in sequential stages. According to Anning, children learn
recognize the learning level of children to help them in understanding things. By
understanding the learning level as well as understanding children characteristics,
teachers are able to select the appropriate media, activities, learning style and
materials.
2. Most teachers believe that children learn through concrete experiences,
particularly structured play. Children need to think in a simpler way rather than
complicated one. This can be accommodated by the existence of pictures. In order to
remember the name of some animals, teachers can help the children by showing the
pictures when students visited the zoo. By looking at the pictures, the children will
memorize the name of the animals.
3. In social development, children move from egocentrism to be more socializing.
In the school, children learn how to become social being. Teacher’s role is needed in
encouraging children to realize the value of working together in a group or pairs. In
teaching young learners, creative teachers are needed in creating a good atmosphere
of learning. In order to create a joyful learning, teachers can select some media,
activities, technique, as well as materials.
4. Children need to develop competence in their first language to function
efficiently as learners. In order to understand the second language, in this case
English, children have to master their first language to help them in communication
and understand things.
5. Every child is an individual learning in their own unique way. It implies that
and understanding to each new learning situation. Anning (1991) adds that it is
important to keep insight into the uniqueness of each child to respect their
individuality but we also need to concern and to recognize the similarities.
Multiple intelligences are also known as one of learning styles. Berman
(1998) said that we take in information in line with our learning style. If students are
visual learning, they will mainly gain the information through eyes. In other case, if
students have mainly auditory learning style; therefore information will be learned
through hearing, whereas if students have mainly bodily kinesthetic learning style,
they will easily learn something through movement or manipulating things. These
three learning style provided by Berman (1998) are also suggested by Gardner (1993)
in his theory of multiple intelligences. They are linguistic intelligence,
logical-mathematical intelligence, spatial intelligence, musical intelligence, kinesthetic
intelligence, interpersonal intelligence, and intrapersonal intelligence (Gardner, 1993)
d. Teaching English to Young Learners
Berman (1998) mentions about learning style, he states there learning styles,
such as visual learners, auditory learners and kinesthetic learners. There are some
teaching activities that can accommodate the learning styles.
a. Visual learners
The learners understand the content of the lesson by seeing through their eyes.
Therefore, teachers can present something that can be seen by the learners, such as
pictures, diagrams, videos and hand-outs. The techniques for this style can be games
b. Auditory learners
The learners will learn best through their ears. Therefore, the technique for this style
can be through songs. Children can learn something easily through songs. By
listening to the songs, they can learn the pronunciation of words, numbers, and
animals.
c. Kinesthetic learners
The learners will learn best by doing something and moving their body. The
technique for this style can be TPR (Total Physical Response). For example, children
can learn parts of body by touching their body and they can learn something by
dancing or acting.
In addition to 7 intelligences introduced by Gardner (1993), Campbell et al.
(1996) elaborates the intelligences into learning styles that consider children’s
characteristics. They are as follows.
1. Linguistic Intelligence
Teachers can provide models by playing with words. Therefore, story telling becomes
one of familiar styles of linguistic intelligence in which young learners can develop
their intelligences in linguistic by using their ability in selecting words and language.
2. Logical Mathematical Intelligence
This intelligence is related with mathematic, science and logic and numbers. The
most interesting technique which can be implemented to develop this intelligence is
3. Visual-Spatial Intelligence
This intelligence includes an aggregate of related skills that encompasses visual
recognition. In the ages of young learners, many visually oriented learners respond
well to movies, television, slides, posters, colorful images (Campbell et al, 1996). To
develop this intelligence there are techniques that can be implemented, such as,
puzzle building, watching movie, drawing, coloring pictures, and observing pictures.
4. Bodily-Kinesthetic Intelligence
This intelligence is described as the ability to unite body and mind to perfect physical
performance. The technique for this intelligence are TPR (Total Physical Response),
dancing, acting, and sports.
5. Musical Intelligence
Children immediately respond to music either appreciating or criticizing what they
hear. The techniques for this intelligence can be singing, playing instruments and
remembering melodies.
6. Interpersonal Intelligence
This intelligence enables us to deal and communicate with others. In the age of young
learners, it is a bit difficult to develop this, since they are more comfortable working
by their own. That is why the teacher’s role is really important to encourage the
learners to works with others. Grouping will be the best way to develop this
7. Intrapersonal Intelligence
This intelligence deals with personal activities. Teachers may ask the learners create a
thing that they are interested in, drawing a picture to express their feeling, and
coloring pictures to show what they feel.
3. Perception and Perception Process
Perception is the process whereby one becomes aware of the world around
oneself (Kemp and Smellie, 1989). In perception we use our sense to catch objects
and event. Through our senses, such as eyes, ears, skin, and so on, we maintain
contact with our environment.
Kemp and Smellie (1989) also provide to major importance of perception.
First, any perceptual event consists of many sensory massages that do not occur in
isolation but are related and combined into complex patterns. These become the basis
of person’s knowledge of the world. Second, an individual reacts to only a small part
of all that is taking place at any one instance. The part of an event to be experienced
is selected by a person on the basis of desire or what attract his or her attention at any
one time (Kemp and Smellie, 1989).
Kemp and Smellie (1989) argue that the experience of perception is individual
and unique. The perception of two different people will not similar because a person
perceives an event in terms of individual past experiences, present motivation, and
present circumstances. Additionally, they state that while any one perceptual
related to become nearly identical. Thus a succession of individual experiences
enables us to agree upon what we have experienced, even though the individual
experiences are somewhat different.
Fleming and Levie (1978) mention the basic principles of perception. First,
perception is relative rather than absolute since it provides reference points to which
unknown objects or events can be related and it also presents a difficult concept
through small steps. Second, perception is selective, since it will limit the range of
aspects being presented to essential factors. Third, perception is organized. It uses
numbering and verbal clues to give order to a massage. Forth, perception is
influenced by expectation. It provides instructions that call attention to elements or
directions for finding an answer in an illustration.
Fleming and Levie (1978) also state the relation between perception and
cognition. The better an object or event is perceived (by means of applying the
perception principles), the more feasible and reliable will be memory, concept
formation, problem solving, creativity, and attitude change.
Perception is also defined as an active process of selecting, organizing, and
interpreting their sensory impression in order to give meaning to their environment
(Robbins, 2001: Huffman, Vernoy& Vernoy, 2002) together with his experiences,
motivation, and attitudes (Suparinah, 1986). There are three basic perceptual
processes based on Huffman, Vernoy& Vernoy (2002). The first basic perceptual
process is selection. Every person may select certain stimuli as incoming information
case, motivation, personal needs, and interests have a role in selecting stimuli. The
second basic perceptual process is organization. In order to form a meaningful
pattern, the selecting stimuli should be organized. The last basic perceptual process is
interpreting. After selecting stimuli and organized it into pattern, then make an
interpretation. Interpretation is influenced by some factors; they are life experiences,
perceptual expectation, cultural factors, and personal motivations, needs, and interests
(Huffman, Vernoy& Vernoy, 2002; Bootzin, Loftus & Zajonc, 1979)
After selecting certain stimuli, someone can organize then interpret the stimuli
meaningfully. Furthermore, as the response of the stimuli, people will react to the
stimuli in the form of behavioral response or attitudes whether the response is
negative or positive.
B. Theoretical Framework
Pictures have been implemented as media in teaching and learning process.
The presence of pictures can help the teachers in creating a joyful atmosphere in the
classroom, especially for young learners. Based on the School Based Curriculum’s
socialization, English learning for elementary school should be active, creative,
effective and joyful learning. Besides, pictures are also believed as effective media in
helping the children in learning things. According to Pieget, children at the age of
7-11 years old are categorizing in the concrete levels (Clarke, 1985) in which children
can solve problem in a concrete way. On the other hand, Hamalik (1994) states one of
concreteness. He also believes that pictures can accommodate the children’s
characteristics.
The other theories which also supported Hamalik’s theory are the functions of
pictures. Rawntree (1990) mentions that amusment and description become two of
the pictures functions in which those functions can more deliberately motivate the
learners in learning and can help the learners understand something that cannot be
explained in words alone. Therefore, these theories can help the researcher
understands the role of pictures in teaching process especially teaching English to
young learners.
Furthermore, in answering the first problem formulation, the researcher used
the theories about perception. The researchers need to know the definition of the
perception to help the researcher in understanding how the perception is formed.
However, the way the teachers perceive something, whether it is in positive or
negative way, influences the teachers’ behavioral responses (Altman et.al, 1985: 86).
Therefore, the behavioral responses could be positive responses or negative responses
and it depends on the teachers’ perception. If the teachers perceive the use of pictures
in teaching English to young learners in a positive way, the teachers’ behavioral
responses would be positive, whereas, if the teachers perceive the use of picture in
teaching young learners in a negative way, the teachers’ behavioral responses would
be negative. Besides finding the teachers’ perception on the use of pictures in
recommendations on the use of pictures to maximize and to improve the use of
26 CHAPTER III
METHODOLOGY
This chapter presents specific discussion about the methodology of this study.
There are six sections, including description of the research method, research
participants, research instruments, data gathering technique, data analysis technique
and research procedure.
A. Research Method
In this research the researcher attempted to found the teachers’ perceptions on
the use of picture in teaching English to young learners. To accomade the study, the
resercher conducted survey research. According to Wiersma (1995), survey is also
used to answer the study, which is related to social and emotional aspects. In
addition, Ary, Jacobs and Ravazieh (2002:381) define a survey as a kind of research
method for gathering data ranging from physical counts and frequencies to attitudes
and opinions by asking some questions of a group of people called respondents The
survey of this study took the form both the questionnaire and interview. In order to
obtain clear information, the researcher collected the information from sample rather
B. Research Participants
The participants of this research were 20 young learner’s teachers who
graduated from the English Language Education Study Program. The participants are
also teachers who have at least six-month experiences in teaching young learners. The
researcher believed that by having more experiences, the participants would give
depth information about their perception on the use of pictures in teaching English to
young learners. In order to obtain representative sample of population, the researcher
used purposive sampling technique. As Guba and Lincoln (1981) states that sampling
is almost never representative or random but purposive, intended to exploit
competing views and fresh perspectives as fully as possible. Consequently, the
researcher chose the 20 teachers purposively around Yogyakarta and Klaten as the
subjects of this research.
C. Research Instruments
In this study, the researcher utilized two instruments, namely, questionnaire
and interview guide. The researcher employed quantitative and qualitative data. The
quantitative data were taken from the close-ended questions whereas the qualitative
data were taken from open-ended question and interview result.
1. Questionnaire
According to Ary, et al. (1990), questionnaire as a data gathering device is not
expensive and time-consuming. It is possible to comprise large number of the
By making use of a questionnaire, the researcher intended to assess data about the
teachers consisting of their thought and perception in accordance with the
implementation of pictures in teaching English to young learners.
In this questionnaire, the researcher provided two types of questions. They are
open-ended question and close-ended question. For the close-ended question, the
researcher provided 20 statements related to the teachers’ thought, feeling and view
on the use of pictures in teaching English to young learners while for the open ended
questions, the researcher only provided 1 question related to the suggestions of the
young learners’ teachers on the use of pictures in teaching and learning process.
In this study, the researcher used Likert scale, a scale with a number of points
that provides ordinal scale measurement (Wiersma, 1995). The score of each column
is from 1 to 4. The high score represent positive answer in responding the
questionnaire while the low score represent the negative answer. To make the
explanation of the score clearer, the researcher provided the score of each column
concerned the following agreements,
1 was for totally disagree
2 was for disagree
3 was for agree
2. Interview
In order to verify the result of main instrument, the researcher used interview
as the second devices to collect the data. Fatterman in Fraenkel and Wallen (1993:
385) stated that interview is the most important data gathering technique a qualitative
research possesses. The interview was set to make certain of the data and also to
recheck the teachers’ answer in the questionnaire. According to Cohen et al (2000),
“the use of interview in research marks a move away from seeing human subjects as
simply manipulable and data somehow external to individuals and toward regarding
knowledge as generated between human, often through conversation”. To make the
interview effective, the researcher chose three participants as the representative of all
participants. They are teacher who has the highest score on the questionnaire, teacher
who has the lowest score on the questionnaire and teacher who has the most
interesting answer on the questionnaire. In the interview, the researcher provided
some questions to investigate the teachers’ perception on the use of pictures. The
questions were about the teachers’ thought and feeling when they used pictures, the
reasons in choosing pictures in teaching process, the advantages and disadvantages of
using pictures, and the suggestions on the use of pictures in teaching process.
D. Data Gathering Technique
The first data were collected from the questionnaires. In this research, there
were 20 respondents who were selected by purposive sampling method. The
respondents were young learners’ teachers who have experiences in teaching English
to young learners using pictures. As Huffman and Vernoy say that the previous
experiences will influence the perception of the perceiver (Huffman, Vernoy &
Vernoy, 2002). Therefore, the researcher believed that by having at least six month
experiences in teaching English to young learners, they would able to perceive the
use of picture in teaching and learning process.
Furthermore, before the researcher distributed the questionnaires to all the
respondents, the researcher had to make an appointment first to make sure that the
researcher met the respondent. Besides, the researcher also provided brief explanation
about the research and asked for permission to the respondent to be willing to
participate to this research. The researcher preferred to distribute the questionnaire in
the end of the class, so that it would not disturb the teaching activities in their
classroom. Being realized that the teachers were busy with their own tasks, the
researcher distributed the questionnaire and made a new appointment with the
respondents to collect the questionnaire. However, some of the respondents preferred
to submit the questionnaire to the researcher on the same day.
The second data were collected by conducting the interview. The interview was
conducted after the respondents filled the questionnaires in order to recheck and
enrich the data from previous instrument. The researcher only chose three young
learners’ teachers as the interviewee. Therefore, the researcher chose the interviewee
based on young learners’ teachers who had interesting answer on their questionnaire
representatives of both who has positive and negative answer in their questionnaire.
The researcher interviewed the young learners’ teachers one by one on different day
to avoid the researcher from being exhausted and to respect the participants’
schedule. During the interview, the researcher chose to use tape recorder in order to
avoid missed data and the researcher also took notes to make sure that the researcher
had reserve data in order to avoid unexpected condition.
E. Data Analysis Technique
After gathering the data, the researcher analyzed the data by discussing them
based on two categories that were related to the problem formulation in this study.
The total response score helped the researcher in determining the perceptions of
young learners’ teacher on the use of pictures in teaching English to young learners.
The teachers who tended to choose the totally agree and agree column showed that
they had positive perception on the use of picture in teaching English to young
learners. On the other hand, teachers who tended to choose disagree and totally
disagree column showed that they had negative perception on the use of pictures in
teaching English to young learners.
In this study, the researcher made some classifications on perceptions of young
learners’ teachers based on questionnaire results. The categories of making these
classifications were based on the following consideration.
The maximum total score of agree was 60 (3x 20 items)
The maximum total score of disagree was 40 (2x 20 items)
The maximum total score of totally disagree was 20 (1x 20 items)
There are three classifications on perception of young learners’ teachers. They
are classifications to measure the perception of each respondent, classification to
measure perception of young learners’ teachers on each questionnaire statements, and
classification to measure the perception of total respondents.
1. Classification of perception based on each respondent
Based on the total score of each questionnaire, the classification on perception
of young learners’ teachers was described below.
20-35 : very bad perception
36-50 : bad perception
51-65 : good perception
66-80 : very good perception
From description above, it could be classified that the young learners’ teachers
had positive perception on the use of picture in teaching English to young learners if
he/she had total score x, in which 51≤ x ≤80 and the young learners’ teachers had negative perception on the use of picture in teaching English to young learners if
2. Classification of perception based on each statement
In this study, the researcher investigated 20 young learners’ teachers, so that the
total response of each statement ranged from 20 to 80. The score 20 was calculated
from 20x1 (the total amount of respondent x the score of totally disagree column (if
all the respondents answer “totally disagree” on the statement)) while the score 80
was calculated from 20x4 (the total amount of respondent x the score of totally agree
(if all the respondents answer “totally agree” on the statement)). This classification
was done by the researcher in order to see the response of each statement. The
response could be very bad, bad, good, or very good. The classification of response
ranges of young learners’ teachers was described as follows.
20-35 : very bad response
36-50 : bad response
51-65 : good response
66-80 : very good response
From description above, it could be classified that the young learners’ teachers
had positive perception on the use of picture in teaching English to young learners if
he/she had total score x, in which 51≤ x ≤80 and the young learners’ teachers had negative perception on the use of picture in teaching English to young learners if
3. Classification of perception based on total respondents
In order to conclude the perception of the young learners’ teachers on the use
of pictures in teaching English to young learners, the researcher analyzed total
response score of all the respondents. The total response score ranged from 400 to
1600. The score 400 was calculated from 20 x 20 x 1 (the total amount of respondents
x the amount of statements x the score of “totally disagree” column (if all the
respondents answer “totally disagree”)). The score 1600 was calculated from 20 x 20
x 4 (the total amount of respondents x the amount of statements x the score of “totally
agree” (if all the respondents answer “totally agree”)). Furthermore, the classification
on perception of young learners’ teachers was described below.
400-700 : very bad perception
701-1000 : bad perception
1001-1300 : good perception
1301-1600 : very good perception
From description above, it could be classified that the young learners’ teachers
had positive perception on the use of picture in teaching English to young learners if
he/she had total score x, in which 1001≤ x ≤1600 and the young learners’ teachers had negative perception on the use of picture in teaching English to young learners if
he/she had total score x, in which 400≤ x ≤1000. After doing these three classifications from close-ended questions, the researcher analyzed the two open
Furthermore, the researcher analyzed the data from the interview that was done
to verify and to enrich that data that the researcher already had. Then the researcher
triangulated all the data from questionnaire result and the interview.
F. Research procedure
First, the researcher decided the topic of the research and formulated the
research questions. In order to answer the research questions, the researcher designed
a set of questionnaire as one of the instruments which contained with several
statements. After designing the questionnaire, the researcher distributed the
questionnaire to the respondents. After distributing the questionnaires, the researcher
read the questionnaires and classified the data into some categories. In order to verify
and enrich the data, the researcher conducted interviews by selecting three
respondents who had the most interesting answer on their questionnaire. The last step
was the data analysis. All the data that the researcher had were gathered and
36 CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION
This chapter presents detail information about data gathered in this study. As
mentioned in Chapter 1, this research was conducted to seek out teachers’ perception
on the use of picture in teaching English to young learners and teachers’
recommendations to improve and to maximize the use of pictures in teaching English
to young learners. The findings were divided into two parts. They were part A that
explained the teachers’ perception and part B that explained the teachers’
recommendations.
A. Teachers’ Perception on the Use of Pictures in Teaching English to Young
Learners.
The data in this research were gathered by combining two instruments, they
were questionnaire and interview. The researcher would explain these instruments
separately. The researcher would present the teachers’ perception on the use of
pictures in teaching English to young learners based on data from questionnaire and
1. Teachers’ Perception on the Use of Pictures in Teaching English to Young
Learners Based on the Questionnaire
In order to answer the first problem that was teachers’ perception on the use
of pictures in teaching English to young learners, the researcher analyzed the 20
statements in the questionnaire in the form of table. The Table 4.1 is the distribution
of the close-ended statements and the results.
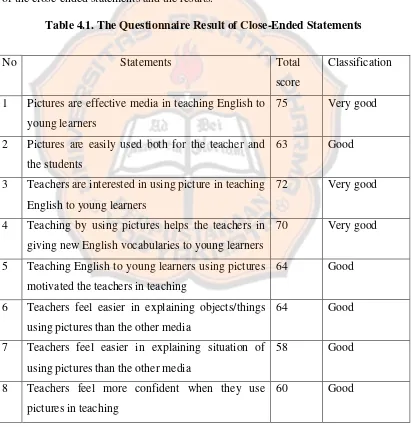
Table 4.1. The Questionnaire Result of Close-Ended Statements
No Statements Total
score
Classification
1 Pictures are effective media in teaching English to young learners
75 Very good
2 Pictures are easily used both for the teacher and the students
63 Good
3 Teachers are interested in using picture in teaching English to young learners
72 Very good
4 Teaching by using pictures helps the teachers in giving new English vocabularies to young learners
70 Very good
5 Teaching English to young learners using pictures motivated the teachers in teaching
64 Good
6 Teachers feel easier in explaining objects/things using pictures than the other media
64 Good
7 Teachers feel easier in explaining situation of using pictures than the other media
58 Good
8 Teachers feel more confident when they use pictures in teaching
No Statements Total score
Classification
9 Teaching using pictures spend more time in preparation
61 Good
10 Teaching using pictures spend more money in preparation
58 Good
11 Young learners will be happier in studying when they are taught by using pictures
68 Very good
12 Young learners will be happier in studying when 66 Very good they are taught by using pictures (based on
teacher’s experiences)
13 Young learners will be more excited in studying when they are taught by using pictures
67 Very good
14 Young learners will be more excited in studying when they are taught by using pictures (based on teacher’s experiences)
66 Very good
15 Children will understand easily the material of discussion by using pictures
65 Good
16 Children will understand easily the material of discussion by using pictures
65 Good
17 The teaching atmosphere were more fun when teachers use pictures (based on teacher’s experiences)
64 Good
18 Pictures are more concrete in which students can see clearly the items being discussed through pictures than other media
62 Good
19 Pictures in classroom can represent situation (e.g. pictures of zoo)
No Statements Total score
Classification
20 Teachers often use pictures in teaching to young learners
72 Very good
Notes:
20≤x≤35 : very bad response, categorized as negative perception 36≤x≤50 : bad response, categorized as negative perception 51≤x≤65 : good response, categorized as positive perception 66≤x≤80 : very good response, categorized as positive perception
Based on the questionnaire result above, it was clear that most of teachers
have positive perception toward the use of pictures in teaching English to young
learners. It could be seen from the classification on the table 4.1. Almost all of the
teachers had very good responses toward the effectiveness of the pictures as media,
teachers’ interest, the outcomes of using pictures for the teachers, the outcomes of
using pictures for the students, and the frequency of using pictures in teaching
(statements number 1, 3, 4, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 20). They also gave good responses on
the implementation of the pictures for the teachers and the students, teaching
motivation, the effects of using pictures for the teachers, the class’ atmosphere, the
concreteness of pictures and the function of pictures (statements number 2, 5, 6, 7, 8,
which teachers gave bad responses, which were statements number 9 and 10 about
the time and money consumed during the preparation.
The statement number 1 asked whether the teachers agreed that pictures were
effective media in teaching English to young learners. The score for this statement
was 75 in which almost all of the teachers had positive perception by admitting that
pictures were effective media in teaching English to young learners. The next
statement, which was statement number 2, asked whether the teachers admitted that
pictures were easily used by both the teachers and the students. The response for this
statement was good and categorized as positive perception in which teachers agreed
that both the teachers as well as the students could use pictures easily.
The statements number 3 wanted to seek out whether the teachers were
interested in pictures as media in teaching English to young learners. They gave very
good responses toward this statement in which the score was 72. This meant that the
teachers themselves are interested in pictures as media in teaching to young learners.
The statements number 4 up to number 8 showed the implications on the use
of pictures in teaching English to young learners for the teachers. The statement
number 4 showed that all the teachers admitted that the use of pictures helped them in
giving new vocabularies to young learners. This could be seen from the score of this
statement that was 70, which meant teachers had very good responses. The next
statement gave clear information that most of the teachers agreed that they were
motivated to teach better when they taught English to young learners by using