Christoper Tambunan, 2015
THE USE OF EDMODO TO MOTIVATE STUDENTS IN WRITING
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
THE USE OF EDMODO TO MOTIVATE STUDENTS IN WRITING (A Quasi Experimental Study in 10th Grade Students at a Senior High School in
Bandung)
Submitted to the English Education Department of FPBS UPI in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirement for Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
By
Christoper Tambunan
1005408
DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH EDUCATION
FACULTY OF LANGUAGE AND LITERATURE EDUCATION
INDONESIA UNIVERSITY OF EDUCATION
Christoper Tambunan, 2015
THE USE OF EDMODO TO MOTIVATE STUDENTS IN WRITING
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
THE USE OF EDMODO TO MOTIVATE STUDENTS IN WRITING (A Quasi Experimental Study in 10th Grade Students at a Senior High School in
Bandung)
Oleh
Christoper Tambunan
Sebuah skripsi yang diajukan untuk memenuhi salah satu syarat memperoleh gelar Sarjana Pendidikan pada Fakultas Pendidikan Bahasa dan Sastra
© Christoper Tambunan 2015 Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia
Juni 2015
Hak Cipta dilindungi undang-undang.
Christoper Tambunan, 2015
THE USE OF EDMODO TO MOTIVATE STUDENTS IN WRITING
Christoper Tambunan, 2015
THE USE OF EDMODO TO MOTIVATE STUDENTS IN WRITING
Christoper Tambunan, 2015
THE USE OF EDMODO TO MOTIVATE STUDENTS IN WRITING
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu ABSTRACT
Edmodo is a social-learning network that helps students, parents, administrators, and teachers collaborate about resources, assessment and content on a secure and safe learning management platform. This study utilised Edmodo to find out its effectiveness in motivating students in writing and to see the students’ responses towards the use of Edmodo itself. The subjects of this study were tenth grade students at Senior High School in Bandung. This study employed two different classes, namely experimental and control group. The result showed that the experimental group had improvement of pre-test and post-test from 64.8 to 71.6. While the control group had improvement from 67.2 to 68.8. It indicates that the experimental group got the improvement higher than the control group. Based on the statistical analysis by using SPSS, data showed that experimental group had tobt 3.781 with p=0,05, df=24, and tcrit 1,71. In other words, tobt > tcrit. It indicates that there is statistically significant improvement between pre-test and post-test in experimental group. In addition, the responses of students showed that almost 80% students agreed that Edmodo is interesting, flexible, as well as able to improve critical thinking, expression, confidence, motivation and writing.
Christoper Tambunan, 2015
THE USE OF EDMODO TO MOTIVATE STUDENTS IN WRITING
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu ABSTRAK
Edmodo adalah sebuah jaringan pembelajaran sosial yang membantu siswa, orangtua, pengelola, dan guru dalam mengkolaborasikan sumberdaya, penilaian dan isi dalam sebuah platform manajemen pembelajaran yang aman dan terjaga. Penelitian ini menggunakan Edmodo untuk mengetahui keefektifannya dalam memotivasi siswa dalam menulis and untuk melihat bagaimana respon siswa terhadap penggunaan Edmodo itu sendiri. Subjek dari penelitian ini adalah siswa kelas 10 SMA di Bandung. Penelitian ini menggunakan dua kelas yang berbeda, yaitu kelompok eksperimen dan kontrol. Hasil menunjukan bahwa kelas eksperimen berdasarkan pre-tes dan pos-tes memiliki peningkatan dari 64.8 menjadi 71.6. Sementara kelas kontrol dari 67.2 menjadi 68.8. Itu mengindikasikan bahwa kelas eksperimen meningkat lebih besar dari pada kelas kontrol. Berdasarkan analisis statistik dengan menggunakan SPSS, data menunjukan bahwa kelas eksperimen mempunyai tobt 3.781 dengan p=0,05, df=24 dan tcrit 1,71. Dengan kata lain, tobt
> tcrit. Hal ini menunjukan bahwa secara statistik ada peningkatan yang signifikan antara pre-tes
dan pos-tes dalam kelas eksperimen. Selanjutnya, respon siswa menunjukan bahwa hampir 80% siswa setuju bahwa Edmodo menarik, fleksibel, serta mampu meningkatkan berpikir kritis, ekspresi, percaya diri, motivasi, dan menulis siswa.
Christoper Tambunan, 2015
THE USE OF EDMODO TO MOTIVATE STUDENTS IN WRITING
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu TABLE OF CONTENTS
STATEMENT OF AUTHORIZATION ... Error! Bookmark not defined. PREFACE ... Error! Bookmark not defined. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT ... Error! Bookmark not defined. ABSTRACT ... Error! Bookmark not defined.
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... vi
LIST OF TABLES ... ix
LIST OF FIGURES ... x
LIST OF APPENDICES ... xi
CHAPTER I - INTRODUCTION ... Error! Bookmark not defined. 1.1 Background ... Error! Bookmark not defined. 1.2 Research Questions ... 3
1.3 Aims of the Study ... Error! Bookmark not defined. 1.4 Scope of the Study ... Error! Bookmark not defined. 1.5 Significance of the Study ... 4
1.6 Clarification of Key Terms ... 5
1.7 Organization of the Paper ... 5
CHAPTER II - LITERATURE REVIEW ... 7
2.1. Writing ... 7
2.1.1 The Nature of Writing ... 7
2.1.2. The Aspects of Writing ... Error! Bookmark not defined. 2.1.3. Process of Writing ... 9
2.2 The Principles and Strategies in Teaching Writing... 10
2.2.1 Basic Principles in Teaching Writing ... 10
2.2.2. Teaching Writing in Indonesian Context ... 11
2.2.3 Strategies in Teaching Writing... 12
2.3. E-Learning... 13
2.3.1 Types of E-learning ... 14
2.3.2. The Advantages of E-learning ... 16
2.4. Edmodo ... 17
Christoper Tambunan, 2015
THE USE OF EDMODO TO MOTIVATE STUDENTS IN WRITING
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
2.4.2 Edmodo in English Language Teaching ... 19
2.4.3 Edmodo in Teaching Writing ... 19
2.4.4 The Advantages of Edmodo ... 20
2.5. Motivation ... 21
2.5.1 Definitions of Motivation ... 21
2.5.2 Theory of Motivation: Self-Determination Theory ... 22
2.5.2.1 Intrinsic Motivation ... 23
2.5.2.2 Extrinsic Motivation ... 24
2.5.3 Motivation in Learning English ... Error! Bookmark not defined. 2.5.4 Motivation and Writing ... 27
2.6. Feedback ... 28
2.6.1 Feedback on Edmodo ... 32
2.6.2 Feedback and Writing Improvement ... 32
2.7. Related Studies ... 34
2.8. Concluding Remark ... 37
CHAPTER III - RESEARCH METHODOLOGY ... 38
3.1 Research Design ... 38
3.2.Research Hypothesis ... 39
3.3.Research Site and Participants ... 40
3.4. Data Collection... 40
3.4.1. Research Instrument ... 40
3.4.2. Teaching Material ... 40
3.4.3. Questionnaire ... 41
3.4.3.1 Pre Test and Post Test ... Error! Bookmark not defined. 3.4.3.2 Research Procedure ... 44
3.5. Data Analysis ... 46
3.5.1 Reliability ... 46
3.5.2. Data analysis on Pre Test and Post Test ... 47
3.5.2.1 The Normal Distribution Test ... 47
3.5.2.2 Homogeneity of Variance Test ... 47
3.5.2.3. The Independent t-Test ... 48
Christoper Tambunan, 2015
THE USE OF EDMODO TO MOTIVATE STUDENTS IN WRITING
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
3.5.3. Data Analysis on Students’ responses... 50
3.6. Concluding Remark ... 51
CHAPTER IV - FINDINGS & DISCUSSIONS ... 52
4.1. Findings and Discussions on Students’ Writing Motivation ... 52
4.1.1 Pre-Test Score Analysis ... 52
4.1.1.1 Normality Distribution Test ... 53
4.1.1.2 The Homogeneity of Variance Test ... 53
4.1.1.3 The Independent T-test Analysis ... 54
4.1.2. Post-Test Score Analysis ... 54
4.1.2.1 The Normal Distribution Test ... 55
4.1.2.2 The Homogeneity of Variance Test ... 55
4.1.2.3 The Independent t- Test ... 56
4.1.2.4. Dependent t-test ... 56
4.1.2.5 The Effect Size of The Treatments ... 57
4.3. The Graphic of the Performance ... 57
4.3.1. Pre-Test Comparison ... 58
4.3.2. Pre-Test and Post-Test Comparison ... 58
4.3.2.1. Control Group ... 58
4.3.2.2. Experimental group ... 59
4.4 Students’ Responses towards the Use of Edmodo ... 61
4.4.1 The Questionnaire Analysis ... 61
4.5. Concluding Remark ... Error! Bookmark not defined. CHAPTER V - CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS ... 68
5.1. Conclusions ... 68
5.2. Recommendations ... 69
Christoper Tambunan, 2015
THE USE OF EDMODO TO MOTIVATE STUDENTS IN WRITING
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
This chapter presents covers background of the study, research questions, the aim of the study, scope of study, significance of study, clarification of terms, and organization of the paper.
1.1 Background
English, in Indonesia, is learnt as a foreign language. There are four fundamental skills students have to learn in English, those are listening, speaking, reading, and writing. Of those four English skills, writing is acknowledged as the most difficult skill for learners to master (Richards and Renandya, 2002). Richard and Renandya further elaborate that the difficulties lie from high level skills, such as planning and organizing ideas, and to low level skills, such as spelling, punctuation, and word choice. However, in spite of the difficulties, it is important for students to master the skill of writing since it is needed in both academic and career settings (Barrass, 2005; Harmer, 2004).
Absolum et al (2009) states that to make students more able and motivated in writing, engagement of practicing writing is needed. In Indonesian context, Indonesians are known to have the lack of engagement in writing which is shown by small number of Indonesian intellectuals who publish their own writing (Alwasilah, 2005). Therefore, a means is necessarily needed to make students engaged in writing.
Christoper Tambunan, 2015
THE USE OF EDMODO TO MOTIVATE STUDENTS IN WRITING
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
teaching and learning attracts students’ attention, develop interests, and increases student motivation. More specifically, regarding media richness and instructional appropriateness, Newby, Stepich, Lehman & Russell (2000, cited in Scanlan, 2011) specifies the various characteristics of media to be considered; those are first real things, texts (handout, book, modul), whiteboard, OHP, slide film, video, graph (picture and image), audio (tape, CD, DVD), and last software computer. Through media with basis of ICT, some benefits can be found such as visualizing abstract concepts, easing difficult materials, enabling interaction between learners and learning materials, handling limitation of space, time and energy, and improving users’ skill. In Indonesia, however, there are still many schools that do not use media of ICT but still rely on traditional teaching media such as textbook and whiteboard a lot. Rahmatullah (2011) states that students taught through textbook and whiteboard often do not pay attention during learning process since the students get bored and regard it less fun. She further states that the existence of textbook as a medium of teaching is still not optimal yet to be implemented. In line with this, Munir (2008) also states that learning should not depend on textbook as only material resource since teaching process is not about accomplishing presentation of books but helping learners to attain competence. Thus teachers should apply as many material resources as possible in teaching.
One kind of media that is often found existing is in technology, which is computer-based learning. Computer-based learning such as e-learning has recently been implemented and given a lot of contribution towards learning process (Rusman, Kurniawan & Riyana, 2012). It is supported by British Council in 2007 that asserts that 69% of learners around the world with strong social network performed well academically.
Christoper Tambunan, 2015
THE USE OF EDMODO TO MOTIVATE STUDENTS IN WRITING
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
Educational Social Networking Sites (ESNSs) (Ali, M., 2004). Cauley (2013) said that edmodo is an educational website that takes the ideas of a social network and refines them and makes it appropriate for classroom. Ajjan & Hartshorne (2008, cited in Çankaya, Durak & Yünkül, 2013) also added that edmodo has benefit in improving students’ writing abilities. Writing in edmodo is highly engaging and interactive (Sanders, 2012; Ali, M., 2004). Learners show that they feel encouraged and comfortable using edmodo (Sanders, 2012; Turkmen, 2012). Besides, learners also show that edmodo is favorable which appears to be as attracting student’s attention as well as making the lesson effective and organized (Çankaya, Durak & Yünkül, 2013). Learners tend to read their writing first and check it more detailed before posting it to the edmodo (Duffy, 2011 cited in Anbe, 2013). It is likely to ensue because they like and enjoy using the edmodo, particularly its features, such as posting their work to class, getting feedback from the teacher, studying their classmates’ work, voting the best work of classmates, so on and so forth (Kongchan, 2008; Turkmen, 2012). In other words, writing in edmodo can help stimulate students to develop the habit of thinking on SNSs, come up with a lot of interesting ideas, structuring their writing, so on and so forth.
Based on the findings of several studies above, the use of media with technology, particularly edmodo may also give benefits in improving teaching EFL writing in Indonesia. It is seen from both teachers and students that seem to get the benefits of using edmodo as a medium in teaching and learning writing. Therefore this study regards edmodo as a means expected to give positive attribution towards motivation for students in writing, particularly EFL students in Senior High School. Furthermore, this study also aims to find out students’ responses towards the use of edmodo itself.
Christoper Tambunan, 2015
THE USE OF EDMODO TO MOTIVATE STUDENTS IN WRITING
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
This research is conducted to answer the research questions formulated below: 1. How does edmodo help motivate students in writing?
2. What are students’ responses to the use of edmodo?
1.3 Aims of the Study
In accordance with the background and research questions, the aims of this research are to find out:
a. The use of edmodo as a means to motivate students in writing. b. Student’s responses to edmodo technique on the activity.
1.4 Scope of the Study
This study focuses on how edmodo enhances students’ writing motivation. This study also aims to find out what benefits of edmodo could give to the students during the implementation through their responses on the activity.
1.5 Significance of the study
The result of this study is expected to provide a clear picture of how edmodo is employed in improving students’ writing motivation and their writing ability, especially EFL students in Senior High School. Besides, it is also expected to have certain significances for:
1. Teachers, in providing description of how edmodo can be used as a media of teaching in improving students’ writing motivation and their writing ability, especially EFL students in Senior High School and it may probably later be used as foundation of how to implement so.
Christoper Tambunan, 2015
THE USE OF EDMODO TO MOTIVATE STUDENTS IN WRITING
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
3. Next researchers, as a reference of further research related to e-learning, especially edmodo.
4. General Readers, to find out more of how e-learning especially edmodo is related to writing skill, specifically for EFL students in Senior High School and also benefit that could be obtained, afterwards.
1.6 Clarification of Key Terms
This section contains some terms related to this study to be cleared and defined. Here are some terms to be clarified:
a. Writing
Writing is a prime means of our thinking and our emotions (Wilkinson, 1985:45). Writing is a process of expressing feeling, idea, and thought from a writer to the readers (Byrne, 1995:5). Writing can also be defined as a means of developing ideas, reformulating knowledge and discovering personal expeience (Aridah, 2003).
b. Motivation
Motivation in this research has definition as “why people decide to do something, how hard they ar going to pursue it and how long they are willing to sustain the activity” (Dornyei, 2001).
c. Edmodo
Christoper Tambunan, 2015
THE USE OF EDMODO TO MOTIVATE STUDENTS IN WRITING
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu 1.7 Organization of the Paper
This study will be arranged in five chapters. Chapter I: Introduction
It provides all kind of information related to the background of the study, research questions, aim of the study, research method, hypothesis, significance of the study and organization of the paper.
Chapter II: Literature Review
It describes the relevant theories for the study. Chapter III: Research Methodology
It specifically describes the research method, which will be applied in this study. It includes the research design, data collection, procedures, instruments, participants, and data analysis. Chapter IV: Finding and Discussion
It presents the findings and discussion. It elaborates and interprets the finding and the discussion of the data obtained from the research.
Chapter V: Conclusion and Recommendation
Christoper Tambunan, 2015
THE USE OF EDMODO TO MOTIVATE STUDENTS IN WRITING
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHOD
This chapter describes the procedure used to answer the research questions in chapter one. It covers research design of the study, data collection, and data analysis. The data collection explained the process of how the data were gained, and elaborated. While data analysis was justifying of how the data were analyzed in the frame of the theories accounted in the previous chapter.
3.1 Research Design
This research was directed to employ quasi-experimental. Quasi experimental, in this study, will be used to identify, test, observe and analyze the data. Johnson (1999) states that quasi-experimental design is an adaptation of true experimental design where one of three elements such as manipulation, randomization, and control group is missing. Besides, Hatch and Farhady (1982) say that quasi-experimental designs are practical compromise between true experimental and the nature of human language behavior, which is used to investigate. Thus, it can be used to provide the completeness of the elements of true experimental. The design of the study described as follows:
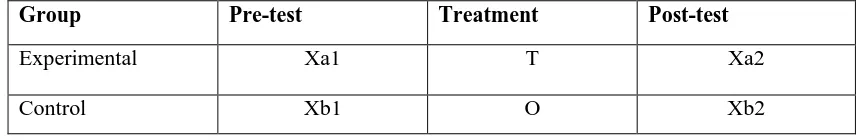
Table 3.1
The Quasi-Experimental Design
Group Pre-test Treatment Post-test
Experimental Xa1 T Xa2
Christoper Tambunan, 2015
THE USE OF EDMODO TO MOTIVATE STUDENTS IN WRITING
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu Where:
Xa1: Pre-test for experimental group Xb1: Pre-test for control group T: Treatment
O: Non-Edmodo treatment
Xa2: Post-test for experimental group Xb2: Post-test for control group
From the table above, there were two groups of the students. Those were experimental group and control group. The both of groups were given a pre-test in order to know their competence before giving the treatment. The difference came from the experimental group. This group was given a treatment of edmodo which is the writing assignment during the learning and giving of feedback. However, the control group did not use edmodo in terms of giving writing task or receiving feedback. The control group used paper as a medium in case of doing the writing assignment and receiving the feedback. After conducting the treatment to the experimental group, both of the groups were given a post-test to see whether the treatment works well or not.
3.2 Research Hypothesis
Christoper Tambunan, 2015
THE USE OF EDMODO TO MOTIVATE STUDENTS IN WRITING
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
Ho = there is no significant difference between the students’ post test scores of the experimental group and the students’ post test scores of the control group.
HA = there is significant difference between the students’ post test scores of the experimental group and the students’ post test scores of the control group. 3.3 Research Site and Participants
This research was conducted in one of the Senior High Schools in Bandung. The participants were from two different classes of tenth grade, which are for experimental group and control group. According to Kothari (2004: 59) this kind of sample is called as non-probability sampling since they are chosen by the researcher. Besides, they were chosen since it was found out that the students had an awareness of using technology and its application. In the research, all of the students from experimental group were given edmodo technique as a form of assignment in English class.
3.4 Data collection
In collecting the data, this study employed two techniques, those were questionnaire and edmodo. Yildirim & Simsek (2008, cited in Çankaya, Durak & Yünkül, 2013) state that using more than one data collection technique supports the validity and reliability of the study. Each technique of data collection were described below.
3.4.1 Research Instruments
Christoper Tambunan, 2015
THE USE OF EDMODO TO MOTIVATE STUDENTS IN WRITING
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
items of the questionnaire were selected to be a real questionnaire that was given to the real sample of group in pre and post test. The purpose of the pretest was to measure the students’ writing motivation before the treatment, and post test was used to measure the students’ writing motivation after the treatment using edmodo. Technique of data collection was described as follows:
3.4.2 Teaching Material
In this study, the teaching materials used are recount text about experience. It is chosen because it was appropriate to the standard competence of syllabus released by the National Education Ministry of grade X of Senior High School.
In conducting this, several preparations need to take into account. First is the preparation of all the materials and teaching procedure that will be used. Second is preparing the medium which is edmodo. Edmodo is prepared to be introduced and used by the students.
Furthermore, all the teaching materials and the procedures are prepared in experimental group that is completely related to the use of edmodo in teaching recount text. However, in the control group, the conventional method is used where the medium and the teacher feedback used is conducted through paper, not edmodo.
3.4.3 Questionnaire
Christoper Tambunan, 2015
THE USE OF EDMODO TO MOTIVATE STUDENTS IN WRITING
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
The purpose of the research in using questionnaire was to find out how the edmodo can help motivate the students to write and how the students’ responses towards the use of edmodo.
3.4.3.1 Pre Test and Post Test
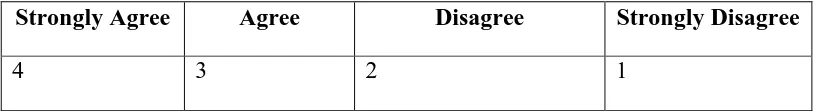
Pre-test is one of the research instruments. It was implemented to firstly know and find out the initial differences between experimental group and control group. It was used to measure student’s capability before the treatment is given. Meanwhile post-test will be used to find out the improvement of students’ motivation in writing (Frankel and Wallen, 1993). The procedure of both instruments was actually the same. Both the pre-test and post-test were questionnaire form and consisted of ten items. The questionnaire was then distributed to experimental group only. It was designed as close-ended questionnaire with four optional answers based on Likert-Scale questionnaire, those are:
Table 3.2
The Likert-Scale in the Questionnaires
Strongly Agree Agree Disagree Strongly Disagree
4 3 2 1
The questionnaire was aimed to gain specific data that were needed to analyze the students’ writing motivation. The questionnaire was designed based on the existing theoretical frameworks such as Self-Determination theory by Ryan and Deci (1985), supported by Vallerand (et al., 1992, cited in Blais, 1995) namely dividing motivation into two categories: intrinsic and extrinsic motivation.
Christoper Tambunan, 2015
THE USE OF EDMODO TO MOTIVATE STUDENTS IN WRITING
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
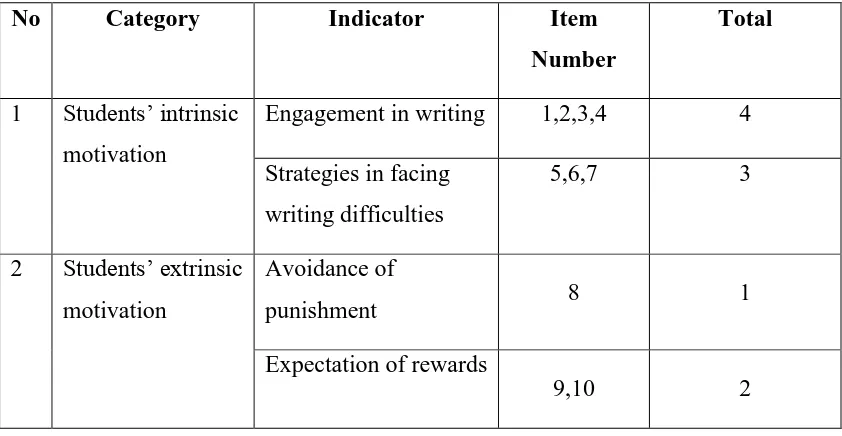
The Framework of Students’ Writing Motivation Questionnaire
No Category Indicator Item
Number
Total
1 Students’ intrinsic motivation
Engagement in writing 1,2,3,4 4
Strategies in facing writing difficulties
5,6,7 3
2 Students’ extrinsic motivation
Avoidance of
punishment 8 1
Expectation of rewards
9,10 2
In addition, more another questionnaire was distributed to examine students’ responses to the use of edmodo as described below:
Table 3.4
The Aspects of Students’ Responses to the Edmodo Activity Questionnaire
No Category Indicator Item
Number
Total
1 Students’ responses to
edmodo activity
Students’ enjoyment in writing on edmodo
1, 2, 4,10 3
Students’ perception in writing
Christoper Tambunan, 2015
THE USE OF EDMODO TO MOTIVATE STUDENTS IN WRITING
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu 2 Benefits from edmodo
activity
Students’ improvements on
writing skill 3 1
Students’ improvement on
self-expression 5 1
Students’ improvement on
critical thinking 6 1
Students’ improvement on self
-reflection 7,9 2
Students’ improvement on self
-confidence 8 1
Students’ improvement on
writing motivation 11 1
3.4.3.2 Research Procedure
This research conducted following research procedure as follows.
1. Administering the pilot questionnaire instrument
Christoper Tambunan, 2015
THE USE OF EDMODO TO MOTIVATE STUDENTS IN WRITING
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu 2. Administering pre test
The first questionnaire administered to the real sample will be pre-questionnaire which is to find out the initial ability of the students (Freankel & Waleen, 1993). The students will be required to fill in the first questionnaire about their writing motivation.
3. Conducting the edmodo treatment to the experimental group
The step, first, is to introduce the edmodo to the students. The researcher will lead the students into the understanding of the Edmodo by directly showing the Edmodo application, give them a guide, introduced all the stuff in Edmodo, ask them to create account in Edmodo, and explain the interface and function of every single component in this learning platform. The researcher will ensure the students will understand the use of Edmodo. The treatment will be conducted for three weeks in a month. During the treatment of using Edmodo, students will be told that they will start writing on edmodo as form of assignment. In doing the task on edmodo, they will have to write in a form of minimum 200 words compositions in recount text concerning their experience.
Christoper Tambunan, 2015
THE USE OF EDMODO TO MOTIVATE STUDENTS IN WRITING
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
feedback to the students twice. In doing the drafts, the students will be asked to make recount text related to their experience. They will be asked to submit or post it on edmodo feature which is assignment feature, then teacher will check whether the generic structure of their writing is correct or not. If there are some mistakes on the generic structure, teacher will give indirect feedback by posting it on “comment” feature so that the students can revise it again. Both teacher and students will use those features. After they accept the teacher feedback, they have to revise it as a second draft of their writing based on the feedback teacher gives. Then for the second time, teacher re-checks their writing, focusing on the generic structure and if there are still mistakes on it, teacher will give feedback again and post it to the students’ account. Then students who accept it have to revise it again as a final draft until it is appropriately correct. Then they have to resubmit it again on edmodo for the last time.
4. Conducting treatment to the control group
The treatment that will be given to the control group is conventional technique. The students in this group will use paper as the medium. They will write the essay and receive the teacher feedback through paper only, not edmodo. However, they will receive exact material like experimental group from the teacher. After final draft, teacher will distribute the post test to the control group to see and find out the difference of results between experimental group and control group concerning their motivation in writing after using edmodo treatment.
4. Administering Post-test
Christoper Tambunan, 2015
THE USE OF EDMODO TO MOTIVATE STUDENTS IN WRITING
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu 5. Distributing Response Questionnaire
The response questionnaire in this study will only be given to the experimental group. It aims to find out the responses of the students toward the implementation of Edmodo in enhancing students’ motivation in writing. Purposely, this questionnaire is used to answer the third research question of the study.
3.5 Data Analysis
3.5.1 Reliability
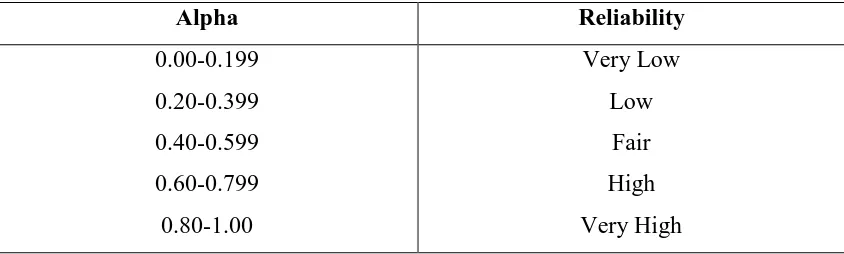
Reliability is the extent that a test is produced in constant result when administered under similar condition (Hatch & Farhady, 1982). The formula that was used to measure the reliabilty is Cronbach’s formula in SPSS 20.00 for windows. The result was interpreted by using the following criteria :
Table 3.5
r Coefficient Correlation
Alpha Reliability
0.00-0.199 0.20-0.399 0.40-0.599 0.60-0.799 0.80-1.00
Very Low Low
Fair High Very High
Christoper Tambunan, 2015
THE USE OF EDMODO TO MOTIVATE STUDENTS IN WRITING
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu 3.5.2.1 The Normal Distribution Test
Pre-test was administered in the very beginning of the study before the treatment is given to the experimental group. This test was applied to both of the group. In order to investigate the normal distribution of thhe set of data, the Kolmogrov-Smirnov test was employed. Therefore, this test is appropriate to be used because the sample of this research took two classes of tenth grade students where each of the class has 25 students. The test employed SPSS 20 for windows.
There were several steps in using Kolmogrov-Smirnov test. The first step was stating the hypothesis and setting the alpha level. The second was analyzing the
groups’ scores by employing Kolmogrov-Smirnov through SPSS 20 for windows.
In the first step, 0.05 (two-tailed) is set as the alpha level. Thus, hypotheses are as follow:
Ho = the score of the experimental and control groups are normally distributed
HA = the score of the experimental and the control groups are not normally distributed.
Finally, the data were analyzed by using Kolmogrov-Smirnov through SPSS 20 for windows. The output data were interpreted by these ways: If Asymp.sig > 0.05, the null hypothesis is accepted. Meaning that data distribution is normal. If Asymp.sig <0.05, the hypothesis is rejected, meaning the data is not normal (Field, 2005).
3.5.2.2 Homogeneity of Variance Test
Christoper Tambunan, 2015
THE USE OF EDMODO TO MOTIVATE STUDENTS IN WRITING
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu Stating the Hypothesis and setting the alpha level at 0.05
H0 = the variance of experimental and control groups are homogenous. H1 = the variance of experimental and control groups are not homogenous
Analyzing the variance homogeneity by using SPSS 20.00 for windows
Comparing the significant value with significant level for testing the hypothesis. If Levine’s test is significant at p ≤ .05, it can be concluded that the variances are significantly different. If Levine’s test is significant at p>.05 means that the variances are approximately equal (Field, 2005).
3.5.2.3 The Independent t-Test
Hatch & Farhady (1982:155) said that independent t-test was applied to investigate the significant differences between the means of the two groups. Coolidge (2000:143) stated that there are several requirements for conducting t-test; first, the data should be measured in form of interval or ratio. Second, the data should be homogenous. Third, the data should have normal distribution. The procedures of the analysis can be seen as follow:
Stating the Hypothesis and setting the alpha level at 0.05 (two-tailed test) H0 = there is no difference of pre-test and post-test between both of groups
H1 = there is significant difference of pre-test and post-test between both of groups
Calculating the t value by using independent sample test computation in SPSS 20.00 for windows.
Christoper Tambunan, 2015
THE USE OF EDMODO TO MOTIVATE STUDENTS IN WRITING
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
that the hypothesis is accepted, meaning that there is no significant difference of means between experimental and control group (Coolidge, 2000).
3.5.2.4 The Dependent t-test
Hatch and Farhady (1982) stated that the pre-test and post-test score were analyzed by using dependent t-test to investigate whether the difference of the pre-test and post-test is significant or not. Look at the following procedures:
Stating the Hypothesis and setting the alpha level at 0.05 (two-tailed test) H0 = there is no significant difference of pre-test and post-test score H1 = there is significant difference of pre-test and post-test score
Calculating the t value by using dependent sample test computation in SPSS 20.00 for windows.
Comparing tobt and tcrit at p=0.05 and df*= 29 to examine the hypothesis. If tobt> tcrit means that the hypothesis is rejected, meaning that there is significant difference of means between experimental and control group. If tobt< tcrit means that the hypothesis is accepted, meaning that there is no significant difference of means between experimental and control group (Coolidge, 2000)
3.5.2.5 The Calculation of Effect Size
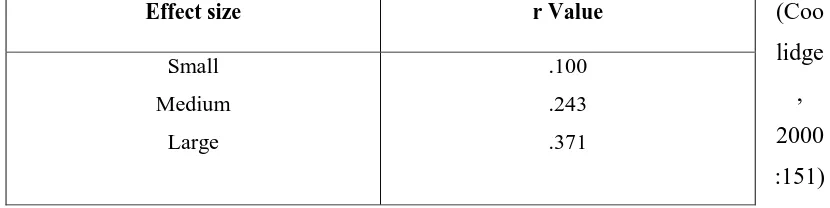
Coolidge (2000) said that it is important to administer the calculation of effect in order to determine the effect of the influence of independent variable upon the dependent variable. If the treatment works well, there will be a large effect. The formula and the steps for calculating the effect size could be seen as follow:
√
Christoper Tambunan, 2015
THE USE OF EDMODO TO MOTIVATE STUDENTS IN WRITING
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu r: Effect size
t: tobt or tcrit value from the calculation of independent t-test df: N1+N2-2
After the r was round, the score was interpreted by using the following table:
Table 3.6 Effect Size Value
(Coo
lidge , 2000 :151)
3.5.3 Data Analysis on Students’ Responses
The data obtained from questionnaire became meaningless until it is classified, organized and interpreted (Alwasilah, 2000). The data from questionnaire were used as quantitative data.
The data gained from the pre- and post- treatment questionnaire were tabulated and presented through some stages, as follows:
1. Examining the data gained from the questionnaire
2. Selecting and classifying the data derived from the questionnaire into categories to simplify the tabulation and interpretation
3. The calculation for the data will be measured by using the following formula:
Effect size r Value
Small
Medium
Large
.100
.243
.371
P= F x 100%
Christoper Tambunan, 2015
THE USE OF EDMODO TO MOTIVATE STUDENTS IN WRITING
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu Where:
P = Number of percentage
F = Frequency of strategies or procedures N = Number of whole samples
The data analyzed from questionnaire showed the actual use of Edmodo in enhancing students’ writing motivation. The data of either students’ writing motivation or responses questionnaire were interpreted through descriptive explanation. The data from this source is expected to bring about general themes found in this research. The result of this analysis was then discussed in chapter 4 of this research.
3.6 Concluding Remark
Christoper Tambunan, 2015
THE USE OF EDMODO TO MOTIVATE STUDENTS IN WRITING
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu CHAPTER V
CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS
This chapter provides the conclusions of the research findings and also further research.
5.1 Conclusions
This study was concerned with the implementation of Edmodo, as a medium
towards the students’ motivation in writing. This study was conducted to tenth grade
students of Senior High School in Bandung. The aims of this study were to find out the effectiveness of using Edmodo in enhancing students’ motivation in writing and
also to find out the students’ responses towards the implementation in the classroom.
Based on the research findings, it was revealed that there was a significant difference between the students using Edmodo in experimental group class and students using paper as a medium in control group class. It was proven by the result of post-test scores after the treatments. The students in the experimental group gained higher scores than students from control group. The data analysis from independent t-test which is tobt < tcrit showed that there was no significant difference between post test means of the experimental and control groups. Furthermore, the data analysis from dependent t-test which is tobt > tcrit showed that there was a significant
difference of the experimental group’s scores in post test. The dependent t-test value was greater than tcritical value. Moreover, based on the calculation of effect size, the correlation obtained was in the level of high, which means the use of Edmodo as a
Christoper Tambunan, 2015
THE USE OF EDMODO TO MOTIVATE STUDENTS IN WRITING
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
Furthermore, findings to second research question, the students generally gave positive responses toward the implementation of Edmodo. Edmodo has given many benefits to the students after the treatment. The benefits were classified into several categories. The percentage showed that almost 80% students agree that Edmodo is interesting, flexible, as well as able to improve critical thinking, expression, confidence, motivation and writing.
5.2 Recommendations
The recommendations are divided into two big parts. The first part is proposed to the teachers, second is proposed to future researchers who have similar area with this study.
For teachers, particularly English teachers struggling in finding interesting, attractive, and interactive medium in teaching in the classroom, particularly in writing, Edmodo could be one of the best alternative media. Teacher could utilize it for many kinds of activities, such as conducting interesting and attractive assignments, discussing the task interactively, grading the task easily and effectively and also controlling the students. All can be done in one learning platform such as Edmodo.
Christoper Tambunan, 2015
THE USE OF EDMODO TO MOTIVATE STUDENTS IN WRITING
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
Christoper Tambunan, 2015
THE USE OF EDMODO TO MOTIVATE STUDENTS IN WRITING
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu REFERENCES
Absolum, M. F. (2009). Directions for assessment in New Zealand. Wellington: Ministry of Education. New Zealand.
Ajjan, H., & Hartshorne, R. (2008). Investigating faculty decisions to adopt web 2.0 technologies: Theory and empirical tests. The internnet and Higher Education, 11(2),71-80.
Ali, M. (2004). E-learning in Indonesian education system. Available: http://gauge.ugakugei.ac.jp/apeid/apeid04/country_papers/indonesia.pdf. Accessed on 07-02-14.
Alwasilah, A. C. (2001). Empowering college student writers through collaboration. TEFLIN Journals. Vol. 1.
Anbe, G. (2013). Using edmodo to incorporate WICOR strategies in the AVID classroom. United States of America.
Barrass, R. (2005). Students must write. A guide to better writing in coursework and examination. New York: Routledge.
Blais, M. R. (1995). Toward a new measure of intrinsic motivation, extrinsic motivation, and amotivation in Sports: The sport motivation scales (SMS). Human Kinetics Publishers, Inc.
Christoper Tambunan, 2015
THE USE OF EDMODO TO MOTIVATE STUDENTS IN WRITING
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
Brouwer, K. L. (2010). Writing motivation of students with specific language impairments. University of Nebraska-Lincoln.
Brown, H.D. (2001). Teaching by principles. An interactive approach to language pedagogy. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice Hall.
Burns, M. (2010). How to help teachers use technology in the classroom the 5J approach. ACM publication.
Byrne, D. (1995). Teaching writing skills. Harlow: Longman Group UK Limited.
Campbell, K. (2004). E-ffective writing for e-learning environments. IGI Global.
Candelaria, S & Wernicke A. (2013). Edmodo-ETEC 510. [Online]. Retrieved: http://etec.ctlt.ubc.ca/510wiki/index.php?title=Edmodo&oldid=525 76".
Çankaya, S., Durak, G. & Yünkül, E. (2013). Using educational social networking sites in higher education: Edmodo through the lenses of undergraduate students. European Journal of Educational Technology, 1(1), 3-23.
Christoper Tambunan, 2015
THE USE OF EDMODO TO MOTIVATE STUDENTS IN WRITING
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
Clark, I.L. (2003). Concepts in composition. Theory and practice in the teaching of writing. New Jersey: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc.
Clark, C. R & Mayer, E. R (2011). E-learning and the science of instruction: proven guidelines for consumers and designers of multimedia learning. Third Edition.
Cohen, L., Manion, L., Morison, K., Morison K, R, B. (2007). Research method in education: Sixth Edition. New York: Routledge.
Conley, A. M. & Karabenick, S. A. (2006). Construct validity issues in the measurement of motivation to learn. University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
Coolidge, F.L. (2000). Statistics a gentle introduction. London: Sage.
Deci, E.L., & Ryan, M.R. (1985). Intrinsic motivation and self-determination in human behaviour. New York: Plenum.
Dörnyei, Z. (2001). New themes and approaches in second language motivation research. Annual Review of Applied Linguistics, 21:43-59.
Eifring, H. & Theil, R. (2005). Linguistics for students of Asian and African languages. [Online].
Fraenkel, J.R., & Norman, E.W. (1993). How to design and evaluate research in education 2nd ed. Singapore: Mc-Graw Hill.
Christoper Tambunan, 2015
THE USE OF EDMODO TO MOTIVATE STUDENTS IN WRITING
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
Harmer, J. (2004). How to teach writing. Edinburgh Gate: Pearson Education.
Hatch & Farhady. (1982). Research design and statistics for applied linguistics. Los Angeles: Newbury House Publishers, Inc.
Hourdequin, P. (2014). Edmodo: A simple tool for blended learning. Tokoha University.
Hyland, K., & Hyland, F. (2006). Feedback on second language students' writing. language teaching, 39(02), 83-101.
Hyland, K.. (2006). English for academic purposes: an advanced resource book. New York: Routledge.
Johnson. (1999). Ways of improving research: quantitative designs. Retrieved from http://www.southbama.edu/coe/bset/jhonson/lectures/lec.
Keh, C. L. (1990). Feedback in the writing process: a model and methods for implementation. ELT journal, 44(4), 294-304.
Kongchan, C. (2008). How a non-digital-native teacher makes use of edmodo. In 5th Intenational Conference ICT for Language Learning. Florence.
Christoper Tambunan, 2015
THE USE OF EDMODO TO MOTIVATE STUDENTS IN WRITING
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
Lie, A. (2013). Social media in a content course for the digital natives. TEFLIN Journal.
Moussaid, S. (2014). The significant role of media in the EFL learning process. Morocco: Yesmorocco.com.
Munir. (2008). Kurikulum berbasis teknologi informasi dan komunikasi. Bandung: Alfabeta.
Oxford, R.L. & Ehrman, M. (1993). Second language research on indivual differences. Annual Review of Applied Linguistics. 13:188-205.
Pape, L., Sheehan, T. & Worrell, C. (2012). Learning & leading with technology. ISTE (International Society for Technology in Education). Vol. 39, No.6, pp.18-22.
Purnawarman, P. (2011). Impacts of different types of teacher corrective feedback in
reducing grammatical errors on ESL/EFL students’ writing (Doctoral Dissertation, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University).
Pop, A. (2013). Edmodo E-portfolios in EFL – A Case Study. The 8th International Conference on Virtual Learning ICVL 2013. Romania.
Roy, A.A. (2013). Edmodo. Edmodo: creating a connected classroom. [Online]. Available:http://www.framingham.edu/continuingeducation/documents/pr dv-70924.pdf. Google Voice.
Christoper Tambunan, 2015
THE USE OF EDMODO TO MOTIVATE STUDENTS IN WRITING
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
Richards, J.C & Renandya, W.A. (2002). Methodology in language teaching. An anthology of current practice. New York: Cambridge University Press.
Roy, A.A. (2013). Edmodo. Edmodo: creating a connected classroom. [Online]. Available:http://www.framingham.edu/continuingeducation/documents/pr dv-70924.pdf. Google Voice.
Rusman, Kurniawan, D & Riyana, C. (2012). Pembelajaran berbasis teknologi informasi dan komunikasi: mengembangkan profesionalitas guru. Jakarta: Rajawali Pers.
Sanders, K. S. (2012). An examination of the academic networking site edmodo on student engagement and responsible learning. (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). University of South Carolina College of Education.
Saville-Troike. (2006). Introducing second language acquisition. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Scanlan, C.L (2014). Instructional media: selection and use. Retrieved on August 06,2014,from:http://www.umdnj.edu/idsweb/idst5330/instructional_medi a.htm
Siahaan, S. (2004). E-Learning (pembelajaran elektronik) sebagai salah satu alternatif kegiatan pembelajaran. Available: http://www.depdiknas.go.id.
Soehadi, G. (2007). In becoming EFL writing teacher: a diary study. In Jurnal K@ta[Online],9(2)16pages.
Available:http://puslit.petra.ac.id/files/published/journals/ING/ING07090 2/ING07090204.pdf.
Christoper Tambunan, 2015
THE USE OF EDMODO TO MOTIVATE STUDENTS IN WRITING
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
Tremblay, M. A & Villeneuve, M. (2009). Work extrinsic and intrinsic motivation scale: Its value for organizational psychology research. Canadian Psychological Association.
Turkmen, H. G. (2012). Using social networking in efl classroom in higher education. In conference proceedings of" eLearning and software for education"(eLSE). (No. 01, pp. 350-354).
Wallace, A. (2014). Social learning platforms and the flipped classroom. International Journal of Information and Education Technology. 4, (4).
Warschauer, M., & Healey, D. (1998). Computers and language learning: an overview. Language teaching, 31, 57-71. [Online]. Available: http://www.gse.uci.edu/person/warschauer_m/overview.html. [December 24th, 2012].
Weber, A. (2012). Consideration for social network site (SNS) use In education. International Journal of Digital Information and Wireless Communications (IJDIWC). Hongkong. (Vol. 2, No. 4). Hongkong.
Weigle, S. C. (2002). Assessing writing. New York: Cambridge University Press.
Widodo, H. (2006). English teaching: Practice and Critique.
Widodo, H. P. (2008). Process-based academic essay writing instruction in an EFL context. In Bahasa dan Seni [Online], Vol 36 (1), 15 pages.
Wilkinson, A. (1985). The writing of writing. East of Anglia: Open University Press.