Informasi Dokumen
- Penulis:
- Dave Chaffey
- Mata Pelajaran: E-business and E-commerce Management
- Topik: E-Business and E-Commerce Management: Strategy, Implementation and Practice
- Tipe: Textbook
- Tahun: 2009
- Kota: Harlow
Ringkasan Dokumen
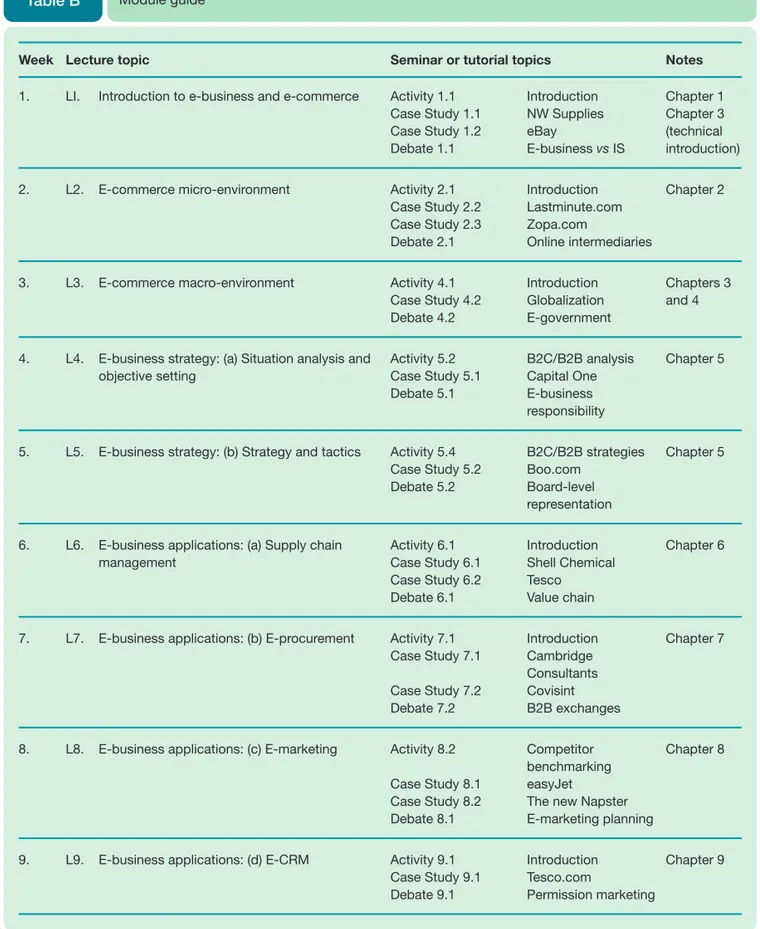
I. Introduction to e-business and e-commerce
This chapter lays the groundwork for understanding the fundamental concepts of e-business and e-commerce. It begins by defining both terms, emphasizing the distinction between e-commerce (electronically mediated exchanges with external stakeholders) and e-business (encompassing both internal and external exchanges across various business processes). The chapter examines the impact of electronic communications on traditional business models, using real-world examples like HP.com to illustrate the transformation. It then delves into various e-commerce models (B2C, B2B, etc.), exploring opportunities and risks associated with online business adoption. The chapter also analyzes the factors driving both business and consumer adoption of digital technologies, highlighting key barriers to adoption and corresponding management responses. Case studies of Facebook, North West Supplies, and eBay provide practical examples of e-business successes and challenges, strengthening the pedagogical value by providing real-world context.
1.1 The impact of electronic communications on traditional businesses
This section explores how the advent of electronic communications has fundamentally altered traditional business operations. It analyzes the shifts in market dynamics, customer expectations, and competitive landscapes brought about by the digital revolution. Real-world examples, such as the evolution of HP's online presence, are used to demonstrate how companies have adapted their strategies and operations to thrive in the digital age. The discussion also includes the challenges faced by businesses in this transformation, highlighting the need for strategic adaptation and technological innovation for long-term sustainability and competitive advantage. The section sets the stage for later discussions on e-business strategies and their implementation.
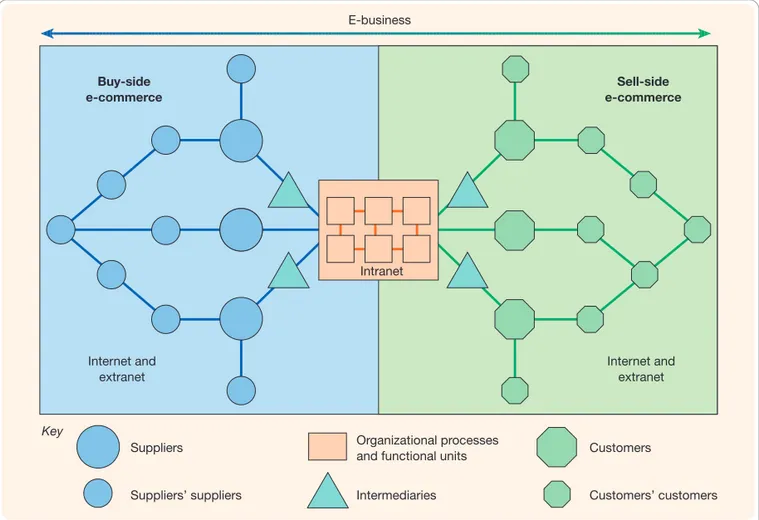
1.2 What is the difference between e-commerce and e-business?
This section clarifies the often-blurred lines between 'e-commerce' and 'e-business'. While both involve using electronic means to conduct business, the chapter distinguishes between the narrower scope of e-commerce, focused on transactions with external stakeholders, and the broader scope of e-business, encompassing all electronically mediated information exchanges, both internally and externally. This distinction is crucial for strategic planning and understanding the overall impact of digital technologies on organizational functions. The pedagogical strength of this section lies in its clear definition of key terminology and its emphasis on consistent usage within organizations, essential for effective communication and collaboration.
1.3 Business or consumer models of e-commerce transactions
This section delves into various business models and consumer behaviors within e-commerce transactions. It examines different types of e-commerce interactions, such as B2C (business-to-consumer) and B2B (business-to-business), outlining their unique characteristics and management challenges. The section also explores how consumer behavior differs across various online marketplaces. Understanding these models and their nuances is critical for developing effective e-business strategies and for aligning organizational resources with market opportunities. The analysis of different consumer models provides a foundation for subsequent chapters that address more specific aspects of e-business applications like e-marketing and customer relationship management.
1.4 E-business opportunities and risks
This section presents a balanced view of the opportunities and risks inherent in adopting e-business strategies. It explores potential benefits, such as increased market reach, cost reduction, and improved efficiency. Simultaneously, it discusses potential risks, such as security breaches, technological challenges, and the need for significant investments. The pedagogical value lies in emphasizing the importance of a comprehensive risk assessment before embarking on e-business initiatives. The chapter underlines the need for a strategic approach to weighing the potential benefits against the associated risks, preparing students for real-world decision-making in the context of e-business.
II. E-commerce Fundamentals
This chapter dives into the core principles of e-commerce, exploring the environment in which online businesses operate. It introduces the concept of strategic agility in responding to market changes and analyzes online marketplaces, emphasizing the importance of multi-channel strategies. The chapter explores different types of online intermediaries and their roles in facilitating e-commerce transactions, including the significance of search engines. It covers various e-commerce business and revenue models, using examples such as auction models and online publishing. The chapter also examines the dot-com boom and bust, drawing lessons from the failures and successes of early internet companies. Case studies of More Th>n, lastminute.com, and Zopa provide real-world illustrations of diverse e-commerce approaches and their outcomes.
2.1 The e-commerce environment and strategic agility
This subsection introduces the dynamic nature of the e-commerce environment and underscores the need for businesses to be strategically agile. It discusses the rapidly evolving technological landscape, changing consumer preferences, and the intensifying competition. The pedagogical value lies in emphasizing the importance of adaptability and continuous improvement in navigating the challenges and harnessing the opportunities presented by the online marketplace. It prepares students to consider the ever-changing environment and the need for businesses to be responsive and innovative to succeed in e-commerce.
2.2 Online marketplace analysis and multi-channel models
This section focuses on analyzing the complexities of online marketplaces. It explores the geographical distribution of online businesses, examining the implications of location and the increasing importance of multi-channel approaches that integrate online and offline channels. The discussion of different types of online intermediaries, such as online retailers, marketplaces, and aggregators, provides a critical framework for understanding the intricacies of online business ecosystems. This analysis is crucial for strategic decision-making and for devising effective market entry and expansion strategies. The inclusion of a detailed analysis of search engines highlights the crucial role of organic and paid search in online business success.
2.3 Business models for e-commerce and revenue models
This section provides a detailed overview of various e-commerce business models, exploring how different companies generate revenue online. It includes detailed examinations of different revenue models such as advertising, subscriptions, affiliate marketing, and transaction fees. Specific examples and case studies are used to illustrate how different business models work and how successful companies have chosen different models that are most appropriate for their strategy. This detailed analysis equips students with a strong foundation in the economic aspects of online business and enables them to critically evaluate the suitability of different models for specific business contexts. The section also includes a discussion on the evolution and challenges faced by internet start-ups.
III. E-business Infrastructure
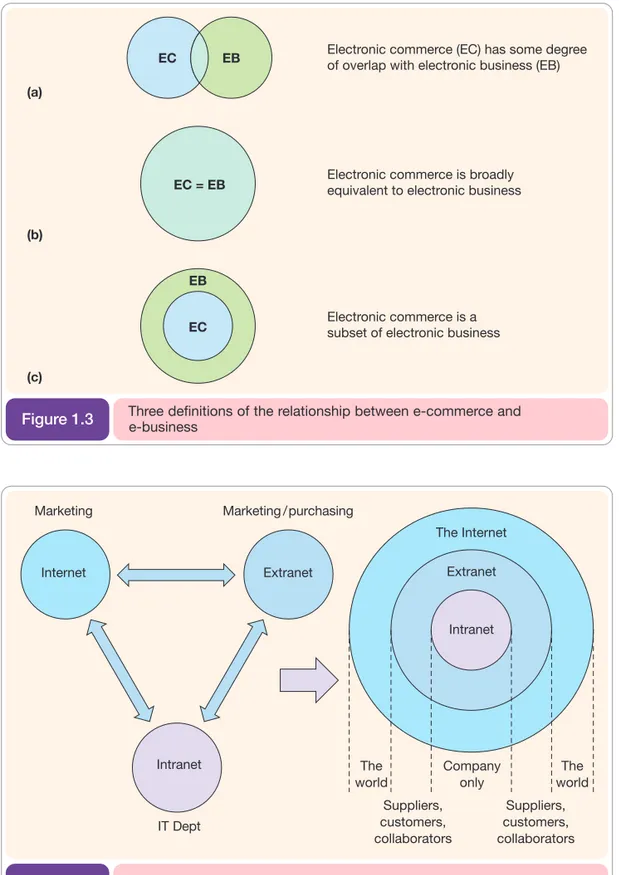
This chapter explores the technological foundation of e-business, covering the hardware, software, and telecommunications components crucial for successful online operations. It examines the evolution of the Internet and its components, providing a historical context for understanding current technologies. The chapter addresses various web technologies, including blogs, email, feeds, and VoIP, and explores relevant networking standards, like HTTP and URL protocols. Intranets and extranets are also discussed as integral parts of internal and external communication networks. The chapter also addresses the importance of managing e-business infrastructure, encompassing hardware and software, internet service providers, and employee access. Case studies on Google and the challenges of adopting new architectures illustrate both innovation and practical implementation issues.
3.1 E-business infrastructure components and internet technology
This section provides a comprehensive overview of the technological building blocks of e-business. It explores the hardware, software, and telecommunications infrastructure needed to support online operations. It provides a historical perspective on the development of the internet, tracing its evolution from early networks to the sophisticated systems of today. The section also examines different types of web technologies, including blogs, e-mail, feeds, and VoIP, and explains the importance of networking standards and protocols. By understanding the technical foundation of e-business, students can better appreciate the management challenges involved in deploying and maintaining online systems.
3.2 Managing e-business infrastructure
This section addresses the crucial managerial aspects of e-business infrastructure. It moves beyond the technical details to explore the practical challenges of managing various components of the infrastructure. This includes the management of hardware and software systems, the selection and management of Internet service providers (ISPs), and the implementation of secure access controls for employees. It explores the importance of effectively managing e-business applications, highlighting the benefits and challenges of web services, SaaS (Software as a Service), and SOA (Service-Oriented Architecture). The section also examines the growing area of mobile commerce and its implications for infrastructure management.
IV. E-environment
This chapter analyzes the external factors influencing e-business strategy and implementation. It examines the social, legal, economic, political, and technological environments, focusing on their impact on e-commerce adoption and sustainability. The chapter addresses issues such as privacy, trust, and e-commerce legislation. It explores the influence of globalization on consumer attitudes and international B2B trading, as well as the role of political factors and e-government initiatives. Technological innovation and assessment are also discussed, emphasizing the need for companies to anticipate and adapt to emerging technologies. The chapter provides a thorough overview of the macro-environment, equipping students with the knowledge to conduct thorough environmental scans before developing any e-business strategy.
4.1 Social and legal factors governing e-commerce
This section examines the social and legal context of e-commerce. It explores the importance of trust and privacy in online transactions, highlighting the various legal and regulatory frameworks governing data protection and consumer rights. It discusses different legislation related to e-commerce across various jurisdictions, including data privacy laws and consumer protection regulations. The section also addresses emerging concerns about environmental impact and the need for sustainable e-commerce practices. Understanding these social and legal factors is crucial for responsible and sustainable e-commerce operations.
4.2 Economic and competitive factors influencing e-business
This section focuses on the economic and competitive landscape of e-business. It explores the impact of globalization on e-commerce, examining how businesses can leverage global markets while navigating the challenges of international trade. It emphasizes the role of competition and the need for businesses to develop a competitive advantage in the online marketplace. The pedagogical value lies in helping students understand how economic forces shape e-business strategies and how businesses can position themselves for success in a competitive global environment. The section includes discussion on the impact of industry analysts and their reports on technological adoption.
4.3 Political and technological factors
This section discusses the influence of political and technological factors on e-business. It covers the roles of government regulations, e-government initiatives, and international internet governance. It also explores the continuous evolution of technology and the importance of technological assessment in predicting future trends and shaping e-business strategies. Understanding these factors is crucial for businesses to navigate the policy landscape and adapt to technological advancements effectively. The emphasis on technological innovation and forecasting prepares students to proactively address the challenges and opportunities of technological change.
V. E-business Strategy
This chapter delves into the strategic aspects of e-business, focusing on the development and implementation of e-business strategies. It explores various strategic analysis methods and defines the role of strategic objectives and vision. The chapter emphasizes the importance of creating business value through e-business initiatives. It outlines a decision-making process for prioritizing e-business channels, market and product development, and positioning strategies. The chapter also examines successful and failed e-business strategies, highlighting key success factors for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). The integration of information systems (IS) strategy with e-business strategy is also covered. Case studies on Standard Life, Capital One, Sandvik Steel, and Boo.com provide valuable insights into real-world strategic choices and their outcomes.
5.1 What is e-business strategy and the imperative for it?
This section introduces the concept of e-business strategy and explains its importance in today's digital economy. It clarifies the differences between traditional business strategies and those specifically tailored for the digital environment. The pedagogical value lies in highlighting the unique challenges and opportunities presented by the internet and the need for companies to develop distinct strategies to leverage these. It emphasizes the need for strategic thinking and planning when venturing into e-business or transforming existing operations to incorporate digital technologies. The section sets the stage for the discussion of strategic analysis and strategic planning for e-business.
5.2 Strategic analysis and objective setting
This section focuses on the strategic analysis process for e-business. It covers various analytical frameworks, providing students with tools and techniques for assessing the competitive landscape, identifying market opportunities, and evaluating internal capabilities. This section integrates resource and process analysis with competitive environment analysis, providing a holistic view of the strategic decision-making process. It emphasizes the importance of aligning strategic objectives with organizational vision and mission, ensuring that e-business initiatives contribute to the overall success of the organization. The use of frameworks allows for systematic analysis of strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats within the e-business context.
5.3 Strategy definition and implementation
This section outlines the process of defining and implementing e-business strategies. It presents a structured approach to making key strategic decisions, including the prioritization of e-business channels, market and product development strategies, positioning and differentiation approaches, and the selection of appropriate business models. The section also explores successful and failed e-business strategies, providing students with real-world examples of both effective and ineffective approaches. The pedagogical value is in understanding how to translate strategic analysis into actionable plans and how to overcome common challenges in e-business implementation. The discussion includes aspects of investment appraisal, organizational change, and IS strategy integration.
VI. Supply Chain Management
This chapter explores the application of e-business principles to supply chain management (SCM). It examines the challenges of traditional SCM and presents a model for integrating technology to enhance efficiency and effectiveness. The chapter covers the concepts of push and pull supply chain models, value chain analysis, and value networks. It outlines various options for restructuring supply chains using e-business tools and technologies. It further discusses the different technology options and standards used in SCM, examining their adoption rates. The chapter includes discussions on downstream supply chain management, outbound logistics, and the human resource implications of implementing SCM initiatives. Case studies on Shell Chemicals and Tesco provide illustrative examples of how companies are leveraging e-business for supply chain optimization.
6.1 What is supply chain management and its problems?
This section defines supply chain management (SCM) and discusses the inherent challenges in managing a modern supply chain. It highlights the complexities of coordinating various activities across an organization's network of suppliers, partners, and customers. The pedagogical emphasis is on demonstrating how traditional supply chain processes are often inefficient and costly, thus setting the stage for explaining how e-business solutions can address these challenges. The discussion lays the groundwork for later sections, which will focus on the role of technology in optimizing various stages of the supply chain.
6.2 Using technology to support supply chain management
This section explains how technology can enhance supply chain processes and create significant value. It describes how e-business tools, such as electronic data interchange (EDI), enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, and other technologies, improve efficiency and effectiveness in various stages of the supply chain. It provides real-world examples illustrating successful implementations and the associated benefits. The pedagogical value lies in illustrating how technology can transform traditional supply chain operations, creating greater visibility, reducing costs, and enhancing responsiveness to market demands. It emphasizes the importance of aligning technology investments with overall business strategy.
6.3 Restructuring the supply chain with e-business
This section focuses on using e-business to restructure supply chains. It examines the concepts of push and pull supply chain models, value chain analysis, and value networks. It explores the different approaches for restructuring the internal value chain and creating a more efficient and responsive organization. The pedagogical value lies in understanding how the integration of e-business technologies can lead to radical improvements in supply chain design and management. The section also explores how the concept of the ‘virtual organization’ can be implemented through e-business to leverage external partnerships and resources.
VII. E-procurement
This chapter delves into the specifics of e-procurement, exploring its benefits, challenges, and implementation strategies. It defines e-procurement and outlines the procurement process, discussing various types of procurement and the roles of different participants in online procurement. The chapter examines the key drivers for adopting e-procurement, including cost savings and efficiency gains. It also explores the potential risks and challenges associated with e-procurement, such as integration issues, security concerns, and the risk of failing to achieve cost reductions. The chapter examines the use of electronic B2B marketplaces and their role in facilitating e-procurement. Case studies on Cambridge Consultants and Covisint showcase real-world examples of e-procurement implementations, highlighting both successes and failures.
7.1 What is e-procurement and its drivers?
This section defines e-procurement and discusses the main reasons why organizations adopt it. It explains how the automation of purchasing processes through electronic means can lead to substantial cost savings and increased efficiency. The pedagogical value lies in understanding the strategic rationale behind e-procurement adoption and its potential benefits. The section also highlights the importance of understanding the different types of procurement and their unique characteristics before embarking on an e-procurement initiative.
7.2 Risks and impacts of e-procurement
This section presents a balanced view of the risks and potential negative consequences of e-procurement implementation. It explores the potential pitfalls, such as integration challenges with existing systems, security vulnerabilities, and the risk of failing to realize anticipated cost savings. The pedagogical value lies in emphasizing the importance of a thorough risk assessment before embarking on e-procurement initiatives. This ensures that organizations can take proactive steps to mitigate potential problems and maximize the chances of successful implementation. The section also highlights the importance of managing organizational change effectively.
7.3 Implementing e-procurement and B2B marketplaces
This section provides a practical guide to implementing e-procurement solutions. It discusses various strategies for integrating company systems with supplier systems and explores the role of electronic B2B marketplaces in streamlining procurement processes. The pedagogical value lies in providing students with a framework for planning, executing, and evaluating e-procurement projects. It emphasizes the importance of careful planning, effective change management, and continuous monitoring and improvement to ensure the success of e-procurement initiatives. The discussion on B2B marketplaces provides insight into the different types of marketplaces and their potential roles in e-procurement.
VIII. E-marketing
This chapter focuses on the application of e-business principles to marketing, exploring the development and implementation of e-marketing strategies. It defines e-marketing, distinguishing it from e-business and e-commerce. The chapter outlines an e-marketing planning process, including situation analysis, demand analysis, competitor analysis, and objective setting. It discusses various marketing strategies and tactics, covering product, price, place, and promotion aspects of the marketing mix. The chapter examines the unique characteristics of digital marketing communications and explores various online marketing channels, such as search engine marketing, email marketing, and social media marketing. Case studies on Guess, easyJet, Dell, and Napster illustrate successful and innovative approaches to e-marketing.
8.1 What is e-marketing and its place in the overall e-business strategy?
This section introduces the concept of e-marketing and its relationship to broader e-business strategies. It carefully defines e-marketing and distinguishes it from e-commerce and e-business, providing a clear understanding of the scope and importance of digital marketing within the overall business strategy. The pedagogical value lies in understanding that e-marketing is not simply a matter of using the internet to sell products but rather a fundamental shift in how companies connect with their customers. This section lays the foundation for a comprehensive understanding of the e-marketing planning process.
8.2 E-marketing planning process and analysis
This section presents a detailed framework for developing an e-marketing plan. It outlines a systematic approach to conducting market research, analyzing the competitive landscape, identifying target markets, and setting marketing objectives. The pedagogical emphasis is on providing a structured approach to strategic planning and decision-making in the digital environment. This section prepares students to conduct market analysis, develop marketing strategies, and execute marketing campaigns tailored to the specific demands of the digital space. The detailed breakdown ensures that students have a thorough understanding of all aspects of the planning process.
8.3 E-marketing strategies and tactics
This section focuses on the development and implementation of e-marketing strategies and tactics. It explores the marketing mix (product, price, place, and promotion) in the context of the digital environment, highlighting the unique challenges and opportunities afforded by different online channels. The pedagogical emphasis is on understanding how digital technologies change the rules of traditional marketing and how businesses should adapt their marketing strategies to reflect this change. The section also emphasizes the importance of understanding customer behavior in online environments and leveraging data analytics to optimize marketing effectiveness.
IX. Customer Relationship Management
This chapter focuses on customer relationship management (CRM) in the context of e-business. It explores the application of e-commerce techniques for acquiring and retaining customers, emphasizing the importance of permission marketing, customer profiling, and conversion marketing. The chapter analyzes the online buying process, highlighting the differences in buyer behavior across various target markets and between B2C and B2B contexts. It discusses techniques for managing customer activity and value, such as lifetime value modeling, and explores the role of online communities in building customer relationships. The chapter also covers advanced online segmentation and targeting techniques and the role of technology solutions in supporting CRM initiatives. Case studies on Warner Breaks and Tesco.com provide examples of how companies are leveraging e-commerce to build and maintain strong customer relationships.
9.1 What is e-CRM and its benefits?
This section introduces the concept of e-CRM and its benefits. It defines e-CRM and explains how integrating digital technologies into customer relationship management can enhance customer interactions and strengthen relationships. The pedagogical value lies in emphasizing the importance of using digital tools to manage customer data effectively, personalize customer experiences, and build loyalty. The section lays the foundation for a more detailed exploration of specific e-CRM techniques and strategies. It also discusses the concept of permission marketing as a crucial element of building trust and maintaining positive customer relationships.
9.2 Customer acquisition and retention management
This section addresses the key aspects of customer acquisition and retention in the context of e-CRM. It examines techniques for attracting new customers using digital channels, emphasizing the importance of understanding online consumer behavior and leveraging digital marketing tools. It also explores various strategies for retaining existing customers, including loyalty programs, personalized communications, and community building. The pedagogical value lies in providing students with a practical framework for managing the customer lifecycle using e-commerce tools. The section also explores concepts such as conversion marketing and the net promoter score to measure customer satisfaction and loyalty.
9.3 Technology solutions and advanced techniques for e-CRM
This section focuses on the technological aspects of e-CRM. It explores the various software and applications used to manage customer data, personalize communication, and automate customer service processes. It discusses the importance of integrating CRM systems with other back-office systems and the choice between single-vendor and multi-vendor solutions. The pedagogical value is in providing an understanding of the various technological options available and the implications of different choices for e-CRM implementation. The section also covers advanced techniques such as online segmentation and targeting and the use of data analytics to gain insights into customer behavior. It also discusses the importance of high-quality data for effective e-CRM.
X. Change Management
This chapter explores the crucial aspect of managing organizational change during e-business transformation. It examines the challenges of implementing e-business systems, particularly in sell-side e-commerce. The chapter discusses different types of organizational change and presents planning frameworks for managing the transition. It emphasizes the importance of project governance and outlines a project plan and schedule for an e-business system. The chapter also addresses human resource requirements, staff retention strategies, outsourcing options, and organizational restructuring. It reviews various approaches to managing change, including models for achieving successful transformation and fostering a supportive organizational culture. The role of knowledge management in supporting e-business initiatives is also discussed. Case studies on process management at an unnamed company and the use of Web 2.0 tools at Janssen-Cillag Australia provide examples of effective change management practices.
10.1 The challenges of e-business transformation and types of change
This section highlights the significant challenges businesses face when implementing e-business initiatives. It focuses on the complexities of organizational change, emphasizing the need for careful planning and effective execution. The pedagogical value lies in understanding the potential disruptions and difficulties that organizations may encounter during the transition. The section also categorizes different types of organizational change to provide a framework for analyzing the specific challenges encountered in e-business projects. It sets the stage for later sections dealing with planning and managing the change process effectively.
10.2 Planning change and managing human resources
This section focuses on the planning phase of e-business transformation and the crucial role of managing human resources. It highlights the importance of effective project governance and outlines a structured approach to project planning and scheduling. It emphasizes the human resource requirements of such projects, including staff training, recruitment, and retention. The section also discusses strategies for managing staff resistance to change and improving employee morale. The pedagogical value lies in understanding the need to involve people in the change process and address their concerns early on. The section provides a step-by-step guide to planning e-business projects and managing the human aspect effectively.
10.3 Approaches to managing change and knowledge management
This section presents different approaches to managing organizational change during e-business transformation. It explores various models for achieving change, emphasizing the importance of leadership, communication, and stakeholder involvement. The section also emphasizes the importance of organizational culture and the need to foster a culture of innovation and adaptation. The role of knowledge management in supporting the transition to e-business is also addressed, outlining strategies for capturing, sharing, and leveraging organizational knowledge. The pedagogical value lies in understanding the interconnectedness of these elements in driving successful e-business implementations. The section also discusses risk management and the importance of building a robust risk management plan.
XI. Analysis and Design
This chapter delves into the analysis and design phase of e-business system development. It covers workflow management, process modeling, and data modeling techniques. The chapter focuses on user-centered site design, use-case analysis, and designing the information architecture. It emphasizes the importance of customer orientation and outlines various elements of effective website design. The chapter addresses the crucial aspect of website accessibility. Security design for e-business is also thoroughly explored, including discussions on managing computer viruses, controlling information service usage, monitoring electronic communications, email management, and preventing hacking. Secure e-commerce transactions and approaches to developing secure systems are discussed. Case studies on Arena Flowers and Dabs.com illustrate effective analysis and design processes.
11.1 Analysis for e-business: workflow management and process modeling
This section focuses on the initial analysis phase of e-business system development. It covers workflow management, process modeling, and data modeling techniques. The pedagogical value lies in providing a structured approach to analyzing existing business processes and identifying opportunities for improvement through e-business solutions. This systematic approach ensures that e-business projects are aligned with business needs and lead to tangible improvements in organizational efficiency and effectiveness. The section emphasizes the importance of understanding business processes before designing and implementing new systems.
11.2 Design for e-business: user-centered design and information architecture
This section examines the design phase of e-business system development, focusing on user-centered design and information architecture. It explains how to create websites that are intuitive, easy to use, and accessible to all users. The pedagogical value lies in teaching students how to design websites that meet user needs and support effective user interaction. The section emphasizes the importance of creating a positive user experience and delivering relevant information efficiently. It also discusses website accessibility guidelines and best practices for ensuring inclusivity.
11.3 Security design for e-business
This section addresses the critical issue of security in e-business systems. It covers various security threats and vulnerabilities, including computer viruses, hacking attempts, and data breaches. It provides students with a comprehensive understanding of security design principles and best practices for protecting sensitive information and ensuring secure e-commerce transactions. The pedagogical value lies in understanding the importance of proactive security measures and the need to build secure systems from the ground up. The section includes detailed discussion on specific security threats and countermeasures and highlights the need for ongoing security monitoring and updates.
XII. Implementation and Maintenance
This chapter covers the implementation and ongoing maintenance of e-business systems. It discusses various options for acquiring e-business systems, including in-house development and outsourcing. The chapter explains how to develop web-based content and services, covering both static and dynamic content creation. It addresses the importance of testing, outlining the testing process and different testing environments. The chapter explores database creation and data migration, deployment planning, and content management and maintenance. It also covers performance management and improvement, providing a framework for measuring and improving the performance of e-business systems. A case study on Amazon illustrates how leading companies use metrics to drive continuous improvement. The chapter concludes by addressing budgeting considerations for e-business projects.
12.1 Acquiring and developing e-business systems
This section discusses the different options available to businesses when acquiring or developing e-business systems. It explores the trade-offs between in-house development, outsourcing, and using ready-made software packages. The pedagogical value lies in providing students with the knowledge to assess these different approaches, weigh the pros and cons, and choose the best option for their specific needs and context. The section emphasizes the importance of making informed decisions based on factors such as cost, time, expertise, and risk tolerance. The selection of the right approach is crucial for the successful implementation of e-business projects.
12.2 Implementing and testing e-business systems
This section covers the implementation and testing phases of e-business projects. It provides a practical guide to developing web-based content, managing databases, and conducting thorough testing to ensure system stability and functionality. The pedagogical value lies in providing a step-by-step approach to implementing e-business projects. The emphasis on rigorous testing ensures that students understand the importance of quality assurance and preventing errors in production environments. The discussion includes various testing methodologies and guidelines for effective testing.
12.3 Maintaining and improving e-business systems
This section emphasizes the importance of ongoing maintenance and improvement for e-business systems. It covers content management, performance monitoring, and continuous improvement strategies. The pedagogical value lies in understanding that e-business projects are not completed upon deployment; instead, they require ongoing attention and optimization. The section emphasizes the importance of using metrics to track system performance, identify areas for improvement, and ensure the long-term sustainability of e-business solutions. The section also highlights the importance of budgeting for ongoing maintenance and upgrades.