commit to user
A LIBRARY RESEARCH ON TEACHER-STUDENTS POSITIVE
INTERACTION TO IMPROVE STUDENTS MOTIVATION TO LEARN
ENGLISH AS FOREIGN LANGUAGE
Agung Budi Winarto
K2211005
ARTICLE
ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
TEACHER TRAINING AND EDUCATION FACULTY
SEBELAS MARET UNIVERSITY
commit to user
A LIBRARY RESEARCH ON TEACHER-STUDENTS POSITIVE
INTERACTION TO IMPROVE STUDENTS MOTIVATION TO LEARN
ENGLISH AS FOREIGN LANGUAGE
Agung Budi W., JokoNurkamto, HefySulistyawati
English Education Department of Teacher Training and Education Faculty SebelasMaret University Surakarta
E-mail: [email protected]
Abstract: The objective of this library research is to investigate the way the teachers-students positive interaction in the classroom improves students’ motivation in learning English as foreign language. The method used in this research is library research method by collecting theories from various sources. The theories were then critically analyzed by elaborating the ideas and comparing them. As the conclusion, the researcher made synthesis from those theories and answered the research problem. The finding of the research is that teacher-students positive interaction can improve students’ motivation to learn English as foreign language. The interaction works through intrinsic and extrinsic motivation that is shown on the researcher’s foreign language learning motivation framework. The framework is made by modifying Gardner’s socio-educational model with other theories to make the theory able to be applied in the classroom.
Keywords: teacher-students positive interaction, students’ motivation, library research.
Abstrak: Tujuan dari penelitian ini adalah untuk mengidentifikasi cara interaksi positif guru-murid di dalam kelas untuk meningkatkan motivasi siswa untuk belajar Bahasa Inggris sebagai bahasa asing. Metode yang digunakan pada penelitian ini adalah metode kajian pustaka dengan mengumpulkan teori dari berbagai sumber. Teori-teori kemudian dianalisis secara kritis dengan menguraikannya pada bab kedua dan ketiga. Sebagai kesimpulan, peneliti membuat sintesis dari teori-teori tersebut. Hasil dari penelitian ini adalah bahwa interaksi positif guru-murid dapat meningkatkan untuk belajar Bahasa Inggris sebagai bahasa asing. Interaksi ini bekerja melalui motivasi intrinsik and ekstrinsik yang ditunjukan pada kerangka berpikir motivasi belajar bahasa asing peneliti. Kerangka berpikir dibuat dengan memodifikasi model socio-educational Gardner dengan teori lainya supaya teori tersebut dapat diaplikasikan di dalam kelas.
commit to user
Motivation is very important in teaching and learning process. Students’
motivation level determines their behavior and attitude in the class (Dornyei, 1998). Motivation can also determine students’ success in learning (Brown, 2001: 72).
The absence of motivation will create a complex problem. Without
motivation teaching learning process will not go well. The unmotivated students
will make the class not conducive. This motivational problem can be caused by both
students and teachers. Thosalis and Nakkula (2012) say that students’ motivation is low because of incapable of the students, social condition, and the students’ belief. In the other hand, the way the teacher teach or teachers’ creativity and method used determine the students’ motivation level.
Jafari (2013) says that motivation has different definition according to its
point of view. From the cognitive point, there are intrinsic motivation and extrinsic
motivation. From social aspect, Gardner and Lambert (in Babaee, 2012) distinguish
between motivation and orientation. The last is process of motivation such as
behavior reinforcement theory, needs theory, goal theory, and aspiration theory,
achievement theory and expectancy theory. In the term of second language motivation, Gardner created a model to show how the process of students’ motivation to learn English as second language.
Teachers and students positive interaction is very important. Studies (Ilias
and Nor, 2012; Nugent, 2009) showpositive correlations between teacher-students interaction and students’ motivation. However, the interaction does not directly affect students’ motivation (Ilias and Nor, 2012).
The researcher assumed that teacher-students positive interaction can improve students’ motivation to learn English as foreign language by modifying Gardner’s socio-educational model. The researcher conducted a library research aimed to find out teacher-students interaction can improve students’ motivation in
commit to user RESEARCH METHOD
The method that the researcher used in this paper was library research.
Library research that is also called theoretic research is not a compilation of other
researches or arguments, but a research that is conducted through critical analysis so
that what is written can be justified. Library research gives more understanding
about the decided topic because this research analyzes more data from many
researches than other kinds of research that collect the data only in a situation.
Several steps should be taken to conduct library research (Richards, Platt, dan Platt,
1993), namely: (1) Define the variables as clear as possible; (2) Choose the source
of the data or theories that are relevant to the variables above and read it; (3)
Describe every single theory; (4) Do critical analysis towards every theory above by
explaining the strength and weakness of every theory (Kerlinger, 1990); (5) Do
comparison analysis between theory to decide which theory has more strengths and
which theory has more weaknesses; (6) Make conclusion, the researcher has two
choices: choose one of the theories that are assumed to be the best theory, or make
synthesis from many theories (Lemlit IKIP Jakarta, 1991).
After doing the steps above, the researcher makes the framework for every
chosen variable. Basically, the framework is the rational explanation about the
relationship between variables. The researcher relates the variables based on the
concept from the theories by using the strength of his analysis. The step should be
done perfectly to make the readers able to follow the explanation. This is also the
step where the researcher shows his intelligent, skill, and style.
The framework is made as the background to conduct hypothesis. Therefore,
hypothesis does not come suddenly but through processes that have been passed
before. The accuracy of the hypothesis is determined by the critical framework, and
critical thinking of the researcher is determined by his understanding of the concept
from the theoretical review. As explained before, hypothesis is the estuary of the
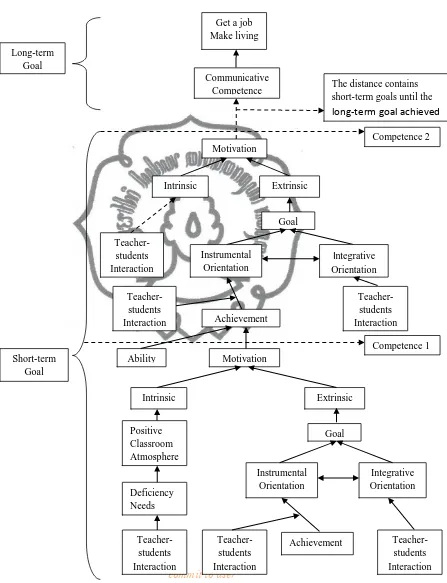
commit to user Get a job Make living
Communicative Competence
Motivation
The distance contains short-term goals until the long-term goal achieved
Intrinsic Extrinsic
Goal Instrumental Orientation Integrative Orientation Teacher-students
Interaction Achievement
Ability Motivation
Intrinsic Extrinsic
[image:5.594.108.555.118.701.2]Teacher-students Interaction Positive Classroom Atmosphere Deficiency Needs Goal Instrumental Orientation Integrative Orientation Achievement Teacher-students Interaction Teacher-students Interaction Short-term Goal Long-term Goal Teacher-students Interaction Competence 2 Competence 1 Teacher-students Interaction
commit to user RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSIONS
The researcher extend Gardner’s socio-educational model of L2 learning by
incorporating it new elements from intrinsic-extrinsic motivation, expectancy-value,
goal theories, achievement theory, level of aspiration theory, needs theory, and
behavior reinforcement theory. The researcher uses the important point from every
motivation theory as explained in the previous chapter to be used to conduct the
most appropriate theory for Indonesia students who learn English as foreign
language. The researcher also adds teacher-students positive interaction as one of the elements that modified Gardner’s socio-educational model.
Intrinsic and Extrinsic Motivation
The researcher agrees that there are two kind of motivation, intrinsic and
extrinsic motivation (Ryan and Deci, 2000). The biggest issue in this theory is
which one is more important than another. Instead of arguing which one is more
important and better, the researcher suggest that both intrinsic and extrinsic are
important.
Many researchers assume intrinsic motivation is better than extrinsic
motivation. Ames & Archer (in Johansson, 2010) says intrinsic motivation is very
important for students; the students who have intrinsic motivation will lean in more
advanced way than the students who learn because of the reward and punishment.
Although intrinsic motivation is very important for the students, intrinsic motivation
cannot be expected to be developed continuously (Brophy, 2004: 14).Students who
have both kinds of motivation will be self-determined rather than controlled by the
extrinsic reward so that they will have better effort, behavior, attitude, and
resistance in learning foreign language (Ryan & Decy, 2000). The researcher
suggests that the students should have both kinds of motivation because intrinsic
motivation will make the students enjoy their learning and extrinsic motivation will
give them the vision of what they do. Furthermore, the teacher-students positive
commit to user Develop Intrinsic Motivation
In Indonesia, English is a difficult subject so that not all the students in the
classroom like English, except only one or two students. However, if the teacher can
provide positive learning atmosphere that invites the students to learn and they find
that English is fun and enjoyable, the intrinsic motivation will be developed.
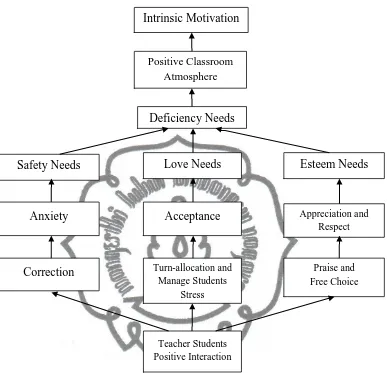
Developing intrinsic motivation can be done by establishing positive
classroom atmosphere that invites the students to learn. The researcher assumes Maslow’s hierarchy of needs can be applied in creating this motivating classroom atmosphere.
According to Maslow (in Slavin, 2006) the deficiency needs are
physiological needs, safety needs, love needs, and esteem needs. Teacher may not have chance to satisfy every students’ psychological needs like food and liquid because it is impossible for the teacher to provide the foods and liquids for students.
In language learning, Maslow (in Brophy, 2004: 6) suggests that safety
needs are associated with language anxiety. Teacher should correct the students’
error in appropriate way. The correction should be seen as feedback (Harmer, 2004:
100) and in right moment and not to offense the students (Harmer, 2004: 105).
The third deficiency needs are love needs. Maslow (in Brophy, 2004: 6)
defines love needs as acceptance from parents, teacher, and peers. Teacher should
treat the students equally by not differentiating them based on their ability by
recognizing the importance of turn-allocation. In addition, Daniels (2010: 27) says that teacher should know how to manage the students’ stress.
The last deficiency needs are esteem needs. Maslow (in Brophy, 2004: 6)
says that esteem needs are based on desires for appreciation and respect. Students need to be appreciated for doing well of something. In this situation, teacher’s feedback, once again, plays important role. Teacher’s praise towards students’ success is important to boost their confidence. In addition, as Daniels (2010: 26-27)
says that to make the students feel confident of what they do the teacher should give
commit to user
Fig. 2 The researcher’s intrinsic motivation model
Develop Extrinsic Motivation
The extrinsic motivation is quite different from intrinsic motivation. Teacher
should first know the kind of the students’ external motivation. The researcher suggests Gardner’s concept of integrative and instrumental orientation can be categorized as extrinsic motivation.
In this study, the researcher will focus on English as foreign language (EFL).
In the EFL situation, the students only learn English in the classroom, but will not
continue to use English when they leave the classroom. Brown (2007: 205) says that
Learning EFL is where the learners will not easily learn English as English as Intrinsic Motivation
Positive Classroom Atmosphere
Safety Needs
Deficiency Needs
Esteem Needs Love Needs
Anxiety Acceptance Appreciation and
Respect
Correction Turn-allocation and Manage Students
Stress
Praise and Free Choice
commit to user
second language (ESL) where English is already accepted and used language for
education, government, and business within the country.
By understanding the differences between learning ESL and learning EFL
above, it can be concluded that which motivation theory is the most appropriate for
students is based on who, what and where they are learning the language (Dornyei,
1994a: 275). ESL learners, of course, have intention to integrate with the cultures
who speak the target language. While EFL learners who do not have chance to
apply what they have learned in school and will never be able to use it with native
speakers. Furthermore, Indonesian students rarely think to travel and integrate with
native speakers in the English speaking country.
The researcher suggests that generally Indonesian students rarely think to go
abroad neither for educational purpose nor travel and immigration. Therefore in this
study, the researcher agrees that instrumental motivation is more dominant for EFL
learners especially in Indonesia.
Most researchers agree that integrative is related to intrinsic motivation and
instrumental is related to extrinsic motivation. Chambers (in Kheradmandan, 2011)
says both intrinsic motivation and integrative motivation are internal while extrinsic
motivation and instrumental motivation are both external. Even though most
researcher agree that integrative motivation is related to intrinsic but according to Brown’s idea the researcher assumes that integrative can be categorized as the highest extrinsic motivation. The researcher categorizes integrative as extrinsic
motivation is based on Brown (in Carreira, 2005) who says that motivation is
divided into four categories: intrinsic-integrative, intrinsic-instrumental,
extrinsic-integrative, and extrinsic-instrumental. In this research, the researcher categorizes
integrative orientation as extrinsic-integrative. The purpose of learning English is to
integrate with the target language culture (integrative) because to get a job he/she
needs to integrate with those target language users.
commit to user
For those reasons, many researchers have attempted to modify and adapt Gardner’s
theory and other theories of motivational psychology and apply them to educational situations. Thus, the researcher decides to combine Garner’s theory with the theory of motivation as process as the practical theory so that Gardner’s theory can be
applied in the language classroom setting.
From the researcher’s framework theory, there are long-term and short-term goal. The researcher suggests that in EFL learning, the long-term goal is to make the
students able to communicate along with get a job and make living and the
short-term goals are the competences the students should achieve, for example, students
should learn from the very beginning level of listening based on their present ability,
if they have passed the level they can go to the next level (e.g., Listening 2). The
students may see that English is difficult, but if they see their progress of what they
have achieved in short-term goals it will keep their motivation until they reach the
long-term goal. Thus, long-term and short-term goals refer to instrumental and
integrative orientation.
Teacher-students positive interaction is very important in this framework.
Teacher-students positive interaction is very important in this framework. Teacher
should start from the long-term goal. By understanding that general Indonesian
students are not motivated to learn English because they do not understand what
opportunities that English can give. The role is to make the students believe that
English is very important for their life. The ability to communicate will bring them
into the desired job or other extrinsic rewards. This will make the students eager to
learn English. To keep that motivation, the teacher should maintain their motivation
though short-term goals. Every goals passed will make the students feel that they are
closer to the long-term goal that is the ability to communicate.
If those two motivations, intrinsic and extrinsic, have been successfully
developed by the teacher and the most appropriate short-term goal has been set, the
researcher suggests that the students will achieve the goal. Although students have
commit to user
that determined by their motivation as expectancy theory says. The students’
achievement is then used as the consideration to conduct the next goal, whether the
students success or fail (Hoppe in Quaglia and Cobb, 1996). The cycle of the
short-term goals repeatedly run until the long-short-term goal achieved.
CONCLUSION
Based on the discussion above, there are two conclusions obtained. First, to
solve motivational problems that occur in the classroom teacher should first understand what kind of motivation the students have. The kind of students’ motivation is not the same in different countries because the students’ motivation is strongly influenced by their environment. By knowing the kind of students’ motivation then the teacher will be able to develop the most appropriate strategies to
be applied in the classroom.
Second, the teacher-students positive interaction can improve students’ motivation by initiate, develop and maintain students’ motivation. Initiating students’ motivation is not enough without following up by developing and maintaining the motivation. Developing and maintaining motivation is very
important to ensure that students will not lose their motivation until they reach their
expected goals. The short-term goals tend to develop and maintain motivation that is
initiated by the long-term goal.
Based on the discussion above teacher-students positive interaction can work
through both intrinsic and extrinsic motivation. The teacher-students positive interaction’s role is to manipulate students’ motivation by influence their perception about English and learning English. The perception is then followed by the progress
that can from their achievement. The more goals the students achieve, the more they
commit to user BIBLIOGRAPHY
Babaee, N. (2012). Motivation in Learning English as a Second Language: A Literature Review. University of Manitoba, Canada.
Brophy, Jere. (2004). Motivating Students to Learn. New Jersey: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Brown, H. Douglas. (2001). Teaching by Principles, An Interactive Approach to Language pedagogy. New York: Pearson Education Ltd.
Brown, H. D. (2007). Principle of Language Learning and Teaching, Fifth Edition. San Francisco: Pearson Education, Inc.
Buku Pedoman Penelitian Teoretis & Penyusunan Usul Penelitian. 1991. Jakarta: Lembaga Penelitian IKIP Jakarta.
Carreira, J. M. (2005). New Framework of Intrinsic/Extrinsic and Integrative/Instrumental Motivation in Second Language Acquisition. The Keiai Journal of International Studies,16.
Daniels, Erika. (2010). Creating Motivating Learning Environments: What We Can Learn from Researchers and Students. English Journal100.1: 25-29.
Dornyei, Zoltan. (1994a). Motivation and Motivating in the Foreign Language Classroom. The Modern Language Journal, Vol.78, No. 3, pp 273-284.
Dornyei, Zoltan. (1998). Motivation in Second and Foreign Language
Learning.Language Teaching, 31, pp 117-135.
Doi:10.1017/S026144480001315X.
Harmer, Jeremy. (2004). The Practice of English Language Teaching New Edition. Longman: England.
Kerlingr, Fred N. 1990. Asas-Asas Penelitian Behavioral. Yogyakarta: Gajah Mada University Press.
commit to user
Jafari, S. S. (2013). Motivated Learners and Their Success in Learning a Second Language. Theory and Practice in Language Studies, Vol. 3, No. 10, pp. 1913-1918. Doi:10.4304/tpls.3.10.1913-1918.
Johansson, A. (2010). What Influences Students’ Motivation for Learning English Grammar? G3-paper 15 hp. Linnaeus University.
Kheradmandan, Peter M. (2011). How Can We Maintain Learners’ LS Motivation in a Classroom Setting?
Liuolienė, A., &Metiūnienė, R. (2006).Second Language Learning Motivation.Santalka.Filologija Edulologija,14(2), 93-98.
Nugent, T. T. (2009). The impact of teacher-students interaction on students motivation and achievement.Doctor of Education Dissertation, University of Central Florida Orlando, Florida.
Quaglia, R. J., & Cobb, C.D. (1996). Toward a Theory of Student Aspirations.Journal of Research in Rural Education, Vol. 12, No. 3, 127-132.
Richards, Jack C.; Platt, John; dan Platt, Heidi.1993. Longman Dictionary of Language Teaching & Applied Linguistics. England: Longman.
Ryan, Richard M., &Deci, L. (2000). Intrinsic and Extrinsic Motivations: Classic Definitions and New Directions. Contemporary Educational Psychology 25, pp. 54-67. doi:10.1006/ceps.1999.1020.
Slavin, R. (2006). Educational Psychology (8th ed.). Boston: Pearson/ Allyn & Bacon.