Journal of Theoretical and Applied I nformati on Technology
© 2005 - 2014 JATIT & LLS. All rights reserved
ISSN: 1992-8645 www.jatit.org E-ISSN: 1817-3195
JOURNAL OF THEORETICAL AND APPLIED
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
EDITORIAL COMMITTEE
NIAZ AHMAD
(Chief Editor)
Professor, FCE, MOE, H-9 Islamabad
PAKISTAN
SHAHBAZ GHAYYUR
(Co- Chief Editor)
Assistant Professor, DCS, FBAS, International Islamic University Islamabad,
PAKISTAN
SAEED ULLAH
(Associate Editor)
Assistant Professor, DCS, Federal Urdu University of Arts, Science & Technology Islamabad,
PAKSITAN
MADIHA AZEEM
(Associate Editor)
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology, Islamabad.
PAKISTAN
SALEHA SAMAR
(Managing Editor)
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology, Islamabad.
PAKISTAN
KAREEM ULLAH
(Managing Editor)
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology, Islamabad.
PAKISTAN
SHAHZAD A. KHAN
Lecturer IMCB, FDE Islamabad, PAKISTAN
(Managing Editor/Linguists & In-charge Publishing)
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology, Islamabad.
PAKISTAN
January 2014. Vol. 59 No.3
.
i
Journal of Theoretical and Applied I nformati on Technology
© 2005 - 2014 JATIT & LLS. All rights reserved
ISSN: 1992-8645 www.jatit.org E-ISSN: 1817-3195
JOURNAL OF THEORETICAL AND APPLIED
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
REGIONAL ADVISORY PANEL
Dr. SIKANDAR HAYAT KHIYAL
Professor &Chairman DCS& DSE, Fatima Jinnah Women University, Rawalpindi, PAKISTAN
Dr. MUHAMMAD SHER
Professor &Chairman DCS, FBAS, International Islamic University Islamabad, PAKISTAN
Dr. ABDUL AZIZ
Professor of Computer Science, University of Central Punjab, PAKISTAN
Dr. M. UMER KHAN
Asst. Professor Department of Mechatronics, Air University Islamabad, PAKISTAN
Dr. KHALID HUSSAIN USMANI
Asst. Professor Department of Computer Science, Arid Agriculture University,
Rawalpindi, PAKISTAN
January 2014. Vol. 59 No.3
.
Journal of Theoretical and Applied I nformati on Technology
© 2005 - 2014 JATIT & LLS. All rights reserved
ISSN: 1992-8645 www.jatit.org E-ISSN: 1817-3195
JOURNAL OF THEORETICAL AND APPLIED
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
January 2014. Vol. 59 No.3
.
iii
Dr. CHRISTEL BAIER
Technical University Dresden, GERMANY
Dr KHAIRUDDIN BIN OMAR UniversitiKebangsaanMalysia, 43600 Bangi
Selangor Darul-Ehsan, MALYSIA
Dr. YUSUF PISAN
University of Technology, Sydney, AUSTRALIA
Dr. S. KARTHIKEYAN Department of Electronics and Computer Engineering, Caledonian College of Engineering,
OMAN (University College with Glascow University, Scotland, UK) DR. YUXIN MAO
School Of Computer & Information Engineering Zhejiang Gongshang University, CHINA
Dr. ZARINA SHUKUR
FakultiTeknologidanSainsMaklumat, University Kebangsaan MALYSIA
Dr. NOR AZAN MAT ZIN
Faculty of Information Science & Technology, National University of MALYSIA
Dr. R.PONALAGUSAMY
National Institute of Technology, Tiruchirappalli, Tamil Nadu, INDIA
Dr. MOHAMMAD TENGKU SEMBOK Universiti Kebangsaan MALYSIA
Dr. PRABHAT K. MAHANTI University of New Brunswick, Saint John, New
Brunswick, CANADA
Dr. NITIN UPADHYAY
Birla Institute of Technology and Science (BITS), Pilani-Goa Campus, INDIA
Dr. S.S.RIAZ AHAMED
Mohamed Sathak Engineering College, Kilakarai, &Sathak Institute of Technology, Ramanathapuram , Tamilnadu, INDIA
Dr. A. SERMET ANAGÜN
Eskisehir Osmangazi University, Industrial Engineering Department, Bademlik Campus,
26030 Eskisehir, TURKEY.
Dr. YACINE LAFIFI
Department of Computer Science, University of Guelma, BP 401, Guelma 24000, ALGERIA.
Dr. CHRISTOS GRECOS
School Of Computing, Engineering And Physical Sciences University Of Central Lancashire.
UNITED KINGDOM
Dr. JAYANTHI RANJAN Institute of Management Technology Raj Nagar, Ghaziabad, Uttar Pradesh, INDIA
Dr. ADEL M. ALIMI
National Engineering School of Sfax (ENIS), University of SFAX, TUNISIA
Dr. RAKESH DUBE
Professor & Head, RKG Institute of Technology, Ghaziabad, UP, INDIA
Dr. ADEL MERABET
Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering, Dalhousie University, Halifax,
CANADA
Dr. HEMRAJ SAINI
CE&IT Department, Higher Institute of Electronics, BaniWalid. LIBYA
Journal of Theoretical and Applied I nformati on Technology
© 2005 - 2014 JATIT & LLS. All rights reserved
ISSN: 1992-8645 www.jatit.org E-ISSN: 1817-3195 January 2014. Vol. 59 No.3
.
iv Dr. SEIFEDINE KADRY
Lebanese International University, LEBONON
Dr. AIJUAN DONG Department of Computer Science Hood College Frederick, MD 21701. USA
Dr. ZURIATI AHMAD ZUKARNAIN University Putra Malaysia,
MALAYSIA
Dr. HEMRAJ SAINI
Higher Institute of Electronic, BaniWalid LIBYA
Dr. CHELLALI BENACHAIBA University of Bechar, ALGERIA
Dr. MOHD NAZRI ISMAIL
University of Kuala Lumpur (UniKL) MALYSIA
Dr. VITUS SAI WA LAM The University of Hong Kong, CHINA
Dr. WITCHA CHIMPHLEE SuanDusitRajabhat University, Bangkok,
THAILAND
Dr. SIDDHIVINAYAK KULKARNI University of Ballarat, Ballarat,
AUSTRALIA
Dr. S. KARTHIKEYAN Caledonian College of Engineering,
OMAN
Dr. DRAGAN R. MILIVOJEVIĆ Mining and Metallurgy Institute BorZelenibulevar
35, 19210 Bor, SERBIA
Dr. E. SREENIVASA REDDY Principal - VasireddyVenkatadri Institute of
Technology, Guntur, A.P., INDIA
Dr OUSMANE THIARE Gaston Berger University, Department of Computer Science, UFR S.A.T, BP 234 Saint-
Louis SENEGAL
Dr. SANTOSH DHONDOPANT KHAMITKAR RamanandTeerthMarathwada University, Nanded.
Maharashtra 431605, INDIA
Dr. M. IQBAL SARIPAN
(MIEEE, MInstP, Member IAENG, GradBEM) Dept. of Computer and Communication Systems Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Universiti
Putra MALAYSIA
Dr. E. SREENIVASA REDDY Principal - VasireddyVenkatadri Institute of
Technology, Guntur, A.P., INDIA
Dr. T.C.MANJUNATH, Professor & Head of the Dept., Electronicis& Communication Engg. Dept,
New Horizon College of Engg., Bangalore-560087, Karnataka, INDIA.
Dr. SIDDHIVINAYAK KULKARNI
Graduate School of Information Technology and Mathematics University of Ballart AUSTRALIA
Dr. SIKANDAR HAYAT KHIYAL Professor & Chairman DCS& DSE, Fatima
Jinnah Women University, Rawalpindi,
PAKISTAN
Dr. MUHAMMAD SHER Professor & Chairman DCS, FBAS, International Islamic University Islamabad,
PAKISTAN
Dr. ABDUL AZIZ
Professor of Computer Science, University of Central Punjab, PAKISTAN
Dr. M. UMER KHAN
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Informati on Technology
© 2005 - 2014 JATIT & LLS. All rights reserved
ISSN: 1992-8645 www.jatit.org E-ISSN: 1817-3195
Elite Panel Members Have A Decision Weight Equivalent of Two Referees (Internal OR External). The Expertise Of Editorial Board Members Are Also Called In For Settling Refereed Conflict About
January 2014. Vol. 59 No.3
Acceptance/Rejection And Their Opinion Is Considered As Final.
.
v Dr. RIKTESH SRIVASTAVA
Assistant Professor, Information Systems Skyline University College P O Box 1797, Sharjah, UAE
Dr. BONNY BANERJEE
PhD in Computer Science and Engineering, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USA
Senior Scientist Audigence, FL, USA
PROFESSOR NICKOLAS S. SAPIDIS DME, University of Western Macedonia
Kozani GR-50100, GREECE.
Dr. NAZRI BIN MOHD NAWI Software Engineering Department, Faculty of
Science Computer Information Technology,
Universiti Tun Hussein Onn MALAYSIA
Dr. JOHN BABALOLA OLADOSU Ladoke Akintola University of Technology,
Ogbomoso, NIGERIA
Dr. ABDELLAH IDRISSI
Department of Computer Science, Faculty of Science, Mohammed V University - Agdal,
Rabat, MOROCCO
Dr. AMIT CHAUDHRY
University Institute of Engineering and Technology, Panjab University, Sector-25,
Chandigarh, INDIA
Dr. ASHRAF IMAM
Aligarh Muslim University, Aligarh-INDIA
Dr. MOHAMMED ALI HUSSAIN Dept. of Computer Science & Engineering, Sri Sai Madhavi Institute of Science & Technology,
Mallampudi, Rajahmundry, A.P, INDIA
Dr. KHALID HUSSAIN USMANI Asst. Professor Department of Computer Science,
Arid Agriculture University, Rawalpindi, PAKISTAN
Dr. GUFRAN AHAMD ANSARI Qassim University, College of Computer Science,
Ministry of Higher Education, Qassim University, KINGDOM OF SAUDI
ARABIA
Dr. Defa Hu
School of Information, Hunan University of Commerce
Changsha 410205, Hunan, P. R. of China
Journal of Theoretical and Applied I nformati on Technology
© 2005 - 2014 JATIT & LLS. All rights reserved
ISSN: 1992-8645 www.jatit.org E-ISSN: 1817-3195
PREFACE
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology (JATIT) published since 2005 (E-ISSN 1817- 3195 / ISSN 1992-8645) is an International refereed research publishing journal with a focused aim of promoting and publishing original high quality research dealing with theoretical and scientific aspects in all disciplines of Information Technology. JATIT is an international scientific research journal focusing on issues in information technology research. A large number of manuscript inflows, reflects its popularity and the trust of world's research community. JATIT is indexed with various organizations and is now published on monthly basis.
All technical or research papers and research results submitted to JATIT should be original in nature, never previously published in any journal or undergoing such process across the globe. All the submissions will be peer-reviewed by the panel of experts associated with JATIT. Submitted papers should meet the internationally accepted criteria and manuscripts should follow the style of the journal for the purpose of both reviewing and editing. All of its articles also appear online as per policy of JATIT
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology receives papers in continuous flow and we will consider articles from a wide range of Information Technology disciplines encompassing the most basic research to the most innovative technologies. Please submit your papers electronically to our submission system at http://jatit.org/submit_paper.php in an MSWord, Pdf or compatible format so that they may be evaluated for publication in the upcoming issue. This journal uses a blinded review process; please remember to include all your personal identifiable information in the manuscript before submitting it for review, we will edit the necessary information at our side. Submissions to JATIT should be full research / review papers (properly indicated below main title).
It is the sole responsibility of the submitting authors to make sure that the submitted manuscript is not in process of publication anywhere in any conference/journal across the globe, nor part or whole of it is copied from any source.
The review process may take anywhere from five days to two months depending on the response time to referees. Authors will be informed about the updated status via e-mail as soon as we receive the evaluation results. After submission of publication dues for accepted manuscripts a publication slot will be allocated to your manuscript for its publication in upcoming monthly issues of JATIT.
******************
January 2014. Vol. 59 No.3
.
vi
Journal of Theoretical and Applied I nformati on Technology
© 2005 - 2014 JATIT & LLS. All rights reserved
ISSN: 1992-8645 www.jatit.org E-ISSN: 1817-3195
ABSTRACTING & INDEXING
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology Islamabad Pakistan is focused, double blind peer reviewed journal that is now being published monthly and is published by Asian Research Publishing Network and is Indexed / Abstracted by the following International Agencies and institutions. JATIT has been regularly published since 2005 and now has a well reputed international standing and invites contributions from researchers, scientists, and practitioners from all over the world.
*- Ulrich's Periodicals Directory
*- DataBase systems and Logic Programming (DBLP) *- EBSCO Publishing USA
*- Directory of Open Access Journals (DOAJ) *- Google & Google Scholar Journals
*- The Index of Information Systems Journals *- Information Technology Resources Collection *- ZDNet Australia
*- NLM Catalog
*- Computing Research and Education Association of Australasia *- CiteSeer
*- Elsevier *- SCOPUS
*- Engineering Village *- TOC Premier
******************
Feel free to suggest JATIT to any Indexing & Abstracting Services which are appropriate to its scope TM
January 2014. Vol. 59 No.3
*- Computer Science Journals
*- Computers and Applied Sciences Complete *- N|W Switzerland
*- Microsoft Academic Search *- Cabell Publishing
*-OpenJgate
*- INSPEC
*- IAOR Palgrave Macmillan
.
vii
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology
31st January 2014. Vol. 59 No.3 © 2005 - 2014 JATIT & LLS. All rights reserved.
ISSN: 1992-8645 www.jatit.org E-ISSN: 1817-3195
COMPARING FUZZY LOGIC AND FUZZY C-MEANS (FCM)
ON SUMMARIZING INDONESIAN LANGUAGE DOCUMENT
1
DWI ADE RIANDAYANI, 2I KETUT GEDE DARMA PUTRA, 3PUTU WIRA BUANA
123Department of Information Technology, Udayana University, Indonesia
E-mail: [email protected]
,
2[email protected], [email protected]
ABSTRACT
Text summarization is one way to get the information which is quite effective. Approach techniques of the text summarization are classified into two, namely abstractive and extractive. This paper is focused on the extractive techniques so that the output of the application is important sentences which are taken from the original text intact without modification verbally. There are four majors processes in this research namely preprocessing stage, scoring features, optimization of summarization by two methods (Fuzzy Logic and Fuzzy C-Means), and extraction of summary results. This research use 7 features to calculate the score of each sentence. The core of this research is to compare reliability Fuzzy logic and Fuzzy C-Means method in optimizing process of summary results. The results showed that the method of Fuzzy Logic is outperformed Fuzzy C-Means method with the closest similarity ratio to summarize manually by humans with percentage accuracy of Fuzzy Logic is 58.25% while Fuzzy C-Means method is 54.33%. Increased accuracy occurs when there is additional compression rate in the amount of 1.67% for Fuzzy Logic Method and 4.5% for Fuzzy C-Means.
Keywords: Summarization, Text Features, Scores Sentences, Fuzzy Logic, Fuzzy C–Means
1. INTRODUCTION
Text Summarization is very important and useful technique to identify the topic of a text quickly and accurately[1]. Summarization is the process of condensing a source text into a shorter version preserving its informationcontent[2]. The goal is to help prospective readers save time and effort in finding useful information in a text.
In a research, automatic text summarization uses variety of methods and approaches[1]. The previous research use the genetic algorithm as a method to select the best sentence of text and use a variety of combination feature amount. The result is percentage of accuracy in each feature combination [3]. Another research use Pseudo Genetic And Probabilistic method for text summarization [4].
Techniques of text summarization can be classified into two categories: extractive and
abstractive. Development of automatic text
summarization can apply one of the method or both at once. Extractive summarization is technique of sentence selection that represents the topic of a text and incorporates it into the new text which is shorter than the original, without modified from the original text, while abstractive method produces a summary with phrases that may not be found in the original text [4]. This research use 3 kind of
summarizing: deductive, inductive and ineratif. Deductive is a kind of finding mind topic in first sentence of each paragraph. So the first sentence have a biggest score among the following text whole the paragraph. While the topic where located in the end of each paragraph is named inductive and topic where located in the centre of paragraph named ineratif.
Process of summarizing includes four stages, as follows: 1. text preprocessing (phase separation process includes the sentence, the case folding, the process of filtering the sentence, the word tokenizing and stemming), 2. Feature Scoring, 3. Sentence Selection (this stage optimized by using Fuzzy Logic and Fuzzy C-Means), 4. Process of preparing selected sentences. The research in this thesis is more focused on a comparison of the results of summarizing using the Fuzzy Logic and Fuzzy C–Means thus, it will proof which method will give better results of summarizing.
Fuzzy Logic is a knowledge representation that is constructed by if-then rules. One key feature
of fuzzy rule based systems is their
comprehensibility because each fuzzy rule is linguistically interpretable [5]. Characteristics of Fuzzy Logic method are: 1. problem solving is done by describing the system not by numbers, but
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology
31st January 2014. Vol. 59 No.3 © 2005 - 2014 JATIT & LLS. All rights reserved.
ISSN: 1992-8645 www.jatit.org E-ISSN: 1817-3195
719 uncertainty/ambiguity , 2. Use of if-then rules to clarify the relationship between one variable with another, 3. Describe the system using fuzzy algorithm [6]. While Fuzzy C-Means is a technique of data clustering where the existence of each data point in a cluster is determined by the degree of membership.
This technique was first introduced by Jim Bezdek in 1981 which then continues to develop [7]. At first basic concept of FCM is to determine cluster centers that will mark the location of the average for each cluster. In the initial condition, the cluster center is still not accurate. Each data point has a degree of affiliation for each cluster. By improving the cluster center and the degree of affiliation of each data point repeatedly thus, it will be seen that the cluster center will move towards the right location. The Fuzzy C-Means clustering algorithm is based on the minimization of an objective function called C-means functional [8]. Both of these methods will be the focus of the test in this paper.
2. SUMMARIZATION APPROACH
2.1 Data Set and Preprocessing
Preprocessing is early stages to prepare summarizing input text into data that is ready to be processed. Stage that is contained in the text preprocessing are segmentation paragraph, sentence segmentation, folding case, sentence filtering, tokenizing and stemming.
Paragraphs Segmentation is a limitation and separation of text into paragraphs. Sentence Segmentation is the separation paragraphs into sentences. Characters besides the 'a- z' characters are removed from the text and capital letters converted to lowercase, this process is called case folding. Each sentences have to be filtered from stop word towards the text content. Tokenizing is the stage to separate the sentence into its constituent words using the character "white space" as delimiter. In the end, the results of tokenizing processes will be processed to the stage again to stemming phase to get the base word of each word [9] [10].
2.2 Selected Feature
After preprocessing, each sentence in the text is represented by weight which is obtained from scoring towards several features. Features are carefully selected so that the system is able to deliver approximately correct results. This paper focus on seven features for each sentence. Each feature will be worth between '0' and '1' [9].
2.2.1 Sentence Position (F1)
Sentence position can determine whether the sentence is important or not in representing the content of text. In general, the first sentence in each paragraph has the highest score is called the deductive types of summarizing. But it is possible that the main topic of the text is exist at the end of paragraph it is named inductive summarizing. Paragraph that the main topic is in the end of paragraph named ineratif summarizing. In this study, we use the three types of summarizing. Value of the feature position is determined from the results of division of this sentence position (X) on each paragraph by the number of sentences of each paragraph which is contained in the paragraphs (N). Sentence Position can be calculated as Eq. 1.
(1)
2.2.2 Sentence Length Feature (F2)
Sentence length feature is used for filtering short sentences that sometimes only contain names or other authors. This short sentence is not expected to be part of the summary. Calculation of the value of this feature is the result of length sentences divided with the number of words in a sentence (X) and the number of the entire text (S).
(2)
2.2.3 Title feature (F3)
The words in the sentence that contain the title has a high score. This stage calculates the suitability of the words with content in the title. The title is generally made up of several words, then the text of the title text needs to undergo preprocessing. Then token in the text checked against token title. Title feature can be calculated as Eq. 3. Eq. 3.
(3)
2.2.4 Term Weight (F4)
Number of occurrences of the term in a sentence can be used for detecting important phrase. Score each sentence can be determined by summing the scores of each constituent word. The term weight Method calculates weights sentence so that this method is referred as tf.isf (Term Frequency. Inverse Sentence Frequency). Weight of each sentence in the text is obtained by the multiplication of the number of occurrences of the i term in the text with its inverse value, this method can be calculated as Eq. 4.
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology
31st January 2014. Vol. 59 No.3 © 2005 - 2014 JATIT & LLS. All rights reserved.
ISSN: 1992-8645 www.jatit.org E-ISSN: 1817-3195
The next score for each sentence is calculated by dividing the sum of all the scores contained in I
sentence to score maximum sentence on
mathematical text. The calculation can be seen in equation 5.
(5)
2.2.5 Entity Word or term (F5)
Frequency of occurrence of the term or entity that occurs in the source text can be become a factor to calculate importance words. The word entity can be a one's name, job title, name of the country and so forth. Scores on this feature can be calculated from the ratio of the number of entities/terms that appear in the sentence to the sentence length.
(6)
2.2.6 Numerical Data (F6)
Sentences containing numerical data are assumed to be the word that is quite important and most likely have to be included into the results summary. Score of features numerical data were calculated as the ratio of the number of numerical data contained in the sentence to sentence length.
(7)
2.2.7 Thematic Word (F7)
Thematic word is a word that appears quite frequently in a text. This feature is important because the words which contain thematic word can be indicated as important sentences. The 10 words with the highest frequency is used as thematic word in this feature. Score calculation of thematic word feature is the quotient between the number of words in sentences with thematic maximum value of the thematic word whole the sentence.
(8)
3. THE METHODOLOGHY
In this section explain how to extract the summary result that will be optimized by using Fuzzy Logic and Fuzzy C-Means method. As explained in the Introduction, the core of this paper is to compare the reliability of the two methods that use in this research. Before describing more about
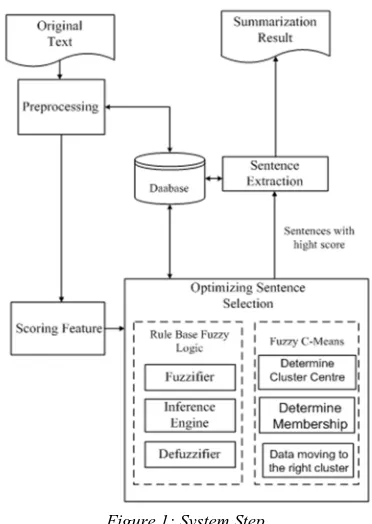
these methods, the following stages of the system is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1: System Step
From Figure 1, the results of the optimization phase using Fuzzy Logic and Fuzzy C-Means is done after preprocessing stage and scoring feature. Success of automatic text summarizing is the selection of sentence at this stage of the optimization results [9]. Optimization phase will produce sentences with high scores as a result of a summary.
3.1 Optimizing with Fuzzy Logic
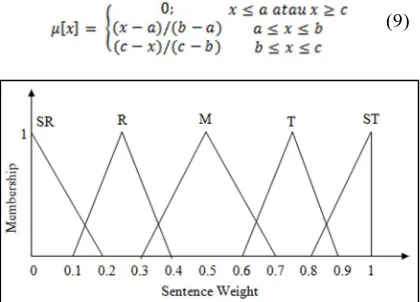
Shown earlier in Figure 1, that there are 3 processes in stages of Optimization of Fuzzy Logic: Fuzzifier, Inference Engine and Defuzzifier. Input on fuzzy logic method is score 7 feature of all sentences. Enter the crisp fuzzification stage that will be supposed to be into some fuzzy sets namely: very low (SR), low (L), medium (M), high (H) and very high (ST). Membership functions which are used in here is "Curve Triangle" with a membership limit shown in Table 1.
Table 1: Boundary Value of Fuzzy Logic Membership
SR R M T ST
a 0.1 0.3 0.6 0.8
b 0 0.25 0.5 0.75 1
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology
31st January 2014. Vol. 59 No.3 © 2005 - 2014 JATIT & LLS. All rights reserved.
ISSN: 1992-8645 www.jatit.org E-ISSN: 1817-3195
721 Rules of Fuzzy Logic membership functions shown in Eq. 9 and the affiliation function graph which is shown in Figure 2.
(9)
Figure 2:Graph of Fuzzy Logic Membership
Degree of fuzzy logic affiliation are in the range 0-1. Later, each sentence in the text will be measured by degrees 7 features that have been described previously.
In many studies, antecedent fuzzy sets were generated and tuned by numerical input data for rule base construction to improve the classification accuracy of FRBCSs [11] [12]. The most important part of inference engine is fuzzy IF-Then rules [9]. The experience of the human controller is usually expressed as some linguistic "IF-THEN" rules that state in what situation(s) which action(s) should be taken [13]. One example of IF-THEN rule is as follows: IF (Position sentence is Very High) and (Long sentence is Low) and (Title Feature is High) and (Term Weight is Medium) and (Noun Entities is Low) and ( Data Numerical is Very High ) and ( Thematic Word is Very High) THEN sentence is important. Tsukamoto is a settlement that will be used in the Inference Engine [14]. In the end of the stage, defuzzifier crisp sentences are classified into categories important, average and not important, then the next set is converted into crisp numbers of sentence weight.
3.2 Optimizing with Fuzzy C-Means
Optimization with Fuzzy C-Means method will classify the input sentence into three clusters include: cluster of important sentences, sentence of the average cluster and cluster sentences are not important. The input which is used in the form of sentences and sentence attributes in form of features. There are 7 Attributes that are used namely: Position Sentence (x1), length of sentence (x2), Title Feature (x3), Term Weight (x4), Entities
word (x5), Numerical Data (x6), Thematic Words (x7).
FCM output is not fuzzy inference system, but a row of cluster centers and several degree of affiliation for each data point. This information can be used to construct fuzzy inference system. Fuzzy C-Means algorithm is as follows:
Step 1: Input data that will be clustered, X , in the
form of matrix n x m (n = number of data samples , m = attributes of each data = 70, where Xij = data
sample i (i = 1,2,…, n), attribute j (j = 1,2,…,7)
Step 2: Set the number of clusters = c = 3, Rank =
w = 2, Maximum iterations = 100, Error smallest expected = 0.00001, initial objective function (P0) = 0, the initial iteration (t) = 1.
Step 3: Generate random numbers µik, i = 1,2,…,n;
k = 1,2,3; as elements initial partition matrix U. Count the number of each column:
(10)
with i = 1,2,…,n Calculate:
(11)
Step 4: Calculate cluster k: Vkj, with k = 1,2,3; and
j = 1,2,…,m.
(12)
Step 5: Calculate the objective function at iteration
t, Pt
(13)
Step 6: Calculate the change in the partition matrix
(14)
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology
31st January 2014. Vol. 59 No.3 © 2005 - 2014 JATIT & LLS. All rights reserved.
ISSN: 1992-8645 www.jatit.org E-ISSN: 1817-3195
Step 7: Check the condition to stop. If the value of
(|Pt – Pt-1| < 0.00001) or (t > 100) then stop and
then specify the cluster affiliation. If not: t = t + 1, repeat step 4.
3.3 Sentence Extraction
Extraction of Fuzzy Logic and Fuzzy C-Means will generate sentences with high scores in descending order as a result of a summary. Sentences were extracted and taken as much as 30% and 25% the text of the original text. Possibilities of extraction is designed varied to determine the composition of the best summaries results of Fuzzy Logic and Fuzzy C-Means were compared with the ideal of summarization by humans. The sentence will be re-ordered according to the actual order of the original text. In addition, this study will also compare the results of summarization is deductive, inductive, ineratif by using a composition of the best extraction results summaries. This study examined a sample of 20 Indonesian language text obtained from several news sites are: kompas.com, kapanlagi.com and yahoo.co.id.
4. RESULT AND ANALYSIS
The main objective of this study was to compare the reliability of the method of Fuzzy Logic and Fuzzy C-Means in terms of optimization of the results of summarization text in Indonesian language. Therefore, we obtain two results, one for
summarization method (deductive, inductive,
inertif) and the other for extraction composition. Research has also been done by summarizing the 20 samples Indonesian language text that comes from multiple news sites.
Outcome evaluation system using the formula precision, recall and f-measure which is called intrinsic method [15]. Evaluation creates an ideal set of summaries, one for each text to test the text then comparing the results with a summary of the ideal system summary. Measurement is in overlap of content, it is often referred to recall and precision sentence or phrase, but sometimes with a single word overlap.
(15)
(16)
Combination of recall and precision values then generate f -measure.
(17)
Table 2 shows the sample text that will be processed by our system.
Table 2: Sample of Indonesian Text
Memaknai Kemerdekaan Di Hari Kemenangan
Jakarta - Ya, 68 tahun sudah Indonesia merdeka. Sebagai Negara maritim dan kepulauan terbesar di dunia, Indonesia juga memiliki ragam etnis dan budaya terbanyak dibandingkan Negara lain. Suatu kerukunan dalam keberagaman yang patut dibanggakan sekaligus pencapaian yang tak mudah dilakukan. Tentu, sepanjang perjalanan itu, banyak kemajuan yang sudah dicapai, meski juga menyisakan keberharapan. Salah satu yang perlu kita renungkan adalah kesejahteraan bagi seluruh rakyat Indonesia.
Jika kita merenungkan kembali cita-cita bangsa yang dituangkan dalam pembukaan Undang-Undang Dasar 1945, terlihat bahwa Indonesia adalah bangsa yang besar. Dan oleh karenanya, kemerdekaan harus diwujudkan untuk melindungi segenap bangsa, memajukan kesejahteraan umum, mencerdaskan kehidupan bangsa, sekaligus ikut melaksanakan ketertiban dunia. Sebuah cita-cita luhur yang diwariskan kepada kita untuk mencapainya, bahkan di kala kondisi perekonomian dunia sedang lesu.
Meski banyak lembaga ekonomi dunia memuji pertumbuhan ekonomi Indonesia, namun banyak hal membutuhkan pembenahan guna lebih menguatkan ekonomi nasional. Sebagaimana yang kita alami, harga berbagai kebutuhan pokok sudah merangkak naik sejak awal Ramadhan, mencapai puncaknya di hari Kemenangan. Atas berbagai kenaikan harga ini, banyak saudara kita yang merasakan ketidaknyamanan bahkan kesulitan dalam menjalani hidupnya.
Satu hal yang pasti, Negara ini masih membutuhkan pembenahan di berbagai bidang. Tentu saja, seluruh masyarakat harus terlibat dalam pembenahan, sekaligus memperkuat nasionalisme yang ada dalam konsensus bersama: UUD 1945, Pancasila, Negara Kesatuan Republik Indonesia, serta Bhinneka Tunggal Ika. Yang harus kita lakukan adalah menjalani peran masing-masing dalam kehidupan bernegara: giat bekerja untuk membangun bangsa, aktif mengawasi jalannya pemerintahan serta memenuhi kewajiban perpajakan.
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology
31st January 2014. Vol. 59 No.3 © 2005 - 2014 JATIT & LLS. All rights reserved.
ISSN: 1992-8645 www.jatit.org E-ISSN: 1817-3195
723 the filtering stage and thus case folding. Table 3 show the result.
Table 3: Separated Text into Sentences
No.
Sentence Sentences
1. jakarta 68 indonesia merdeka
2. maritim kepulauan indonesia ragam etnis budaya dibandingkan
3. kerukunan keberagaman patut
dibanggakan pencapaian
4. perjalanan kemajuan dicapai menyisakan keberharapan
5. renungkan kesejahteraan Indonesia
6. merenungkan cita cita bangsa
dituangkan pembukaan undang undang 1945 indonesia bangsa
7. kemerdekaan diwujudkan melindungi
segenap bangsa memajukan
kesejahteraan mencerdaskan bangsa melaksanakan ketertiban
8. kemerdekaan diwujudkan melindungi
segenap bangsa memajukan
kesejahteraan mencerdaskan bangsa melaksanakan ketertiban
9. ekonomi memuji ekonomi indonesia membutuhkan pembenahan menguatkan ekonomi
10. alami pokok merangkak ramadhan puncaknya kemenangan
11. saudara merasakan ketidaknyamanan kesulitan hidupnya
12. membutuhkan pembenahan
13. terlibat pembenahan memperkuat nasionalisme konsensus uud 1945 pancasila kesatuan indonesia bhinneka tunggal ika
14. lakukan peran bernegara giat membangun bangsa aktif mengawasi jalannya memenuhi kewajiban perpajakan
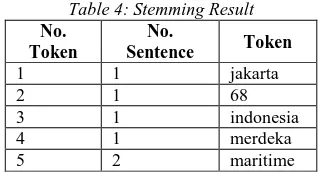
The result of stemming for the sample shown on Table 4 below.
Table 4: Stemming Result
No. Token
No.
Sentence Token
1 1 jakarta
2 1 68
3 1 indonesia
4 1 merdeka
5 2 maritime
Table 5 shows the f-measure comparison results between the method of Fuzzy Logic and Fuzzy C-Means with the composition of the extraction of 40 %, 30 %, 25 % and 20 %.
Table 5:Result of Comparison Compression Rate
Optimizing Method
Average F-measure
30% 25%
Fuzzy Logic 0.47632 0.47572 Fuzzy C-Means 0.46759 0.45592
Table 6 shows the f-measure Fuzzy Logic outperformed Fuzzy-C Means and following by the graphic show in figure 3. This result are calculated with 30% compression rate.
Table 6:Result of Comparison F-Measure
Teks Precission Recall F-measure Accuration
1 0.2000 0.6667 0.3077 33.33%
2 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0
3 0.5000 0.6000 0.5455 60%
4 0.6000 0.7500 0.6667 75%
5 0.4000 0.6667 0.5000 33.33%
6 0.2500 0.3333 0.2857 33.33%
7 0.2000 0.3333 0.2500 33.33%
8 0.1429 0.2500 0.1818 75%
9 0.6667 1.0000 0.8000 100%
10 0.7500 1.0000 0.8571 100%
11 0.5000 1.0000 0.6667 100%
12 0.4000 0.5000 0.4444 50%
13 0.5000 1.0000 0.6667 100%
14 0.6667 1.0000 0.8000 50%
15 0.2500 0.5000 0.3333 50%
16 0.5000 0.6667 0.5714 67%
17 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0%
18 0.7500 1.0000 0.8571 100%
19 0.3333 0.5000 0.4000 50%
20 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0%
Average Accuration : 58.83%
Figure 3:Graph of Comparison F-measure 0.0000 0.2000 0.4000 0.6000 0.8000 1.0000
1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology
31st January 2014. Vol. 59 No.3 © 2005 - 2014 JATIT & LLS. All rights reserved.
ISSN: 1992-8645 www.jatit.org E-ISSN: 1817-3195
5. CONCLUSION
This paper have compared Fuzzy Logic and Fuzzy C-Means as a method to optimize the extraction of sentences in the automatic text summarization. The research selected important sentences based on 7 features: sentence position, sentence length, feature title, term weight, entity word or term, numerical data and thematic word. The deductive type is use on summarization and then this research applied to two sentences compression rate was equal to: 30% and 25%. It turned out the best combination on the compression rate of the summary which is obtained by 30%. From research obtained accuracy of 58.25% for the Fuzzy Logic method and 55.5 % for Fuzzy C-Means method. Acuracy increase occur when there is additional compression rate in the amount of 1.67% for Fuzzy Logic Method and 4.5% for Fuzzy C-Means. Fuzzy Logic method was able to optimize the results of summarizing text better than the Fuzzy C-Means method in automatic text summarization.
REFRENCES :
[1] H. P. Luhn, "The automatic creation of literature abstracts," IBM J. Res. Dev., vol. 2, pp. 159-165, 1958.
[2] Regina Barzilay, Michael Elhadad, "Using lexical chains for text summarization," Proceedings of Intelligent Scalable Text Summarization Workshop, 1997.
[3] Aristoteles. "Pembobotan Fitur Pada
Peringkasan Teks Bahasa Indonesia
Menggunakan Algoritma Genetika." Thesis, Pertanian Bogor Institute, 2011.
[4] Albaraa Abuobieda M. Ali, et all., "Pseudo Genetic And Probabilistic-Based Feature Selection Method For Extractive Single Document Summarization," JATIT, Vol. 32 No.1, 2011.
[5] O. Dehzangi Et. all., "Efficient fuzzy rule generation: A new approach using data mining principles and rule weighting," IEEE FSKD, 2007.
[6] Anto Satriyo Nugroho, “Pengantar
Softcomputing,” 2003. Available at:
http://asnugroho.net/papers/ikcsc.pdf
[7] James C. Bezdek et all., "FCM: The Fuzzy C-Means Clustering Algorithm," Computers & Geosciences, Vol. 10, No. 2-3, pp. 191-203, 1984.
[8] Neha Jain and Seema Shukla, "Fuzzy
Database Using Extend Fuzzy C-Means
Clustering," IJERA. Vol. 2, Issue 3, May-Jun 2012, pp.1444-1451.
[9] Ladda Suanmali, et all., "Fuzzy Logic Based Method for Improving Text Summarization," IJCSIS, Vol. 2, No. 1, 2009.
[10] Talla, fadillah Z. "A Study of Stemming Effects on Information Retrieval in Bahasa Indonesia," Master of Logic Project. Institute for Logic, Language and Computation.
Universiteit van Amsterdam. The
Neatherlands.
[11] D. Nauck and R. Kruse, “A neuro-fuzzy
method to learn fuzzy classification rules from data,” Fuzzy Sets and Systems, pp. 277-288, 1997.
[12] S. Abe and R. Thawonmas, “A fuzzy classifier
with ellipsoidal regions,” IEEE Trans. on Fuzzy Systems, pp. 358-368, 1997.
[13] Li-Xin Wang and M. Mendel, "Generating Fuzzy Rules by Learning from Examples," IEEE Transaction on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Vol.22, No. 6, 1992.
[14] Kamble P.N, “FLC Modeling of Classical
EEG Signals Model by the Technique Tsukamoto Fuzzy Rule Base,” International Journal of Statistika and Mathematika. Volume 7, Issue 3, 2013 pp 52-57.
[15] Martin Hassel. “Evaluation of Automatic Text
Summarization,” Stockholm. Licentiate
Home
Journal Rankings
Journal Search
Country Rankings
Country Search
Compare
Map Generator
Help
About Us
Display journal title
Just copy the code below and paste within your html page:
<a href="http://www.scimagojr.com/journalsearch.php?q=19700182903&tip=sid&exact=no" title="SCImago Journal & Country Rank"><img border="0" src="http://www.scimagojr.com/journal_img.php?id=19700182903&title=true" alt="SCImago Journal & Country Rank" /></a>
How to cite this website?
F o l l o w u s :
SJR is developed by:
J o u r n a l S e a r c h
in Journal Title Search
Exact phrase
J o u r n a l o f T h e o r e t i c a l a n d A p p l i e d I n f o r m a t i o n T e c h n o l o g y
Country: Pakistan
Subject Area: Computer Science | Mathematics
Subject Category: Computer Science (miscellaneous) , Theoretical Computer Science
Publisher: Asian Research Publishing Network (ARPN). Publication type: Journals. ISSN: 18173195, 19928645
Coverage: 2010-2013
H Index: 5
Charts Data
Indicators 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012
SJR 0,000 0,000 0,000 0,000 0,000 0,000 0,000 0,000 0,000 0,000 0,000 0,000 0,137 0,167
Total Documents 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 222 229 622
Total Docs. (3years) 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 222 451
Total References 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 3.880 4.120 9.475
Total Cites (3years) 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 61 178
Self Cites (3years) 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 4 17
Citable Docs. (3years) 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 222 451
Cites / Doc. (4years) 0,00 0,00 0,00 0,00 0,00 0,00 0,00 0,00 0,00 0,00 0,00 0,00 0,27 0,39
Cites / Doc. (3years) 0,00 0,00 0,00 0,00 0,00 0,00 0,00 0,00 0,00 0,00 0,00 0,00 0,27 0,39
Cites / Doc. (2years) 0,00 0,00 0,00 0,00 0,00 0,00 0,00 0,00 0,00 0,00 0,00 0,00 0,27 0,39
References / Doc. 0,00 0,00 0,00 0,00 0,00 0,00 0,00 0,00 0,00 0,00 0,00 17,48 17,99 15,23
Cited Docs. 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 43 101
Uncited Docs. 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 179 350
% International
Collaboration 0,00 0,00 0,00 0,00 0,00 0,00 0,00 0,00 0,00 0,00 0,00 5,86 5,68 5,31
Scimago Lab, Copyright 2007-2014. Data Source: Scopus®