!""##!"$%&%' '
!""##!"$%&%' '
International Journal of Applied Business and Economic
Research (IJABER) Vol 14 No 11, 2016
The International Journal of Applied Business and Economic Research is a peer-reviewed journal.The International Journal of Applied Business and Economic Research (JABER) is a refereed scientific periodical published quarterly (March, June, Septermber & December) in a year by Serials Publishers, New Delhi, India, featuring the latest research findings in business and economics. It provides a forum to both academics and decision makers to advance theory and application in the fields of business and economics. JABER publishes original research in accounting, economics, finance, management and quantitative methods, which has an international orientation.
Editorial Board
Editor in Chief
ARDI GUNARDI
Dept. of Management,
Faculty of Economics & Business, Universitas Pasundan,
Indonesia
Associate Editor
Prof. Dr. Hapzi Ali, CMA
Mercu Buana University, Jakarta, Indonesia
Managing Editor
Vijay Kumar Jha
Serials Publications Pvt. Ltd. New Delhi
Editorial Board Members
XIE Wenjing
Department of Economics,
Baptist University of Hong Kong, Kowloon Tong,
Hong Kong, China.
HU Yichuan
Department of Economics,
YANG Yixin
Department of Economics
The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Shatin, Hong Kong, China
XU Xinyi
Department of Economics,
The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Shatin, Hong Kong, China
Liu Ziyuan
Ph.D candidate in Department of World Economy, School of International Business and Administration Shanghai U of finance and Economics,
China
Yi Guanxi
UCLA Anderson Business School 110 Westwood Plaza. Suite C-310 Los Angeles,
Wang Danli Wang
Chinese University of Hong Kong HYS 509, Shatin, N.T.,
Hong Kong, China
Prof. N. Narayana
Department of Economics, University of Botswana,
College of Business Administration, Al Ain University,
Articles
THE EFFECTS OF ORGANIZATION TRUST AND JOY ON ORGANIZATIONS’ STRATEGIC BEHAVIOR
Author : Majdi Anwar Quttainah
Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016)
Pages : 7361-7385
Show/Hide Abstract
FACTORS INFLUENCING ENGAGEMENT OF EMPLOYEES TOWARDS PHOENIX PULP AND PAPER PUBLIC CO., LTD.
Author : Dusadee Ayuwat, Wanichcha Narongchai and Nattawat Auraiampai Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016)
Pages : 7387-7396
Show/Hide Abstract
THE APPLICATION OF PERFORMANCE MEASUREMENT SYSTEM MODEL USING MALCOLM BALDRIGE MODEL (MBM) TO SUPPORT CIVIL STATE APPARATUS LAW (ASN) NUMBER 5 OF 2014 IN INDONESIA
Author :Doli M Ja’far Dalimunthe, Fadli and Iskandar Muda Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016)
Pages : 7397-7407 Show/Hide Abstract
FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT BEHAVIOR AND FINANCIAL DISTRESS ON SMALL MEDIUM ENTERPRISE IN INDONESIA
Author : Isfenti Sadalia and Syahyunan
Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016) Pages : 7409-7416
Show/Hide Abstract
THE SKILLS AND UNDERSTANDING OF RURAL ENTERPRISE MANAGEMENT OF THE PREPARATION OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS USING FINANCIAL
ACCOUNTING STANDARDS (IFRS) FINANCIAL STATEMENT ON THE ENTITIES WITHOUT PUBLIC ACCOUNTABILITY (ETAP) FRAMEWORK ON THE
IMPLEMENTATION OF VILLAGE ADMINISTRATION LAW
Author : Nurzaimah, Rasdianto and Iskandar Muda
Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016) Pages : 7417-7429
Show/Hide Abstract
VOLCANIC DISASTER MANAGEMENT PRACTICES FOR PEOPLE WHO LIVED IN DISASTER PRONE II
Author : Diah Setyawati Dewanti, Dusadee Ayuwat, and Sekson Yongvanit
Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016) Pages : 7431-7450
Show/Hide Abstract
Author : Hapzi Ali, Mukhtar and Sofwan Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016)
Pages : 7451-7471
Show/Hide Abstract
ANTHROPOMORPHIC ANIMALS IN ADVERTISING: CREATING POSITIVE CONSUMER’S BRAND ATTITUDE
Author : Dwinita Laksmidewi and Edward Giovandru Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016)
Pages : 7473-7489
Show/Hide Abstract
NEXUS BETWEEN TOURISM AND ECONOMIC GROWTH: EMPIRICAL EVIDENCE FROM ODISHA, INDIA
Author : Himanshu B. Rout, P. K. Mishra and B. B. Pradhan Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016)
Pages : 7491-7513 Show/Hide Abstract
NEW TRENDS OF MASS TOURISM MANAGEMENT IN PR. CHINA, CASE STUDY OF XISHUANGBANNA DAI AUTONOMOUS PREFECTURE
Author : Chuanchen BI, Sekson Yongvanit and Warangkana Thawornwiriyatrakul Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016)
Pages : 7515-7536 Show/Hide Abstract
COMMERCIALIZATION DETERMINANT OF MANGO FARMERS IN WEST JAVA- INDONESIA
Author : Lies Sulistyowati and Ronnie S. Natawidjaja
Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016)
Pages : 7537-7557 Show/Hide Abstract
THE ANTECEDENTS OF JOB SATISFACTION AND ORGANIZATIONAL COMMITMENT AND THE EFFECTS ON THE PERFORMANCES OF CIVIL SERVANTS (PNS) IN PROVINCIAL GOVERNMENT OF NORTH SUMATERA-INDONESIA
Author : Indra Sakti Harahap, Ritha F Dalimunthe, Prihatin Lumbanraja and Yenni Absah Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016)
Pages : 7559-7573
Show/Hide Abstract
THE URGENCY OF IMPLEMENTING BALANCED SCORECARD SYSTEM ON LOCAL GOVERNMENT IN NORTH SUMATRA – INDONESIA
Author : Arifin Lubis, Zainul Bahri Torong and Iskandar Muda Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016)
Pages : 7575-7590
THE ROLE OF ENTERPRISE RESOURCE PLAN (ERP) CONFIGURATION TO THE TIMELINESS OF THE FINANCIAL STATEMENT PRESENTATION
Author : Ade Fatma Lubis, Tapi Andasari Lubis and Iskandar Muda
Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016) Pages : 7591-7608
Show/Hide Abstract
IMPACT OF INVESTOR CONFIDENCE TOWARDS OPERATIONAL STABILITY (AN EVIDENCE FROM SHARIA BANKING AS THE DEPOSIT BENEFICIARY OF HAJJ FUND IN INDONESIA)
Author : M. Arief Mufraini
Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016) Pages : 7609-7629
Show/Hide Abstract
EFFECT OF THE POLITICAL MARKETING MIX ON THE VOTER’S DECISION (STUDY ON THE LEGISLATIVE COUNCIL ELECTION OF REPRESENTATIVES OF THE REPUBLIC OF INDONESIA YEAR 2014 CONSTITUENCY II WEST JAVA)
Author : Nur Hayati and Randi Purnama Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016)
Pages : 7631-7646
Show/Hide Abstract
AN EMPIRICAL STUDY OF FOREIGN EXCHANGE RESERVE THROUGH THE BALANCE OF PAYMENT OF INDONESIA BASED ON THE KEYNESIAN AND THE MONETARY APPROACH
Author : Gregorius N. Masdjojo, FX. Sugyanto, Myasto and R. Mariatmo
Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016)
Pages : 7647-7674 Show/Hide Abstract
THE EFFECT OF SPIRITUAL LEADERSHIP ON WORKPLACE SPIRITUALITY, JOB SATISFACTION AND IHSAN BEHAVIOUR (A STUDY ON NURSES OF AISYIAH ISLAMIC HOSPITAL IN MALANG, INDONESIA)
Author : Achmad Sani , Budi Eko Soetjipto and Vivin Maharani Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016)
Pages : 7675-7688
Show/Hide Abstract
SOCIO- ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACTS OF URBAN EXPANSION: CASE OF ARAB COUNTRIES
Author : Muawya Ahmed Hussein and Hanaa Mahmoud Sid Ahmed Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016)
Pages : 7689-7706
Show/Hide Abstract
MODEL DEVELOPMENT AND ENHANCING COMPETITIVENESS STRATEGY BASED BUSINESS ENTREPRENEUR IN MEDAN
Author : Ritha F. Dalimunthe
Show/Hide Abstract
SOCIAL CLASS OF THE RURAL HOUSEHOLDS IN THE NORTHEAST, THAILAND
Author : Wanichcha Narongchai, Dusadee Ayuwat and Oranutda Chinnasri Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016)
Pages : 7717-7736
Show/Hide Abstract
A 21ST CENTURY TOURISTIC PERSPECTIVE ON UNITED ARAB EMIRATES, QATAR AND SULTANATE OF OMAN
Author : Alexandrina Maria PAUCEANU, PhD, Moinuddin AHMAD, PhD and
AbubakrAlsdiq Abbas ABUMRAEN, PhD
Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016)
Pages : 7737-7749 Show/Hide Abstract
MANGO AGRICULTURAL SUPPLY CHAIN: ACTORS, BUSINESS PROCESS, AND FINANCING SCHEME
Author : Tuti Karyani, Hesty N. Utami1**, Agriani H. Sadeli, Elly Rasmikayati, Sulistyodewi and Nur Syamsiyah
Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016) Pages : 7751-7764
Show/Hide Abstract
VOLUNTARY DISCLOSURE, MONITORING MECHANISM AND FIRM VALUE
Author : Rina Br Bukit and Fahmi N. Nasution
Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016)
Pages : 7765-7774 Show/Hide Abstract
IS DEMAND FOR STAPLE FOOD SENSITIVE TO PRICE CHANGE? EVIDENCE FROM INDONESIA
Author : Agus Widarjono
Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016) Pages : 7775-7790
Show/Hide Abstract
MODEL OF EMPOWERMENT-BASED MANAGEMENT CHANGE AND ITS RELATION TO THE COLLEGE QUALITY IMPROVEMENT
Author : Anuar Sanusi, Anggalia Wibasuri and Andi Desfiandi
Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016) Pages : 7791-7809
Show/Hide Abstract
IMPROVING THE SUPERIOR APPARATUS PERFORMANCE BY CONSIDERING SATISFACTION, COMPETENCE AND MOTIVATION
Author : Yusuf Samad
Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016) Pages : 7811-7823
IMPLEMENTATION OF MANAGEMENT STRATEGY ON BUDGETING FOR
CULTURAL PRESERVATION CASE STUDY OF TOURISM AND CULTURE AFFAIR AGENCY IN WEST JAVA
Author : Azhar Affandi, Atty Tri Juniarti and Sidik Priadana Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016)
Pages : 7825-7837 Show/Hide Abstract
HOME FINANCING THROUGH MODIFIED DIMINISHING PARTNERSHIP
Author : R. Aboulaich and N. Yachou
Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016)
Pages : 7839-7861
Show/Hide Abstract
IMPACT OF CAPITAL INVESTMENTS AND CASH DIVIDEND POLICY ON REGIONAL DEVELOPMENT BANK (BPD) PT. BANK SUMUT TO THE DISTRICT OWN SOURCE REVENUE AND ECONOMIC GROWTH
Author : Iskandar Muda, Abykusno Dharsuky, Isfenti Sadalia and Hasan Sakti Siregar
Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016)
Pages : 7863-7880 Show/Hide Abstract
SERVICE QUALITY AS KEY FACTOR IN REVITALIZING TRADITIONAL MARKETS THROUGH LOYALTY
Author : ArlinaNurbaity Lubis and Prihatin Lumbanraja
Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016)
Pages : 7881-7892 Show/Hide Abstract
RISK MANAGEMENT AND PERFORMANCE OF CONVENTIONAL BANKING IN INDONESIA
Author : Sutrisno
Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016) Pages : 7893-7902
Show/Hide Abstract
A SIMULATION OF THE IMPACT OF INDONESIAYEMEN BILATERAL TRADE LIBERALIZATION ON THE INDONESIAN AND YEMENI ECONOMIES: A SMART MODEL APPROACH
Author : Wajid Fauzi, Abas Basori, Sulthon Sjahril Sabaruddin and Rediatma Ihsan
Supriyadi
Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016)
Pages : 7903-7919 Show/Hide Abstract
AN ECONOMETRIC ANALYSIS OF FOREIGN DIRECT INVESTMENT AND
ECONOMIC GROWTHA STUDY WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO SAARC MEMBER ECONOMIES
Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016) Pages : 7921-7933
Show/Hide Abstract
THE ENVIRONMENTAL FRIENDLY ECONOMIC CREATIVE MODEL TOWARDS THE PEOPLE AROUND THE RESERVOIRS OF CIRATA THE PROVINCE WEST JAVA INDONESIA
Author : Bambang Heru Purwanto, Soleh Suryadi and PO Abas Sunarya Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016)
Pages : 7935-7952
Show/Hide Abstract
CORRUPTION OPPORTUNITIES IN DIMENSION OF REGIONAL FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
Author : Mukhamad Rachmat
Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016)
Pages : 7953-7960 Show/Hide Abstract
FACTORS DETERMINING VALUE AND CUSTOMER TRUST BUILDING
Author : Sri Sustariyah, Sucherly, Undang Juju and Otong Karyono Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016)
Pages : 7961-7968
Show/Hide Abstract
CUSTOMER SATISFACTION TOWARDS SHOPPING MALLS AT CHENNAI CITY – AN EMPIRICAL STUDY
Author : J. Radha and R. Jayam
Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016)
Pages : 7969-7982
Show/Hide Abstract
DETERMINACY OF ACTUAL USAGE THROUGH BEHAVIORAL INTENTION CIMB NIAGA AIR ASIA BIG CARD
Author : Ronald and Amelia
Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016)
Pages : 7983-7995
Show/Hide Abstract
HUMAN RESOURCE: TO INCREASING INDONESIAN COMPETITIVENESS ON ASEAN ECONOMIC COMMUNITY
Author : Wilson Bangun
Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016)
Pages : 7997-8003 Show/Hide Abstract
HUMAN CAPITAL, BOARD MONITORING AND CORPORATE PERFORMANCE
Author : Makaryanawati, Made Sudarma, Erwin Saraswati and Abdul Ghofar Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016)
Show/Hide Abstract
THE IMPLEMENTATION OF SUSTAINED POVERTY ALLEVIATION PROGRAM IN RURAL COMMUNITY BASED ON LOCAL COMMUNITY
Author : Herry Maridjo, Lukas Purwoto & Y.M.V. Mudayen Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016)
Pages : 8021-8037 Show/Hide Abstract
FAIR VALUE AND HISTORICAL COST ACCOUNTING: EVIDENCE FROM INSURANCE COMPANIES IN INDONESIA
Author : Antonius Diksa Kuntara and Lilis Setiawati
Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016)
Pages : 8039-8047 Show/Hide Abstract
THE BEST MODEL GOVERNMENT BASED ON TRUSTEESHIP GOVERNANCE (STUDY CASES: BOJONEGORO DISTRICT)
Author : Sri Suryaningsum, Moch. Irhas Effendi and R. Hendri Gusaptono
Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016)
Pages : 8049-8060 Show/Hide Abstract
THE EFFECT OF PARTICIPATIVE BUDGETARY, ASSYMETRIC INFORMATION, PRESSURE-HANDLING, AND ORGANIZATIONAL COMMINTMENT ON THE BUDGETARY SLACK
Author : Lita Yulita Fitriani, Sri Suryaningsum, Indra Kusumawardhani and Valannisa Sally
Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016) Pages : 8061-8070
Show/Hide Abstract
IMPULSE BUYING BEHAVIOR ON CONSUMER RETAIL FASHION IN SURABAYA - INDONESIA
Author : Robertus Sigit Haribowo Lukito and Diyah Tulipa Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016)
Pages : 8071-8086
Show/Hide Abstract
IMPLEMENTATION OF CORPORATE SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY BY MICRO, SMALL AND MEDIUM ENTERPRISES CASE STUDY IN SEMARANG CITY
Author : Indarto
Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016) Pages : 8087-8101
Show/Hide Abstract
AVELLIATING POVERTY THROUGH DEVELOPING MICROCREDIT BASED SELF HELP GROUP STUDIES IN UP2K-PKK SEMARANG
Author : Chatarina Yekti Prawihatmi
Show/Hide Abstract
THE INFLUENTIAL FACTORS TO THE POSTPONE AUDIT IN MINING COMPANIES
Author : Noto Pamungkas, Rusherlistyani, Indra Kusumawardhani and Candra Wijang
Asmorosanto
Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016)
Pages : 8115-8129 Show/Hide Abstract
INTEGRATED APPROACH MODEL TOWARDS UNIVERSITY SUSTAINABILITY: ANALYSIS OF BEST PRACTICES OF SUSTAINABLE UNIVERSITIES
Author : Paulina Permatasari and Paulina Tindaon
Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016)
Pages : Paulina Permatasari and Paulina Tindaon Show/Hide Abstract
DECONSTRUCTION OF EQUITABLE TAX AMNESTY
Author : I Nyoman Darmayasa, I Made Sudarma, M. Achsin and Aji Dedi Mulawarman Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016)
Pages : 8167-8179
Show/Hide Abstract
ENTREPRENEURIAL SUCCESS WITH SOCIAL CAPITAL IN JAVA (MINANG ETHNIC AND THIONGHOA)
Author : Primadona
Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016)
Pages : 8181-8193
Show/Hide Abstract
A STUDY OF NON-STATIONERITY MACROECONOMIC INDICATOR (GROWTH) EVIDANCE FROM INDONESIA
Author : Wuri Septi Handayani
Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016)
Pages : 8195-8209 Show/Hide Abstract
NAÏVE BAYES IMPLEMENTATION INTO BAHASA INDONESIA STEMMER FOR CONTENT BASED WEBPAGE CLASSIFICATION
Author : Andreas and Lusia Permata Sari Hartanti
Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016)
Pages : 8211-8223 Show/Hide Abstract
DOES THE FORMULATION OF TAX AMNESTY CONSIDERING SMES?*
Author : Yuyung Rizka Aneswari, Gugus Irianto and Ali Djamhuri Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016)
Pages : 8225-8236
THE IMPACT OF FOREIGN DEBT AND INVESTMENT ON INDONESIA’S ECONOMIC GROWTH AND AN ANALYSIS OF INDONESIA’S POLICY FOR LEAVING IMF
Author : Yohanes Maria Vianey Mudayen and Herry Maridjo Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016)
Pages : 8237-8254
Show/Hide Abstract
ANALYSIS OF MARKET BOUNDARIES ON TRADITIONAL MARKET PLACES MANAGED BY LOCAL GOVERNMENT IN PADANG
Author : Yosi Suryani
Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016)
Pages : 8255-8269
Show/Hide Abstract
HUMAN ASSET MANAGEMENT, A CHALLENGE FOR SERVICE SECTOR: AN ANALYSIS FROM EMPLOYEE RETENTION PERSPECTIVE
Author : Sasmita Mohanty and Dr. Kalyani Mohanty Volume : Vol.14 (2016) Issue No. :11 (2016)
Pages : 8271-8298
SERVICE QUALITY AS KEY FACTOR IN REVITALIZING
TRADITIONAL MARKETS THROUGH LOYALTY
ArlinaNurbaity Lubis1* and Prihatin Lumbanraja2
Abstract:The growth of modern markets in Medan has been very rapid. Nowadays, almost every region, even each of the main streets in the city of Medan has a small supermarket modern market as Indomaret and Alfamart. People are starting to switch to the modern market for services more enjoyable supported by physical evidence convenient services when compared with the modern market. The traditional market is the economic backbone of society and should be preserved. Efforts to do is to revitalize the market, the key to quality of service. Revitalization will be achieved if people become loyal to the traditional market. This study evaluates the factors that shape customer loyalty traditional markets. The study was conducted in four major traditional markets in Medan with a sample of 250 people. The data collection is done by using a questionnaire. Data were analyzed using structural equation analysis. The results of the study indicate that the location is not a significant factor in improving customer satisfaction and loyalty traditional markets. The main factors that should be improved is the quality of service. Improved service quality can significantly improve satisfaction, and customer loyalty. In addition, satisfaction plays a role as a mediator in effect between service quality with customer loyalty.
Keywords: Quality of Service, Location Market, Customer Satisfaction, Customer Loyalty, and Market Revitalization.
1. INTRODUCTION
The market is a meeting place between buyers and sellers, meeting requests with offers, where the balance of price and trade transactions. Ideally, at the going market price balance the trade-off between buyers and sellers to price the deal happen. This situation is what characterizes the traditional market. The times have shifted the market mechanism that gave birth to the modern market. In the modern market, no longer occur bargaining interaction between buyers and sellers in determining the price. Sellers typically include a price tag on every product it sells with fixed prices, can not be compromised by the consumer.Until now, the traditional markets continue to operate despite the growth and popularity in the
I J A B E R, Vol. 14, No. 11, (2016): 7881-7892
1,2 Management Department, Faculty of Economics and Business, University of Sumatera Utara–Indonesia.
7882 � ArlinaNurbaity Lubis and Prihatin Lumbanraja
bottom of the modern markets such as supermarkets. Incessant growth of small supermarkets like Indomaret, Alfamart, and Alfamidi coupled with large supermarkets such as Irian, Carrefour and Giant making traditional market growth is inhibited. In fact, the traditional markets are the economic backbone of society in general. Not all communities are able to market their products through self-supermarkets that have the criteria of product quality standards. Without the traditional market, the people who produce everyday products are losing market to market its products.
The modern market offers a service that is generally better than the traditional market. In terms of tangibility of the market, for example, is identical to the traditional market situation muddy, dirty, smells even not well organized. On the other hand, set the modern market its products with a neat, clean, beautiful, even with support equipment such as air-conditioning. This bid is what makes modern market competitiveness becomes higher than the traditional market, especially among young people who are not familiar with either the traditional markets.
Nielsen (2004) in his research revealed that the growth of the modern market in Indonesia until the year reached 31.4% per year. This figure is much higher than traditional market growth moving in point 8% per year. If this situation is left unchecked, one day traditional market will disappear from public life, regardless of the benefits that it provides to the community, especially the small traders. In Medan alone, there are 50 traditional markets accounted for more than 37ribu head of the family. If the traditional markets disappeared, more than 37ribu heads of households coupled with a workforce that brought trouble.
Activation key in the back of traditional markets is loyalty. Kotler and Keller (2012) states that consumers who are satisfied will do three things,
1. repurchase is to make repeat purchases in traditional markets;
2. retain, by not switching to modern shops are starting to grow in the region; and
3. recommendation, invite others to shop at traditional markets.
Service Quality as Key Factor in Revitalizing Traditional Markets Through Loyalty � 7883
2. PROBLEM FORMULATION
Based on the background of the issue, the focus of this research is to create customer satisfaction and loyalty traditional markets. Specifically, the problem in this research are:
1. How does the quality of service to customer satisfaction and loyalty? 2. How does the location of the market towards customer satisfaction and
loyalty?
3. How does the influence of satisfaction on customer loyalty? 2. LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Customer Loyalty
The situation of intense competition has led companies difficult to increase the number of customers. Therefore, a better alternative is to make efforts to maintain existing markets. One is through efforts to increase customer loyalty, (Suryani, 2008). Evaluation of customer loyalty can be seen from the customer’s behavior after the consumption of the service itself. Behaviors that indicate a loyal customer, according to Kotler and Keller (2012) are
1. Repurchase, which is to buy back;
2. Retain, not easily switch to other products; and 3. Recommend, invite other people to buy the product. 2.2 Customer Satisfaction
Tjiptono (2006) say that customer dissatisfaction is caused by internal factors and external factors. Internal factors are relatively controlled companies, for example, employees were rude, late for work, fault recording transactions. Conversely, external factors beyond the company’s control, such as weather, disruptions in public infrastructure, criminal activity, and personal problems of customers. In connection with the foregoing, customer satisfaction is also strongly influenced by the level of service.
2.3 Quality of Service
7884 � ArlinaNurbaity Lubis and Prihatin Lumbanraja
Parasuraman et. al. (1988) as well as Tjiptono (2006) provides the basic concepts in evaluating the quality of services delivered by service providers, namely:
1. Reliability, namely the ability to provide the services promised with accurate and always consistent with consumer expectations.
2. Responsiveness, ie the ability of the staff to help and respond to customer requests quickly and swiftly
3. Assurance, ie assurance of service provided, includes the knowledge, competencies, products, as well as things to avoid risks for customers 4. Empathy, the ability of service providers to position itself in the viewpoint
of the consumer, the consumer would understand, build relationships and good communication in addressing the needs of individuals.
5. Tangibility, the physical evidence of the facilities used in delivering services.
2.4 Market Location
Lupiyoadi and Hamdani (2009) stated that the decision about the location and achievement system should be in line with the overall strategy of the institution. If the strategy is to offer a specialization of certain products in certain markets show the location is definitely necessary criteria for evaluation purposes. Location facilitate consumer market, must meet the following criteria:
1. The location is easy to reach the consumer market with public transport 2. The location is easy to find consumer market
3. Smooth traffic flow
4. The neighborhood around the market were comfortable
5. The neighborhood around the market safe
2.5 Conceptual Framework and Hypotheses
Service Quality as Key Factor in Revitalizing Traditional Markets Through Loyalty � 7885
The location of traditional markets to enable consumers to reach out and find these traditional markets. Selection of convenient location, have access to the complete transport, not complicate crossing the street can be a key to improving customer satisfaction through a pleasant shopping experience. Thus, the location pasr has a positive and significant impact on customer satisfaction. Moreover, given the easiness that will make consumers loyal in the market, thus the location of the market has a positive and significant impact on customer loyalty.Consumers who are satisfied in services would make repeat purchases, and even invite others to shop at traditional markets. Thus, there is a unidirectional relationship between satisfaction and loyalty.
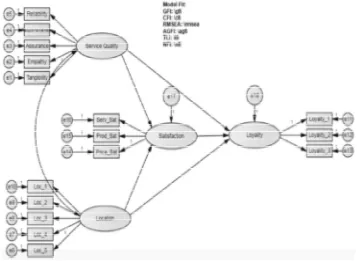
Customer satisfaction has a positive and significant impact on customer loyalty. Quality of service is divided into five main indicators, namely reliability, responsiveness, assurance, empathy, and tangibility. Location market judged on indicators relating to the performance of the choice of location of the market, which consists of five indicators. Satisfaction is divided into satisfaction with the services, products, and prices. Loyalty identified through three behavioral indicators that show loyalty, ie repurchase, retain, recommend. Thus, the conceptual framework proposed in the study is shown in Figure 1.
7886 � ArlinaNurbaity Lubis and Prihatin Lumbanraja
3. RESEARCH METHODS
The study was conducted in major traditional markets in the city of Medan in the period June 2016 to September 2016. The market is traditionally used to represent all the traditional markets in the city of Medan is a traditional market Petisah, Medan Olimpia, Glugur and Pringgan with broad market area. The study was conducted using a sample of 250 visitors a traditional market shoppers in each of the markets within the scope of the study. If the adequacy of the sample can not be met, it will be withdrawn additional samples.
Data used in this study are primary data measured using a 5-point Likert scale. Likert scale is used to measure the perceptions of the respondents to the items of the statement filed related to research variables. Statement by using a structured questionnaire which is based on theoretical study. Validity and reliability of the instrument is tested before collecting field data. The data obtained were evaluated with statistical tools. Evaluation is done with structural equation models using AMOS.
4. RESULTS
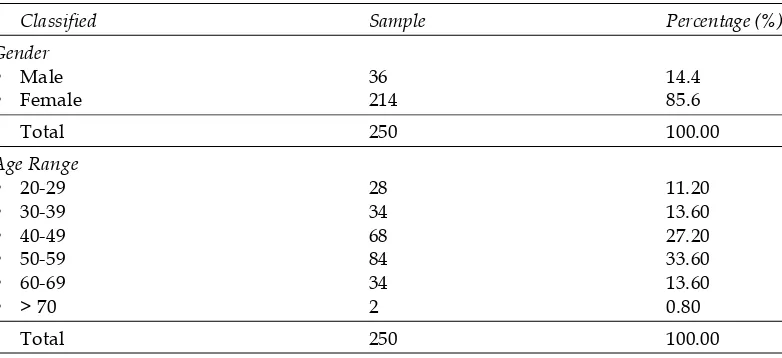
In an effort to understanding visitor characteristics of traditional markets in the city of Medan, the evaluation of the characteristics of respondents do. Respondents in this study is the traditional market visitors who are shopping in the traditional market needs. Characteristics of respondents described based on gender, age range, income, transportation, and the distance from the residence to the market. Table 1 extend to the characteristics of respondents visitors traditional market research.
Table 1
General Characteristics of Respondents
Classified Sample Percentage (%)
Gender
• Male 36 14.4
• Female 214 85.6
Total 250 100.00
Age Range
• 20-29 28 11.20
• 30-39 34 13.60
• 40-49 68 27.20
• 50-59 84 33.60
• 60-69 34 13.60
• > 70 2 0.80
Service Quality as Key Factor in Revitalizing Traditional Markets Through Loyalty � 7887
• Public transportation 88 35.20
• Motorcycles 125 49.00
Source: Data Processing Results (2016).
Table 1 provides information that, in general, visitors to the traditional market is the surrounding community with the distance < 5 KM, generally using a motorbike or public transport, income < £ 5 million, is in the range of age > 30 years, as well as female.Descriptive statistical analysis on each of the indicators the study are summarized in Table 2 below:
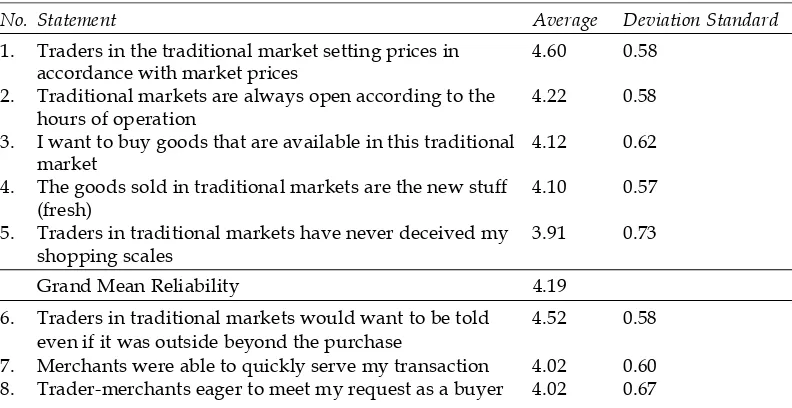
Table 2 Descriptive Statistic
No. Statement Average Deviation Standard
1. Traders in the traditional market setting prices in 4.60 0.58 accordance with market prices
2. Traditional markets are always open according to the 4.22 0.58 hours of operation
3. I want to buy goods that are available in this traditional 4.12 0.62 market
4. The goods sold in traditional markets are the new stuff 4.10 0.57 (fresh)
5. Traders in traditional markets have never deceived my 3.91 0.73 shopping scales
Grand Mean Reliability 4.19
6. Traders in traditional markets would want to be told 4.52 0.58 even if it was outside beyond the purchase
7888 � ArlinaNurbaity Lubis and Prihatin Lumbanraja
9. Merchants want to respond to my complaint as a buyer 3.51 0.77 10. Merchants quickly cultivate my advice as a buyer 3.52 0.92
Grand Mean Responsiveness 3.92
11. I feel secure on hygiene products in this market 3.90 1.02 12. I feel secure on merchant explanation about the products 3.70 0.95
it sells
13. I feel assured of my products in accordance with what 3.98 0.55 my message
14. I feel secure always comfortable while shopping in this 3.39 0.72 market
15. I feel my security when shopping at this market is 2.98 0.93 guaranteed
Grand Mean Assurance 3.59
16. I feel traders focused on my needs, not just for profit 3.54 0.94 17. I welcome suggestions from merchants when selecting 3.79 0.64
a product
18. I feel that the merchant never make me offended while 3.29 0.95 shopping in this market
19. I see that the merchant is always steadfast in serving me 3.63 0.80 as a buyer
20. I see that the merchant is always polite to me 3.57 0.60
Grand Mean Empathy 3.56
21. The parking lot at traditional markets are adequate 2.30 1.30 22. Views market from the outside looks beautiful 1.98 0.98 23. The streets in the traditional market net 2.01 1.00 24. I feel the location of the stalls in this market has been 2.12 0.95
regularly
25. Places of worship are conveniently available in this 2.02 0.93 market
26. The public toilets in the traditional market is feasible to 2.00 0.93 use
27. Security post in the traditional markets help security 2.10 1.04 market
Grand Mean Tangibility 2.08
28. The traditional market is easily accessible by public 4.50 0.53 transport (e.g. public transportation)
29. I easily found the traditional markets while walking 4.19 0.58 around the site
30. Traffic around the market always smoothly 3.88 1.04 31. The neighborhood around the market feels comfortable 3.43 0.88 32. The neighborhood around the market is a safe 3.51 1.02
neighborhood
Grand Mean Location 3.90
Sources: Data Processing Results (2016).
Service Quality as Key Factor in Revitalizing Traditional Markets Through Loyalty � 7889
Table 2 provides information that at this time, the perception of respondents on the variables are generally quite good. Problems that should be raised is the problem of the dimension of service parts tangibility of service.Results of testing the goodness of fit index at the end of the model after the modification of the model are as follows:
Table 2
Goodness of Fit Index Model
Criteria Value Conclusion
Probability Chi-Square 0.053 Good
GFI 0.915 Good
CFI 0.975 Good
RMSEA 0.049 Good
AGFI 0.861 Marginal
TLI 0.965 Good
NFI 0.904 Good
Sources: Data Processing Results (2016).
Based on Table 2, the model in the study categorized good in explaining the influence between variables that occur. Two indicator locations were excluded from the research model because it does not meet the standards specified loading factor in the study. The standard used was 0.4 considering this study is to explore the interest of the quality of service in the traditional markets of Medan City which began to be forgotten and rarely noticed. Loading factor below 0.4 excluded because it is not able to explain the formation of latent variables.
Table 4
Regression Weight Estimate
Estimate Standardized S.E. C.R. P Hypothesis
Result
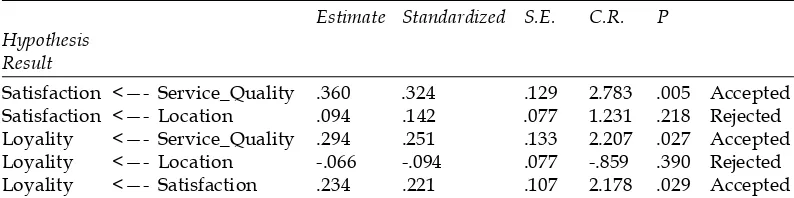
Satisfaction <—- Service_Quality .360 .324 .129 2.783 .005 Accepted Satisfaction <—- Location .094 .142 .077 1.231 .218 Rejected Loyality <—- Service_Quality .294 .251 .133 2.207 .027 Accepted Loyality <—- Location -.066 -.094 .077 -.859 .390 Rejected Loyality <—- Satisfaction .234 .221 .107 2.178 .029 Accepted Sources: Data Processing Results (2016).
7890 � ArlinaNurbaity Lubis and Prihatin Lumbanraja
5. DISCUSSION AND DISCUSSION
The findings in this study indicate that the quality of service is a very important factor in building customer satisfaction and loyalty. Good quality service will make customers satisfied and make them become loyal. Currently, the most robust quality of service capability of empathy described by traders to consumers (loading factor = 0.91). The next factor to consider is the consumer in the quality of service assurance, guarantee of services provided (loading factor = 0.65). The three-dimensional quality of other services are still not perceived by consumers (loading factor < 0.6), but still be able to explain the quality of the service itself. Factors that are difficult perceived in the current environment is the responsiveness of traders on the needs of consumers. Improving the quality of services in general will encourage increased satisfaction (� = 0324) as well as customer loyalty (� = 0294). If the traditional market is able to improve how that merchants were able to be responsive to customers, more certain and consistent in providing services, as well as to have more physical evidence convenient market, consumers will be happy to shop at traditional markets.
In the short term, where the revitalization of the market has not been implemented by overhauling the mechanism of merchants in general, which can be used in stragetipeningkatakn is to increase the service quality of empathy for the customer, realizing what they needed and provide assurance that the products received in accordance with what is bought. By doing so, consumers will be more happy, feel more exciting experience that drives customer satisfaction and loyalty. Consumers will be more willing to invite others or return to the market if the service provided is very pleasant. The results support the research that states that the positive effect of service quality on customer loyalty (Hafeez, 2012; Ivanauskienë
and Volungënaitë, 2014; Nguyen et. al., 2016). In addition, the influence of service
quality to satisfaction also supports previous research (Hafeez, 2012; Rahman
et. al., 2012; Forsythe, 2015).
Service Quality as Key Factor in Revitalizing Traditional Markets Through Loyalty � 7891
In the absence of adequate parking space, the choice of location does not give satisfaction or customer loyalty. Customer satisfaction and significant positive effect on customer loyalty. This finding is consistent with research. This finding is consistent with research Omar and Sawmong (2007) which states that satisfaction will establish customer loyalty. Consumers who are satisfied traditional markets will be loyal to the traditional markets. Satisfaction role as mediating variables of service quality on customer loyalty. The mediating effect provide additional effect of 0072 (indirect effect) on the relationship. This further encourages efforts to improve the quality of services in generating customer loyalty. Satisfaction can be viewed from the side of services, pricing, and product. The composition of the three almost balanced, but the greatest role in shaping the perception of satisfaction from a consumer standpoint chronologically is the satisfaction of price, service, and products.
6. CONCLUSION
The key in reviving the traditional markets is to improve the service quality of traditional markets. Improved quality of service will increase loyalty, either directly or indirectly through customer satisfaction. The location, on the other hand does not show the effect on the revitalization of the market. Therefore, the focus should be done in the traditional market revitalization is through improved quality of service. The management of the market, along with government and academia have a role in helping to improve the quality of services performed by merchants as well as the traditional market itself. Therefore, in an effort to revitalize the market must be established synergy of the community in developing the quality of service.
References
Bitner, Mary Jo. (1990). Evaluating Service Encounters the Effects of Physical Surroundings and Employee Responses, Journal of Marketing 52(2), 69-82. DOI: 10.2307/1251871. Ennew, Christine and Martin R Binks. (1996), The impact of Service Quality and Service on
Customer Retention Characteristics: Small Businesses and Banks in the UK, British Journal of Management. 7(3), 219-230. Doi: 10.1111/j.1467-8551.1996.tb00116.x
Forsythe, Perry. (2015), Monitoring Customer Perceived Service Quality and Satisfaction during the Construction Process, Construction Economics and Building. 15(1), 19-42. DOI: http:// dx.doi.org/10.5130/ajceb.v15i1.4172.
Dessler, Gary. (2011), Human Resource Management, 12th Edition. New York: Prentice Hall.
7892 � ArlinaNurbaity Lubis and Prihatin Lumbanraja
Ivanauskienë, Neringa, and Justina Volungënaitë. (2014), Relations between Service Quality and Customer Loyalty: An Empirical Investigation of Retail Chain Stores in Emerging Markets, American International Journal of Social Science. 3(2), 113-120.
Kotler, Philip and Kevin Lane Keller. (2012), Marketing Management, 14th Edition. New Jersey: Prentice Hall.
Lupiyoadi, Creep and Hamdani. (2009), Services Marketing Management: Theory and Practice. First Edition. Jakarta: Salemba Empat Publisher.
Nguyen, TheNinh, Hoang Long Nguyen, Cao Tuan Khanh and Phan Thi Thu Hoai. (2016), The Influence of Service Quality on Customer Loyalty Intentions: A Study in the Vietnam Retail Sector, Asian Social Science 12(2), 112-119. Doi: 10.5539/ass.v12n2p112
Nielsen, A.C. (2004), Traditional Markets to Be Ousted, Koran Tempo August 20, 2004, www.tempo.co
Omar, Ogenyi, and SudapornSawmong. (2007), Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty to the British Supermarkets, Journal of Food Products Marketing. 13(2). DOI: 10.1300/J038v13n02_02. Parasuraman, A., Zeithaml, V.A., and Berry, L.L. (1988), A Multiple Item Scale for Measuring
Consumer Perception of Service Quality, Journal of Retailing. 64, 12-40.
Rahman, Mohammad Sabbir, Abdul highe Khan and Md. MahmudulHaque. (2012), A Conceptual Study on the Relationship between Service Quality towards Customer Satisfaction: Servqual and Grönroos’s Service Quality Model Perspective, Asian Social Science. 8(13), 201-210. DOI: 10.5539/ass.v8n13p201
Suryani, Tatik. (2008), Consumer Behavior: Implications for Marketing Strategy. Jakarta: BukuSeru Publishers.