CONTENTS
INTRODUCTION
ROADMAP TO BIOPRINTING
ADVANTAGES OF 3D PRINTING
APPLICATIONS
INDUSTRIAL DESIGN
AUTOMOTIVE AND AVIATION INDUSTRIES
ARCHITECTURE
FOOD INDUSTRY
MEDICAL INDUSTRY
JEWELRY AND FOOTWEAR
ENGINEERING AND CONSTRUCTION
DISADVANTAGES
FUTURE SCOPE
CONCLUSION
INTRODUCTION
Bio-printing is a variant of 3D printing and can be defined as computer-aided, automatic, layer-by-layer deposition, transfer, and patterning of biologically relevant materials. It is also known by other names such as “computer aided tissue engineering” and “bio fabrication”. In simpler words, bioprinting involves printing devices that deposit biological material.
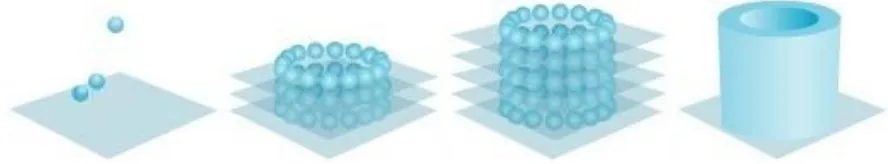
Organ printing is a variant of bio-printing aiming at producing 3D organs. This is among the most promising advances of regenerative medicine. The 3D- Bioprinter was listed among the TIME magazine’s 50 best inventions of 2010. Most of the 3D printers use a modified version of inkjet printers to deposit dots of “bio ink” (cell suspension with 10 to 30 thousand cells per drop) that coalesce to form layers of organ interrupted by layers of biopaper (hydrogel mimicking the microenvironment of tissue) which is water-soluble.
FIGURE XXII: Step-by-Step process of Organ Printing
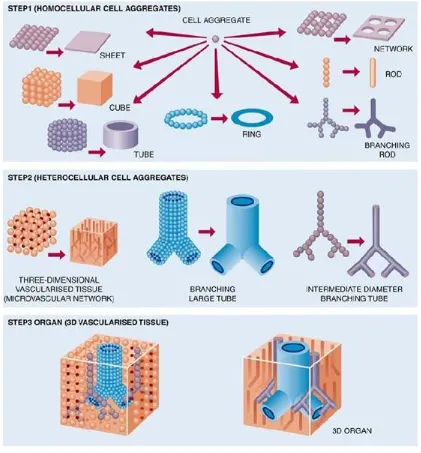
Roadmap to Bioprinting
The 3D bioprinters currently in the market are produced by envisionTEC, Organovo, Tengion, Sciperio, Neatco, etc.
do not create shapes and forms: physical mechanisms and processes do.” Organovo announced the production of first fully bioprinted blood vessels in Dec 2010
FIGURE XXIII: Roadmap to 3D printing
production of this technology will also cripple the illegal trade in human organs fueled by lack of viable organ tissue.
6. ADVANTAGES OF 3D PRINTING
1. New Structures and Shapes
Traditional manufacturing methods depend on cutting and moulding technologies to create a limited number of structures and shapes, with more intricate hollow ones having to be formed from a number of parts and assembled together. However, 3D printing technology transforms this process—the nozzle of the 3D printer can create many complex figures, being confined only by a person’s imagination. This method gives them higher structural integrity and more durability. The use of 3D printing technology takes virtual
designs from animation modeling software or computer-aided design (CAD), converts them into thin, virtual, flat cross-sections and then produces successive layers until the complete model is produced. It is a WYSIWYG (What You See Is What You Get) method where the physical model and the virtual model are almost the same. To create a model, we can hire early adopter communities or enthusiasts, with connections to both the hacker and academic communities.
2. New Combinations of Materials
Combining different raw materials isn’t always possible with mass production methods due to the high costs involved and to their chemical and physical properties that make them tricky to combine using traditional methods. 3D printing has eliminated many of these limitations not only because of the initial dependence on plastic, but also because of a constant innovation made by enthusiasts believing that 3D printing’s potential hasn’t been reached yet. Thus, a lot of companies now provide tens of different materials with unique finishes producing the feel and look of glass, ceramics or metal with a variety of strengths and temperature resistance.
3. Less Waste
Manufacturing plastic and metal objects in particular is generally a wasteful process with a lot of surplus materials and chunky parts. For some aircraft builders, up to 90 percent of the material is usually wasted. Creating a similar object with the use of additive manufacturing not only utilizes less energy, but also minimizes waste. Other objects that can be made with the use of additive manufacturing include jewelry, footwear, automotive parts, and more. Sometimes, the finished product of 3D printing can be up to 60 percent lighter than the machined part but still sturdy. Large cost savings can be attained in this way and a smaller amount of waste also means a lesser effect on the environment.
4. Cheap Manufacturing
3D printing helps companies save up to 70 percent of their manufacturing cost. This is attained through lower packaging and shipping costs related to more reliable and cheaper raw materials and lesser workforce needed, as well as overseas parts suppliers. In the end, this technology makes progressive companies more profitable.
FIGURE XXV: Multiple copies which can be printed directly at consumers place 5. Quick Production
The speed of 3D printing is quicker as compared to the traditional method. It’s similar to comparing the top speed of a sports car to a horse cart. They both take us to our destination, but the travel period differs significantly.
manufacturers because of their independence on offline sellers that commonly purchase in bulk, it can prove very efficient for an online business.
6. Better quality
Avoiding most of the mass manufacturing faults does not only make better products but it also extends their life as they will break less often. This is not necessarily a
great benefit for manufacturers who need the product life cycle to be profitable, but it is certainly a major benefit for the end consumer.
7. Sustainability
Less waste compared to traditional manufacturing methods is not only a cost saving feature of 3D printing but also a possible eco-friendly attribute. Add to this the multi-purpose characteristic of a 3D printer (can build different objects without the need of using specialised machines for each part) and their digital ecosystem (all 3D models are transmitted electronically so in theory they can be printed out where they are needed, minimizing therefore transport costs) and we get a sustainable manufacturing process. Integrating additive manufacturing with more classic production methods – as is the case with 3D printed textiles in the clothing industry – adds another layer (excuse the pun) to the sustainability case.
7. APPLICATIONS
AREAS OF APPLICATION OF 3D PRINTERS
FIGURE XXVI: Industrial 3D Printer
Industrial design
Automotive and aviation industries
Architecture
FOOD INDUSTRY
Medical Industries
Jewelry
Footwear
Engineering and construction
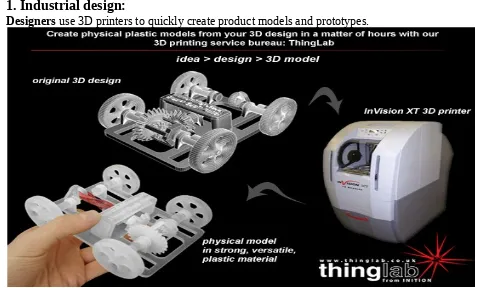
1. Industrial design:
Designers use 3D printers to quickly create product models and prototypes.
FIGURE XXVIII: Figure showing software being used in the industrial application
2. Automotive and aviation industries:
FIGURE XXVIII: First car and aero plane model made from 3D printing
3. Architecture:
Artists can create models of their projects. Also Quick, automated production of beautifully complex architectural models is reality with 3D printing.
FIGURE XXIX: Artistic model and architecture model
4. Food Industry:
Different food items have been printed and in the near future many other food items will be tested for 3D printing.
For example, Burger has been printed by 3D systems.
FIGURE XXX: chocolate being applied on bread and first printed burger
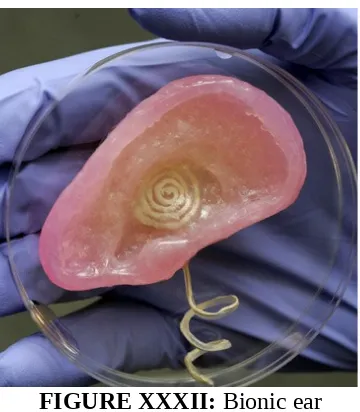
5. Medical industry:
This sector is a booming sector in 3D printing. Research is being done for different body parts to be printed and can be used directly for human body. Many human body parts such as liver, heart, and ear have been printed but they are of no use till now.
Except tooth jaws, no other bio product made can be used for human body. Items like hearing aid printed via 3D printers are found very useful.
FIGURE XXXII: Bionic ear
6. Jewelry and footwear:
3D printing being so versatile in making different shapes that it is being used in producing different designs for jewelry and footwear.
7. Engineering and construction:
3D printing is being used for different fields NASA is sending a 3D printer to space station which will help in constructing the required parts for the space station. Similarly on earth different engineering projects and construction material are being manufactured.
7. DISADVANTAGES
1. Fewer Manufacturing Jobs: As with all new technologies, manufacturing jobs will decrease. This disadvantage can and will have a large impact to the economies of third world countries, especially China, that depend on a large number of low skill jobs.
2. Limited Materials: Currently, 3D printers only manufacture products out of plastic, resin, certain metals, and ceramics. 3D printing of products in mixed materials and technology, such as circuit boards, are still under development.
3. Copyright: With 3D printing becoming more common, the printing of copyrighted products to create counterfeit items will become more common and nearly impossible to determine.
5. More Useless Stuff: One of the dangers of 3D printers is that they will be used to create more useless stuff that is bad for the environment and wallets. Fortunately, there are new methods of automatically recycling objects made by 3D printers that hold promise of better recycling in the future.
6. Size: Currently, 3D printers are limited with the size of the products that they can create. Ultimately, large items, such as houses and building, could be created using 3D printers.
8. FUTURE SCOPE
3D printing has a vast future scope. It is still a developing field. Be it a basic 3d printer or a versatile bio printer, there is a long journey ahead. We have come from time where 3D printers were a dream to time where the printers are available for all but at a high cost.
In the year 2014 key patents of 3D printing technology will expire which will give a boom to 3D manufacturing industry. Following are some of the hot topics for future:
1. COST: Cost of 3D printers will decrease to such an extent that every household will be able to buy a 3D printer.
2. SOFTWARE UPDATE: Windows has announced to bring 3D printer support in its next version of windows.
3. BIOPRINTERS: Human organs will be made through 3D printers and will finish the shortage of organs.
4. FOOD: In few years our dinner will be printed.
5. INDUSTRY: Large 3D printers will be available for printing large parts and machinery. 6. ARMS: With advantages, disadvantages also come such as it will be possible for people
9. CONCLUSION
Nothing communicates ideas faster than a three-dimensional part or model. With a 3D printer we can bring CAD files and design ideas to life – right from the desktop. Test form, fit and function – and as many design variations as there can be – with functional parts.
10. REFERENCES
1. http://www.explainingthefuture.com/3dprinting.html 2. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/3D_printing
3. http://www.mahalo.com/3d-printers/
4. http://net.educause.edu/ir/library/pdf/DEC0702.pdf 5. http://www.inventioncity.com/intro-to-3-d-printing.html 6. http://desktop3dprinters.net/773374/3d-printing-technologies 7. www.entrepreneur.com
8. 'Gadget printer' promises industrial revolution –from NewScientist.com 9. www.stratasys.com
10. 3dprintingindustry.com