DAFTAR PUSTAKA
Abidin,H.Z.,2000, Penentuan Posisi dengan GPS dan Aplikasinya: Pradnya Paramita
Adams, W.G., Comparison of simultaneous magnetic disturbance at several observatories, Phil. Trans. London (A), 183, 131, 1892.
Akasofu, S.-I. and S. Chapman, On the asymmetric development of magnetic storm field in low and middle latitudes, Planet. Space Sci., 12, 607, 1964. Akasofu, S.-I. and S. Chapman, Solar Terrestrial Physics, Oxford University
Press, Oxford, 1972.
Bishop, G.J., Mazzella, A.J., Holland, E., and Rao, S., 1996. Algorithms that use the ionosphere to control GPS errors, in Proceedings of the IEEE 1996
Position Location and Navigation Symposium (PLANS), IEEE Press,
Piscataway, N.J., pp. 145-152.
Bishop, G.J., Coco, D.S., Lunt, N., Coker, C., Mazzella, A.J., and Kersley, L., 1997. Application of SCORE to extract protonospheric electron content from GPS/NNSS observations, in Proceedings of ION GPS ’97, Inst. of Navig., Alexandria, Va., pp. 207-216.
Broun, J.A., On the horizontal force of the Earth's magnetism, Proc. Roy. Soc. Edinburgh, 22, 511, 1861.
Cahill, L.J., Jr, Inflation of the inner magnetosphere during a magnetic storm, J. Geophys. Res., 71, 4505, 1966.
Chapman, S., The electric current-systems of magnetic storms, Terr. Mag. Atomos. Phys., 40, 349, 1935.
Chapman, S., The morphology of magnetic storms: an extension of the analysis of Ds, the disturbance local-time inequality, Annali di Geofisica, 5, 481, 1952.
Coco, D. S., C. Coker, S. R. Dahlke, and J. R. Clynch, 1991. Variability of GPS satellite differential group delay biases, IEEE Trans. Aeros. and Electr.
Syst., AES-27, 931–938.
Crooker, N.U., and G.L. Siscoe, Birkeland currents as the cause of the low-latitude asymmetric disturbance field, J. Geophys. Res., 86, 11201, 1981. Davies, K., 1990. Ionospheric Radio, Peter Peregrinus Ltd., 580pp.
Frank, L. A., Direct detection of asymmetric increases of extraterrestrial ring proton intensities in the outer radiation zone, J. Geophys. Res., 75, 1263, 1970.
Fraser-Smith, A., Bernardi, C.A., McGill, P.R., Ladd, M.E., Hellowell, R.A., and Villard Jr.,O.G., 1990. Low-frequency magnetic field measurements near the epicenter of the Ms 7.1 Loma Prieta earthquake, Geophysical Research Letter, 17, 1465-1468.
Fukushima, N., and Y. Kamide, Partial ring current models for world geomagnetic disturbances, Rev. Geophys. Space Phys., 11, 795, 1973.
Hayakawa, M., O.A. Molchanov, N. Shima, A.V. Shvets and N. Yamamoto., 2002. Wavelet analysis of disturbances in subionospheric VLF propagation correlated with earthquakes, in “Seismo Electromagnetics (Lithosphere-Atmosphere-Ionosphere Coupling)”, Ed. By M. Hayakawa and O.A. Molchanov, TERRAPUB, Tokyo, 223-228.
Hofmann-Wellenhof, B., Lichtenegger, H., Collins, J., 1997, GPS - Theory and
Practice, 4th revised edition, Springer, Wien - New York.
Hunscucker, R.D., 1991. Radio Techniques for Probing the Ionosphere, Springer Verlag, New York.
Kamogawa, M., 2004. Atmospheric Field Variations before the March 31, 2002 M6.8 Earthquake in Taiwan. TAO, 15, no.3, 397-412.
Kleusberg, A. and Teunissen, P. (eds), 1996. GPS for Geodesy, International School, Delft, The Netherlands, 26 March - 1 April 1995, Springer Verlag, New York.
Komjathy, A., 1997. Global Ionospheric Total Electron Mapping Using the
Global Positioning System, PhD Thesis, The Univ. of New Brunswick,
Kopytenko, Y.A., Matishvili, T.G., Voronov, P.M., Kopytenko, E.A., and Molchanov, O.A., 1993. Detection of ultra-low frequency emissions connected with the Spitak eartgquake and its aftershock activity, based on magnetic pulsations data at Dusheti and Vardzia observatories, Phys. Earth Planet. Inter., 77, 85-93.
Langel, R.A., R.H. Estes, G.D. Mead, E.B. Fabiano, and E.R. Lancaster, Initial geomagnetic field model from Magsat vector data, Geophys. Res. Letters, 7, 793, 1980.
Langel, R.A., J. Berbert, T. Jennings, and R. Horner, Magsat data processing: a report for investigators, NASA Technical Memorandum 82160, Goddard Space Flight Center, 1981.
Langley, R.B., 1997. NAVSTAR GPS Internet Connections, http://gauss.gge.unh.ca/gps.internet.services.html.
Lanyi, G.E. and Roth, T., 1988. A comparison of mapped and measured total ionospheric electron content using global positioning system and beacon satellite observations, Radio Sci., 23 (4), 483-492.
Leick, A., 1995. GPS satellite surveying, John Wiley, New York, 560 pp.
Liu, J.Y., Tsai, H.F., and Jung, T.K., 1996. Total electron content obtained by using the global positioning system, J. Terr. Atmos. and Oceanic Sci. (TAO), 7(1), 107-117.
Liu, J.Y., Chen, Y.I., Pulinets, S.A., Tsai, Y.B., and Chuo, Y.J., 2000. Seismo-ionospheric signatures prior to M ≥ 6.0 Taiwan earthquakes, Geoph. Res. Lett., 27(19), 3113-3116.
Liu, J.Y., Chuo, Y.J., Shan, S.J., Tsai, Y.B., Chen, Y.I., Pulinets, S.A., and Yu, S.B., 2004. Pre-earthquake ionospheric anomalies registered by continuous GPS TEC measurements, Ann. Geoph., 22, 1585-1593.
Mc. Namura, L.F., 1994. Radio Amateurs Guide to the Ionosphere, Krieger Publ. Comp., Malabar, FL.
Moos, N.A.F., Magnetic observations made at the government observatory, Bombay, for the period 1846 to 1905, and their discussion, Part II: the phenomenon and its discussion, Bombay, 1910.
Puspito, N.T., Barus, P.A., dan Widaro, D.S., 2007. Anomali Total Electron
Content (TEC) Di Ionosphere Di Sumatera Dan Hubungannya Dengan Gempa Besar Aceh 26 Desember 2004, Jurnal Geofisika, edisi 2007 No.2,
Bandung.
Parkinson, B.W., Spilker, J.J., Axelrad, P., and Enge, P. (eds), 1996. Global
Positioning System : Theory and Applications, Vol. 163, Progress in
Austronautics, Am. Inst. Aero. Astro., Washington, D.C.
Rothacher, M., and Mervart, L. 1996. Bernese GPS Software Ver. 4.0,
Astronomical Institute, University of Bern.
Sardon, E., Rius, A., and Zarraoa, N., 1994. Estimation of the transmitter and receiver differential biases and the ionospheric total electron content from Global Positioning System observations, Radio Sci., 29 (3), 577-586. Shelley, E.O., Heavy ions in the magnetosphere, Space Sci. Rev., 23, 465, 1979. Smith, P.H., N.K. Bewtra, and R.A. Hoffman, Inference of the ring current ion
composition by means of charge exchange decay, J. Geophys. Res., 86, 3470, 1981.
Sugiura, M., Hourly values of equatorial Dst for the IGY, Ann. Int. Geophys. Year, 35, 9, Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1964.
Sugiura, M., Quiet time magnetospheric field depression at 2.3-3.6 Re, J. Geophys. Res., 78, 3182, 1973.
Sugiura, M., and S. Chapman, The average morphology of geomagnetic storms with sudden commencement, Abandl. Akad. Wiss. Göttingen Math. Phys. Kl., Sondernheft Nr.4, Göttingen, 1960.
Sugiura, M., and D.J. Poros, A magnetospheric field model incorporating the OGO-3 and-5 magnetic field observations, Planet. Space Sci., 21, 1763, 1973.
Vestine, E.H., L. Laporte, I. Lange, and W.E. Scott, The geomagnetic field, its description and analysis, Carnegie Institution of Washington Publication 580, Washington D.C., 1947.
Widarto, D.S., 2005. Pemetaan total electron content di lapisan ionosfer menggunakan data global positioning system: tinjauan teori, J. Geofisika, Bandung.
Williams, D.J., Ring current composition and sources, in Dynamics of the magnetosphere, ed. S.-I. Akasofu, D. Reidel Publishing Company, p.407, 1980.
Williams, D.J., Ring current composition and sources: an update, Planet. Space Sci., 29, 1195, 1981.Additional References (quoted in the Foreword)
Wilson, B.D., Mannucci, A.J., Edwards, C.D., and Roth, T., 1992. Global ionospheric maps using a global network of GPS receivers, the Internatl.
LAMPIRAN I
Hasil Analisis Differensial TEC tahun 2004-2005
I.1 I.2 I.3 I.4 I.5 I.6 I.7 I.8 I.9 I.10
Kondisi dTEC bulan Desember 2004 Kondisi dTEC bulan Februari 2005 Kondisi dTEC bulan Februari 2005 Kondisi dTEC bulan Februari 2005 Kondisi dTEC bulan Maret 2005 Kondisi dTEC bulan April 2005 Kondisi dTEC bulan April 2005
Kondisi dTEC saat gempa tanggal 10 April 2005 Kondisi dTEC saat gempa tanggal 16April 2005 Kondisi dTEC saat gempa tanggal 28April 2005
H-19 H-18 H-17 H-0 H-5 DESEMBER 2004 M=9,2 H-20
Gambar L I.1 Kondisi dTEC bulan Desember 2004, 20, 19, 18, 17 hari sebelum Gempabumi Aceh terjadi penurunan TEC karena ada Badai Magnetic (warna biru) 5 hari sebelum Gempabumi Aceh terjadi Penurunan TEC sebagai persiapan Gempabumi (warna biru).
FEBRU
H-0,M=6,8
Gambar L I.3 Kondisi dTEC bulan Februari 2005, 5 Hari sebelum Gempa bumi terjadi penurunan TEC ( warna biru)
Origin time : 26 Februari 2005, Jam 12 56 52,6 UTC Episenter : 2,9 LU-95,59 BT
Magnitudo : 6,8 SR, Kedalaman 36 Km Dirasakan di Banda Aceh III MMI H-5
H-0
H-6 H-5
H-4
Kondisi dTEC bulan Maret 2005
Gambar L I.5 Kondisi dTEC bulan Maret 2005, Terjadi penurunan dTEC 6, 5, 4 hari sebelum Gempabumi terjadi
Origin time : 28 Maret, Jam 16 09 36,51 UTC Episenter : 2,08 LU-97,10 BT
Magnitudo : 8,6 SR Kedalaman 40 Km Dirasakan di P.Nias, Simeleue, Kep.Banyak
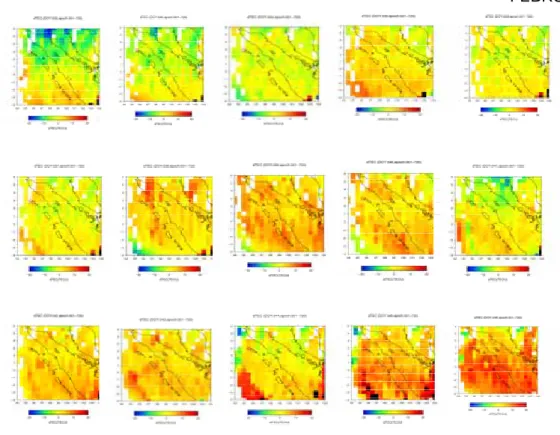
H=0,M=6,3
H-5 H-4 H-3
H=0,M=6,3,pada 3 -4-2005
23-3-05
Gambar L I.6 Kondisi dTEC bulan April 2005, Terjadi penurunan 5 hari sebelum gempabuni terjadi
Origin time : 3April 2005 jam 00 59 15,1 UTC Episenter : 0,24 LS-97,64BT
Magnitudo : 6,3 SR kedalaman 33 Km Dirasakan di P.Nias dengan intensitas V MMI
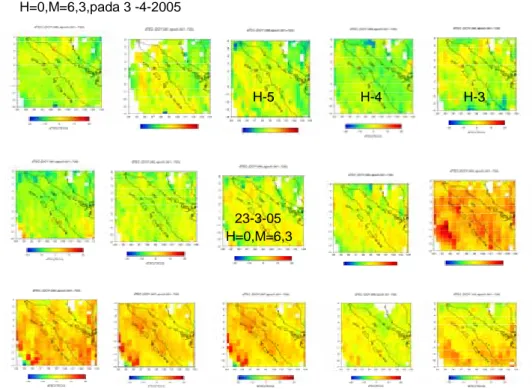
H=0,M=6,7
8-4-2005 H-4
H-7
Gambar L I.7 Kondisi dTEC bulan April 2005, Terjadi penurunan TEC 7 hari sebelum Gempabumi
Origin time : 8 April 2005 jam 05 48 36,0 UTC Episenter : 0,21 LU-97,97 BT
Magnitudo : 6,0 SR Kedalaman 30 Km
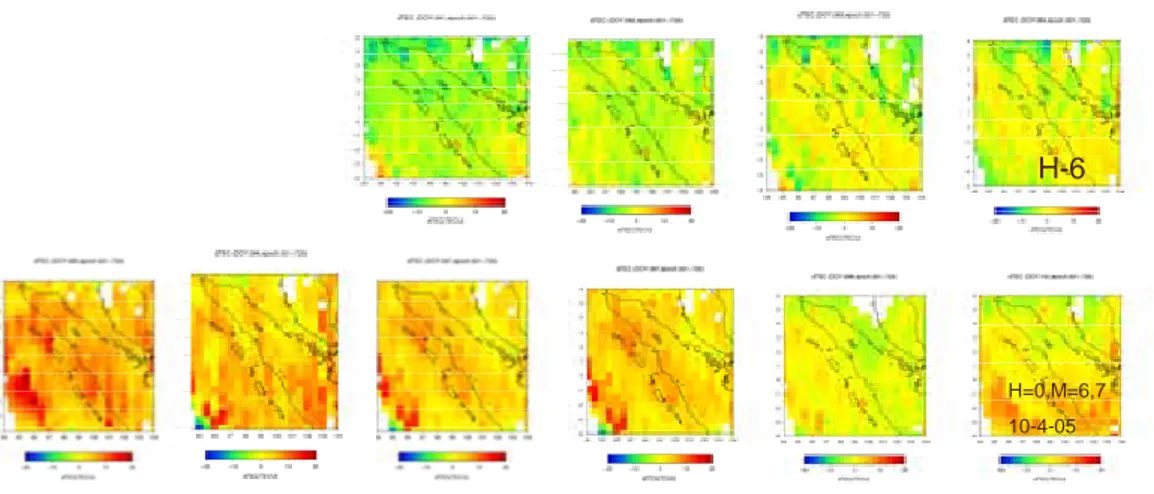
H=0,M=6,7 10-4-05
H-6
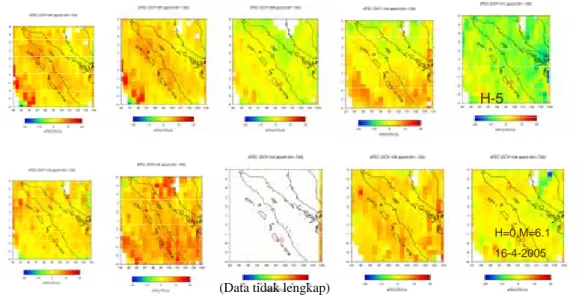
H=0,M=6.1 16-4-2005
H-5
Gambar L I.9 Kondisi dTEC saat gempa tanggal 16April 2005
H=0,M=6,0 28-4-2005 H-8
Gambar L I.10 Kondisi dTEC saat gempa tanggal 28April 2005