Management
Management
Information Systems,
Information Systems,
10/e
10/e
Raymond McLeod and George
Raymond McLeod and George
Schell
© 2007 by Prentice Hall
© 2007 by Prentice Hall Management Information Systems, 10/e RManagement Information Systems, 10/e R
aymond McLeod and George Schell
aymond McLeod and George Schell
2
2
Chapter 1
Chapter 1
Introduction to Information
Introduction to Information
Systems
Learning Objectives
Learning Objectives
►
Understand how computer hardware has
Understand how computer hardware has
evolved to its present level of sophistication
evolved to its present level of sophistication
►
Know the basics of computer and
Know the basics of computer and
communications architectures.
communications architectures.
►
Understand the distinction between physical
Understand the distinction between physical
and virtual systems.
and virtual systems.
►
Describe how business applications have
Describe how business applications have
evolved from an initial emphasis on
evolved from an initial emphasis on
accounting data to the current emphasis on
accounting data to the current emphasis on
information for problem solving.
© 2007 by Prentice H all
Management Information S ystems, 10/e Raymond Mc Leod and George Schell
4
Learning Objectives (Cont’d)
Learning Objectives (Cont’d)
►
Understand what enterprise resource planning
Understand what enterprise resource planning
systems are and the reasons for their
systems are and the reasons for their
popularity.
popularity.
►
Know how to tailor information systems to
Know how to tailor information systems to
managers based on where they are located in
managers based on where they are located in
the organizational structure and what they do.
the organizational structure and what they do.
►
Understand the relationship between problem
Understand the relationship between problem
solving and decision making and know the
solving and decision making and know the
basic problem-solving steps.
basic problem-solving steps.
►
Know what innovations to expect in
Know what innovations to expect in
History of Information
History of Information
Systems
Systems
►
Evolution in computer hardware
Evolution in computer hardware
Mainframe
Mainframe
Multitasking
Multitasking
►
Smaller computers
Smaller computers
Minicomputers
Minicomputers
Microcomputers
Microcomputers
© 2007 by Prentice H all
Management Information S ystems, 10/e Raymond Mc Leod and George Schell
6
Intro to Computer
Intro to Computer
Architecture
Architecture
►
Moore’s Law
Moore’s Law
– computer power
– computer power
doubles every year for a given cost.
doubles every year for a given cost.
►
Hardware
Hardware
– processor, keyboard,
– processor, keyboard,
monitor, mouse, printer, etc.
monitor, mouse, printer, etc.
►
Software
Software
– application, operating,
– application, operating,
etc.
etc.
►
Used to support managerial decision
Used to support managerial decision
making.
Computer Architecture
Computer Architecture
(Cont’d)
(Cont’d)
►
Modem
Modem
– hardware device that
– hardware device that
modulates the digital signals from a
modulates the digital signals from a
computer into analog signals
computer into analog signals
(telephone system), and vice versa.
(telephone system), and vice versa.
►
Direct communication standards
Direct communication standards
© 2007 by Prentice H all
Management Information S ystems, 10/e Raymond Mc Leod and George Schell
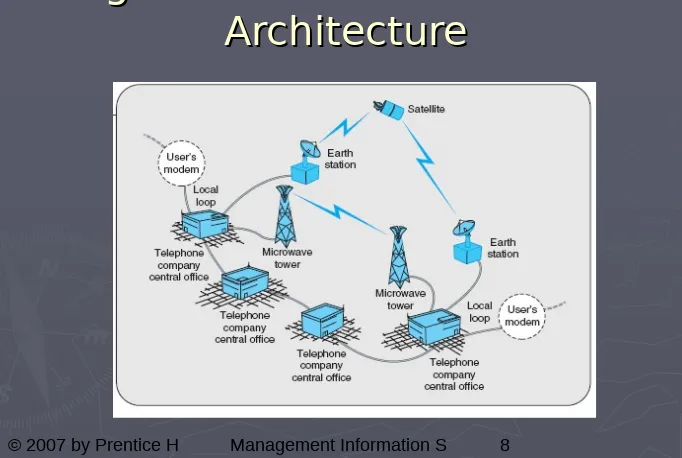
[image:8.720.23.705.62.520.2]8
Figure 1.5 Communications
Figure 1.5 Communications
Architecture
Evolution in Computer
Evolution in Computer
Applications
Applications
►
Information systems
Information systems
are
are
virtual systems
virtual systems
that enable management to control the
that enable management to control the
operations of the
operations of the
physical system
physical system
of the
of the
firm.
firm.
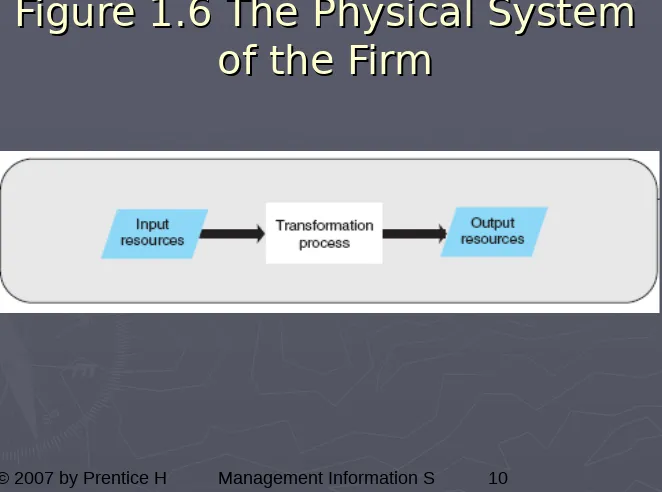
►
Physical system
Physical system
– tangible resources such
– tangible resources such
as materials, personnel, machines, and
as materials, personnel, machines, and
money.
money.
►
Virtual system
Virtual system
– information resources that
– information resources that
are used to represent the physical system.
© 2007 by Prentice H all
Management Information S ystems, 10/e Raymond Mc Leod and George Schell
[image:10.720.35.697.29.521.2]10
Figure 1.6 The Physical System
Figure 1.6 The Physical System
of the Firm
Computer Applications
Computer Applications
(Cont’d)
(Cont’d)
►
Open system
Open system
is a firm’s physical
is a firm’s physical
system that interacts with its
system that interacts with its
environment by means of physical
environment by means of physical
resource flows.
resource flows.
►
Closed system
Closed system
is one that does not
is one that does not
communicate with its environment.
© 2007 by Prentice H all
Management Information S ystems, 10/e Raymond Mc Leod and George Schell
12
Transaction Processing
Transaction Processing
Systems
Systems
►
Data
Data
– facts and figures that are
– facts and figures that are
generally unusable due to their large
generally unusable due to their large
volume and unrefined nature.
volume and unrefined nature.
►
Information
Information
– processed data that is
– processed data that is
meaningful; tells users something.
meaningful; tells users something.
►
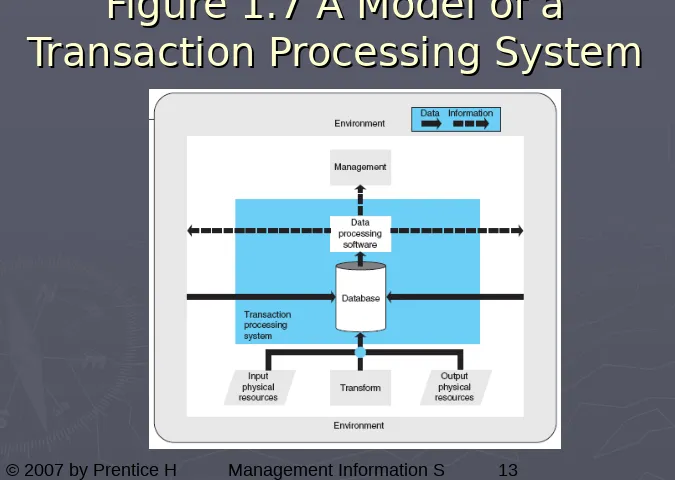
Transaction Processing System
Transaction Processing System
(TPS)
(TPS)
processes data that reflects the
processes data that reflects the
activities of the firm.
Figure 1.7 A Model of a
Figure 1.7 A Model of a
Transaction Processing System
© 2007 by Prentice H all
Management Information S ystems, 10/e Raymond Mc Leod and George Schell
14
Management Information
Management Information
Systems
Systems
►
Management Information System
Management Information System
(MIS)
(MIS)
is a computer-based system
is a computer-based system
that makes information available to
that makes information available to
users with similar needs.
users with similar needs.
►
Report-writing software
Report-writing software
– produces
– produces
both periodic and special reports.
both periodic and special reports.
►
Mathematical models
Mathematical models
– produces
– produces
information as a simulation of the
information as a simulation of the
firm’s operations.
© 2007 by Prentice H all
Management Information S ystems, 10/e Raymond Mc Leod and George Schell
16
MIS (Cont’d)
MIS (Cont’d)
►
Information provided by MIS describes
Information provided by MIS describes
the firm or one of its major systems.
the firm or one of its major systems.
What has happened in the past.
What has happened in the past.
What is happening now.
What is happening now.
What is likely to happen in the future.
What is likely to happen in the future.
►
Interorganizational information
Interorganizational information
system
Virtual Office Systems
Virtual Office Systems
►
Office automation
Office automation
– use of electronics
– use of electronics
to facilitate communication.
to facilitate communication.
►
Personal productivity systems
Personal productivity systems
– use
– use
technology to self-manage clerical tasks
technology to self-manage clerical tasks
such as calendars, address books, etc.
such as calendars, address books, etc.
►
Virtual office
Virtual office
– performing office
– performing office
activities independent of a particular
activities independent of a particular
physical location.
© 2007 by Prentice H all
Management Information S ystems, 10/e Raymond Mc Leod and George Schell
18
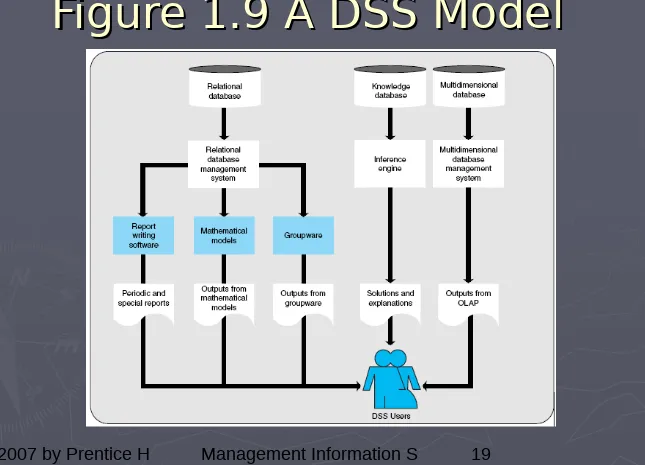
Decision Support Systems
Decision Support Systems
►
Decision Support System (DSS)
Decision Support System (DSS)
–
–
assists management in solving a problem.
assists management in solving a problem.
►
Groupware
Groupware
– group-oriented software.
– group-oriented software.
►
Group decision support system
Group decision support system
(
(
GDSS
GDSS
)
)
combines groupware and the DSS.
combines groupware and the DSS.
►
Artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence
(
(
AI
AI
) – the science
) – the science
of providing computers with human
of providing computers with human
intellegence.
© 2007 by Prentice H all
Management Information S ystems, 10/e Raymond Mc Leod and George Schell
20
Enterprise Resource Planning
Enterprise Resource Planning
Systems
Systems
►
Enterprise Resource Planning
Enterprise Resource Planning
System (ERP)
System (ERP)
is a computer-based
is a computer-based
system that enables the management
system that enables the management
of all of the firm’s resources on an
of all of the firm’s resources on an
organization-wide basis.
organization-wide basis.
Y2K complaint
Y2K complaint
Information System Users
Information System Users
►
First users were clerical users on TPSs.
First users were clerical users on TPSs.
►
MISs added problem-solvers as users.
MISs added problem-solvers as users.
►
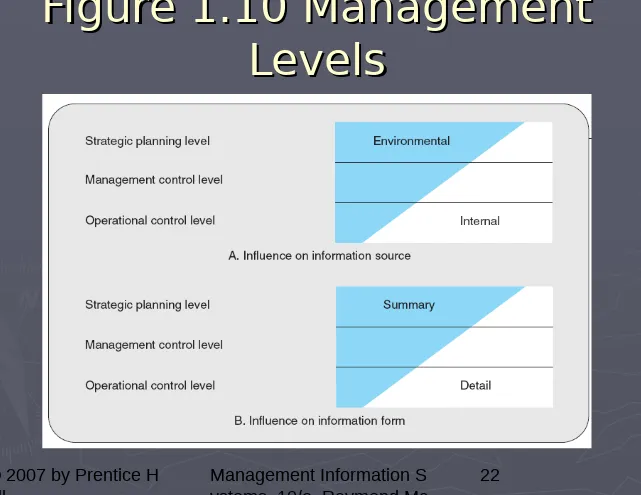
Managerial Levels
Managerial Levels
© 2007 by Prentice H all
Management Information S ystems, 10/e Raymond Mc Leod and George Schell
[image:22.720.43.684.32.527.2]22
Figure 1.10 Management
Figure 1.10 Management
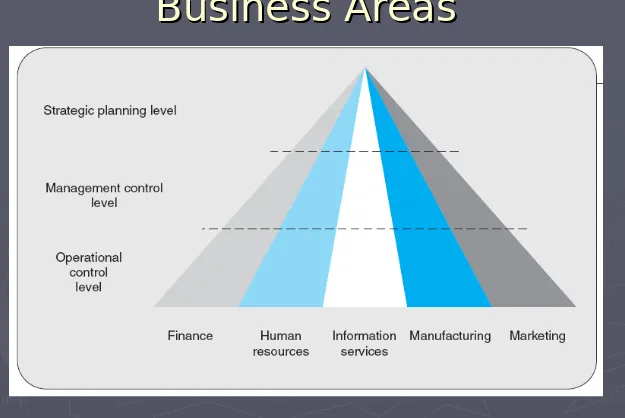
Figure 1.11 Managers in
Figure 1.11 Managers in
Business Areas
© 2007 by Prentice H all
Management Information S ystems, 10/e Raymond Mc Leod and George Schell
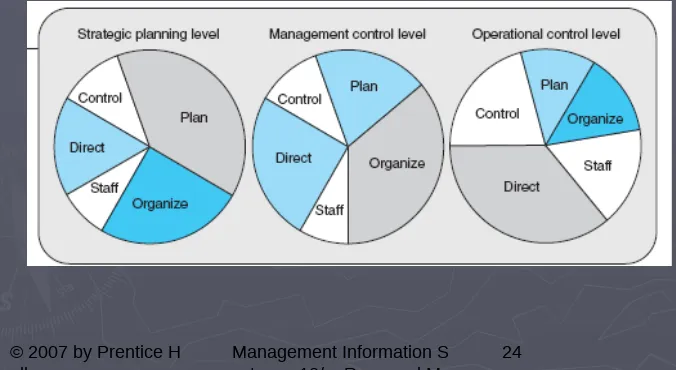
[image:24.720.21.697.155.525.2]24
Figure 1.12 Management
Figure 1.12 Management
Table 1.2 Mintzberg’s
Table 1.2 Mintzberg’s
Managerial Roles
© 2007 by Prentice H all
Management Information S ystems, 10/e Raymond Mc Leod and George Schell
26
Problem Solving & Decision
Problem Solving & Decision
Making
Making
►
Problem – a condition or event that is
Problem – a condition or event that is
harmful or potentially harmful to a firm
harmful or potentially harmful to a firm
or that is beneficial or potentially
or that is beneficial or potentially
beneficial.
beneficial.
►
Solution – outcome of the problem-
Solution – outcome of the
problem-solving activity.
solving activity.
►
Decision – a particular selected course
Decision – a particular selected course
of action.
Four Problem-Solving Phases
Four Problem-Solving Phases
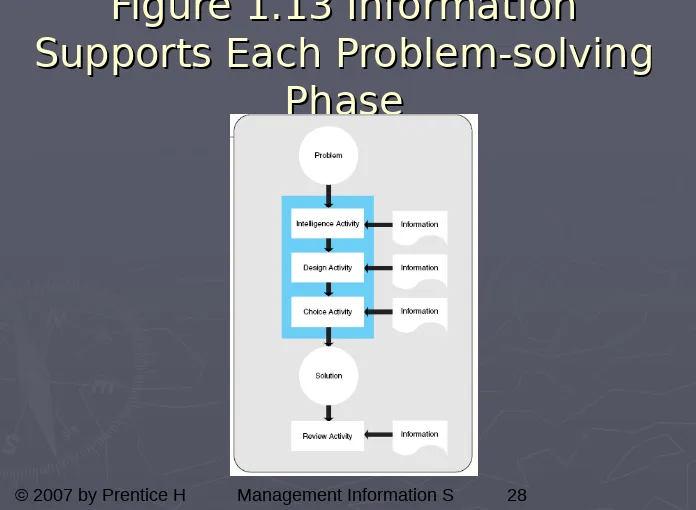
►
Intelligence activity
Intelligence activity
. Search the
. Search the
environment for conditions calling for
environment for conditions calling for
a solution.
a solution.
►
Design activity
Design activity
. Invent, develop, and
. Invent, develop, and
analyze possible courses of action.
analyze possible courses of action.
►
Choice activity
Choice activity
. Select a particular
. Select a particular
course of action from those available.
© 2007 by Prentice H all
Management Information S ystems, 10/e Raymond Mc Leod and George Schell
[image:28.720.16.712.12.522.2]28
Figure 1.13 Information
Figure 1.13 Information
Supports Each Problem-solving
Supports Each Problem-solving
Phase
The Future of Information
The Future of Information
Technology
Technology
►
Reduced cost & increased power of
Reduced cost & increased power of
both computers and communications.
both computers and communications.
►
Computers & communications are
Computers & communications are
converging, i.e. cell phones with
converging, i.e. cell phones with
browsers.
browsers.
►
Future computing will be low cost,
Future computing will be low cost,
small in size, mobile, and connected.