TOPIC 2
INTERACTIVE MEDIA TECHNOLOGIES
T.J. Iskandar Abd. AzizINTRODUCTION
Interactive media technologies play an important role in today’s communications industry as well as applications in business, education, entertainment, and telecommunications. Designing and producing effective presentations which combine graphics, text, sound, music, video and animation requires an imaginative blend of art, science, technology, and communications skills.
These media technology has drastically changed the way we view, interact with, and use computers. Multimedia technology succeeded in transforming computers to the real “second person.” Like never before, multimedia technology has made it possible for us to see, hear, read, feel, and talk to computers. Furthermore, multimedia technology has transformed and deepened our understanding and use of computers in a more meaningful way. Without doubt, interactive media technology is a key topic for current and future application of information technology.
This topic discusses some of the common types of media and the related technologies available in the market nowadays.
OBJECTIVES
By the end of this topic, you should be able to:
1. define the terms and concept related to media technology;
2. identify three different types of mass media technology;
3. identify ten different types of new media technology; and
MIND MAP
2.1 WHAT IS MEDIA TECHNOLOGY?
How does a user interact with media? Elaborate.
John Waterworth (1991), in an attempt to draw our attention to the significance of multimedia technology, states:
Sheu and Ismail (1998) have further stated how multimedia technology has pervaded our lives and has forever changed the way we live, work, entertain, and learn.
According to Steve Heath (1999),
From all these different views and definitions, one thing is for sure; interactive multimedia technology is the latest development in the information communication world and it is still evolving in various areas of interest.
2.2 MASS MEDIA TECHNOLOGY
Now, we will discuss three types of mass media technology, which are:
x Newspaper,
x Radio, and
x Television.
2.2.1 Newspaper
“The widespread application of technology that combines photographic images, graphics, text, motion video and audio material in a well-integrated way is bound to have a major impact on the development of information systems that are more than word processors, computational number crunchers, or a combination of the two.
This impact will be seen in business, in science, in education, in the home, and in public places. It will reach people at almost all levels of society, and will have significant, but as yet unknown, societal impacts. This makes multimedia a uniquely exciting field to be working at the moment.”
“With wide access to the Internet, kids can spend more time online experimenting with and learning from computers through the Information Super-highway than on the TV. Once the power of image, video, and graphic through high-speed fiber-optics transmission or wireless communication is enjoyed, the old-fashioned approach of using plain text as a main source of information will be a thing of the past”
social and political happenings, government scandals, military campaigns, upcoming events, trials and executions. The news was written on large white boards and exhibited at popular places like the public baths.
A newspaper is a lightweight and disposable publication, usually printed on low-cost rough paper called newsprint. It contains a journal of current news in a variety of topics, advertisements, etc. and published every day or every week. Text and graphics or images are the elements of multimedia used in a common newspaper.
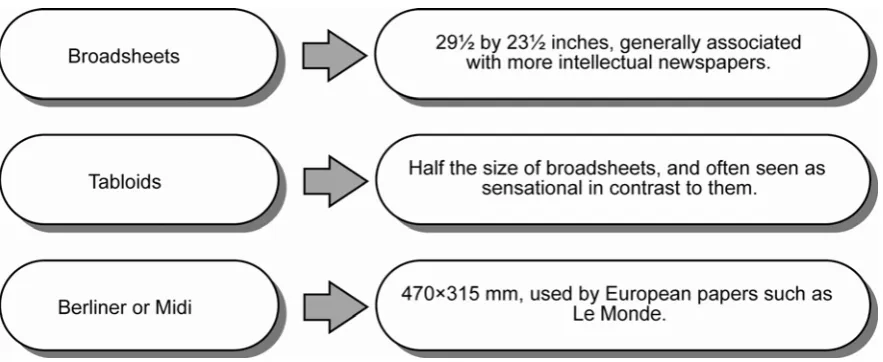
Most modern newspapers are in one of three sizes as shown in Figure: 2.1.
Figure 2.1: Three sizes of modern newspapers
Since the 1980s, many newspapers have been printed with three-colour process photography and graphics. This highlights the fact that the layout of the newspaper is of major importance in getting readers’ attention so they will see and enjoy large sections of the newspaper.
Through the World Wide Web (WWW), e-newspaper services has also been introduced, even in Malaysia. Major newspaper company like Utusan Malaysia and The Star had already started their own e-newspaper to try to compete and offer better services for their readers. Other multimedia elements such as audio and video have also been incorporated to attract and provide fullest satisfaction to the readers.
Some of the advantages of these e-papers are:
x Instant delivery of your selected digital publications on time, every day.
x Searchable text on any research topic instantly, in current and past issues.
x Easy to read as you can zoom in to text and pictures with a single click.
x Advanced navigation; jump to sections and article continuations with a single click.
x Environmentally friendly as we save trees by reading electronic editions.
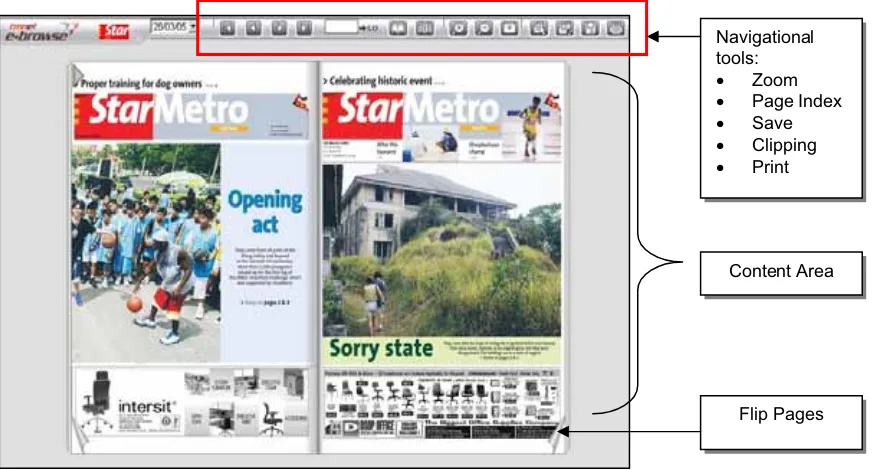
See Figure 2.2 and Figure 2.3 for some examples of e-newspaper services available in Malaysia (TMNET e-browse) and worldwide.
Figure 2.2: An example of an e-newspaper services in Malaysia
Source: http://ebrowse.bluehyppo.com/e_preview.asp?PubNameID=4#
Navigational tools:
x Zoom
x Page Index
x Save
x Clipping
x Print
Figure 2.3 : Pressdisplay: an electronic paper viewer
Source: http://www.pressdisplay.com/pressdisplay/viewer.aspx
2.2.2 Radio
The origin of radio as a medium of communications dated as far back to 1893, when
Nikola Tesla, a physicist demonstrated radio communication to his colleagues in the United States. Radio communication has been based on the studies of:
x James Clerk Maxwell, who developed the mathematical theory of electromagnetic waves; and
x Heinrich Hertz, who devised an apparatus for generating and detecting them.
Web radio (or Internet radio) is a broadcasting service transmitted via the Internet. Not every web "radio station" has a corresponding traditional radio station. Many web radio stations are completely independent from traditional ("terrestrial") radio stations and broadcast only on the Internet. Broadcasting on the Internet is usually referred to as web casting.
students studying in the United Kingdom can now listen to Malaysian radio station like Era.fm, using Internet streaming technology. This makes it a popular service for expatriates and for people who have interests that may not be adequately catered for by their local radio stations (e.g., country music). Some of the web radio services available via the Internet offer news, sports, talkback, and various genres of music—everything that is on the radio station is being re-broadcast. See Figure 2.4 for an example of a website that offers Internet radio broadcast services in Malaysia.
Figure 2.4: A website offering digital radio broadcast services
Source: http://www.dvrplayer.com/03/
2.2.3 Television (TV)
Do you still remember the first time that you saw a TV and watched a program on air? How old were you at that time? How did you feel? Was it a wonderful experience? You might not realised all these things, since you were probably a child and just did not bother to know how the TV set works. TV is now a part of our everyday lives that most people take the technology for granted.
Regular TV services started some 60 years ago in a number of countries, and early demonstrations including the recording of video took place some 70 years ago, in the late 1920s. Figure 2.5 refers to some of the earliest introductory advertisement about tube TV in America.
Welcome to Digital Visual Radio - Version 2.0
The all new dvrplayer is designed to enhance your listening experience, by combining digital sound and visual images, through the convergence of digital audio, text and graphics technologies.
Figure 2.5: Some of the earliest articles and advertisement on tube TV
Wikipedia.org defined TV as:
The first successful TV transmissions occurred between 1928 and 1935. Because the pictures in this system were composed of only 30 lines, small details could not be reproduced. This system was known as a low definition system. Several hundred lines are needed to give definition comparable to 35 mm film.
The first high definition system was introduced by the "BBC" in 1936. This system consisted of 405 lines. In 1964, they introduced a second high definition set. This was a 625 line system that was better suited to many other broadcasting authorities, so it enabled an even higher picture resolution than before.
In Malaysia, the first TV services were introduced on 28 December 1963 by Radio Television Malaysia (RTM), a government own company, from its studio at Dewan Tunku Abdul Rahman, Jalan Ampang, Kuala Lumpur. The first commercialised TV station,
Sistem Televisyen Malaysia Berhad (STMB) or TV3 was incorporated in 1983 and began broadcasting in the Klang Valley on 1st June 1984.
Since its introduction in the 1920s, TV systems had evolved and undergone some drastic changes, parallel to changes in communication technology and media. What has not changes all these times is its popularity among user as the main source of entertainment. Currently, there are quite a few different TV system, such as:
x Tube TV (curved or flat screen)
x Flat panel TV (LCD or Plasma)
x Projection TV (front and rear)
x Combo TV ( + DVD/ VCD, +VCR)
From the advertisements and articles in Figure 2.5, can you see the differences between the original TV system sets in 1920s and the current systems that we have nowadays (2005)? Try to list down a few differences and you will be amazed at how fast technology has evolved within a short
“a telecommunication system for broadcasting and receiving moving pictures and sound over a distance. The term has come to refer to all the aspects of TV programming and transmission as well.
(a) Television System
(i) Tube/Standard TV
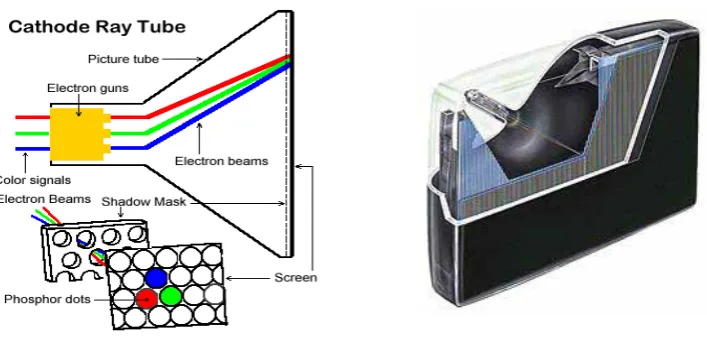
The standard tube TV that we have seen in the market for the past 10-15 years is also known as direct view. The picture device used is a cathode ray tube (CRT), which is a specialised vacuum tube (see Figure 2.6). They feature a good picture from all angles, and the best black level. Despite their bulky and heavy build, tube TVs are long-lasting and acclaimed for retaining a good picture throughout its lifespan, which can last for decades.
Figure 2.6: Inside view of the cathode ray tube of a TV
Source: http://www.doom9.org/images/crt-color.gif
A Flat Screen TV is a term used to describe any tube TV where the screen is a level plane. These TVs have a wider viewing angle than ones with ormal curved screens. That means you can still see the whole picture even when you sit farther away from the TV screen. But, even though the flat screen improves the quality of the TV, the total size of the TV is still the same as a normal TV has always been, which is to say rather big.
(ii) Flat Panel TV
Flat panel displays are the opposite of tube TVs, namely because they are light enough to be hung on a wall or ceiling. At about 3 to 4 inches thick, they are the ultimate space-saver for a room of any size. The flat panel you have probably seen many times in commercials is the plasma, and the LCD or Liquid Crystal Display is another.
(iii) Projection TV
Projection TV is also known as big screens, and comes in two different styles:
front and rear. Front and rear projections display pictures by forming a small image and reflecting it onto a larger screen. The difference is where the receiver is located. Rear projection TVs house the receiver inside the viewing unit, while front projection models feature a receiver apart from the viewing source (i.e. across the room). The strength of projection lies in its ability to showcase large images.
For example, rear projection screen sizes are measured upwards of 70 inches. Rear projection TVs comes in four styles:
x CRT (Cathode Ray Tube),
x DLP (Digital Light Processing),
x LCD (Liquid Crystal Display), and
x LCOS (Liquid Crystal on Silicon).
Front projection TVs come in CRT, DLP, and LCD. A front projection TV is essentially the same thing as a traditional projection TV, but it comes in two parts. The projector mounts somewhere on the ceiling or on a table, and the screen is placed on the wall. The benefit of having a TV in two pieces is that it takes up less space, and you get to decide how big you want your screen to be.
(iv) TV-DVD-VCR Combos
These TVs incorporate either a DVD player, VCR, or both. Most TV-DVD-VCR combos are tube TVs, but some of the smaller units come in flat panel LCDs and fit under a counter.
(v) Handheld/Mobile TV
Just imagine how interesting it would be if you could watch TV programmes everywhere you go. No longer that you had to be at home or at certain places just to watch your favourite programme, with the latest development in TV technology, anything is possible.
Refer to Figure 2.7 to see some of the examples of TV systems available in the market.
Figure 2.7: Examples of TV systems available in the market
Source:http://www.tweeter.com Plug In TV
(Car) Wrist Watch TV
Portable 5-inch TFT screen TV
Combo TV Rear Projection TV LCD
Front Projection TV Tube TV (Flat Screen)
Flat Panel TV (Plasma/LCD) Tube TV
(Curve Screen)
Nokia 7700s
Handheld/ Mobile TV MSN WEB TV (Set Top Box)
Newspaper, radio and TV are effective mass media which make information transfer possible throughout the nation. With the advancement in computer technology and the birth of Internet, information is at our fingertips and has no boundry. What are the effects of this to people’s knowledge, culture and mindset?
2.3
NEW MEDIA TECHNOLOGY
With the invention of the computer, the rapid evolution of computer technology and the birth of Internet, digital interactive media has evolved to the point of what we currently experiencing today. According to Miller (2004), there are quite a number of new digital media available nowadays, such as:
x Video Games/Multiplayer Online Games
x The Internet/World Wide Web (WWW)
x Interactive television
x Web TV
x Mobile TV
x Streaming media/Video on Demand (VoD)
x Wireless devices
x Kiosk
x Virtual Reality/Immersive Environments
x DVDs
2.3.1 Video Games/Multiplayer Online Games
Have you ever played a video games before? Where did you go to play video games, at games arcade, on the TV set or on your personal computer? Which one do you prefer? State your reason(s).
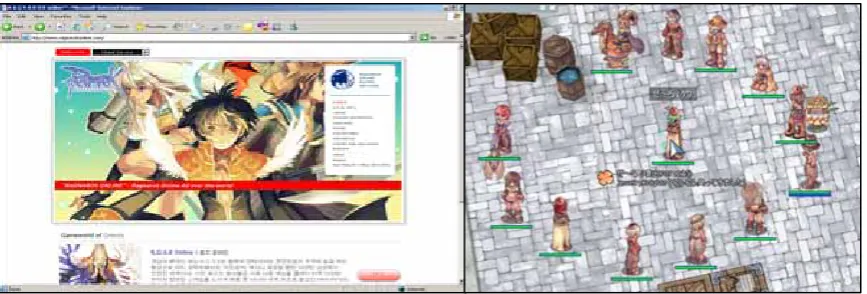
opposed to sitting at a desk playing on a computer. Figure 2.8 illustrates a website that offers online multiplayer games (Ragnarok Online), which is quite popular in Asia.
Figure 2.8:Ragnarok Online : an online multiplayer games
Source:http://www.ragnarokonline.com/
Numerous types of games have been created since the first game was introduced back in the 1970s. What kinds of games might we be playing a few decades from now? And what role will games play in the overall universe of interactive entertainment, and entertainment in general? There are unlimited possibilities that can be achieved with video games and multiplayer online games. And the best thing is that this media technology can attract the younger generation to use it.
2.3.2 The Internet (WWW)
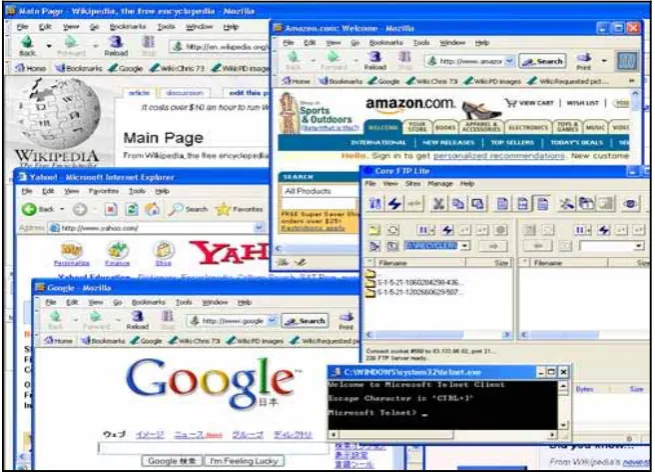
The Internet is the publicly available worldwide system of interconnected computer networks that transmit data by packet switching using a standardised Internet Protocol (IP) and many other protocols. It is made up of thousands of smaller commercial, academic, and government computer networks. It carries various information and services, such as electronic mail, online chat and the interlinked web pages and other documents of the World Wide Web (WWW). See Figure 2.9 for a screenshot of some of the different applications available on the Internet. Hypertexts and hypermedia documents can be distributed and accessed by millions of consumers, thus making the Internet the most promising medium of content and information communications.
Figure 2.9: Different Internet applications, such as Web browsers, FTP and Telnet
Source: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/a/ad/Internet.png
2.3.3 Interactive TV (iTV)
State at least 5 advantages you would love to enjoy by having Interactive TV services at home.
TV had remained as a one-way medium all this while, until the year 2002 came. Inexpensive technologies are making it possible for cable and satellite TV providers to offer interactive services to subscribers. Two areas that are emerging with potentially great implications for interactive TV services are Personal Video Recorders (PVRs) and
Video-on-Demand (VoDs). Just as streaming media has spread throughout the web in the 1990s, interactive TV services are currently being rolled out.
What if you could view tonight's local news headlines while watching your favourite network shows? See plot summaries for upcoming shows? Look up for individual player
iTV combines digital TV and Internet technology to deliver a mix of programming, restricted or open Web access, email, online shopping and customer service to viewers watching at home. Current generation of iTV systems offer basic Internet browsing functionality. The next generation of technologies promise to give far greater flexibility both to viewers and to content providers.
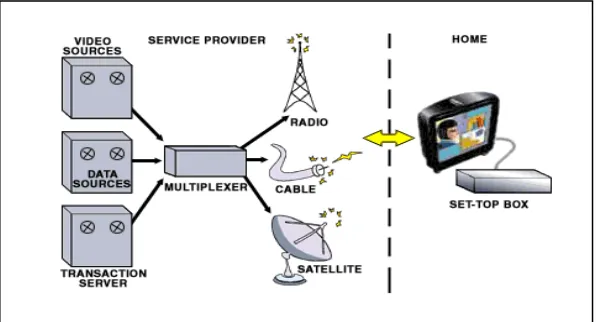
Much of the world's communications infrastructure is now digital all the way to the home, making it possible for a single communications service provider to offer the entire range of entertainment, information, commercial and personal communications services to subscribers in a single package (refer to Figure 2.10 for a digital iTV usage scenario for home viewers).
Figure 2.10: Digital iTV usage scenario
Source: http://java.sun.com/products/consumer-embedded/digitaltv/usage.html
An important possibility with iTV is to emphasise the direct interaction of the viewer. For example, take a political show where they are discussing an upcoming election. They could run a viewer poll in real-time. The TV viewer can select their favourite candidate, and the results of all the viewers are shown in real time as they participate. Imagine if we can do that in Malaysia.
Figure 2.11: What can be achieved with iTV technologies
Source:http://www.broadbandbananas.com/vvenhanced.html
2.3.4 WebTV
What is a WebTV? It is an approach to interactive TV. Originally it is a Microsoft product that uses Web-based content to create the interactive TV experience. The original WebTV box was not made for interactive TV. It was strictly a way to browse the Web with your TV instead of buying a complicated computer. When in Web mode, the viewer could no longer see any TV shows at all. This product is now referred to as WebTV Classic. It does not do interactive TV. The WebTV Plus product adds the ability to watch TV while seeing the Web content. With this, they also added some features that make an actual interactive TV experience possible.
Wikipedia.org defined webTV as:
While webTV does not allow as much functionality as a computer-based browser (eg. they cannot run JavaScript or multi-task, and they do not have nearly as much versatility, power or memory as an actual computer), it is nonetheless a popular and low-cost alternative in some countries. A recent alternative to webTV are game consoles with a built-in Internet
x Programming credits could be available anytime during the show instead of only at the beginning and/or end.
x Answer trivia questions in real time during a TV show
x Customized and localized information (such as news, weather and sports).
x While viewing one program, you can keep abreast of specifics of other TV program(s), including sports.
x Interactive Program/Entertainment Guides.
x Answering Polls/Surveys during or after a program without having to pay for a toll call or log onto a special computer.
x Interactive Game Shows – Compete with other viewer.
x Interactive Sports (to watch an event from your choice of camera angles.)
x Interactive advertising.
x Videoconferencing.
x Distance learning.
x Interactive video magazines & music selection
x Instant Messaging and Email
WebTV technology was invented in 1996 by Diba Inc. and Zenith Electronics, who produced and marketed the first WebTV sets. Figure 2.12 and Figure 2.13 illustrate a general concept of WebTV and some screen shot of a WebTV programmes.
Figure 2.12: A general WebTV diagram
Source: http://itv.wpt.org/about/
Figure 2.13: A screenshot of a WebTV and a WebTV sport programme
2.3.5 Mobile TV
DVB-H (Digital Video Broadcast - Handheld) is a new technology that enables the simultaneous transmission of multiple TV, radio and video channels to mobile handheld devices. It combines traditional broadcasting standards with specific features for handheld devices. In order to receive DVB-H transmissions, handsets require an additional integrated receiver.
Mobile TV presents a number of unique challenges, such as battery-powered receivers and a variety of situations of use (e.g. indoor, outdoor, pedestrian, inside moving vehicle). DVB-H provides the most efficient way of carrying multimedia services over digital terrestrial broadcasting networks to handheld terminals.
To overcome these challenges, DVB-H uses a variety of techniques including time-slicing to reduce a device's average power consumption, cell identifiers to support quicker signal scan and frequency handover as well as methods to improve signal strength in the mobile environment. The technical specification work has been done in the Digital Video Broadcasting Project (DVB), which is an industry-led consortium committed to designing global standards for the global delivery of digital TV and data services. Figure 2.14 and Figure 2.15 refer to the mobile TV service platform available in Finland.
Figure 2.14: An advertisement promoting mobile TV services in Europe
Figure 2.15: Finnish Mobile TV platform in a nutshell
Source:http://www.finnishmobiletv.com
Mobile TV can be accessed through handphones that utilise 3G (3rd Generation) mobile telephone technology. The services associated with 3G provide the ability to transfer both voice data (a telephone call) and non-voice data (such as downloading information, exchanging email, and instant messaging). Figure 2.16 refers to SingTel websites on 3G technology and services being offered in Singapore.
2.3.6 Streaming Video/Video on Demand (VoD)
Streaming video is a video that is consumed (read, heard, viewed) while it is being delivered. Streaming is more of a property of the delivery system than the media itself. The distinction is usually applied to media that is distributed over computer networks; most other delivery systems are either inherently streaming (radio, television) or inherently non-streaming (books, video cassettes, audio CDs).
A media stream can be on demand or live. On demand streams are stored on a server for a long period of time, and are available to be transmitted at a user's request. Live streams are only available at one particular time, as in a video stream of a live sporting event.
Video-on-Demand systems are interactive media systems that allow users to select and watch video content over a network as part of an interactive television system. VoD systems are either "streaming", in which viewing can start as the video streams over the Internet (or other network), or "download", in which the program is downloaded first into the user’s set-top box’s space before the viewing starts.
All download and some streaming VoDs allow the user to pause, fast forward, fast rewind, slow forward, slow rewind, jump to previous/future frame etc. It works just like a personal video cassette recorder/player. For streaming systems this requires more effort on the part of the server, and may also require greater network bandwidth. VoD software like
Clipstream, enables the delivery of streaming video on demand through any web medium including web pages, email and online advertising. Figure 2.17 illustrates the Clipstream website that provides examples of streaming videos.
Figure 2.17: An example of a streaming video on Clipstream’s website Streaming
2.3.7 Wireless Devices
In modern usage, the term wireless refers to:
Most common uses include the various communications defined by the IrDA (Infrared Data Association) and the wireless networking of computers. Some examples of popular wireless devices are handphones and PDA (Personal Digital Assistant).
When we talk about wireless devices, you might ponder upon yourself, asking questions such as:
x “What about wireless devices that make them an attractive medium for entertainment?”;
x “How can something as portable and small as a cell phone or a PDAs deliver a full entertainment experience?”; and
x “What are some of the innovative ways that wireless devices are being used to create new kinds of entertainments?”.
All these questions has yet to be answered as the wireless devices and technologies are still in its infant stages and rapid research and development are underway. New technology such as WiFi and Bluetooth has also reach a greater marketforce. Figure 2.18 shows some examples of wireless devices and the application area.
Figure 2.18: Wireless devices that supports WAN, LAN and PAN
Source:http://www.palmsource.com/developers/wireless/wirelessOverview.html
owners are making it clear that they care about wireless connectivity. Users want access to the web, email, and messaging, as well as applications and content which keep them connected to the world in real-time, where ever they are. As such, the market for wireless devices is still fresh and new way of representing content and information are still open for development.
2.3.8 Kiosk
Information technology through interactive media has a potential to improve information and services for the general public. These can be done through information kiosks which are often interactive. Kiosks are hardy computers in strong housing that are placed in public places. The public can use them to find out information and conduct transactions. Usually, the user will touch the screen in appropriate places to access the information. Kiosk can be found at shopping malls, parking decks, hotels, airports, business premiseses and transit terminals. See Figure 2.19 for an example of a kiosk located at a train station in France and Figure 2.20 for example of different design of kiosks.
There are three fundamental components of a kiosk solution:
x Physical enclosure which houses the hardware,
x Physical hardware (touch-screen monitor, CPU, stereo speakers, printer, cables, etc); and
x A software application that stores information, processes transactions, and delivers the messages, services, and/or products.
Figure 2.19: MASK Kiosk presently used for field trials at the St-Lazare station in Paris
Source:http://www.limsi.fr/tlp/kiosk-sncf.html
Figure 2.20: Different types of Interactive Kiosk
Source:http://gco-interactive-kiosks.com/interactive_kiosk-pgs/interactive_kiosk_pho.html
For more information on interactive kiosk programme development, visit: http://gco-interactive-kiosks.com/interactive_kiosk-pgs/interactive_kiosk_pgm.html
2.3.9 Virtual Reality
Virtual reality can be generally defined as:
Being a medium for education, it allows an individual to project him or herself into a computer generated world and move freely within it. The term is used here to include a variety of the newer multimedia data-types that give the viewer more information and more control over how the information is viewed than traditional graphic, photographic or video elements.
Virtual reality is not a new technology as its development dates back almost 50 years ago. The flight simulators used by the aircraft inductry and U.S. Air Force to train warship pilot during World War II is the first application of virtual reality. Virtual reality can be used for unlimited possibilities, from medical imaging and interior design to intercontinental videoconferencing and exploration of future worlds. Figure 2.21, 2.22 and 2.23 illustrate the various application that can be developed using virtual reality technology. Detail discussions will be provided in later topics.
Figure 2.21: Virtual reality applications
Source:http://ligwww.epfl.ch/multimedia/multimedia_index.html
Figure 2.22: Indiana University’s Cave Automatic Virtual Environment (CAVE)
Source: http://www.indiana.edu/~rcapub/v21n2/p28.html
Figure 2.23: Virtual Environments and Computer Graphics: Exploring a Virtual Kitchen and a SMART Car Driving Simulator
Source:http://www.cs.ucl.ac.uk/research/vive/
There are quite a number of new digital media available nowadays, such as the Internet, interactive television, webTV, mobile TV and Video Games to name a few. What do you think would happen to our quality of life without the existance of this technology, describe briefly.
2.3.10 DVD
DVD are commonly thought of as a convenient medium for watching high quality movies at home. Although it is very popular among consumers, there is very limited original
x The IU CAVE measures eight feet in width, depth, and height and can accommodate several collaborators at the same time.
x High-resolution stereo images are projected onto the three walls and the floor and are synchronized with shutter glasses to provide the illusion of depth.
A single DVD disc can hold a large amount of high-quality multimedia data (from 4.7 GB) and very easy to use with any DVD players, thus helped promotes its popularity for watching feature films and compilations of favourite TV series.
DVDs can be used by content developers as the medium to deliver interactive media for the following reasons (Miller, 2004):
x multiple audio and subtitle tracks that opens up a variety of content possibilities.
x various degrees of interactivity can be built into them, from basic menu choices to the more diverse experiences of video games.
x relatively simple to produce content for them, especially if using digital video.
x It does not have narrow restrictions in terms of audio and video.
x compared to the Web, they can easily support video.
Though the DVD has only been available to us since 1997, it has caught on with consumers at lightning speed. We can use DVDs to create feature films and television programs that allow consumers to choose their own path through narrative material, as in digital storytelling. This can include audio commentary that is timed to the film sequence, documentary features, unused footage, trivia text commentary, simple games and film shorts, which all of these can be part of an interactive multimedia system.
x Video
x The Internet/Games/Multiplayer Online Games
x Wide Web (WWW)
x Interactive television
x Web TV
x Mobile TV
x Streaming media/Video on Demand (VoD)
x Wireless devices
x Kiosk
x Virtual Reality/Immersive Environments
x DVD
Exercise 2.1
1. What are the advantage of knowing the suitable media technology to be used to deliver specialised contents?
2. Identify the benefits that can be derived from the use of interactive television.
SUMMARY
We live in a dynamic, changing environment, full of sounds and moving objects that we usually attend to. Newspaper, radio and television are among the many media that are visual and audible types of media technology. Still and moving pictures, audio, sound effects, spoken or written words, all are combined in a digital environment together with interactivity features, to create a new interactive media.
Interactive media technology provides us with the freedom to choose the best medium to represent a complex concept and communicate directly with users, to meet their needs. Not only that, we could reach nonverbal learners especially the young and uses a more natural language to approach them.
GLOSSARY
Bluetooth Bluetooth provides a way to connect and exchange information
between devices like personal digital assistants (PDAs), mobile phones, laptops, PCs, printers and digital cameras via a secure, low-cost, globally available short range radio frequency.
Hypermedia A term used as a logical extension of the term hypertext, in which audio, video, plain text, and nonlinear hyperlinks intertwine to create a generally non linear medium of information.
WebTV A general term for a whole category of products and technologies that enable you to surf the Web on your TV.
Wi-Fi "Wireless Fidelity", is a set of standards for wireless local area networks (WLAN) currently based on the IEEE 802.11 specifications. To be used for wireless devices and LANs, but is now often used for Internet access.
TEST 1
Instructions: Answer all questions within 15 minutes.
1. What do you understand by the term “media technology”?
(3 marks)
2. List THREE (3) types of TV system available nowadays.
(3 marks)
3. What is the difference between WebTV and Interactive TV?
(4 marks)
4. What are the basic elements of a kiosk? Discuss.
(6 marks)
5. Identify TWO (2) advantages of virtual reality.
(4 marks)
TEST 2
Instructions: Answer all questions within 30 minutes.
1. Elaborate the meaning of multimedia technology as defined by Steve Heath (1999). (4 marks)
2. Explain briefly how a web radio works.
(4 marks)
3. List THREE (3) advtanges of e-newspaper services.
(3 marks)
4. Discuss briefly the following TV systems:
(i) Projection TV
(ii) Mobile TV
(iii) WebTV
(9 marks)
5. How do you think we could use virtual reality to help us in our daily work in the future?