A. Definition of Grammar
A grammar is a description of certain organized aspect of a particular language. It usually includes phonological (sound), morphological (word composition), and syntactic (sentence composition) points Hall (1993:3). As a complex system by which people speak and write it is not taught separately from the four language skills, listening, speaking, reading, and writing.
Grammar is very ambiguous since it has several meaning. There is no fixed definition of grammar because many experts often define the term grammar differently. Grammar may mean an analytical and terminological study of sentence.
Billow (1961:156), has two definitions of grammar. First, grammar is a description in word of verbal behavior; just a drill book is a description in word of parade behavior. Second, grammar is recognition of the pattern and unity underlying verbal experience.
B. Definition of Relative Clause
A relative clause is sub clause that is preceded by words like who, whom, whose, that, which or adverb’s connector like where, when, and why (Salim.1996: 1617). It describes, identifies, or gives information about noun.
In “Guide to pattern and usage in English” :(Hornby, 1975: 154-163) categories relative clause as follows: defining relative clause and noun defining relative clause.
1. Defining Relative Clause
A defining relative clause describes the preceding noun in such a way as to distinguish it from other noun of the same class. A clause of this kind is essential to the clear understanding of nouns.
- For persons we can use who and that as subject, whom/ who and that as an object and whose as possessive.
- For things we can use which and that as subject, which and that as an object and whose of which as possessive.
a. Who
1) Who as Subject
Who is used with an antecedent that stands for a person if the
Example:
- The boy who broke the window is called Jim
- Will all those who are in four of resolution please hold up their hands?
Example:
- People who are in glass houses should not throw stones
(Hornby, 1975: 156).
2) Whom as Direct Object
Whomas the object of a relative clause (in more formal
English), thought it is increasingly common to replace it with who. Example:
- The lawyer (whom) I consulted gave me some useful advice. In colloquial styles, who or that may replace whom, though omission is more usual.
Example:
- The lawyer (who, that) I consulted gave me some useful advice (Hornby, 1975: 158).
3) Whom as Prepositional Object
Whom, is usually omitted in a defining clause and the
Example:
- That man you lent your dictionary seldom return the books he borrows
That man to whom you lent your dictionary is formal (Hornby, 1975: 158).
4) Whose as Possessive Form of Who
Whose, is used to show possession. Whose connects to a noun be omitted.Whose usually modifies people, but it may also be used to modify things.
Example:
- He is a novelist whose reputation has grown fast (Hornby, 1975:158-159).
b. Which
1) Which as subject
Which as subject in defining clause, is replaced by that and that
is more usual. Example:
The cinema which/ that used to stand corner was destroyed by bombing in 1940(Hornby, 1975: 159).
2) Which as Direct object
Which is replaceable by that is usually preferred. However,
Example:
- The books (which/ that) I lent you belong to my brothers (Hornby, 1975: 159-160).
3) Which as Prepositional Object
This may be omitted, with the prepositional at the end of the clause. Example:
- Are the pan in which you make your omelets / the pan you make your omelets in? (More usual: is this your omelet’s pan?) (Hornby, 1975: 161).
c. That
That is used for person or things as subject or objects and can
be used to replace other relative clause.
That as Subject
Example:
- The crowds that/ which/ surrounded the film star were be having very childishly
- The boy that/ who broke the windows is called Tom
That as Object
Example:
This is one the few really good books (that) this prolific author has written (Hornby, 1975: 161).
2. Non - Defining Clause
Non defining clause is placed after noun which is definite already, they are compared with defining relative clause, non-defining relative clause have some characteristics namely: non defining relative clause are not essential in the sentences and can be omitted without causing confusion, they are separated from their noun by commas. The pronoun can never be omitted in a non-defining relative clause and more over. The construction is fairly formal and more common in written than is spoken English.
a. Who
1) Who as Subject
The relative who, is not replace“define clause”.
Example:
- Mr. Green, who gives me a piano lesson, has been ill recently (Hornby, 1975: 157).
2) Whom as Direct object
Example:
- Anne whom Dick hopes to Marry is very attractive girl (Hornby, 1975: 158).
3) Whom as Prepositional Object
In Non-defining clause whomis not omitted and the preposition precedes it.
Example:
- The man of the village, some, any, a few, of whom are refried business man (Hornby, 1975: 158).
4) Whose, as possessive form of who
Example:
- Nick whose wife teaches singing is himself a teacher of the piano
Mozart whose music you have been listening to is my compose (Hornby, 1975: 159).
b. Which
1) Which as Direct Object
This is replaceable by that in non-defining clause.
Example:
2) Which as With preposition Example:
- This problem to which reference has ready been made has not yet solved
- This long road which poplar tresses were planted many years ago goes to Arras (Hornby, 1975: 160).
3. The Usage of Relative Clause
a. Relative Clause ‘who’ and ‘whom’
1) The relative clause ‘who’ is used for persons Example:
- The man who was kidnapped a week ago has been relieved - The driver who was responsible for the accident has
disappeared from his home
- The woman who was reported missing the papers has come back
2) ‘Who’ is usually followed by verb Example:
- The lady who is the chief tailor on way at the moment.
- Have you written a letter of thanks to the man who found your dog for you
Example:
- This is the clerk whom they spoke rudely to yesterday - The girl with whom she went to the cinema is her cousin - The person whom we met there works at the general hospital. 4) ‘Whom’ sometimes can be left out
Example:
a) The family with whom I’m living has gone to Boston for their holiday
- The family I’m living has gone to Boston for their holiday
b) The man whom you want has just left
- The man you want has just left
5) In modern usage ‘who’ can sometimes replace ‘whom’ Example:
a) To whom you give a lift this morning
- Who did you give a lift this morning b) With whom is she going?
- With is she going with? b. Relative clause ‘that’
1) A the subject of a clause
Example:
2) As the subject of clause and relative that can be omitted
Example:
a) The fish that you brought yesterday was not fresh
- The fish you brought yesterday was not fresh b) The cake that she made just now smells good
- The cake she made just now smells good 3) After definite clause
Example;
- There was not much that we could for him - It was not about anything that would upset her
- She is wearing the some dress that she wore that last time I saw her
- They did all that could be done for him 4) After superlative
Example:
- This is first and the last time I going anything for you
- The say that this clock tower is one of the most beautiful that he has ever seen
- His essay was the best that I had ever read on the subject 5) After noun
Example:
6) When the antecedent is both a person a thing or an animals Example:
- She saw the artist and the paintings that had aroused her interest
- He gave shelter to the boy and his dog that have been rescued from the fire
7) When it replace Example:
- Those boys are the ones that I brought last year
- The types that give my work to everyday has resigned from her job
8) But when preposition precedes the relative clause ‘that’ cannot replace ‘whom’
Example:
- To whom did you give your money?
- With whom will you go the show tomorrow? c. Relative Clause “ which”
1) Usually to refer to things / animals whether the subject or the subject of the sentences.
Example:
2) To refer to collective noun denoting person, but used singularly Example:
- This is group which is going to sing ‘blowing with the wind’ at the singing contest
- The American team which has won the match in planning to go on a tour of Europe
3) Sometimes to refer whole sentences
- She finished the work in less than an hour
- The old man denoted a large sum of money to the old folks home which was very generous of her
4) When it precedes a noun, a pronoun verb
Example:
- We are discussing the plan which he suggested
- The lorry which carries this to the will be back next day - He was reading the letter which the postman had just brought 5) After Preposition
Example:
- This is the machine that broke down yesterday
- The bus that takes us to school comes at seven o’clock d. Relative Pronoun ‘Whose’ and ‘Which’
Whose is used for person and sometimes thought rarely for things
1) To show possession or ownership Example:
- This is lady whose car was damaged in the accident
- The man whose shop was raided by the police last week has to Hong Kong
2) To show a personal characteristic Example:
- Yesterday a met boy whose brother was chosen to be a state player
- This the girl whose won in Dag Hammer scholarship 3) To show a personal characteristic
Example:
- She seems to be a person who obedience to her parents is more important than anything else
- He is a man shoes is good as his bond 4) We used ‘of which’ in the following ways
- She away the mirror, the side of which was chipped
- Mr. Hans brought a big basket a plums of which half were given to our neighbor
C. The Function of Relative Clause
The function of relative clause is to give information or give characteristic to noun or noun phrase, and it is placed before or after noun. Some relative clause (defining relative clause) is used specify which person or things we mean, or which type of person or thing we mean. - The couples who live next to us have ten children
- Alvega stopped the police car that was driving past.
When we use a defining relative clause, the relative pronoun can be the subject or the object of the clause. In the following sentence the relative pronoun is the subject.
- We have friend who plays the piano. - That’s the man who I met at Rizal’s party.
We can’t add a subject to the relative clause in addition to the relative pronoun.
- The man who gave me the book was the librarian.
(Not the man who gave me……)
Notice also that adding a pronoun to the main clause in addition to the relative clause is unnecessary, although it is found in speech. A friend of mine who is a solicitor helped me.
D. Form and Meaning
Relative Clause has two following patterns: 1. Relative Clause pattern without subject.
This is a relative clause pattern there relative pronoun is followed by verb directly. The form of the verb can be simple present, present continuous, simple past, passive verb, etc.
Form of Verb Noun
Simple past (V2) the man Who discovered the gold mine Present
continuous (be + Ving)
the students Who are reading in the library
Present perfect (has/have+ V3)
The Usage relative clause
a. Who : to refer to person Pattern : person who verb b. Whom : to refer to person
Pattern : person whom person c. That for both people and things.
d. Whose : to replace a possessive adjective Pattern : noun whose noun
e. Which : to refer to thing Pattern : thing which verb 2. Relative Clause Pattern with subject.
Relative Clause with subject is relative clause pattern there is a subject after relative pronoun.
Noun Relative Prounoun Subject Verb
The book that I am reading
The magazine
that my father Brought
The boy whom you Saw
The system which we should use
3. Relative Clause with whose
Whose used in relative clause is to state that which behind whose is
translate with “yang…..nya”. With this whose can be possessed subject or not possessed subject.
a. Without subject
Noun Whose Noun Verb
The people Whose house was damage by the flood The woman Whose Bag was seized by the police
A mother Whose child died in the accident
b. With subject
Noun Whose Noun Subject Verb
The man Whose House You saw last night
The secretary Whose Office We will visit The farmers Whose Land The government took to build
airport
E. Relative Clause Position in Sentence
Relative clause always attributed to the noun because the function is giving adds information for noun. But relative clause itself not completed the word. It is only noun phrase. Noun phrase itself can be got position as subject, object, complement and etc.
(Subject)
2. I want to know the man who has this brilliant idea. ( object) 3. This is the house I want to buy. (complement)
4. The man whose husband died in the car crash could not claim the insurance company. (subject)
F. Learning Error analysis
1. The Definition of Error
The relation between language teaching and error cannot be separated. If the learner study about something, it is possible to make an error. Error is defined by Subyakto-Nababan (1993: 132), as deviations of grammatical which reflect the level of ability. In another description, an ‘error' is a systematic deviation from the accepted ‘code” (Norrish, 1995: 127). Code in this respect includes grammar, meaning, and sound.
Based on explanations above, it is concluded that error is the deviations of grammatical, meaning and sound which reflects the level of ability.
2. Type of Error
There are two kinds of casual factor of error:
a. Inte rlingual Error
b. Intralingual Errors
Intralingua errors are the direct result of the learners attempt to create language based on is his hypothesis about the language system he is learning. In his house of errors, there is nothing to do with
interference of mother tongue. It is caused by the target language itself so it is said as developments errors (Richard, 1985).
According to (Richard, 1985), ignorance of the systematic intralingua errors involves overgeneralization, ignorance of the rules and false concept hypnotized or semantic errors.
a. Overgeneralization is a device used when the items do not carry any obvious contrast for the learner.
Example:
I see girl who Abu gives a bag instead of I see girl whom Abu gives
a bag.
Bejo who I saw yesterday will go to Bandung instead of Rizal who
I saw yesterday go to Bandung.
b. Ignorance of rules restrictions is error that occurs when rules are extended to contexts where in target language usage does not apply.
Example:
That is the man whose his wife was on TV today instead of that is the man whose wife was on TV today.
c. Incomplete applications of rules, the students do not apply the complete norm of the target language.
Example:
There is man wait for you instead of there is a man who waits for
you.
d. False concept hypothesized, the students have the wrong concepts of language system.
Example:
The form whoin English is interpreted has a meaning “siapa” and the form thatwill be understood has a meaning “itu”
3. The Differences between Error and Mistake
In our life, many people give opinion that error and mistake as synonym which have the same meaning. Sometime we are confused to compare between error and mistake. Related to Tarigan (1995: 74-75) error and mistake are defined as follow:
a. Error is caused by the competence factor.
b. Mistake is caused by performance factor.
Restrictiveness in remembering something (forgetfulness) causes mistake in pronouncing a certain sound, word, spelling, or stress of word or sentence, etc. those are unsystematically and a little while. In this case, the learner knows about the linguistic system basically and can be corrected so on.
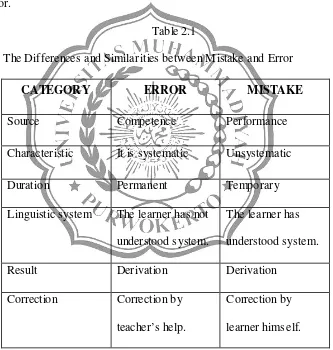
The table below shows the differences and similarities between mistake and error.
Table 2.1
The Differences and Similarities between Mistake and Error
CATEGOR Y ERROR MISTAKE
Source Competence Performance
Characteristic It is systematic Unsystematic
Duration Permanent Temporary
Linguistic system The learner has not understood system.
The learner has understood system.
Result Derivation Derivation
Correction Correction by teacher’s help.
Correction by learner himself.
and “attempts” (that is when a student tries to say something but does not yet know the correct way of saying it).
4. Procedure of Error Analysis
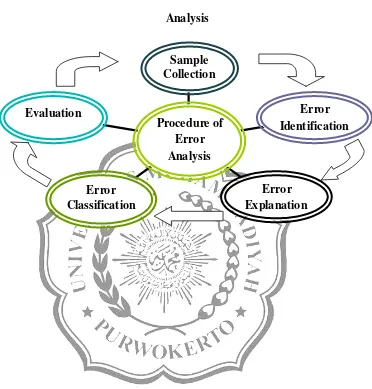
According to Tarigan (1995: 67-68), there are five steps or procedures which cover error analysis. First is sample collection. The researcher collect sample. Second is error identification. Having collected the sample, the researcher identifies the errors in sample collection. Third is error explanation. The researcher explains the errors which are made by students. The fourth is error classification. The researcher classifies the errors based on causes. And the last is evaluation. The researcher evaluates the level of error.
Figure 2.1
Procedure of Error
Analysis
Evaluation
Error Classification
Error Explanation
Error Identification Sample
Collection