Informasi Dokumen
- Penulis:
- Bikramaditya Singhal
- Gautam Dhameja
- Priyansu Sekhar Panda
- Sekolah: Apress Media LLC
- Mata Pelajaran: Blockchain Solutions
- Topik: Beginning Blockchain A Beginner's Guide to Building Blockchain Solutions
- Tipe: guide
- Tahun: 2018
- Kota: New York
Ringkasan Dokumen
I. Introduction to Blockchain
This section provides a foundational understanding of blockchain technology, tracing its historical roots and defining its core principles. The discussion begins with the backstory of blockchain, highlighting its evolution from earlier digital disruptions like TCP/IP to its current role as a transformative technology. It emphasizes the importance of understanding blockchain from both business and technical perspectives, setting the stage for deeper exploration in subsequent chapters. The significance of blockchain in enabling peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries is underscored, demonstrating its potential to reduce costs and enhance transaction efficiency.
1.1 Backstory of Blockchain
The backstory traces the origins of blockchain technology, linking it to earlier innovations that shaped the digital landscape. It discusses the transition from circuit-switched communication to the more open and decentralized TCP/IP protocol, illustrating how these developments laid the groundwork for blockchain. The narrative emphasizes the need for a trustless system in financial transactions, which blockchain aims to provide, thereby addressing the inefficiencies of traditional banking systems.
1.2 What is Blockchain?
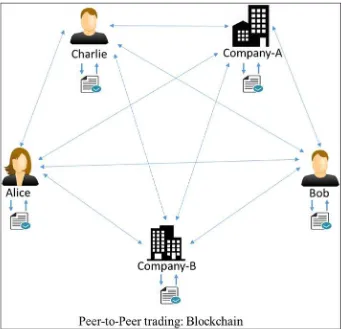
This subsection defines blockchain as a decentralized and immutable ledger that facilitates peer-to-peer transactions without the need for trusted intermediaries. It introduces the concept of a shared database replicated across multiple nodes, ensuring transparency and security. The characteristics of blockchain, such as its append-only nature and the permanence of entries, are highlighted, establishing a clear distinction between traditional and blockchain-based transaction systems.
1.3 Centralized vs. Decentralized Systems
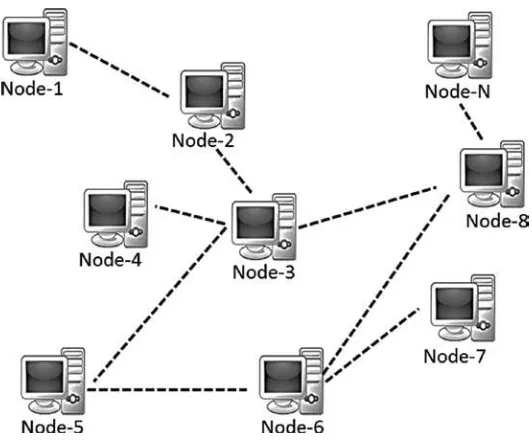
This section contrasts centralized and decentralized systems, outlining the inherent limitations of centralized models, such as single points of failure and increased vulnerability to attacks. It emphasizes that blockchain is designed to be decentralized, allowing equal authority among nodes and enhancing security. The discussion includes technical, political, and logical perspectives on centralization and decentralization, providing a comprehensive understanding of these concepts in the context of blockchain.
1.4 Layers of Blockchain
The layers of blockchain are introduced as a framework for understanding its architecture. This section outlines the various layers, including the application layer, execution layer, semantic layer, propagation layer, and consensus layer. Each layer's role in the overall functionality of blockchain is briefly described, setting the stage for more detailed exploration in later chapters. The importance of a layered approach in building and understanding blockchain applications is emphasized.
II. How Blockchain Works
This section delves into the technical workings of blockchain, focusing on the foundational concepts that underpin its operation. It covers essential topics such as cryptography, consensus mechanisms, and the structure of blockchain transactions. The importance of these elements in ensuring the security and integrity of blockchain networks is highlighted. By explaining how various components interact within the blockchain ecosystem, this section prepares readers for practical applications and development in later chapters.
2.1 Laying the Blockchain Foundation
This subsection lays the groundwork for understanding blockchain technology by introducing key concepts such as decentralization, immutability, and transparency. It explains how these principles contribute to the security and reliability of blockchain systems, setting a strong foundation for the subsequent exploration of cryptographic techniques and consensus algorithms.
2.2 Cryptography
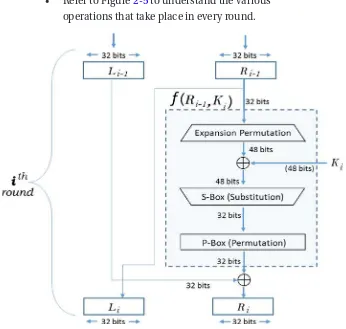
The role of cryptography in blockchain is discussed, emphasizing its importance in securing transactions and maintaining data integrity. This section covers various cryptographic methods, including symmetric and asymmetric encryption, hash functions, and digital signatures. By understanding these techniques, readers can appreciate how blockchain achieves trust and security without centralized authorities.
2.3 Consensus Mechanisms
This subsection introduces consensus mechanisms as critical components of blockchain technology. It explains how nodes in a blockchain network reach agreement on the state of the ledger, ensuring that all transactions are validated and recorded accurately. Different consensus protocols, such as Proof of Work and Proof of Stake, are briefly discussed, highlighting their respective advantages and challenges.
2.4 Blockchain Transactions
The structure and process of blockchain transactions are examined in this section. It explains how transactions are created, validated, and added to the blockchain, emphasizing the immutability and transparency of recorded transactions. The importance of transaction validation and the role of miners in maintaining the integrity of the blockchain are also discussed.
III. How Bitcoin Works
This section focuses on Bitcoin as the first and most well-known application of blockchain technology. It explores the historical context of Bitcoin's creation, its underlying mechanisms, and its significance in the broader blockchain landscape. By examining Bitcoin's architecture, transaction processes, and network dynamics, readers gain a deeper understanding of how blockchain can be applied to real-world scenarios.
3.1 The History of Money
This subsection provides a historical overview of money, tracing its evolution from barter systems to the emergence of digital currencies. It highlights the limitations of traditional financial systems and sets the stage for the introduction of Bitcoin as a revolutionary alternative.
3.2 Dawn of Bitcoin
The inception of Bitcoin is explored in this section, detailing the motivations behind its creation and the vision of its pseudonymous creator, Satoshi Nakamoto. The significance of Bitcoin in the context of blockchain technology and its potential to disrupt traditional financial systems are emphasized.
3.3 What Is Bitcoin?
This subsection defines Bitcoin and explains its fundamental characteristics, such as decentralization, limited supply, and peer-to-peer transactions. The unique aspects of Bitcoin that differentiate it from traditional currencies are discussed, providing readers with a clear understanding of its value proposition.
3.4 Working with Bitcoins
This section outlines the practical aspects of using Bitcoin, including how to acquire, store, and transact with the cryptocurrency. It discusses the various wallets available, transaction processes, and the importance of security in managing Bitcoin holdings.
IV. How Ethereum Works
This section shifts focus to Ethereum, a blockchain platform that extends beyond cryptocurrency to support decentralized applications (DApps) and smart contracts. It explores Ethereum's unique features, design philosophy, and the implications of its programmability. By understanding Ethereum's architecture and capabilities, readers can appreciate its role in the evolution of blockchain technology.
4.1 From Bitcoin to Ethereum
This subsection discusses the transition from Bitcoin to Ethereum, highlighting the limitations of Bitcoin as a platform for more complex applications. It introduces Ethereum as a next-generation blockchain that enables developers to create decentralized applications and smart contracts.
4.2 Ethereum as a Next-Gen Blockchain
This section elaborates on Ethereum's design philosophy, emphasizing its focus on programmability and flexibility. It discusses how Ethereum's architecture allows for the development of diverse applications, setting it apart from traditional blockchain implementations.
4.3 Ethereum Accounts
The concept of accounts in Ethereum is introduced, explaining the distinction between user accounts and contract accounts. This section discusses how accounts function within the Ethereum ecosystem and their role in facilitating transactions and smart contract interactions.
4.4 Ethereum Smart Contracts
This subsection delves into smart contracts, self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. It explains how smart contracts operate on the Ethereum blockchain, their potential applications, and the implications for various industries.
V. Blockchain Application Development
This section provides a practical guide to developing blockchain applications, focusing on the tools, libraries, and frameworks available for building decentralized applications. It emphasizes the importance of understanding blockchain architecture and principles in creating effective solutions. By offering hands-on examples and coding exercises, readers are equipped with the skills needed to engage in blockchain development.
5.1 Decentralized Applications
This subsection introduces decentralized applications (DApps) and their significance in the blockchain ecosystem. It discusses the characteristics of DApps, such as transparency, security, and user control, and highlights their potential to disrupt traditional application models.
5.2 Blockchain Application Development
This section outlines the development process for blockchain applications, covering key considerations such as architecture, design patterns, and user experience. It emphasizes the need for a thorough understanding of blockchain principles to create effective and user-friendly applications.
5.3 Libraries and Tools
The various libraries and tools available for blockchain development are discussed in this subsection. It provides an overview of popular frameworks and programming languages used in building blockchain applications, equipping readers with the knowledge to choose the right tools for their projects.
5.4 Interacting with the Bitcoin Blockchain
This section provides practical guidance on interacting with the Bitcoin blockchain, including setting up development environments and using libraries to create and manage Bitcoin transactions. Hands-on examples illustrate the steps involved in building applications that leverage Bitcoin's capabilities.
VI. Building an Ethereum DApp
The final section focuses on the end-to-end process of building a decentralized application (DApp) on the Ethereum blockchain. It covers the setup of a private Ethereum network, the creation and deployment of smart contracts, and the development of client applications. By following the practical examples provided, readers gain hands-on experience in DApp development, preparing them to tackle real-world blockchain challenges.
6.1 The DApp
This subsection introduces the concept of a decentralized application (DApp) and its unique characteristics compared to traditional applications. It discusses the benefits of DApps, such as increased security, transparency, and user control, setting the stage for practical development.
6.2 Setting Up a Private Ethereum Network
This section provides step-by-step instructions for setting up a private Ethereum network, including the installation of necessary tools and configuration of nodes. Readers learn how to create a controlled environment for testing and development.
6.3 Creating the Smart Contract
The process of creating a smart contract is detailed in this subsection, including best practices for coding and testing. It emphasizes the importance of thorough testing to ensure the reliability and security of smart contracts before deployment.
6.4 Client Application
This section discusses the development of the client application that interacts with the deployed smart contract. It covers user interface design, integration with the Ethereum network, and the overall user experience, providing a comprehensive approach to DApp development.
Referensi Dokumen
- Beginning Blockchain ( Bikramaditya Singhal, Gautam Dhameja, Priyansu Sekhar Panda )
- web3.js Documentation
- Solidity Documentation
- Ethereum Private Networking Tutorial
- Networking-Tutorial