Endocrine Glands
Endocrine Glands
and Their Hormones
and Their Hormones
•
Several endocrine glands in body; each may
produce more than one hormone
Hormonal Regulation
Hormonal Regulation
of Metabolism During Exercise
of Metabolism During Exercise
•
Major endocrine glands responsible for
metabolic regulation
– Anterior pituitary gland – Thyroid gland
– Adrenal gland – Pancreas
•
Hormones released by these glands affect
Endocrine Regulation of Metabolism:
Endocrine Regulation of Metabolism:
Anterior Pituitary Gland
Anterior Pituitary Gland
•
Pituitary gland attached to inferior
hypothalamus
•
Three lobes: anterior, intermediate, posterior
•
Secretes hormones in response to
hypothalamic hormone factors
– Releasing factors, inhibiting factors
– Exercise secretion of all anterior pituitary
Endocrine Regulation of Metabolism:
Endocrine Regulation of Metabolism:
Anterior Pituitary Gland
Anterior Pituitary Gland
•
Releases growth hormone (GH)
– Potent anabolic hormone – Builds tissues, organs
– Promotes muscle growth (hypertrophy) – Stimulates fat metabolism
Endocrine Regulation of Metabolism:
Endocrine Regulation of Metabolism:
Thyroid Gland
Thyroid Gland
•
Secretes triiodothyronine (T
3), thyroxine (T
4)
•
T
3and T
4lead to increases in
– Metabolic rate of all tissues – Protein synthesis
– Number and size of mitochondria – Glucose uptake by cells
Endocrine Regulation of Metabolism:
Endocrine Regulation of Metabolism:
Thyroid Gland
Thyroid Gland
•
Anterior pituitary releases thyrotropin
– Also called thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) – Travels to thyroid, stimulates T3 and T4
•
Exercise increases TSH release
Endocrine Regulation of Metabolism:
Endocrine Regulation of Metabolism:
Adrenal Medulla
Adrenal Medulla
•
Releases catecholamines (fight or flight)
– Epinephrine 80%, norepinephrine 20%
– Exercise sympathetic nervous system epinephrine and norepinephrine
•
Catecholamine release increases
– Heart rate, contractile force, blood pressure – Glycogenolysis, FFA
Endocrine Regulation of Metabolism:
Endocrine Regulation of Metabolism:
Adrenal Cortex
Adrenal Cortex
•
Releases corticosteroids
– Glucocorticoids
– Also, mineralocorticoids, gonadocorticoids
•
Major glucocorticoid: cortisol
– Gluconeogenesis
– FFA mobilization, protein catabolism
Endocrine Regulation of Metabolism:
Endocrine Regulation of Metabolism:
Pancreas
Pancreas
•
Insulin: lowers blood glucose
– Counters hyperglycemia, opposes glucagon – Glucose transport into cells
– Synthesis of glycogen, protein, fat
– Inhibits gluconeogenesis
•
Glucagon: raises blood glucose
Regulation of Carbohydrate
Regulation of Carbohydrate
Metabolism During Exercise
Metabolism During Exercise
•
Glucose must be available to tissues
•
Glycogenolysis (glycogen
glucose)
Regulation of Carbohydrate
Regulation of Carbohydrate
Metabolism During Exercise
Metabolism During Exercise
•
Adequate glucose during exercise requires
– Glucose release by liver
– Glucose uptake by muscles
•
Hormones that circulating glucose
– Glucagon – Epinephrine
Regulation of Carbohydrate
Regulation of Carbohydrate
Metabolism During Exercise
Metabolism During Exercise
•
Circulating glucose during exercise also
affected by
– GH: FFA mobilization, cellular glucose uptake
– T3, T4: glucose catabolism and fat metabolism
Regulation of Carbohydrate
Regulation of Carbohydrate
Metabolism During Exercise
Metabolism During Exercise
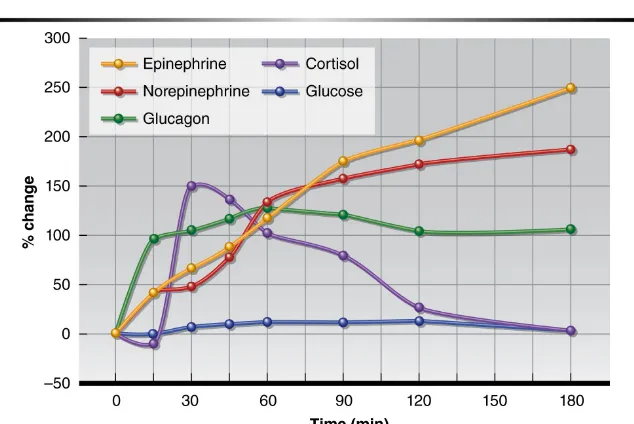
•
As exercise intensity increases
– Catecholamine release
– Glycogenolysis rate (liver, muscles)
– Muscle glycogen used before liver glycogen
•
As exercise duration increases
– More liver glycogen utilized
– Muscle glucose uptake liver glucose release
Figure 4.4
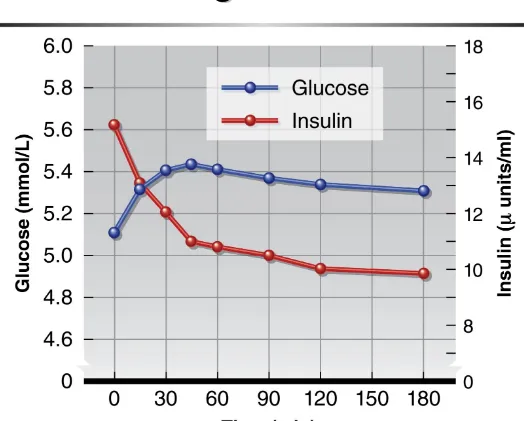
Regulation of Carbohydrate
Regulation of Carbohydrate
Metabolism During Exercise
Metabolism During Exercise
•
Glucose
mobilization
only half the story
•
Insulin: enables glucose
uptake
in muscle
•
During exercise
– Insulin concentrations
– Cellular insulin sensitivity
Figure 4.5
Regulation of Fat Metabolism During
Regulation of Fat Metabolism During
Exercise
Exercise
•
FFA mobilization and fat metabolism critical
to endurance exercise performance
– Glycogen depleted, need fat energy substrates – In response, hormones accelerate fat breakdown
(lipolysis)
•
Triglycerides
FFAs + glycerol
– Fat stored as triglycerides in adipose tissue – Broken down into FFAs, transported to muscle – Rate of triglyceride breakdown into FFAs may
Regulation of Fat Metabolism During
Regulation of Fat Metabolism During
Exercise
Exercise
•
Lipolysis stimulated by
– (Decreased) insulin – Epinephrine
– Norepinephrine – Cortisol
– GH
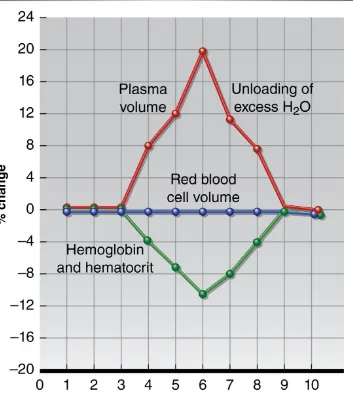
Hormonal Regulation of Fluid and
Hormonal Regulation of Fluid and
Electrolytes During Exercise
Electrolytes During Exercise
•
During exercise, plasma volume
, causing
– Hydrostatic pressure, tissue osmotic pressure
– Plasma water content via sweating
– Heart strain, blood pressure
•
Hormones correct fluid imbalances
– Posterior pituitary gland – Adrenal cortex
Hormonal Regulation of Fluid and
Hormonal Regulation of Fluid and
Electrolytes: Posterior Pituitary
Electrolytes: Posterior Pituitary
•
Posterior pituitary
– Secretes antidiuretic hormone (ADH), oxytocin – Produced in hypothalamus, travels to posterior
pituitary
– Secreted upon neural signal from hypothalamus
•
Only ADH involved with exercise
– Water reabsorption at kidneys
Hormonal Regulation of Fluid and
Hormonal Regulation of Fluid and
Electrolytes: Posterior Pituitary
Electrolytes: Posterior Pituitary
•
Stimuli for ADH release
– Plasma volume = hemoconcentration =
osmolality
– Osmolality stimulates osmoreceptors in
hypothalamus
•
ADH released, increasing water retention
by kidneys
Hormonal Regulation of Fluid and
Hormonal Regulation of Fluid and
Electrolytes: Adrenal Cortex
Electrolytes: Adrenal Cortex
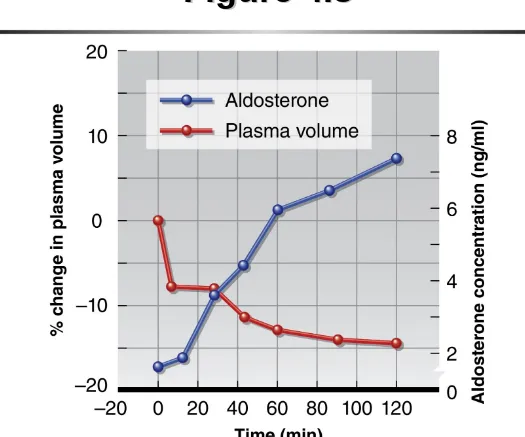
•
Adrenal cortex
– Secretes mineralocorticoids
– Major mineralocorticoid: aldosterone
•
Aldosterone effects
– Na+ retention by kidneys
Hormonal Regulation of Fluid and
Hormonal Regulation of Fluid and
Electrolytes: Adrenal Cortex
Electrolytes: Adrenal Cortex
•
Stimuli for aldosterone release
– Plasma Na+
– Blood volume, blood pressure
– Plasma K+
Hormonal Regulation of Fluid and
Hormonal Regulation of Fluid and
Electrolytes: Kidneys
Electrolytes: Kidneys
•
Kidneys
– Target tissue for ADH, aldosterone – Secrete erythropoietin (EPO), renin
•
EPO
– Low blood O2 in kidneys EPO release – Stimulates red blood cell production
Hormonal Regulation of Fluid and
Hormonal Regulation of Fluid and
Electrolytes: Kidneys
Electrolytes: Kidneys
•
Stimulus for renin (enzyme) release
– Blood volume, blood pressure
– Sympathetic nervous system impulses
•
Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone mechanism
– Renin: converts angiotensinogen angiotensin I
– ACE: converts angiotensin I angiotensin II
Figure 4.8
Figure 4.9
Hormonal Regulation of Fluid and
Hormonal Regulation of Fluid and
Electrolytes: Osmolality
Electrolytes: Osmolality
•
Osmolality
– Measure of concentration of dissolved particles (proteins, ions, etc.) in body fluid compartments – Normal value: ~300 mOsm/kg
•
Osmolality and osmosis
– If compartment osmolality , water drawn in
Hormonal Regulation of Fluid and
Hormonal Regulation of Fluid and
Electrolytes: Osmolality
Electrolytes: Osmolality
•
Aldosterone and osmosis
– Na+ retention osmolality
– Osmolality water retention
– Where Na+ moves, water follows
Hormonal Regulation of Fluid and
Hormonal Regulation of Fluid and
Electrolytes: Osmolality
Electrolytes: Osmolality
•
ADH, aldosterone effects persist for 12 to 48
h after exercise
•
Prolonged Na
+retention abnormally high
[Na
+] after exercise
– Water follows Na+