ABSTRACT
Gilly, Michael Yohanes B. (2015). An Analysis of Non-observance Maxims in The Amazing World of Gumball Cartoon. Yogyakarta: Sanata Dharma University.
Humor is a part of human life. People need humor to reduce their stress from daily life activity. Humor can be performed in various forms, they are in the form of moving pictures, comedy TV and also text with pictures as in comic books and comic strips. Cartoon is one of the film that can be used to entertain people. People from all ages can watch cartoon. Many people love to watch cartoon because the conversation and the animation from the cartoon can create humor. The Amazing World of Gumball cartoon is one of the cartoon that can be analyzed by using pragmatic theory. Theory of conversational maxims, non-observance maxims, implicature and theory of humor are implemented in this study to analyze humor. Benign violation theory also is used in this research to support others theories.
There were two research questions in this research. They are: 1. What are the types of non-observance maxims in The Amazing World of Gumball cartoon? 2. How frequent do the non-observance maxims occur to create comedy in The Amazing World of Gumball cartoon?
In this research, mixed was used. The Amazing World of Gumball cartoon was used as a subject to do research. The film was taken from season 3. The researcher chose 20 episodes on purpose. Those 20 episodes have rich data to be analyzed. This research used document analysis method in analyzing the data. Human instrument became the primary instrument in gathering and analyzing the data. GOM Player, scripts, and video was used as a secondary instrument to gather and analyze the data.
The answer for the first research question, there were only two types of non-observance maxims to create humor. Namely violating maxims and flouting maxims. The use of implicature helps the researcher to find the meanings behind the words and the humor effect that is created. The meanings are understood through the two non-observance maxims, namely violating maxims and flouting maxims. For the second research question reveals that in this cartoon, violating and flouting maxims appeared frequently. There were 13 dialogues which are violating maxims (52%) and 12 dialogues are flouting maxims (48%). Meanwhile, opting out and infringing maxims did not appear in this cartoon to support humor effect. Flouting and violating maxims had an important role in creating humor in this cartoon.
ABSTRAK
Gilly, Michael Yohanes B. (2015). An Analysis of Non-observance Maxims in The Amazing World of Gumball Cartoon. Yogyakarta: Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Humor adalah bagian dari kehidupan manusia. Orang memerlukan humor untuk mengurangi stres dari aktivitas kehidupan sehari-hari. Humor bisa dalam bentuk film dan teks, misalnya film, buku komik, komik strip, komedi di serial TV dan kartun. Kartun merupakan salah satu film yang dapat digunakan untuk menghibur orang. Semua orang dari segala usia dapat menonton kartun. Banyak orang suka menonton kartun karena percakapan dan animasi dari kartun dapat membuat efek humor. Kartun The Amazing World of Gumball merupakan salah satu kartun yang dapat dianalisis dengan menggunakan teori pragmatis. Teori conversational maxims, non-observance maxims dan implicature diimplementasikan untuk menganalisis efek humor dalam kartun ini. Teori benign violation juga digunakan dalam penelitian ini untuk mendukung teori lain.
Ada dua pertanyaan dalam penelitian ini, yaitu: 1. Jenis-jenis non-observance maxims apa yang didalam kartun The Amazing World of Gumball? 2. Seberapa sering non-observance maxims terjadi untuk membuat komedi dalam kartun The Amazing World of Gumball?
Dalam penelitian ini, metode campuran digunakan. Kartun The Amazing World of Gumball digunakan sebagai subjek untuk melakukan penelitian. Film ini diambil dari musim 3 dan mengambil 20 episode dengan tujuan . 20 episode itu memiliki data yang kaya untuk dianalisis. Penelitian ini menggunakan metode analisis dokumen dalam menganalisis data. Instrumen manusia menjadi instrumen utama dalam pengumpulan dan menganalisis data. Laptop, GOM Player, skrip, video digunakan sebagai instrumen sekunder untuk mengumpulkan dan menganalisis data.
AN ANALYSIS OF NON-OBSERVANCE MAXIMS IN THE
AMAZING WORLD OF GUMBALL CARTOON
A SARJANA PENDIDIKAN THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By
Michael Yohanes Berchmans Gilly Student Number: 111214074
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM
DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION
FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY
YOGYAKARTA
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY
I honestly declare that this thesis, which I have written, does not contain the work or parts of the work of other people, except those cited in the quotations and the references, as a scientific paper should.
Yogyakarta, July 29, 2015
The Writer
PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI
LEMBAR PERNYATAN PERSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI KARYA ILMIAH UNTUK KEPENTINGAN AKADEMIS
Yang bertanda tangan di bawah ini, saya mahasiswa Universitas Sanata Dharma:
Nama : Michael Yohanes Berchmans Gilly
Nomor Mahasiswa : 111214074
Demi pengembangan ilmu pengetahuan, saya memberikan kepada Perpustakaan Universitas Sanata Dharma karya ilmiah saya yang berjudul:
AN ANALYSIS OF NON-OBSERVANCE MAXIMS IN THE AMAZING WORLD OF GUMBALL CARTOON
beserta perangkat yang diperlukan (bila ada). Dengan demikian, saya memberikan kepada Universitas Sanata Dharma hak untuk menyimpan, mengalihkan dalam bentuk media lain, mengelolanya dalam bentuk pangkalan data, mendistribusikan secara terbatas, dan mempublikasikannya di internet atau media lain untuk kepentingan akademis tanpa perlu minta ijin dari saya maupun memberikan royalti kepada saya selama tetap mencantumkan nama saya sebagai penulis. Demikian pernyataan ini saya buat dengan sebenarnya.
Dibuat di Yogyakarta Pada tanggal: July 29, 2015 Yang menyatakan
ABSTRACT
Gilly, Michael Yohanes B. (2015). An Analysis of Non-observance Maxims in The Amazing World of Gumball Cartoon. Yogyakarta: Sanata Dharma University.
Humor is a part of human life. People need humor to reduce their stress from daily life activity. Humor can be performed in various forms, they are in the form of moving pictures, comedy TV and also text with pictures as in comic books and comic strips. Cartoon is one of the film that can be used to entertain people. People from all ages can watch cartoon. Many people love to watch cartoon because the conversation and the animation from the cartoon can create humor. The Amazing World of Gumball cartoon is one of the cartoon that can be analyzed by using pragmatic theory. Theory of conversational maxims, non-observance maxims, implicature and theory of humor are implemented in this study to analyze humor. Benign violation theory also is used in this research to support others theories.
There were two research questions in this research. They are: 1. What are the types of non-observance maxims in The Amazing World of Gumball cartoon? 2. How frequent do the non-observance maxims occur to create comedy in The Amazing World of Gumball cartoon?
In this research, mixed was used. The Amazing World of Gumball cartoon was used as a subject to do research. The film was taken from season 3. The researcher chose 20 episodes on purpose. Those 20 episodes have rich data to be analyzed. This research used document analysis method in analyzing the data. Human instrument became the primary instrument in gathering and analyzing the data. GOM Player, scripts, and video was used as a secondary instrument to gather and analyze the data.
The answer for the first research question, there were only two types of non-observance maxims to create humor. Namely violating maxims and flouting maxims. The use of implicature helps the researcher to find the meanings behind the words and the humor effect that is created. The meanings are understood through the two non-observance maxims, namely violating maxims and flouting maxims. For the second research question reveals that in this cartoon, violating and flouting maxims appeared frequently. There were 13 dialogues which are violating maxims (52%) and 12 dialogues are flouting maxims (48%). Meanwhile, opting out and infringing maxims did not appear in this cartoon to support humor effect. Flouting and violating maxims had an important role in creating humor in this cartoon.
ABSTRAK
Gilly, Michael Yohanes B. (2015). An Analysis of Non-observance Maxims in The Amazing World of Gumball Cartoon. Yogyakarta: Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Humor adalah bagian dari kehidupan manusia. Orang memerlukan humor untuk mengurangi stres dari aktivitas kehidupan sehari-hari. Humor bisa dalam bentuk film dan teks, misalnya film, buku komik, komik strip, komedi di serial TV dan kartun. Kartun merupakan salah satu film yang dapat digunakan untuk menghibur orang. Semua orang dari segala usia dapat menonton kartun. Banyak orang suka menonton kartun karena percakapan dan animasi dari kartun dapat membuat efek humor. Kartun The Amazing World of Gumball merupakan salah satu kartun yang dapat dianalisis dengan menggunakan teori pragmatis. Teori conversational maxims, non-observance maxims dan implicature diimplementasikan untuk menganalisis efek humor dalam kartun ini. Teori benign violation juga digunakan dalam penelitian ini untuk mendukung teori lain.
Ada dua pertanyaan dalam penelitian ini, yaitu: 1. Jenis-jenis non-observance maxims apa yang didalam kartun The Amazing World of Gumball? 2. Seberapa sering non-observance maxims terjadi untuk membuat komedi dalam kartun The Amazing World of Gumball?
Dalam penelitian ini, metode campuran digunakan. Kartun The Amazing World of Gumball digunakan sebagai subjek untuk melakukan penelitian. Film ini diambil dari musim 3 dan mengambil 20 episode dengan tujuan . 20 episode itu memiliki data yang kaya untuk dianalisis. Penelitian ini menggunakan metode analisis dokumen dalam menganalisis data. Instrumen manusia menjadi instrumen utama dalam pengumpulan dan menganalisis data. Laptop, GOM Player, skrip, video digunakan sebagai instrumen sekunder untuk mengumpulkan dan menganalisis data.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
First of all, I want to dedicate this thesis for Jesus Christ. He always gives me strength in finishing my thesis. Without Him, I will be nothing. He always guide me when I have difficult time.
My special gratitude goes to Paulus Kuswandono, Ph.D. for giving me his advice, comments, suggestions and also corrections on my thesis. He supported me in finishing my thesis. I also thank to Maria Septiyani, S.Pd., M.Hum. and Drs. Barli Bram, M.Ed., Ph.D. for helping me in finishing my
thesis. I want to thank to Chosa Kastuhandani, S.Pd., M.Hum. as my Academic Supervisor who always guided me and my friend and also to all lecturers in Sanata Dharma University who taught me everything.
For my beloved family, Uballdus Yohanes Gilly, Yustina Sri Wahyuti, Emmanuel Giovani Batista Gilly and Maria Immaculata Angelina Gilly, I
thank them for supporting me to finish my Sarjana Pendidikan degree. They always give me support.
For my beloved girlfriend Denyk Aprilia Kartikawati, I thank her for her support, care and love to me so that I can finish my thesis. Without her, I could not have finished my thesis on time. I am really glad to have her beside me.
For my friends from campus Heni, Sri, Sasa, Riri, Leo, Gaiety, Rozalina Monic, Joko, Cinde, and all my friends, I thank them so much for being such a
good friend for me. I will not forget the friendship with them.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TITLE PAGE ... i
APPROVAL PAGES ... ii
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY ... iv
PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI ... v
ABSTRACT ... vi
ABSTRAK ... vii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ... viii
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... ix
LIST OF TABLES ... xii
LIST OF FIGURES ... xiii
LIST OF APPENDICES ... xiv
CHAPTER I. INTRODUCTION A. Research Background... 1
B. Research Questions ... 4
C. Problem Limitation ... 4
D. Research Objectives ... 5
E. Research Benefits ... 6
F. Definition of Terms ... 7
CHAPTER II. REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE A. Theoretical Description ... 10
1. Theory of Conversational Maxims ... 11
2. Theory of Non-observance maxims ... 12
a. Violating Maxims ... 12
b. Flouting Maxims ... 16
c. Opting out Maxims ... 19
d. Infringing Maxims ... 20
4. Benign Violation Theory... 21
5. Theory of Humor... 24
B. Theoretical Framework ... 24
CHAPTER III. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY A. Research Method ... 27
B. Research Setting ... 28
C. Research Data... 28
D. Research Instruments ... 29
E. Data Analysis Technique ... 30
F. Research Procedure ... 31
CHAPTER IV. RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSIONS A. The Types of Non-observance maxims... 36
a. Violating Maxims ... 36
1.) Violating Maxim of Quality ... 37
2.) Violating Maxim of Relevance ... 39
3.) Violating Maxim of Quantity ... 40
b. Flouting Maxims ... 41
1.) Flouting Maxim of Quality ... 41
2.) Flouting Maxim of Quantity ... 42
3.) Flouting Maxim of Manner ... 43
4.) Flouting Maxim of Relevance ... 44
c. The Use of Benign Violation Theory ... 45
B. The Frequency of Non-observance maxims ... 48
CHAPTER V. CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS A. Conclusions ... 54
REFERENCES ... 57
LIST OF TABLES
2.1 Types of Violating Maxims (Dornerus, 2005) ... 14
2.2 Types of Flouting Maxims (Levinson, 1987) ... 17
4.1 Table of Violating Maxims ... 49
LIST OF FIGURES
2.1 Advertisement from department store ... 13
2.2 Benign Violation Venn (McGraw & Warner, 2014, p. 10) ... 22
2.3 Love letter from a kid to his mother ... 23
2.4 Diagram Venn Love Letter ... 23
4.1 Diagram Venn Dialogue 1 ... 46
LIST OF APPENDICES
1 Classifying Non-observance maxims and Applying
Benign violation Theory ... 60 2 The Script The Amazing World of Gumball season 3 episode 1 entitled
“The Fan” ... 68 3 Script The Amazing World of Gumball season 3 episode 10 entitled
“The Procrastinator”... 76 4 Script The Amazing World of Gumball season 3 episode 32 entitled
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION
This chapter discusses the background of the research. There are six parts in
this chapter to be discussed. The first is research background, the second is research
questions, the third is problem limitation, the fourth is research objectives, the fifth is
research benefits and the last is definition of terms.
A. Research Background
In daily life, humor is a part of human life. McGhee (1994) says sense of
humor is one of the most powerful tools that can change daily mood and emotional
state. People need humor to reduce their stress from daily life activity. Humor can be
performed in various forms, they are in the form of moving pictures, comedy TV and
also text with pictures as in comic books and comic strips (Septiyani, 2014). Since
people like to watch movies or read books that contain humor, many TV producers
take the advantages in making comedy TV program on their channel. Cartoon is one
of the film that use humor in the conversation. Cartoon is a two dimensional
illustrated visual arts that appear on a television or comics in this era. Cartoon can be
watched by many people from young to old age nowadays. Many people love to
watch cartoons because it has simple humor with animation that makes many people
In this study, pragmatic theories are important to analyze the study which is
related to the conversation. The researcher uses theory which is introduced by Grice
(1995). There are four maxims or conversational maxims from Grice (1995). Those
four maxims are maxim of quality, maxim of quantity, maxim of relevance and
maxim of manner. Those maxims can be implemented on the non-observance
maxims.
This study focuses on the non-observance maxims (Grice, 1995; Dornerus,
2005; Levinson, 1987; Thomas, 1995). They are violating maxims, flouting maxims,
opting out maxims and infringing maxims. These non-observance maxims help the
researcher to analyze the conversation on the cartoon. The researcher also uses theory
of humor from Attardo (1994) to analyze humor on the conversation. The researcher
uses theory of conversational implicature from Levinson (1987) to help analyzing the
meaning from what speaker said and the listener heard. Theory from McGraw and
Warren (as cited in McGraw and warner, 2014) is used to help conducting the
research to support theory from Grice in the conversation that is funny.
In this research, there are two reasons why the researcher chose The Amazing
World of Gumball cartoon as a subject to be analyzed. The first reason why the
researcher chose The Amazing World of Gumball as the subject because it provides
cases where humorous conversation can be identified using pragmatic theories.
Humor in pragmatics can be explained by using several theories from several experts,
and McGraw and Warren (as cited in McGraw and warner, 2014). Theory of
conversational maxims and theory of non-observance maxims are the theories which
can be used to analyze humor. The Amazing World of Gumball is one of the famous
cartoon in America nowadays that provides simple jokes with good animation. This
cartoon has been aired since 2011 until now. The Amazing World of Gumball has
released 3 seasons and 112 episodes. There are five characters in The Amazing World
of Gumball cartoon. They are Richard Watterson as the father, Nicole Watterson as
the mother, Gumball Watterson as the son, Anais Watterson as the sister and Darwin
Watterson that used to be the pet and now become the Wattersons. Secondly, as a
personal reason, this cartoon is different with the other cartoon, because the
characters of the cartoon are always giving ambiguous word in their conversation.
This ambiguous word can be analyzed by using non-observance maxims.
There is a researcher who has already conducted research about humor by
using pragmatics theories. One research from Septiyani (2014) discusses the violation
of two maxims. They are violation maxim of quantity and violation maxim of
relevance in Peanut comic strips. However, this research is different from her
research. The researcher does not only use one observance maxim but four
non-observance maxims (Grice, 1995; Dornerus, 2005; Levinson, 1987; Thomas, 1995).
They are violating maxim, opting out maxim, flouting maxim and infringing maxims.
By conducting this research, the researcher believes the result of the finding
will be beneficial to the academic field, especially for English Language Education
Study Program students in the drama class or play performance class. This research
deals with pragmatics especially the use of non-observance maxims in the cartoon.
The researcher expects that from this research, students can learn the use of
non-observance maxims in creating humor both verbally and written. The researcher also
expects that from this research, lecturers can teach the students how to use
non-observance maxims both verbally and written.
B. Research Questions
There are two research questions that the researcher provides, they are:
1. What are the types of non-observance maxims in The Amazing World of
Gumball cartoon?
2. How frequent do the non-observance maxims occur to create comedy in The
Amazing World of Gumball cartoon?
C. Problem Limitation
The focus on this research is pragmatics in humor. There are studies and
theories in pragmatics that can be used to analyze humor. The researcher uses four
theories in this research. The first one is theory of conversational maxims that
manner. The second is the theory of non-observance maxims that includes violating
maxims, flouting maxims, opting out maxims and infringing maxims. The third is
theory of conversational implicature and the last is theory of benign violation in The
Amazing World of Gumball cartoon. This study only focuses on kind of the
non-observance maxims which can be seen in the conversation and how non-non-observance
maxims can make a humor effect in the conversation. The researcher uses 20
episodes of The Amazing World of Gumball cartoon which are considered to have
rich data for the purpose of the study from season 3 as the data. The researcher wants
to take the funniest films from the season 3. The Amazing World of Gumball cartoon
is different from other cartoons because the combination of the animation and choice
of words in this cartoon can make the audience laugh. That is why the researcher used
The Amazing of Gumball cartoon as an object to be analyzed.
D. Research Objectives
There are two objectives from this research. The first one is to know the types
of non-observance maxims that occur in the conversation in The Amazing World of
Gumball cartoon. The second one is to see the frequency of non-observance maxims
which can create comedy in the conversation in The Amazing World of Gumball
E. Research Benefits
This research hopefully will be beneficial for students, lecturers and also the
future researchers. There are benefits that they can get it, they are:
1. For Students
Students will know pragmatic study in daily life conversation, especially
non-observance maxims from Grice. The use of non-non-observance maxims for students,
especially for English Language Education students can help them to create comedy
scripts both in drama class and play performance class. Students may know and
understand how to create humor verbally or written and also a good conversation or
an effective conversation.
2. For Lecturers
Pragmatic study especially the use of non-observance maxims, can be
implemented not only in pragmatic class but also the other classes. Drama class and
play performance class can be used by lecturers to teach non-observance maxims for
students. Lecturers can teach the students how a good conversation or an effective
conversation can be created. Lecturers can also guide them in making the script,
especially for those who want to create comedy scripts.
3. For Future Researchers
This research can be a reference for the future researchers to do research in
pragmatic world, especially related to the Grice’s theory. This research can enrich the
researchers can do the research about humor by using different data, like other
cartoons, comic books or novels.
F. Definition of Terms
The terms that are used by the researcher to analyze humor in The Amazing
World of Gumball cartoon are conversational maxims, non-observance maxims,
cartoon itself, The Amazing World of Gumball cartoon and humor. The researcher
uses these terms because these terms are the main point to analyze humor in The
Amazing World of Gumball cartoon. The functions of these terms are used to help the
readers to understand the contents of this study.
1. Non-observance Maxims
In the non-observance maxim theory, if the conversation between the speaker
and the listener fails, it is called non-observance maxims. Grice (1995) states that
there are four non-observance maxims, they are violating maxims, flouting maxims,
opting out maxims and infringing maxims. In this study, the researcher finds the
humor from the cartoon by using non-observance maxims.
2. Conversational Maxims
According to Grice (1995), conversational maxims are the rules to guide
people in communication. There are four maxims from theory of conversation
maxims that Grice believes as a rule to guide people in communication, namely
conversation, what people need is accurate information from the speaker so the
listener will not get wrong information. If someone gets an accurate information, they
will trust you as the speaker.
In this research, the researcher uses conversational maxims in identifying the
data. To find the humor from the conversation, conversational maxims work with
non-observance maxims to find the humor from the conversation.
3. The Amazing World of Gumball Cartoon
The Amazing World of Gumball is a British–American animated television
series from cartoon network. Ben Bocquelet is the producer of this cartoon. This
cartoon is aired on the cable TV only. This cartoon has been aired 3 seasons with 112
episodes. The length of the videos are more or less 11 minutes. This cartoon is
popular among kids and teenagers nowadays. There are five characters on this
cartoon, they are Gumball Watterson, Darwin Watterson, Anais Watterson, Richard
Watterson, and Nicole Watterson. The researcher believes that The Amazing World of
Gumball has rich data to be analyzed.
4. Humor
Humor is a part of human life. People usually use it to reduce their stress from
their daily life activity. Attardo (1994) states “humor to be an all-encompassing
category, covering any event or object that elicits laughter, amuses, or is felt to be
The details of those terms are found in the following chapter. The next chapter
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
This chapter reviews the theories which are used as the framework for this
study that applied pragmatics in The Amazing World of Gumball cartoon. In this
chapter, the researcher will divide this chapter into two parts. They are: theoretical
description and theoretical framework. The first part reviews the relevant theories on
theory of conversational maxims, theory of non-observance maxims, theory of
conversational implicature, theory of humor and theory of benign violation. The
second part of this chapter reviews the summary of those theories which are helpful
to analyze the problem.
A. Theoretical Description
There are five theories discussed in this research. They are theory of
conversational maxims, theory of non-observance maxims, theory of conversational
implicature, theory of humor and theory of benign violation. Theory of
non-observance maxims, conversational maxims, conversational implicature, humor
become the main point of this research to analyze humor effect from the dialogue and
also to find types of maxims that appear in The Amazing World of Gumball cartoon.
Those four theories help the researcher to answer the research. The last theory
1. Theory of Conversational Maxims
Conversation is the form of interaction between two or more people to
develop social development in social life. In the conversation, it is important for
people who are having conversation to give accurate information to the listener.
Therefore, they will have a good conversation. Grice (1995) suggests that
conversation is based on the cooperative principle and he stated, “Make your conversational contribution what is required, at the stage at which it occurs, by the
accepted purpose or direction of the talk exchange in which you are engaged.” (p.26).
According to Grice (1995), there are four maxims that work in this principle. They
are, maxim of quality means try to make the contribution that is true. People cannot
give false information and say if it is lack evidence. Maxim of quantity means to
make the contribution as informative as required (for the current purposes of the
exchange). The contribution should not be more informative and less informative
than is required. Maxim of relevance means be relevant, while maxim of manner
must be perspicuous. In other words, the contribution from this maxim are avoiding
obscurity of expression, avoiding ambiguity, being brief and being orderly.
Good conversation happens when the speaker follows those four maxims.
Those four maxims can help the speaker to have good conversation with others. The
information that the speaker gives must be true, be informative as required, be
relevant and be perspicuous, so the listener will get correct information from the
2. Theory of Non-observance Maxims
In having daily conversation with someone, the speaker does not know
whether he or she follows the rules or fail to observe the maxims. Non-observance
maxims happens when someone fails to observe the maxims (Thomas, 1995). He also
states that non-observance maxims are often used to show the humors parts from the
conversation. There are four ways that someone may fail in observing the maxims,
they are violating maxim, opting out maxim, infringing maxims and flouting maxim
(Grice, 1995; Dornerus, 2005; Levinson, 1987; Thomas, 1995).
a. Violating Maxims
According to Dornerus (2005), someone or the speaker will be responsible to
mislead the others. What Dornerus wants to say is that in violating the maxim the
speaker has plan to mislead the listener. Violating maxim is one of the example
which is not an effective communication in the conversation, because it will make
someone or the listener believes something that is not true. Dornerus (2005) says
violating maxim can be found in the conversation or it can be found in the form of
advertisement on the street. Here is the example of violating maxim in a form of
Figure 2.1 Advertisement from department store
The advertisement above shows that there is 50% discount, plus 20% discount in that
department store. However, there is a condition applied. To get the 20% discount,
people must buy something in that department with the minimum purchase of Rp
200.000 and have MCC card (member of Matahari department store). This
advertisement can mislead someone because the condition to get more 20% discount
is written with small size font. If someone does not pay attention to the advertisement
well, they will be trapped by the advertisement.
Attardo (1994) says that violating maxims can make humor effect in the
conversation. Here are the examples of violating maxim in the conversation: With minimum purchase Rp. 200.000 for MCC card
Table 2.1 Types of Violating Maxims (Dornerus, 2005)
1. Violating Maxim of Quality:
Dialogue:
Mike: Kindra and I are just friends. Susan: And I came here to ride the bull.
In this dialogue Susan is violating maxim of quality because she is trying to
tell a lie to Mike. She does not give the true answer to Mike. She tries to convince
Mike that she only rides a mechanical bull not to spy them.
2. Violating Maxim of Quantity:
Dialogue:
[Susan and Mike have recently kissed for the first time after a long time of flirting. She walks over to his house to pick him up for their first big date when she sees another woman there. Mike meets her on the veranda and cancels their date. He begins to explain:]
Mike: I know how this looks but there is nothing between us, Kindra is just an old friend. Susan: Old friend?
Mike: Yeah, you know
From the dialogue, Mike is violating maxim of quantity because he does not
give the right amount of information to Susan and he tries to mislead Susan. He is
violating maxim of quantity by saying “Yeah, you know”. Susan thinks there is nothing more to know from Mike. By violating this maxim, he looks like a
mysterious man.
3. Violating Maxim of Manner:
Dialogue:
[Gabi offers to help sponsoring Bree’s daughter Danielle to get into modeling school
but without the permission from Bree. Bree gets furious and goes over to Gabi to confront her.]
Gabi: What? Yes, no, is that how she took it?
In this dialogue Gabi is violating maxim of manner. Gabi is violating maxim
of manner because she gives a confusing answer to Bree. Gabi does not give a brief
answer to Bree. Gabi misleads Bree into thinking that she had nothing to do with.
4. Violating Maxim of Relevance:
Dialogue:
[Gabi has offered to sponsor Bree’s daughter’s modeling career by helping offering
her a place at a modeling school in New York. In that way she will stay away from
Gabi’s lover John. When Bree finds out she is a furious; she wants her daughter at home.]
Bree: Yes. Gabrielle, did you or did you not offer to sponsor her? Gabi: I just wanted to help out.
From the conversation, Gabi is violating maxim of relevance because she
gives irrelevant answer to Bree in order to save her friendship with Bree. This
conversation only makes her look helpless but actually Gabi is trying to be a good
friend for her by trying to get Danielle out of the way. Gabi is violating this maxim
by convincing Bree about her goodness.
b. Flouting Maxims
Flouting maxims are different from the violating maxims. Maxims can be
violated, which means that they are not adhered to. Violation maxims happens for
instance when someone is liable to mislead someone. In flouting maxims, Levinson
see the person who hear or see another meaning from the word that the speaker talk.
There are several examples in flouting the maxims, they are:
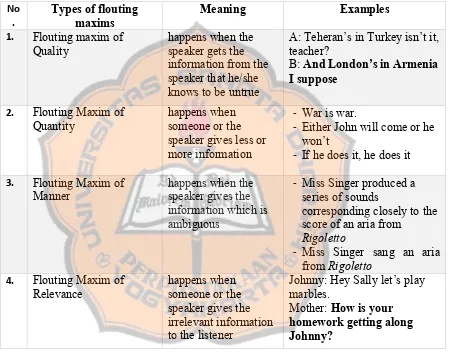
Table 2.2 Types of Flouting Maxims (Levinson, 1987)
1. Flouting Maxim of Quality:
Dialogue:
A: Teheran’s in Turkey isn’t it, teacher? B: And London’s in Armenia I suppose No
In this conversation, B’s utterance means that B wants A to know that A gives
the wrong answer. B uses other words to say that A’s answer is wrong. B does not say directly to A that A’s answer is wrong.
2. Flouting Maxim of Quantity:
(1) War is war.
(2) Either John will come or he won’t. (3) If he does it, he does it.
In case (1), it might be concluded that in the middle of war, terrible things
always happen, and that is its nature and it is not good lamenting in that situation; In
case (2) it might be concluded that the person should calm down, because there is
nothing that person do whether he is going to come or not; In case (3), it might be it is
not our concern.
3. Flouting Maxim of Manner:
(1) Miss Singer produced a series of sounds corresponding closely to the score of an aria from Rigoletto.
(2) Miss Singer sang an aria from Rigoletto.
In the case (1) that sentence is flouting maxim manner because that sentence
breaks the sub-maxim ‘be brief’ from maxim of manner. Case (2) is the simple answer that can be made from case (1).
4. Flouting Maxim of Relevance:
Dialogue:
Johnny: Hey Sally let’s play marbles.
In this conversation, Johnny’s mother is flouting maxim of relevance. From
the example, Johnny’s mother cuts the conversation between Johnny and Sally by telling Johnny about his homework. What Levinson wants to explain in this
conversation is that this is not the conversation between two persons directly, but
what Levinson wants to emphasize in this conversation is that the irrelevant respond
from Johnny’s mother can create flouting maxims of relevance. Actually, Johnny’s mother can directly say to Johnny not to play with Sally, but Johnny’s mother
responds with asking his homework to Johnny.
c. Opting Out Maxims
According to Thomas (1995), the meaning of opting out the maxim is when
people do not want to corporate with others and when others need to have the
information. In this case, the speaker or someone only gives less information that
he/she already has. There are several responses in opting out the maxims. They are
opting out of quantity, for examples: my lips are sealed, I cannot say more; Opting
out of quality, for examples: I am not sure, but I think….; Opting out of manner, for example: I do not know how to say this more simply….; Opting out of Relation, for example: I do not know if this answers your questions….
Thomas (1995) says that “the example of opting out occurs frequently in public life, when the speaker cannot, perhaps for legal or ethical reason, reply in the
way normally expected. The speaker usually wishes to avoid generating a false
usually happens in public life. For example, a conversation which is found in the
hospital:
[There is a man who got serious injury on his head because of an accident on the road. His sister asked to the doctor about his condition now.]
Jean : Doctor, how was the condition of my brother? Doctor : I cannot say more.
In this case, the doctor does not want to tell the condition of Jean’s brother.
The doctor wants to keep the information secretly. In this conversation, opting out
maxim of quantity is used.
d. Infringing Maxims
Grice (1995) states that someone may violate one maxim in order to preserve
another. For example:
A: Where does C live?
B: Somewhere in the South of France
This conversation uses violating maxim of quantity. In this case, there is clash
between two maxims, they are maxim of quantity and quality. In this conversation, B
gives weak information and also less information. B does not know where the
specific location is and he gives less information without violating maxim of quality.
3. Theory of Conversational Implicature
According to Levinson (1987), implicature is a component of speaker
meaning that constitutes an aspect of what is meant in a speaker’s utterance without
implicature and conversational implicature. Levinson (1987) states that
conversational implicature is related to the certain general features of discourse.
Implicature, cooperative principle and the four maxims are related each other. The
function of cooperative principle and the four maxims are to make good and effective
conversations, for example:
A: Do you see my pudding in the refrigerator? I put my pudding yesterday..
B: Wow today is so hot..
From the example above, B is flouting maxim of relation, because B gives irrelevant
answer to A. B uses another word because B does not want to answer directly to A.
Actually, B wants to avoid A’s question by giving irrelevant information. It implies
that B does not want to answer and avoid A’s question by giving an irrelevant answer to the A.
4. Benign Violation Theory
Benign violation theory actually came from N+V theory that was developed
by Veatch (as cited in McGraw and Warner, 2014). He states that “the idea that humor occurs when someone perceives a situation is a violation of a ‘subjective moral principle’ (V) while simultaneously realizing that the situation is normal (N)”
(as cited in McGraw & Warner, 2014, p.8). Because there is no one who paid much
attention to his theory, then McGraw with Warren developed Veatch’s theory became benign violation theory. There are three things in this theory that can create humor:
simultaneously (as cited in McGraw & Warner, 2014). Situation is benign when it
seems okay, acceptable or safe and the situation is a violation when it seems wrong,
unsettling or threatening. McGraw and Warner (2014) believe that the situation
becomes funny when those two situations happen simultaneously. Here is the venn
diagram:
Figure 2.2 Benign Violation Venn (as cited in McGraw & Warner, 2014, 10) This theory explains that the things are funny when situation is benign,
situation is a violation and those situations happen simultaneously. If the benign
situation and violation do not happen simultaneously, it will not create a humor. Here
is the example of benign violation:
Figure 2.3 Love letter from a kid to his mother
From that letter, what the kid wants to explain is that he does not want to have
another mother or step mother. If he has step mother, he will punch his step mother
and find the original one. So in this example, the situation is benign and it has
violation; it creates humor from that letter. Venn diagram from the Figure 2.3 will be
like this.
In this case, the situation is benign when he loves his mother so much. Then, the
situation is a violation when he does not want to have another mother and want to
punch if he has another mother or stepmother. Those situation will create humor if
they happen simultaneously.
5. Theory of Humor
Attardo (1994) believes that humor can be produced from any event or object
that elicits laughter, amuses and also what people felt to be funny. Humor is useful
for people to reduce their stress from daily life activity. Wilson states:
“Humour, as it is felt by people, has personal functions such as relieving one’s tension or repressed feelings, boosting friendship, and reducing hostilities. It also has social functions since it can be a powerful means of reinforcing the ideal ideology, power, status, morality, norms, and values within a society.” (1979, pp. 226-231)
Attardo (1994) believes that humor involves violation of one or more of Grice’s
maxims. It means that humor can be produced if one or more non-observance maxims
appears.
B. Theoretical Framework
There were two theories used to analyze the first research question. They were
theory of conversational maxims and non-observance maxims (Grice, 1995;
Dornerus, 2005; Levinson, 1987; Thomas, 1995). The first research question is about
the types of the non-observance maxims. This question was answered by using theory
theory. Grice (1995) says theory of conversational maxims, which consists of maxim
of quality, maxim of relevance, maxim quantity and maxim of manner supported
theory of non-observance maxims. The theory of non-observance maxims consist of
violating maxims, flouting maxims, opting out maxims and infringing maxims
(Grice, 1995; Dornerus, 2005; Levinson, 1987; Thomas, 1995). Levinson (1987) says
implicature is used to know the meaning behind the conversation. In this research,
implicature is used to help the researcher to know the meaning that implies in the
conversation, so the researcher can analyze the meaning from the conversation itself.
The second research question is about how frequent the four maxims are
broken to create humor in The Amazing World of Gumball cartoon? In analyzing this
movie, first, the researcher used the conversational maxims that is shown in the
cartoon. Grice (1995) states conversational maxims are divided into four, they are
maxim of quality, maxim of quantity, maxim of relation and maxim of manner. Those
maxims helped the researcher to categorize kind of maxim in the conversation.
Second, types of non-observance maxims were used by the researcher in analyzing
the conversation in The Amazing World of Gumball cartoon. Theory of
non-observance maxims consist of violating maxims, flouting maxims, opting out maxims
and infringing maxims. Theory of non-observance maxims help the researcher to
analyze the conversation (Grice, 1995). And the last, theory of benign violation from
McGraw and Warren (as cited in McGraw and Warner, 2014) to support other
In this chapter, the researcher has discussed the theories that are used to help
the researcher in analyzing The Amazing World of Gumball cartoon. The next chapter
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
In this chapter, the researcher discusses the methodology that is used to
answer the two research problems. The discussion that the researcher discussed are
the research method, the research subject, the instruments and data gathering
technique, the data analysis technique and the research procedures.
A. Research Method
This research used mixed method. Naggy and Hesse-Biber (2010) state
“mixed methods employ a research design that uses both quantitative and qualitative
data to answer a particular question or set of questions” (p. 3). In mixed methods,
both qualitative and quantitative method are used at the same time to answer the
questions. Naggy and Hesse-Biber (2010) also state:
“qualitative data – “words, pictures, and narrative”- can be combined with quantitative, numerical data from a larger scale study on the same issue, allowing our research results to be generalized for future studies and examinations.” (p.3)
The combination of qualitative and quantitative data can be used in the research to
get the results.
The researcher used document analysis method to analyze the data. According
to Ary, Jacobs, Sorensen and Razavieh (2010), “Content or document analysis is a
specified characteristics of the material” (p. 457). Document analysis method was
used when the researcher would like to analyze physical document in the form of
written or visual (Ary, Jacobs, Sorensen & Razavieh, 2010). The researcher used
transcripts of the movie from the internet as the data.
B. Research Setting
The researcher conducted this research from February, 2015 to July, 2015.
The researcher did this research in Yogyakarta by conducting library study.
C. Research Data
The Amazing World of Gumball is a British–American animated television
series created by Ben Bocquelet and produced by Cartoon Network. The genre of the
film is comedy and fantasy. It was first aired on May 3, 2011. This film has aired 3
seasons with 112 episodes in total. The length of each episode is 11 minutes. The
story is about the life of The Wattersons. The Wattersons live in the Elmore. Gumball
Watterson, a 12-year-old cat who attends middle school in Elmore and he is
accompanied by adoptive goldfish brother as his best friend named Darwin. They
have one sister named Anais. She is the smartest child in Watterson. Nicole
D. Research Instruments
The researcher as a human instrument became the primary instrument in
gathering and analyzing the data (Merriam, 2002; Creswell, 2007; Ary, Jacobs,
Sorensen & Razavieh, 2010). The researcher categorized kinds of non-observance
maxims applied in the conversation. To get the data, the researcher used four sources,
they were scripts, the video from the internet and video player. Those four sources
were also used to help the researcher to analyze the data.
1. GOM Player
The researcher used GOM Player to play the video. The researcher used GOM
Player because it was easy to use. Features from GOM Player were easy to be used,
like shortcut keys. Shortcut keys were used to play, stop, open subtitles, set the
playback speed and increase or decrease the volume. The researcher used playback
speed feature in typing the conversation from the video. Playback speed feature was
one of the features from GOM Player to set the speed of the video. The researcher
used it to decrease the speed. Next, the researcher used GOM Player because the
volume of the video can be increased up to 200%. It was useful because some of the
videos have low quality audio. This feature helped the researcher listens to the video
clearly.
2. The Scripts
The researcher used the retyped script. First, the researcher took the scripts
understand the story, complete the missing dialogues and change the wrong word into
the good one. The transcripts were attached in the Appendices 2, 3 and 4.
3. Videos
For the video, because The Amazing World of Gumball only shows on the
cable TV in Cartoon Network, the researcher used the internet to download The
Amazing World of Gumball cartoon season 3. The researcher took the cartoon from
season 3 only because it was a new season and it was easier to be downloaded rather
than season 1 and 2. There are 36 episodes until now on The Amazing World of
Gumball cartoon season 3. However, the researcher only took 20 episodes from
season 3 on purpose. The researcher decided to take randomly because the researcher
tried to find the episode that was rich for the analysis. It made easier for the
researcher to analyze the cartoon.
E. Data Analysis Technique
The researcher analyzed the movie transcripts by watching the video and then
the researcher typed the conversation. Then, the researcher analyzed the data into
four categories of non-observance maxims. Those four categories include flouting
maxims, violating maxims, maxims clash and opting out maxims was introduced by
Grice (1995: 30). There are four maxims which are introduced by Grice, they are
maxim of quantity, maxim of quality, maxim of manner and maxim of relation (1995:
Make the contribution as informative as required (for the current purposes of the
exchange). Maxim of Relation: Try to be relevant. Maxim of Manner: Try to be
perspicuous.
The researcher found out the frequency of the occurrence from each
non-observance maxims. The researcher analyzed the frequency of non-non-observance
maxims by deciding the highest frequency of the occurrence from each
non-observance maxim. Then, the researcher explained the types of non-non-observance
maxims that appeared in this cartoon by using the format that the researcher has
made. After that, the researcher made the conclusion.
F. Research Procedure
In this chapter, the researcher explains the steps in conducting the research,
they are:
1. Choosing the videos
In choosing the videos, the researcher took the videos from The Amazing
World of Gmball cartoon season 3 only. There are 36 episodes and the researcher
already watched all episodes. Thus, the researcher only took the videos that were rich
to be analyzed. The researcher took 20 episodes only.
2. Taking the script
For the scripts, the researcher used retyped scripts. The researcher took the
researcher completed the missing dialogues by listening the dialogues again and
typing the missing dialogues. The researcher also adjusted some dialogues, which
were ungrammatical construction, for example the word “more” should be “last”. The
researcher watched the film more or less fifty times each episode.
3. Classifying the conversations
In classifying the conversations, the researcher chose the conversations which
were funny from those 20 episodes. The researcher also watched the film and read the
scripts. After that, the researcher classified the conversation that had humor.
4. Identifying the conversations
The researcher wanted to identify the sentence which broke the maxims.
There are four non-observance maxims that the researcher used in identifying the
conversations. The researcher used the non-observance maxims and also theory of
humor in identifying the conversations.
5. Calculating the appearance of non-observance maxims in the conversation
The researcher calculated the appearance of non-observance maxims in the
conversation. The researcher calculated the data to get the percentage of the
appearance of non-observance maxims. The researcher formulated the formula. Here
is the formula:
The appearance of non − observance maxims flouting, opting out, infringing, violating
6. Analyzing non-observance maxims in the conversation
After identifying the dialogues which consisted of the non-observance
maxims, the researcher analyzed types of the non-observance maxims which
consisted of the violating maxims, the flouting maxims, the opting out maxims and
the infringing maxims that produced funny conversation. There were four maxims
that the researcher used. They were maxim of quality, quantity, manner and relation.
Those four maxim which were introduced by Grice (1995) were used by the
researcher to analyze non-observance maxims. The researcher also used benign
violation theory to support the observance maxims theory. In analyzing the
non-observance maxims in the conversation, the researcher had a format to analyze it.
Here is the format:
Dialogue (Number):
Dialogue: _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________
Analysis : _____________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________
In analyzing the conversation by using benign violation theory, the researcher used
another format to analyze the conversation. Here is the format:
Dialogue (Number):
Analysis: _____________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________
7. Making conclusions
After the process of analyzing, the researcher made the conclusions. The last
step in this research was the researcher analyzed the data from the result that the
researcher obtained. The researcher decided the highest frequency of occurrence of
non-observance maxims from the The Amazing World of Gumball cartoon. After that,
the researcher analyzed the videos by using the format that the researcher made. After
knowing the result, the researcher made the conclusion. Then, the readers will know
how the non-observance maxims can create a humor. The result of the data were used
to answer two research questions that the researcher formulated in the previous
chapter.
In this chapter discussed the method to answer two research questions. They
are 1) What are the types of non-observance maxims in The Amazing World of
comedy in The Amazing World of Gumball cartoon?. The next chapter discusses the
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSIONS
This chapter discusses the research findings. In this chapter, the researcher only focuses on how non-observance maxims in the cartoon entitled The Amazing
World of Gumball is applied and how theory benign violation is applied in the
dialogues. The researcher analyzed kind of non-observance maxims that appears in the dialogues and also the implicature from the dialogues. Two main problems on this
research are answered based on the findings that the researcher obtained.
To show the result of the findings which applied in The Amazing World of
Gumball cartoon, the researcher discusses the findings in the next paragraph.
A. The Types of Non-Observance Maxims
In this part, the researcher gives 25 dialogues, but the researcher only provides 8 examples of the dialogues. The complete 25 dialogues were presented in appendix
1. The researcher only provided small dialogues from the cartoon and also the analysis from it in the following paragraph.
a. Violating Maxims
In violating maxims, the speaker may tell other people that the speaker knows to be false, gave irrelevant information, fails to mention the information enough, and
flouting maxims. In violating maxims, the person who gave information is intended
to give someone information that is not true. Based on the findings, this breaking maxim mostly showed in the dialogues and create the humor. The researcher showed
the violating of maxims which showed in the dialogues. There were four maxim based on Grice (1995), and for this breaking maxim only three which showed. They were violating maxim of quality, violating maxim of quantity and violating maxim of
relevance. Violating maxim of manner did not appear in this cartoon. The use of violating maxim could create the humor.
1.) Violating Maxim of Quality
In this case, the person intends to give false information to others, but the others will believe with the information that the person gives. Dornerus (2005) states
someone may violates maxim of quality, if someone may tell false information to other people but actually the person who tell the information know to be false. Here,
there was dialogue on The Amazing World of Gumball which used violating maxim of quality by telling that the person know to be false:
Dialogue 1:
[Gumball and Darwin is chasing Sarah because they want to explain about they feel. Then, Gumball and Darwin take off after her trail. Sarah is trapped in the dead end of a hallway, and the brothers corner her. Sarah hears them, gasps, and pretends to be distressed as they arrive]
Gumball : Sarah, listen-
Sarah : I know what you're gonna say. I'm sorry about the hair. Gumball : Eh-what? What hair? [He turns around, revealing a spot of Shaved hair behind his head] Is there something wrong with my hair?
In this episode, Sarah is obsessed with Gumball and Darwin. She wants to be noticed by Gumball and Darwin, but they feel annoyed because of her. Gumball and
Darwin want to explain their feeling to her but she is running away. They try to chase her because they want to explain something. In this conversation, Sarah is violating
maxim of quality because in this scene Sarah is obsessed with Gumball and Darwin, Sarah take a small piece of Gumball’s hair but Gumball doesn’t know that his hair
was taken by Sarah and there was a spot of shaved hair behind his head. Sarah doesn’t want Gumball knows about condition of his hair and she tells the information
that she knows to be false.
The next example from violating maxim of quality is when someone gives information with lack of knowledge or information to others:
Dialogue 2:
[The film starts when their mother tells to Gumball and Darwin as a procrastinator] Darwin: Wait, what?
Nicole : You are procrastinators. Darwin : What does that mean?
Gumball : Procrastinators: derived from the Mexican word,
"Procratalamation" which means mid-night snack, and the Viking word "Astinator" which means puckered cheese. It describes a person who sits on a sandwich in the dark.
Darwin : [confusingly stares at gumball]
In this scene, Nicole, their mother, tells to both of Gumball and Darwin that
with a right answer because Gumball is lack of knowledge. Procrastinator itself
means a person who always avoids his/her responsibility by doing something else instead. Here, Gumball is violating maxim of quality by giving a wrong answer.
2.) Violating Maxim of Relevance
In this case, the speaker is trying to mislead others by giving irrelevant information. Here is the case of violating maxim of relevance when the speaker gives
irrelevant information: Dialogue 3:
[The turtle is burned because of strong sunlight, Gumball, Darwin, Anais and His Father, Richard pray for the turtle]
Darwin : Before we say goodbye to our beloved family pet, evil turtle. I think we should all say a few word to let know just how much he meant to us. I always think fondly of the way he put fear into my heart.
Anais : Everytime I stood down at the scar tissue on my hand, I think of him Richard : Only once in your life time does something touch your heart in
the way that “awesome store” did. Gumball : Dad, you’ve got to move on
Violating maxim of relevance or usually called violating maxim of relation happens when someone gives the irrelevant information to others (Dornerus, 2005). In this scene, their pet, evil turtle, is burned because Darwin puts the turtle outside.
Gumball, Darwin, Anais and Richard are praying for the turtle. In this scene everyone has a chance to reveal something to the turtle. Richard is giving an irrelevant answer by praying for “awesome store” not the turtle. Richard is trying to mislead Gumball
3.) Violating Maxim of Quantity
In violating maxim of quantity, people will violate this maxim if they give too much or less information. Here is the case of violating maxim of quantity that
someone gives too much information to others: Dialogue 4:
[Gumball and Anais walk towards the entrance to Darwin's lair.] Gumball : Ugh! We need a code. How are we gonna get that? Anais : Don't worry. I have my
ways. [Types] H [Types] A [Types] C [Types] K: Hack. Press enter. [The door opens. ]
Gumball : Really? "Hack"?
Anais : Just kidding. Actually, I bypassed the storage controller, tapped directly into the V and X array head, decrypted the neoline SAS disk–
Gumball : [Nods] Mhm. [Nods] Mhm. [Nods] Mhm.
Anais : Injected the flash drivers into the network's fiber pack, before disabling the IDS, brought in incoming traffic to a bunch of short
proxies–
Gumball : [Steps back and nods.] Mhm. Mhm.
Anais : Accessed the ESXI server plus during the primal digi-centre, and disabled the inter-V stand routing in the layer three–
[Gumball leaves Anais, and sees Darwin in his "lair," smiling almost innocently.]
In this episode, Darwin wants to make everyone safe and he makes the world of safety because he does not want everyone gets hurt. Gumball and family want to save Darwin who rules the world of safety. In this scene, Gumball and Anais have entered to Darwin’s lair. They cannot get in because the door is locked with
password. Because Anais is a smart girl, she can unlock the door easily. Gumball is shocked because Anais can open the door easily, when Gumball wants to convince
violates maxims of quantity, because she gives too much information to Gumball that
actually he does not need that much.
b. Flouting Maxims
In this cartoon, the researcher found 12 dialogues which broke the maxims. Levinson (1987) says that if people are flouting the maxim, they expect the listener to know and notice that is intended from them. In this breaking maxim, the speaker does
not want to mislead others, but the speaker wants the other to know that the speaker has a purpose in giving the information.
There were several dialogues which flouted the maxims. In this non-observance maxims, all maxims were broken, those were maxim of quality, quantity, relation and manner. This flouting maxims also created the humor, even it was not
mostly used in this cartoon. The findings of flouting maxim can be found in the next paragraph.
1.) Flouting Maxim of Quality
People sometimes use irony, hyperbole, meiosis and metaphor in flouting this maxim. They want the listener expect something else from the speaker said. Here is
the example of flouting maxim of quality: Dialogue 5:
[The trio open the box and are grossed out at what they see]
Anais : Ugh. What is that? It looks like an angry, green hat.
Gumball : Nah, more like a very mean, old man carrying a sad house on his back.